Effect of Si Doping on Microstructure and Mechanical and Electrochemical Properties of (AlCrFeNi)100-xSix (x = 2, 4, 6) Dual-Phase Eutectic High-Entropy Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Alloy Preparation
2.2. Microstructure Characterization
2.3. Properties Test
3. Results and Discussion
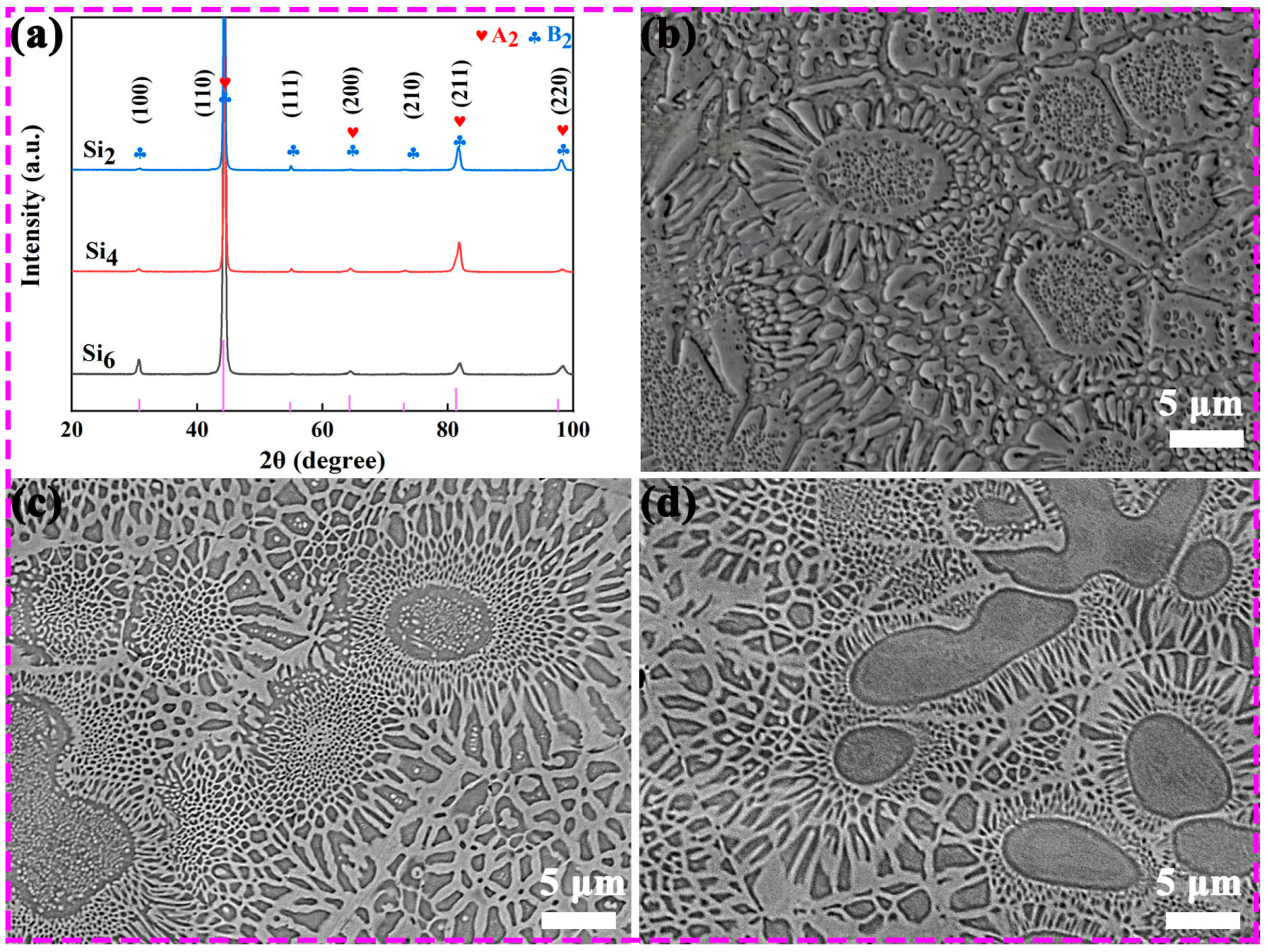
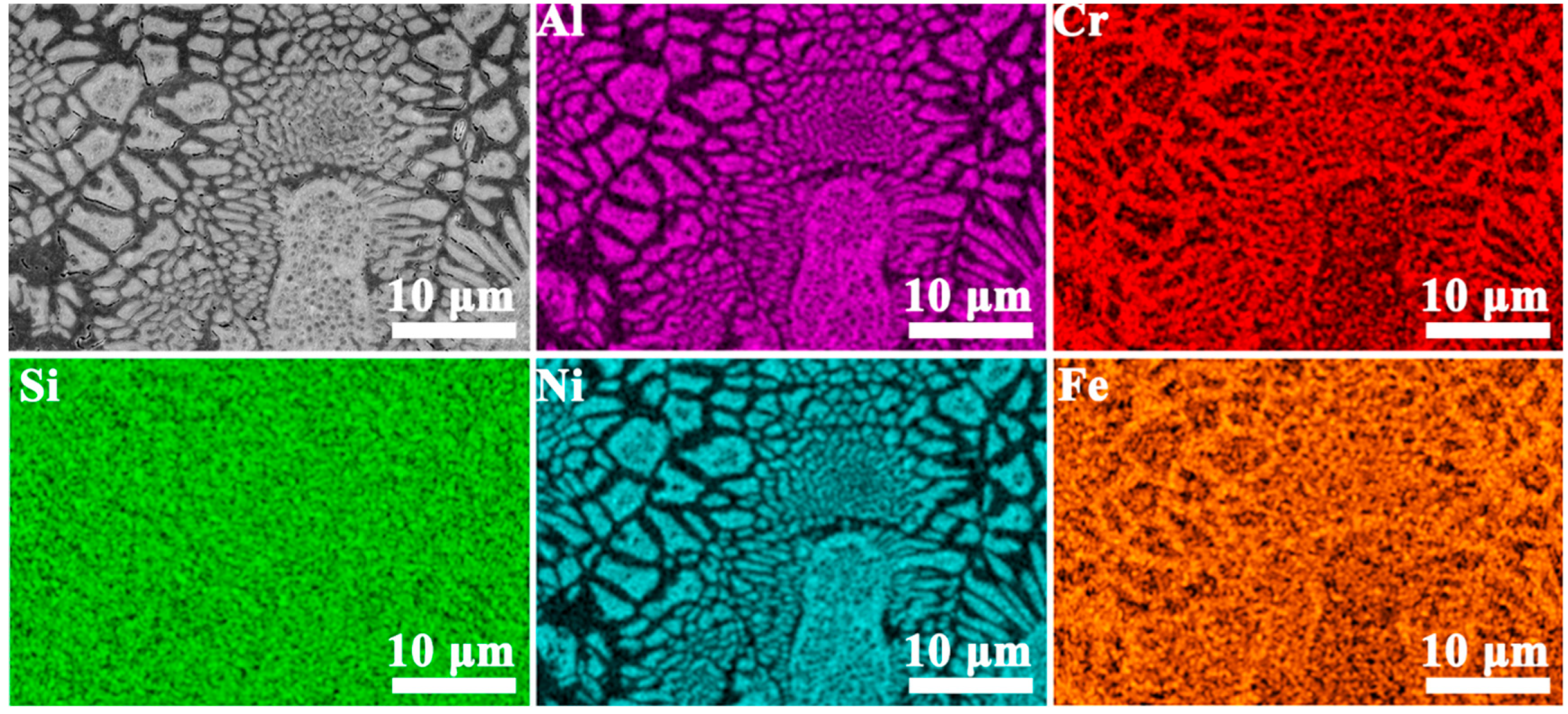
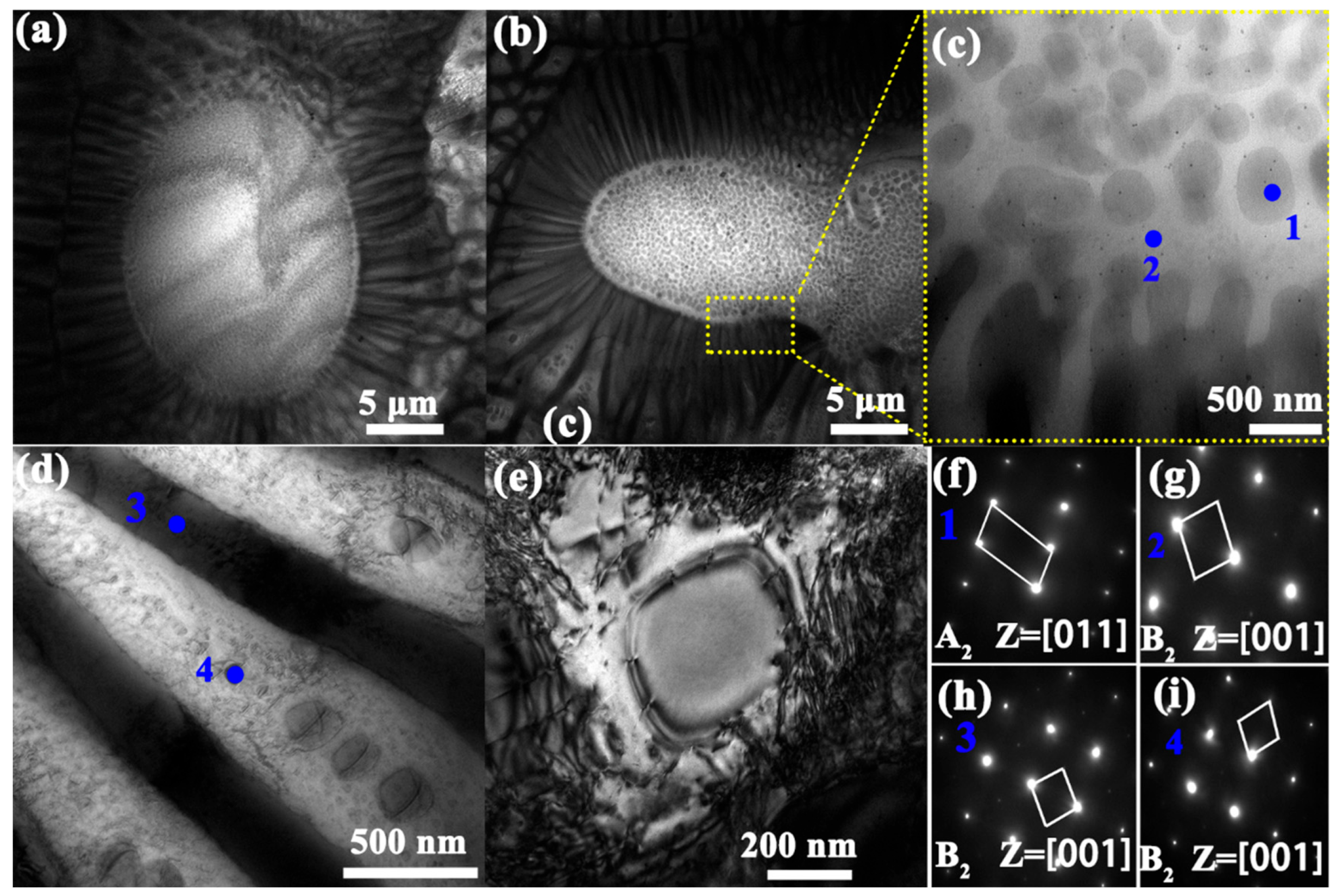
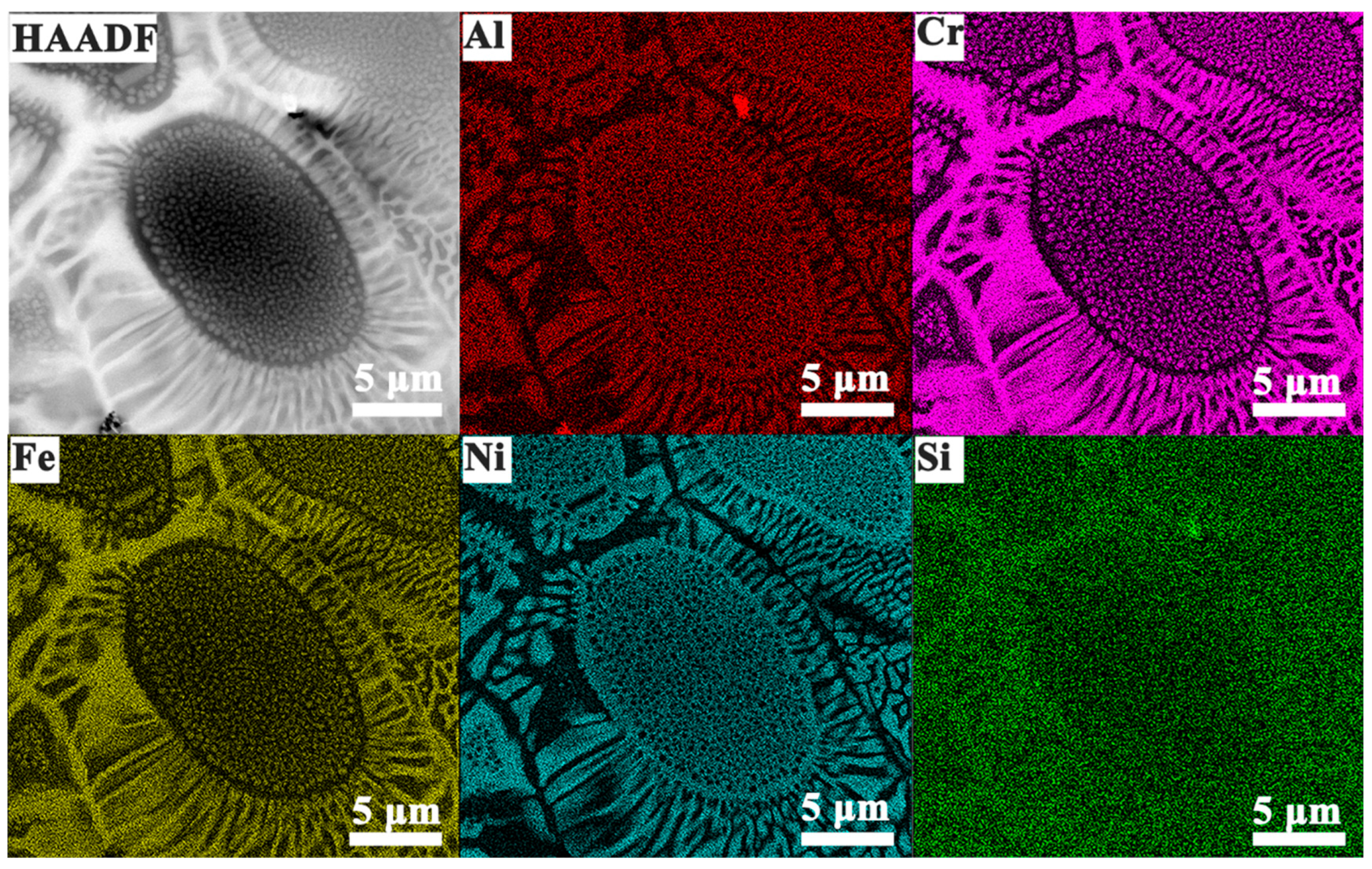
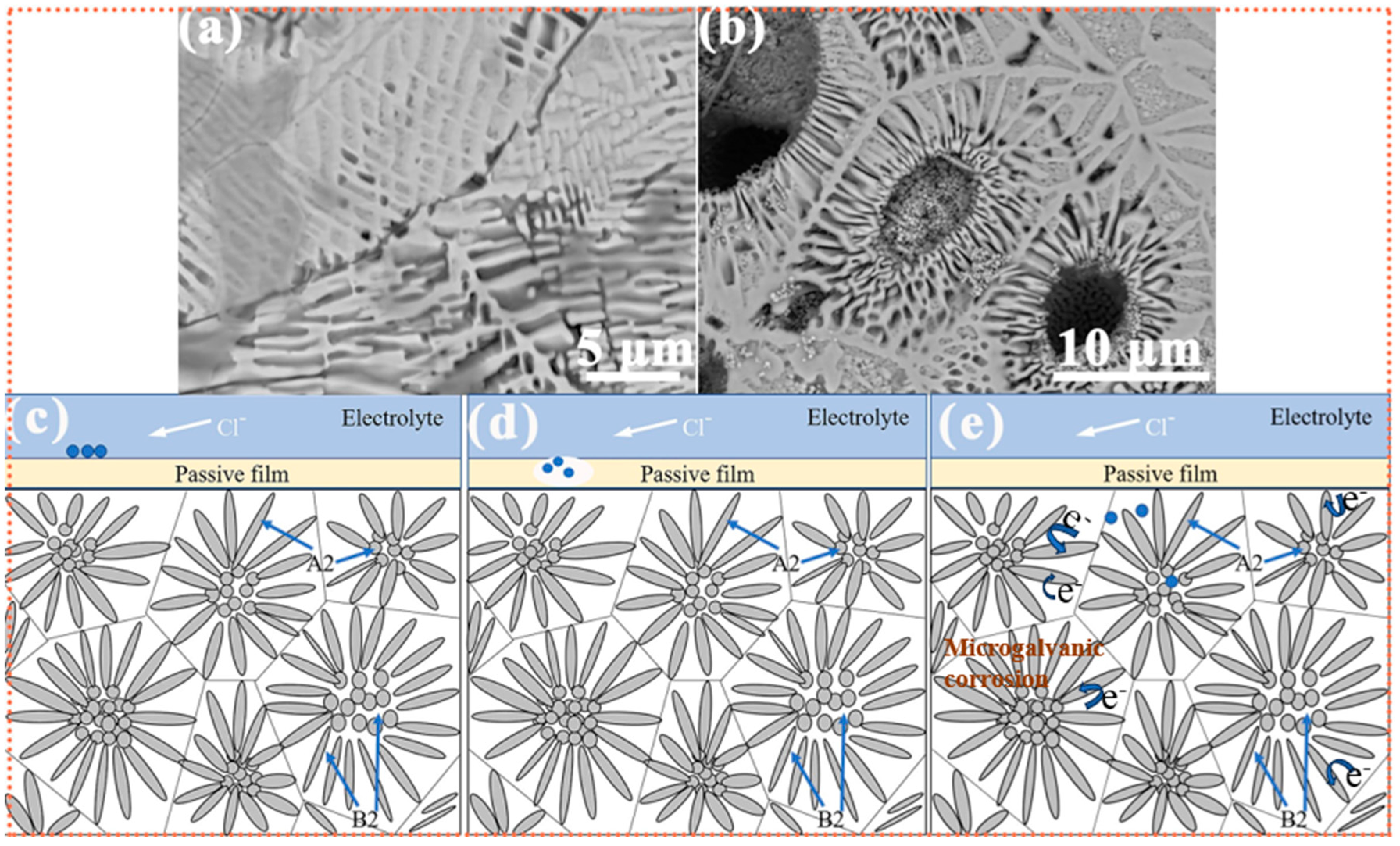
3.1. Phase and Microstructure
3.2. Electrochemical Test
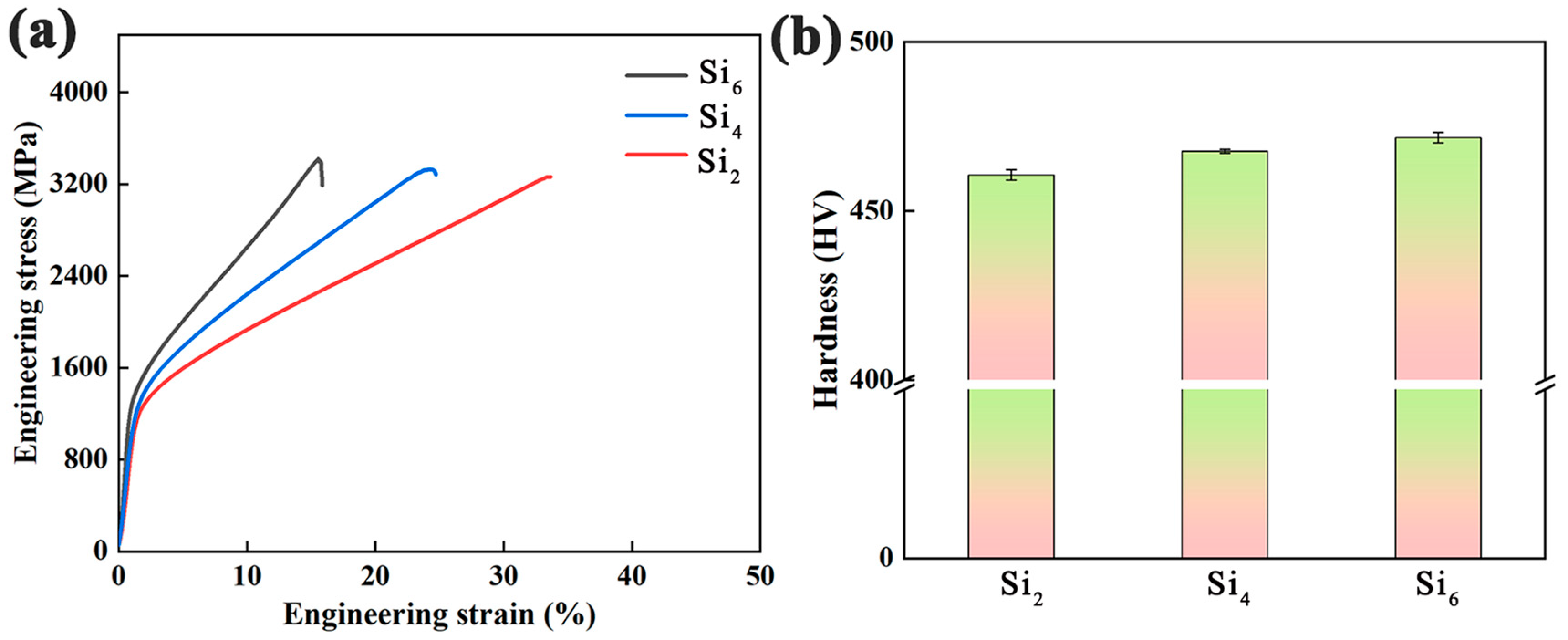
3.3. Mechanical Property Test
4. Conclusions
- With increasing Si content, all three alloys retained a sunflower-like eutectic microstructure composed of A2 and B2 phases. The central region of the microstructure gradually expanded, while the two-phase lamellar “petal” regions became denser and more refined. The volume fraction of the ordered B2 phase increased from ~20.9% to ~27.8% as Si content increased from 2 to 6 at.%. The B2 phase was enriched in Al and Ni elements, whereas the A2 phase was enriched in Cr, Fe, and Si. Nanometer-scale B2 precipitates were observed in both phases within the petal regions.
- The corrosion resistance of the alloys decreased with increasing Si content. Among them, the Si2 alloy exhibited the best corrosion performance, with a corrosion potential (Ecorr) of −381.6 mV (vs. Ag/AgCl) and a corrosion current density (Icorr) of 486.9 nA/cm2. Galvanic corrosion occurred between the two phases, where the A2 phase acted as the cathode and was protected, while the B2 phase served as the anode and was preferentially corroded.
- The compressive strength and Vickers hardness of the alloys increased with higher Si content, while the plasticity showed a significant decline. The Si2 alloy demonstrated excellent comprehensive mechanical properties, with a fracture strength of 3261 MPa, plastic strain of 33.8%, and a Vickers hardness of 461 HV.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsu, W.L.; Tsai, C.W.; Yeh, A.C.; Yeh, J.W. Clarifying the four core effects of high-entropy materials. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2024, 8, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaji, V.; Xavior, M.A. Development of high entropy alloys (HEAs): Current trends. Heliyon 2024, 10, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.P.; Wang, H.; Chen, M.W.; Baker, I.; Yeh, J.W.; Liu, C.T.; Nieh, T.G. An assessment on the future development of high-entropy alloys: Summary from a recent workshop. Intermetallics 2015, 66, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Q.; Liaw, P.K.; Li, R.X.; Zhang, W.R.; Geng, G.H.; Yan, X.H.; Liu, G.Q.; Zhang, Y. Relationship between the unique microstructures and behaviors of high-entropy alloys. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2024, 31, 1350–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.P.; Raabe, D.; Ritchie, R.O. High-entropy alloys. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Jiang, X.S.; Fang, Y.; Fang, Y.J.; Liu, B.; Sun, H.L.; Shao, Z.Y.; Song, T.F. Research and development of welding methods and welding mechanism of high-entropy alloys: A review. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 28, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W. Alloy Design Strategies and Future Trends in High-Entropy Alloys. JOM 2013, 65, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Xing, F.; Xu, G.J.; Liu, W.J.; Bian, H.Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of additive manufactured TiC-reinforced Fe55Cr25Co10Ni10 high-entropy alloy composites. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 187, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Guo, H.; Yang, W.; Pang, S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, T. Al0.3CrXFeCoNi high-entropy alloys with high corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 860, 158436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.W.; Li, A.X.; Zhang, J.S.; Xu, M.K.; Huang, D.; Che, C.N.; Liu, S.K.; Jiang, Y.T.; Li, Y.Q.; Li, G. Revealing the oxidation behavior of AlCrXFeNi lightweight multi-principal element alloys via experimental and first-principles calculations. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1008, 176622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, X.S.; Yu, P.F.; Fan, X.F.; Tong, X.; Liu, Q.Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Li, G. Synthesis and characterization of a ultrafine grained (CoCrFeNi)80Mn10Ti10 multi-principal element alloy nanocomposite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 833, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.F.; Li, R.; Liu, X.S.; Liu, Q.Q.; Tong, X.; Li, A.X.; Xu, S.; Yang, H.; Yu, P.F.; Li, G. Synergistic strengthening of heterogeneous structures and dual-morphology nano-precipitates in Co1.5CrNi1.5Al0.2Ti0.1V0.1 medium-entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 832, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Liu, X.; Li, R.; Yu, S.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, J.; Che, C.; Huang, D.; Yu, P.; Li, G. Double heterogeneous structures induced excellent strength–ductility synergy in Ni40Co30Cr20Al5Ti5 medium-entropy alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 181, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.T.; Li, A.X.; Kang, K.W.; Zhang, J.S.; Huang, D.; Che, C.N.; Liu, S.K.; Xu, M.K.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhang, B.R.; et al. Effect of Multi-Phase Composite Structure on the Mechanical Properties of AlXFe1.5CoNiC0.12 High Entropy Alloys. Metals 2025, 15, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.K.Y.; Sharma, P.; Singh, P.; Kundu, A.; Balasubramanian, G.; Chan, H.M. Solid State Reduction Driven Synthesis of Mn Containing Multi-principal Component Alloys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2024, 55, 3799–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.L.; Liu, Y.Z.; Zhang, H.R.; Li, C.Z.; Chen, S.N.; Yang, Y.J.; Liang, S.X.; Ma, M.Z. Synergistic strength-ductility enhancement of CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys with regulated Co/Cr atomic ratios. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 912, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraj, C.; Borda, E.J.L.; Walle, A.; Samanta, A. A systematic analysis of phase stability in refractory high entropy alloys utilizing linear and non-linear cluster expansion models. Acta Mater. 2021, 220, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.H.; He, Q.F.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, S.; Shi, S.Q.; Hu, A.; Fan, J.; Yang, Y. Atomic-scale distorted lattice in chemically disordered equimolar complex alloys. Acta Mater. 2018, 150, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.P.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Z.J.; Cao, Z.Q.; Guo, S.; Wang, T.M.; Li, T.J.; Liaw, P.K. Promising properties and future trend of eutectic high entropy alloys. Scr. Mater. 2020, 187, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.P.; Jiang, H.; Guo, S.; Wang, T.M.; Cao, Z.Q.; Li, T.J. A new strategy to design eutectic high-entropy alloys using mixing enthalpy. Intermetallics 2017, 91, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Liu, X.S.; Fan, X.F.; Li, R.; Tong, X.; Yu, P.F.; Li, G. Designing novel AlCoCrNi eutectic high entropy alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2022, 904, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Lu, Y.P.; Wang, T.M.; Kundu, A.; Balasubramanian, G.; Chan, H.M. A novel bulk eutectic high-entropy alloy with outstanding as-cast specific yield strengths at elevated temperatures. Scr. Mater. 2021, 204, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.C.; Diao, Z.H.; Kang, H.J.; Li, Z.; Li, J.H.; Qu, Z.X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, G.W.; Li, B. A New Strategy for the Design of Triple-Phase Eutectic High-Entropy Alloys Based on Infinite Solid Solution and Pseudo-Ternary Method. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 6117–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.B.; Xiong, Z.P.; Xu, Z.Q.; Cheng, X.W. Varying the eutectic composition of Co-Cr-Fe-Ni-Hf high-entropy system using a modified simple mixture method. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2020, 786, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Zheng, S.J.; Pang, J.Y.; Ma, X.L. High-strength and high-ductility AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloy achieved via precipitation strengthening in a heterogeneous structure. Scr. Mater. 2020, 186, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.Z.; Lu, Y.P.; Zhang, B.; Liang, N.N.; Wu, G.Z.; Sha, G.; Liu, J.Z.; Zhao, Y.H. Microstructural origins of high strength and high ductility in an AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2017, 141, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.P.; Dong, Y.; Guo, S.; Jiang, L.; Kang, H.J.; Wang, T.M.; Wen, B.; Wang, Z.J.; Jie, J.C.; Cao, Z.Q.; et al. A Promising New Class of High-Temperature Alloys: Eutectic High-Entropy Alloys. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.J.; Ren, W.L.; Zheng, T.X.; Ren, Z.M.; Hou, X.L.; Peng, J.C.; Hu, P.F.; Gao, Y.F.; Zhong, Y.B.; Liaw, P.K. Enhanced strength-ductility synergy in ultrafine-grained eutectic high-entropy alloys by inheriting microstructural lamellae. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Jiang, H.; Xie, W.L.; Kong, X.; Qin, S.X.; Yao, H.W.; Li, Y. Effect of Mo addition on microstructural evolution and corrosion behaviors of AlCrFeNi3 eutectic high-entropy alloy. Corros. Sci. 2024, 229, 111879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Li, Z.H.; Lin, D.Y.; Tang, Z.X.; Song, X.G.; He, P.; Zhang, S.Y.; Bian, H.; Fu, W.; Song, Y.Y. Eutectic high-entropy alloys and their applications in materials processing engineering: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 189, 211–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.F.; Chai, Z.S.; Zheng, J.; Wu, Q.F.; He, F.; Yang, Z.N.; Li, J.J.; Wang, J.C.; Yang, H.O.; Wang, Z.J. Design Fe-based Eutectic Medium-Entropy Alloys Fe2NiCrNbX. Acta Metall. Sin. Engl. Lett. 2021, 34, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.P.; Gao, X.Z.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Z.N.; Wang, T.M.; Jie, J.C.; Kang, H.J.; Zhang, Y.B.; Guo, S.; Ruan, H.H.; et al. Directly cast bulk eutectic and near-eutectic high entropy alloys with balanced strength and ductility in a wide temperature range. Acta Mater. 2017, 124, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.P.; Gao, X.X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, T.M.; Chen, H.L.; Mao, H.H.; Zhao, Y.H.; Jiang, H.; Cao, Z.Q.; Li, T.J.; et al. Preparing bulk ultrafine-microstructure high-entropy alloys via direct solidification. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 1912–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.P.; Wu, X.X.; Fu, Z.H.; Yang, Q.K.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.M.; Li, T.X.; Tian, Y.Z.; Tan, H.; Li, Z.M.; et al. Ductile and ultrahigh-strength eutectic high-entropy alloys by large-volume 3D printing. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 126, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Du, X.Y.; Li, B.S. A novel Fe20Co20Ni41Al19 eutectic high entropy alloy with excellent tensile properties. Mater. Lett. 2018, 216, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, W.B.; Li, P.B.; Huang, Z.H.; Luo, G.Q.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, L.M. Eutectic MoNbTa(WC)X Composites with Excellent Elevated Temperature Strength. Metals 2023, 13, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuang, S.; Ding, Z.Y.; Chung, D.; Shi, S.Q.; Yang, Y. Corrosion resistant nanostructured eutectic high entropy alloy. Corros. Sci. 2020, 164, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.Y.; Zhang, L.J.; Wei, X.M.; Zhang, C.Z.; Jia, Q.X.; Sun, K.; Duan, D.T.; Li, G. Corrosion and passive behaviors of the Co-Cr-Fe-Ni-Nb eutectic high-entropy alloys in different electrolyte solutions. Intermetallics 2025, 177, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.X.; Gong, W.; Tsuru, T.; Lobzenko, I.; Li, X.Q.; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, T.; Do, H.S.; Bae, J.W.; Wagner, C.; et al. Si-addition contributes to overcoming the strength-ductility trade-off in high-entropy alloys. Int. J. Plast. 2022, 159, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.K.; Hua, K.; Cao, Y.; Song, Y.Q.; Li, X.L.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, H.F. Microstructures and properties of FeCrAlMoSix high entropy alloy coatings prepared by laser cladding on a titanium alloy substrate. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 478, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravindh, S.A.; Kistanov, A.A.; Alatalo, M.; Kömi, J.; Huttula, M.; Cao, W. Incorporation of Si atoms into CrCoNiFe high-entropy alloy: A DFT study. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2021, 33, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Yang, Y.L.; He, R.J.; Tan, C.W.; Huttula, M.; Cao, W. A novel high entropy CoFeCrNiCu alloy filler to braze SiC ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 3391–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.B.; Feng, M.Y.; Chen, C.R.; Lian, G.F. Microstructure evolution, wear resistance and corrosion resistance of CoCrCu0.5FeNiSiX high-entropy alloy coatings fabricated by laser cladding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. JmrT 2025, 36, 5539–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Gong, M.L.; Huang, L.T.; Wagn, K.Y.; Qu, H.Z.; Liu, F.F.; Bai, J.; Gao, Q.Z.; Zhao, X.; Li, S. Microstructure and Properties of FeCoNiCuSix High Entropy Alloys. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2022, 14, 122–129. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.X.; Feng, M.Y.; Lian, G.F.; Lu, H.; Chen, C.R.; Huang, X. Effects of Si content on the microstructure and properties of CoCrFeMnNiSix high-entropy alloy coatings by laser cladding. Mater. Charact. 2024, 216, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Chen, D.Z.; Fu, Y.A.; Shi, Q.S.; Yin, Y.J.; Zhang, S.Y. Microstructure characteristics and mechanical properties of NbMoTiVWSix refractory high-entropy alloys. China Foundry 2022, 19, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.K.; Li, A.X.; Kang, K.W.; Zhang, J.S.; Huang, D.; Che, C.N.; Jiang, Y.T.; Xu, M.K.; Zhang, B.R.; Li, Y.Q.; et al. Microstructure and Performance of Body-Centered Cubic-Based Dual-Phase Composite Eutectic High-Entropy Alloys Prepared by Si Doping. Metals 2025, 15, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Ng, C.; Liu, C.T. Anomalous solidification microstructures in Co-free AlxCrCuFeNi2 high-entropy alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2013, 557, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Ng, C.; Liu, C.T. Sunflower-like Solidification Microstructure in a Near-eutectic High-entropy Alloy. Mater. Res. Lett. 2013, 1, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.F.; Chen, W.P.; Xia, Z.B.; Xiong, W.; Fu, Z.Q. Influence of synthesis method on microstructure and mechanical behavior of Co-free AlCrFeNi medium-entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2019, 108, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.Z.; Yang, B.; Xie, X.; Brechtl, J.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K. Corrosion of Al xCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys: Al-content and potential scan-rate dependent pitting behavior. Corros. Sci. 2017, 119, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.Z.; Collins, L.; Balke, N.; Liaw, P.K.; Yang, B. In-situ electrochemical-AFM study of localized corrosion of AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys in chloride solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 439, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Pan, Z.; Wang, X.; Luo, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Corrosion and passive behavior of AlXCrFeNi3−X (x = 0.6, 0.8, 1.0) eutectic high entropy alloys in chloride environment. Corros. Sci. 2022, 208, 110666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.D.; Li, Y.S.; Zhu, Y.T.; Chen, Y.F.; Yang, B. Layer-by-layer corrosion behavior of 316LN stainless steel with a gradient-nanostructured surface. Electrochem. Commun. 2020, 110, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, A.; Merino, M.C.; Coy, A.E.; Viejo, F.; Arrabal, R.; Matykina, E. Pitting corrosion behaviour of austenitic stainless steels—combining effects of Mn and Mo additions. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 1796–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Rovere, C.A.; Alano, J.H.; Silva, R.; Nascente, P.A.P.; Otubo, J.; Kuri, S.E. Characterization of passive films on shape memory stainless steels. Corros. Sci. 2012, 57, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, G.H.; Fan, X.H.; Jin, J.; Zhang, L.; Du, Y.X. Corrosion behavior and surface characterization of an equiatomic CoCrFeMoNi high-entropy alloy under various pH conditions. J. Alloy. Compd. 2022, 900, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankin, A.; Bedoya-Lora, F.E.; Alexander, J.C.; Regoutz, A.; Kelsall, G.H. Flat band potential determination: Avoiding the pitfalls. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 26162–26176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.Z.; Macdonald, D.D.; Dong, C.F. Passive film on 2205 duplex stainless steel studied by photo-electrochemistry and ARXPS methods. Corros. Sci. 2019, 146, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
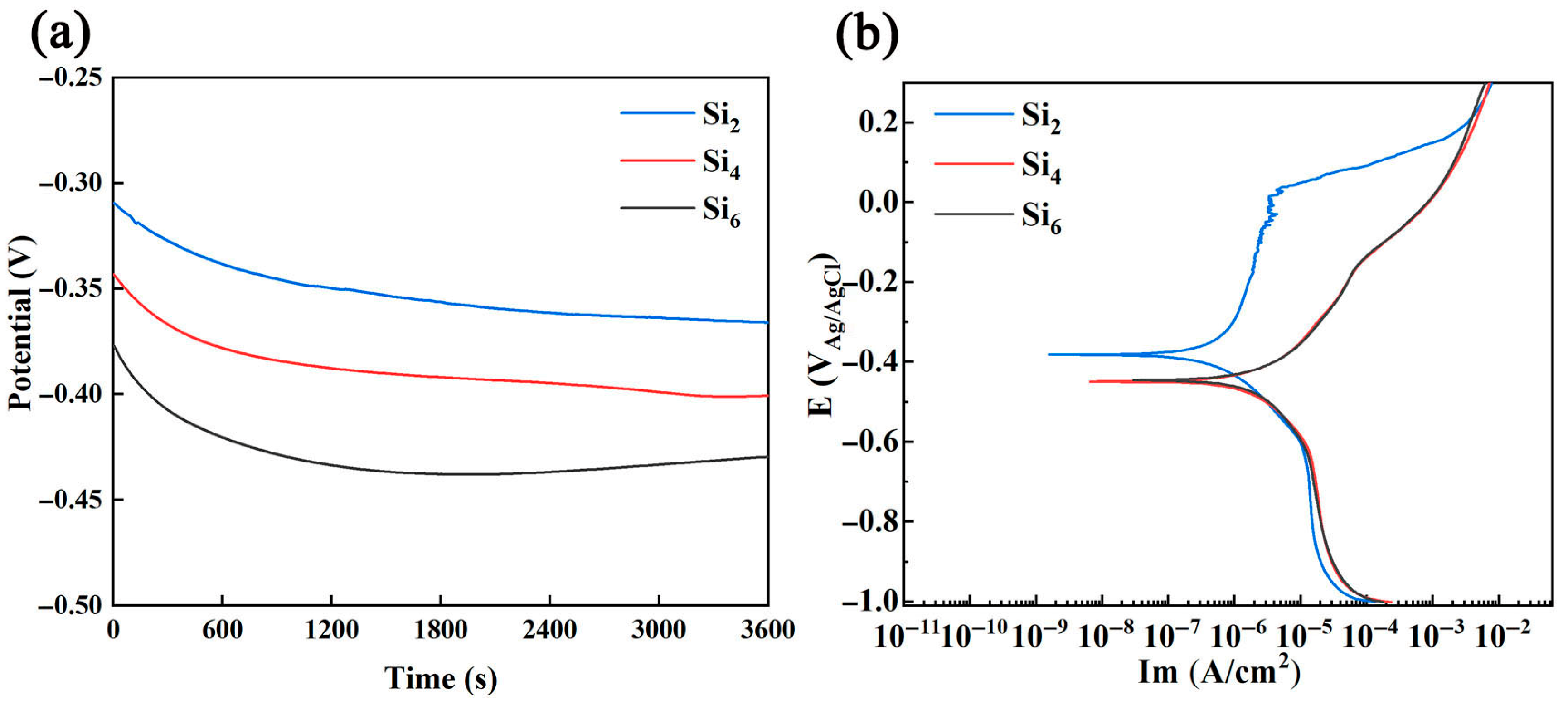


| Alloys | Icorr (nA/cm2) | Ecorr (mVAg/AgCl) | Ip (μA/cm2) | Epit (mVAg/AgCl) | ΔEp (mVAg/AgCl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si2 | 486.92 ± 15 | −381.6 ± 7 | 4.66 ± 0.13 | 35 ± 0.61 | 416.6 ± 7.61 |
| Si4 | 1860.15 ± 31 | −462.1 ± 16 | 71.94 ± 0.44 | −157 ± 1.21 | 305.1 ± 18.21 |
| Si6 | 2024.71 ± 25 | −465.3 ± 18 | 64.43 ± 0.41 | −170 ± 1.50 | 295.3 ± 19.5 |
| Alloys | Rs (W·cm2) | Rf (W·cm2) | Rct (W·cm2) | CPEf | CPEdl | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y0f (Ω−1·cm−2·sn) | nf | Y0dl (Ω−1·cm−2·sn) | ndl | ||||
| Si2 | 33.32 | 7.85 × 104 | 8.12 × 104 | 15.83 | 0.89 | 36.75 | 0.94 |
| Si4 | 32.29 | 2.81 × 104 | 3.40 × 104 | 18.02 | 0.94 | 34.01 | 0.80 |
| Si6 | 31.92 | 2.65 × 104 | 3.42 × 104 | 27.84 | 0.92 | 15.83 | 0.73 |
| Alloys | NA (1020 cm−3) | ND (1020 cm−3) | EFB (mVAg/AgCl) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Si2 | 0.68 | 1.49 | −0.67 |
| Si4 | 2.39 | 2.86 | −0.64 |
| Si6 | 3.09 | 2.95 | −0.66 |
| Alloys | Vickers Hardness (HV) | Yield Strength σy (MPa) | Fracture Strength σf (MPa) | Fracture Strain εf (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si2 | 461 ± 3 | 1272 ± 11 | 3260 ± 21 | 33.8± 0.3 |
| Si4 | 468 ± 2 | 1380 ± 15 | 3319 ± 24 | 24.7 ± 0.5 |
| Si6 | 475 ± 3 | 1447 ± 13 | 3436 ± 27 | 15.2 ± 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, S.; Kang, K.; Zhang, B.; Li, A.; Li, G. Effect of Si Doping on Microstructure and Mechanical and Electrochemical Properties of (AlCrFeNi)100-xSix (x = 2, 4, 6) Dual-Phase Eutectic High-Entropy Alloys. Metals 2025, 15, 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070762
Yu S, Kang K, Zhang B, Li A, Li G. Effect of Si Doping on Microstructure and Mechanical and Electrochemical Properties of (AlCrFeNi)100-xSix (x = 2, 4, 6) Dual-Phase Eutectic High-Entropy Alloys. Metals. 2025; 15(7):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070762
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Subo, Kaiwen Kang, Borui Zhang, Aoxiang Li, and Gong Li. 2025. "Effect of Si Doping on Microstructure and Mechanical and Electrochemical Properties of (AlCrFeNi)100-xSix (x = 2, 4, 6) Dual-Phase Eutectic High-Entropy Alloys" Metals 15, no. 7: 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070762
APA StyleYu, S., Kang, K., Zhang, B., Li, A., & Li, G. (2025). Effect of Si Doping on Microstructure and Mechanical and Electrochemical Properties of (AlCrFeNi)100-xSix (x = 2, 4, 6) Dual-Phase Eutectic High-Entropy Alloys. Metals, 15(7), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070762





