Abstract
The A286 iron-based superalloy has wide-ranging applications in replacing expensive nickel-based and cobalt-based superalloy to manufacture the turbine disk as well as the pipelines and valves of the fourth-generation supercritical water reactor (SCWR) working below 650 °C. The recrystallization texture importantly affects the mechanical properties and oxidation resistance of superalloys. However, very few investigations are available on the recrystallisation texture of A286 alloy. The current work reports the texture of A286 alloy fabrication using various rolling routes, including one-stage cold rolling with the rolling rates of 83% (Route I) and 91% (Route II), and two-stage cold rolling with the rolling rate of 83% + 50% (Route III). Route III is preferentially recommended to manufacture A286 alloy thin plates due to the obviously reduced work hardening as well as the weakened recrystallization texture and anisotropy; moreover, compared with other routes, the recrystallized grain size of Route III did not significantly coarsen. We also revealed the mechanism for the effect of cold rolling textures on the final recrystallization texture and the role of the deformation twin in {110} <115> grain. In this study, recrystallization texture develops through two independent mechanisms related to different deformation microstructures, including the recrystallization texture inherited from deformation texture and the recrystallization texture depended on deformation twins.
1. Introduction
Superalloy is a kind of metal based on iron, nickel or cobalt, which can work at high temperatures above 600 °C and under certain stress for a long time. It has excellent high temperature strength, good oxidation and hot corrosion resistance, good fatigue performance and fracture toughness and has been an indispensable advanced engineering material for high-temperature application in aerospace and energy fields [1]. The A286 iron-based superalloy containing 25% Ni (wt.%) and 15% Cr has high yield strength and plasticity, good corrosion resistance and excellent creep resistance below 650 °C [2,3]. It has wide applications in replacing expensive nickel-based and cobalt-based superalloy to manufacture the turbine disk as well as the pipelines and valves of the fourth-generation supercritical water reactor (SCWR).
A lot of work has been carried out on the microalloying, aging treatment and properties of A286 alloy. It has been found that adding a little element B in A286 alloy can be used for promoting the precipitates on grain boundaries from cellular η phase to carbides, which effectively improves the ductility of the alloy without sacrificing strength and especially alleviating hydrogen damage in special environments [4]. Moreover, multicomponent Boride layers (consist of FeB, Fe2B, CrB and Ni4B3) can be formed on the surface of iron-based A286 superalloy via a boriding treatment, and the surface hardness can thus be significantly increased from 320 HV to 1498–1961 HV. The boron activation energies of FeB and Fe2B are estimated to be 176 and 199 kJ·mol−1, respectively [5]. The microalloying of Nb optimizes the yield strength, fatigue and creep properties of A286 alloy [6], as Nb increases the number and stability of γ′ precipitates during aging treatment. The γ′ is the main strengthening phase of A286 alloy, composed of Ni3 (Ti, Al), which is coherent with the matrix [6]. The strength of A286 alloy can be increased by changing the aging temperature from 650 °C to 680 °C to control the precipitation of the γ′ phase [2]. However, the excessively high temperature of aging at 730 °C causes the dissolution of the γ′ phase and the formation of the η phase, resulting in a decrease in creep resistance and the intergranular fracture [7]. Cissé et al. [8] also investigated the oxidation behavior of A286 alloy, including preferential oxide growth channels and the interaction between oxidation and localized deformation bands.
A286 alloy is a typical wrought superalloy. Currently, the study on the deformation of A286 alloy mainly focuses on forging, compression and tensile [9,10], while the research on rolling is limited. Rolling is a key method for the industrial production of superalloy plates, and has advantages in processing efficiency, dimensional accuracy and surface quality. Many defects including dislocations, low-angle grain boundaries (LAGBs) and high-angle grain boundaries (HAGBs) occur during rolling, which increase the strength of the superalloy but decrease properties such as the plasticity and the resistance of corrosion and nuclear irradiation. Therefore, recrystallization annealing is required after rolling to improve the comprehensive performance. During recrystallization, the strain stored energy and the defects continuously decrease; meanwhile, new recrystallized grains nucleate and growth, and the recrystallized textures develop [11,12].
As is well known, the existence of textures widely affects the mechanical properties and oxidation resisting of superalloys [13]. For FCC materials with high SFE (stacking fault energy), such as Al, Cu, and Ni, the typical recrystallization texture is Cube component ({100} <001>) [14]. In contrast, the recrystallization texture of FCC metals of low SFE is very complex, and the formation and evolution of recrystallization texture are highly controversial [15,16]. Additionally, very few investigations are available on the recrystallisation texture of iron-based superalloy A286 with low SFE.
The earliest research on the recrystallization texture of low SFE metals mainly focused on Cu alloys, and later on austenitic steels. Wang et al. [17] reported the texture transformation from the deformation to the recrystallization in copper tubes. Research showed that the Copper texture developed during the drawing, while after recrystallization, the Goss texture dominated the metal. For austenitic steel Fe-30Mn-3Al-3Si, retained α- fiber (<110> parallel to ND, normal direction) was observed after recrystallization [18]. For the Fe-22Mn-0.6C TWIPs steel, de las Cuevas et al. [19] verified a retention of Brass texture ({110} <112>), and found that its intensity decreased with the grain growth. Hamed et al. [13] reported that the 90% cold rolling and annealing at 1050 °C promoted the evolution of recrystallization textures of Goss ({110} <001>), Copper ({112} <111>), and R-Brass ({110} <111>) in Incoloy 800H/HT superalloys. Zeng et al. [20] found that the textural composition in cold-rolled GH159 superalloy was weakened by annealing, showing weak textural fractions of Goss, Cube, {552} <115> and Copper.
Currently, the industrial method for manufacturing superalloy thin plates includes one- or two-stage cold rolling. Among them, one-stage method has significant advantages of high production efficiency, low-cost and short time. However, the superalloy usually has high yield strength at room temperature, and the two-stage cold rolling including intermediate annealing is beneficial for reducing work hardening and making it easier to manufacture thin plates [21]. In this study, A286 superalloy thin plates with a thickness of 1.2–2.4 mm using both one- and two-stages cold rolling were prepared, and the influence of rolling routes on recrystallization texture and the evolution mechanism of main recrystallization components was further explored.
2. Experimental Procedure
The forging A286 alloys with 100 × 50 × 14 mm produced by Gaona Aero Material Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China) were used as the raw material, and their composition is shown in Table 1. The forging plates (As-received plates) were put into a furnace of 850 °C, and then heated to 1076 °C and kept for 120 min. The alloys were taken out and forged with a final temperature of 900 °C, followed by air cooling. Then, the forging plates were kept at 980 °C for 60 min and cold-rolled through three different routes (Route I, II and III) at room temperature. Finally, all cold-rolled plates were annealed at 980 °C for 60 min. The rolling and annealing process is shown in Figure 1. Route I and Route II were cold-rolled from 14 mm to 2.4 mm and 1.3 mm using one-stage cold-rolling, corresponding to the rolling rates of 83% and 91%, respectively. Route III used two-stage cold-rolling with intermediate annealing at 980 °C for 60 min. The first- and second-stage rolling rates in Route III were 83% and 50%, respectively, and the final thickness is 1.2 mm. The cold-rolling experiment used a four-roll reversible rolling mill. The diameter, width and rotation speed of the roller are 160 mm, 350 mm and 2 m/min, respectively. The diameter and width of the support roller are both 350 mm.

Table 1.
The chemical composition of A286 alloy (wt. %).
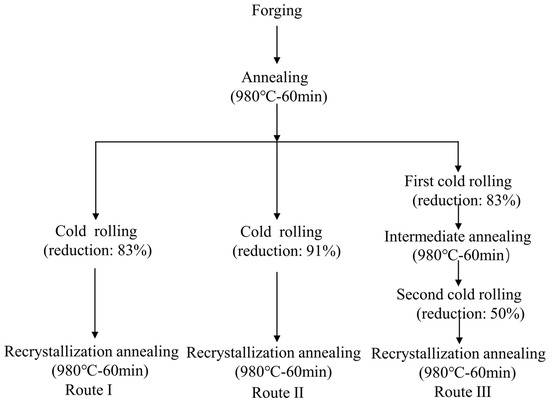
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of fabricating A286 iron-based superalloy plates via various rolling routes.
The samples including the forging plate (as-received), the intermediate annealed plate and the final annealed plates were mechanically polished and electropolished, and then analyzed using electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD). Electropolishing used a mixed solution containing 20% perchloric acid and 80% ethanol, and the working voltage and time are 15.5 V and 6–8 s, respectively. The test section is RD-ND, where RD represents the rolling direction and ND represents the normal direction. The SEM equipment is JSM-7001F SEM equipped with HKL Channel 5 system. Grain boundaries with a misorientation angle of 2–15° are defined as LAGBs, and boundaries with a misorientation angle greater than 15° are defined as HAGBs, and the orientation image map (OIM) of typical texture components was calculated within a 15° tolerance around their ideal position in the Euler space using the Channel 5 (5.0.9.0) for data analysis. The orientation distribution functions (ODFs) of the rolled plate under Route I were measured and calculated based on X-ray diffraction (XRD). The test was carried out using the Schulz back-reflection method with a Smart Lab-type X-ray diffractometer. Here, the thickness layer of the sample is defined as the parameter S = 2a/d, where a represents the distance from the center layer and d represents the entire sheet thickness. The S value of the test location is 0.5 and the size of the sample is 20 mm × 20 mm. The measurements were carried out using Co Kα radiation with a tube voltage of 35 KV and current of 40 mA, an anti-scattering slit of 5 mm, and a receiving slit of 5 mm. Three incomplete polar plots were measured for {110}, {200}, and {220} with a measurement step size of 5°. The grain orientation distribution function (ODF) was calculated using the 3D orientation analysis technique, and the test results are represented by constant φ2 cross sections.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Recrystallization Microstructure and Texture under Various Rolling Routes
Figure 2 illustrates the microstructure of as-received plates of the A286 alloy, which consist of equiaxed grains with the average grain size of about 13.6 μm. The distribution of the grain size is not uniform and the proportion of grains with size less than 12 μm exceeds 50%. The distribution of the misorientation angle of the grain boundary is shown in Figure 2d. It can be seen from Figure 2 that the misorientation angles for the as-received sample not only contains a large number of HAGBs, as shown by the black line in Figure 2a, but also includes a large number of 0–2° LAGBs and 60° grain boundaries, indicating that the grain boundary type in forging A286 alloys includes HAGBs LAGBs and Σ3 annealing twin grain boundaries. Additionally, the grain boundaries with a misorientation of 60° have the highest proportion, reaching 22%, which can be attributed to the annealing twins formed during the forging process.
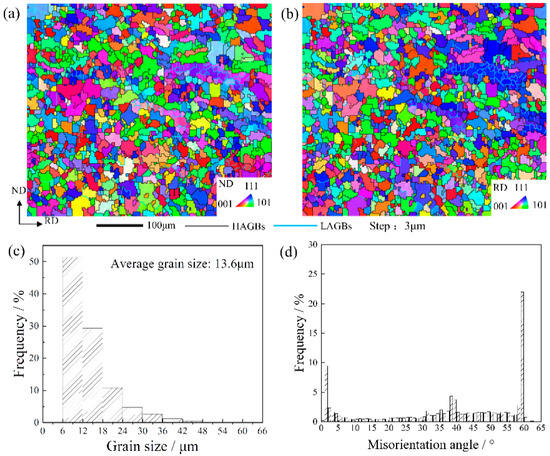
Figure 2.
Microstructure of as-received sample. (a,b) the orientation image map and the distribution of (c) grain size and (d) the misorientation angle.
The microstructure and texture after recrystallization annealing are shown in Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6. For the convenience of texture comparison, only the constant φ2 = 0°, 45°, and 65° sections of ODFs of samples are provided here, since the main texture components of deformation and annealing textures in FCC metals occur in these sections. The definitions of common texture components and fibers in FCC alloys are shown in Table 2. Both Route I and II adopt one-stage cold rolling. The average grain size of Route I is 4.6 μm (Figure 4) and the texture of Route I is mainly composed of the α-fiber and β-fiber. The α-fiber has peaks of Goss, Brass and R-Goss ({110} <110>), and the β-fiber has peaks of Brass, S and Copper (Figure 5 and Figure 6). The recrystallization annealing texture in Route I is significantly different from the recrystallization texture of other low SFE iron-based superalloys that have been reported [13]. The recrystallization texture of 90% cold-rolled Incoloy 800H/HT alloy is characterized by β-fiber with peaks of Brass, S and Copper components, and the α-fiber cannot be observed. However, as shown in the orientation image map (OIM) of Figure 3, green grains with an orientation of <110>//ND, i.e., α-fiber grains, appear extensively in ND-OIM.
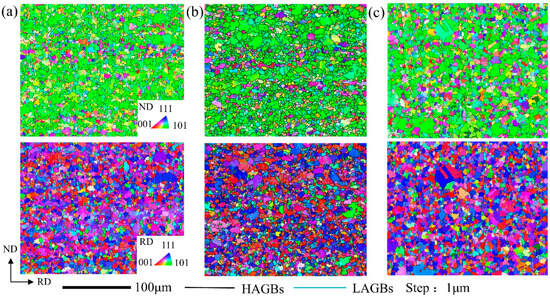
Figure 3.
Orientation image map of recrystallization annealing plates corresponding to (a) Route I, (b) Route II and (c) Route III.
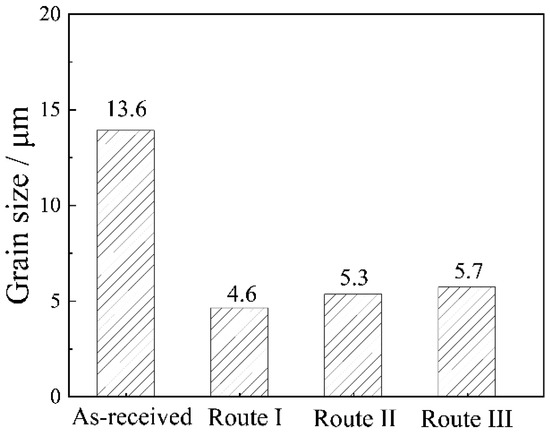
Figure 4.
Average grain size of the as-received and recrystallization annealing plates with various routes.
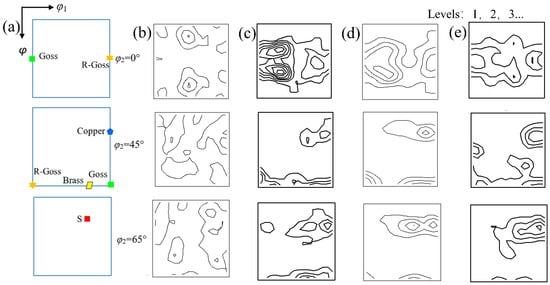
Figure 5.
Constant φ2 = 0°, 45° and 65° sections of ODFs of (a) the major texture components, (b) as-received plate and the recrystallization annealing plates corresponding to (c) Route I, (d) Route II and (e) Route III.
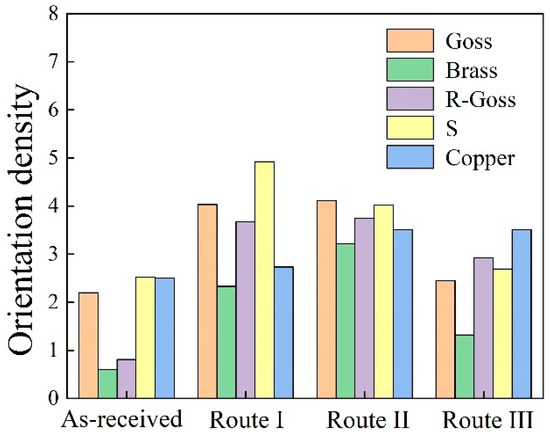
Figure 6.
Orientation density of as-received and recrystallization annealing plates in A286 superalloy.

Table 2.
Miller indices and Euler angles for the important texture components and fibers in FCC metals.
For Route II and III, the average grain size is 5.3 μm and 5.7 μm, respectively. The grain size is similar to that of Route I, which indicates that the adopted three rolling routes have little effect on the average grain size of the A286 alloy sheet. Both the type and orientation density of recrystallization texture under Route II are similar to those of Route I (Figure 6), which can be explained by the relatively close cold-rolling rate between them. The α- and β-fibers also develop in Route III. The results illustrate that the texture type of Route III is identical to those of Route I and II, but the orientation density of α- and β-fibers of Route III weakens, as shown in Figure 6. On the other hand, compared with the as-received state, the orientation density after recrystallization is higher. There were no obvious Copper, Brass, Goss and S textures observed in the as-received state, while these texture components are stronger after recrystallization.
In FCC metals with low SFE, the orientation density of α and β-fibers is closely related to the cold-rolled strain before annealing, and the cold-rolled strain changes with the cold-rolling rates. According to reports [13], in Incoloy 800H/HT superalloy, as the cold-rolling rate decreases from 90% to 50%, the texture of recrystallized Brass, Goss, and Copper significantly weakens, and {013} <031> and {212} <031> textures develop. The cold-rolling rate of the second-stage of Route III is also 50%, which results in weaker recrystallization textures in Figure 5e compared to those in Figure 5c,d.
3.2. The Origin of the Recrystallization Texture of A286 Superalloy
Figure 7 indicates the cold-rolling texture in Route I, which is mainly composed of β-fiber with peaks of Goss, Brass, and S components. This is consistent with the results of other low SFE alloys such as copper alloys, austenitic steels and superalloys. Wang et al. [22] reported that Copper, Brass and Goss texture dominated the cold-rolling sheets with a 25–55% rolling reduction in Fe-36.8%Ni-16.4%Cr superalloy. Figure 8 illustrates the distribution of typical texture components in thin plates prepared via different routes. These texture components exhibit a relatively uniform distribution and no obvious colony phenomenon forms. Orientation pinning may occur in the colony grains, limiting the following growth of these grains. It should be noted that a large number of {110} <115> (blue grains) and R-Goss grains (yellow grains) neighbor each other, which are connected by twin boundaries, as observed in the black circle of Figure 8.
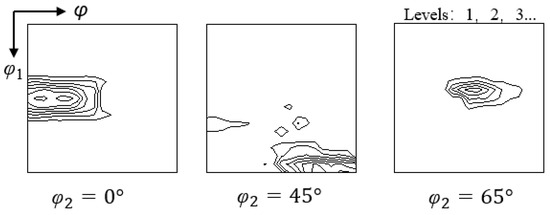
Figure 7.
Constant φ2 = 0°, 45° and 65° sections of ODFs of the cold-rolled plates under Route I.
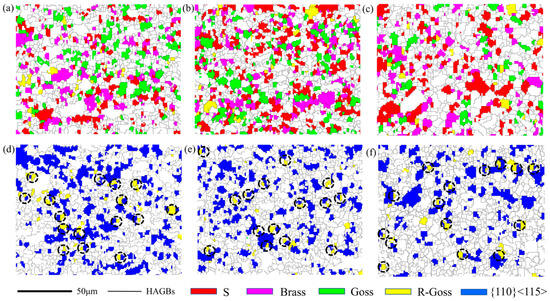
Figure 8.
OIM of typical texture components in thin plates of various routes, (a–c) components of Brass, S and Goss, (d–f) components of R-Goss and {110} <115>, (a,d) Route I, (b,e) Route II, (c,f) Route III.
Generally speaking, the results on the rolling texture of FCC metals of low SFE are basically consistent, but there is significant controversy over their recrystallization texture to date. There are three mechanisms for the origin of recrystallization texture, namely orientation nucleation (ON), selective growth (SG), and the combined effect of ON-SG. In the ON mechanism, the recrystallization nuclei form in the early stage of recrystallization is closely related to the orientation of the deformed matrix and the special positions (such as shear bands, grain boundaries, etc.), and it is believed that the texture after complete recrystallization is similar to the texture of all recrystallized grains in the early stage of recrystallization. The SG mechanism suggests that the orientation of nuclei is random, and some nuclei have faster growth rates, leading to the formation of recrystallization textures. The ON-SG mechanism suggests that both ON and SG play a simultaneous role. The reports in recent decades have provided more support for the theory of ON [16,23,24].
In this study, the recrystallization texture develops in A286 superalloy plates annealed at 980 °C for 60 min through two independent mechanisms related to different deformation microstructures, as schematically illustrated in Figure 9.
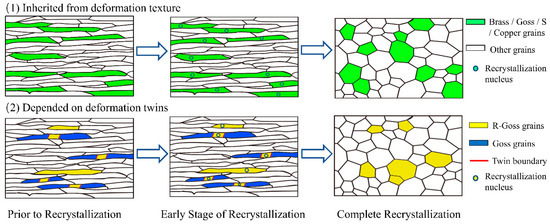
Figure 9.
Schematic of the formation mechanism of main recrystallization texture components.
- (1)
- Recrystallization texture inherited from deformation texture
Szpunar [13] confirmed that the cold rolling and recrystallization of Incoloy 800H/HT alloy exhibits the same type of textures including Brass, Goss, and Copper. The fixed relationship between recrystallized grains and deformed matrix strongly supports the ON mechanism despite an obvious decrease in orientation density after recrystallization. The retention of Brass, Goss, S and Copper textures can be explained by the nucleation process of near-site saturation during recrystallization [24].
If the distribution of deformation energy is uniform, it is difficult to obtain a preferred site for nucleation, and nucleation may occur in a randomly dispersed manner throughout the entire deformed matrix. In this way, the deformation texture of Brass, Goss, Copper and S in A286 cold-rolled plates will be retained until the recrystallization is completed, as shown in Figure 5 and Figure 7.
- (2)
- Recrystallization texture depended on deformation twins
The formation of R-Goss recrystallization texture can be understood from the perspective of twinning. The R-Goss component has a twinning relationship with the G/B orientation ({110} <115>) [15], and the G/B orientation is located between Goss and Brass. As shown in Figure 5, the G/B component has a relatively high orientation density, which results in the existence of more regions with the orientation of R-Goss in the deformed matrix (Region A). In addition, some R-Goss oriented grains are usually randomly distributed in the deformed matrix (Region B). During recrystallization, the new R-Goss recrystallized grains nucleate in both Region A and Region B, leading to the formation of R-Goss texture. That is to say, the orientation density of the R-Goss texture formed after recrystallization heavily depends on the orientation density of the G/B deformation texture and the number of deformation twins in G/B grains.
In addition, both the Brass and Copper textures deviate from the ideal orientation in Euler space observed in Route II and Route III, as shown in Figure 5, which are referred to in this study as Brass and Copper textures. The components of Brass and Copper can arrive at the orientations of Brass’ and Copper’ by deviating 10° along the coordinate axis of φ and φ1, respectively, as shown in Figure 5d,e. Twins more easily develop during the deformation of metals with low SFE [25]. Under the condition of large deformation, the obstruction of the slip leads to an increase in local stress. Once the local stress exceeds the critical resolved shear stress (CRSS) for twinning initiation, deformation twinning starts [26], consequently leading to more complex recrystallization textures such as Brass and Copper textures.
4. Conclusions
In the current work, A286 iron-based superalloy plates were prepared using rolling and annealing methods, and the relationship between rolling routes and recrystallization texture was characterized. The main conclusions are as follows:
- (1)
- Goss, Brass, S, Copper and R-Goss textures dominate the recrystallized plates. Moreover, similar recrystallization textures develop under different rolling routes including one- and two-stage cold rolling.
- (2)
- Under various rolling routes, the recrystallization grain size is similar. The growth of recrystallized grains is slow in the thin plates annealed at 980 °C, and the grain size only increases from 4.6 μm to 5.3 μm, as the annealing time extends from 5 min to 60 min.
- (3)
- The route of two-stage cold rolling that can weaken work hardening also helps to decrease the recrystallization texture, thereby reducing the anisotropy of the recrystallized thin plates.
- (4)
- The recrystallization texture of A286 superalloy plates develops through two independent mechanisms related to different deformation microstructures. The formation of textures of Goss, Brass, S and Copper relies on the heredity of deformation texture, while the R-Goss recrystallization texture is more dependent on deformation twins.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L. and C.Z.; methodology, J.L. and R.Z.; formal analysis, R.Z. and J.L.; investigation, R.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, R.Z.; writing—review and editing, J.L. and Z.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the special fund of the basic scientific research business fund of the central universities (No. N2002008), Shenfu Demonstration Zone Science and Technology Plan Project (2021JH05).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Geddes, B.; Leon, H.; Huang, X. Superalloys. In Alloying and Performance; ASM International: Almere, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 71–72. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.C.; Gao, Y.; Lin, Z.L.; Guo, S.S.; Zhang, X.B.; Yin, X.J. Microstructure and properties after deformation and aging process of A286 superalloy. Rare Met. 2019, 38, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhao, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Z. Microstructure evolution and stress rupture properties of A286 superalloy in the 600 to 750 °C temperature range. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 026521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.J.; Guo, Z.F.; Liang, H.; Rong, L.J. Effect of boron on the microstructure, mechanical properties and hydrogen performance in a modified A286. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 5844–5851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günen, L.; Keddam, M.; Alkan, S.; Erdoğan, A.; Çetin, M. Microstructural characterization, boriding kinetics and tribo-wear behavior of borided Fe-based A286 superalloy. Mater. Charact. 2022, 186, 111778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, B.S.; Nam, S.W. Fatigue-induced precipitates at grain boundary of Nb-A286 alloy in high temperature low cycle fatigue. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 291, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cicco, H.; Luppo, M.I.; Gribaudo, L.M.; Ovejero-Garcıa, J. Microstructural development and creep behavior in A286 superalloy. Mater. Charact. 2004, 52, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cissé, S.; Laffont, L.; Lafont, M.C.; Tanguy, B.; Andrieu, E. Influence of localized plasticity on oxidation behaviour of austenitic stainless steels under primary water reactor. J. Nucl. Mater. 2013, 433, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bulloch, J.H.; Younes, C.M.; Bernard, P.J.; Heard, P. A detailed fitness-for-purpose assessment of turbine valve spindles. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2006, 13, 747–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahedi, R.; Kheirandish, S.; Shirazi, F.; Seifollahi, M. The effect of solid solution treatment parameters on the microstructure and mechanical properties of A286 superalloy. Metall. Res. Technol. 2021, 118, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, N.; Liu, J.; Sha, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zuo, L. Development of Through-Thickness Cube Recrystallization Texture in Non-oriented Electrical Steels by Optimizing Nucleation Environment. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 2486–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Sha, Y.H.; Zhang, F.; Li, J.C.; Yao, Y.C.; Zuo, L. Development of {2 1 0}<0 0 1> recrystallization texture in Fe-6.5 wt.% Si thin sheets. Scr. Mater. 2011, 65, 292–295. [Google Scholar]
- Akhiani, H.; Nezakat, M.; Szpunar, J.A. Evolution of deformation and annealing textures in Incoloy 800H/HT via different rolling paths and strains. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 614, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervasyeva, I.V.; Beaugnon, E.; Milyutin, V.A.; Volkova, E.G.; Rodionov, D.P.; Khlebnikova, Y.V.; Shishkin, D.A. Formation of structure and crystallographic texture in Fe-50% Ni thin tapes under high magnetic field annealing. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2015, 468, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.A.; Pereloma, E.V.; Gazder, A.A. Texture evolution of cold rolled and annealed Fe–24Mn–3Al–2Si–1Ni–0.06C TWIP steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 4537–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabizada, A.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Abedi, H.R.; Barati, M.H.; Asghari-Rad, P.; Kim, H.S. The high temperature mechanical properties and the correlated microstructure/ texture evolutions of a TWIP high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 802, 140600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.W.; Song, H.W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.H.; Li, H.H. Evolution of Annealing Twins and Recrystallization Texture in Thin-Walled Copper Tube During Heat Treatment. Acta Metall. Sin. 2022, 33, 1618–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercammen, S. Processing and Tensile Behaviour of TWIP Steels, Microstructural and Textural Analysis; Katholieke Universiteit Leuven: Leuven, Belgium, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- De las Cuevas, F.; Reis, M.; Ferraiuolo, A.; Pratolongo, G.; Karjalainen, L.P.; García Navas, V.; Gil Sevillano, J. Kinetics of recrystallization and grain growth of cold rolled TWIP steel. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 89, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.T.; Yang, Y.; Tan, Y.B.; Zhang, W.W.; Xiang, S.; Ma, M.; Zhao, F. Recrystallization behavior and texture evolution of cryo-rolled GH159 superalloy with an ultra-high strength. Mater. Charact. 2023, 197, 112656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Q.; Li, H.B.; Chen, M.S.; Lin, Y.C.; Zeng, W.D.; Ma, Y.Y.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, Y.Q. Effect of initial mixed grain microstructure state of deformed Ni-based superalloy on its refinement behavior during two-stage annealing treatment. Mater. Charact. 2021, 176, 111130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Cheng, S.H.; Wu, Y.S.; Wang, T.T.; Qin, X.Z.; Zhou, L.Z. Effect of cold rolling on microstructure, texture, and tensile properties of a Ni-Fe-based superalloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 937, 68383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, B.; Saha, R.; Bhattacharjee, P.P. Microstructure and unusually strong recrystallization texture of the FCC phase of a cost-effective high-strength dualphase AlCrFe2Ni2 high entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2022, 145, 107559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracke, L.; Verbeken, K.; Kestens, L.; Penning, J. Microstructure and texture evolution during cold rolling and annealing of a high Mn TWIP steel. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 1512–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.K.; Shekhar, S. New insights into the evolution of twin boundaries during recrystallization and grain growth of low-SFE FCC alloys. Mater. Charact. 2020, 159, 110015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, X.; Dong, Z.; Li, W.; Huang, S.; Meng, D.; Lai, X.; Liu, T.; Zhu, S.; Vitos, L. Critical stress for twinning nucleation in CrCoNi-based medium and high entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2018, 149, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).