Extraction of Valuable Metals from Spent Li-Ion Batteries Combining Reduction Smelting and Chlorination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
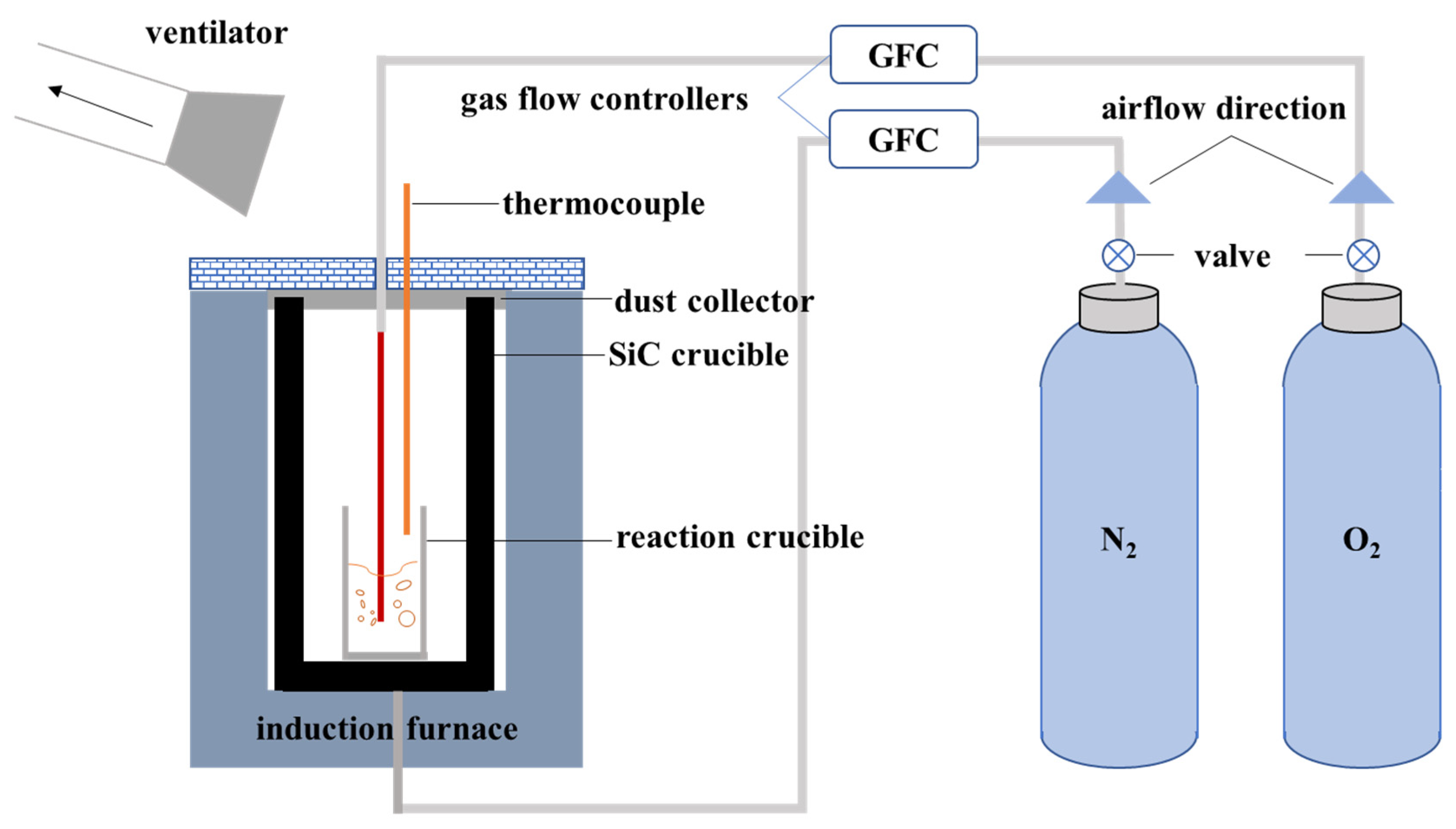
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.2.1. Pretreatment of Spent Batteries
2.2.2. Preliminary Experiments
2.2.3. Validating Experiment on the Actual Spent LIBs
2.3. Materials Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
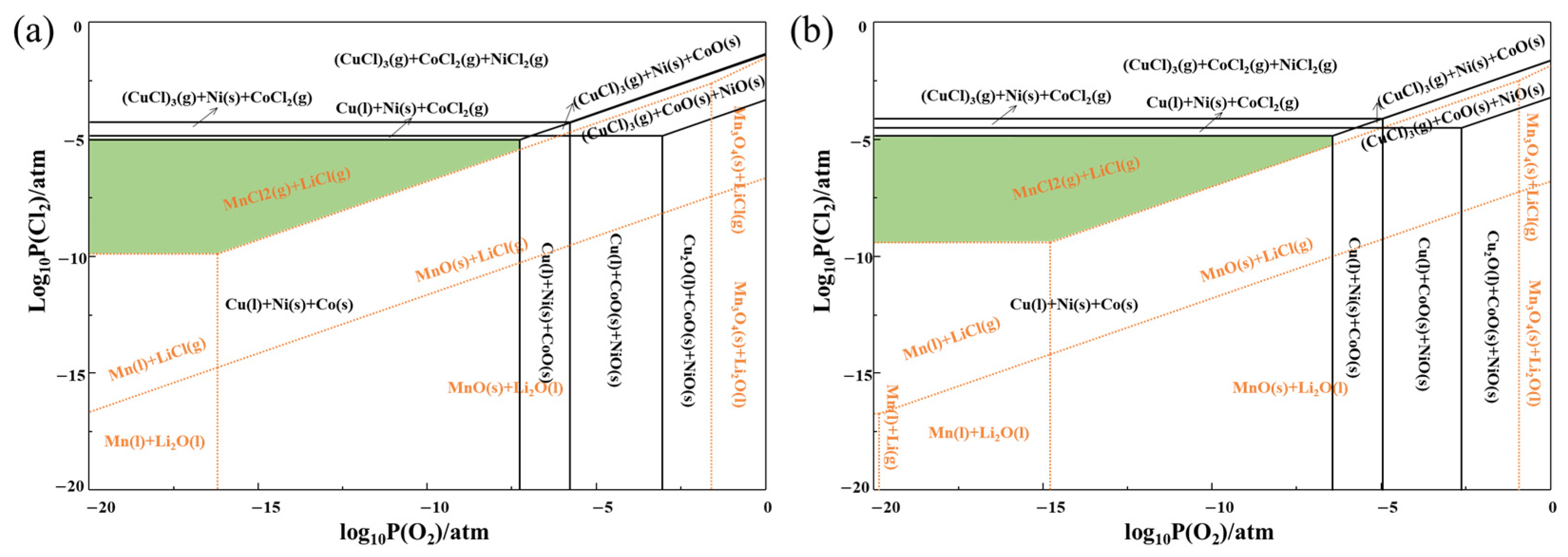
3.1. Thermodynamic Analysis
3.1.1. Predominance Phase Diagrams of Li-Mn-Cl-O and Cu-Co-Ni-Cl-O Systems
3.1.2. Slag Selection and Adjustment for Reduction Smelting
3.2. Effect of Smelting Conditions on the Recovery Rate of Valuable Metals
3.2.1. Dosage of Calcium Chloride
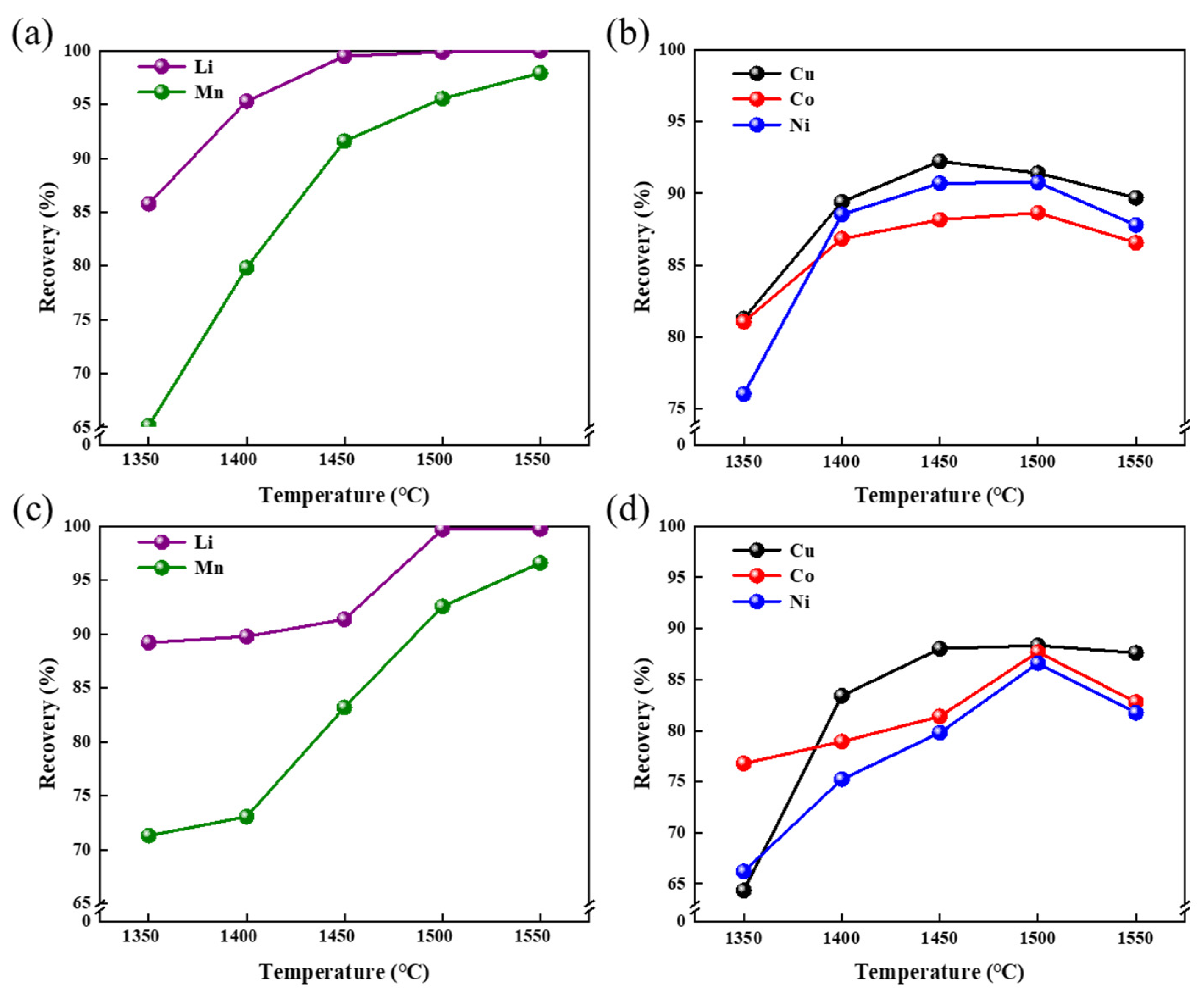
3.2.2. Smelting Temperature
3.2.3. Smelting Duration Time
3.3. Validation Experiment
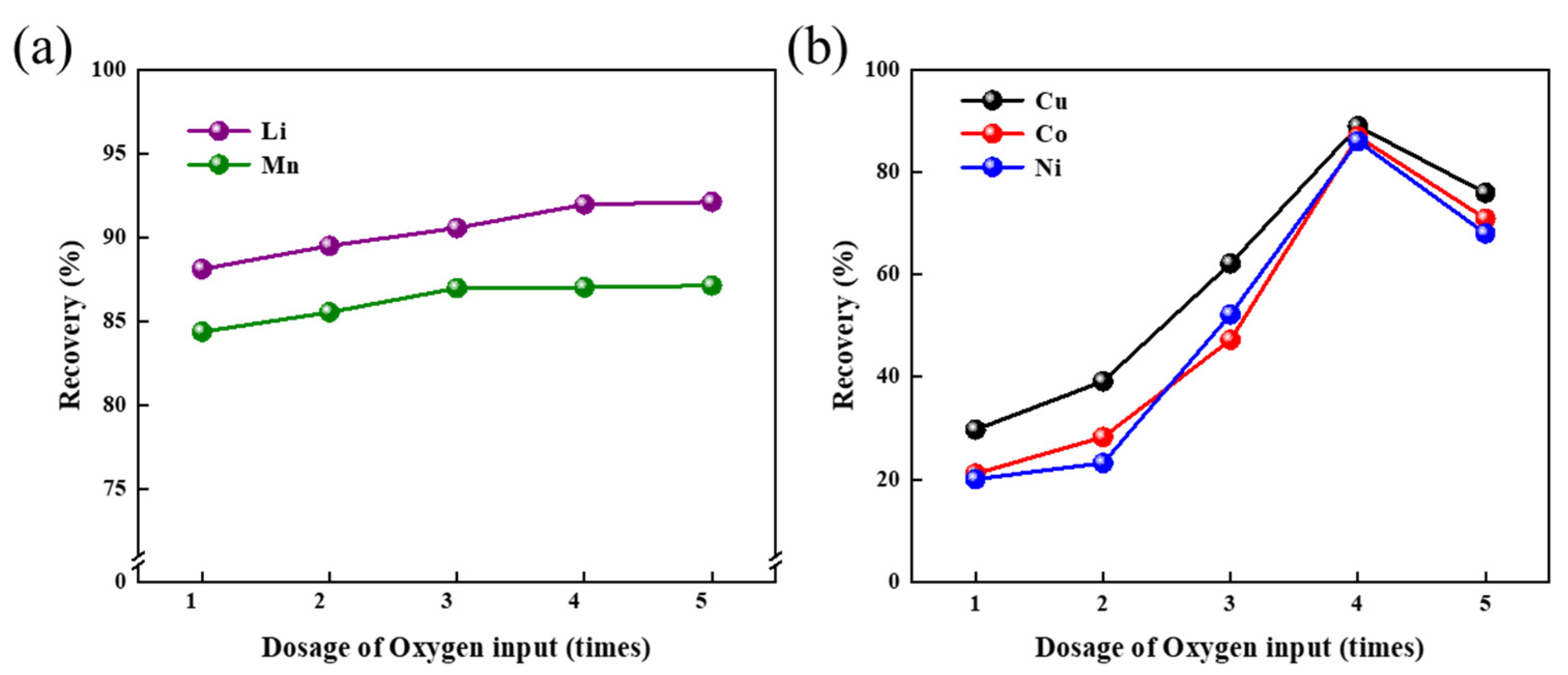
3.3.1. The Influence of Oxygen Flux on Metal Recovery
3.3.2. Characterization of the Smelting Products
3.3.3. Mechanism Analysis of the Smelting Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bresolin, B.M.; Zanoletti, A.; Bontempi, E. Recent improvements in salt-sssisted and microwave-assisted recovery methods for sustainable metal extraction from NCM cathodes in spent lithium-ion batteries: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 363, 131918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yuan, X.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Xie, W. Recent advances in pretreating technology for recycling valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 406, 124332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Y.; Tan, L.; Wu, N.; Wen, J.; Yao, W.; Tang, Y.; Cheng, H.M. Current status and outlook of recycling spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Energy Storage 2025, 110, 115374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lv, W.; Huang, H.; Yan, W.; Li, X.; Ning, P.; Cao, H.; Sun, Z. Recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries in view of green chemistry. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 6139–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lin, J.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z. Recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries in view of lithium recovery: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Quan, J.; Wang, T.; Song, D.; Huang, J.; He, W.; Li, G. Unveiling the recycling characteristics and trends of spent lithium-ion battery: A scientometric study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 9448–9461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.C.; Cheng, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.H.; Shao, X.X.; Chen, X.H.; Li, X.; Xin, B.P. A comprehensive review of full recycling and utilization of cathode and anode as well as electrolyte from spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhang, J.; Ou, L. A comprehensive review on the separation and purification of valuable metals from the leachate of spent lithium-ion batteries. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 360, 130847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, W.; Duan, H.; Zhao, Q.; Liang, Z. A comprehensive review of the recovery of spent lithium-ion batteries with molten salt method: Progress, shortcomings and prospects. J. Energy Storage 2024, 99, 113407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Z.T.; Su, Y.Y.; Meng, Q.; Dong, P.; Zhang, Y.J. Direct regeneration of spent cathode materials by deep eutectic solvent. Energy Storage Mater. 2023, 60, 102833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, J.X.; Jia, K.; Liang, Z.; Ji, G.J.; Zhuang, Z.F.; Zhou, G.M.; Cheng, H.M. Adaptable Eutectic Salt for the Direct Recycling of Highly Degraded Layer Cathodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 20306–20314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B. Research progress on bioleaching recovery technology of spent lithium-ion batteries. Environ. Res. 2023, 238, 117145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.; Hwang, G. Iron removal and valuable metal recovery from spent lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) using solvent extraction after bioleaching. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2025, 144, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Ma, X.; Liu, Y.; Hao, J.; Xie, W.; He, Y. A review of research progress on combined pyro-hydrometallurgical technology for spent lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.F.; Mousa, E.; Tian, Y.; Ye, G.Z. Recovery of Co, Ni, Mn, and Li from Li-ion batteries by smelting reduction Part I: A laboratory-scale study. J. Power Sources 2021, 483, 228936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, H.; Cao, H. An overview on the processes and technologies for recycling cathodic active materials from spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2013, 15, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinne, M.; Lappalainen, H.; Lundström, M. Evaluating the possibilities and limitations of the pyrometallurgical recycling of waste Li-ion batteries using simulation and life cycle assessment. Green Chem. 2025, 27, 2522–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hoof, G.; Robertz, B.; Verrecht, B. Towards Sustainable Battery Recycling: A Carbon Footprint Comparison between Pyrometallurgical and Hydrometallurgical Battery Recycling Flowsheets. Metals 2023, 13, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaeifar, M.A.; Raugei, M.; Steubing, B.; Hartwell, A.; Anderson, P.A.; Heidrich, O. Life cycle assessment of lithium-ion battery recycling using pyrometallurgical technologies. J. Ind. Ecol. 2021, 25, 1560–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Lin, K.; Wu, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhu, J.; Huang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Ruan, J. From spent lithium-ion batteries to functional materials: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 209, 107772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, W.S.; Hanson, J.; McBreen, J.; Yang, X.Q. A study on the newly observed intermediate structures during the thermal decomposition of nickel-based layered cathode materials using time-resolved XRD. Electrochem. Commun. 2006, 8, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Ni | Co | Mn | Li |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20.1 | 20.2 | 18.7 | 7.8 |
| Ni | Cu | Mn | Co | Al | Li |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13.8 | 8.2 | 7.7 | 5.4 | 5.2 | 3.4 |
| Sample | Element | Grade/% | Distribution Rates/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dust | Li | 3.2 | 94.1 |
| Mn | 6.8 | 88.3 | |
| Cu | 0.6 | 7.3 | |
| Co | 0.3 | 5.6 | |
| Ni | 1.1 | 8.0 | |
| Alloy | Li | ND | ND |
| Mn | 1.3 | 4.6 | |
| Cu | 27.1 | 89.9 | |
| Co | 17.5 | 88.1 | |
| Ni | 44.7 | 88.1 | |
| Slag | Li | 0.2 | 5.9 |
| Mn | 0.5 | 6.5 | |
| Cu | 0.2 | 2.4 | |
| Co | 0.3 | 5.6 | |
| Ni | 0.5 | 3.6 |
| Reaction | Gibbs Free Energy (kJ/mol) | No. |
|---|---|---|
| Li2O + CaCl2 = 2LiCl(g) + CaO | 1 | |
| MnO2 + CaCl2 + C = MnCl2(g) + CO(g) + CaO | 2 | |
| 3MnO2 + 3CaCl2 + 2Al = 3MnCl2(g) + Al2O3 + 3CaO | 3 | |
| NiO + C = Ni + CO(g) | 4 | |
| 3NiO + 2Al = 3Ni + Al2O3 | 5 | |
| Co3O4 + 4C = 3Co + 4CO(g) | 6 | |
| 3Co3O4 + 8Al = 9Co + 4Al2O3 | 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Yang, C.; Ling, H. Extraction of Valuable Metals from Spent Li-Ion Batteries Combining Reduction Smelting and Chlorination. Metals 2025, 15, 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070732
Wang C, Liu W, Yang C, Ling H. Extraction of Valuable Metals from Spent Li-Ion Batteries Combining Reduction Smelting and Chlorination. Metals. 2025; 15(7):732. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070732
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chen, Wei Liu, Congren Yang, and Hongbin Ling. 2025. "Extraction of Valuable Metals from Spent Li-Ion Batteries Combining Reduction Smelting and Chlorination" Metals 15, no. 7: 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070732
APA StyleWang, C., Liu, W., Yang, C., & Ling, H. (2025). Extraction of Valuable Metals from Spent Li-Ion Batteries Combining Reduction Smelting and Chlorination. Metals, 15(7), 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070732






