Study on Liquid Metal Embrittlement Susceptibility of T91 Exposed to Liquid Lead-Bismuth Eutectic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Slow Strain Rate Tensile Test
2.3. Microstructure Characterization
3. Result
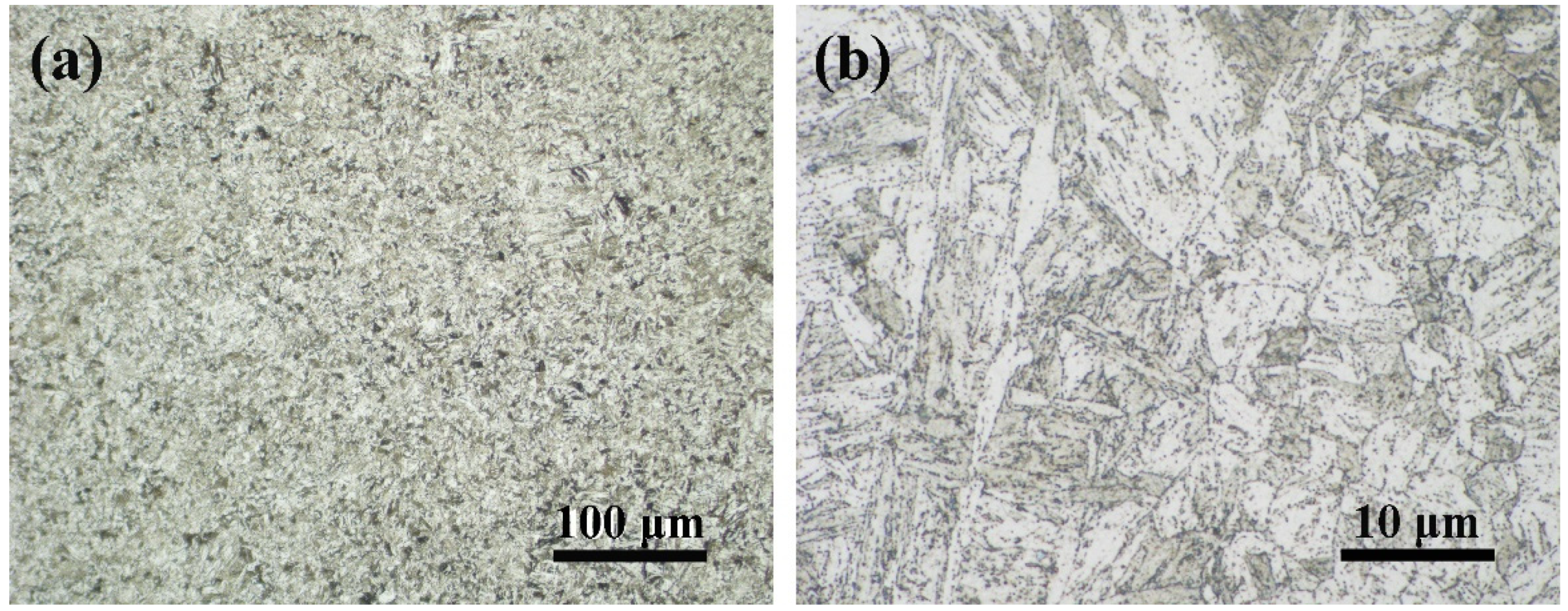
3.1. As-Received Microstructure
3.2. Tensile Mechanical Behavior
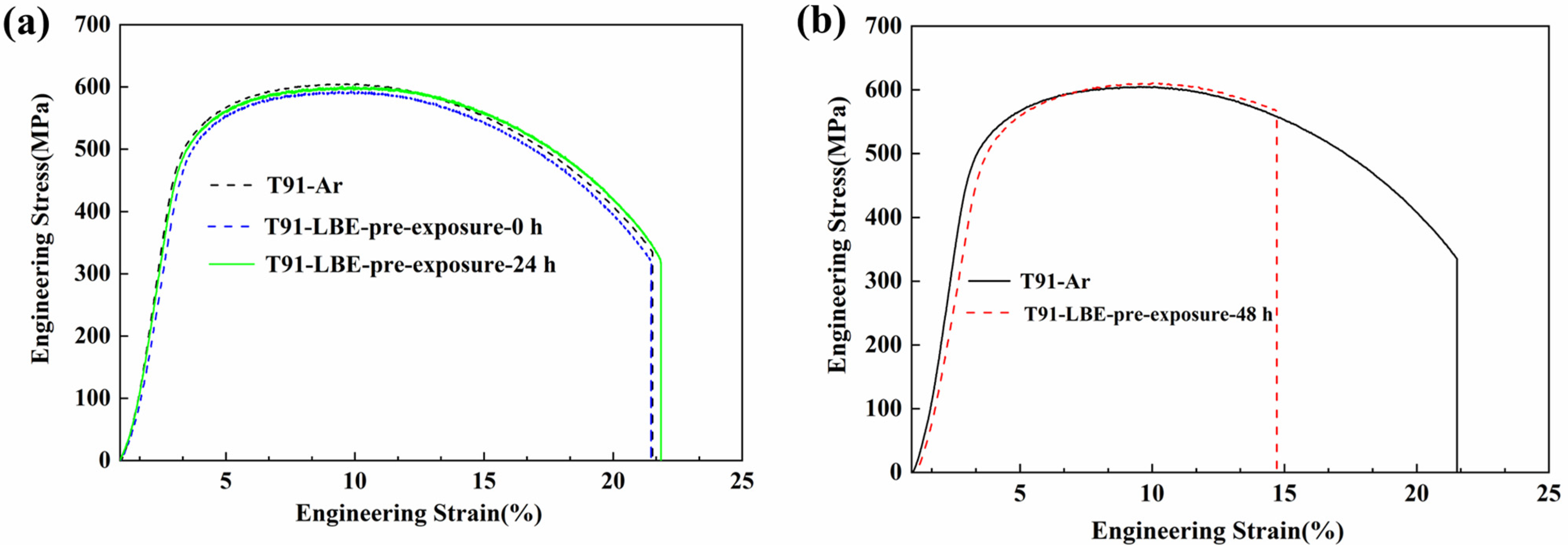
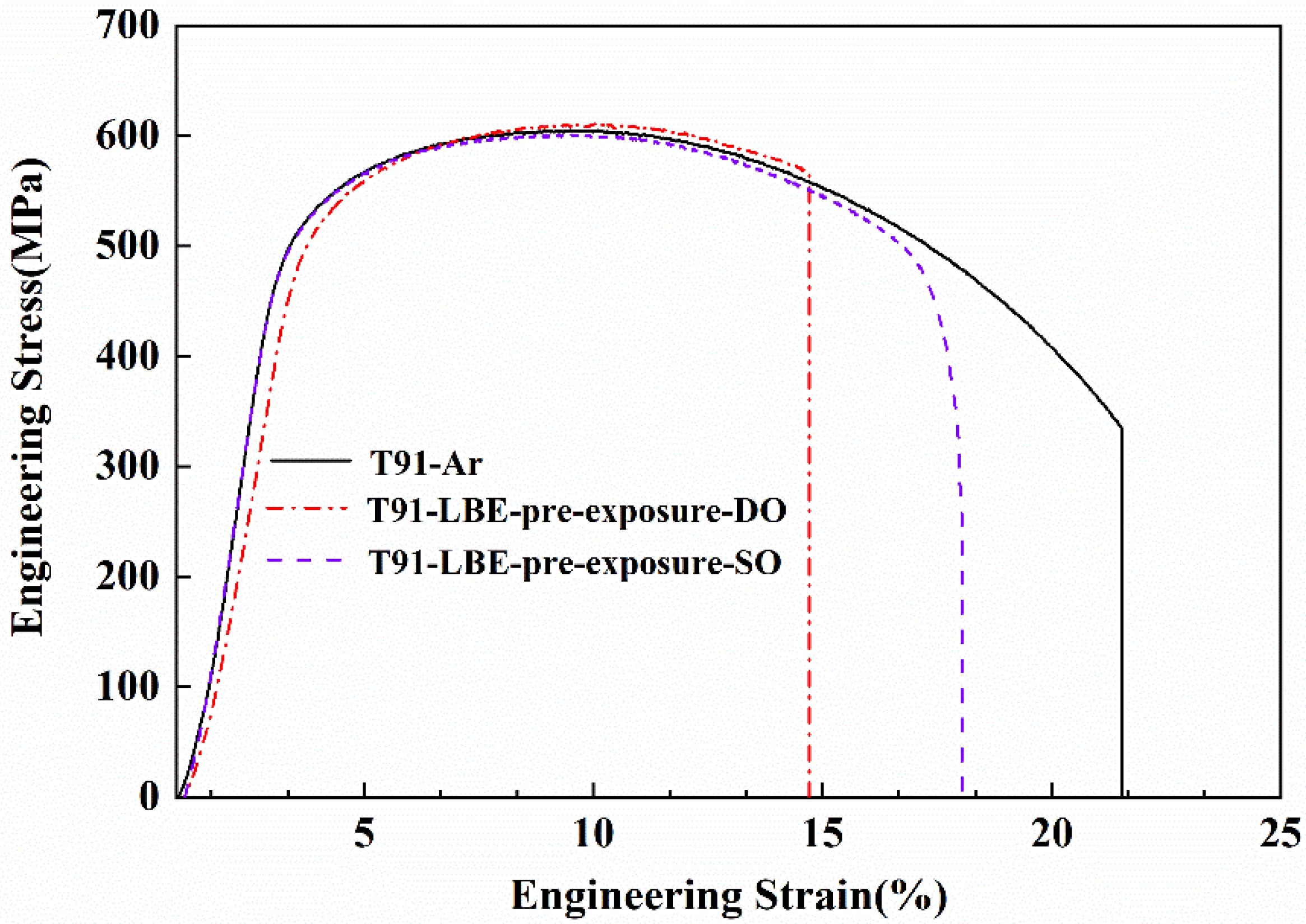
3.2.1. Tested After Different Pre-Exposure
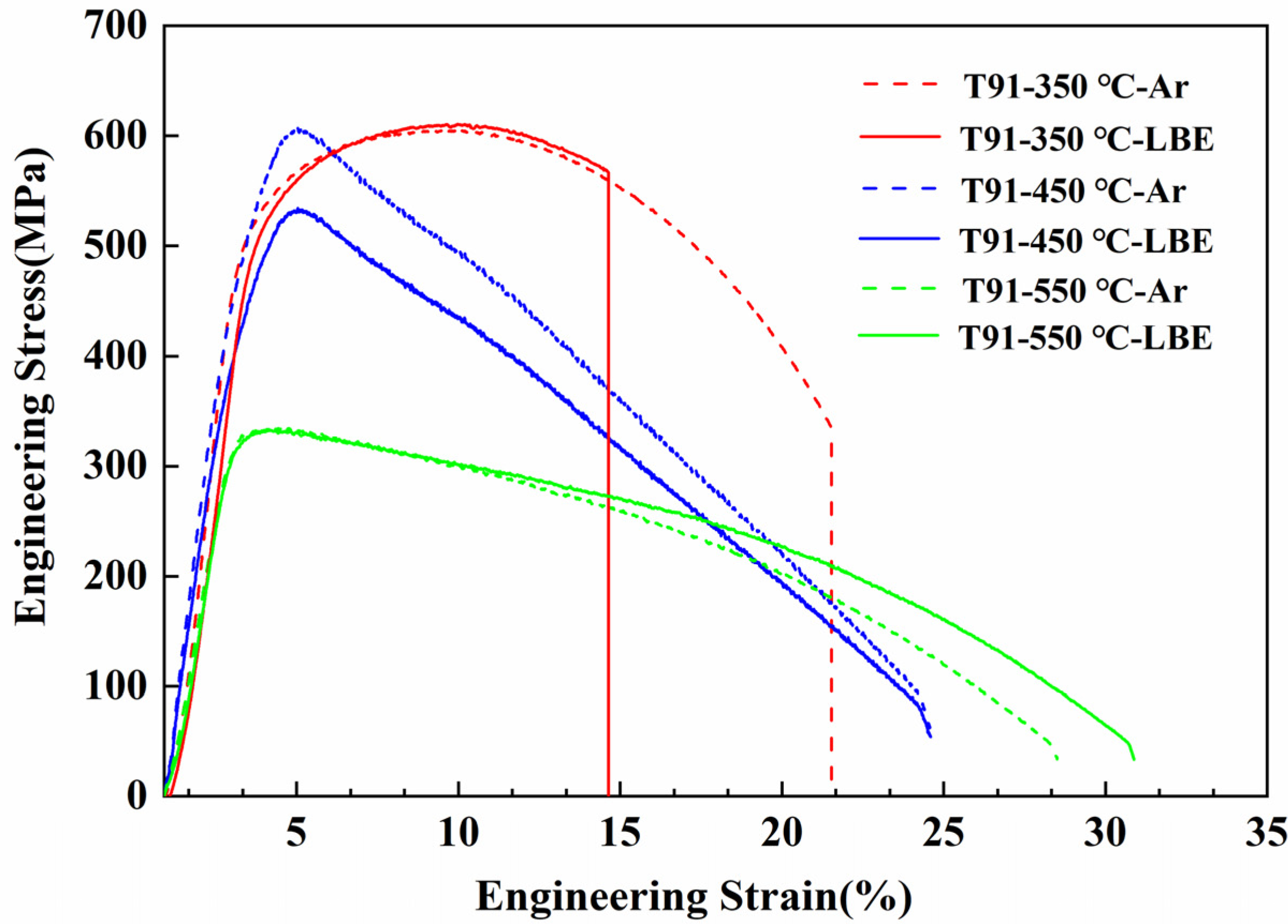
3.2.2. Test at Different Temperature
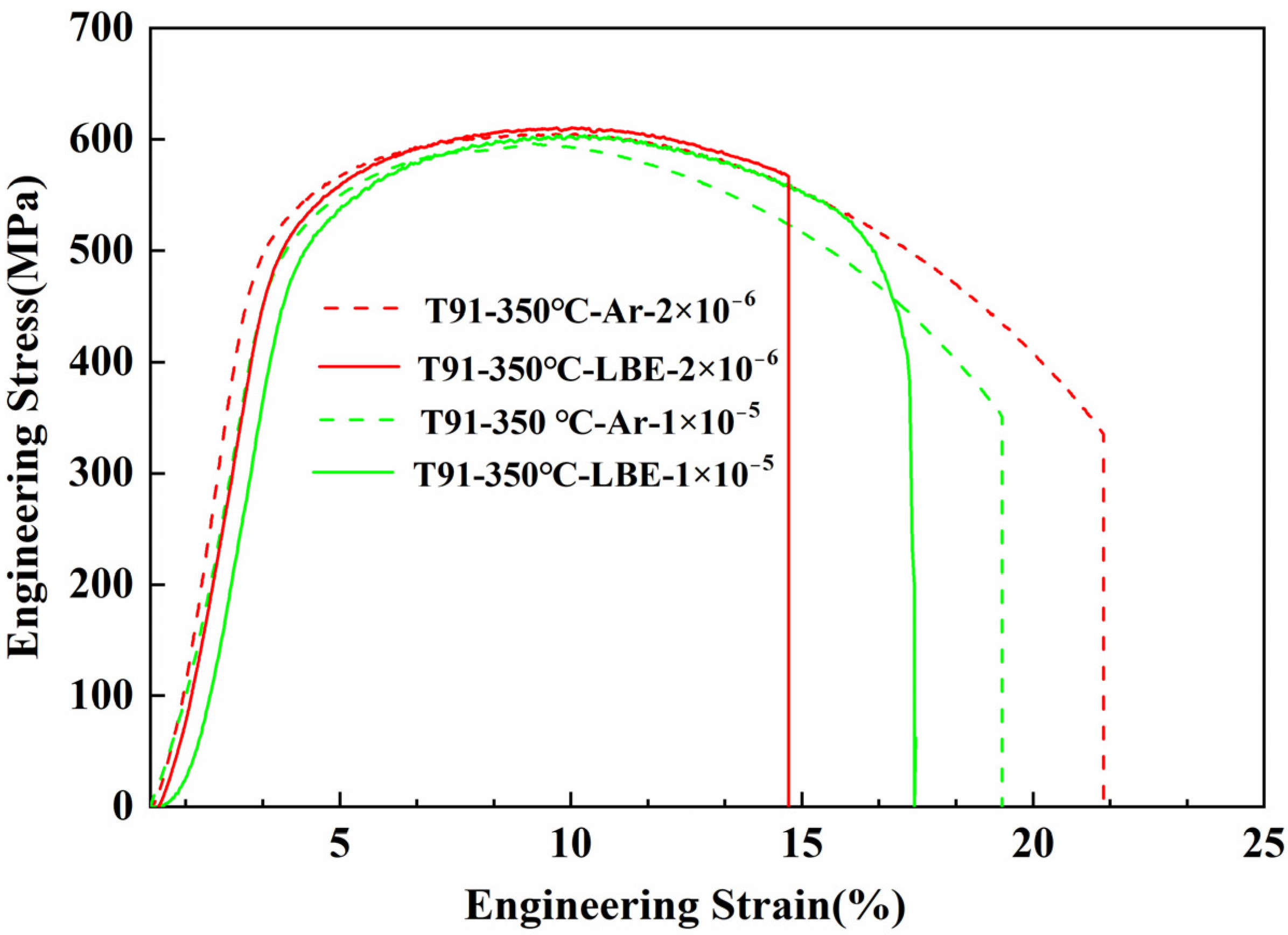
3.2.3. Test with Different Strain Rate
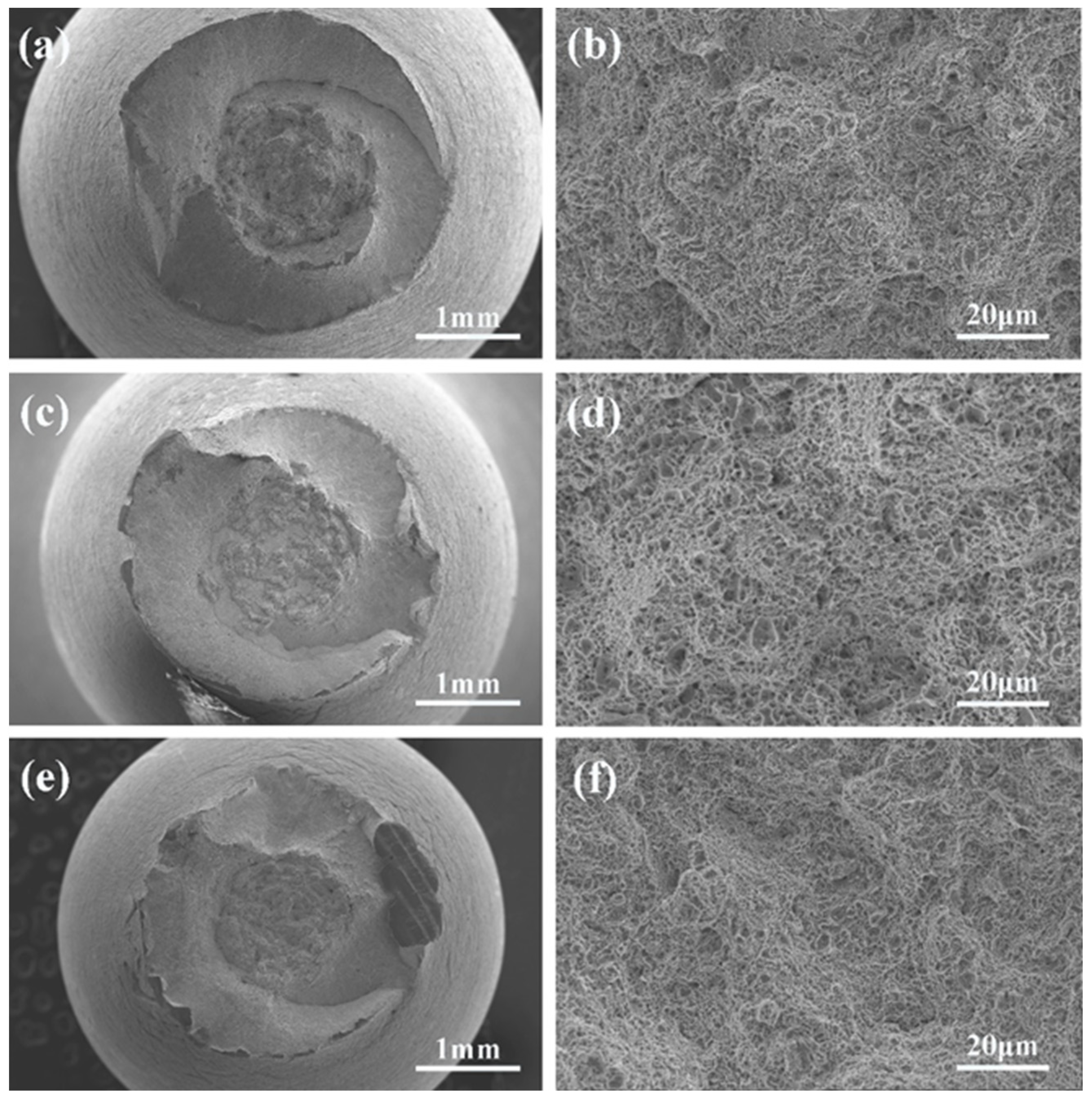
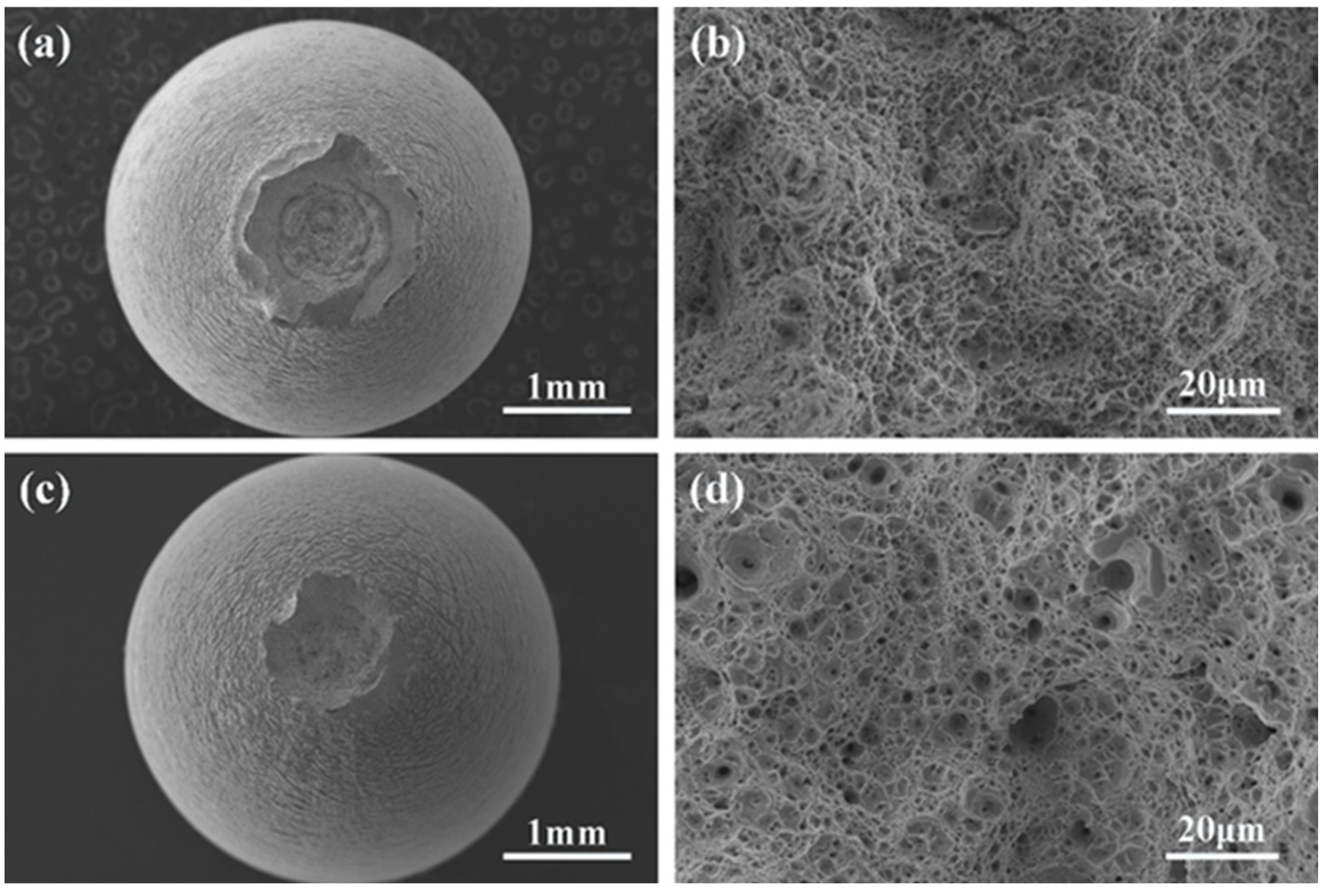
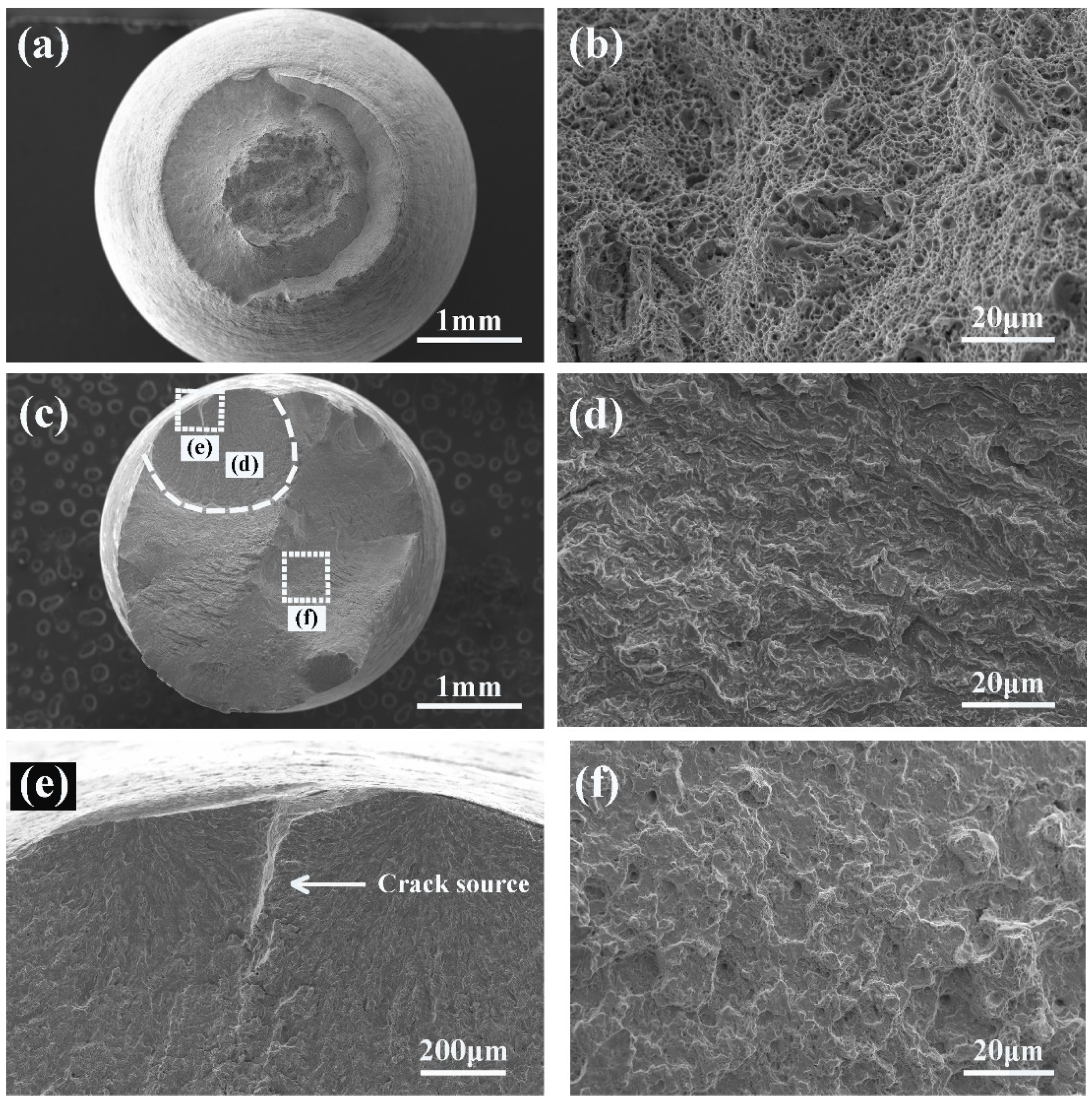
3.3. SEM Fractography
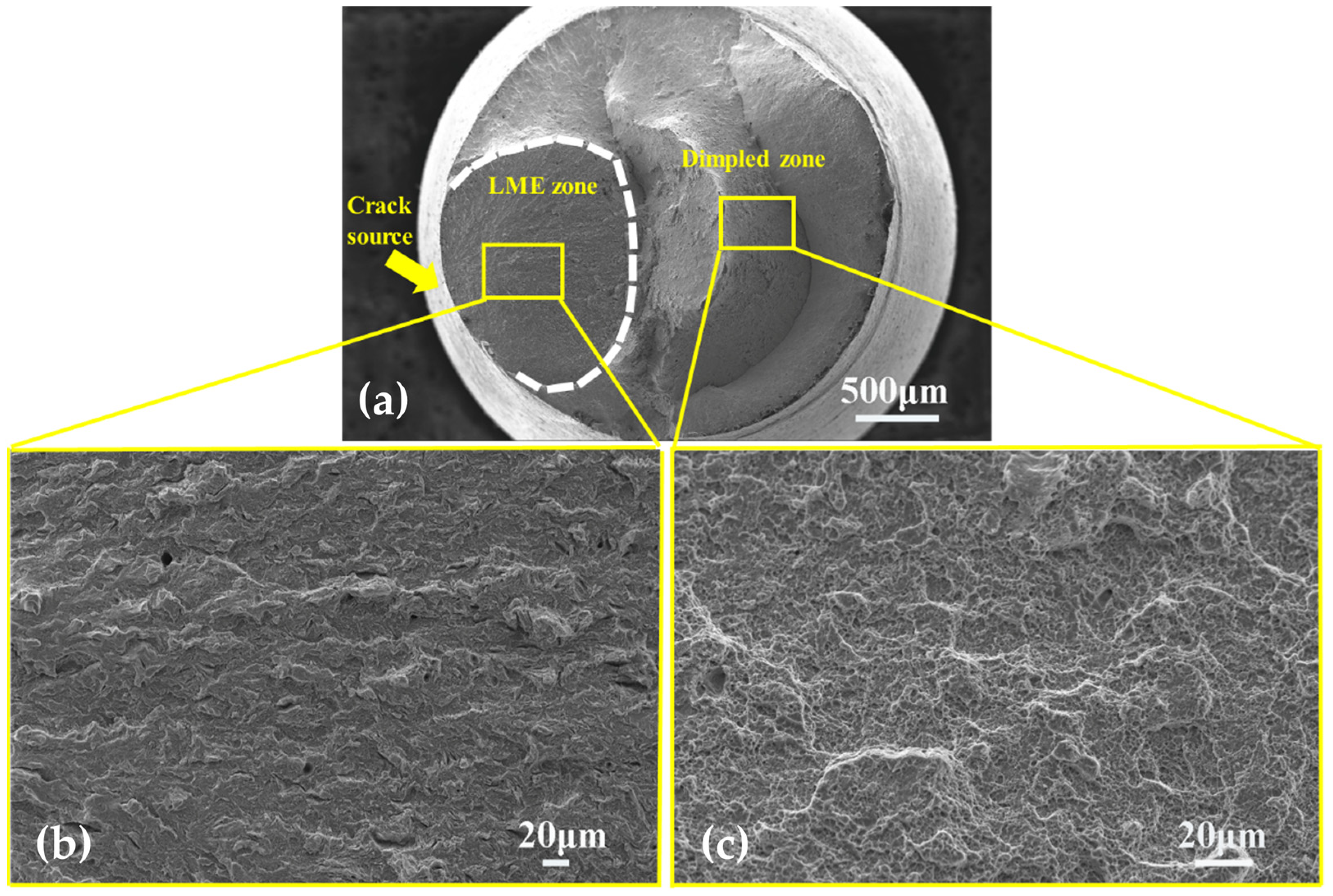
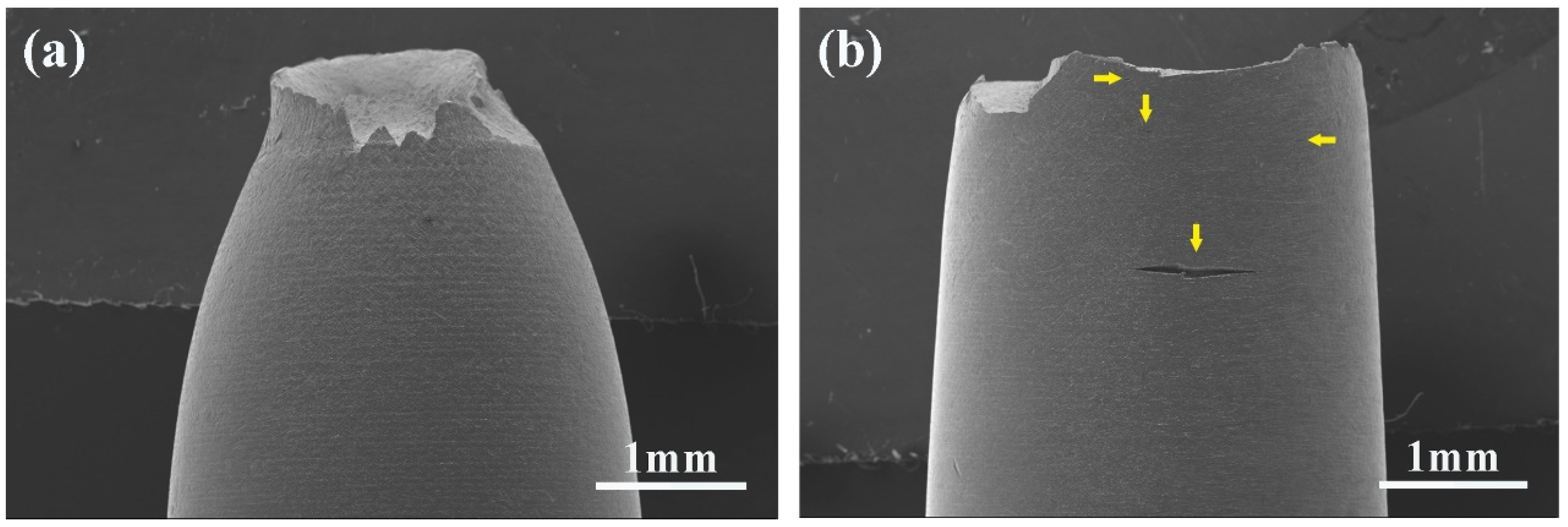
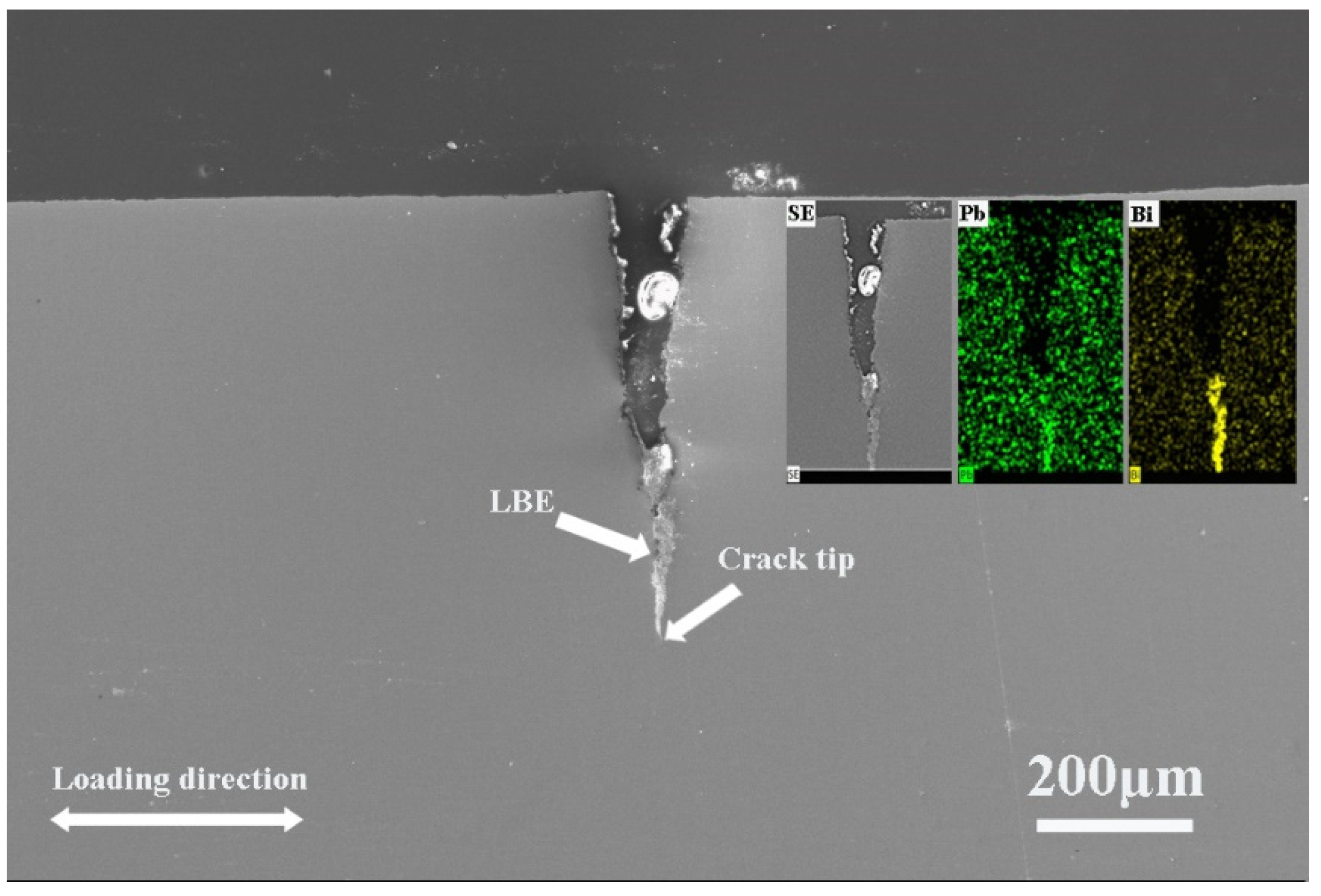
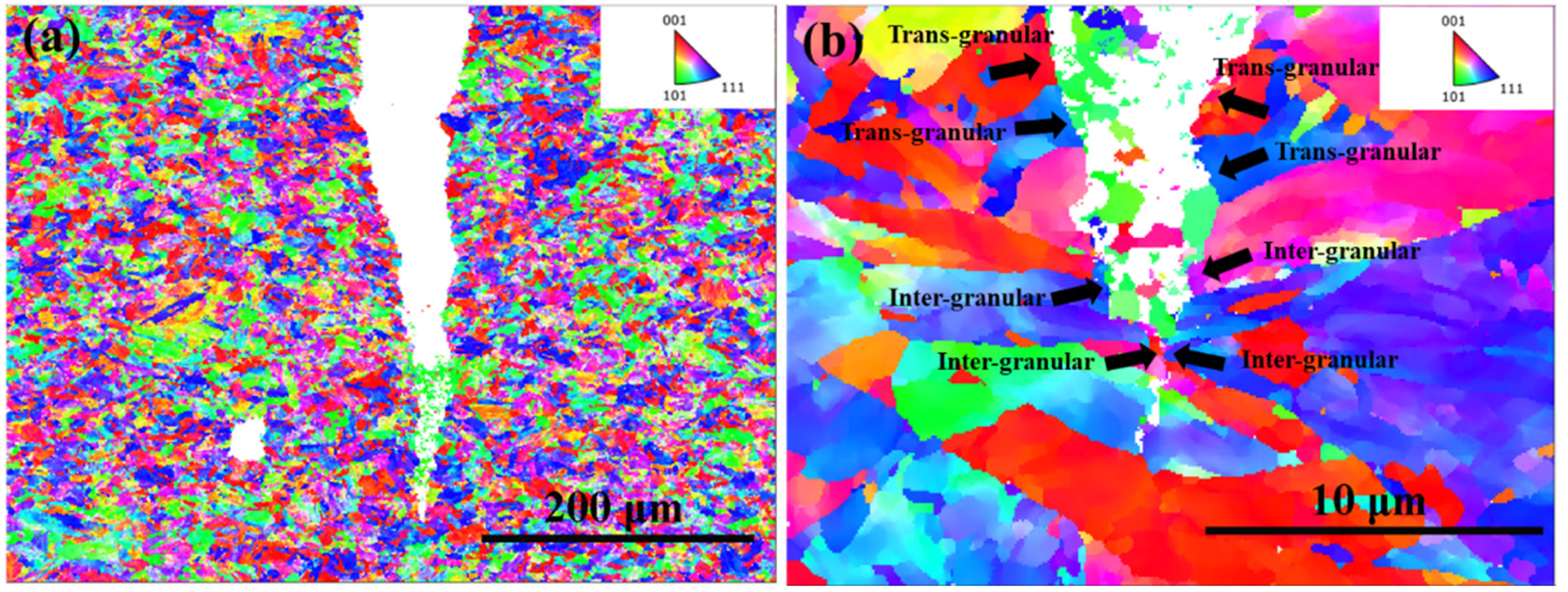
3.4. Surface Crack
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Pre-Exposure
4.2. Effect of Temperature and Strain Rate
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Effect of pre-exposure on LME
- T91 steel pre-exposure in low oxygen LBE for 48 h showed a significant LME effect in the LBE environment at 350 °C, which was characterized by a sharp decrease in elongation and brittle fracture.
- There were many long cracks on the surface of the specimens, and the SEM images of the fracture surface showed that the crack source was located at the edge of the fracture surface. This was because the pre-exposure caused the T91 steel matrix to be in close contact with LBE, which promoted the initiation of surface cracks, resulting in the LME phenomenon.
- (2)
- Effect of temperature on LME
- T91 exhibits LME sensitivity at 350 °C. When the temperature is increased to 450 °C and 550 °C, the LME phenomenon disappears.
- This is attributed to increased dislocation mobility at higher temperatures, which blunts the crack tip and restores material ductility. Additionally, the adsorption kinetics of LBE atoms at the crack tip and desorption at high temperatures contribute to this effect.
- (3)
- Effect of strain rate on LME
- LME sensitivity in T91 increases at lower strain rates. Low strain rates allow for thorough wetting of the LBE and crack tip, thus promoting LME phenomena.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, M.S.; Bai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zou, X. Conceptual design and numerical assessment of compact heat exchanger for lead-based reactor. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2020, 124, 103348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrodnikov, A.V.; Toshinsky, G.I.; Komlev, O.G.; Stepanov, V.S.; Klimov, N.N. SVBR-100 module-type fast reactor of the IV generation for regional power industry. J. Nucl. Mater. 2011, 415, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, P.; Bassini, S.; Del Nevo, A.; Di Piazza, I.; Giannetti, F.; Tarantino, M.; Utili, M. GEN-IV LFR development: Status & perspectives. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2018, 105, 318–331. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.; Li, R.; Sun, M.; Ren, Q.; Liu, T.; Short, M.P. Opportunities for the LWR ATF materials development program to contribute to the LBE-cooled ADS materials qualification program. J. Nucl. Mater. 2016, 482, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Fu, Q.; Wang, X.; An, C.; Chen, J. Research on the structure design of the LBE reactor coolant pump in the lead base heap. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2019, 51, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bosch, J.; Bosch, R.W.; Sapundjiev, D.; Almazouzi, A. Liquid metal embrittlement susceptibility of ferritic–martensitic steel in liquid lead alloys. J. Nucl. Mater. 2008, 376, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, N. Review of the studies on fundamental issues in LBE corrosion. J. Nucl. Mater. 2008, 373, 351–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroer, C.; Wedemeyer, O.; Skrypnik, A.; Novotny, J.; Konys, J. Corrosion kinetics of Steel T91 in flowing oxygen-containing lead–bismuth eutectic at 450 °C. J. Nucl. Mater. 2012, 431, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli; Jean-Louis; Fanny, B.C. Oxidation of steels in liquid lead bismuth: Oxygen control to achieve efficient corrosion protection. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2011, 241, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, C.; Kleber, X.; Fabregue, D.; Bouzekri, M. Liquid zinc embrittlement of twinning-induced plasticity steel. Scr. Mater. 2012, 66, 1030–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicaise, G.; Legris, A.; Vogt, J.B.; Foct, J. Embrittlement of the martensitic steel 91 tested in liquid lead. J. Nucl. Mater. 2001, 296, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojna, A.; Di Gabriele, F.; Chocholousek, M.; Spirit, Z.; Halodova, P.; Lorincik, J. Initiation of LME crack in ferritic martensitic steel in liquid lead-bismuth. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 511, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Long, B.; Groeschel, F. Slow strain rate tensile tests on T91 in static lead–bismuth eutectic. J. Nucl. Mater. 2006, 356, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojna, A.; Di Gabriele, F. On the kinetics of LME for the ferritic–martensitic steel T91 immersed in liquid PbBi eutectic. J. Nucl. Mater. 2011, 413, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Chen, J.; Xiang, C.; Yu, Z.; Gong, H.; Yin, Y. A comparative study on liquid metal embrittlement susceptibility of three FeCrAl ferritic alloys in contact with liquid lead-bismuth eutectic at 350 °C. Corros. Sci. 2021, 183, 109346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yan, W.; Sha, W.; Wang, W.; Shan, Y.; Yang, K. Effects of temperature and strain rate on the tensile behaviors of SIMP steel in static lead bismuth eutectic. J. Nucl. Mater. 2016, 473, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Vogt, J.B.; Serre, I.P. Liquid metal embrittlement of the T91 steel in lead bismuth eutectic: The role of loading rate and of the oxygen content in the liquid metal. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 608, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, T.; Lorang, G.; Guérin, S.; Pastol, J.L.; Gorse, D. Effect of contact conditions on embrittlement of T91 steel by lead–bismuth. J. Nucl. Mater. 2004, 335, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, J.B.; Proriol-Serre, I. Fatigue behaviour of a martensitic and an austenitic steel in heavy liquid metals. Procedia Eng. 2013, 55, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, S.; Jiang, K.; Yu, J.; Wu, H.; Shi, S.; Lin, Q. Improvement of low-cycle fatigue behavior of modified 9Cr-1Mo steels at 450 °C in liquid LBE environment by the addition of Si element. Nucl. Eng. Design 2023, 413, 112570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Luo, L. Liquid lead–bismuth eutectic embrittlement effect on the tensile properties of T91 steel at 350 °C. Mater. Corros. 2022, 73, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Stergar, E.; Marmy, P.; Gavrilov, S. Tensile fracture behavior of notched 9cr-lmo ferritic-martensitic steel specimens in contact with liquid lead-bismuth eutectic at 350 °C. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 692, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bosch, J.; Coen, G.; Hosemann, P.; Maloy, S.A. On the LME susceptibility of Si enriched steels. J. Nucl. Mater. 2012, 429, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoloff, N.S.; Johnston, T.L. Crack propagation in a liquid metal environment. Acta Metall. 1963, 11, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, A.R.; Kamdar, M.H. Concerning liquid metal embrittlement, particularly of zinc monocrystals by mercury. Philos. Mag. 1963, 8, 787–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.J.; Jones, D.R. Mechanisms of liquid metal induced embrittlement. Int. Mater. Rev. 1997, 42, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolman, D.G. A review of recent advances in the understanding of liquid metal embrittlement. Mater. Corros. 2019, 75, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.; Tong, Z.; Gröschel, F.; Dai, Y. Liquid Pb–Bi embrittlement effects on the T91 steel after different heat treatments. J. Nucl. Mater. 2008, 377, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.; Dai, Y. Investigation of LBE embrittlement effects on the fracture properties of T91. J. Nucl. Mater. 2008, 376, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjem-Hamouche, Z.; Auger, T.; Guillot, I. Temperature effect in the maximum propagation rate of a liquid metal filled crack: The T91 martensitic steel/Lead–Bismuth Eutectic system. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 2580–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Hu, F.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Gong, H.; Xiao, J.; Wang, H.; Deng, Y.; Pang, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Effect of temperature on liquid metal embrittlement susceptibility of an Fe10Cr4Al ferritic alloy in contact with stagnant lead-bismuth eutectic. J. Nucl. Mater. 2020, 537, 152196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Marmy, P.; Qin, L.; Verlinden, B.; Wevers, M.; Seefeldt, M. Temperature dependence of liquid metal embrittlement susceptibility of a modified 9Cr–1Mo steel under low cycle fatigue in lead–bismuth eutectic at 160–450 °C. J. Nucl. Mater. 2016, 468, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Marmy, P.; Yin, Y. The role of oxide films in preventing liquid metal embrittlement of T91 steel exposed to liquid lead-bismuth eutectic. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 509, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorse, D.; Auger, T.; Vogt, J.B.; Serre, I.; Weisenburger, A.; Gessi, A.; Agostini, P.; Fazio, C.; Hojna, A.; Di Gabriele, F.; et al. Influence of liquid lead and lead–bismuth eutectic on tensile, fatigue and creep properties of ferritic/martensitic and austenitic steels for transmutation systems. J. Nucl. Mater. 2011, 415, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
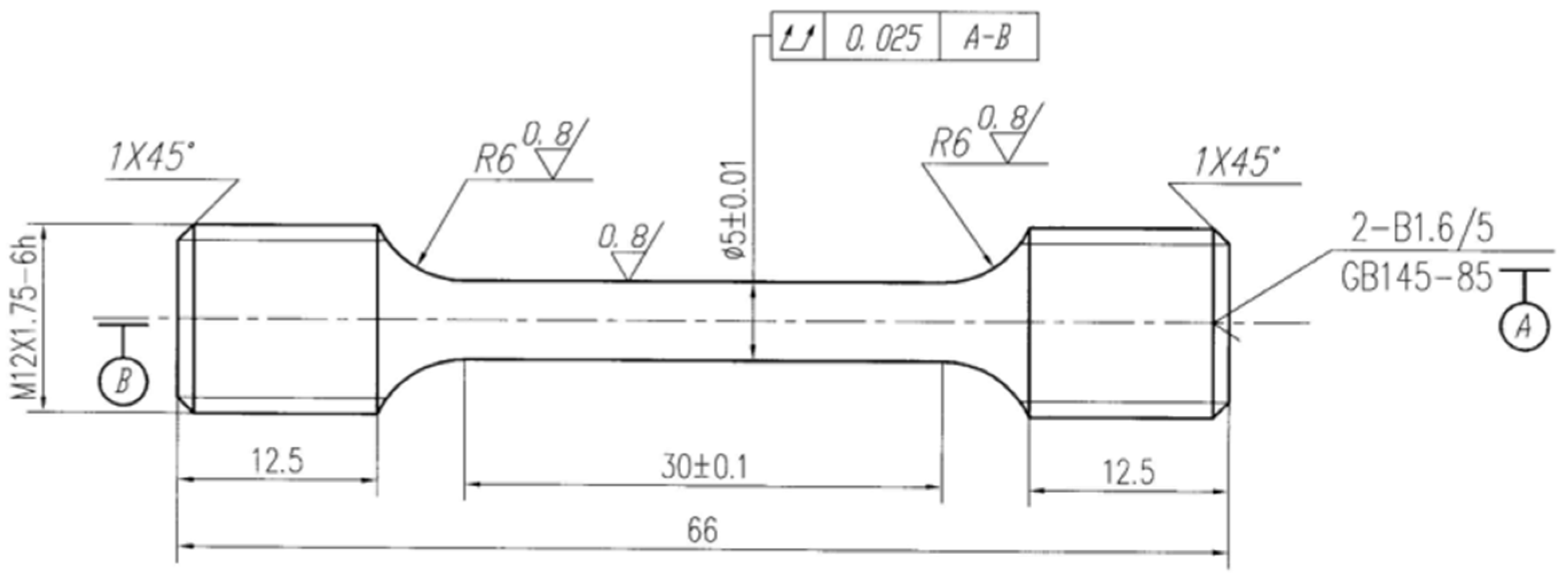

| Element | C | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Mo | Cu | V | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (wt.%) | 0.135 | 0.299 | 0.423 | 8.483 | 0.637 | 0.880 | 0.129 | 0.165 | 88.787 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Qin, B.; Long, B. Study on Liquid Metal Embrittlement Susceptibility of T91 Exposed to Liquid Lead-Bismuth Eutectic. Metals 2025, 15, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15020206
Zhang J, Qin B, Long B. Study on Liquid Metal Embrittlement Susceptibility of T91 Exposed to Liquid Lead-Bismuth Eutectic. Metals. 2025; 15(2):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15020206
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jie, Bo Qin, and Bin Long. 2025. "Study on Liquid Metal Embrittlement Susceptibility of T91 Exposed to Liquid Lead-Bismuth Eutectic" Metals 15, no. 2: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15020206
APA StyleZhang, J., Qin, B., & Long, B. (2025). Study on Liquid Metal Embrittlement Susceptibility of T91 Exposed to Liquid Lead-Bismuth Eutectic. Metals, 15(2), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15020206





