The Magnetocaloric Properties and Critical Behavior of (Gd4Co3)100−xGex Rapidly Quenched Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franco, V.; Blázquez, J.S.; Ipus, J.J.; Law, J.Y.; Moreno-Ramírez, L.M.; Conde, A. Magnetocaloric effect: From materials research to refrigeration devices. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 93, 112–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.W.; Yan, M. Recent progresses in exploring the rare earth based intermetallic compounds for cryogenic magnetic refrigeration. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 823, 153810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.L.; Qian, S.X.; Takeuchi, I. Materials, physics and systems for multicaloric cooling. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 633–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia, U.; Grisolia, G. Magnetocaloric refrigeration in the context of sustainability: A review of thermodynamic bases, the state of the art, and future prospects. Energies 2024, 17, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehan, P.Z.Z.; Vitayaya, O.; Munazat, D.R.; Manawan, M.T.E.; Darmintod, D.; Kurniawan, B. The magnetocaloric effect properties for potential applications of magnetic refrigerator technology: A review. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, 14476–14504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czernuszewicz, A.; Mudryk, Y.; Cui, J.; Griffith, L.; Johnson, D.D.; Slaughter, J. From the discovery of the giant magnetocaloric effect to the development of high-power-density systems. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2025, e00545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecharsky, V.K.; Gschneidner, K.A., Jr. Giant magnetocaloric effect in Gd5(Si2Ge2). Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 4494–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecharsky, V.K.; Gschneidner, K.A., Jr. Tunable magnetic regenerator alloys with a giant magnetocaloric effect for magnetic refrigeration from similar to 20 to similar to 290 K. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1997, 70, 3299–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Nozariasbmarz, A.; Karan, S.K.; Raman, L.; Goyal, G.K.; Sharma, S.; Li, W.J.; Priya, S.; et al. High-performance thermomagnetic Gd−Si−Ge alloys. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 35140–35148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, H.; Tanabe, Y. Giant magnetocaloric effect of MnAs1−xSbx. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 3302–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegus, O.; Brück, E.; Buschow, K.H.J.; de Boer, F.R. Transition-metal-based magnetic refrigerants for room-temperature applications. Nature 2002, 415, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quijano, D.P.; Carlos Infante Ferreira, C.I.; Brück, E. Layering strategies for active magnetocaloric regenerators using MnFePSi for heat pump applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 232, 120962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Tong, W.; Wang, H.J.; Peng, L.M. Enhancing magnetocaloric properties of NiMnGa-based alloys via Dy micro-alloying and pseudoelastic cyclic training. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 123, 022409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, N.; Mishra, S.; Sarkar, S.; Talapatra, S.; Palit, M.; Paliwal, M.; Singh, A.K.; Tiwary, C.S. Magnetocaloric effect in Mn-rich Heusler-derived alloys for room temperature-based applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2025, 13, 10789–10803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Feng, Y.; Yuan, X.Y.; Liu, Q.W.; Zhou, J.J.; Wang, S.X. Zr-doped Ni-Mn-In alloy: A novel solid-state refrigeration material with enhanced magneto-caloric and elasto-caloric effects. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 177765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, J.; Guo, K.L.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.S.; Gu, J.L.; Ma, Q.S.; Gao, Q.Z.; Morley, N.; Zou, L. Enhanced magnetocaloric effect in Ni-Mn-Sn alloys by synergistic manipulation of magnetization difference and lattice volume. Appl. Mater. Today 2025, 42, 102589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Landazábal, J.I.; Recarte, V.; Sánchez-Alarcos, V.; Beato-López, J.J.; Rodríguez-Velamazán, J.A.; Sánchez-Marcos, J.; Gómez-Polo, C.; Cesari, E. Giant direct and inverse magnetocaloric effect linked to the same forward martensitic transformation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.Q.; Westra, K.; Shen, Q.; Batashev, I.; Kiecana, A.; van Dijk, A.; Brück, E. The second-order magnetic phase transition and magnetocaloric effect in all-d-metal NiCoMnTi-based Heusler alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 906, 164337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.C.; Min, J.X.; Zheng, Z.G.; Liu, Z.W.; Zeng, D.C. Critical behavior and magnetocaloric effect of Gd65Mn35−xGex (x=0, 5, and 10) melt-spun ribbons. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 033903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Zou, M. Magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of ternary Gd-Co-Al bulk metallic glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 4613–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.G.; Zhong, X.C.; Yu, H.Y.; Franco, V.; Liu, Z.W.; Zeng, D.C. The magnetocaloric effect and critical behavior in amorphous Gd60Co40–xMnx alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 07A922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.C.; Huang, X.W.; Shen, X.Y.; Mo, H.Y.; Liu, Z.W. Thermal stability, magnetic properties and large refrigerant capacity of ternary Gd55Co35M10 (M=Mn, Fe and Ni) amorphous alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 682, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.S.; Zhang, M.W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, R.; Shen, H.X. Effect of Ni alloying on the microstructure and magnetocaloric properties of Gd-based metallic microffbers. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 961, 170979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.B.; Du, Y.S.; Fu, G.; Wu, X.F.; Deng, J.Q.; Cheng, G.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.T.; Rao, G.H. Manufacture and characterization of RE2Co (RE=Gd, Ho) amorphous alloys with excellent magnetic entropy change. Intermetallics 2024, 167, 108234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.K.; Suresh, K.G.; Nigam, A.K. A comparative study of the magnetocaloric effect in Gd3Co and Gd3Ni. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 306, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Wang, D.H.; Han, Z.D.; Xuan, H.C.; Gu, B.X.; Du, Y.W. Large magnetic entropy changes in Gd-Co amorphous ribbons. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 013912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seixas, T.M.; Machado da Silva, J.M.; Papageorgiou, T.P.; Braun, H.F.; Eska, G. Spin reorientation transition in Gd4Co3. Phys. B 2004, 353, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, B.; Zhao, X.G.; Zhang, Z.D. Magnetic and reversible magnetocaloric properties of (Gd1−xDyx)4Co3 ferrimagnets. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 053902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Zheng, Z.G.; Cao, W.H.; Shek, C.H. Magnetic behavior of Gd4Co3 metallic glass. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 326, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.C.; Gao, B.B.; Liu, Z.W.; Zheng, Z.G.; Zeng, D.C. Amorphous and crystallized (Gd4Co3)100−xBx alloys for magnetic refrigerants working in the vicinity of 200 K. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 553, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.G.; Zhong, X.C.; Liu, Z.W.; Zeng, D.C.; Franco, V.; Zhang, J.L. Magnetocaloric effect and critical behavior of amorphous (Gd4Co3)1−xSix alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 343, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.X.; Zhong, X.C.; Liu, Z.W.; Zheng, Z.G.; Zeng, D.C. Magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effects of Gd-Mn-Si ribbons in amorphous and crystalline states. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 606, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigh, H.E.; Legvold, S.; Spedding, F.H. Magnetization and electrical resistivity of gadolinium single crystals. Phys. Rev. 1963, 132, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneyoshi, T. Amorphous Magnetism; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.G.; Lai, J.H.; Hsieh, C.C.; Fang, Y.K.; Chang, W.C.; Zhang, Z.D. The influence of Si addition on the glass forming ability, magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of the Gd-Fe-Al glassy ribbons. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 07A911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.C.; Tang, P.F.; Liu, Z.W.; Zeng, D.C.; Zheng, Z.G.; Yu, H.Y.; Qiu, W.Q.; Zhang, H.; Ramanujan, R.V. Large magnetocaloric effect and refrigerant capacity in Gd–Co–Ni metallic glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 07A919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, A.; Fukamichi, K. Control of large magnetocaloric effects in metamagnetic La(FexSi1−x)13 compounds by hydrogenation. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 404–406, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, B.K. On a generalised approach to first and second order magnetic transitions. Phys. Lett. 1964, 12, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henchiri, C.; Gu, S.X.; Qi, Q.; Zhou, H.S.; Dhahri, E.; Valente, M.A. Study of the structural, magnetic, magnetocaloric properties and critical exponents of La0.9 0.1MnO2.95 compound. Appl. Phys. A 2025, 131, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, P.D.; Kaul, S.N. Scaling behaviour of magnetization for temperatures in the vicinity of, and far from, the ferromagnetic-paramagnetic phase transition in amorphous Fe90−xCoxZr10 and Fe90+yZr10−y alloys. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1997, 9, 7189–7222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.F.; Peng, J.; Xue, M.Q.; Wang, B.S. Magnetocaloric effect and critical behavior of the Mn-rich itinerant material Mn3GaC with enhanced ferromagnetic interaction. Chin. Phys. B 2020, 29, 047503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouvel, J.S.; Fisher, M.E. Detailed magnetic behavior of nickel near its Curie point. Phys. Rev. 1964, 36, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.O.; Dong, F.X.; Wang, H.C.; Zhao, B.J.; Wang, Y.; Tan, W.S. Magnetic properties, critical behavior, and magnetocaloric effect of Nd1−xSrxMnO3 (0.2 ≤ x ≤ 0.5): The role of Sr doping concentration. J. Appl. Phys. 2024, 136, 093902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, H.E. (Ed.) Introduction to Phase Transition and Critical Phenomena; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Arrott, A.; Noakes, J.E. Approximate equation of state for nickel near its critical temperature. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1967, 19, 786–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharoni, A. Introduction to the Theory of Ferromagnetism; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Widom, B. Degree of the critical isotherm. J. Chem. Phys. 1964, 41, 1633–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.R.; Yu, B.W.; Zheng, H.; Qiu, Y.W.; Wang, S.H.; Ma, C.L.; Wang, C.X.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, J.Y. Magnetic phase transition and critical behavior of the chiral magnet β-Mn type Co7Zn7Mn6. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2024, 856, 141622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, H.E. Scaling, universality, and renormalization: Three pillars of modern critical phenomena. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1999, 71, S358–S366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guillou, J.C.; Zinn-Justin, J. Critical exponents from field theory. Phys. Rev. B 1980, 21, 3976–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
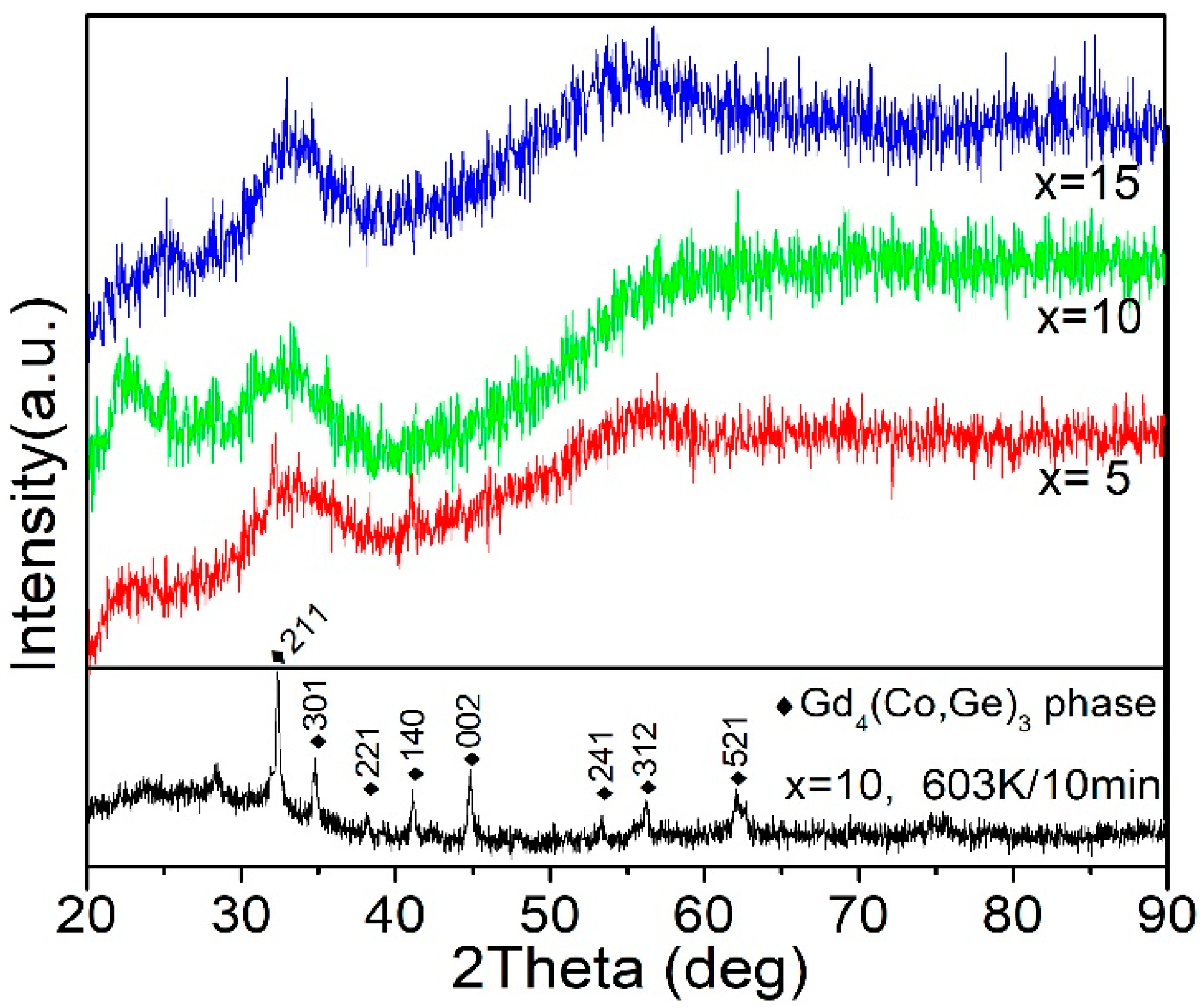
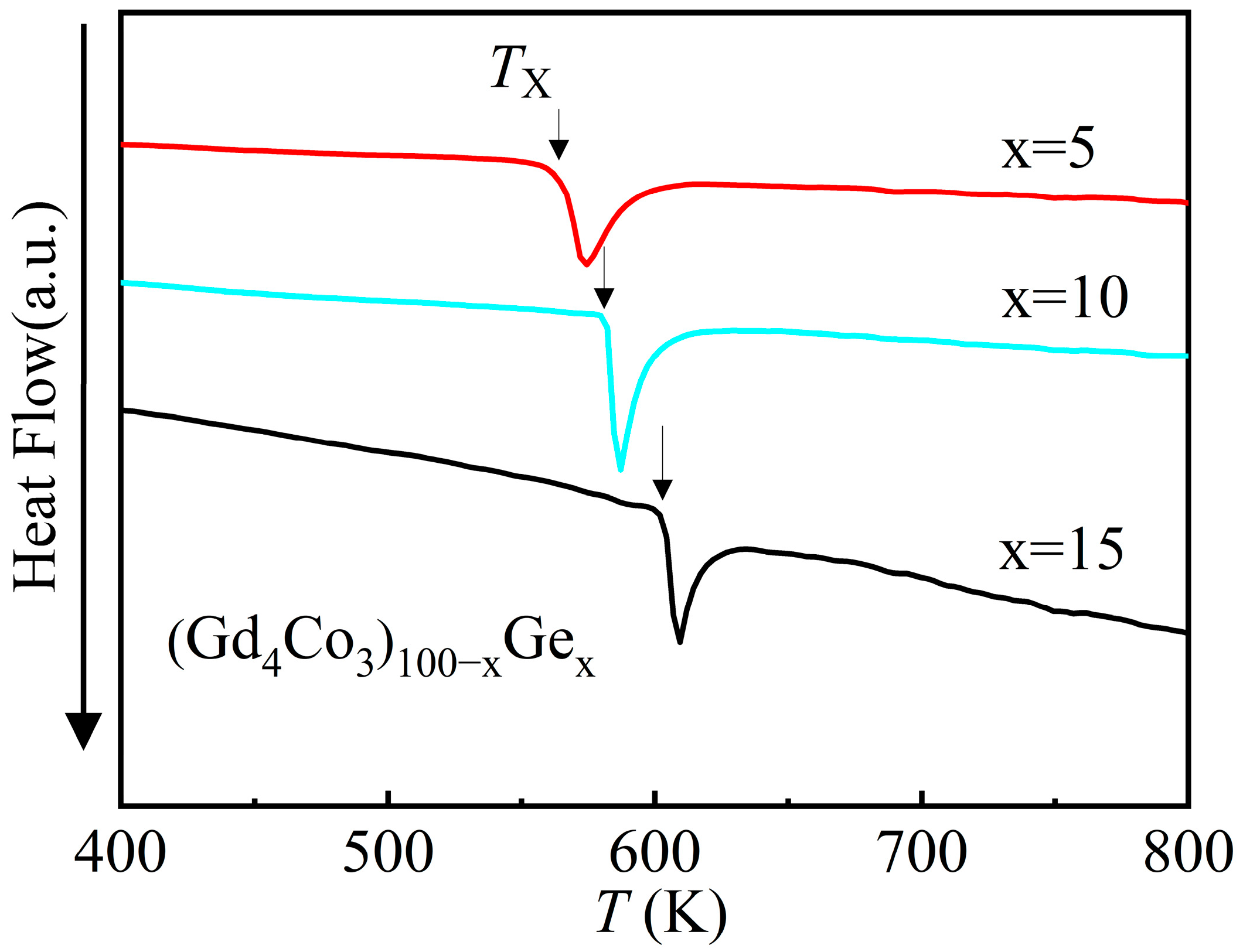
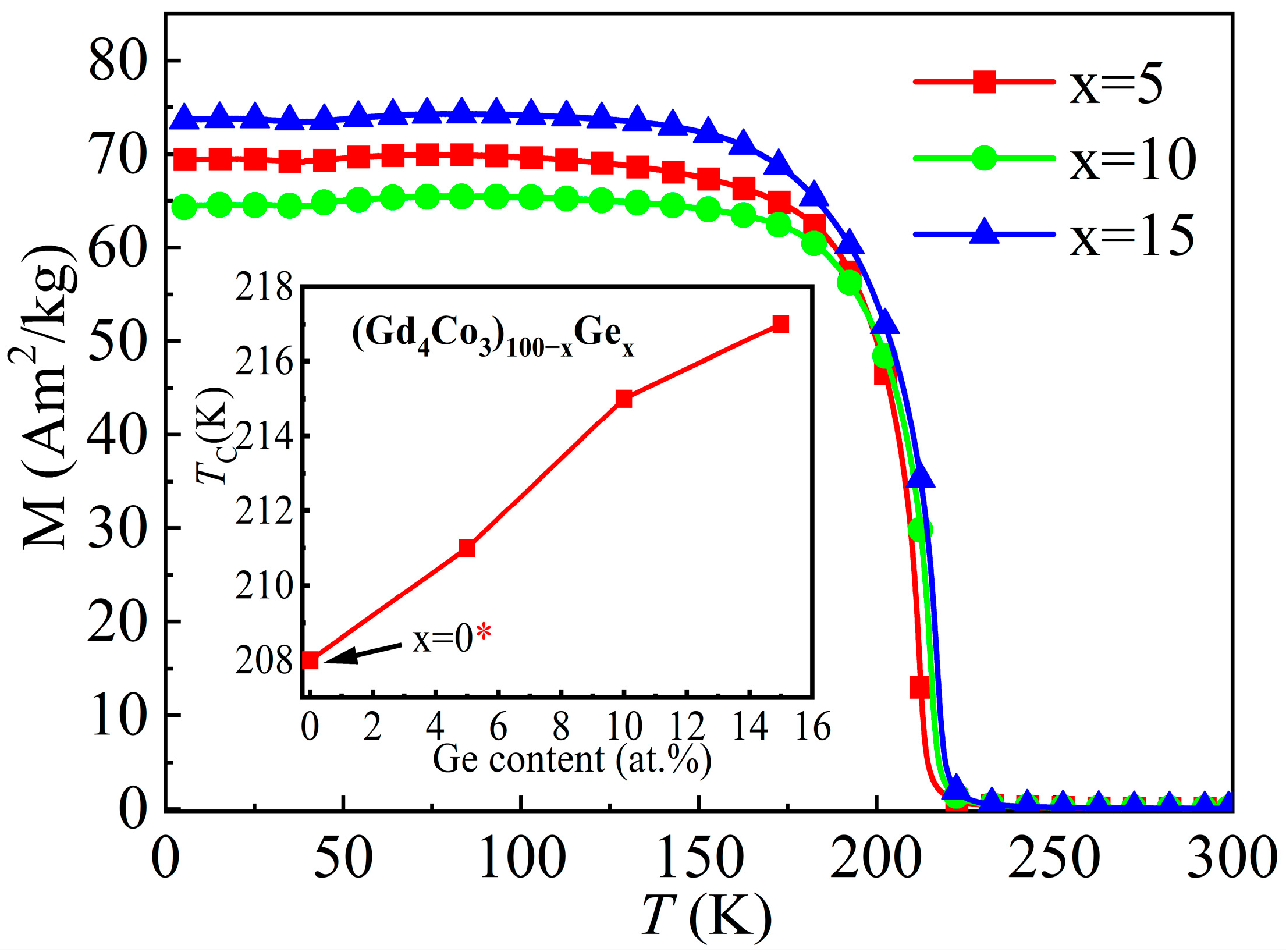
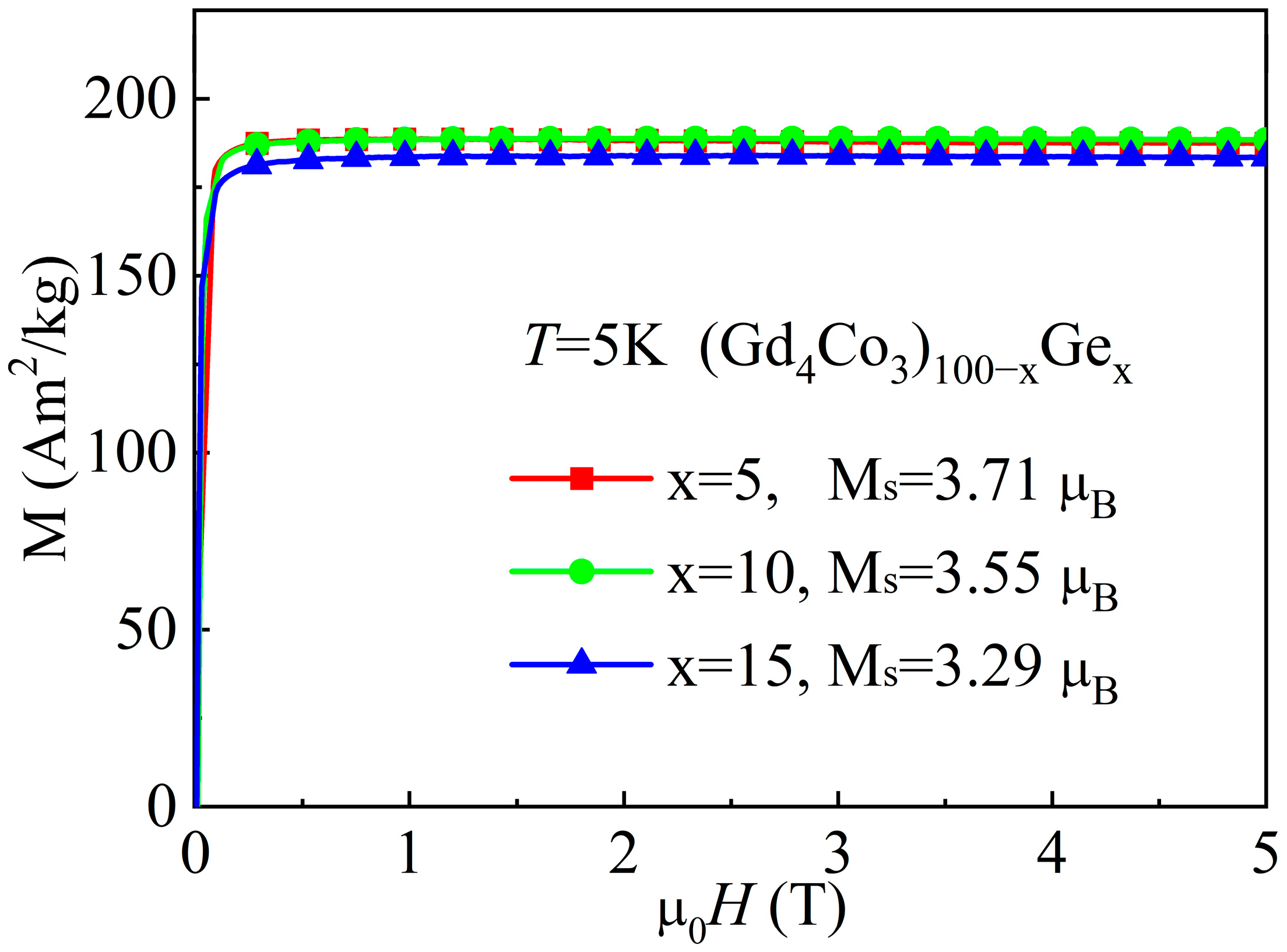

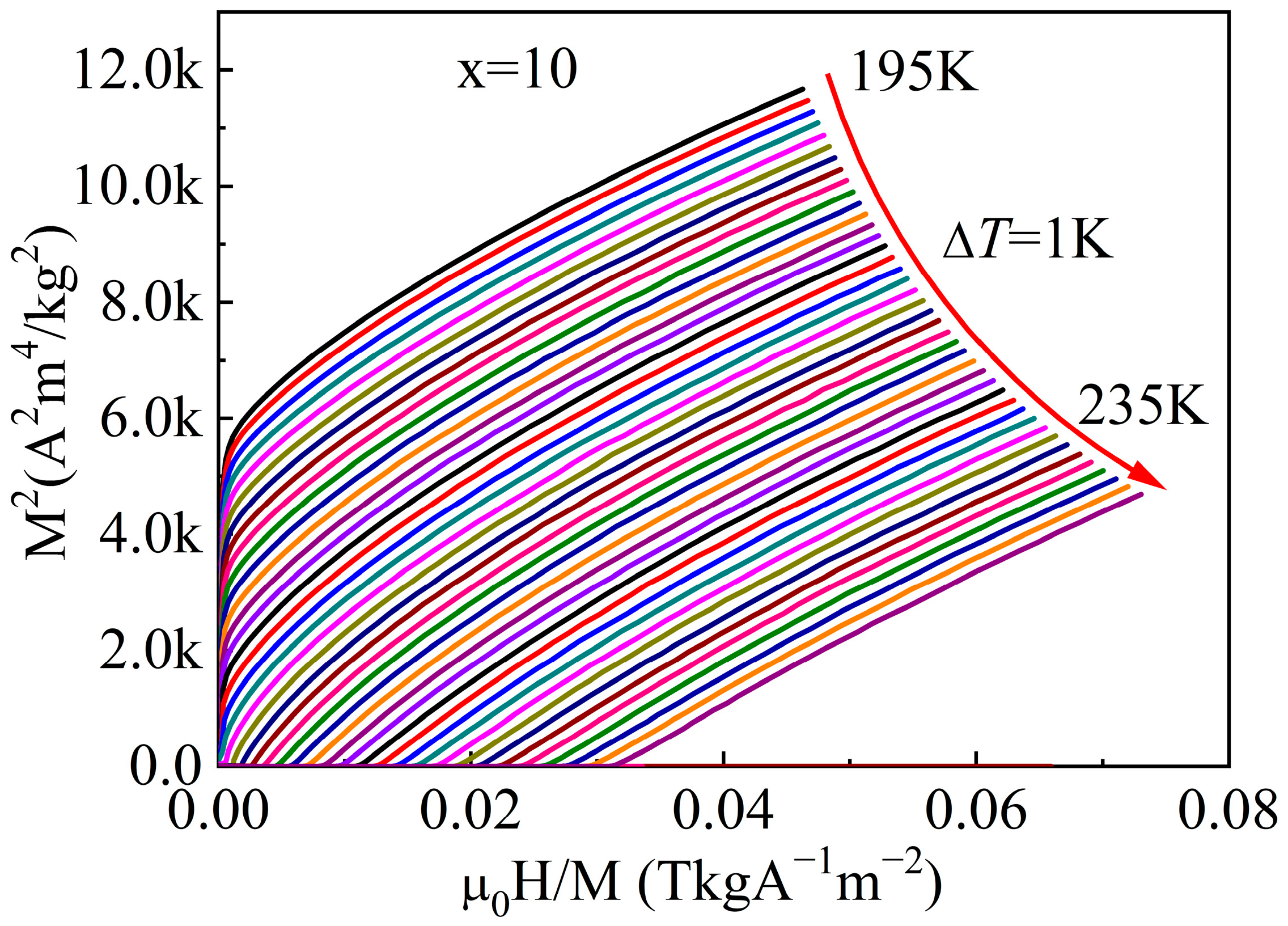

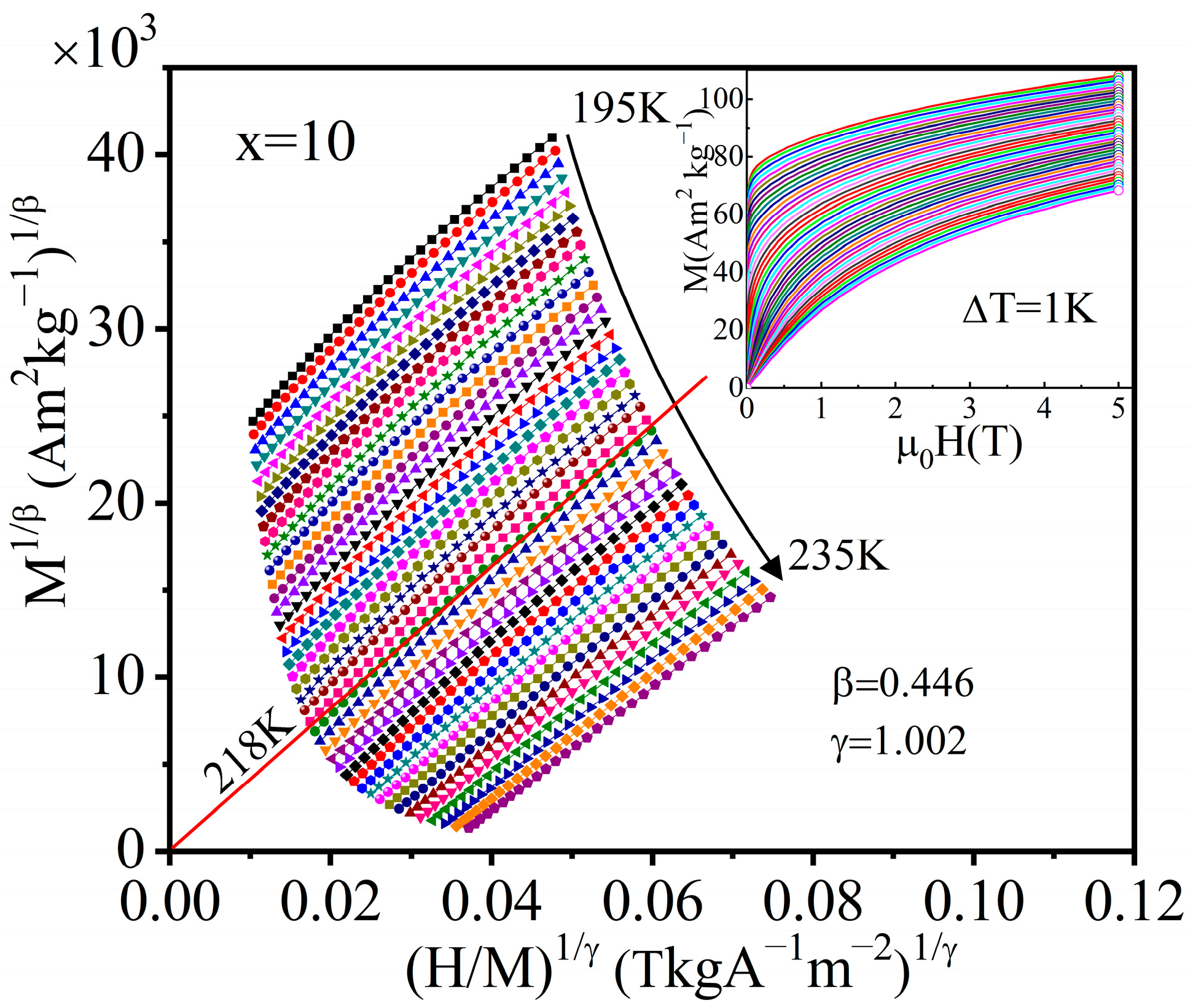
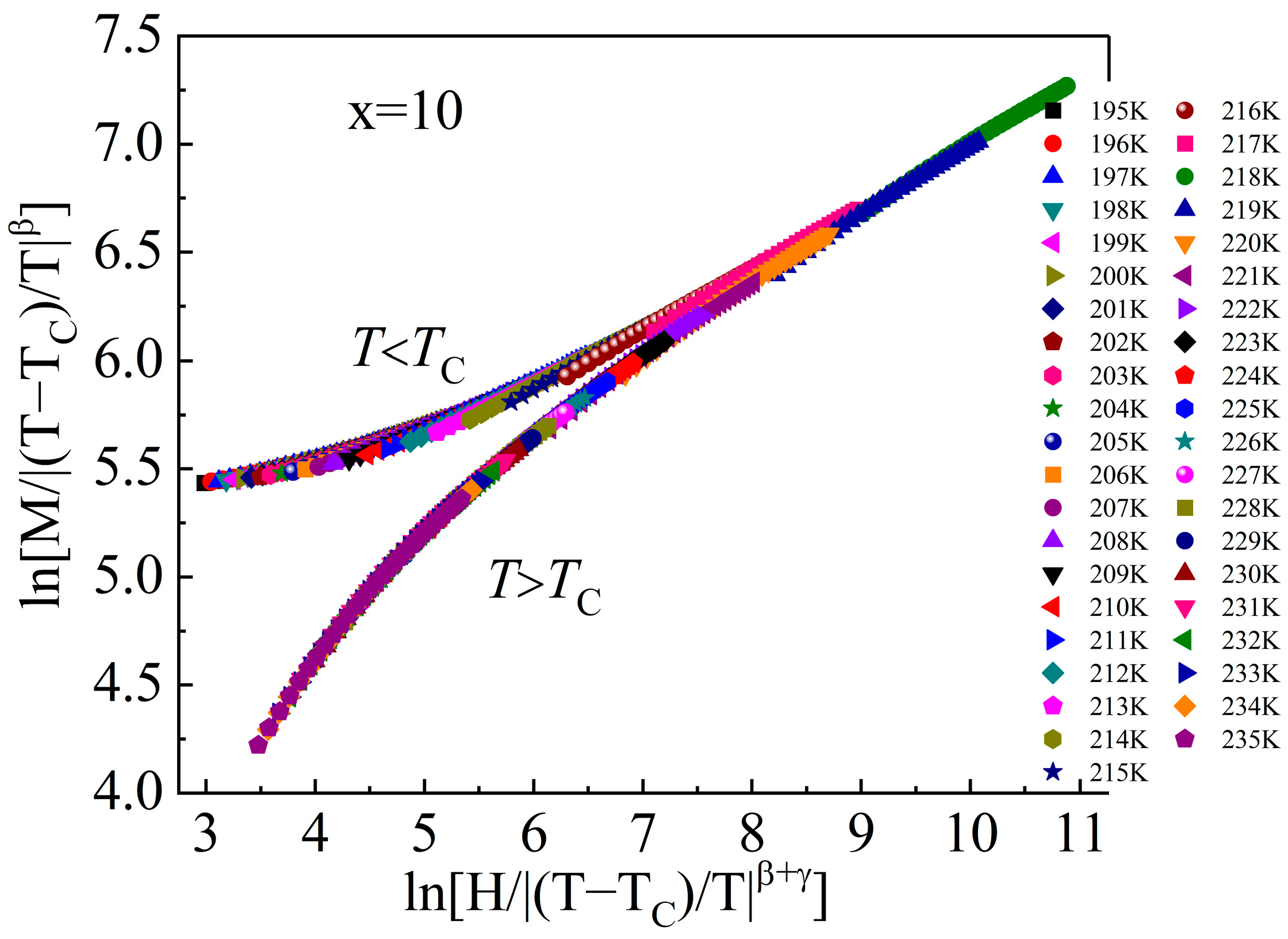
| Material | State | TC (K) | (−ΔSM)max J/(kg·K), 0–5 T | RC J/kg, 0–5 T | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Gd4Co3)95Ge5 | A | 211 | 7.15 | 448 | This work |
| (Gd4Co3)90Ge10 | A | 215 | 6.83 | 435 | This work |
| (Gd4Co3)85Ge15 | A | 217 | 6.71 | 458 | This work |
| (Gd4Co3)95B5 | A | 209 | 7.1 | 520 | [30] |
| (Gd4Co3)90B10 | A | 203 | 7.4 | 527 | [30] |
| (Gd4Co3)85B15 | A | 197 | 7.8 | 535 | [30] |
| (Gd4Co3)0.95Si0.05 | A | 198 | 7.2 | 524 | [31] |
| (Gd4Co3)0.9Si0.1 | A | 213 | 6.4 | 511 | [31] |
| Gd4Co3 | A | 208 | 7.3 | 547 | [31] |
| Gd4Co3 | A | 215 | 6.7 | 510 | [30] |
| Gd4Co3 | C | 220 | 6.4 | 575 | [30] |
| Gd4Co3 | C | 163 a/220 | 5.7 | 575 | [28] |
| Gd60Co35Mn5 | A | 202 | 7.1 | -- | [21] |
| Gd65Fe20Al14Si1 | A | 210 | 4.77 | 762 | [35] |
| Gd65Fe20Al12Si3 | A | 215 | 4.78 | 752 | [35] |
| Gd65Fe20Al10Si5 | A | 220 | 4.68 | 713 | [35] |
| Gd65Fe20Al8Si7 | A | 227 | 4.80 | 741 | [35] |
| Gd55Co35Ni10 | A | 192 | 6.5 | 502 | [36] |
| La(Fe0.88Si0.12)13 | C | 195 | 23 | 452 | [37] |
| Material | β | γ | δ | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x = 10 | 0.446 | 1.002 | 3.247 * | This work |
| x = 15 | 0.484 | 1.109 | 3.292 * | This work |
| H3D | 0.365 | 1.336 | 4.80 * | [50] |
| Is3D | 0.325 | 1.24 | 4.82 * | [50] |
| MFT | 0.5 | 1.0 | 3.0 * | [44] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, X.; Wu, Y.; Yu, H.; Liu, Z. The Magnetocaloric Properties and Critical Behavior of (Gd4Co3)100−xGex Rapidly Quenched Alloys. Metals 2025, 15, 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111267
Zhong X, Wu Y, Yu H, Liu Z. The Magnetocaloric Properties and Critical Behavior of (Gd4Co3)100−xGex Rapidly Quenched Alloys. Metals. 2025; 15(11):1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111267
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Xichun, Yaxiang Wu, Haongya Yu, and Zhongwu Liu. 2025. "The Magnetocaloric Properties and Critical Behavior of (Gd4Co3)100−xGex Rapidly Quenched Alloys" Metals 15, no. 11: 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111267
APA StyleZhong, X., Wu, Y., Yu, H., & Liu, Z. (2025). The Magnetocaloric Properties and Critical Behavior of (Gd4Co3)100−xGex Rapidly Quenched Alloys. Metals, 15(11), 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111267








