Effect of Slag Compositions on Change Behavior of Nitrogen in Molten Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
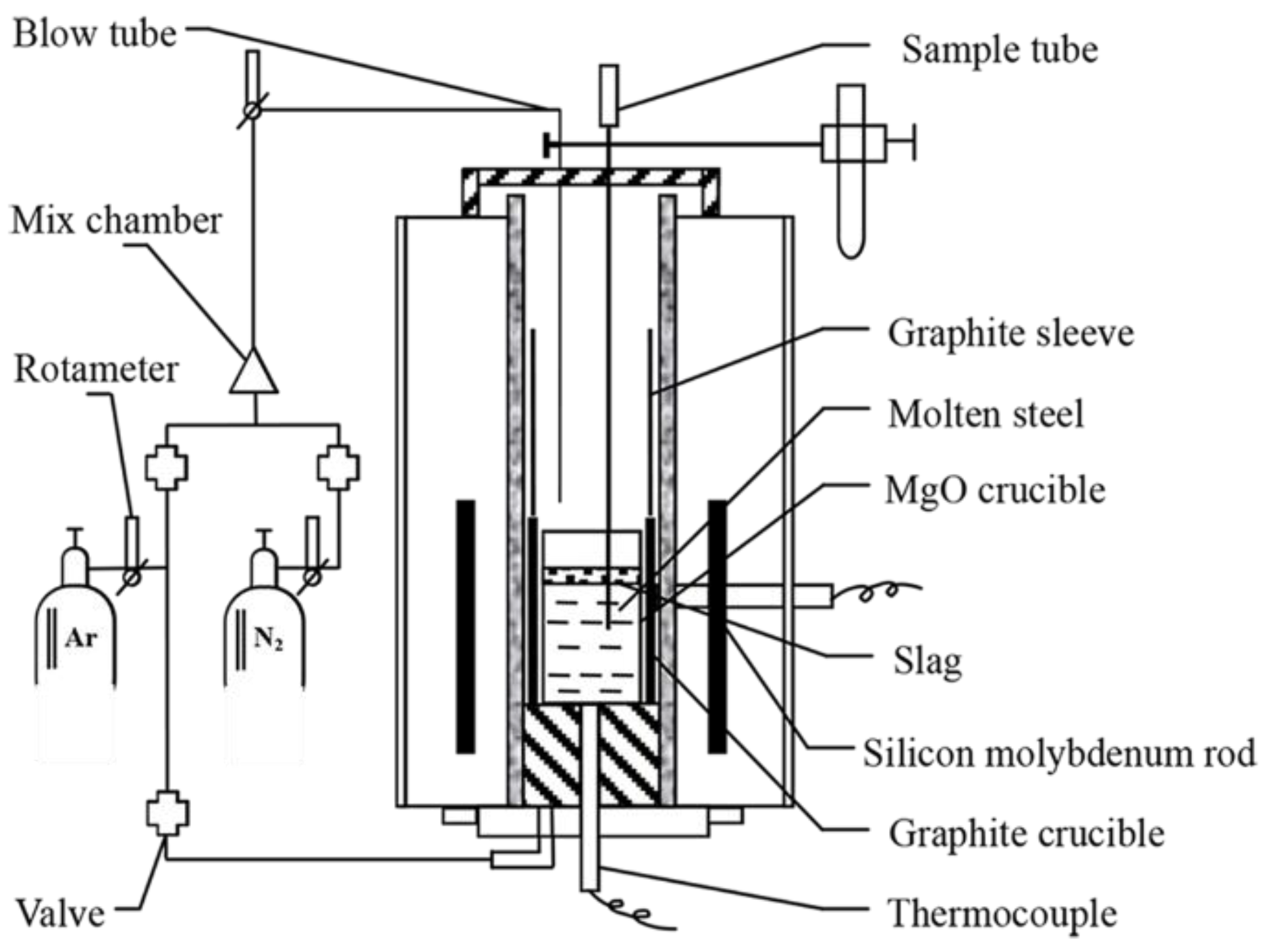
2. Experimental Condition and Procedure
2.1. Experimental Condition
2.2. Experimental Procedure
3. Experimental Results
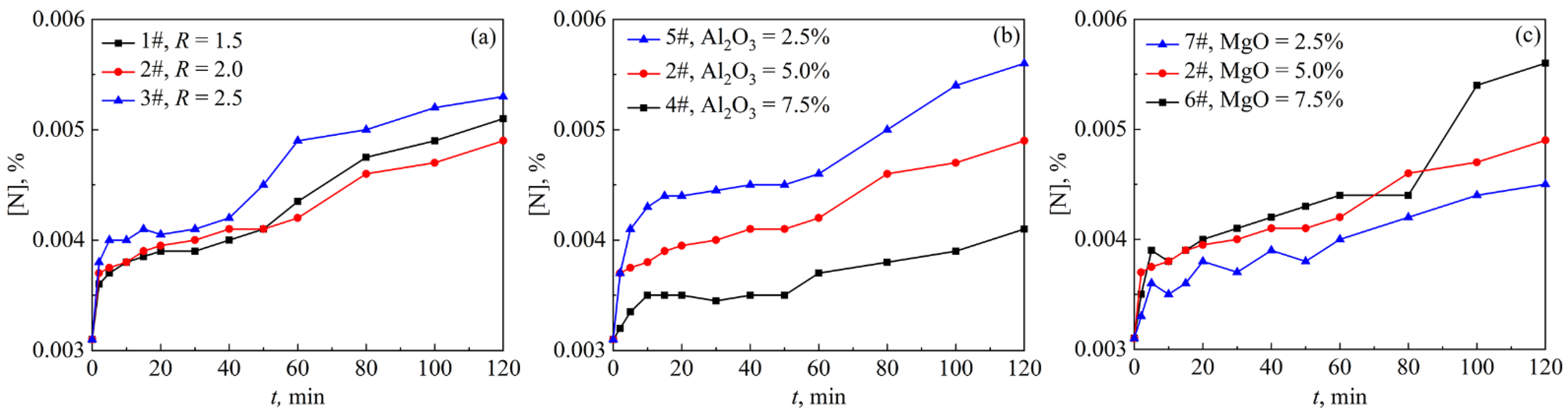
3.1. Effect of Slag Composition on Nitrogen Content in Steel
3.2. Compositions of Experimental Slags and Experimental Steels
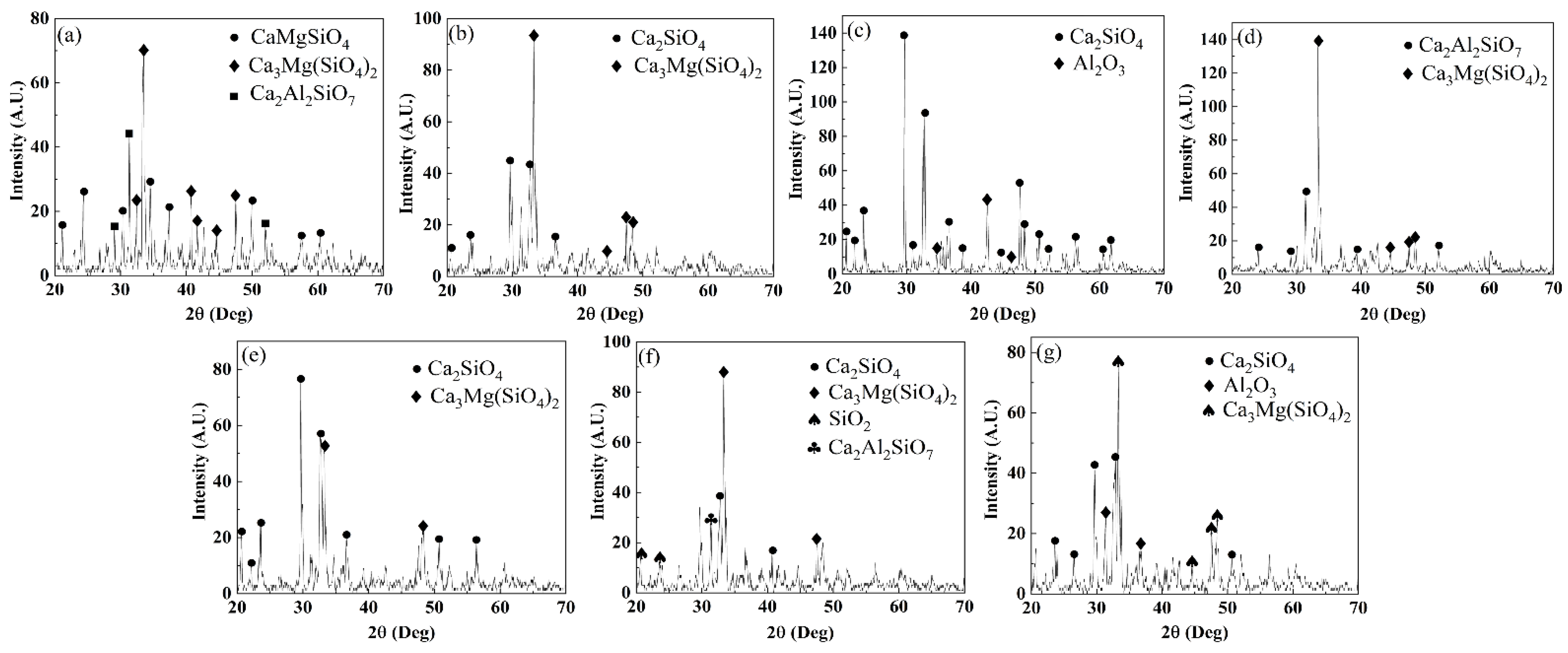
3.3. The XRD Results of the Experimental Slags
4. Discussion
4.1. Relation of Foaming Index of Slag with Nitrogen Capacity
4.2. Relation of Optical Basicity of Slag with Nitrogen Capacity
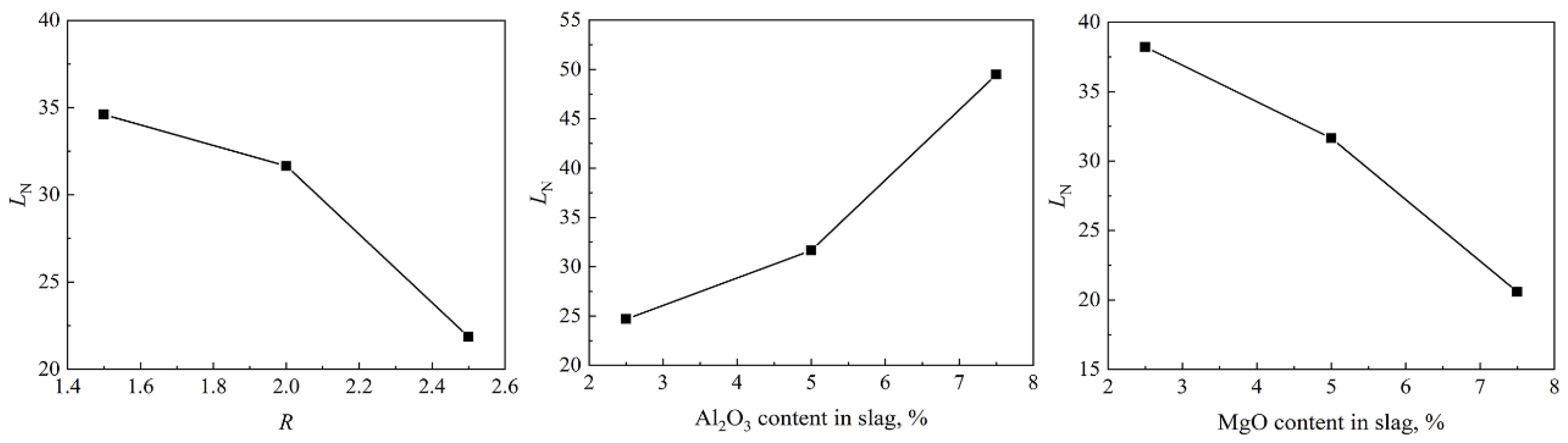
4.3. Effect of Slag Compositions on Equilibrium Distribution Ratio of Nitrogen
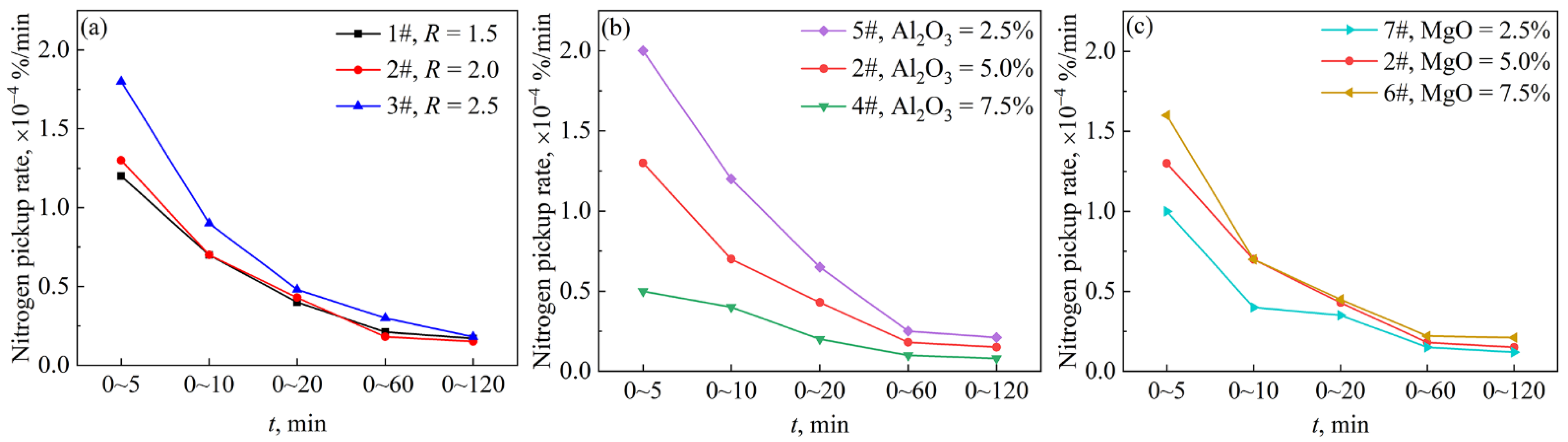
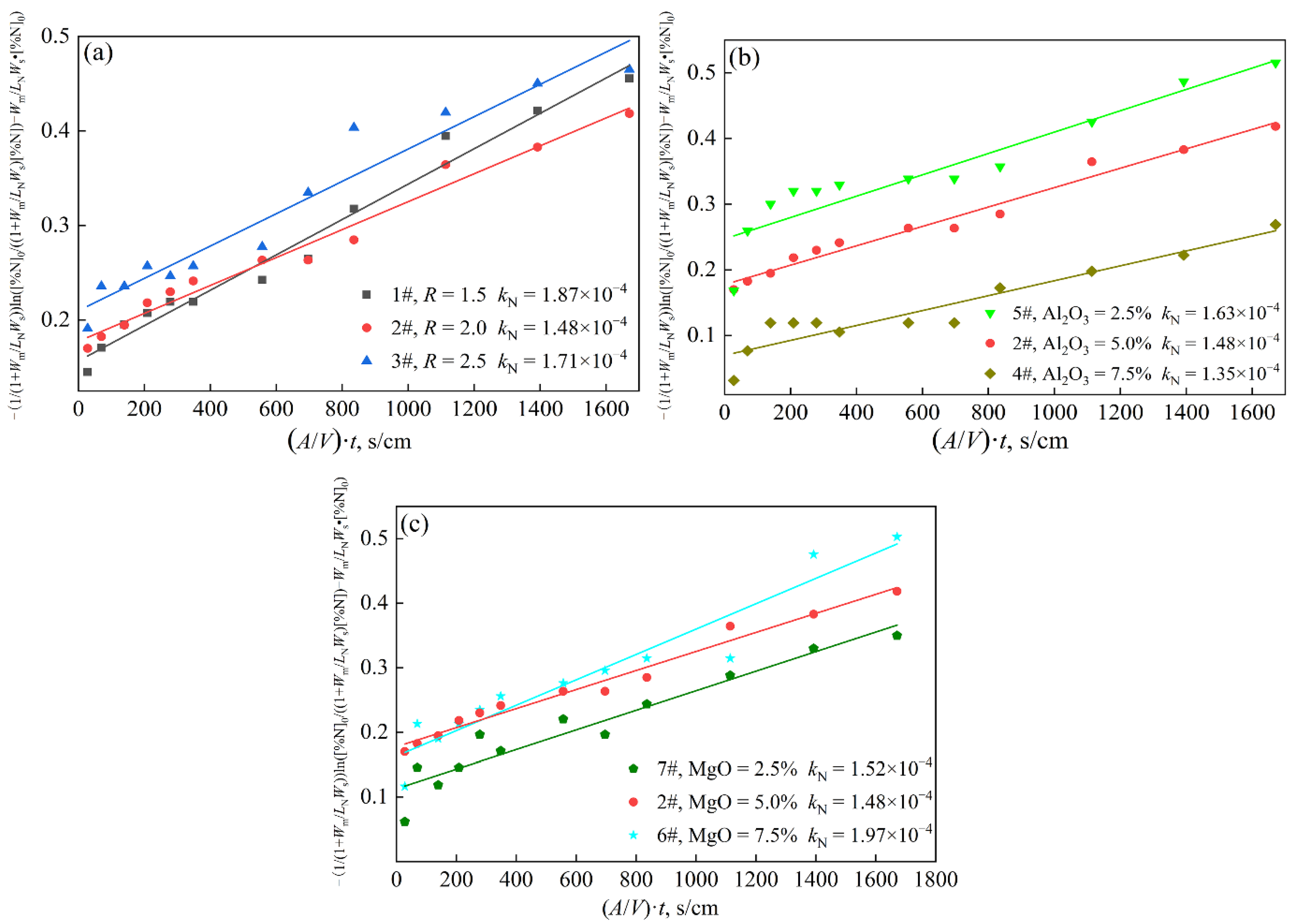
4.4. Effect of Slag Compositions on the Mass Transfer Coefficient of Nitrogen Pickup
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- With the increase in the slag basicity and the MgO content in slag, the nitrogen pickup amount and the nitrogen pickup rate of molten steel increase. The test with MgO = 7.5% had the highest nitrogen pickup rate and the highest nitrogen pickup mass transfer coefficient, which were 0.21 × 10−4%/min and 1.97 × 10−4 cm/s, respectively. With the increase in the Al2O3 content in slag, the nitrogen pickup amount of molten steel decreased and the nitrogen pickup rate decreased. The test with Al2O3 = 7.5% in slag has the lowest nitrogen pickup rate and the lowest nitrogen pickup mass transfer coefficient of 0.08 × 10−4%/min and 1.35 × 10−4 cm/s, respectively.
- (2)
- Increasing the foaming index of slag and reducing the optical basicity of slag will increase the nitrogen capacity of slag, which is conducive to hindering the nitrogen pickup of molten steel. The relationship between the slag optical basicity and nitrogen capacity can be expressed as: lgCN = −5.59lgΛ − 12.41.
- (3)
- The nitrogen equilibrium distribution ratio LN between slag and molten steel decreases with the increase in the basicity, increases with the increase in Al2O3, and decreases with the increase in MgO.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, R.; Wu, X.T.; Wei, G.S.; Tian, B.H. Development of green and intelligent technologies in electric arc furnace steelmaking processes. Iron Steel 2019, 54, 9–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.H.; Yao, C.L.; Zhu, H.C.; Pan, T. Technology development trend in electric arc furnace steelmaking. Iron Steel 2020, 55, 1–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Neuschütz, D.; Spirin, D. Nitrogen removal and arc voltage increase in EAF steelmaking by methane injection into the arc. Steel Res. Int. 2003, 74, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.S.; Zhu, R.; Dong, K.; Li, Z.Z.; Yang, L.Z.; Wu, X.T. Influence of bottom-blowing gas species on the nitrogen content in molten steel during the EAF steelmaking process. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2018, 45, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derda, W.; Siwka, J.; Nowosielski, C.Z. Controlling of the nitrogen content during EAF–technology and continuous casting of steel. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2008, 53, 523–529. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, G.; Irons, G.; Anghelina, D. New approach to nitrogen control in EAF steelmaking. In Proceedings of the 4th High Temperature Processing Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 6–7 February 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.W.; Hu, X.J.; Wang, P.D.; Li, Y. Effects of carbon, aluminum and silicon on the dissolution rate of nitrogen into molten iron. Chin. J. Eng. 2020, 42, 34–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.X.; Zhan, D.P.; Liu, X.; Huang, Q.Q.; Jiang, Z.H.; Zhang, H.S. Research on nitrogen absorption behavior of molten steel during submerged nitro-blowing process in EAF. J. Mater. Metall. 2020, 19, 265–269. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luz, A.P.; Tomba Martinez, A.G.; López, F.; Bonadia, P.; Pandolfelli, V.C. Slag foaming practice in the steelmaking process. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 8727–8741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Tian, B.H.; Wei, G.S. New process of nitrogen content change and control technology in EAF steelmaking process. Ind. Heat. 2020, 49, 19–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Le, K.X.; Dong, Y.C.; Wang, S.J.; Sun, W.; Mao, Y. Experimental study of foaming slag. J. Baotou Univ. Iron Steel Technol. 1999, 18, 256–259. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura, H.; Fruehan, R.J. Slag foaming in an electric arc furnace. ISIJ Int. 2009, 49, 1530–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Q.; Wu, H.J.; Wang, Z. Research progress on denitrification slag. Foundry Technol. 2018, 39, 2620–2624. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Bao, Y.P.; Cui, H.; Wu, H.J.; Liu, J.H. Nitrogen behavior in CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-MgO refining slags. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing 2010, 32, 175–178. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ling, T.Y.; Xu, K.D.; Jiang, G.C. Nitrogen stability in gas-slag and slag-metal systems. J. Shanghai Univ. Technol. 1991, 12, 162–169. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, C.X.; Gammal, T.E. Measurement of transport coefficients of nitrogen between slag and liquid steel. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing 1997, 19, 282–286. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka, R.; Ogawa, K.; Iritani, H.; Koyama, S. Denitrogenization mechanism from molten steel by flux treatment. ISIJ Int. 1992, 32, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shen, F.M. Physical Chemistry of Metallurgy, 1st ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 1–292. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.Y.; Hong, X.; Qiu, X.L.; Zhang, M.M.; Li, Q. Low fluoride foamed slag for manufacturing stainless steel in EAF. J. Iron Steel Res. 2007, 19, 16–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Min, D.J.; Fruehan, R.J. Nitrogen solution in BaO-B2O3 and CaO-B2O3 slags. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1990, 21, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Fruehan, R.J. Thermodynamics of nitrogen in CaO-SiO2-Al2O3 slags and its reaction with Fe-Csat. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1988, 19, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Fruehan, R.J. Slag foaming in bath smelting. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1991, 22, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.J.; Gan, L.; Jiao, L.; Lai, C.B. Accurate density calculation for molten slags in SiO2-Al2O3-CaO-MgO systems. ISIJ Int. 2017, 57, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.G.; Liao, N.B. Calculation model for surface tension of slag melt. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 1999, 6, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Bulter, J.A.V. The thermodynamics of the surfaces of solutions. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1932, 135, 348–375. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamoto, M.; Kiyose, A.; Tanaka, T.; Holappa, L.; Hämäläinen, M. Evaluation of the surface tension of ternary silicate melts containing Al2O3, CaO, FeO, MgO or MnO. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanao, M.; Tanaka, T.; Kawamoto, M.; Takatani, K. Evaluation of surface tension of molten slag in multi-component systems. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Song, Z.Y. Exploration of manufacture progress for reducing line pipe nitrogen content in electric furnace. Ind. Heat. 2019, 48, 14–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shahbazian, F.; Du, S.C.; Seetharaman, S. The effect of addition of Al2O3 on the viscosity of CaO-“FeO”-SiO2-CaF2 slags. ISIJ Int. 2002, 42, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, J.A.; Ingram, M.D.; Sommerville, I.D. Acid-base properties of molten oxides and metallurgical slags. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1978, 74, 1410–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, T.Y.; Xu, K.D.; Jiang, G.C. Thermodynamics of nitrogen in CaO-SiO2-Al2O3. J. Iron Steel Res. 1990, 2, 13–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.M.; Meng, Q.Y.; Fu, J. Removal of nitrogen from liquid metal. J. Iron Steel Res. 1995, 7, 73–79. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
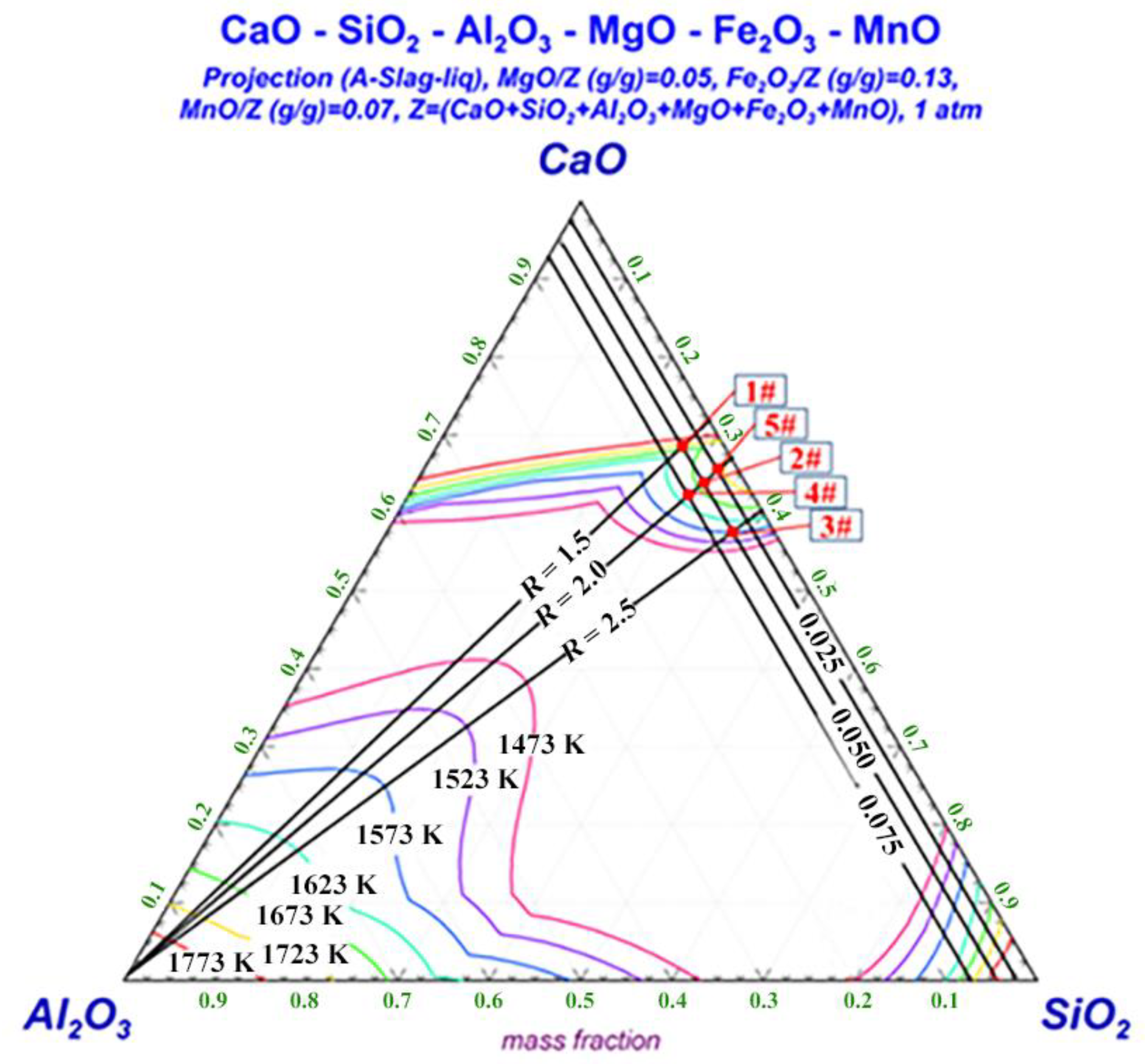


| No. | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | MnO | FeO | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 42.0% | 28.0% | 5.0% | 5.0% | 7.0% | 13.0% | 1.5 |
| 2# | 46.5% | 23.5% | 5.0% | 5.0% | 7.0% | 13.0% | 2.0 |
| 3# | 50.0% | 20.0% | 5.0% | 5.0% | 7.0% | 13.0% | 2.5 |
| 4# | 45.0% | 22.5% | 7.5% | 5.0% | 7.0% | 13.0% | 2.0 |
| 5# | 48.5% | 24.0% | 2.5% | 5.0% | 7.0% | 13.0% | 2.0 |
| 6# | 45.0% | 22.5% | 5.0% | 7.5% | 7.0% | 13.0% | 2.0 |
| 7# | 48.5% | 24.0% | 5.0% | 2.5% | 7.0% | 13.0% | 2.0 |
| No. | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | MnO | FeO | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 41.8% | 32.2% | 7.1% | 11.7% | 4.4% | 2.8% | 1.30 |
| 2# | 51.6% | 31.1% | 4.6% | 6.1% | 3.8% | 2.8% | 1.66 |
| 3# | 55.4% | 27.6% | 7.5% | 3.8% | 2.9% | 2.8% | 2.01 |
| 4# | 48.0% | 29.6% | 8.7% | 7.6% | 4.0% | 2.1% | 1.62 |
| 5# | 54.9% | 31.9% | 3.1% | 4.5% | 3.2% | 2.4% | 1.72 |
| 6# | 52.2% | 31.8% | 4.6% | 6.5% | 2.9% | 2.0% | 1.64 |
| 7# | 53.9% | 31.7% | 4.6% | 5.6% | 2.6% | 1.6% | 1.70 |
| No. | 1# | 2# | 3# | 4# | 5# | 6# | 7# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN, 10−12 | 1.85 | 1.59 | 1.39 | 1.66 | 1.49 | 1.53 | 1.62 |
| No. | 1# | 2# | 3# | 4# | 5# | 6# | 7# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μ, Pa∙s (1873 K) | 0.050 | 0.042 | 0.037 | 0.044 | 0.039 | 0.041 | 0.042 |
| ρ, 103 kg∙m−3 | 2.912 | 2.982 | 3.039 | 2.970 | 3.002 | 2.978 | 2.994 |
| σ, 10−3 N∙m−1 | 528.386 | 528.393 | 528.406 | 527.944 | 528.804 | 529.081 | 527.666 |
| Oxide | CaO | MgO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MnO | FeO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Λ | 1 | 0.92 | 0.48 | 0.68 | 0.95 | 0.93 |
| No. | 1# | 2# | 3# | 4# | 5# | 6# | 7# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Λ | 0.759 | 0.777 | 0.800 | 0.776 | 0.782 | 0.783 | 0.775 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, D.; Wang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H. Effect of Slag Compositions on Change Behavior of Nitrogen in Molten Steel. Metals 2022, 12, 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12050846
Zhan D, Wang J, Huang L, Zhang H. Effect of Slag Compositions on Change Behavior of Nitrogen in Molten Steel. Metals. 2022; 12(5):846. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12050846
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Dongping, Jiaxi Wang, Luoyi Huang, and Huishu Zhang. 2022. "Effect of Slag Compositions on Change Behavior of Nitrogen in Molten Steel" Metals 12, no. 5: 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12050846
APA StyleZhan, D., Wang, J., Huang, L., & Zhang, H. (2022). Effect of Slag Compositions on Change Behavior of Nitrogen in Molten Steel. Metals, 12(5), 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12050846






