Size Effect on Tensile Properties and Fracture Mechanism of Micro-Rolled Ultra-Thin Cu/Al Composite Sheet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Equipment
2.2. Experimental Methods
3. Experimental Results
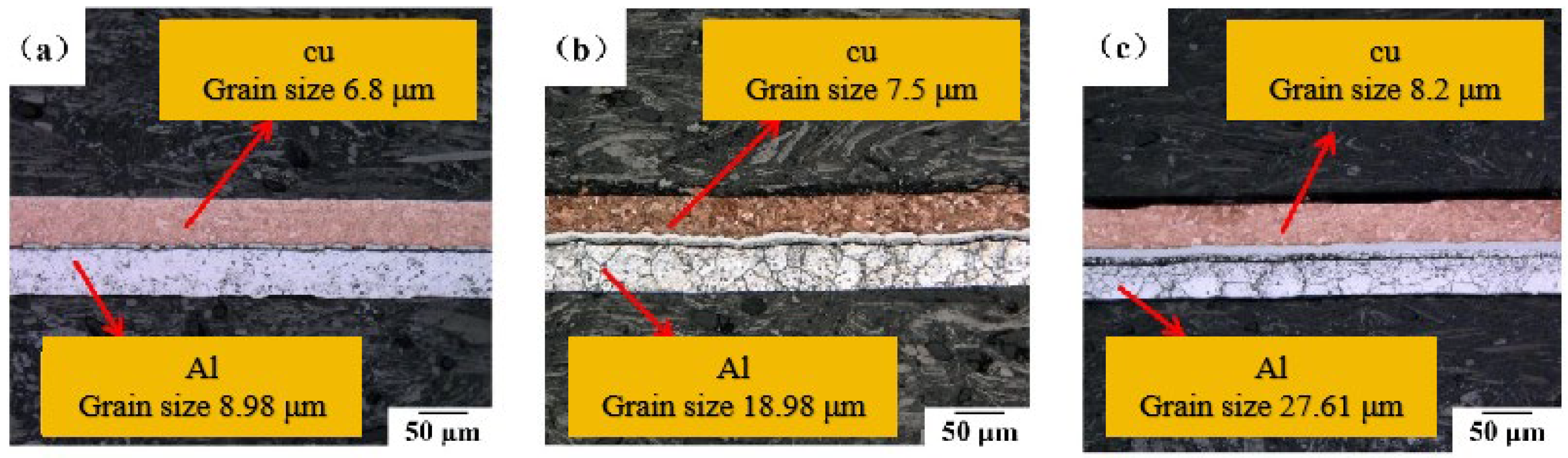
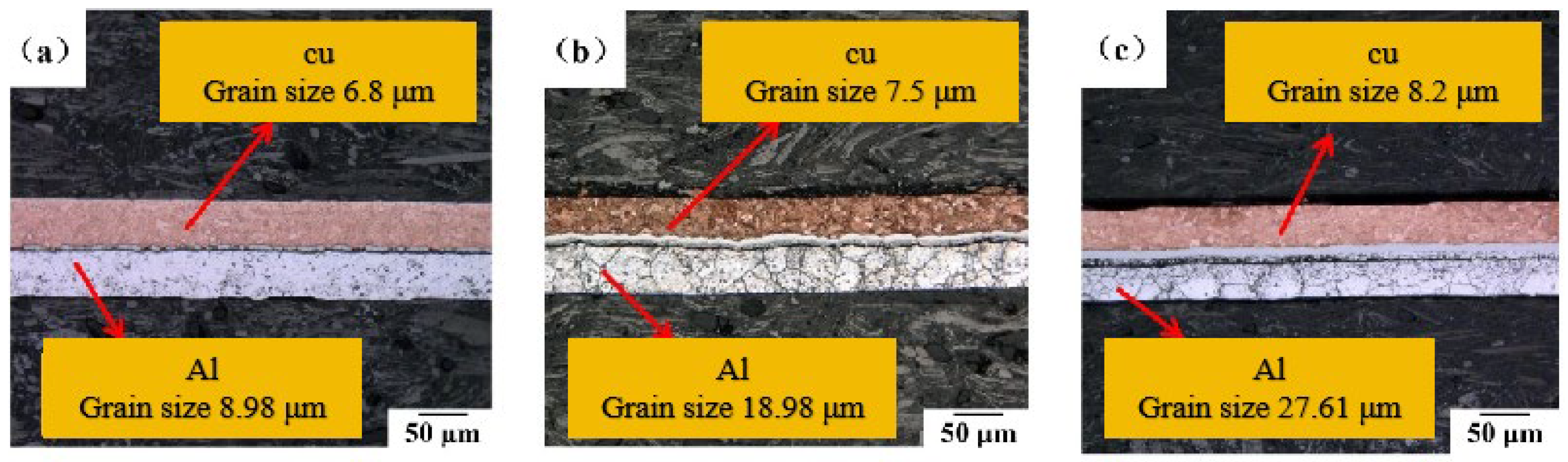
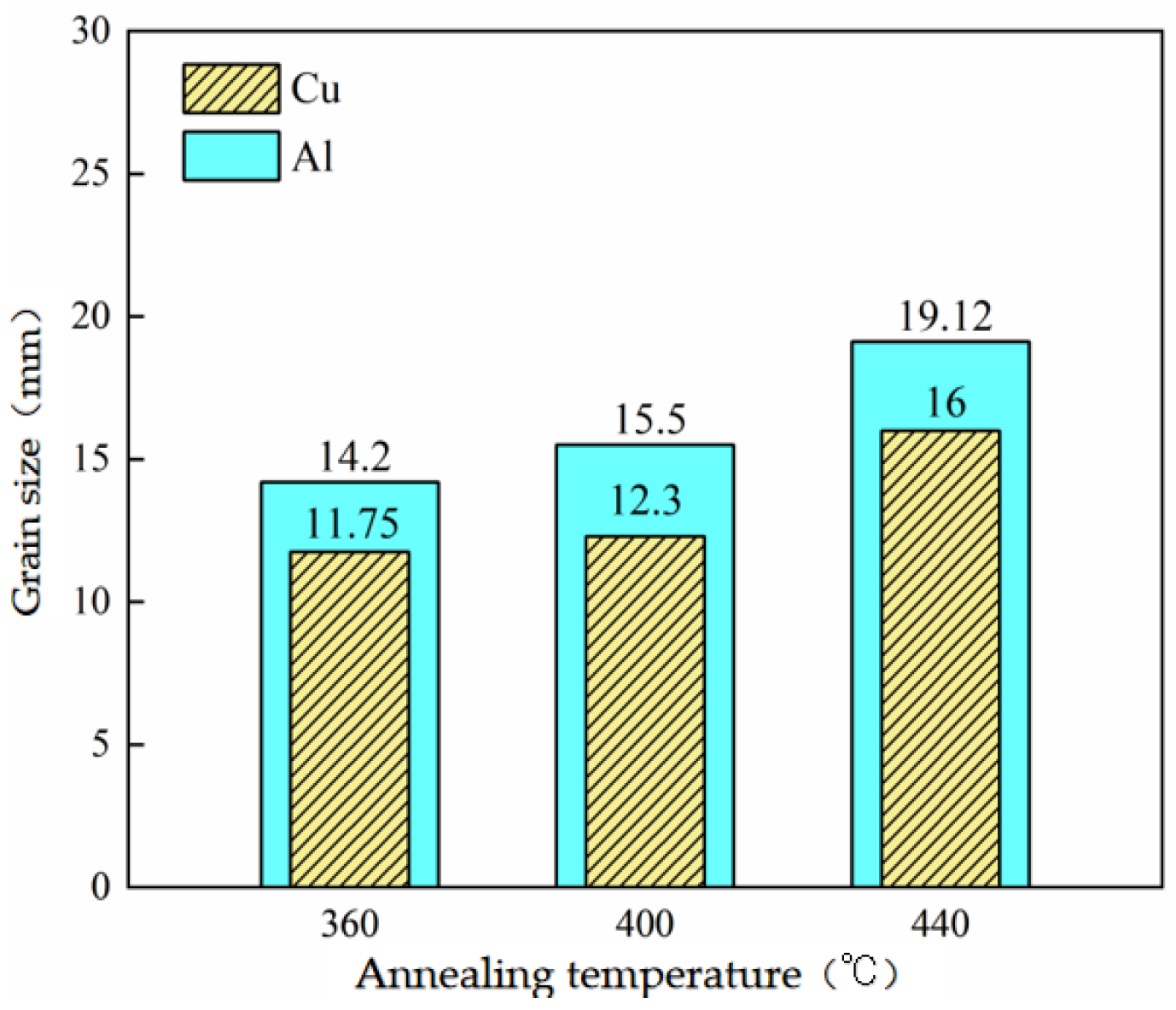
3.1. Effect of Annealing Process on Grain Size of Micro-Rolled Cu/Al Composite Thin Sheets
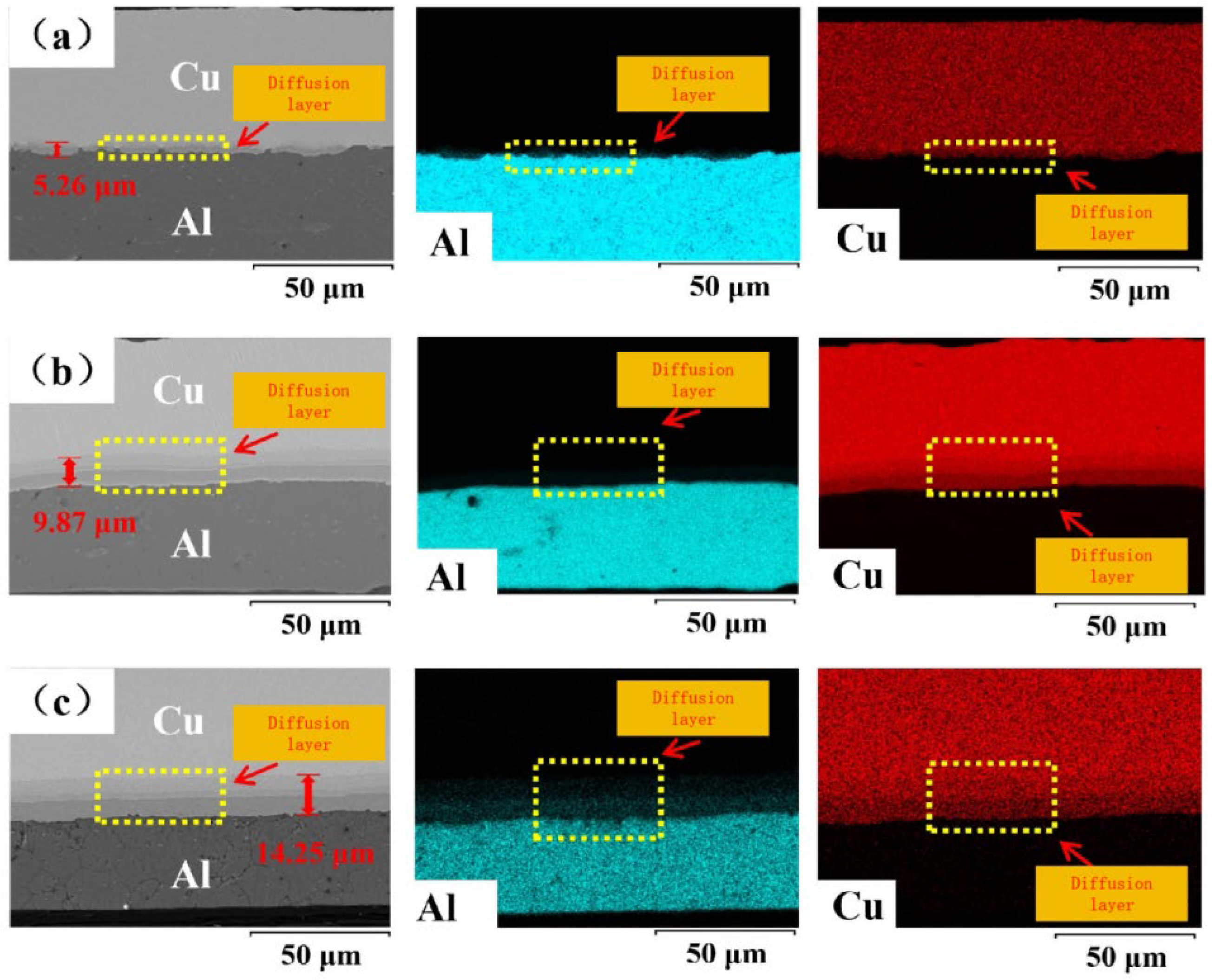
3.1.1. Effect of Annealing Temperature on the Microstructure of Cu/Al Composite Thin Sheets Made by One Round of Micro-Rolling
3.1.2. Effect of Annealing Temperature on the Grain Size of Double-Micro-Rolled Cu/Al Composite Thin Sheets
3.2. Effect of Annealing Temperature on the Tensile Properties of Micro-Rolled Cu/Al Composite Thin Sheets
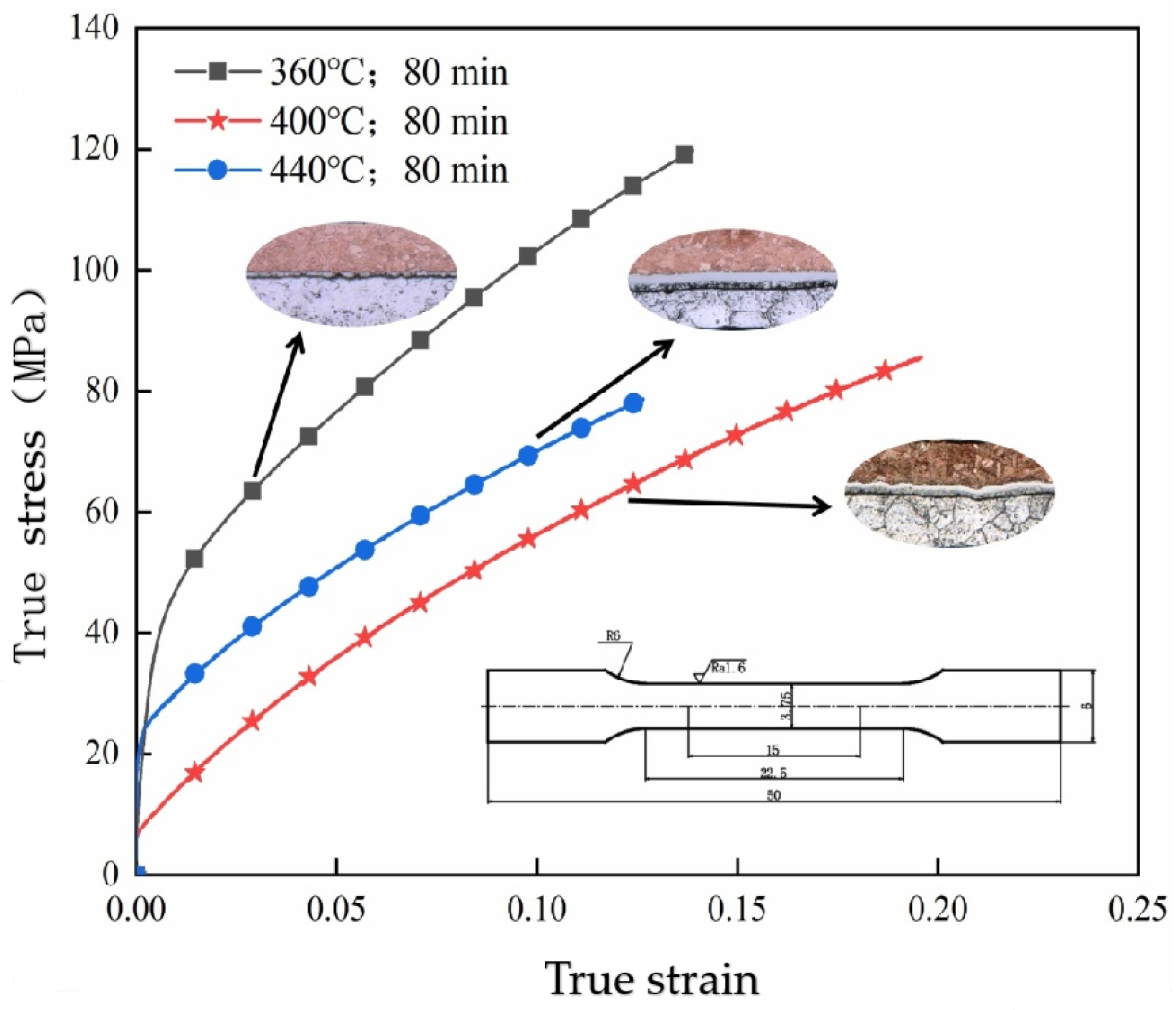
3.2.1. Effect of Annealing Temperature on the Tensile Properties of Cu/Al Composite Thin Sheets Made Through One Round of Micro-Rolling
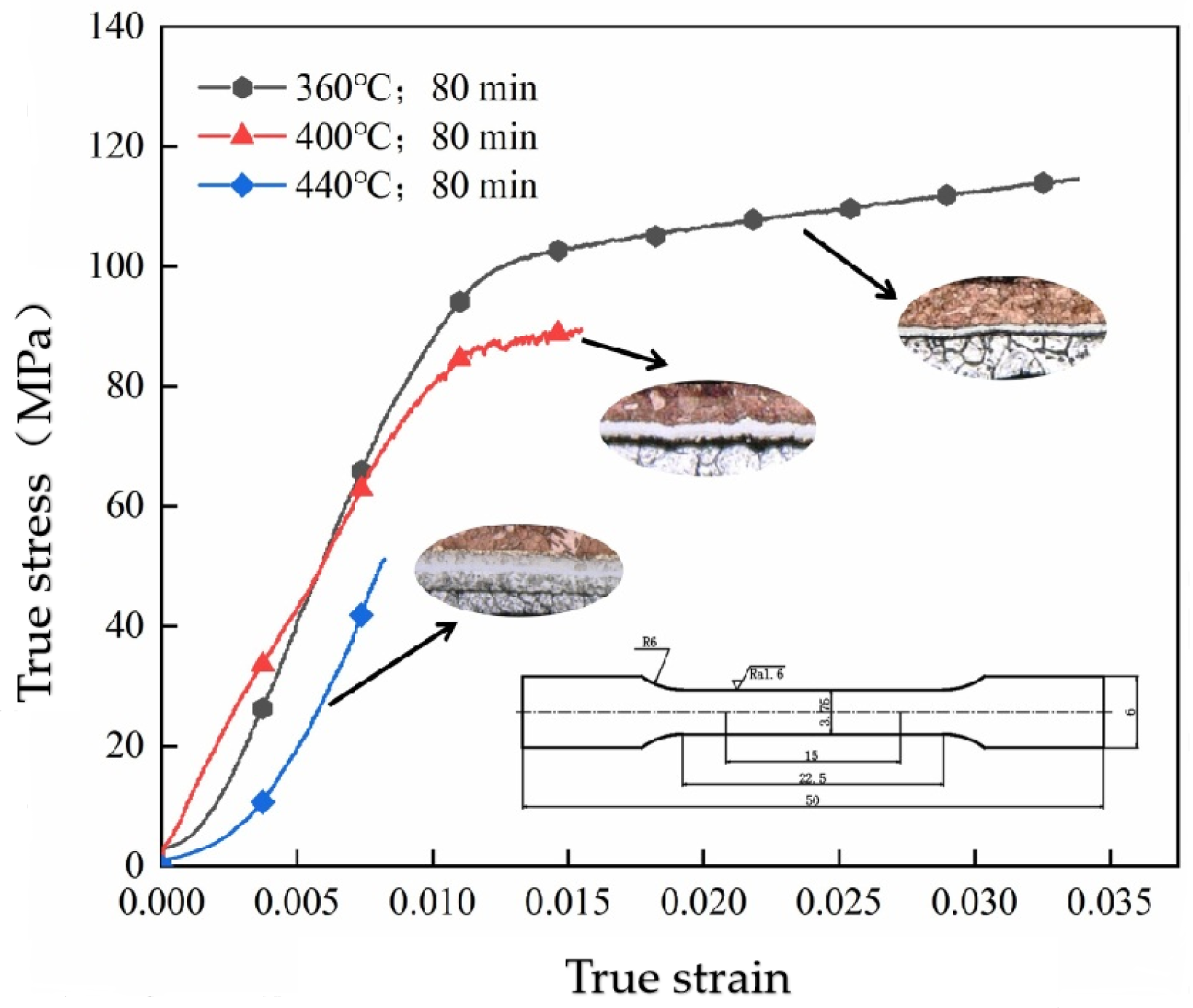
3.2.2. Effect of Annealing Temperature on the Tensile Properties of Double-Micro-Rolled Cu/Al Composite Thin Sheets
3.2.3. Effect of Grain Size on the Tensile Properties of Cu/Al Composite Thin Sheets
3.2.4. Effect of Secondary Rolling on the Tensile Properties of Cu/Al Composite Thin Sheets
3.3. Effect of Annealing Temperature on the Tensile Fracture of Micro-Rolled Cu/Al Composite Thin Sheets
3.3.1. Effect of Annealing Temperature on the Tensile Fracture of Cu/Al Composite Thin Sheets Made by One Round of Micro-Rolling
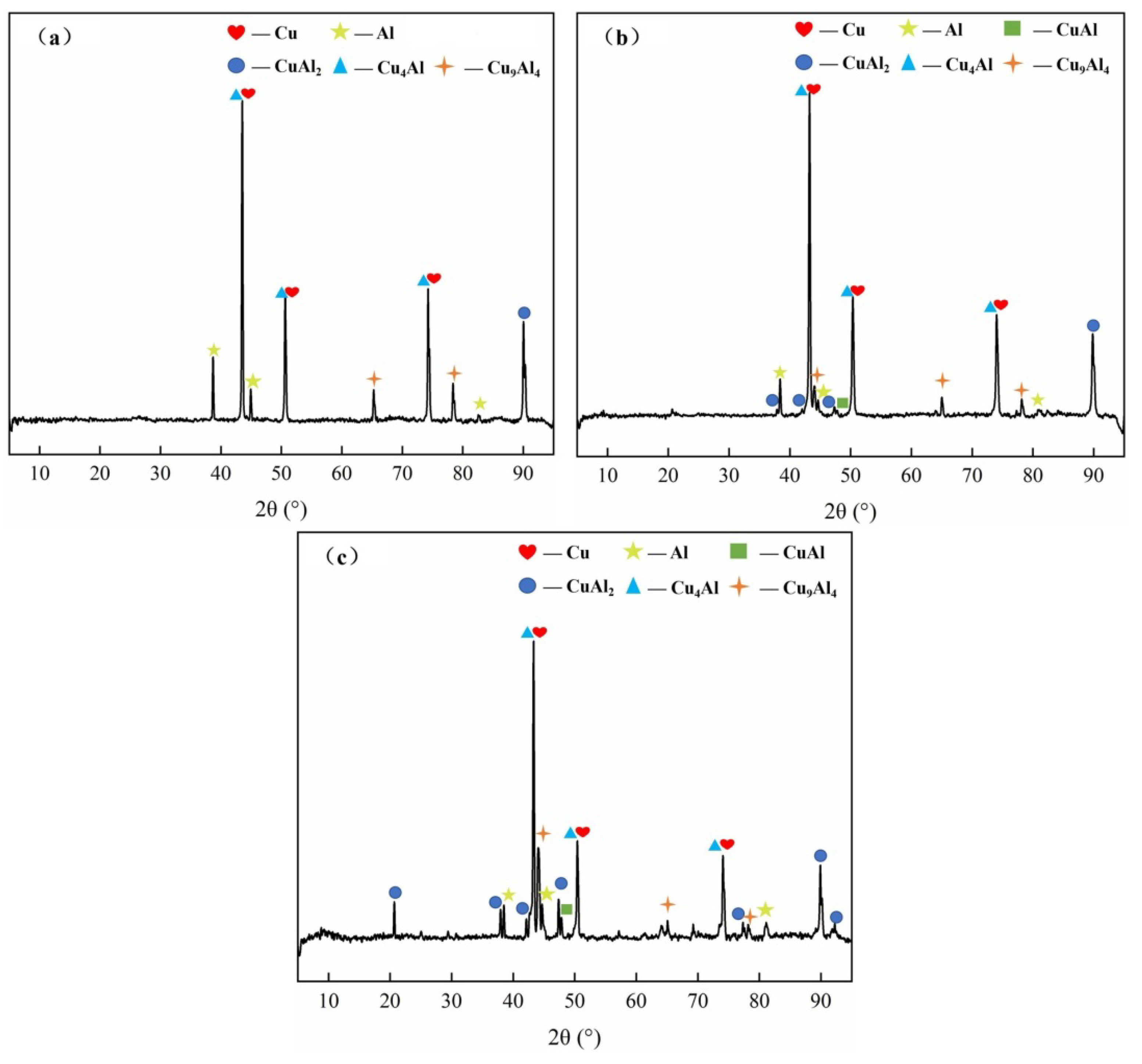
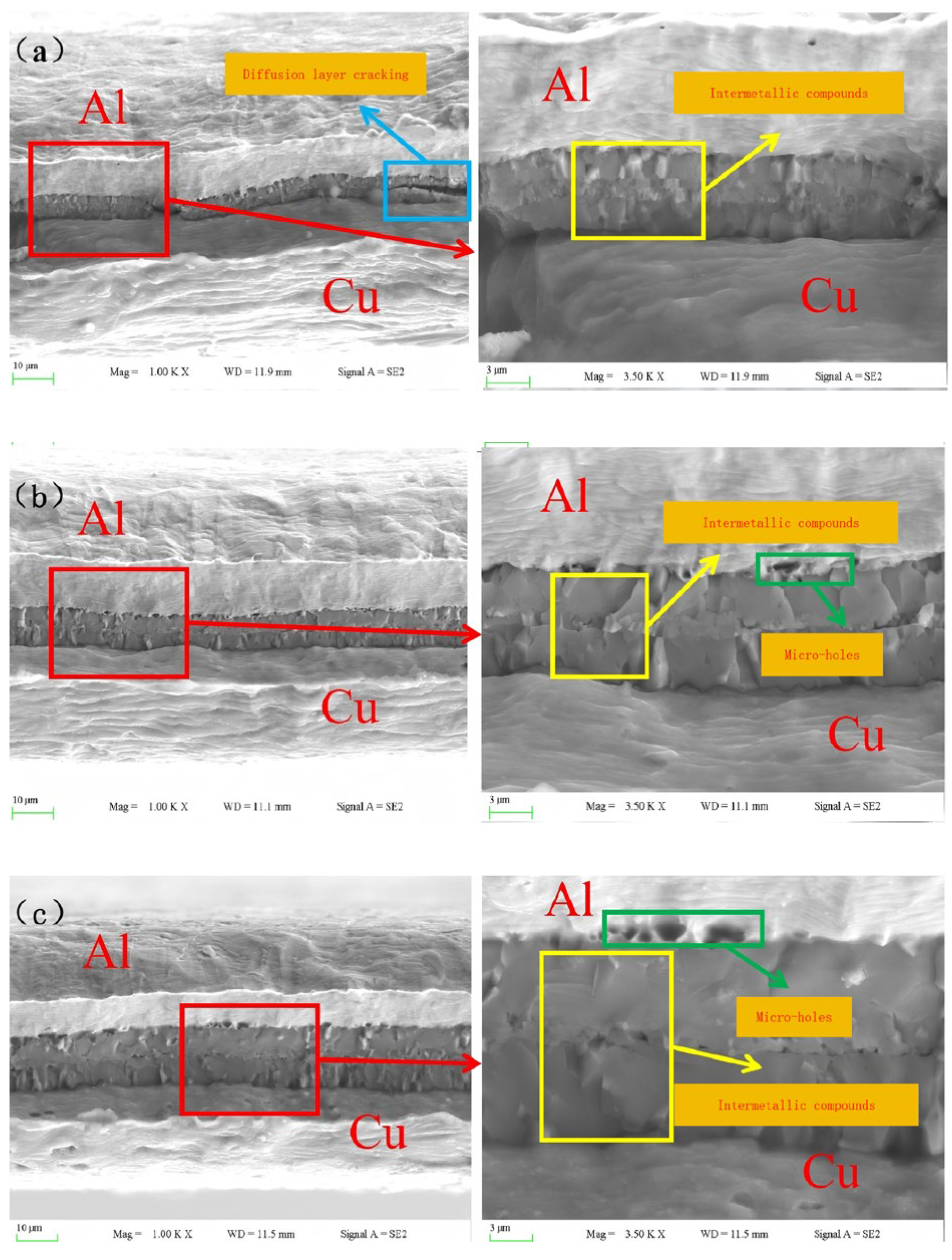
3.3.2. Study on the Fracture Mechanism of Cu/Al Composite Thin Sheets Produced by One Round of Rolling
3.3.3. Effect of Annealing Temperature on the Tensile Fracture of Double-Micro-Rolled Cu/Al Composite Thin Sheets
3.3.4. Study of the Fracture Mechanism of Cu/Al Composite Thin Sheets After Secondary Rolling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, M.W.; Wang, J.L.; Korsunsky, A.M. A review of geometrical and microstructural size effects in micro-scale deformation processing of metallic alloy components. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2016, 109, 94–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.A.C.; Guerrieri, D.C.; Cervone, A. A review of MEMS micropropulsion technologies for cubeSats and pocket qubes. Acta Astronaut. 2018, 143, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.B.; Zhang, J.T. A review on solid propellant micro-thruster array based on MEMS technology. FirePhysChem 2024, 4, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, N.; Hossain, A. Advances of materials science in MEMS applications: A review. Results Eng. 2024, 22, 102115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.K. A quantitative study of the tribological size effect in microforming with a multi-region FEA model. Tribol. Int. 2015, 90, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, G.; Galvão, I.; Mendes, R.; Leal, R.M.; Loureiro, A. Weldability of aluminium-copper in explosive welding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 3211–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.C.; Song, C.; Zhou, J.L.; Ji, H. Dynamic weld evolution during ultrasonic welding of Cu-Al joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 823, 141724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogar, M.N.; Kulkarni, O.; Kakandikar, G. Micro Forming Studies of SS316L as Biomedical Application Material. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2023, 16, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.V.; Reddy, G.M.; Nagarjuna, S. Weld overlay cladding of high strength low alloy steel with austenitic stainless steel-structure and properties. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2496–2506. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Wang, Q.; Shang, Z. An investigation on microstructures and mechanical properties of ultra-low Cu layer thickness ratio Cu/8011/1060 clads. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 5866–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Nagai, K.; Yin, F. Progress in cold roll bonding of metals. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2008, 9, 023001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Kuwabara, T. Micro form rolling: Imprinting ability of microgrooves on metal shafts. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 201, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Peng, L. Crystal plasticity-based analysis and modelling of grain size and strain path dependent micro-scaled deformation mechanisms of ultra-thin sheet metals. Int. J. Plast. 2023, 168, 103696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Z. Effects of annealing temperature on interface microstructure and element diffusion of ultra-thin Cu/Al composite sheets. Mater. Lett. 2022, 322, 132491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.W.; Chan, W.L. Geometry and grain size effects on the fracture behavior of sheet metal in micro-scale plastic deformation. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4738–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Chen, R. Size effect on deformation behavior and fracture in a pure copper microtensile test. Strength Mater. 2021, 53, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Geng, F. Interactive effects of microstructure and interface on tensile deformation behaviors of Cu/Ni clad foils. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 714, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gau, J.T.; Principe, C.; Wang, J. An experimental study on size effects on flow stress and formability of aluminm and brass for microforming. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 184, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, Z.; Peng, L. Intragranularly misoriented grain boundary evolution affected by local constraints and grain size in micro-scale deformation of ultra-thin metallic sheets. Int. J. Plast. 2022, 157, 103377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Tao, W.; Jian, G.Z. Effect of annealing temperature on microstructure and tensile properties of copper/aluminum composite thin strip. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2023, 33, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.B.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.S. Deformation behavior and crack propagation on interface of Al/Cu laminated composites in uniaxial tensile test. Rare Met. 2020, 39, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, X.; Ma, L. A study on the microstructural evolution of copper/aluminum composite strips fabricated by micro flexible rolling. Mater. Charact. 2023, 205, 113315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, R.; Zhu, Q. Effect of annealing on the interface and mechanical properties of Cu-Al-Cu laminated composite prepared with cold rolling. Materials 2020, 13, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Zhu, R.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, Z. Study on Microstructure and Properties of Ultra-thin Cu/Al Composite Sheets Using the Cold-Rolled Composite Method at the Microscale. Metals 2023, 13, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Jiang, Z. Study of Wire Deformation Characterization and Size Effects during the Micro Flat-Rolling Process. Metals 2020, 10, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.; Walley, S. The Hall–Petch and inverse Hall–Petch relations and the hardness of nanocrystalline metals. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 2661–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Xie, J.; Wang, A.; Mao, Z.; Liu, S.; Tian, H. Interfacial phase growth behavior of Cu-Al composite plates. J. Mater. Heat Treat. 2017, 38, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z. Influence of heat treatment on diffusion kinetics and mechanical properties of Mg/Al composite plates for automotive applications. Precis. Molding Eng. 2024, 172, 180. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Su, Z.; Xu, S.; Wang, D.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, Z. Emergence and annihilation of Kirkendall holes during magnetron sputtering aluminum coating to twinning induced plasticity steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 601, 154265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Knez, M.; Scholz, R.; Xu, S.; Wang, D.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, Z. Influence of surface diffusion on the formation of hollow nanostructures induced by the Kirkendall effect: The basic concept. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 993–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Cu | Bi | Sb | As | Fe | Ni | P | Pb | Sn | S | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 99.90 | <0.0004 | <0.0010 | <0.0010 | 0.0074 | 0.0013 | 0.0017 | 0.0037 | 0.0023 | 0.0015 | 0.0099 |
| Al | V | Mn | Mg | Zn | Si | Ti | Fe | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 99.60 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.03 | 0.35 | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Zhang, H.; Yu, G.; Jiang, Z. Size Effect on Tensile Properties and Fracture Mechanism of Micro-Rolled Ultra-Thin Cu/Al Composite Sheet. Metals 2025, 15, 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080907
Zhang P, Zhang H, Yu G, Jiang Z. Size Effect on Tensile Properties and Fracture Mechanism of Micro-Rolled Ultra-Thin Cu/Al Composite Sheet. Metals. 2025; 15(8):907. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080907
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Pengkun, Hongmei Zhang, Guoao Yu, and Zhengyi Jiang. 2025. "Size Effect on Tensile Properties and Fracture Mechanism of Micro-Rolled Ultra-Thin Cu/Al Composite Sheet" Metals 15, no. 8: 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080907
APA StyleZhang, P., Zhang, H., Yu, G., & Jiang, Z. (2025). Size Effect on Tensile Properties and Fracture Mechanism of Micro-Rolled Ultra-Thin Cu/Al Composite Sheet. Metals, 15(8), 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080907







