Investigation on the Quench Sensitivity of 7085 Aluminum Alloy with Different Contents of Main Alloying Elements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Experiments
3. Results
3.1. TTT and Continuous-Cooling-Transformation (CCT) Curves
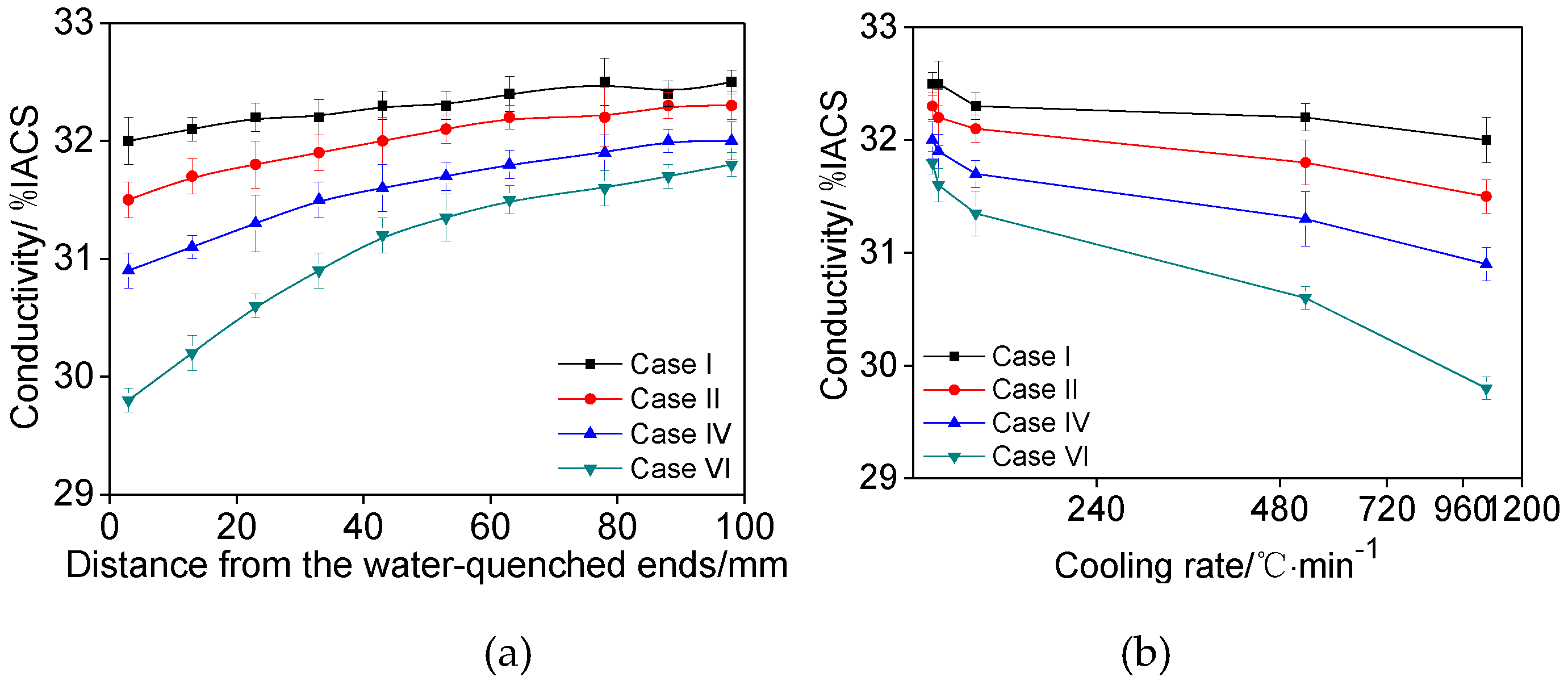
3.2. Effects of Main Alloying Elements Content on Conductivity
3.3. Effects of Main Alloying Elements Content on Hardness
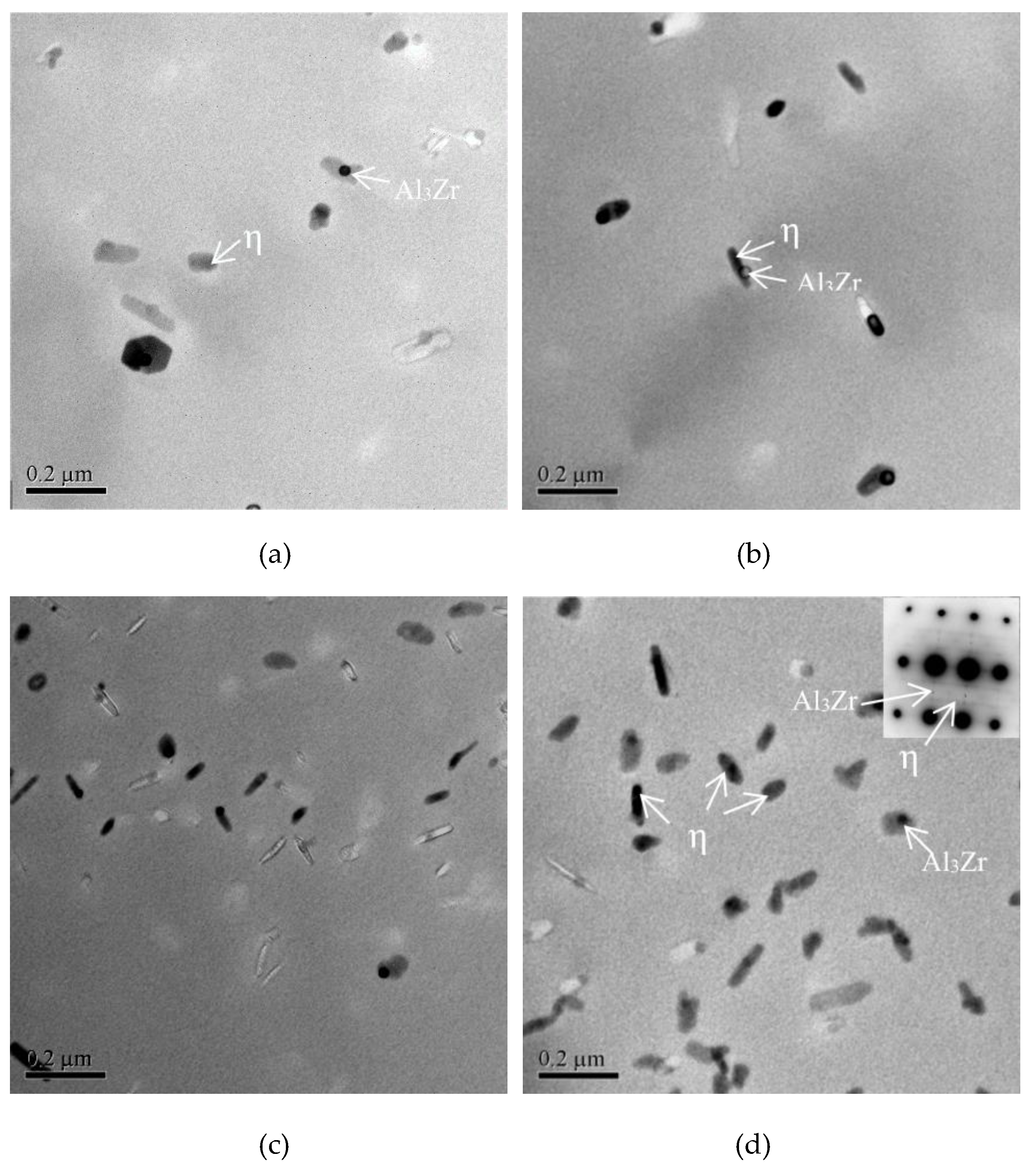
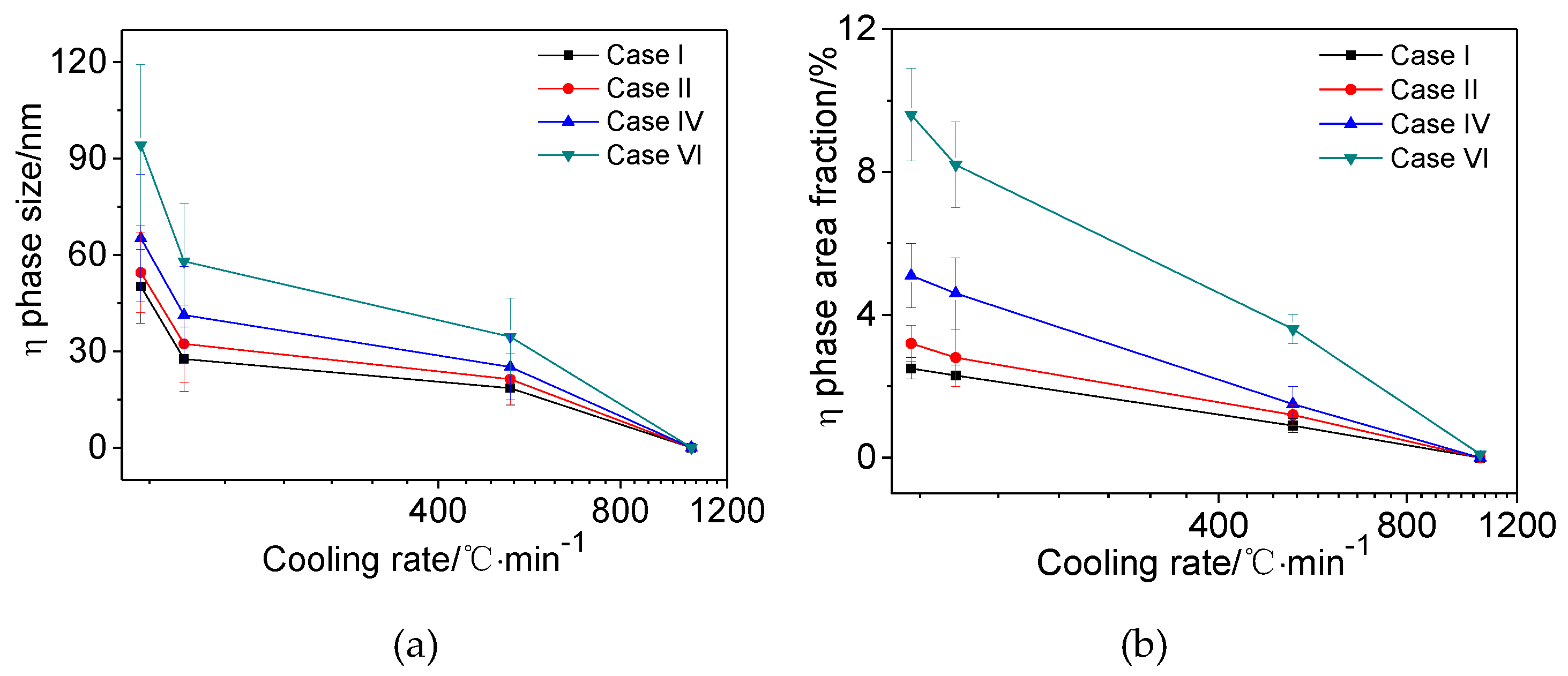
3.4. Effects of Main Alloying Elements Content on η Phase
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, D.; Miao, J.; Zhang, F.; Fu, Z.; Liu, Y. Effects of prebending radii on microstructure and fatigue performance of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu aluminum alloy after creep age forming. Metals 2019, 9, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, G.K.; Scheiber, S.; Antrekowitsch, H.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Pöschmann, D.; Pogatscher, S. differential scanning calorimetry and thermodynamic predictions—A comparative study of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys. Metals 2016, 6, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.B.; Liu, S.D.; Zhang, X.M. Effect of Zener-Hollomon parameter on quench sensitivity of 7085 aluminum alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 688, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.Q.; Li, X.W.; Zhang, Y.A. Development of 7 XXX series aluminum alloy with high strength high toughness and low quench sensitivity. Mater. China 2014, 33, 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, D.J.; Liu, J.; Sawtell, R.R.; Venamav, G.B. New generation high strength high damage tolerance 7085 thick alloy product with low quench sensitivity. Mater. Sci. Forum 2004, 28, 969–974. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhu, T.R. An overview of high-performance aircraft structural Al alloy-AA7085. Acta Metall. Sin. 2015, 28, 909–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evancho, J.W.; Staley, J.T. Kinetics of precipitation in aluminum alloys during continuous cooling. Metall. Trans. 1974, 5, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Tiryakioğlu, M.; Shuey, R.T. Quench sensitivity of an Al-7 Pct Si-0.6 Pct Mg alloy: Characterization and modeling. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2007, 38, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryakioğlu, M.; Shuey, R.T. Modeling quench sensitivity of aluminum alloys for multiple tempers and properties: Application to AA2024. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 41, 2984–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryakioğlu, M.; Shuey, R.T. Quench sensitivity of 2219-T87 aluminum alloy plate. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2010, 527, 5033–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryakioğlu, M.; Robinson, J.S.; Eason, P.D. On the quench sensitivity of 7010 aluminum alloy forgings in the overaged condition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2014, 618, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, A.J. The effect of composition upon the quench-sensitivity of some Al-Zn-Mg alloy. J. Inst. Met. 1966, 94, 94–99. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.G.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.M.; Liu, S.D.; Liu, W.J.; Ouyang, H.; Li, H.P. Influence of quench-induced precipitation on aging behavior of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J. The Research about the Quench Induced Precipitation and Quenching Sensitivity of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys. Master’s Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.T.; Yun, S.J.; Nam, S.W. Improved quench sensitivity in modified aluminum alloy 7175 for thick forging applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2004, 371, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.L.; Wan, L.; Zhang, Y.Y. Influence of Mg content on quench sensitivity of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu aluminum alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 4632–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, H. Influence of Zn/Mg Ratio on Quench Sensitivity of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy. Master’s Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L. Investigation on Microstructures, Mechanical Properties and Quench Sensitivity of Al-9.0Zn-1.5Mg-XCu Alloys. Master’s Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, B.H.; Liu, P.Y.; Zhou, T.T. Effect of compositions on the quenching sensitivity of 7050 and 7085 alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2016, 667, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.S.; Li, X.W.; Xiong, B.Q.; Zhang, Y.A.; Li, Z.H.; Yan, H.W.; Liu, H.W.; Huang, S.H. Quench sensitivity of novel Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys containing different Cu contents. Rare Met. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.D.; Qun, L.; Lin, H.Q.; Lin, S.; Long, T.; Ye, L.Y.; Deng, Y.L. Effect of quench-induced precipitation on microstructure and mechanical properties of 7085 aluminum alloy. Mater. Des. 2017, 132, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.Z.; Xiao, D.H.; Zhu, Z.M.; Li, X.X.; Chen, K.H. Effects of Cu/Mg ratio on microstructure and properties of AA7085 alloys. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 2054–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.Z.; Li, X.H.; Zhu, P.; Cao, Y.H.; Guo, Y.P.; Cui, J.Z. Effects of high magnetic field on the evolutions of constituent phases in 7085 aluminum alloy during homogenization. Mater. Charact. 2012, 71, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Chen, K.H.; Peng, G.S.; Chen, X.H.; Ceng, Q.H. Effect of heat treatment on hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of 7085 aluminum alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 537, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkaldy, J.S.; Thomason, B.A.; Beganis, E.A. Hardenability Concepts with Applications to Steel; American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical and Petroleum Engineers: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1978; p. 82. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.Y.; Xiong, B.Q.; Zhang, Y.A. Quench sensitivity and microstructure character of high strength AA7050. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Tan, Q.; Liu, S.D. Effect of quenching rate on aging behavior of 7085 aluminum alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 871–877. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.B.; Liu, S.D.; Zhang, X.M. Grain structure effect on quench sensitivity of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2016, 26, 2276–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pelliccia, D.; Benjamin, M. Analysis of age hardening precipitates of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys in a wide range of quenching rates using small angle X-ray scattering. Mater. Des. 2018, 142, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheng, X.F.; Lei, Q.; Xiao, Z. Precipitation behavior and quenching sensitivity of a spray deposited Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy. Materials 2017, 10, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.K. Fundamentals of Material Science, 2nd ed.; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2003; pp. 21–65. [Google Scholar]


| Case ID | Zn (wt.%) | Mg (wt.%) | Cu (wt.%) | Zn, Mg and Cu (wt.%) | Zr (wt.%) | Ti (wt.%) | Si (wt.%) | Fe (wt.%) | Al (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| standard | 7.0~8.0 | 1.2~1.8 | 1.3~2.0 | 9.5~11.8 | 0.08~0.15 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.08 | Bal. |
| I | 7.5 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 10.0 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.04 | Bal. |
| II | 7.5 | 1.4 | 1.35 | 10.25 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.04 | Bal. |
| III | 7.5 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 10.5 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.04 | Bal. |
| IV | 7.5 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 10.8 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.04 | Bal. |
| V | 7.5 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 11.0 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.04 | Bal. |
| VI | 7.5 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 11.3 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.04 | Bal. |
| Main Alloying Elements Contents (wt.%) | 10.0 | 10.25 | 10.5 | 10.8 | 11.0 | 11.3 |
| Transitions Temperature (°C) | 404.1 | 415.2 | 416.9 | 420.8 | 425.8 | 435.2 |
| Nose Temperature (°C) | 331.4 | 339.9 | 342.4 | 348.5 | 352.3 | 360.8 |
| Precipitation 0.5% Incubation Period (s) | 1427.0 | 1041.2 | 1003.9 | 932.7 | 841.9 | 660.8 |
| Elements | Radius/Å | Δr = rx − rAl | Δr/rAl | RAM | Density/g∙cm−³ | Electronegativity/ev |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 1.429 | - | - | 26.98 | 2.7 | 1.61 |
| Zn | 1.379 | –0.05 | –3.50% | 65.38 | 7.14 | 1.65 |
| Mg | 1.598 | 0.169 | 11.83% | 24.31 | 1.73 | 1.31 |
| Cu | 1.276 | –0.153 | –10.71% | 63.55 | 8.96 | 1.90 |
| Zn + Mg + Cu Content (wt.%) | Lattice Distortion Energy Induced by Alloying Elements | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | Mg | Cu | Total Values | |
| 10 | 6.573 | 50.289 | 8.696 | 65.558 |
| 10.25 | 6.569 | 58.673 | 9.009 | 74.252 |
| 10.8 | 6.545 | 67.173 | 11.388 | 85.107 |
| 11.3 | 6.569 | 75.816 | 13.468 | 95.854 |
| Zn + Mg + Cu Content (wt.%) | E | t (s) | S (nm) | AF (%) | ΔC (%IACS) | ΔH (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 65.558 | 1427 | 50.2 ± 11.5 | 2.5 ± 0.3 | 0.5 | 4 |
| 10.25 | 74.252 | 1041.2 | 54.5 ± 12.4 | 3.2 ± 0.5 | 0.8 | 5.8 |
| 10.8 | 85.107 | 932.7 | 65.2 ± 19.8 | 5.1 ± 0.9 | 1.1 | 8.6 |
| 11.3 | 95.854 | 660.8 | 94.2 ± 25.1 | 9.6 ± 1.3 | 2 | 12.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Chen, D. Investigation on the Quench Sensitivity of 7085 Aluminum Alloy with Different Contents of Main Alloying Elements. Metals 2019, 9, 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9090965
Li C, Chen D. Investigation on the Quench Sensitivity of 7085 Aluminum Alloy with Different Contents of Main Alloying Elements. Metals. 2019; 9(9):965. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9090965
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chengbo, and Dongdong Chen. 2019. "Investigation on the Quench Sensitivity of 7085 Aluminum Alloy with Different Contents of Main Alloying Elements" Metals 9, no. 9: 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9090965
APA StyleLi, C., & Chen, D. (2019). Investigation on the Quench Sensitivity of 7085 Aluminum Alloy with Different Contents of Main Alloying Elements. Metals, 9(9), 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9090965





