Effect of Austempering Temperature on Stress Corrosion Resistance of 52CrMoV4 Spring Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Observation of Microstructure
2.3. SCC Test
3. Results
3.1. Microstructure
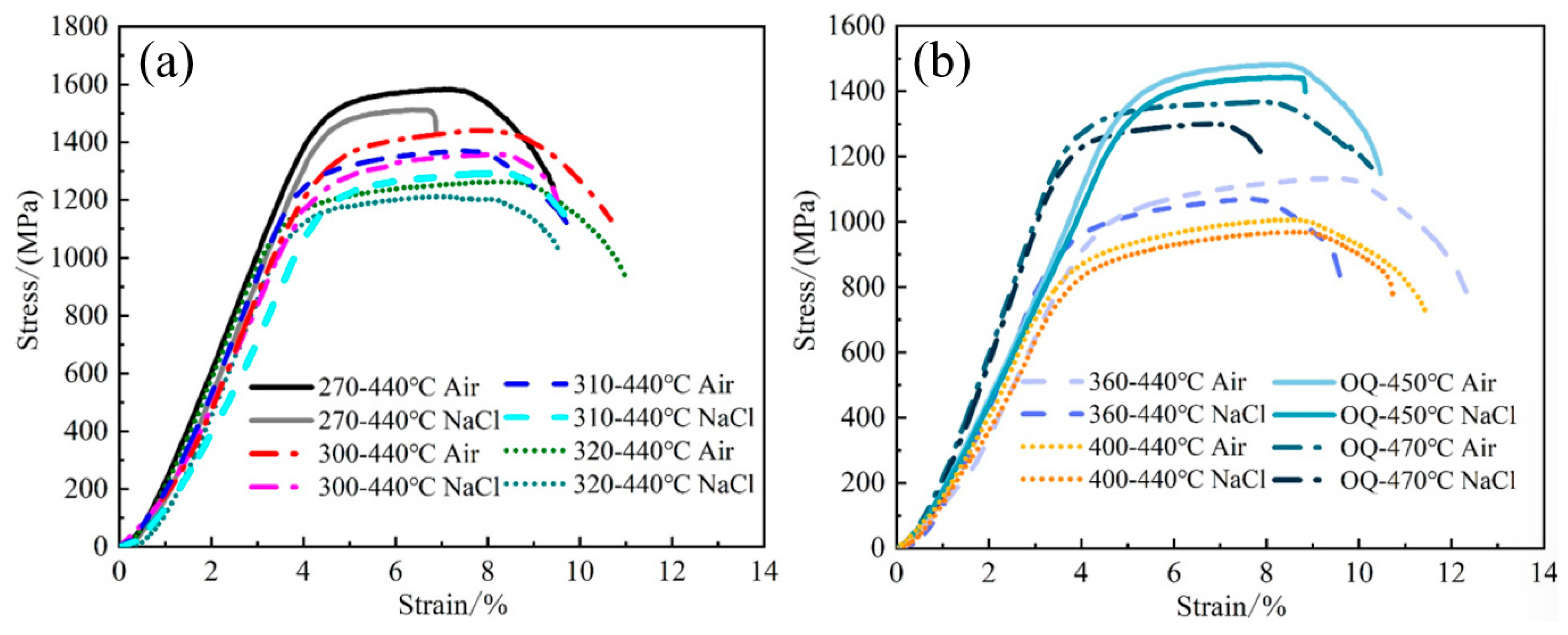
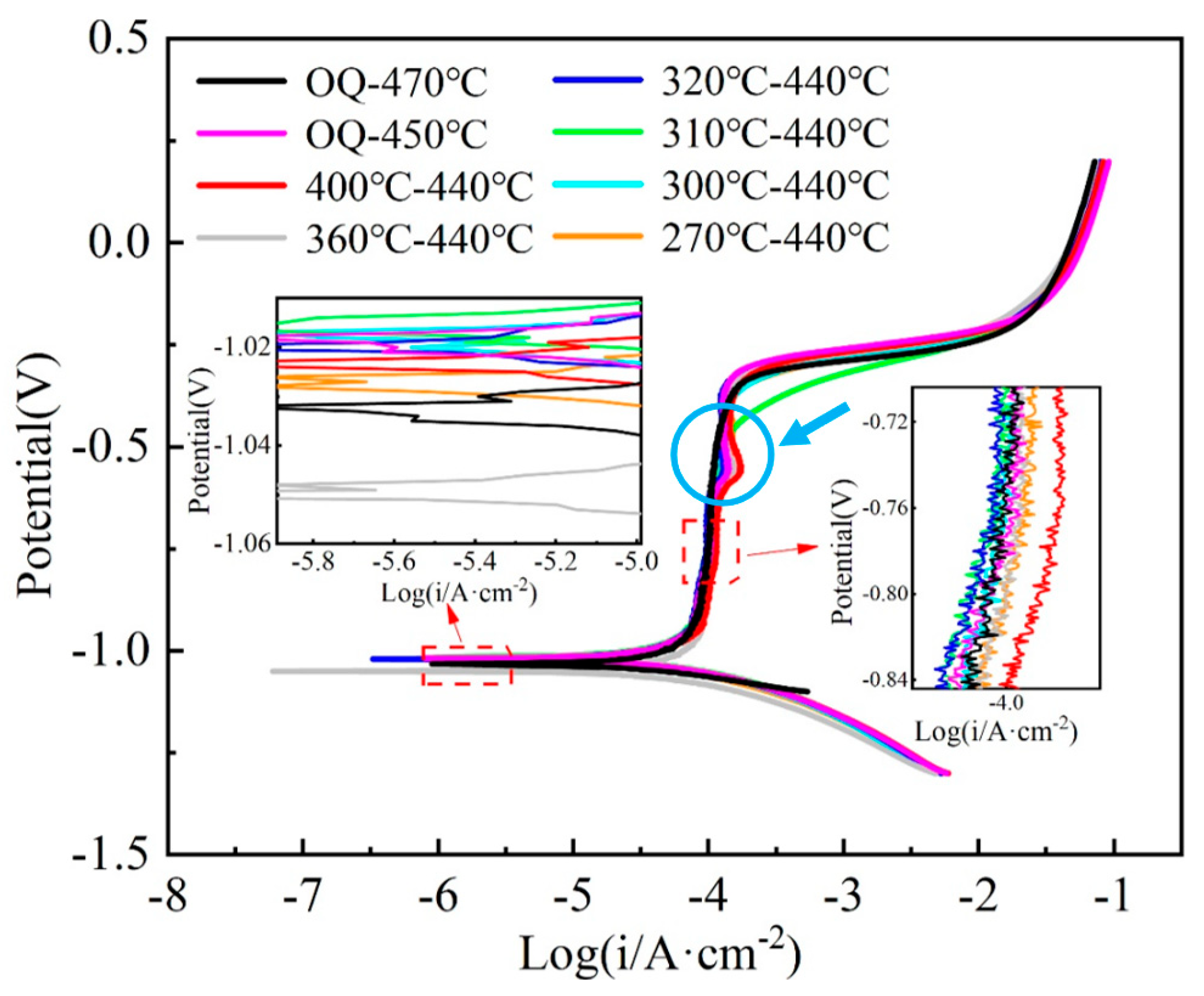
3.2. SCC Test Results
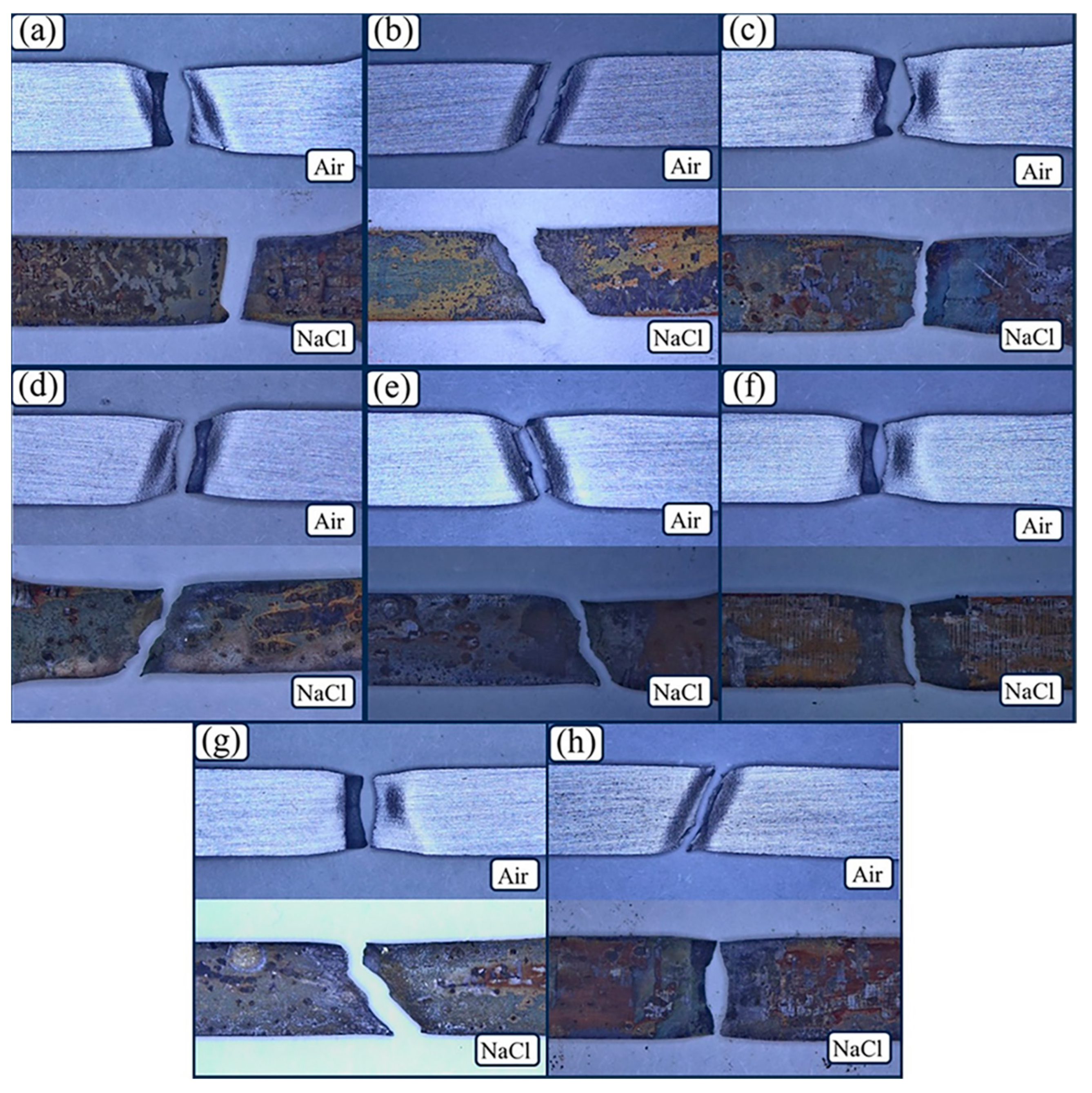
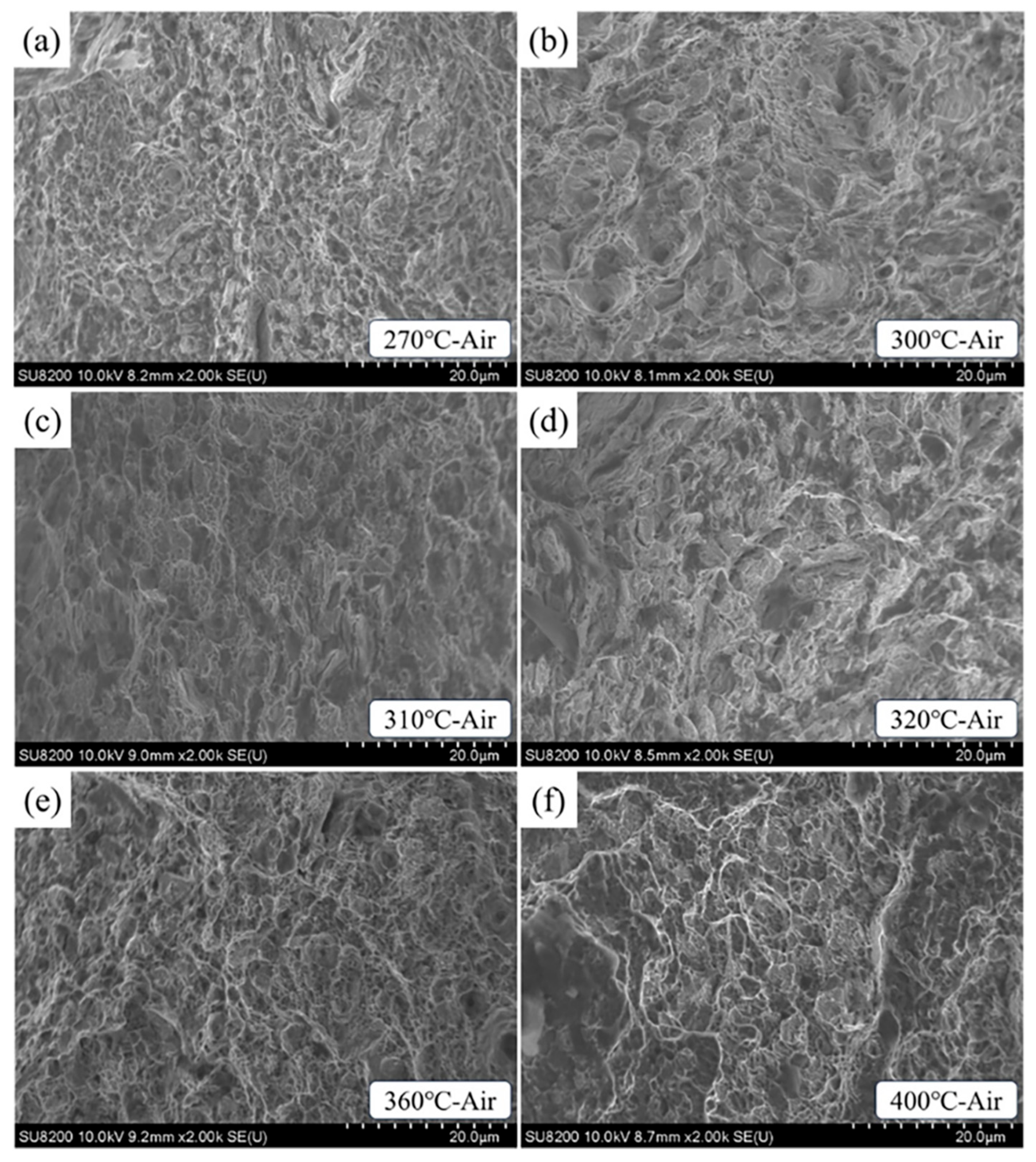
3.3. Fracture Morphology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The main type of cracking that occurs in the SCC process of the test steel is anodic dissolution-type stress cracking. Under the action of tensile stress, stress concentration plays a more important role in SCC initiation than corrosion.
- (2)
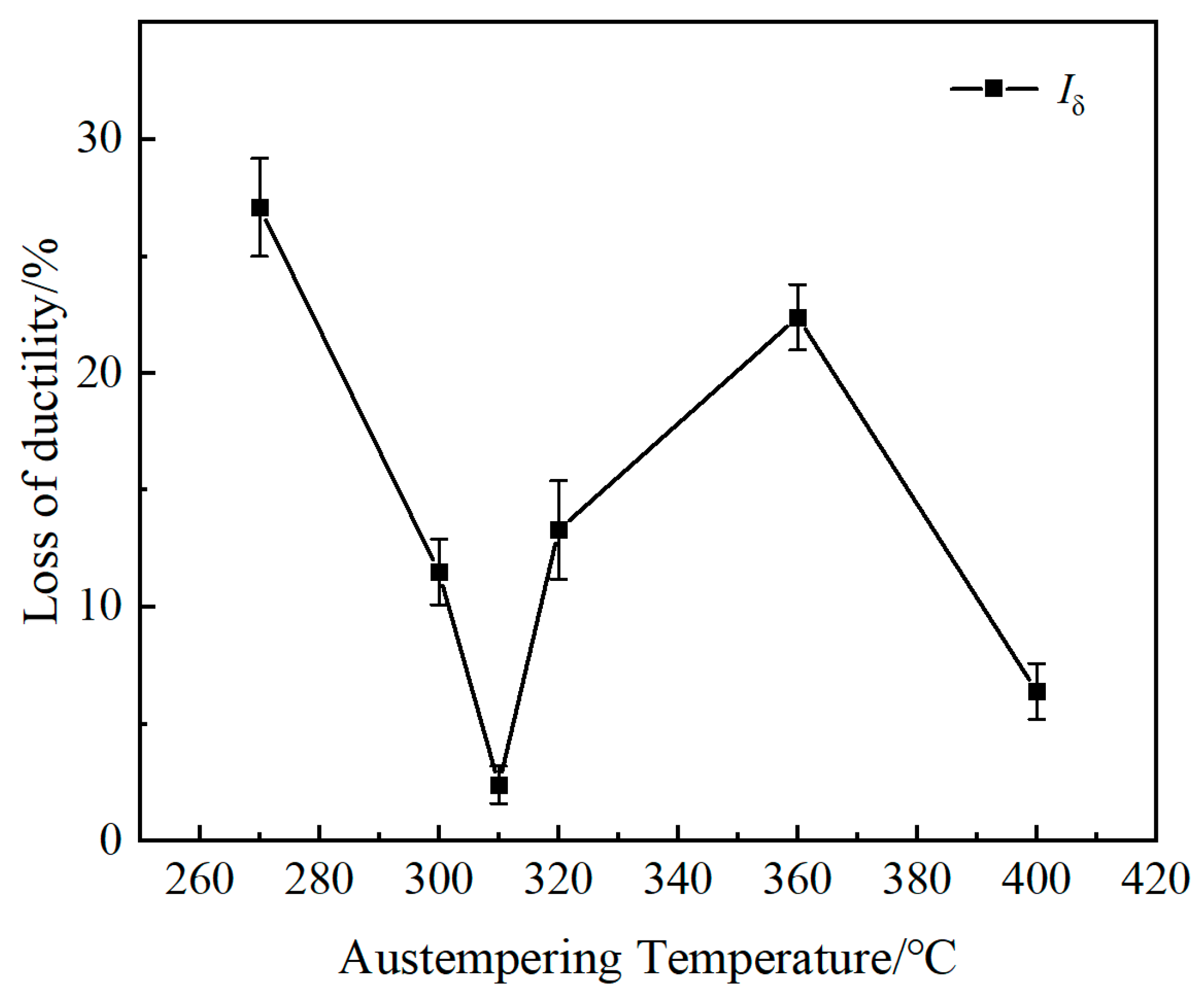
- With the rise in AT, the ability of test steel to resist stress corrosion first rises and then declines, rising again at 400 °C. The test steel austempered at 310 °C has the best stress corrosion resistance, while the test steel austempered at 270 °C has poor resistance due to fine and disordered bainitic laths with more active sites in the microstructure.
- (3)
- When the AT exceeds 310 °C, the coarsening of bainitic laths and the increase in M/A island area in the microstructure increase the possibility of stress concentration. Under the combined action of stress and corrosive media, the plasticity of the test steel decreases when subjected to tensile stress, resulting in reduced resistance to stress corrosion cracking.
- (4)
- The reduction in subgrain boundaries and redistribution of carbides enhance stress corrosion resistance when the steel is austempered at 400 °C. The test steel austempered at 300 °C has a better stress corrosion resistance than that of the test steel treated by the traditional process.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EN 10089: 2002; Hot Rolled Steels for Quenched and Tempered Springs—Technical Delivery Conditions. British Standards Institute: London, UK, 2002.
- Furuya, Y.; Abe, T. Effect of mean stress on fatigue properties of 1800 MPa-class spring steels. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chen, K.; Kang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Ding, S. Effects of V–Nb microalloying on the microstructure and properties of spring steel under different quenching-tempering times. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 779–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Chen, H.; Ramandi, H.L.; Hagan, P.C.; Crosky, A.; Saydam, S. Effects of environmental factors on stress corrosion cracking of cold-drawn high-carbon steel wires. Corros. Sci. 2018, 132, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komazaki, S.I.; Kobayashi, K.; Misawa, T.; Fukuzumi, T. Environmental embrittlement of automobile spring steels caused by wet–dry cyclic corrosion in sodium chloride solution. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 2450–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Yang, F.X.; Wang, N.; Zhu, M.L.; Xuan, F.Z. Improvement of stress corrosion cracking resistance by low cycle fatigue of a CrNiMoV steel. npj Mater. Degrad. 2023, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Huang, W.; Min, X.; Luo, G.; Wang, H.; Zhou, L.; Fang, F. Stress corrosion cracking mechanisms in bridge cable steels: Anodic dissolution or hydrogen embrittlement. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 97, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, P.K.; Ghosh, M.M.; Ghosh, K.S. Influence of aging treatments on alterations of microstructural features and stress corrosion cracking behavior of an Al-Zn-Mg alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 2792–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, H.; Chu, W.; Shu, D.; Wang, J.; Sun, B.D. Effects of silicon content on microstructure and stress corrosion cracking resistance of 7050 aluminum alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 2307–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Jiang, H.C.; Li, Z.M.; Yan, D.S.; Zhang, D.; Rong, L.J. Two-stage double peaks ageing and its effect on stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of Al-Zn-Mg alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, S.P.; Pohl, K.; Holroyd, N.J.H.; Birbilis, N.; Rometsch, P.A.; Muddle, B.C.; Goswami, R.; Lynch, S.P. Some effects of alloy composition on stress corrosion cracking in Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys. Corros. Sci. 2015, 98, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Sun, B.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, B.; Yang, W.; Deng, Y.; Li, X. Investigating the correlation of microstructure with stress corrosion cracking of the high-temperature heat treated 2205 duplex stainless steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 35, 6280–6295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Sun, B.; Chen, H.; Liu, Z.; Dai, W.; Yang, X.; Deng, Y.; Li, X. Stress corrosion cracking behavior and mechanism of 2205 duplex stainless steel under applied polarization potentials. Corros. Sci. 2024, 231, 111978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, E.; Zhang, L.; Fautrelle, Y.; Zhao, X.; Guo, X.; Zhang, D. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of 60Si2CrVNb spring steel under quenching-tempering heat treatment process. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 6829–6842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Zhang, P.; Wang, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z. Effects of quenching temperature on the microstructure and impact toughness of 50CrMnSiVNb spring steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2023, 870, 144856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiGiovanni, C.; Rampelberg, C.; Zhou, T.T.; Cathcart, C.; Amirkhiz, B.S.; Zurob, H.; Scott, C. Impact of boron and titanium on the mechanical properties and recrystallization behaviour of low carbon cold rolled and batch annealed HSLA steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2024, 918, 147424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, K.; Yang, Q.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wu, X.; Han, B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, D.; Feng, J.; et al. Research on the strengthening mechanism of Nb–Ti microalloyed ultra low carbon IF steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 5785–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, D. Effect of austenitizing temperature on isothermal quenching microstructure and mechanical properties of 52100 bearing steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2024, 892, 146051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Miao, L.J.; Yu, X.F.; Liu, T.M.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.L. Effect of isothermal quenching on microstructure and hardness of GCr15 steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 2820–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jiang, H.C.; Cui, Z.J.; Yan, D.S.; Song, Y.Y.; Rong, L.J. Synchronous improvement of mechanical properties and stress corrosion resistance by stress-aging coupled with natural aging pre-treatment in an Al-Zn-Mg alloy with high recrystallization fraction. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 121, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 15970.7-2017; Corrosion of Metals and Alloys—Stress Corrosion Testing—Part 7: Slow Strain Rate Testing. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- ASTM D1141-98; Standard Practice for the Preparation of Substitute Ocean Water. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1998.
- Sun, X.Y.; Zhang, B.; Lin, H.Q.; Zhou, Y.T.; Sun, L.; Wang, J.Q.; Han, E.H.; Ke, W. Correlations between stress corrosion cracking susceptibility and grain boundary microstructures for an Al–Zn–Mg alloy. Corros. Sci. 2013, 77, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.S.; Su, Y.J.; Li, J.X.; Qiao, L.J.; Chu, W.Y. Stress corrosion cracking of A537 steel in simulated marine environments. Corros. Sci. 2012, 65, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Pan, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, X.; Sun, H.; Xu, D.; Yang, Z. Effect of austempering on mechanical properties of Nb/V microalloyed bainitic bearing steel. Crystals 2022, 12, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Tan, J.; Guo, X.; Han, Z. Stress corrosion cracking of a high strength steel in organic salt drilling fluids. Mater. Test. 2020, 62, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A. Geometry of dimples and its correlation with mechanical properties in high-strength bainitic steel. Philos. Mag. 2024, 104, 421–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L. Probing intergranular mixed transgranular stress corrosion cracking under the high constant load. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truschner, M.; Janda, A.; Bodner, S.C.; Keplinger, A.; Mori, G. Effect of cold deformation on the stress corrosion cracking resistance of a high-strength stainless steel. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 20447–20461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Shao, Y.; Guo, L.; Huang, H. Surface topography and stress concentration analysis for corroded high strength steel plate. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2021, 187, 106952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajizad, O.; Kumar, A.; Li, Z.; Petrov, R.H.; Sietsma, J.; Dollevoet, R. Influence of microstructure on mechanical properties of bainitic steels in railway applications. Metals 2019, 9, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lv, Z.; Lu, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, X. Correlation of micro-galvanic corrosion behavior with corrosion rate in the initial corrosion process of dual phase steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 3310–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, Q.; Fan, Y.; Feng, X. Bainite transformation behavior, microstructural feature and mechanical properties of nanostructured bainitic steel subjected to ausforming with different strain. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 9206–9218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhao, M. Influence of residual stress on stress concentration factor for high strength steel welded joints. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2012, 72, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, A. A study of blocky retained austenite and properties under variously heat-treated ultra-fine bainitic steel. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 105607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Sun, H.Q.; Wang, Y.H.; Harvey, C.M.; Zhao, L.J.; Zeng, H.T.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, Y.G.; Chen, Q.A. Effect of austempering temperatures on microstructure and mechanical properties of 52CrMoV4 spring steel. Mater. Des. 2025, 253, 113898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
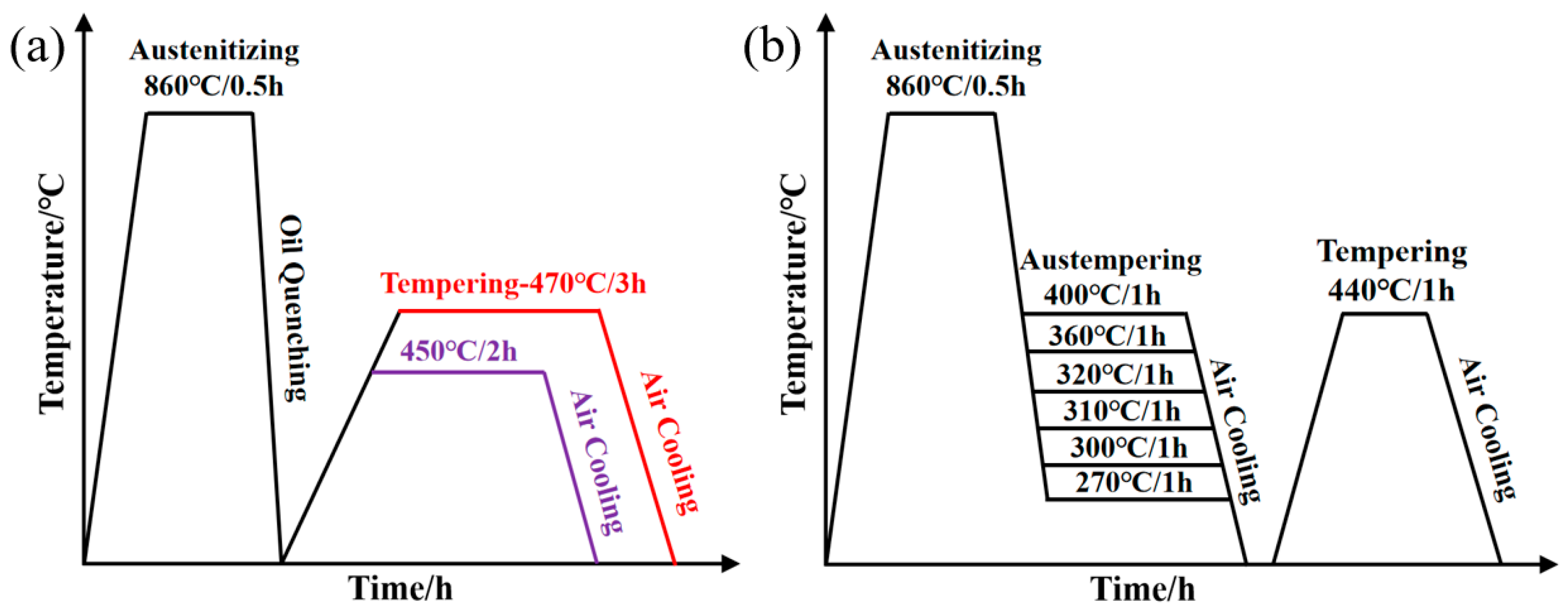
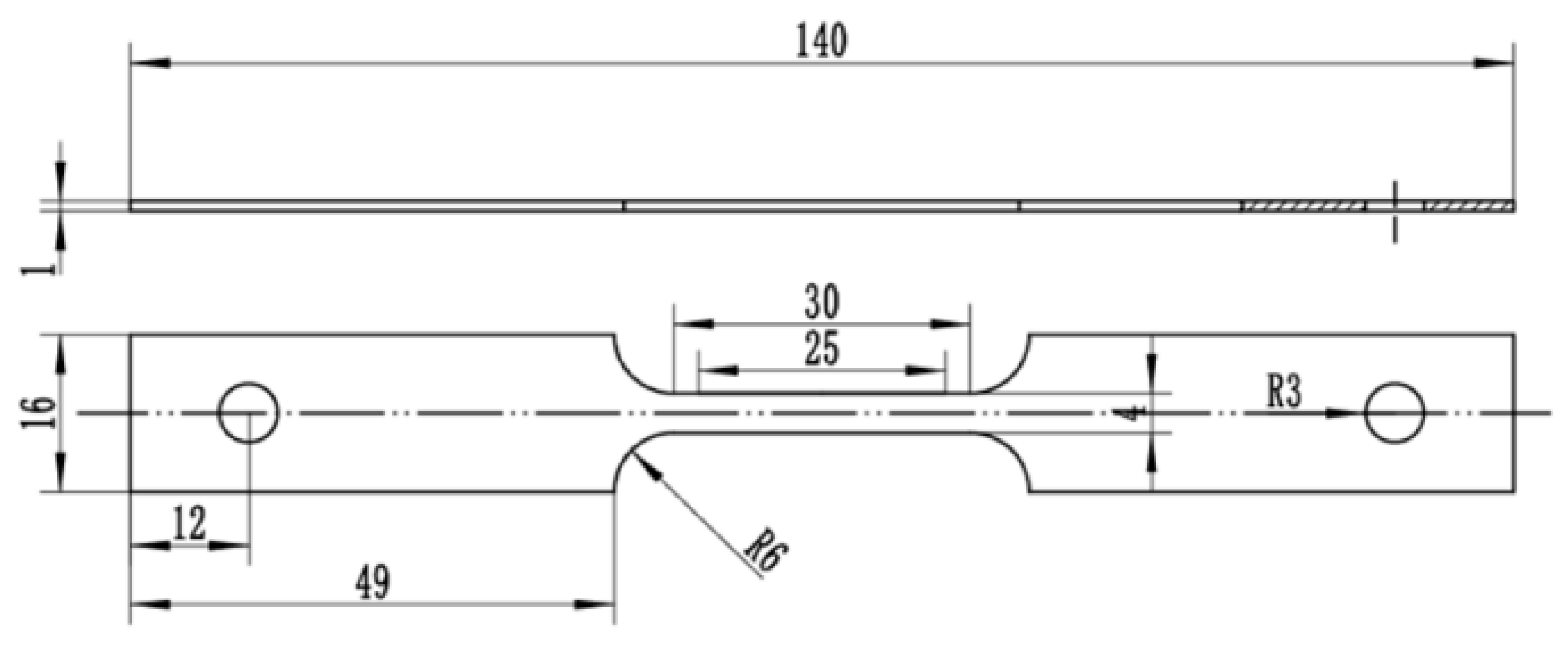




| Element | C | Mn | Si | Cr | Mo | P | S | V | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 0.49 | 0.80 | 0.35 | 1.12 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.15 | balance |
| Temperature/°C | 270 | 300 | 310 | 320 | 360 | 400 | OQ-450 | OQ-470 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium | |||||||||
| Air | 9.42 ± 0.18 | 10.67 ± 0.20 | 9.91 ± 0.16 | 11.0 ± 0.22 | 12.30 ± 0.12 | 11.46 ± 0.18 | 10.48 ± 0.24 | 10.35 ± 0.18 | |
| NaCl | 6.87 ± 0.20 | 9.44 ± 0.15 | 9.67 ± 0.08 | 9.54 ± 0.23 | 9.55 ± 0.17 | 10.73 ± 0.14 | 8.89 ± 0.32 | 7.90 ± 0.24 | |
| Temperature/°C | 270 | 300 | 310 | 320 | 360 | 400 | OQ-450 | OQ-470 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iδ/% | 27.1 ± 2.1 | 11.5 ± 1.4 | 2.4 ± 0.8 | 13.3 ± 2.1 | 22.4 ± 1.4 | 6.4 ± 1.2 | 15.5 ± 3.1 | 23.7 ± 2.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Song, J.; Sun, W.; Zhao, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q. Effect of Austempering Temperature on Stress Corrosion Resistance of 52CrMoV4 Spring Steel. Metals 2025, 15, 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101081
Yang Q, Song J, Sun W, Zhao J, Sun H, Wang G, Wang Y, Li Q. Effect of Austempering Temperature on Stress Corrosion Resistance of 52CrMoV4 Spring Steel. Metals. 2025; 15(10):1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101081
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Qian, Jinhao Song, Wanshuo Sun, Jing Zhao, Huaqiang Sun, Ge Wang, Yanhui Wang, and Qiang Li. 2025. "Effect of Austempering Temperature on Stress Corrosion Resistance of 52CrMoV4 Spring Steel" Metals 15, no. 10: 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101081
APA StyleYang, Q., Song, J., Sun, W., Zhao, J., Sun, H., Wang, G., Wang, Y., & Li, Q. (2025). Effect of Austempering Temperature on Stress Corrosion Resistance of 52CrMoV4 Spring Steel. Metals, 15(10), 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101081







