Influence of Submerged Entry Nozzle Offset on the Flow Field in a Continuous Casting Mold
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical–Physical Modeling of the Mold
2.1. Mathematical Modeling
2.1.1. Basic Fluid Assumptions
2.1.2. Control Equations
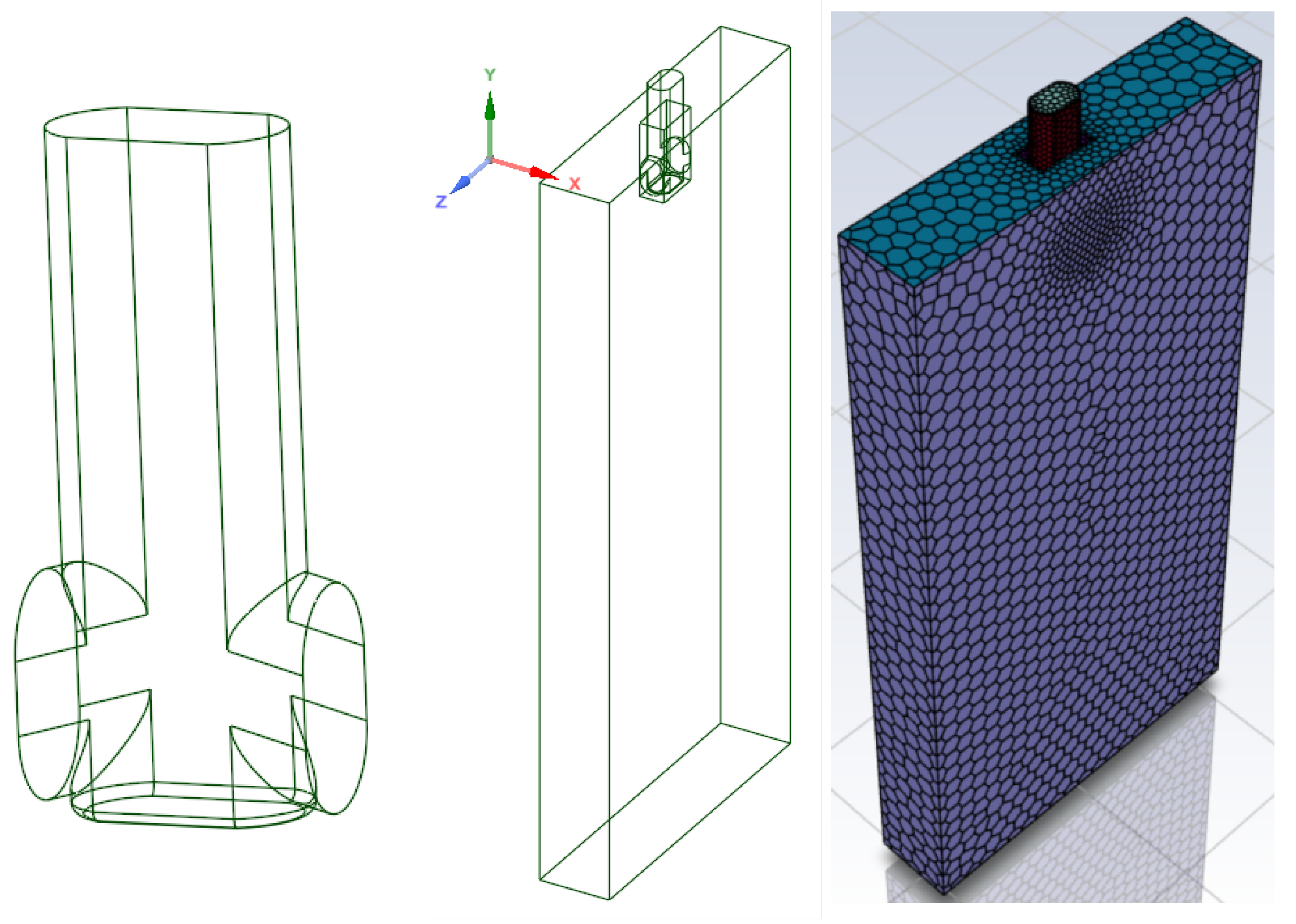
2.1.3. Model and Boundary Conditions
2.2. Physical Modeling
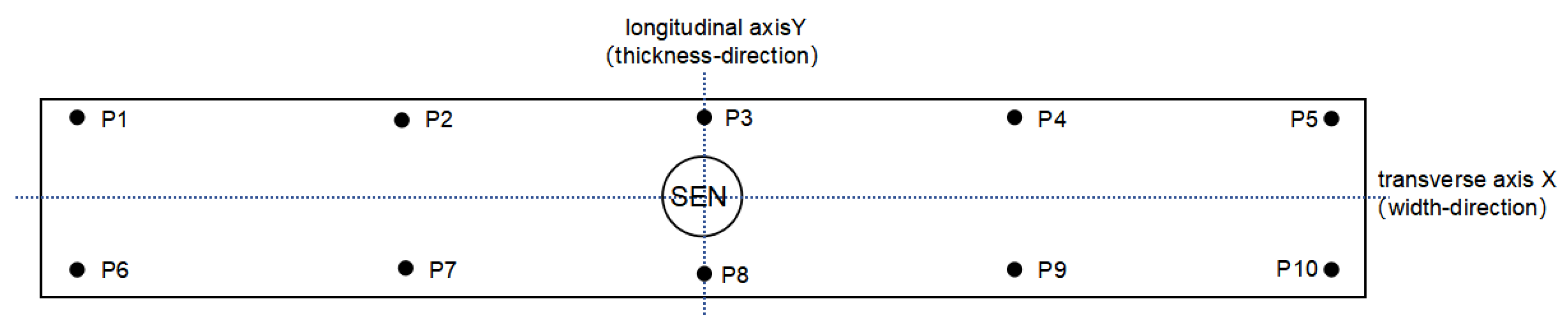
2.3. Experimental Program and Methodology
2.3.1. Symmetry Index (S)
2.3.2. Bias Flow Index (N)
2.3.3. F-Number
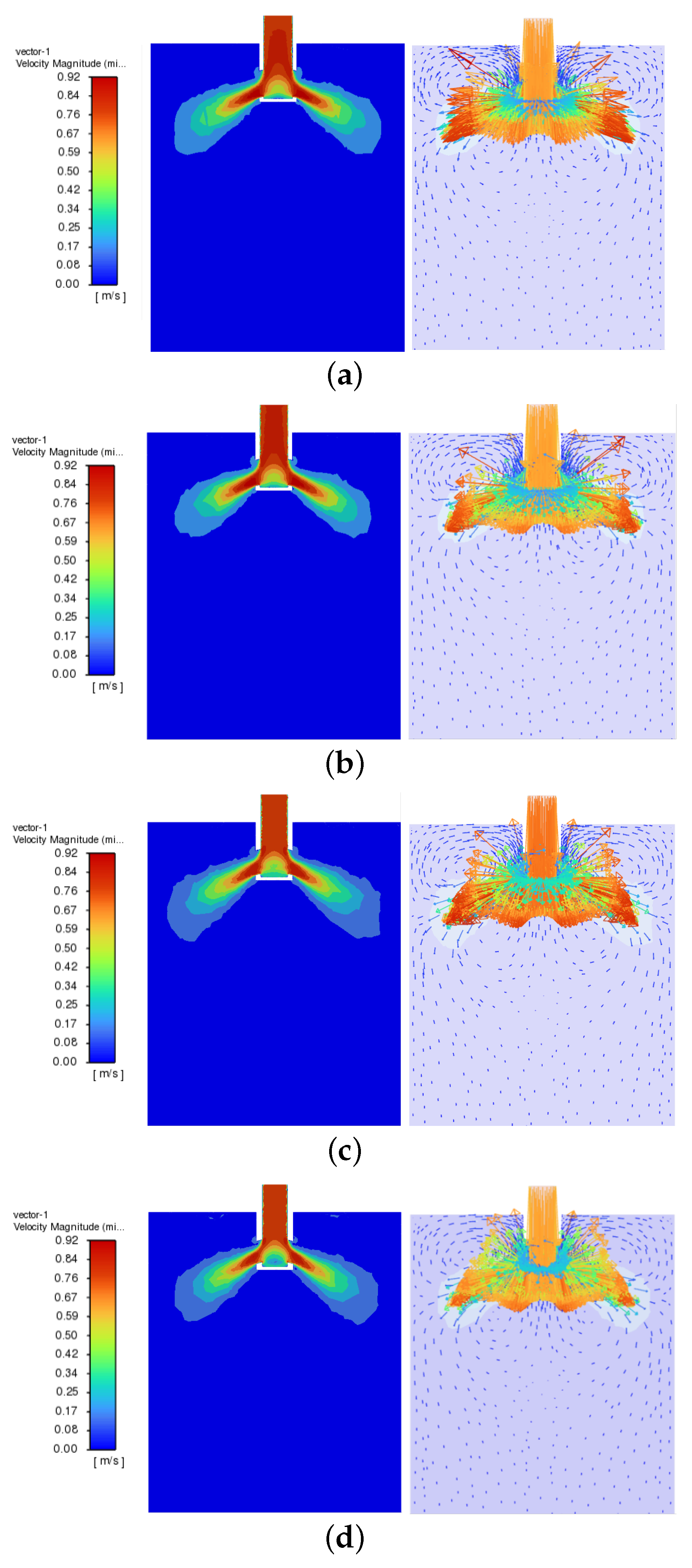
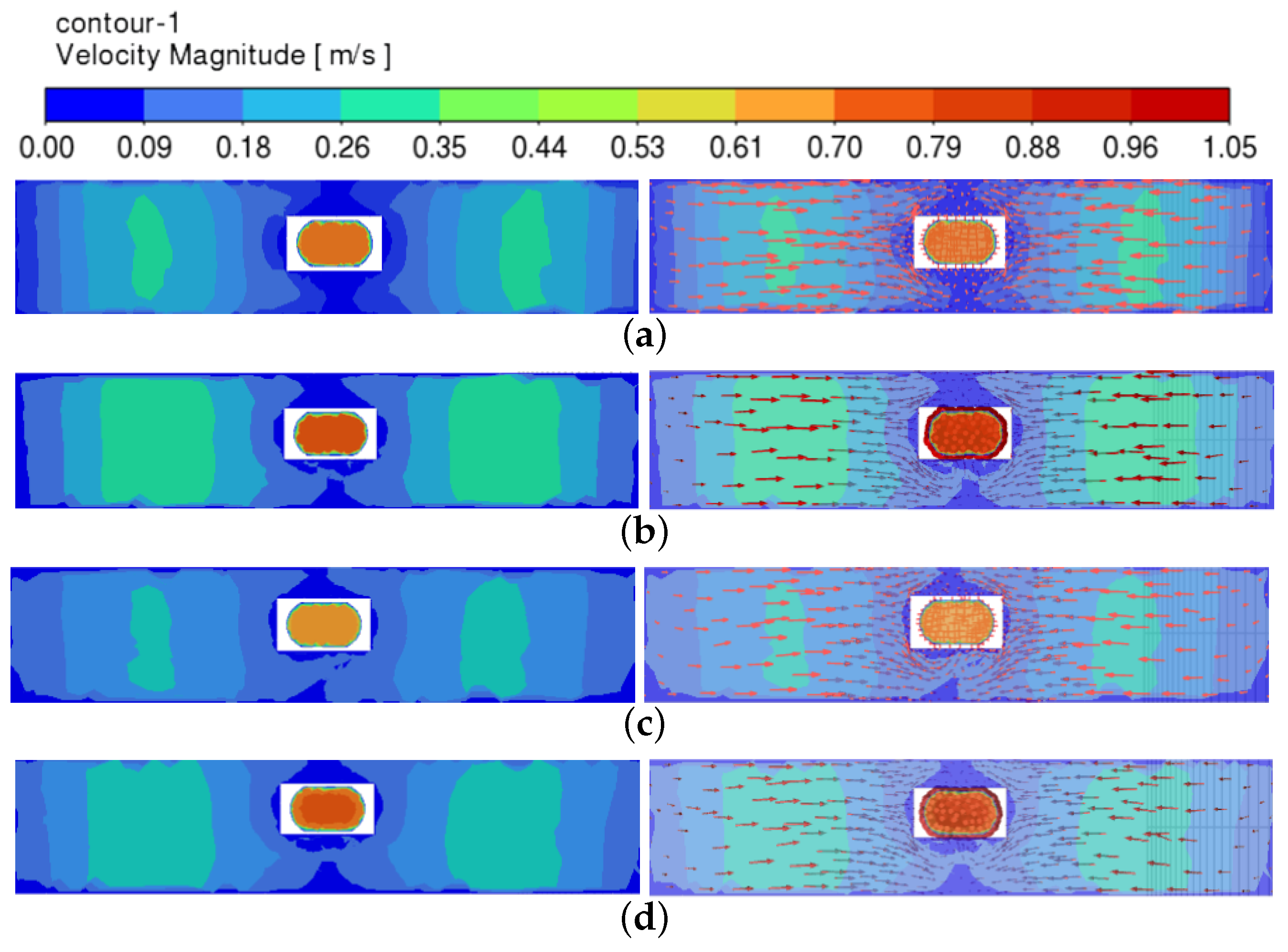
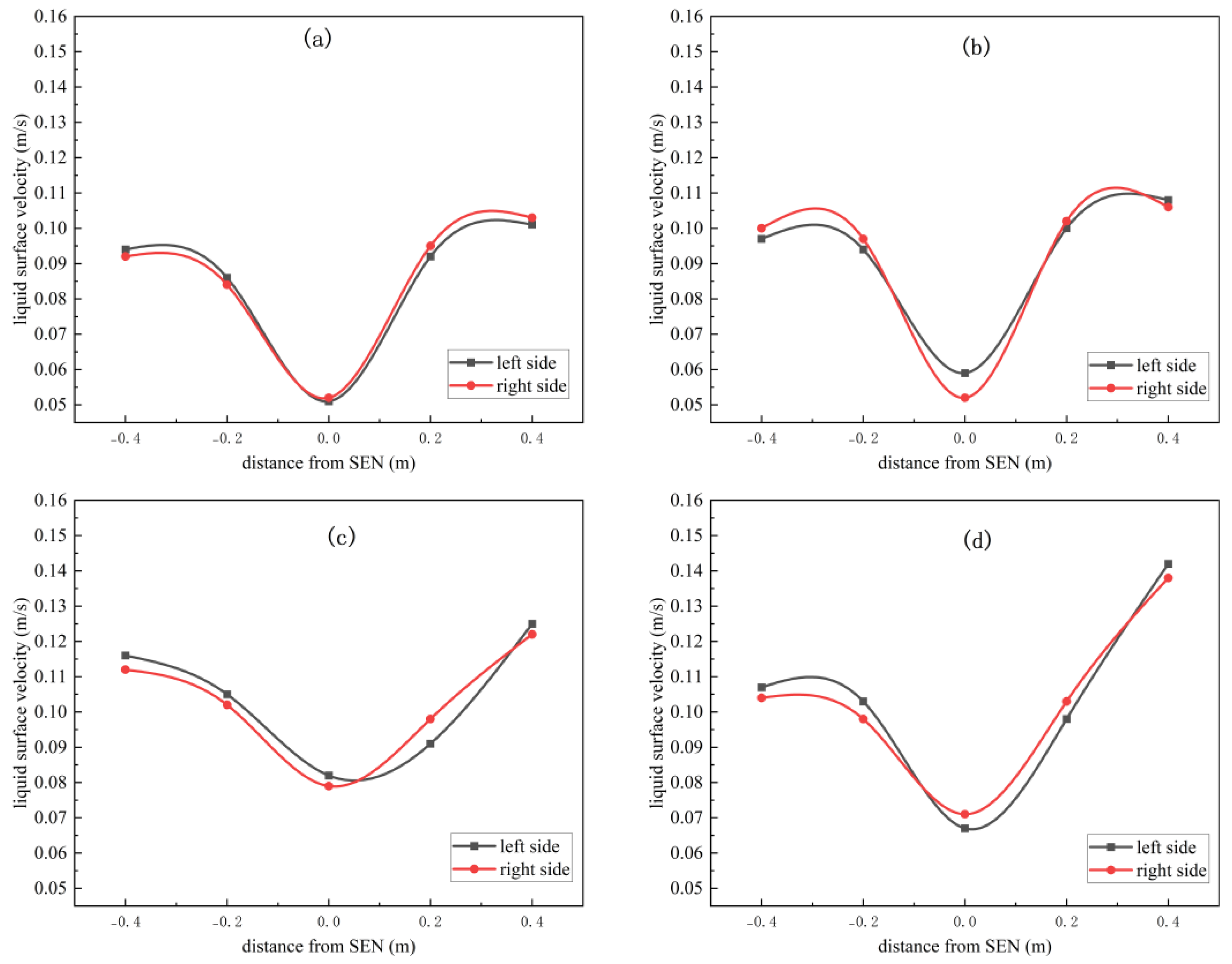
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Molten Steel Flow Behavior in the Mold Under Symmetric Conditions
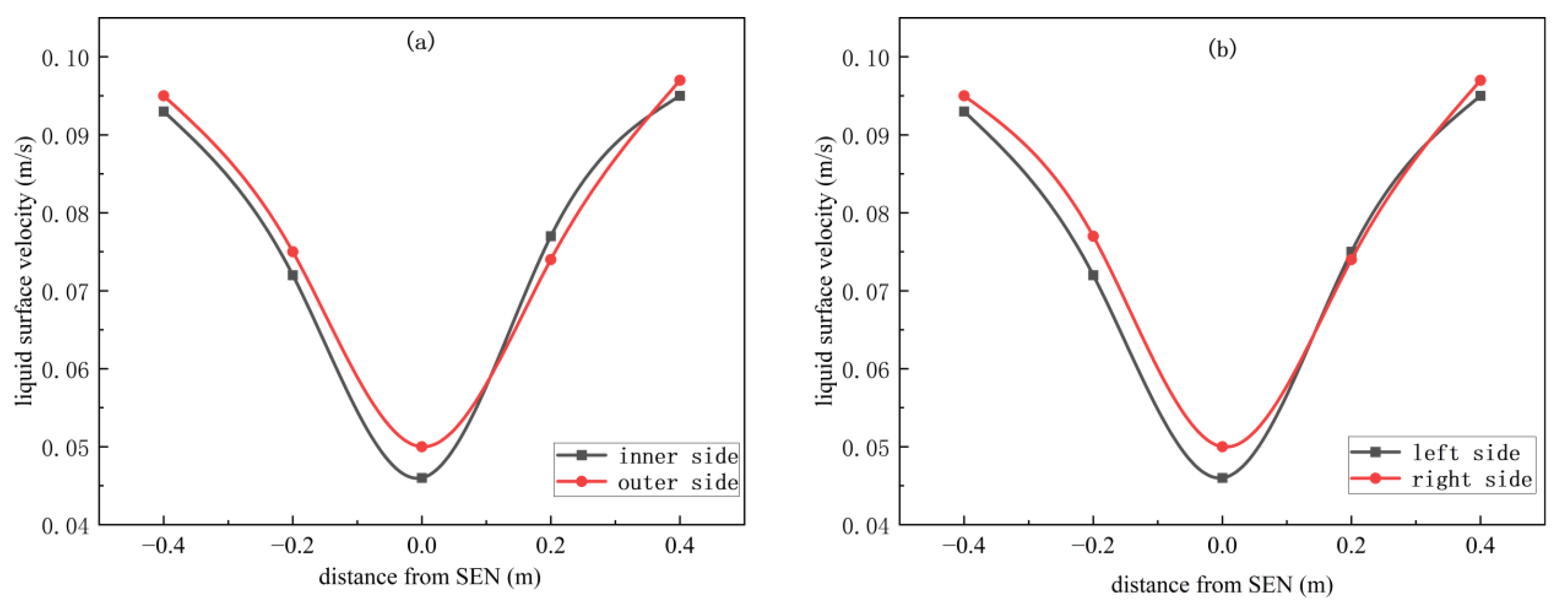
3.1.1. Symmetry Index
3.1.2. Bias Flow Index
3.1.3. F-Number
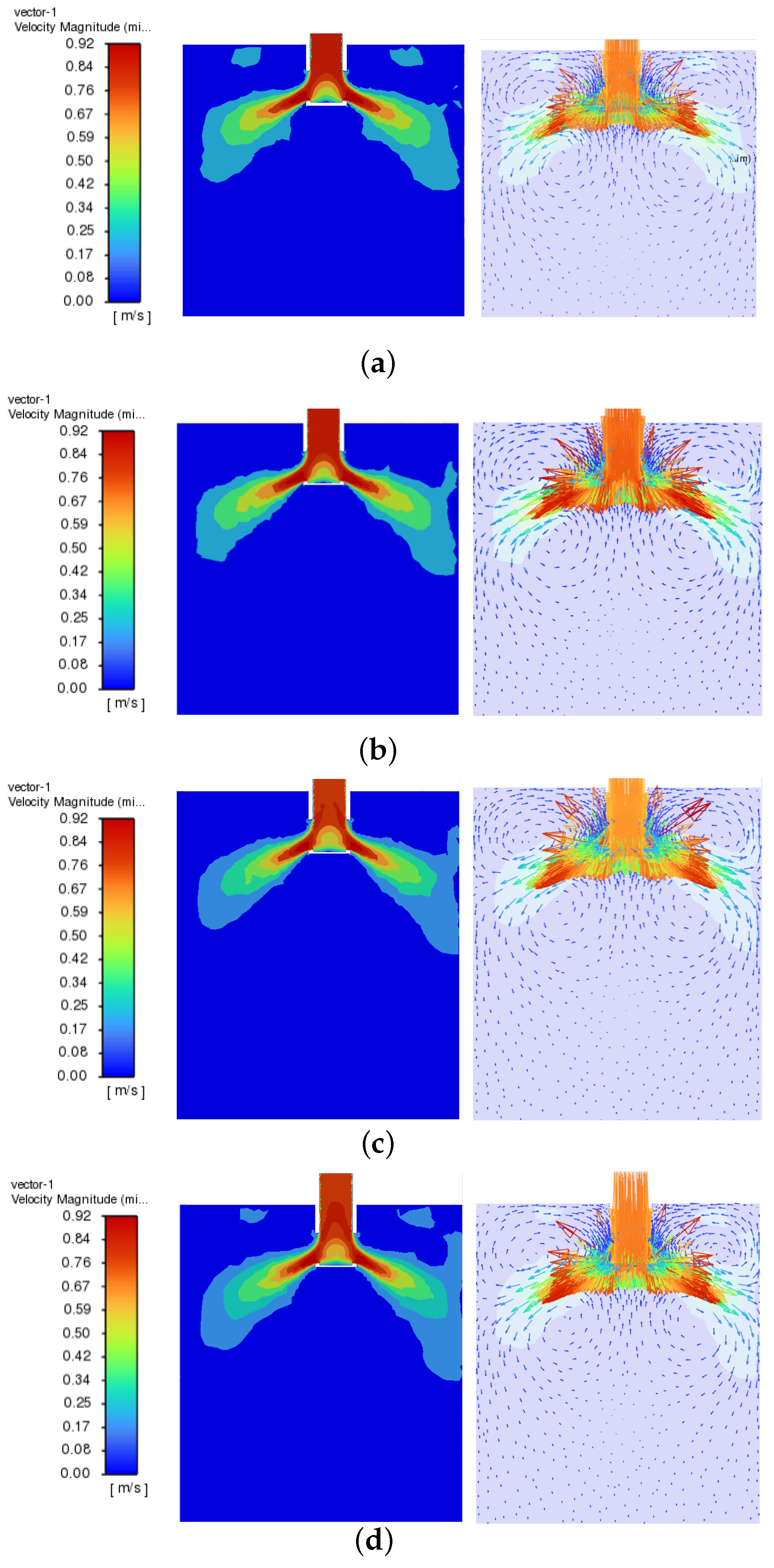
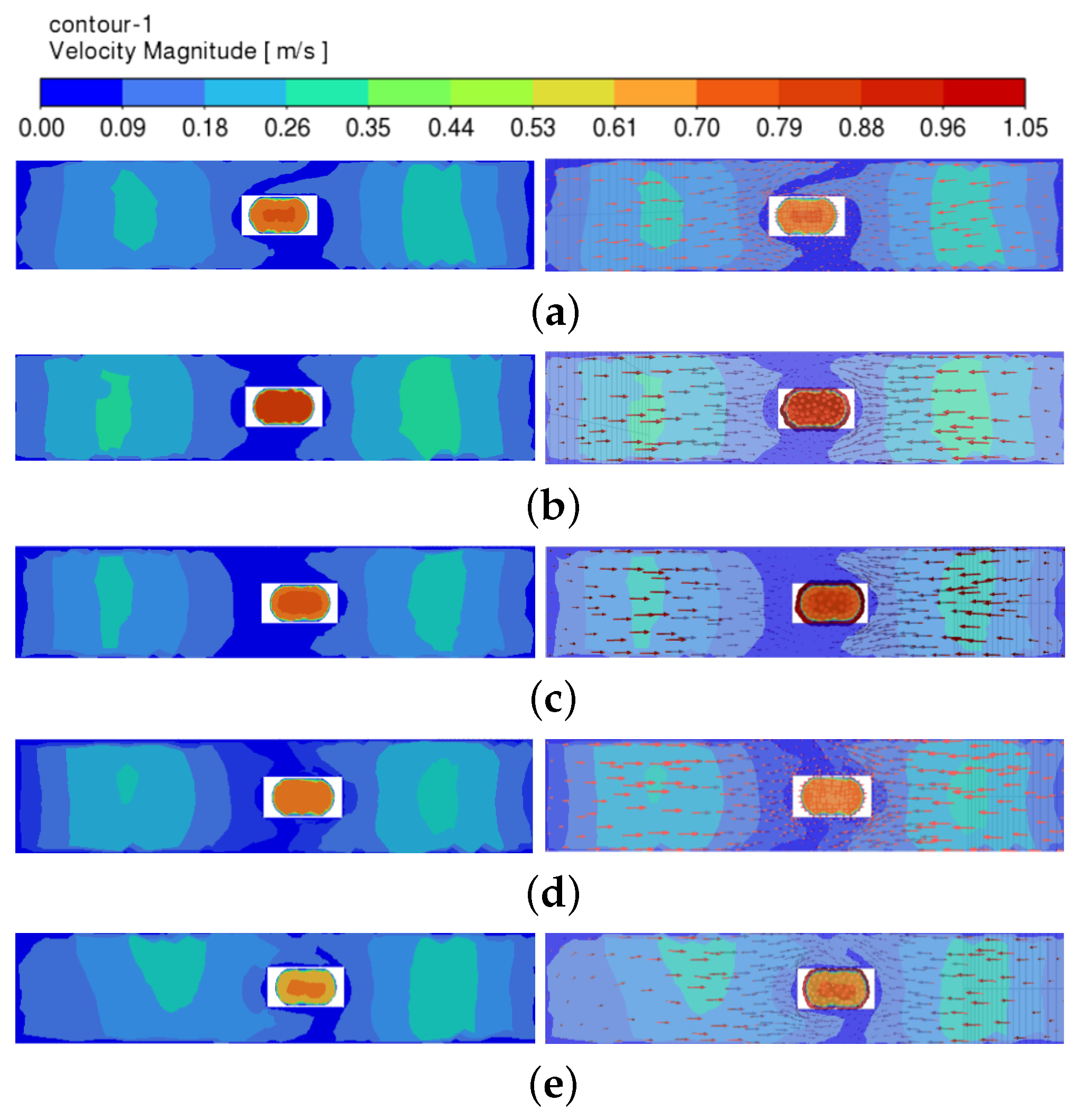
3.2. Effect of Orifice Offset on Liquid Steel Flow Behavior in the Mold
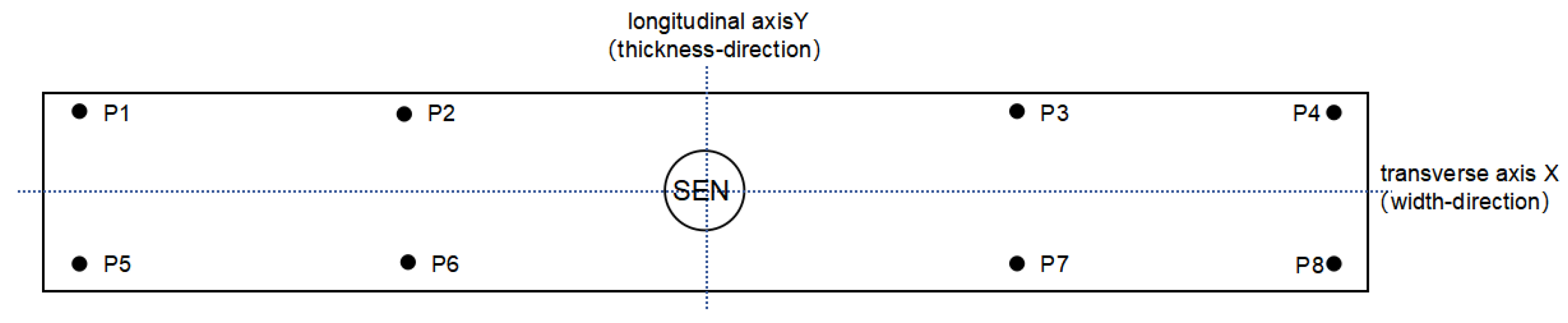
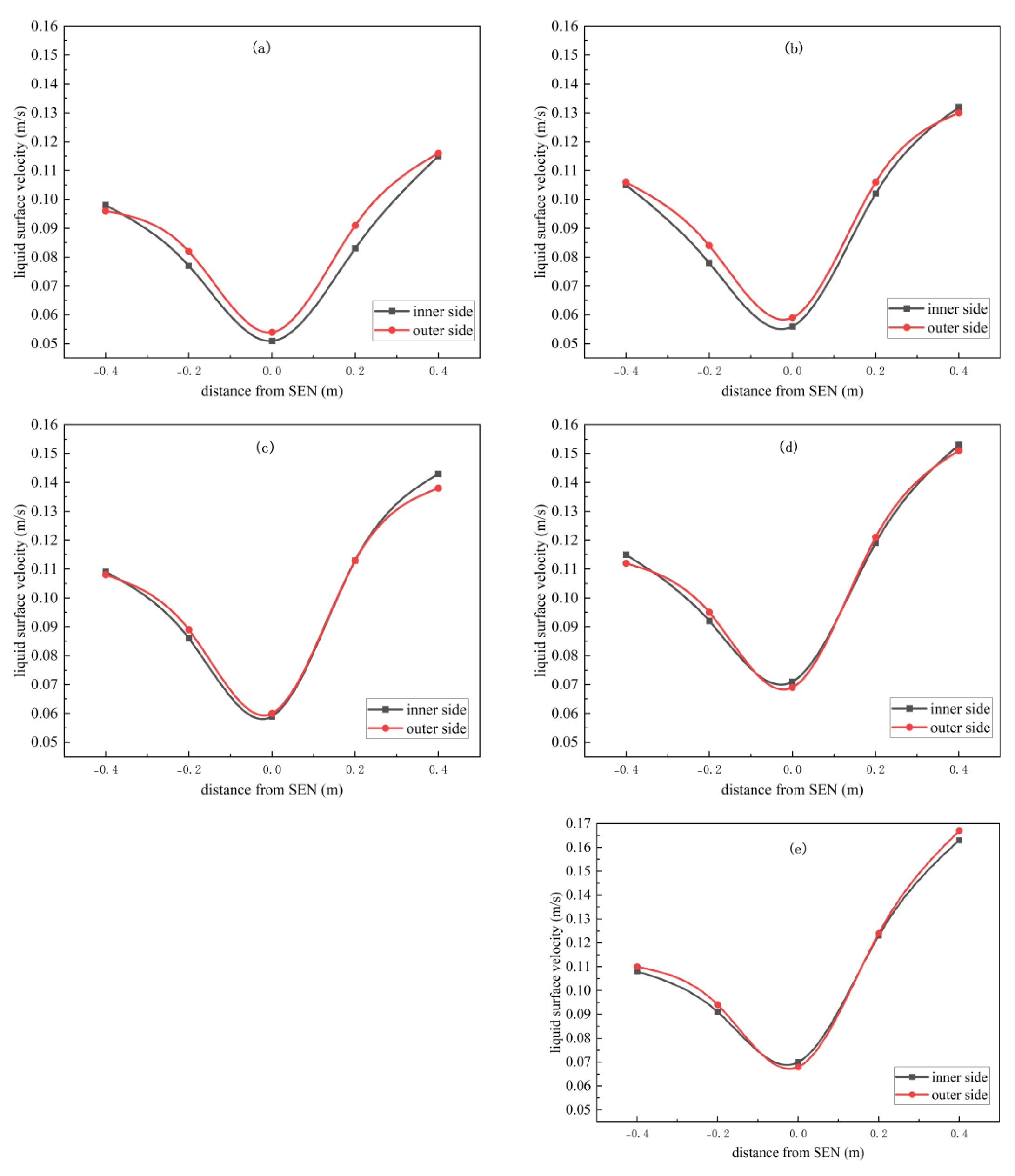
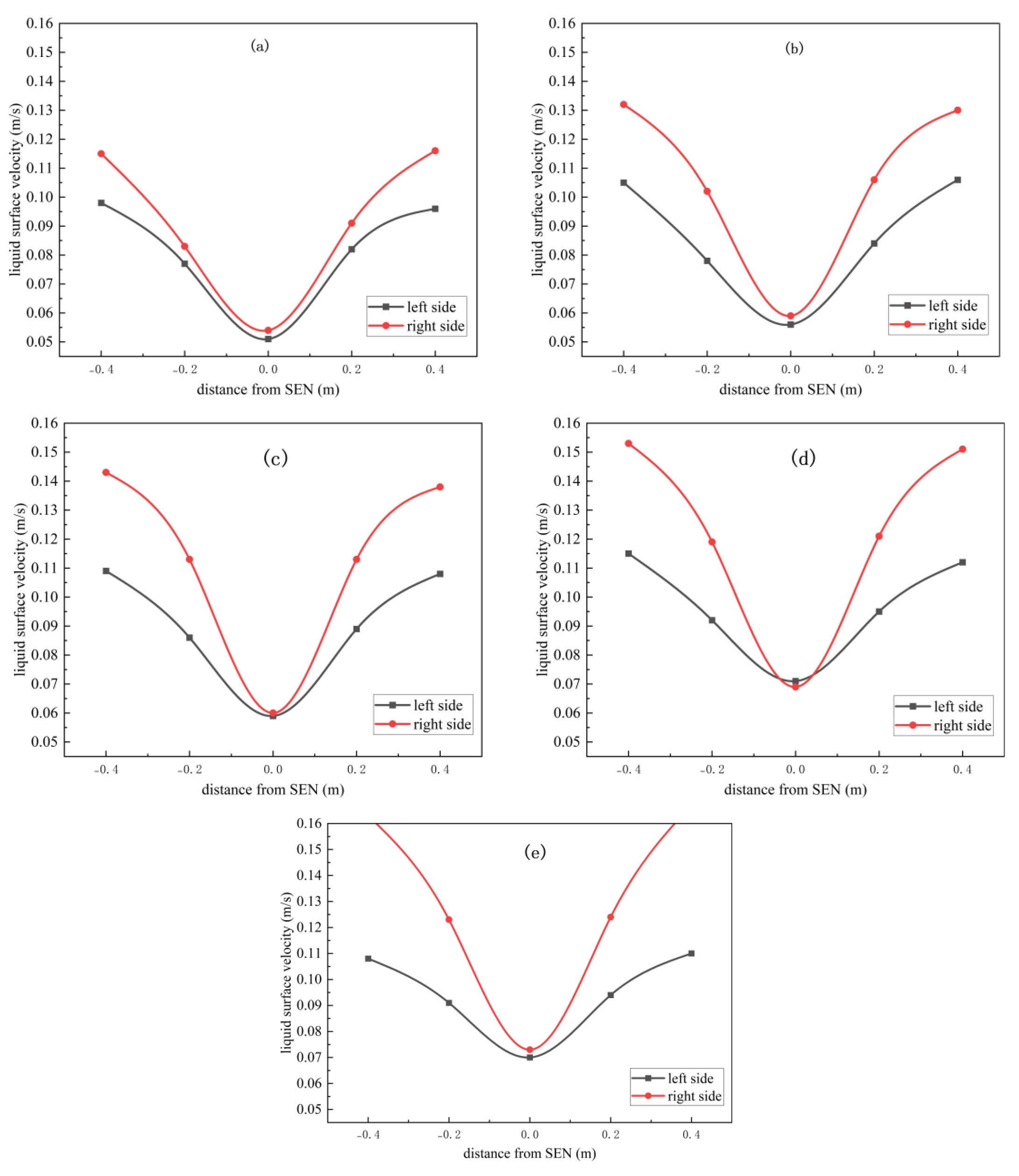
3.2.1. SEN Offset Along the WIDTH Direction
- (1)
- Symmetry index
- (2)
- Bias flow index
- (3)
- F-number
3.2.2. SEN Offset Along the Thickness Direction
- (1)
- Symmetry index
- (2)
- Bias flow index
- (3)
- F-number
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guthrie, R.I.L.; Isac, M.M. Continuous Casting Practices for Steel: Past, Present and Future. Metals 2022, 12, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louhenkilpi, S. Continuous casting of steel. In Treatise on Process Metallurgy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 343–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Li, T.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, K. Influence of Nozzle Design on Flow Characteristic in the Continuous Casting Machinery. Coatings 2022, 12, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiwo, F.S.; Susunaga-Notario, A.d.C.; Betancourt-Cantera, J.A.; Pérez-Bustamante, R.; Mercado-Lemus, V.H.; Méndez-Lozoya, J.; Barrera-Cardiel, G.; García-Herrera, J.E.; Arcos-Gutiérrez, H.; Garduño, I.E. Design and Optimization of the Internal Geometry of a Nozzle for a Thin-Slab Continuous Casting Mold. Designs 2024, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, M.; Pan, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; He, S. Effect of exit shape of submerged entry nozzle on flow field and slag entrainment in continuous casting mold. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2020, 51, 2862–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tan, C.; Huang, A.; Yan, W.; Gu, H.Z.; He, Z.; Li, G.Q. Numerical Simulation on Refractory Wear and Inclusion Formation in Continuous Casting Tundish. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2021, 52, 1344–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.P.; Dou, R.S.; Yin, J.J.; Yao, Y.Y. Intelligent prediction method of quality for continuous casting process. In Proceedings of the IEEE Advanced Information Management, Communications, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IMCEC), Xi’an, China, 3–5 October 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1761–1764. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Xu, K.; Lv, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, M.; He, F.; Xu, G. Intelligent Manufacturing Technology in the Steel Industry of China: A Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 8194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, D.; Long, M.; Duan, H. Optimization of submerged entry nozzle parameters for ultra-high casting speed continuous casting mold of billet. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2022, 29, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, W.; Che, J.; Zhou, F.; Tan, Y.; Li, D.; Dang, J.; Chen, C. Assessment of Inclusion Removal Ability in Refining Slags Containing Ce2O3. Crystals 2023, 13, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.T.; Liu, J.H.; Cui, H. Effect of flow field on surface slag entrainment and inclusion adsorption in a continuous casting mold. Steel Res. Int. 2020, 91, 1900437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.B.; Peng, X.X.; Ren, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhang, L.F. Water modeling on slag entrainment in the slab continuous casting mold. Metall. Res. Technol. 2022, 119, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, W.; Zhao, C.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J. Mathematical Modeling of Transient Submerged Entry Nozzle Clogging and Its Effect on Flow Field, Bubble Distribution and Interface Fluctuation in Slab Continuous Casting Mold. Metals 2024, 14, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Solórzano, M.G.; Dávila, R.M.; Guarneros, J.; Calderón-Ramos, I.; Muñiz-Valdés, C.R.; Nájera-Bastida, A. Unsteady Fluid Flows in the Slab Mold Using Anticlogging Nozzles. Fluids 2022, 7, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Solórzano, M.G.; Morales, R.D.; Gutiérrez, E.; Guarneros, J.; Chattopadhyay, K. Analysis of fluid flow of liquid steel through clogged nozzles: Thermodynamic analysis and flow simulations. Steel Res. Int. 2020, 91, 2000049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Trejo, J.; Miranda-Tello, R.; Gabbasov, R.; Real-Ramirez, C.A.; Cervantes-de-la-Torre, F. Experimental Analysis of the Influence of the Sliding-Gate Valve on Submerged Entry Nozzle Outlet Jets. Fluids 2024, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedillo, V.; Morales, D.R. Biased flows in slab molds induced by slide gates. Part I: Experimental measurements and flow simulation. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2018, 45, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lu, C.; Gan, M.J.; Wang, Q.Q.; He, S.P. Influence of Submerged Entry Nozzle Clogging on the Flow Field and Slag Entrainment in the Continuous Casting Mold by the Physical Model. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2022, 53, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.D.; Liu, J.R.; Heng, C.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.Z. Effect of SEN Asymmetric Clogging on Mold Level Fluctuation and Mold Slag Distribution During Continuous Casting. Metall. Mater. Trans. 2024, 55, 2932–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Li, K.; Li, S.H.; Wang, L.J.; Yang, J.; Feng, L.H. Asymmetric flow behavior of molten steel in thin slab continuous casting mold. Metall. Mater. Trans. 2023, 54, 3542–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Kim, J.G.; Jung, J.I.; Huh, K.Y. Prediction of nozzle clogging through fluid–structure interaction in the continuous steel casting process. Steel Res. Int. 2021, 92, 2000549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Wang, M.; Bao, Y. Effect of nozzle clogging on the fluid flow pattern in a billet mold with particle image velocimetry technology. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2020, 51, 2871–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fang, Q.; Xiao, T.P.; Ni, H.W.; Liu, C.S. Optimization of the flow in a slab mold with argon blowing by divergent bifurcated SEN. ISIJ Int. 2019, 59, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javurek, M.; Wincor, R. Bubbly mold flow in continuous casting: Comparison of numerical flow simulations with water model measurements. Steel Res. Int. 2022, 91, 2000415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Lv, M.; Mi, X.; Xi, X. Numerical Simulation of the Flow Field in an Ultrahigh-Speed Continuous Casting Billet Mold. Metals 2023, 13, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Yang, J.; Zhang, T.; Xu, G.; Liu, H.; Zhou, J.; Qin, W. Optimization of Flow Field in Slab Continuous Casting Mold with Medium Width Using High Temperature Measurement and Numerical Simulation for Automobile Exposed Panel Production. Metals 2020, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, T.; Zheng, G. Research on the Influence of Process Parameters on the Flow Field in Mold. Coatings 2022, 12, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, J. Mathematical modeling on transient multiphase flow and slag entrainment in continuously casting mold with double-ruler EMBr through LES+VOF+DPM method. ISIJ Int. 2021, 61, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Han, S.; Cho, H.J.; Park, I.S. Numerical and experimental study of the meniscus vortex core in a water model of continuous casting mold. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2021, 52, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, L.F.; Scheller, P.R. Numerical simulation of steel and argon gas two-phase flow in continuous casting using LES+ VOF+ DPM model. JOM 2019, 71, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Vanka, S.P.; Thomas, B.G. Mathematical modeling of multiphase flow in steel continuous casting. ISIJ Int. 2019, 59, 956–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Tu, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; He, S. Fluid Flow in Continuous Casting Mold for Ultra-Wide Slab. Materials 2023, 16, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.D.; Shan, Q.L.; Gao, Y.; Pan, H.W.; Lu, B.X.; Wen, J.W.; Cui, H. Physical simulation of mold level fluctuation characteristics. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2023, 54, 2591–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Mold Size | Calculated | Inclination | Depth of | Pulling | Liquid Steel | Steel Liquid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mm × mm) | Length/mm | of SEN/(°) | Immersion of | Speed/(m/ | Density/ | Viscosity/ |
| SEN/(mm) | min) | (kg/m3) | (Pa·s) | |||
| 920 × 200 | 2000 | 15 | 155 | 2 | 7200 | 0.0064 |
| Detection Position | Liquid Surface Flow Rate/m/s |
|---|---|
| P1 | 0.093 |
| P2 | 0.072 |
| P3 | 0.046 |
| P4 | 0.077 |
| P5 | 0.095 |
| P6 | 0.095 |
| P7 | 0.075 |
| P8 | 0.050 |
| P9 | 0.074 |
| P10 | 0.097 |
| Symmetry Index (S) | Numerical Value |
|---|---|
| 0.962 | |
| 0.969 |
| Detection Position | Liquid-Level Fluctuation Value/mm |
|---|---|
| P1 | 3.81 |
| P2 | 2.61 |
| P3 | 2.68 |
| P4 | 3.88 |
| P5 | 3.83 |
| P6 | 2.63 |
| P7 | 2.66 |
| P8 | 3.85 |
| Bias Flow Index (N) | Numerical Value |
|---|---|
| 0.015 | |
| 0.007 |
| Degree of Offset | QL (m3/s) | Ve (m/s) | (°) | D (m) | F-Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| normal symmetry | 0.0061 | 0.21 | 12 | 0.425 | 4.297 |
| Degree of offset | 0 mm | 10 mm | 20 mm | 30 mm | 40 mm | 50 mm |
| Symmetry index | 0.969 | 0.877 | 0.792 | 0.773 | 0.762 | 0.704 |
| Liquid-Level Fluctuation Value/mm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic Point | Normalcy | 10 mm | 20 mm | 30 mm | 40 mm | 50 mm |
| P1 | 3.81 | 4.05 | 4.34 | 3.78 | 4.24 | 4.61 |
| P2 | 2.61 | 2.23 | 3.05 | 2.94 | 3.34 | 2.83 |
| P3 | 2.68 | 2.38 | 3.27 | 2.67 | 3.06 | 2.45 |
| P4 | 3.88 | 4.43 | 4.67 | 4.78 | 5.45 | 6.05 |
| P5 | 3.83 | 4.02 | 4.3 | 3.82 | 4.21 | 4.56 |
| P6 | 2.63 | 2.27 | 3.02 | 2.9 | 3.38 | 2.75 |
| P7 | 2.66 | 2.41 | 3.31 | 2.72 | 3.14 | 2.53 |
| P8 | 3.85 | 4.45 | 4.65 | 4.82 | 5.4 | 6.08 |
| Degree of offset | 0 mm | 10 mm | 20 mm | 30 mm | 40 mm | 50 mm |
| Symmetry index | 0.007 | 0.073 | 0.078 | 0.156 | 0.164 | 0.186 |
| Degree of Offset | QL (m3/s) | Ve (m/s) | (°) | D (m) | F-Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mm | 0.0061 | 0.26 | 13 | 0.420 | 5.267 |
| 20 mm | 0.0061 | 0.3 | 13.5 | 0.416 | 6.069 |
| 30 mm | 0.0061 | 0.33 | 14 | 0.41 | 6.699 |
| 40 mm | 0.0061 | 0.38 | 14.5 | 0.406 | 7.704 |
| 50 mm | 0.0061 | 0.42 | 15 | 0.403 | 8.482 |
| Degree of offset | 0 mm | 5 mm | 10 mm | 15 mm | 20 mm |
| 0.969 | 0.928 | 0.899 | 0.834 | 0.823 |
| Liquid-Level Fluctuation Value/mm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic Point | Normalcy | 5 mm | 10 mm | 15 mm | 20 mm |
| P1 | 3.81 | 4.25 | 4.53 | 4.32 | 4.64 |
| P2 | 2.61 | 2.83 | 2.67 | 2.14 | 2.55 |
| P3 | 2.68 | 2.87 | 2.7 | 2.18 | 2.61 |
| P4 | 3.88 | 4.27 | 4.57 | 4.4 | 4.65 |
| P5 | 3.83 | 4.39 | 4.95 | 4.62 | 4.33 |
| P6 | 2.63 | 3.01 | 2.97 | 2.63 | 3.22 |
| P7 | 2.66 | 3.07 | 3.02 | 2.69 | 3.28 |
| P8 | 3.85 | 4.85 | 4.78 | 4.3 | 4.4 |
| Degree of offset | 0 mm | 5 mm | 10 mm | 15 mm | 20 mm |
| Bias flow index | 0.015 | 0.075 | 0.085 | 0.126 | 0.145 |
| Degree of Offset | QL (m3/s) | Ve (m/s) | (°) | D (m) | F-Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mm | 0.0061 | 0.23 | 12.5 | 0.43 | 4.602 |
| 10 mm | 0.0061 | 0.25 | 13 | 0.435 | 4.891 |
| 15 mm | 0.0061 | 0.27 | 13.5 | 0.44 | 5.165 |
| 20 mm | 0.0061 | 0.3 | 14.5 | 0.445 | 5.548 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, P.; Wang, R.; Zhu, L.; Chen, C. Influence of Submerged Entry Nozzle Offset on the Flow Field in a Continuous Casting Mold. Metals 2025, 15, 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060575
Xiao P, Wang R, Zhu L, Chen C. Influence of Submerged Entry Nozzle Offset on the Flow Field in a Continuous Casting Mold. Metals. 2025; 15(6):575. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060575
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Pengcheng, Ruifeng Wang, Liguang Zhu, and Chao Chen. 2025. "Influence of Submerged Entry Nozzle Offset on the Flow Field in a Continuous Casting Mold" Metals 15, no. 6: 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060575
APA StyleXiao, P., Wang, R., Zhu, L., & Chen, C. (2025). Influence of Submerged Entry Nozzle Offset on the Flow Field in a Continuous Casting Mold. Metals, 15(6), 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060575







