Effect of a Gradient Temperature Rolling Process on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Center of Ultra-Heavy Plates
Abstract
1. Introduction
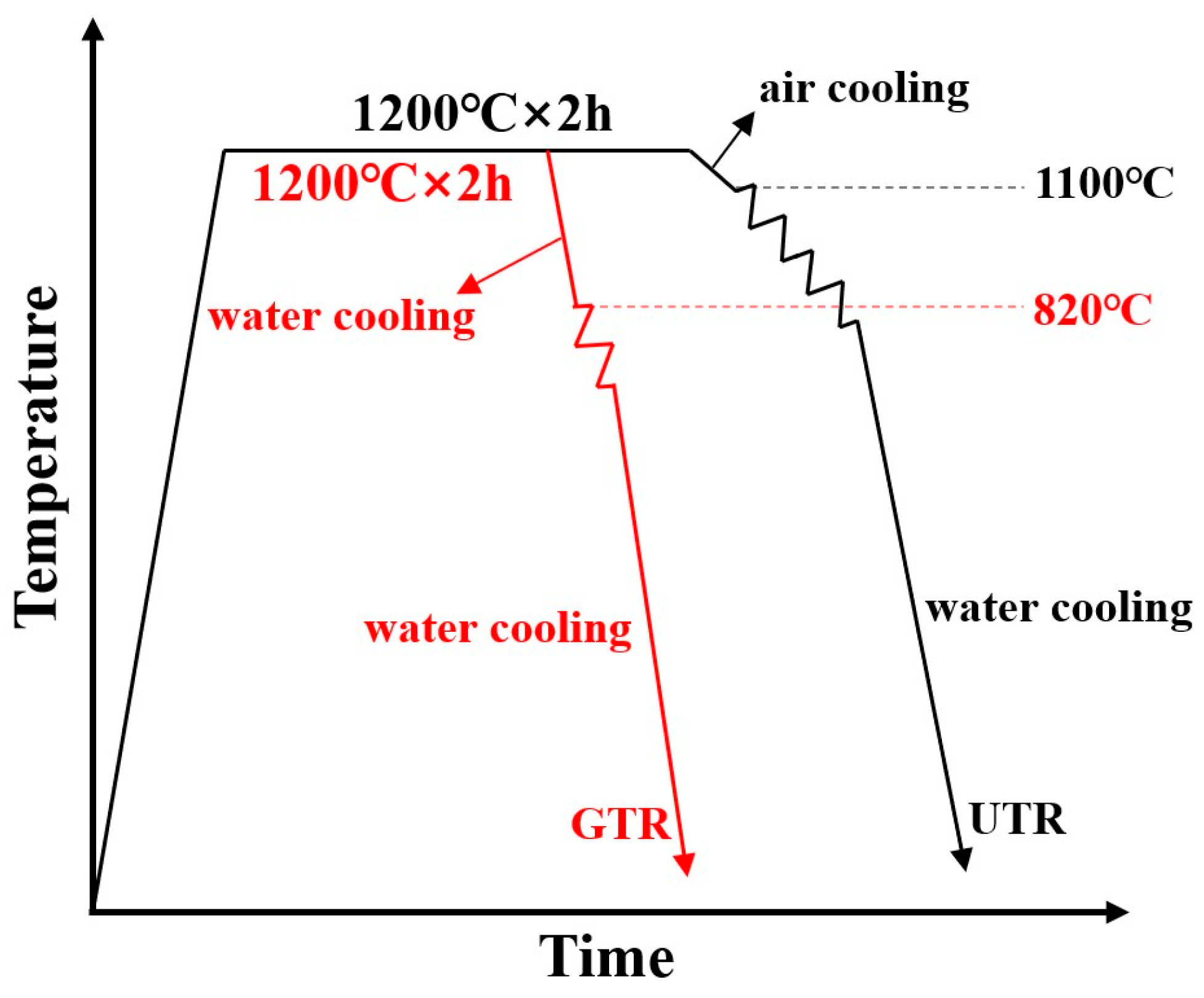
2. Materials and Methods
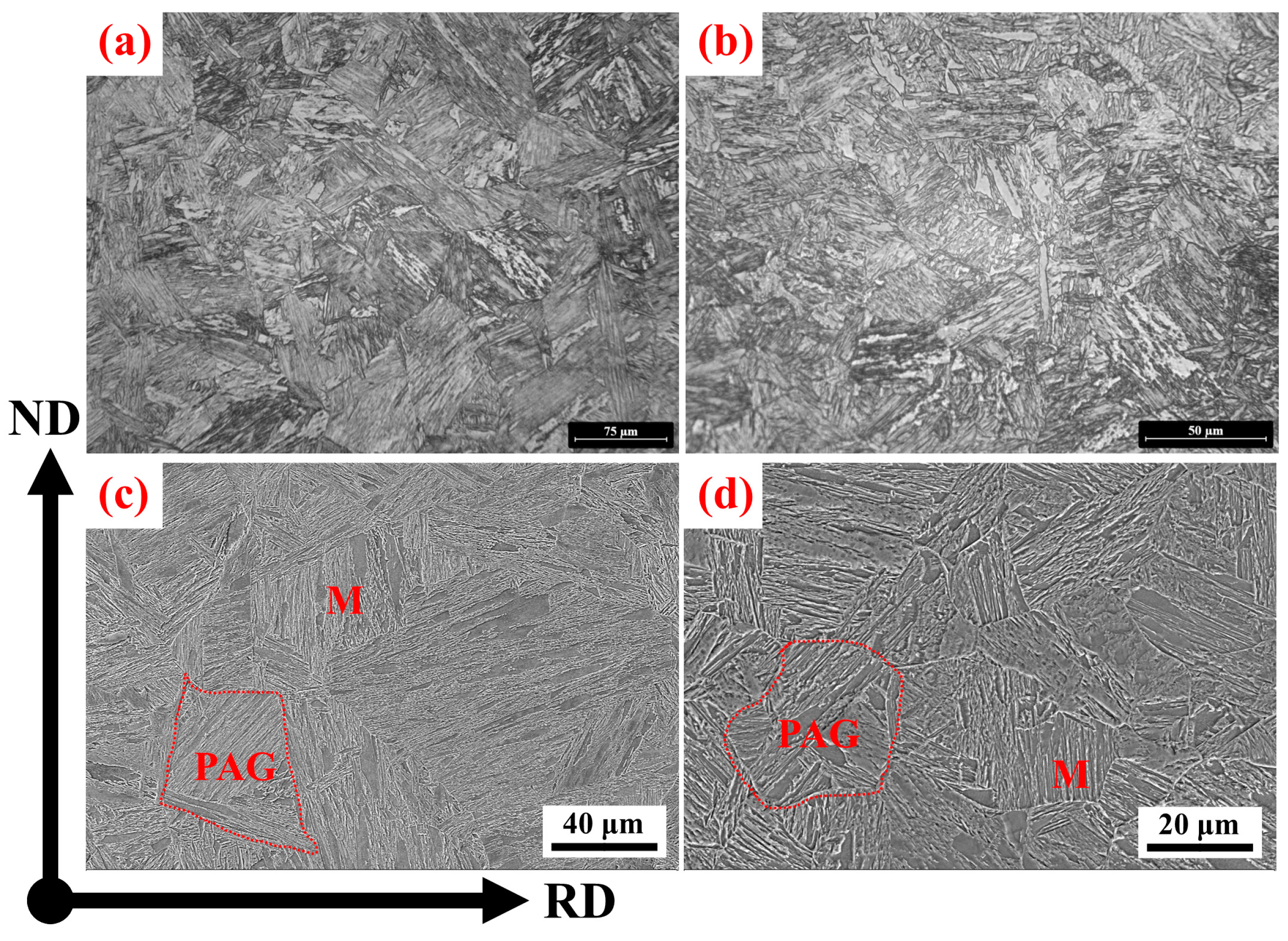
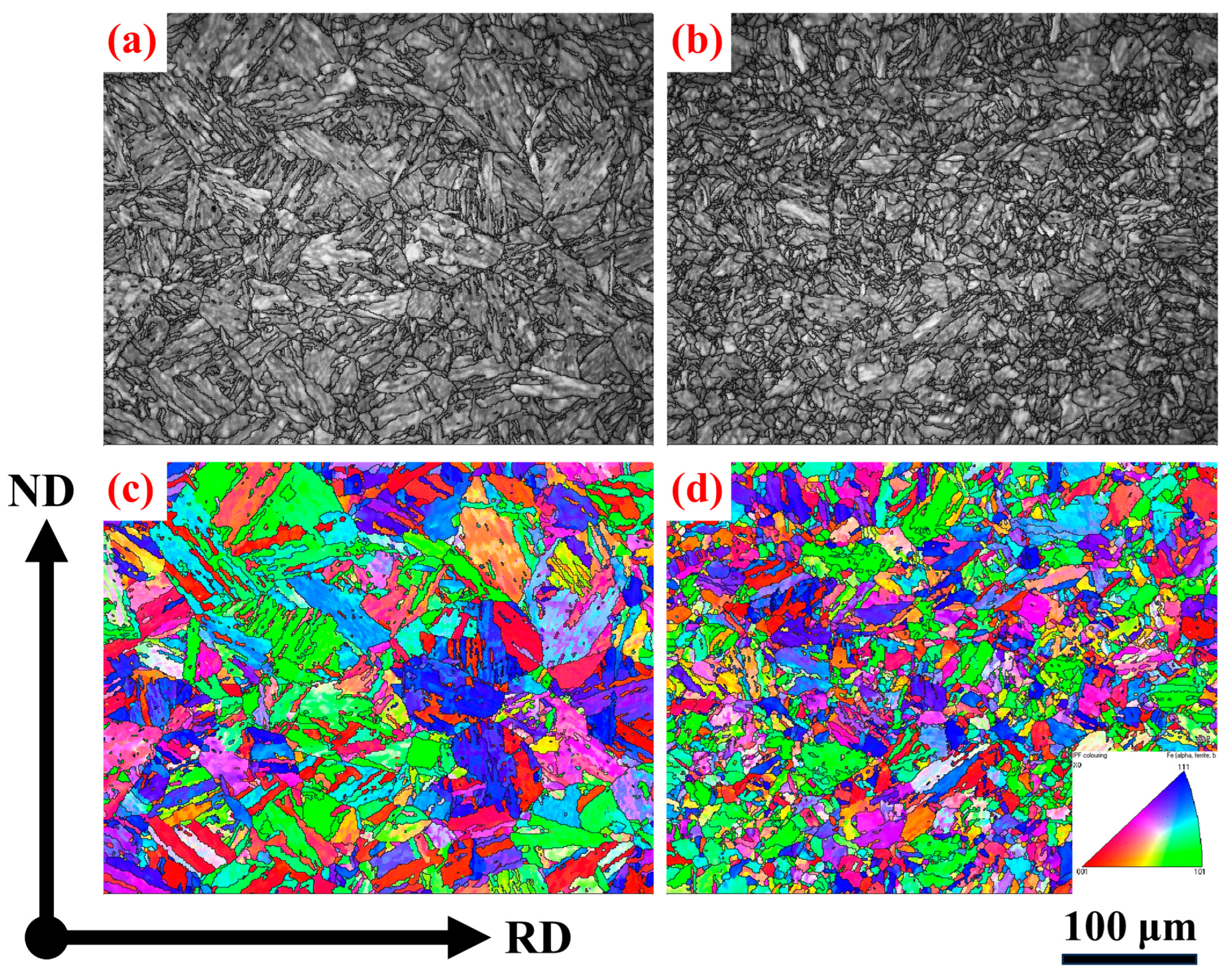
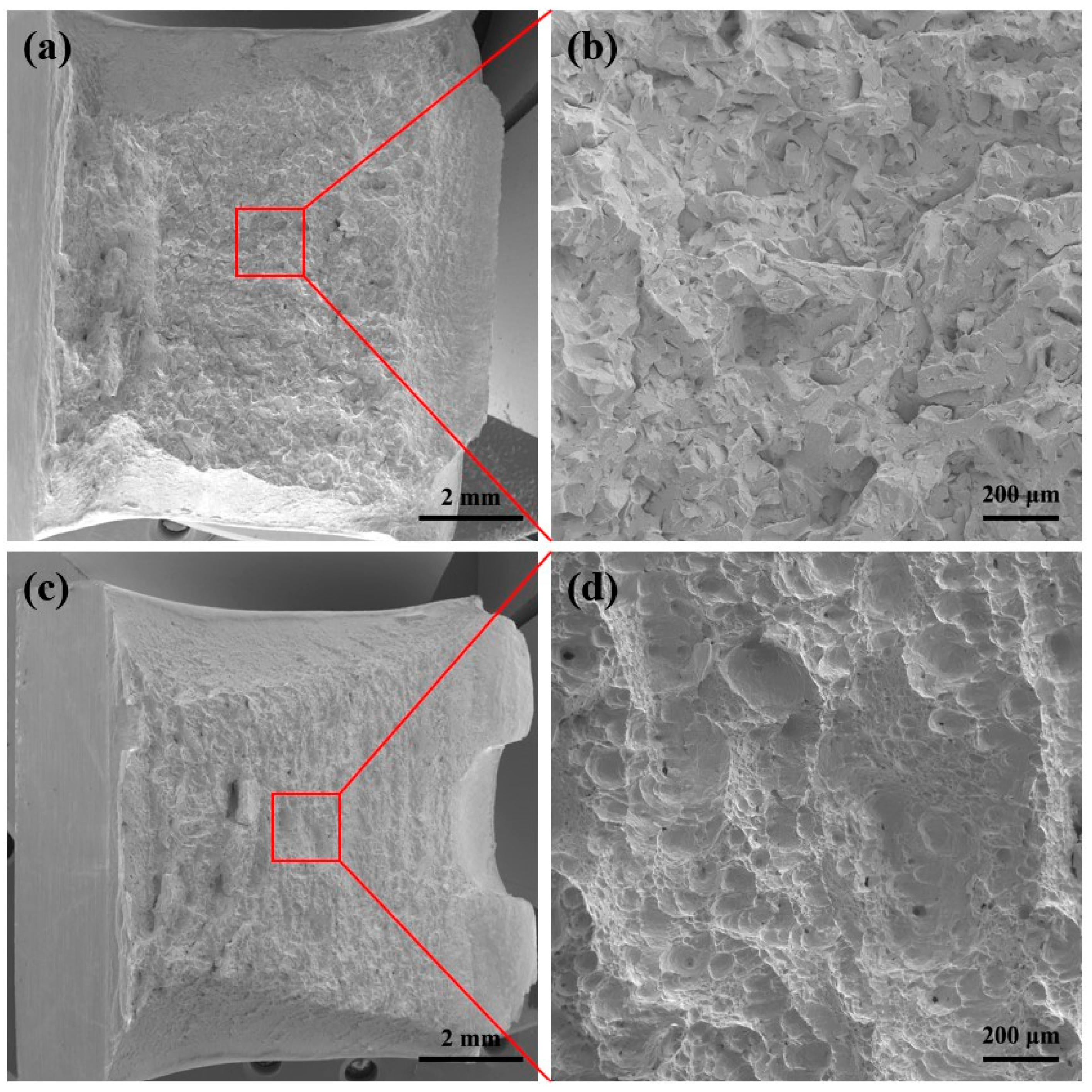
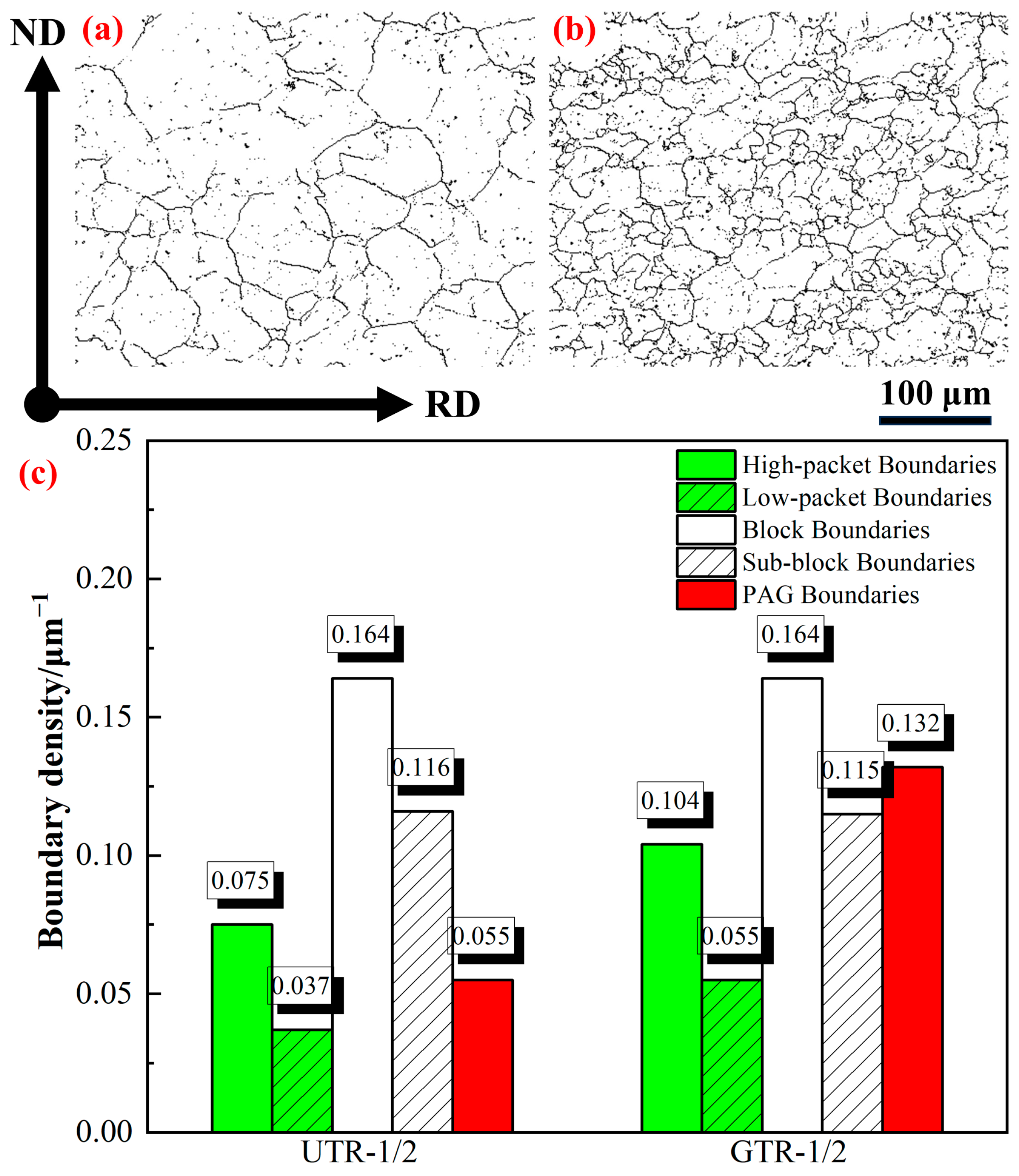
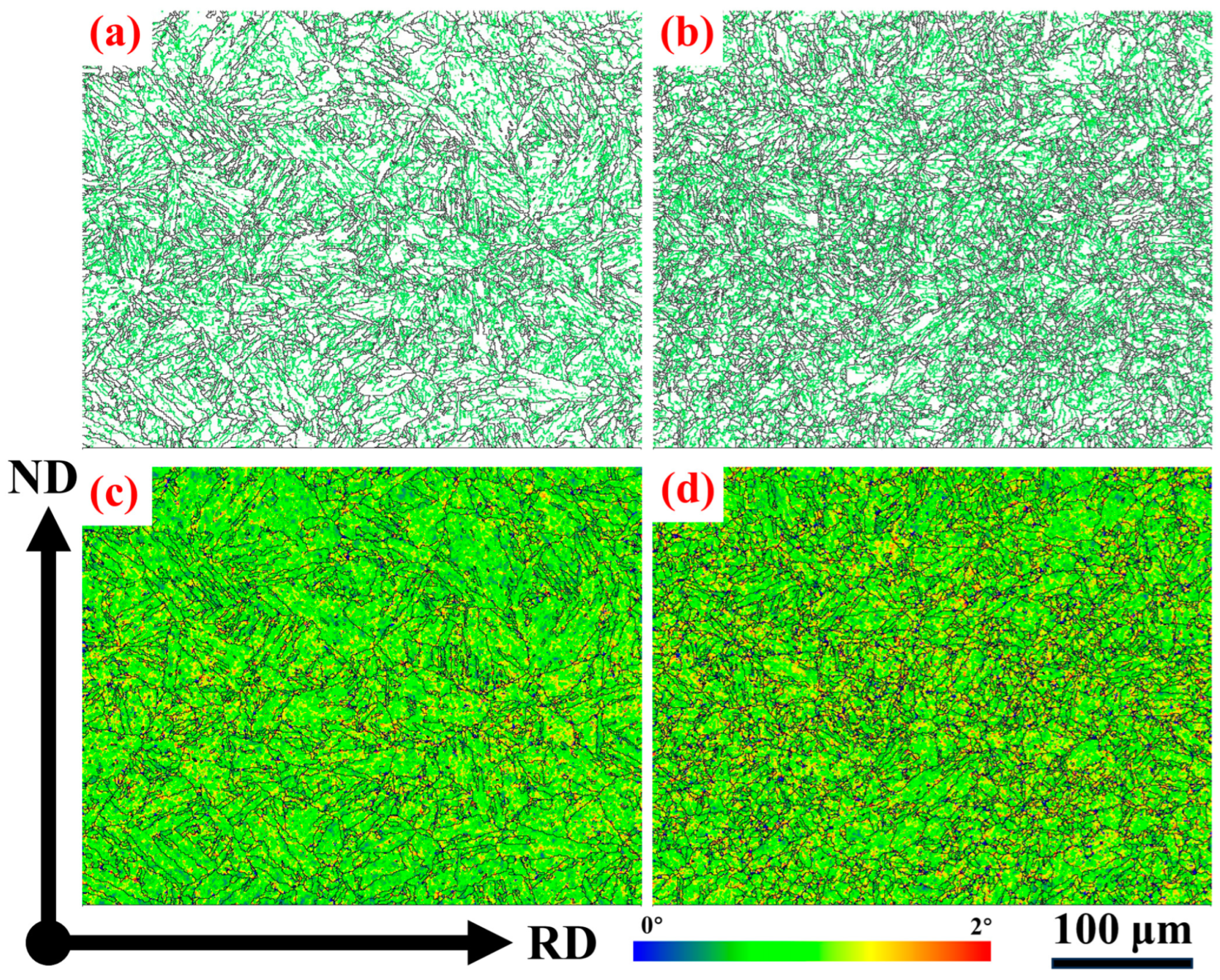
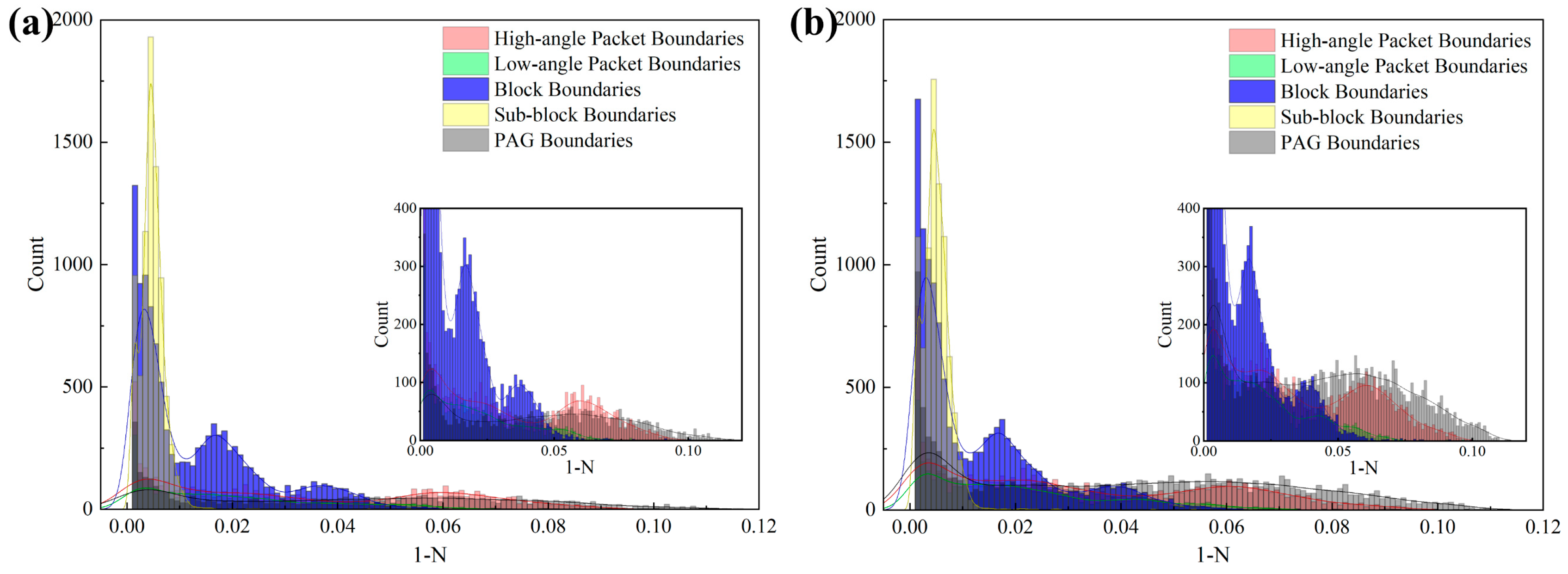
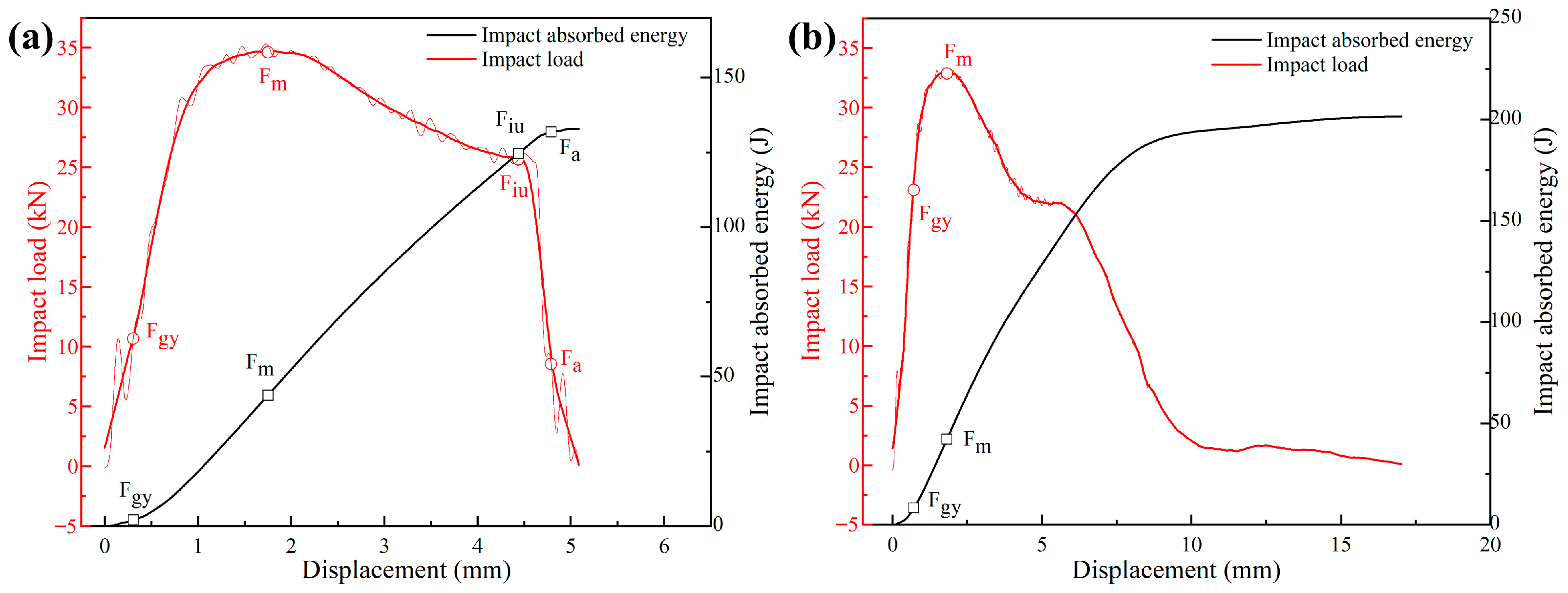
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Research on Strength
4.2. Research on Toughness
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, T.; Yu, H.; Wang, S. Effect of microstructural types on toughness and microstructural optimization of ultra-heavy steel plate: EBSD analysis and microscopic fracture mechanism. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 658, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Cheng, B.; Chen, Y. Strengthening and Toughening of a Heavy Plate Steel for Shipbuilding with Yield Strength of Approximately 690 MPa. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 44, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Yu, H.; Wang, S. Microstructural Characterization and Mechanical Properties across Thickness of Ultra-Heavy Steel Plate. Steel Res. Int. 2017, 88, 1700132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.-S.; Cai, Q.-W.; Yun, Y.; Li, G.-S.; Ning, Z. Development of high strength ultra-heavy plate processed with gradient temperature rolling, intercritical quenching and tempering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 680, 454–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Pan, T.; Zhang, N.; Meng, L.; Luo, X.; Chai, F. Effect of Microstructural Evolution on the Mechanical Properties of Ni-Cr-Mo Ultra-Heavy Steel Plate. Materials 2023, 16, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ye, Q.; Tian, Y.; Fu, T.; Wang, Z. Superior Through-Thickness Homogeneity of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ultraheavy Steel Plate by Advanced Casting and Quenching Technologies. Steel Res. Int. 2021, 92, 2000698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, X.; Du, Y.; Jiang, H.; Pang, H.; Rong, L. Cross-section effect of Ni-Cr-Mo-B ultra-heavy steel plate for offshore platform. Acta Met. Sin. 2020, 56, 1227–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Gaosheng, L.; Qingwu, C. Effect of a novel gradient temperature rolling process on deformation, microstructure and mechanical properties of ultra-heavy plate. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 217, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, P.; Yu, H.; Fan, Y.; Fu, Y. Effects of cooling method after intercritical heat treatment on microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties of as-cast high-strength low-alloy steel. Mater. Des. (1980–2015) 2014, 54, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuyama, S. Thick Plate Technology for the Last 100 Years: A World Leader in Thermo Mechanical Control Process. ISIJ Int. 2015, 55, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, K.; Ichikawa, K. Progress in thermomechanical control of steel plates and their commercialization. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2012, 13, 023001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omata, K.; Yoshimura, H.; Yamamoto, S. Leading high performance steel plates with advanced manufacturing technologies. NKK Technol. Rev. 2003, 88, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Gaosheng, L.; Wei, Y.; Qingwu, C. Investigation of the Evolution of Central Defects in Ultra-Heavy Plate Rolled Using Gradient Temperature Process. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2015, 46, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, G.D. Microstructural characteristics and impact fracture behavior of a high-strength low-alloy steel treated by intercritical heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 553, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Xie, Z.; Misra RD, K.; Shang, C. The Effects of Prior Austenite Grain Refinement on Strength and Toughness of High-Strength Low-Alloy Steel. Metals 2021, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.C.; Zhao, J.X.; Cong, J.H.; Misra RD, K.; Wang, X.M.; Wang, X.L.; Shang, C.J. Machine learning guided automatic recognition of crystal boundaries in bainitic/martensitic alloy and relationship between boundary types and ductile-to-brittle transition behavior. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, J.; Li, J.; Fan, J.; Misra, R.D.K.; Xu, X.; Wang, X. Effect of austenitic state before ferrite transformation on the mechanical behavior at an elevated temperature for seismic-resistant and fire-resistant constructional steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 13, 1220–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Liu, Z.P.; Li, Q.; Xie, Z.J.; Wang, X.L.; Misra, R.D.K.; Shang, C.J. A phenomenological understanding of the novel design of hierarchical structure for 1 GPa ultrahigh strength and high toughness combination low alloy steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 881, 145387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.J.; Han, P.; Liu, Z.P.; Wang, X.L.; Shang, C.J. Influence of initial microstructure on reaustenitization behavior in low alloy steel by in-situ high-temperature EBSD characterization. Mater. Lett. 2023, 350, 134876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Liu, Z.; Xie, Z.; Wang, H.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X.; Shang, C. Influence of band microstructure on carbide precipitation behavior and toughness of 1 GPa-grade ultra-heavy gauge low-alloy steel. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2023, 30, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhara, T.; Kikumoto, K.; Saito, H.; Sekine, T.; Ogawa, T.; Morito, S.; Maki, T. Phase Transformation from Fine-grained Austenite. Isij Int. 2008, 48, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubin, L.P.; Mortensen, A. Geometrically necessary dislocations and strain-gradient plasticity: A few critical issues. Scr. Mater. 2003, 48, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcagnotto, M.; Ponge, D.; Demir, E.; Raabe, D. Orientation gradients and geometrically necessary dislocations in ultrafine grained dual-phase steels studied by 2D and 3D EBSD. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 2738–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, J.; Li, J.; Fan, J.; Liu, P.; Misra, R.D.K.; Shang, C.; Wang, X. The Impact of Interphase Precipitation on the Mechanical Behavior of Fire-Resistant Steels at an Elevated Temperature. Materials 2020, 13, 4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladman, T. The Physical Metallurgy of Microalloyed Steels; The Institute of Materials: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Choi, K.S.; Soulami, A.; Liu, W.N.; Khaleel, M.A. On key factors influencing ductile fractures of dual phase (DP) steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 526, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Hoefnagels, J.P.M.; Vaes, R.; Geers, M.G.D. Block and sub-block boundary strengthening in lath martensite. Scr. Mater. 2016, 116, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hong, H.; Huang, A.; Yang, X.; Qian, R.; Shang, C. New insight into the relationship between grain boundaries and hardness in bainitic/martensitic steels from the crystallographic perspective. Mater. Lett. 2022, 308, 131105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, J.S.; Nan, L.; Mara, N.A.; Jones, D.R.; Hansohl, C.; Bronkhorst, C.A.; Fensin, S.J.; Gray, G.T. Slip transmission of high angle grain boundaries in body-centered cubic metals: Micropillar compression of pure Ta single and bi-crystals. Acta Mater. 2018, 156, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qian, R.; Huang, S.; Shang, C. Effect of Double-Quenching on the Hardness and Toughness of a Wear-Resistant Steel. Metals 2022, 13, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Shang, C.; Chen, B.; Hui, Y. Characterization of the Stretch Flangeabitity of High-Strength Bainitic Steel: The Significance of Variant Pairs. Materials 2022, 15, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Shang, C. Distribution feature of specific misorientation angle in a bainitic steel. Mater. Charact. 2021, 172, 110874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouadi, R.; Fabry, A. On the utilization of the instrumented Charpy impact test for characterizing the flow and fracture behavior of reactor pressure vessel steels. In European Structural Integrity Society; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 30, pp. 103–117. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 14556:2015; Metallic Materials—Charpy V-Notch Pendulum Impact Test—Instrumented Test Method. ES-AENOR: Madrid, Spain, 2016; Volume UNE-EN ISO 14556-2016.

| C | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Cu | Mo | V | P | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.069 | 0.34 | 0.59 | 0.64 | 4.79 | 0.024 | 0.5 | 0.065 | 0.0053 | 0.0004 |
| Number | YS 1 (MPa) | TS 2 (MPa) | Yield Ratio | El 3 (%) | −80 °C CVN 4 (J) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTR-1/2 | 769.5 | 1083.5 | 0.71 | 15.6 | 168.8 |
| GTR-1/2 | 791.5 | 1120.5 | 0.71 | 17.7 | 240.0 |
| Number | Dislocation Density (ρ)/m−2 | ∆σDis/MPa |
|---|---|---|
| UTR-1/2 | 1.42 × 1014 | 283.9 |
| GTR-1/2 | 1.51 × 1014 | 292.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cong, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z. Effect of a Gradient Temperature Rolling Process on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Center of Ultra-Heavy Plates. Metals 2024, 14, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14020199
Cong J, Zhao J, Wang X, Wu Z. Effect of a Gradient Temperature Rolling Process on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Center of Ultra-Heavy Plates. Metals. 2024; 14(2):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14020199
Chicago/Turabian StyleCong, Jinghua, Jingxiao Zhao, Xuemin Wang, and Zhongwen Wu. 2024. "Effect of a Gradient Temperature Rolling Process on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Center of Ultra-Heavy Plates" Metals 14, no. 2: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14020199
APA StyleCong, J., Zhao, J., Wang, X., & Wu, Z. (2024). Effect of a Gradient Temperature Rolling Process on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Center of Ultra-Heavy Plates. Metals, 14(2), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14020199







