Effect of Rare-Earth Ce Addition on Thermal Stability and Corrosion Resistance of Inconel 718 Superalloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
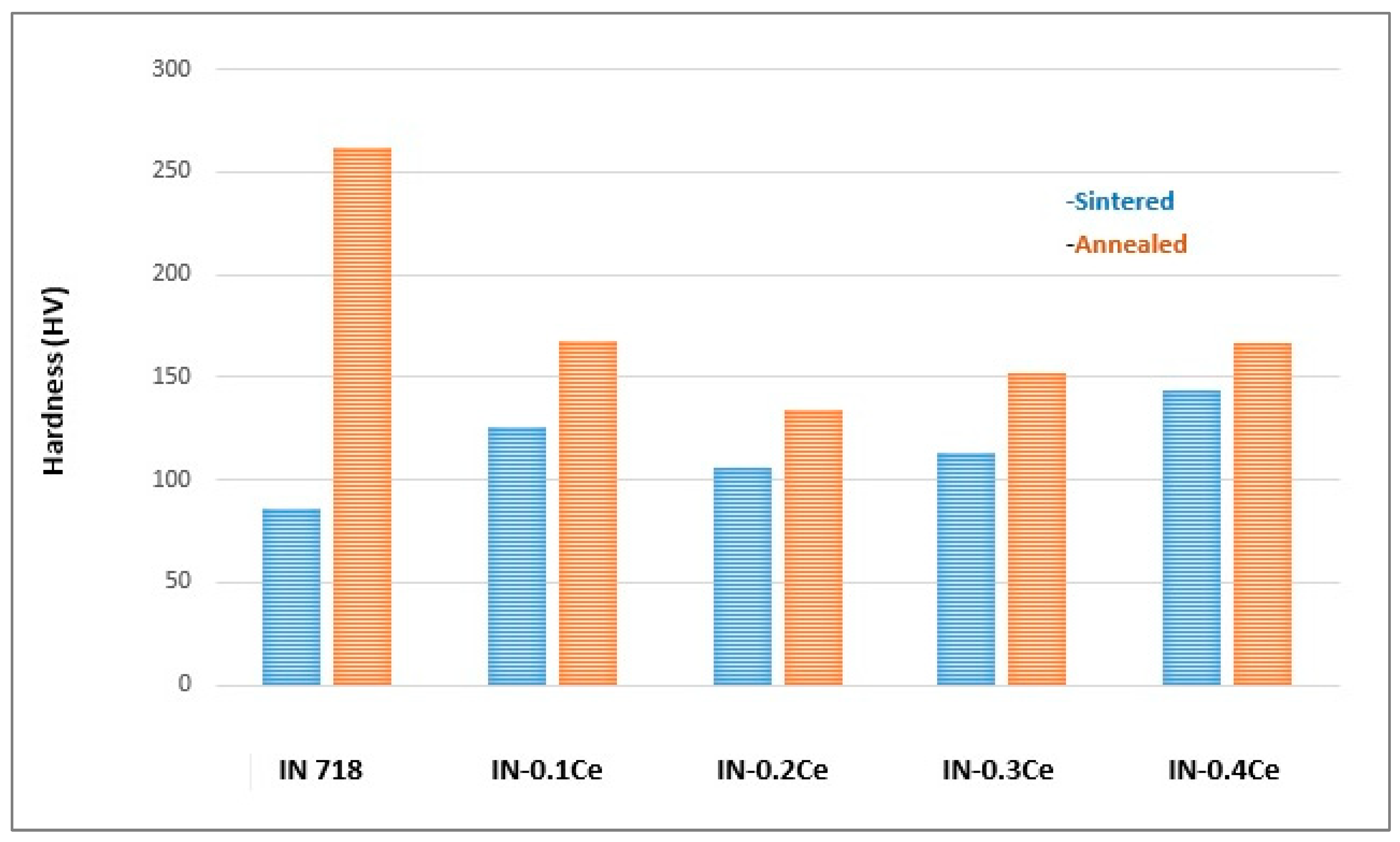
- This investigation determined that an addition of 0.2 wt.% Ce is the optimal composition for enhancing the properties of the Inconel 718 superalloy when processed via powder metallurgy and subsequent annealing.
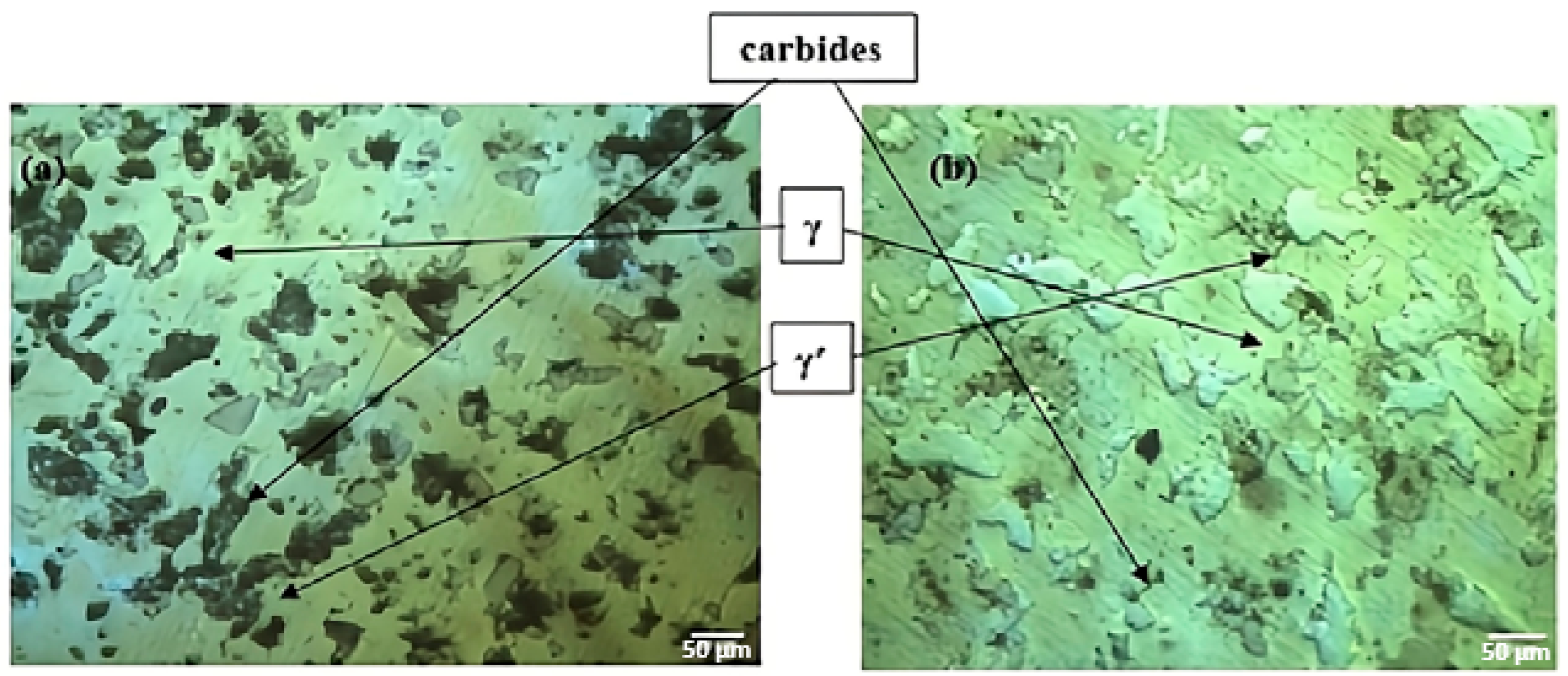
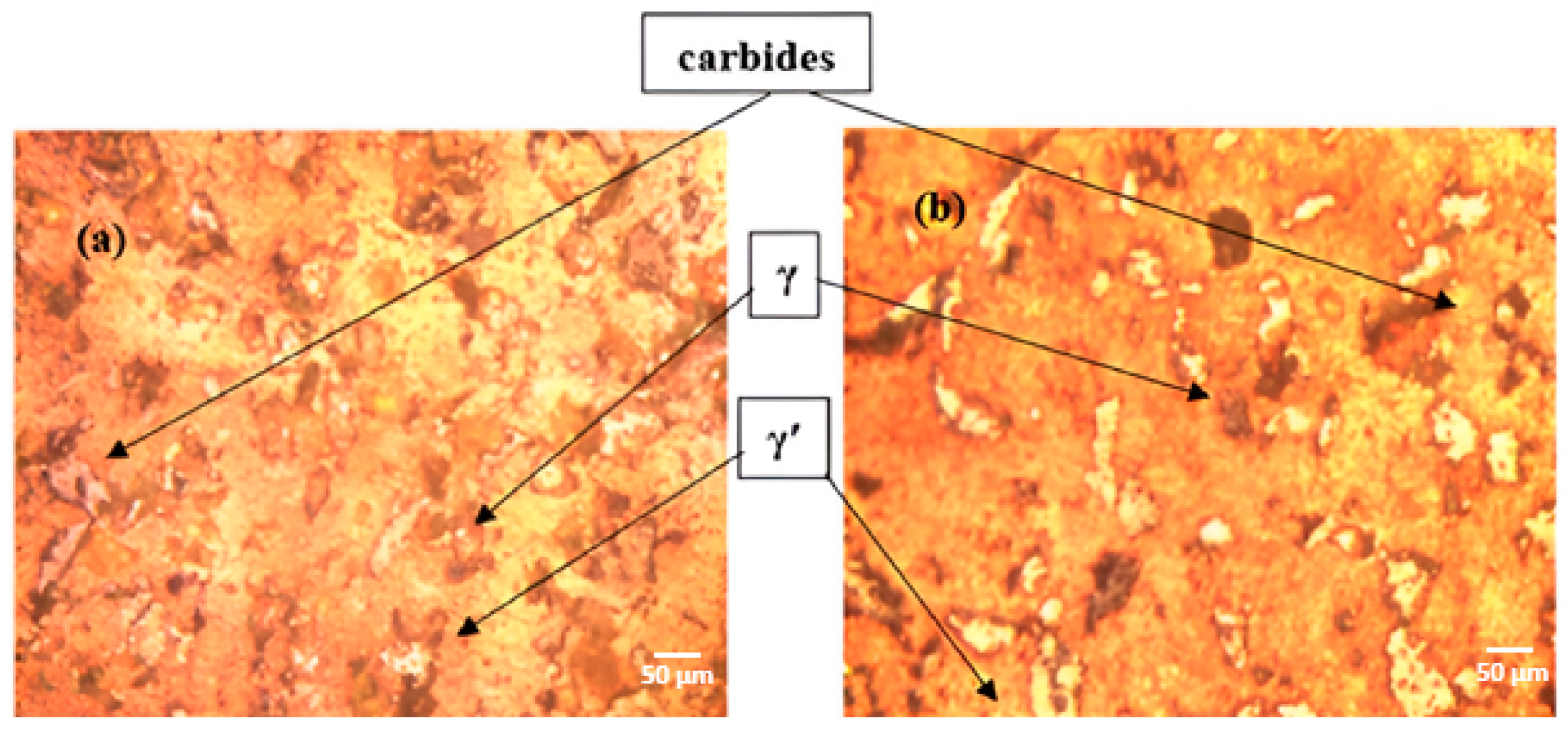
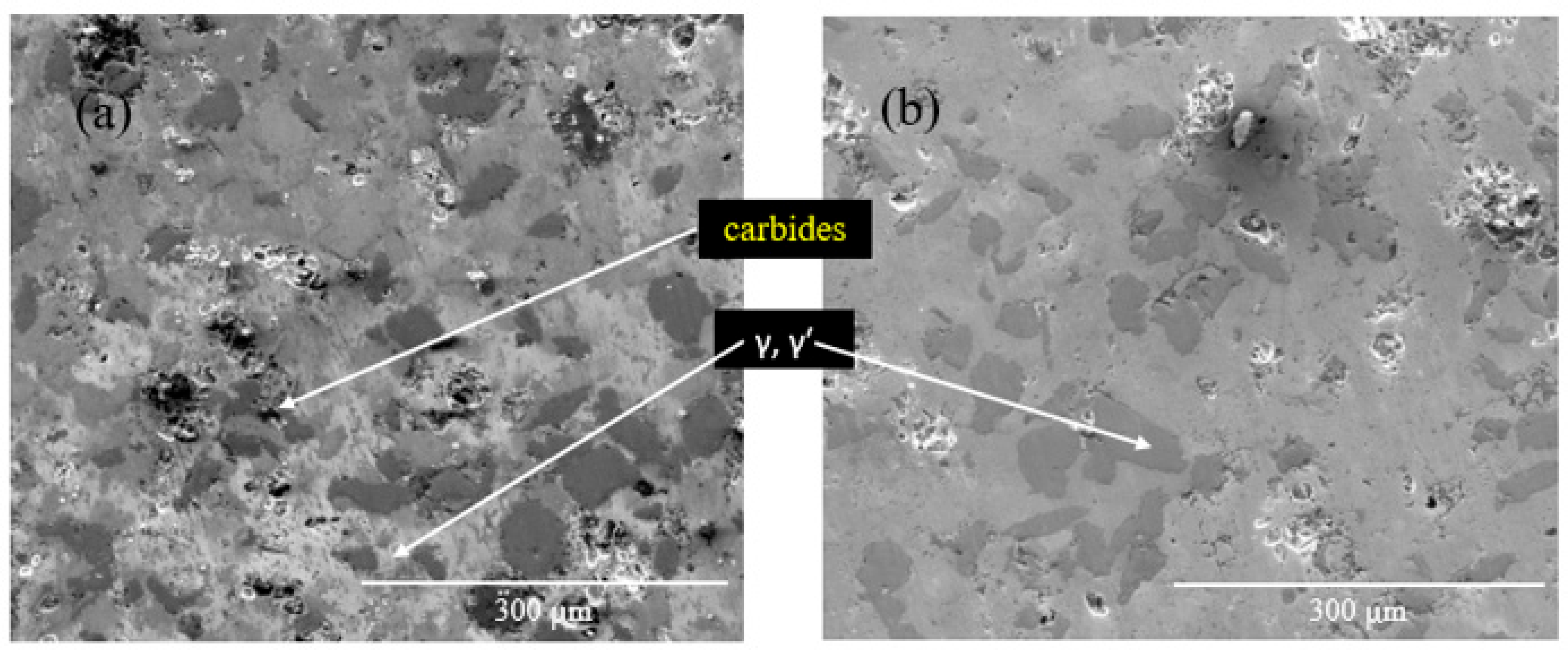
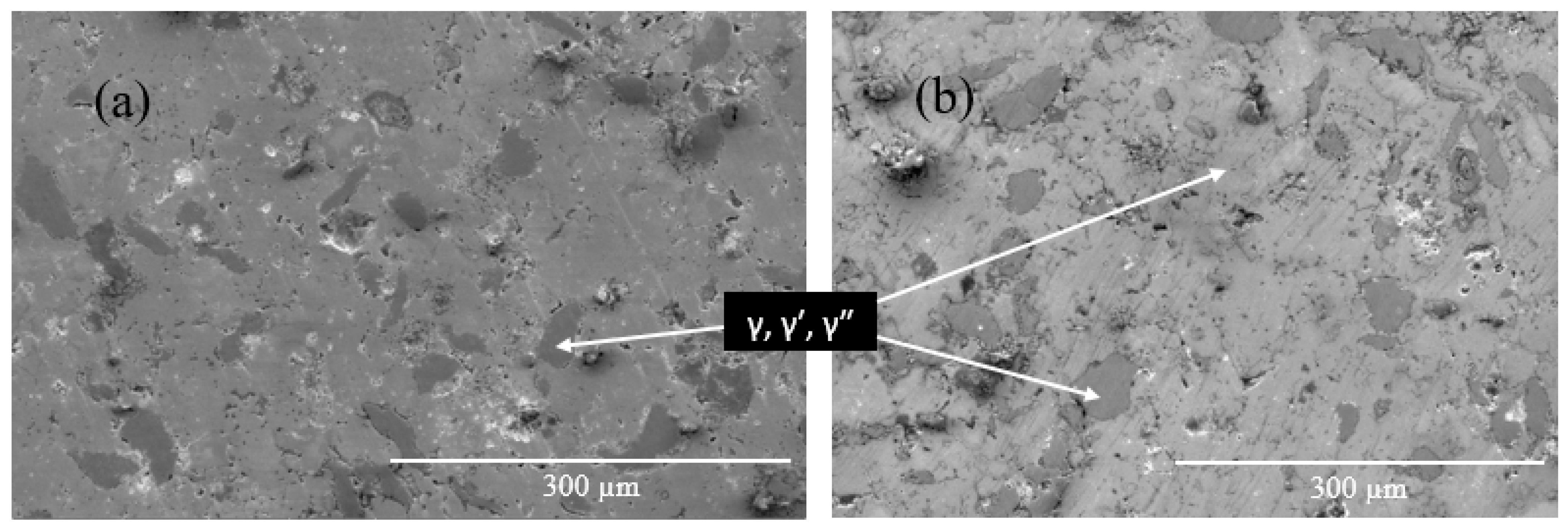
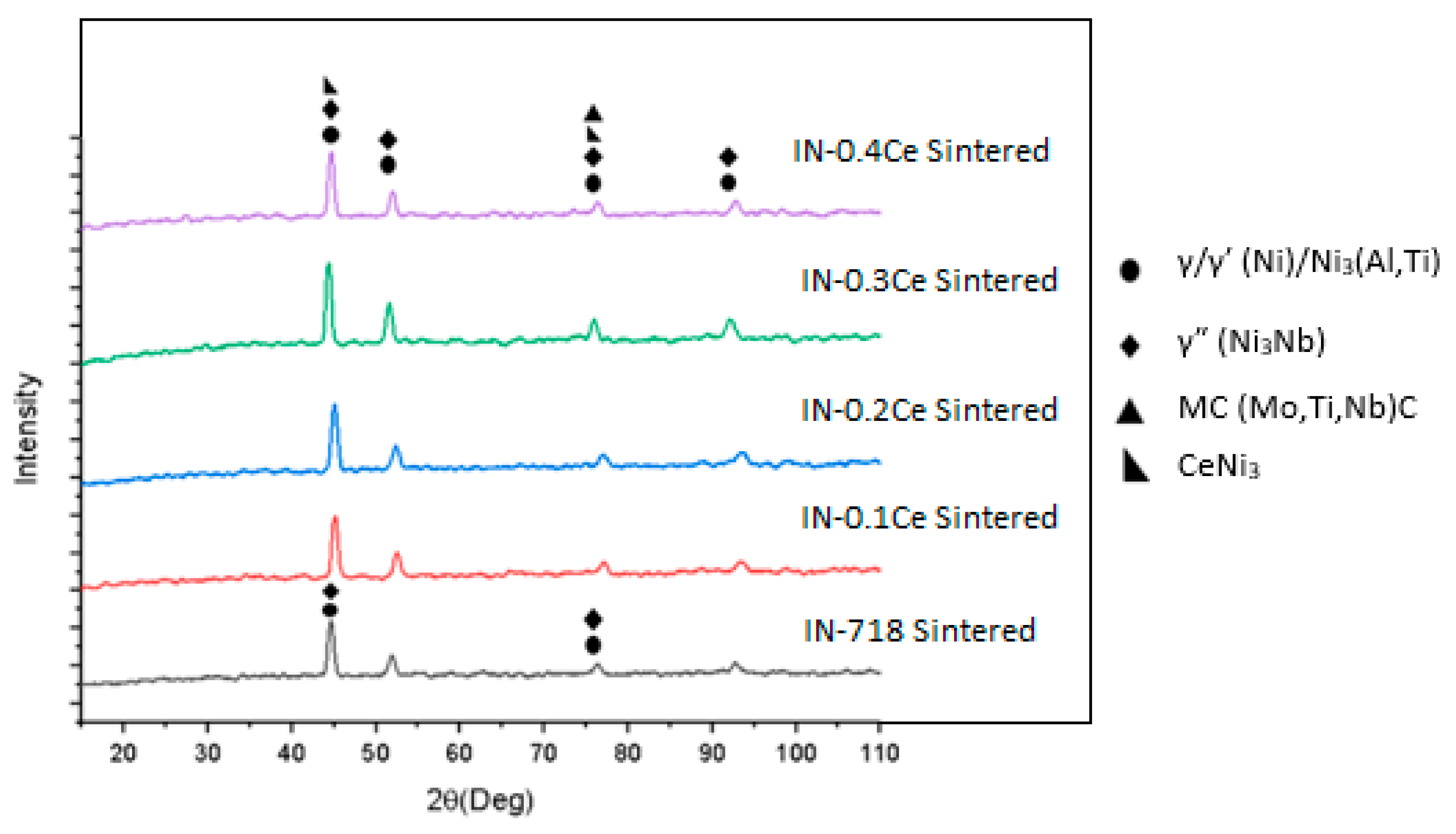
- The addition of Ce led to the formation of homogeneously distributed Ce-Ni intermetallic phases (Ni3Ce and Ce2Ni7) within the alloy matrix.
- The 0.2 wt.% Ce alloy demonstrated superior thermal stability, with a lower rate of mass gain observed at temperatures up to 1200 °C. This improvement was attributed to Ce promoting a more stable and protective surface oxide layer.
- Electrochemical analysis results conclusively showed the enhanced corrosion resistance of the optimized alloy. The IN-0.2Ce sample exhibited the lowest corrosion current density (Icorr = 3.690 × 10−6 A/cm2), which corresponded to the best performance in a 3.5% NaCl solution.
- These findings present a practical method for improving the durability of Inconel 718 in demanding industrial environments. It is recommended that future research focuses on evaluating the creep and fatigue resistance of the IN-0.2Ce alloy to fully validate its potential for high-performance applications.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Zhao, H. A review of the microstructure and properties of superalloys regulated by magnetic field. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 9285–9317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.A. Nickel based superalloys; properties and their applications. Int. J. Mgmt. Tech. Eng. 2018, 8, 268–277. [Google Scholar]
- Sohrabi, M.J.; Mirzadeh, H.; Rafiei, M. Solidification behavior and Laves phase dissolution during homogenization heat treatment of Inconel 718 superalloy. Vacuum 2018, 154, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.H.; Dong, J.X.; Zhang, M.C.; Xie, X.S. Alloy design and development of Inconel 718 type alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 499, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, A.V.; da Silveira, R.M.S.; de Almeida, L.H.; Araujo, L.S.; Farina, A.B.; Dille, J.A.F. Influence of yttrium addition on the microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of superalloy 718. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 776, 139023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Peng, R.L.; Moverare, J.; Avdovic, P.; Zhou, J.M.; Johansson, S. Surface integrity and structural stability of broached Inconel 718 at high temperatures. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 3664–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maj, P.; Cieslak, B.A.; Slesik, M.; Mizera, J.; Pieja, T.; Sieniawski, J.; Gancarczyk, T.; Dudek, S. The precipitation processes and mechanical properties of aged Inconel 718 alloy after annealing. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2017, 62, 1695–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strondl, A.; Fischer, R.; Frommeyer, G.; Schneider, A. Investigations of MX and γ′/γ′′ precipitates in the nickel-based superalloy 718 produced by electron beam melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 480, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Farris, L.; Nolze, G.; Reinsch, S.; Cios, G.; Tokarski, T.; Thompson, S. Microstructure evolution in Inconel 718 produced by powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2022, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayed, E.M.; Saadati, M.; Shahriari, D.; Brailovski, V.; Jahazi, M.; Medra, M. Effect of homogenization and solution treatments time on the elevated-temperature mechanical behavior of Inconel 718 fabricated by laser powder bed fusion. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medrano-Prieto, H.M.; Beltran, A.S.; Garay-Reyes, C.G.; Cabriales, G.R.; Ruiz-Esparza-Rodriguez, M.A.; Guel, I.E.; Castro-Carmona, J.S.; Montes, H.C.; Sánchez, R.M. Influence of rare earths additions on the microstructure and hardness of heat-treated nanostructured superalloy Inconel 718. Microsc. Microanal. 2022, 28, 2844–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Huang, S.; Qin, H.; Duan, R.; Wang, C.; Lian, X. Synergistic effects of boron and rare earth elements on the microstructure and stress rupture properties in a Ni-based superalloys. Materials 2024, 17, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Hou, S. Effects of rare earth elements on properties of Ni-base superalloy powders and coatings. Coatings 2017, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Yan, H.; Zhang, P.; Shi, H.; Li, Z.; Li, R. Influence of rare earth oxides on microstructure and mechanical properties of nickel-based superalloys fabricated by high energy beam processing: A review. J. Rare Eearths 2024, 42, 1629–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; He, S.M.; Zhou, X.T.; Zou, Y.; Li, Z.J.; Li, A.G.; Yu, X.H. Effects of rare earth yttrium on microstructure and properties of Ni–16Mo–7Cr–4Fe nickel-based superalloy. Mater. Charact. 2014, 95, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Liu, F.; Dong, H.; Ouyang, X.; Xiao, X.; Tan, L.; Huang, L. Investigation on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ni-based superalloy with scandium. Metals 2023, 13, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Hui-ping, M.A. Effects of temperature and rare earth content on oxidation resistance of Ni-based superalloy. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2011, 21, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.G.; Wang, N.; Liu, J.D.; Xu, W. Influence of rare earth elements (Y, La and Ce) on the mechanical properties and oxidation resistance of nickel-based superalloys: A critical review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 195, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrano-Prieto, H.M.; Santos-Beltrán, A.; Gallegos-Orozco, V.; Santos-Beltrán, M.M.; Camacho-Montes, H.; Garay-Reyes, C.G.; Ruiz-Esparza-Rodriguez, M.A.; Estrada-Guel, I.; Rodríguez-Cabriales, G.; Guía-Tello, J.C.; et al. Effect of rare earth elements addition and sintering conditions on the microstructure and microhardness of Inconel 718. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2024, 13, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez A., L.E.; Bedolla-Jacuinde, A.; Guerra, F.V.; Ruiz, A. Influence of rare earth additions to an Inconel 718 alloy. MRS Adv. 2020, 5, 3035–3043. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, C.; Han, G.; Sun, X. Effect of Ce addition on the microstructures and mechanical properties of a Ni-Co-based superalloy. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 415–417, 2062–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.; Wang, M.; Xing, W.; Hao, X.; Ma, Y. Effects of cerium addition on the microstructure and stress-rupture properties of a new nickel-based cast superalloy. J. Mater. Sci. Tchnol. 2023, 159, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, H.M.; Farooq, A.; Ammar, M.; Hakeem, A.S.; Ahmed, B.A.; Shahgaldi, S.; Ehsan, M.A.; Askar, K. Fabrication effect on SLM and cast Inconel 718 properties for energy conversion. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 38, 2453–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Yang, L.; Ling, G. Thermodynamic assessment of the Ce-Ni system. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 375, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, E.; Popovich, V.A. A review of mechanical properties of additively manufactured Inconel 718. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 30, 100877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Ma, Z.; Bai, Y.; Duan, H.; Tao, D.; Shi, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. Influence of cerium content on the microstructure and thermal expansion properties of suction cast Al-Cu-Fe alloys. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 210584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, F.; Shahriari, D.; Jahazi, M.; Cormier, J.; Devaux, A. Kinetics and mechanisms of γ′ reprecipitation in a Ni-based superalloy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migas, D.; Liptakova, T.; Moskal, G. Effect of rare earth cerium addition on oxidation behavior of Co-Al-W alloys at 800 °C. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2022, 67, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalcová, A.; Vojtech, D.; Schumacher, G.; Novák, P.; Plizingrová, E. Effect of iron and cerium additions on rapidly solidified Al-TM-Ce alloys. Mater. Technol. 2013, 47, 757–761. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.N.; Ojo, O.A. Corrosion behavior of wire arc additive manufactured Inconel 718 superalloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 829, 154455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudry, U.M.; Han, S.C.; Tayyab, K.; Farooq, A.; Kim, W.S.; Jun, T.S. Unraveling the anisotropic corrosion behavior along the building direction in laser powder bed fusion processed Hastelloy X. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Ji, G.; Kumar, S. An investigation on corrosion behavior of additively manufactured IN 718 in nitric acid. Can. Metall. Q. 2025, 2486648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhan, J.; Kolawole, S.K.; Tan, L.; Yang, K.; Wang, J.; Su, X. Effects of different rare earth elements on the degradation and mechanical properties of the ECAP extruded Mg alloys. Materials 2022, 15, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.Z.; Deng, C.P.; Su, Y.C. Comparative study on the electrochemical performance of the Cu-30Ni and Cu-20Zn-10Ni alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 491, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliu, S., Jr. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for the measurement of the corrosion rate of magnesium alloys: Brief review and challenges. Metals 2020, 10, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhu, A.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Y. Surface characterization and corrosion behavior of a novel gold-imitation copper alloy with high tarnish resistance in salt spray environment. Corros. Sci. 2013, 76, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Jaffery, S.H.; Khan, A.N.; Qadir, N.; Jing, X. Effect of cerium on mechanical, metallurgical and biomedical properties of NiCrMoB dental alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 5082–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Liang, H.; Li, Z.; Jin, H. Microstructure, wear and corrosion properties of Inconel 718-CeO2 composite coating. Coatings 2025, 15, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
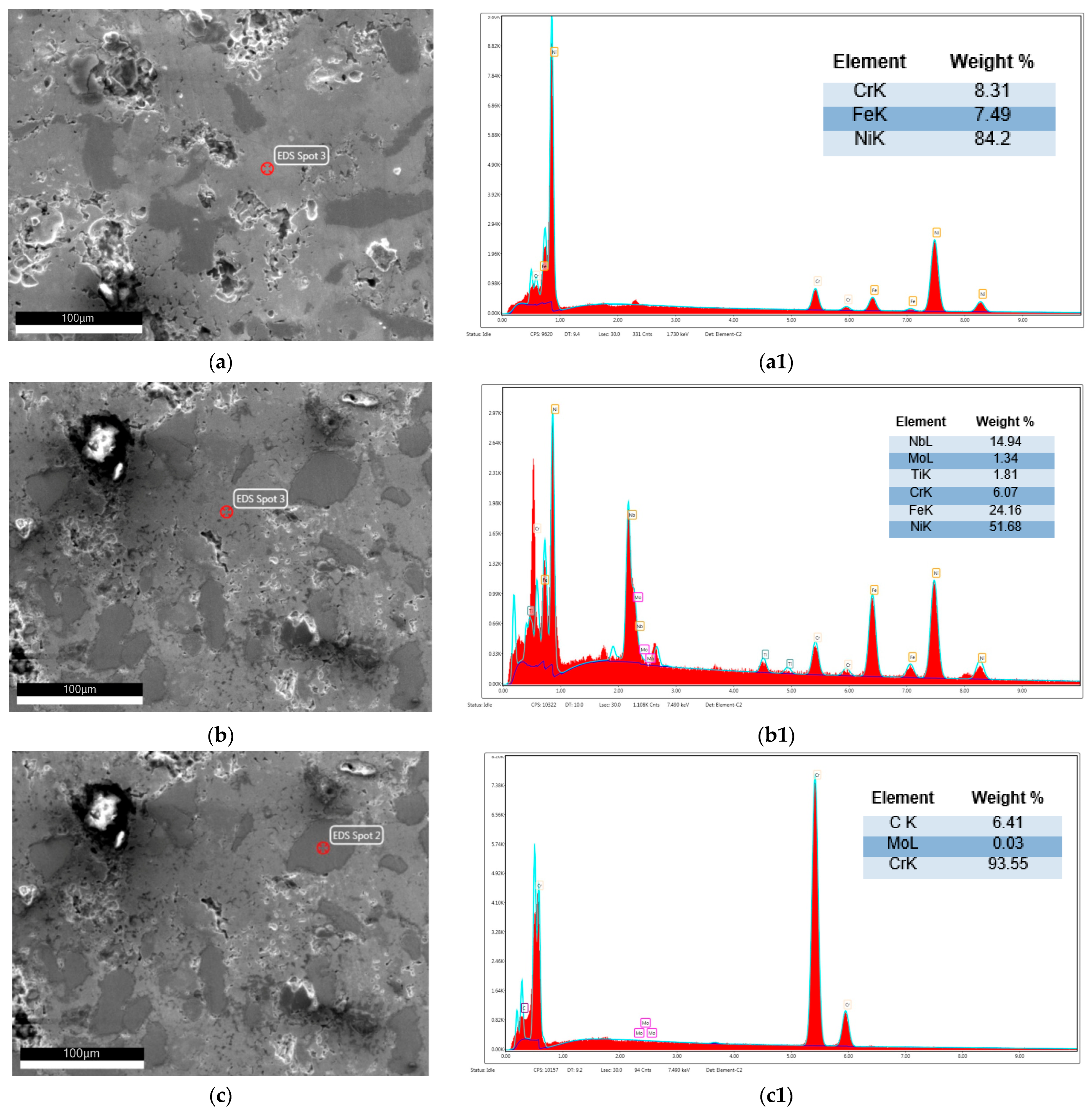
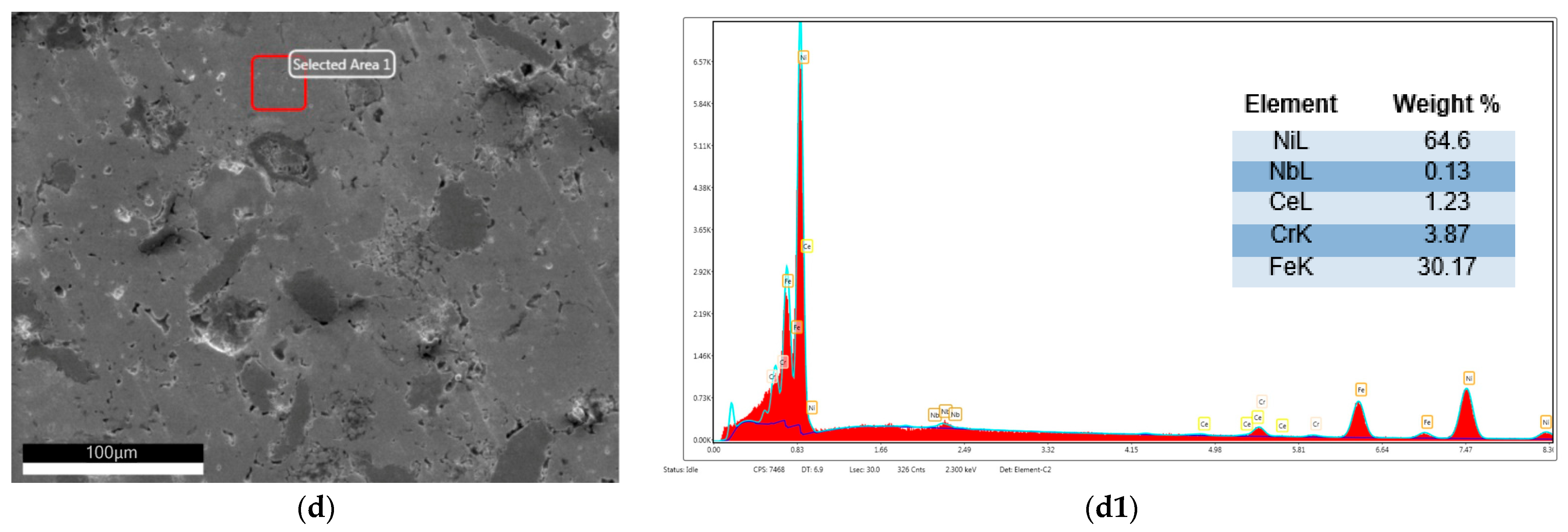

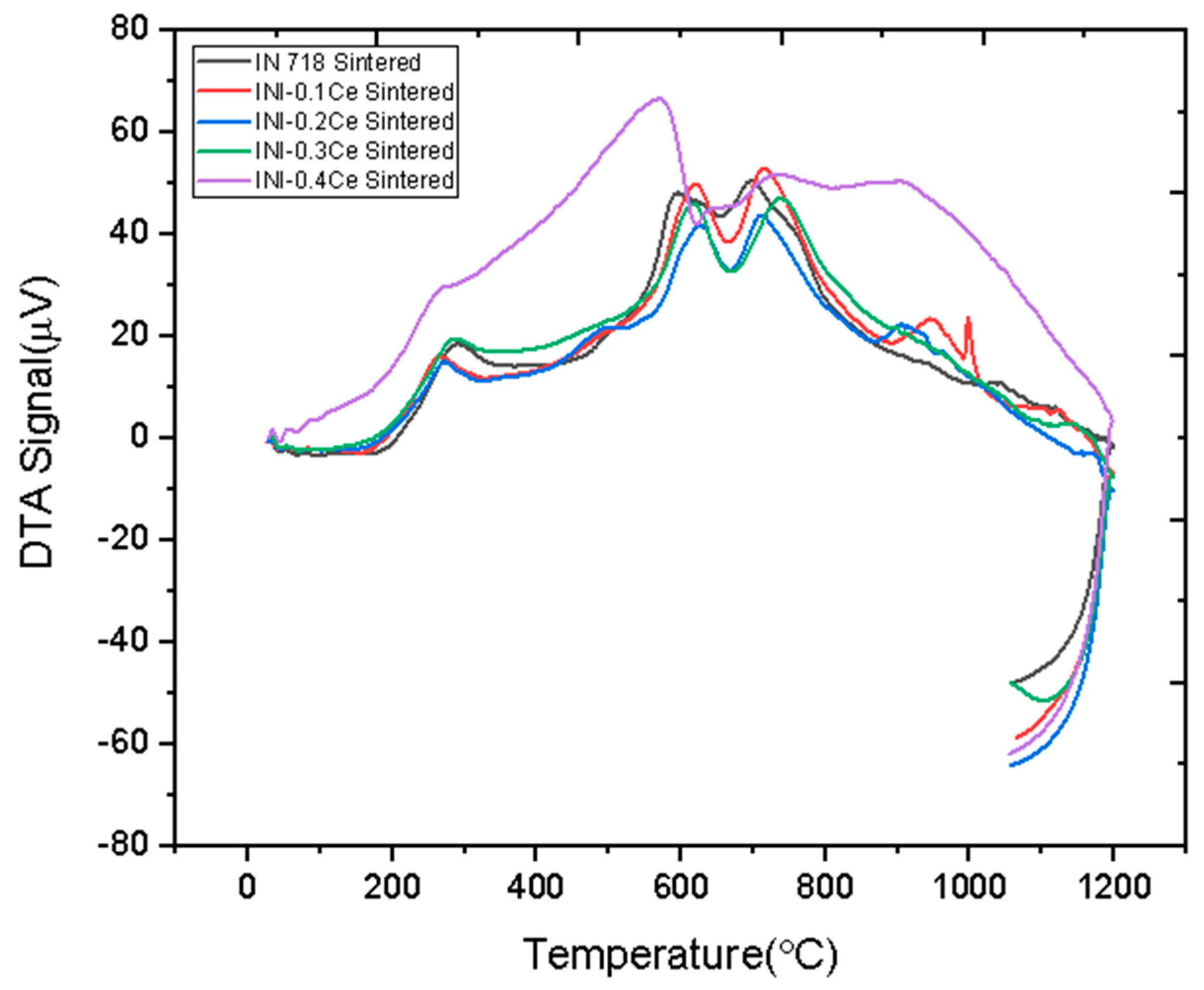

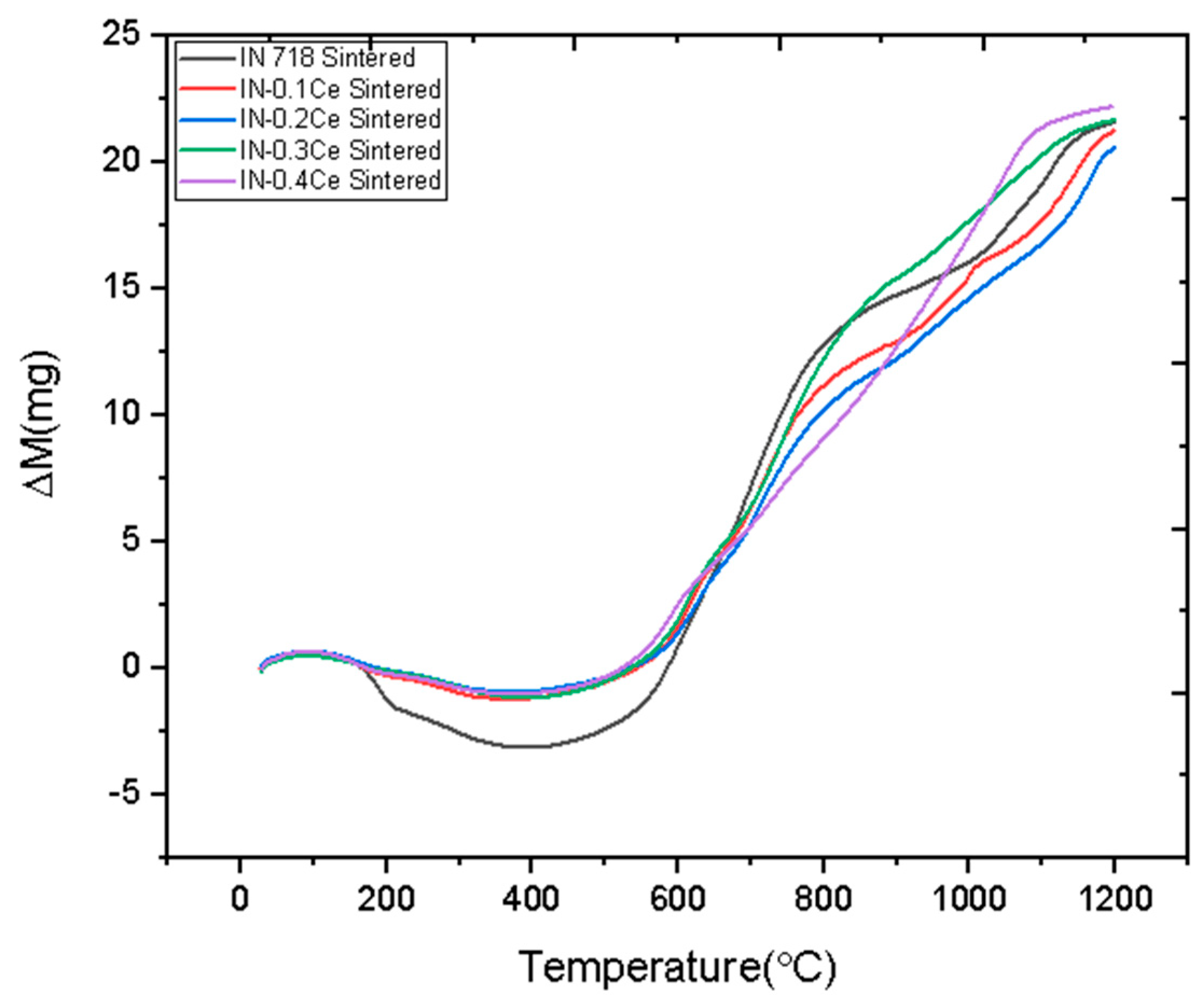
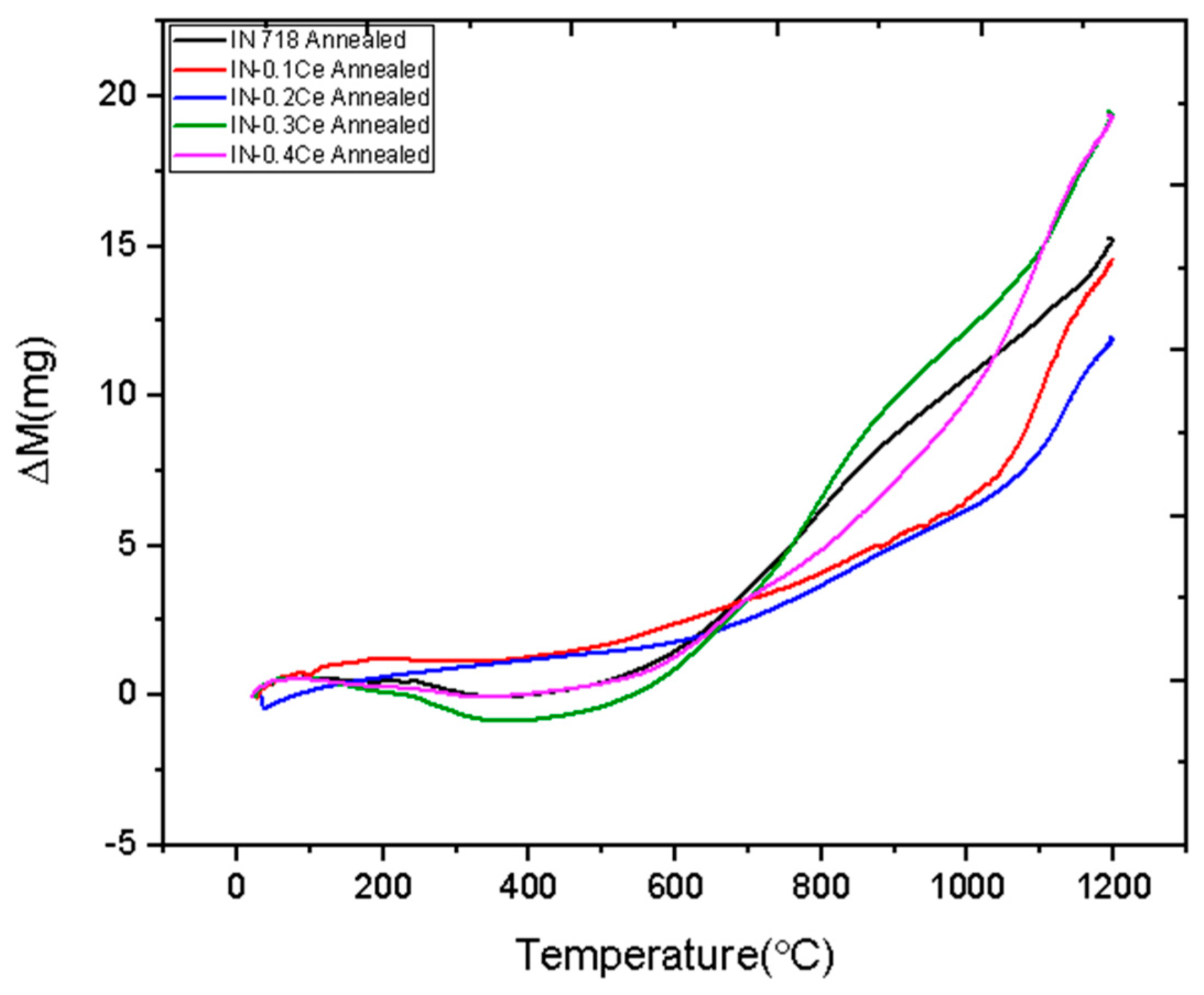

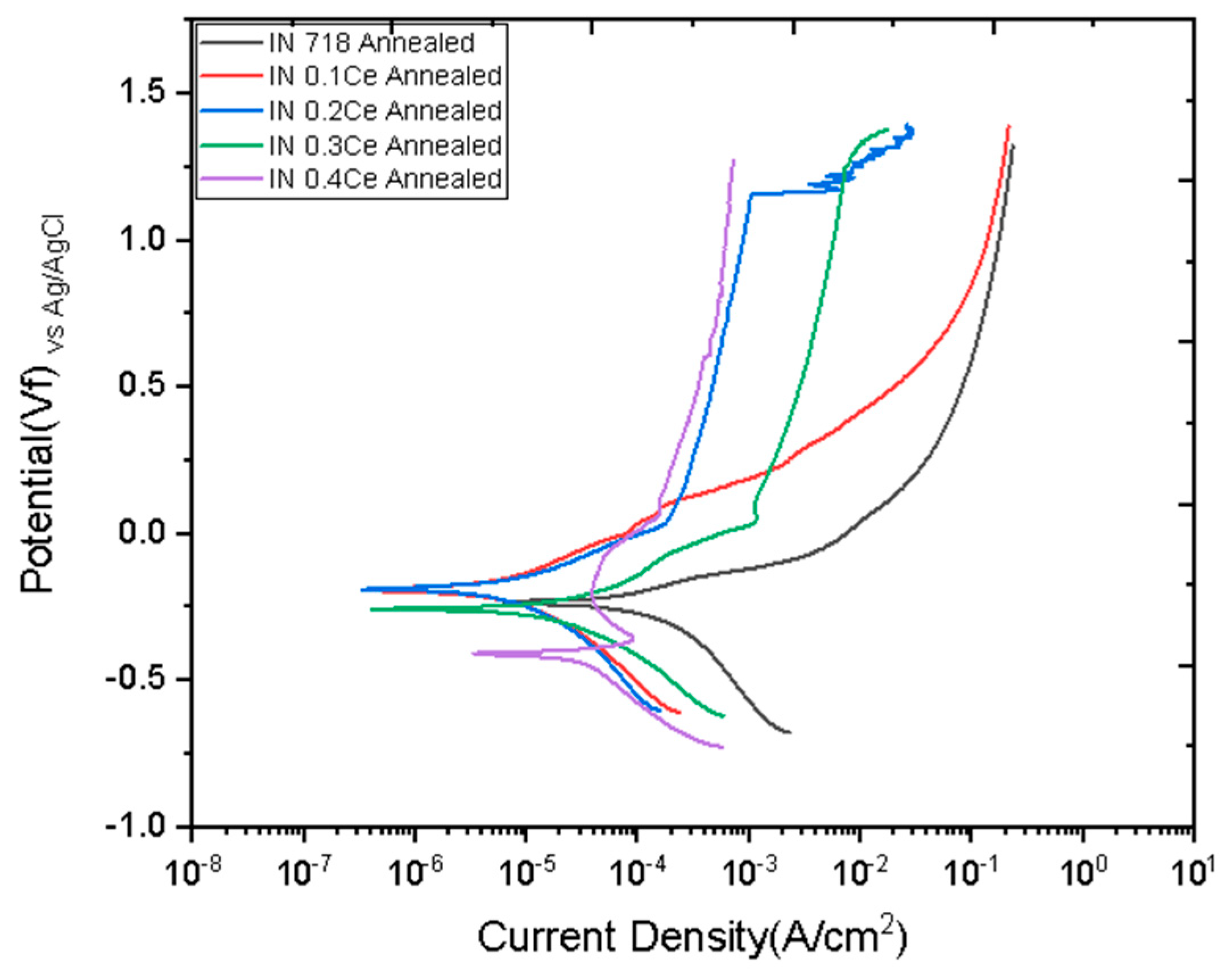

| Alloy | Elements | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Cr | Mo | Nb | Ti | Al | Cu | C | Ce | Fe | |
| IN 718 | 52.5 | 19 | 3 | 5.1 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.15 | 0.08 | - | 18.77 |
| IN-0.1Ce | 52.5 | 19 | 3 | 5.1 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.1 | 18.67 |
| IN-0.2Ce | 52.5 | 19 | 3 | 5.1 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.2 | 18.57 |
| IN-0.3Ce | 52.5 | 19 | 3 | 5.1 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.3 | 18.47 |
| IN-0.4Ce | 52.5 | 19 | 3 | 5.1 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.4 | 18.37 |
| Phases | 2θ |
|---|---|
| γ | 44.3, 51.3, 75.5, 92.0 |
| γ′ | 44.3, 51.3, 75.5, 92.0 |
| γ″ | 44.5, 51.5, 75.6, 92.1 |
| MC | 35.0, 75.2 |
| CeNi3 | 34.2, 36.2, 45.1 |
| Ce2Ni7 | 36.2 |
| Samples | Vf (mV) | Ecorr (mV) | Icorr (A/cm2) | Corrosion Rate (mpy) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IN 718 | −178.0 | −198.0 | 103 × 10−6 | 42.49 |
| IN-0.1Ce | 255.0 | 243.0 | 22.60 × 10−6 | 9.298 |
| IN-0.2Ce | −340.0 | −358.0 | 12.30 × 10−6 | 5.056 |
| IN-0.3Ce | −315.0 | −329.0 | 41.80 × 10−6 | 17.25 |
| IN-0.4Ce | −291.0 | −306.0 | 12.40 × 10−6 | 5.098 |
| Samples | Vf (mV) | Ecorr (mV) | Icorr (A/cm2) | Corrosion Rate (mpy) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IN 718 | −220.0 | −234.0 | 65 × 10−6 | 26.74 |
| IN-0.1Ce | −175.0 | −189.0 | 14.10 × 10−6 | 5.785 |
| IN-0.2Ce | −170.0 | −186.0 | 3.690 × 10−6 | 1.521 |
| IN-0.3Ce | −245.0 | −256.0 | 12.50 × 10−6 | 5.152 |
| IN-0.4Ce | −390.0 | −408.0 | 28.70 × 10−6 | 11.85 |
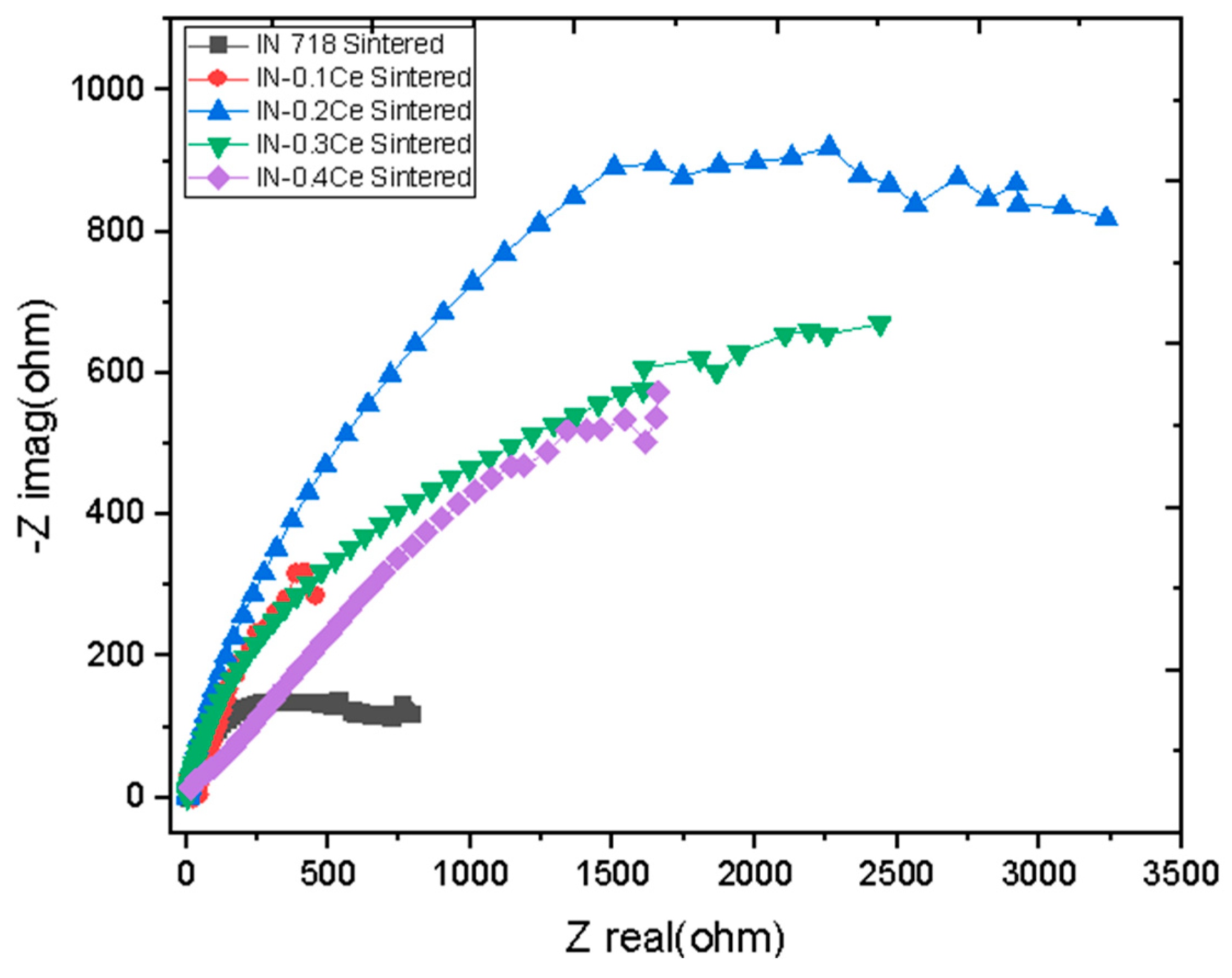
| Samples | Rs (Ω.cm2) | Rct (Ω.cm2) | Yo (µS.secn/cm2) | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IN 718 | 298.3 | 31.02 | 8.647 × 10−4 | 0.3446 |
| IN-0.1Ce | 23.11 | 626.4 | 4.594 × 10−5 | 0.7402 |
| IN-0.2Ce | 3.69 | 12,550 | 2.978 × 10−6 | 1 |
| IN-0.3Ce | 168.8 | 144.3 | 7.64 × 10−5 | 0.5988 |
| IN-0.4Ce | 7.386 | 822.5 | 1.294 × 10−5 | 0.7733 |
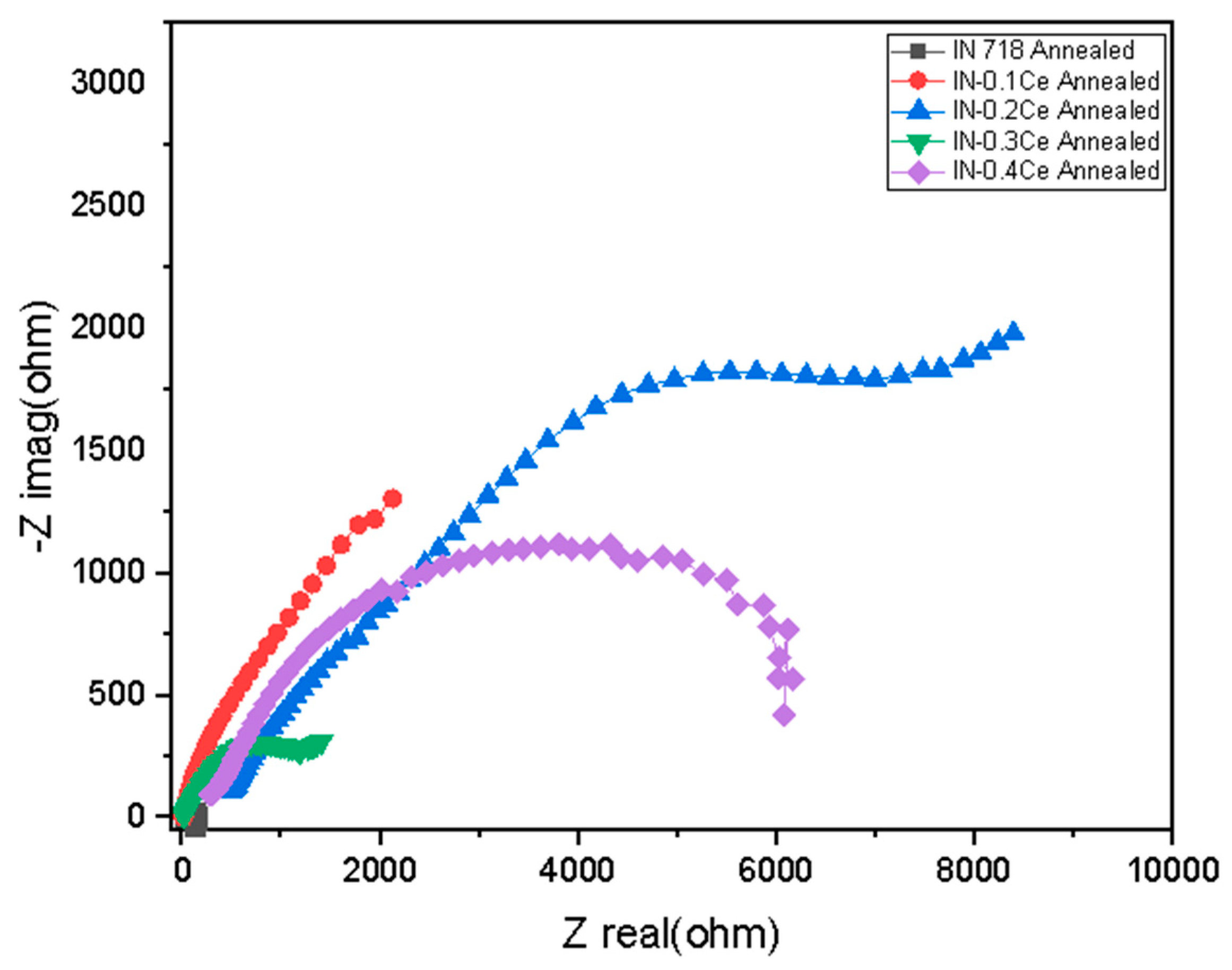
| Samples | Rs (Ω.cm2) | Rct (Ω.cm2) | Yo (µS.secn/cm2) | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IN 718 | 64.8 | 521.7 | 7.744 × 10−4 | 0.3508 |
| IN-0.1Ce | 6.343 | 543.8 | 3.149 × 10−4 | 0.6222 |
| IN-0.2Ce | 4.812 | 4795 | 8.27 × 10−5 | 0.8524 |
| IN-0.3Ce | 5.174 | 3751 | 1.136 × 10−4 | 0.7014 |
| IN-0.4Ce | 5.263 | 670.2 | 2.124 × 10−4 | 0.6976 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shakeel, M.; Ahmad, T.; Kamran, M.; Khan, M.A.; Brechtl, J. Effect of Rare-Earth Ce Addition on Thermal Stability and Corrosion Resistance of Inconel 718 Superalloy. Metals 2025, 15, 1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101090
Shakeel M, Ahmad T, Kamran M, Khan MA, Brechtl J. Effect of Rare-Earth Ce Addition on Thermal Stability and Corrosion Resistance of Inconel 718 Superalloy. Metals. 2025; 15(10):1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101090
Chicago/Turabian StyleShakeel, Muhammad, Tahir Ahmad, Muhammad Kamran, Muhammad Abubaker Khan, and Jamieson Brechtl. 2025. "Effect of Rare-Earth Ce Addition on Thermal Stability and Corrosion Resistance of Inconel 718 Superalloy" Metals 15, no. 10: 1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101090
APA StyleShakeel, M., Ahmad, T., Kamran, M., Khan, M. A., & Brechtl, J. (2025). Effect of Rare-Earth Ce Addition on Thermal Stability and Corrosion Resistance of Inconel 718 Superalloy. Metals, 15(10), 1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101090






