Effect of Intercritical Deformation on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Quenching and Partitioning Low Carbon Multiphase High-Strength Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
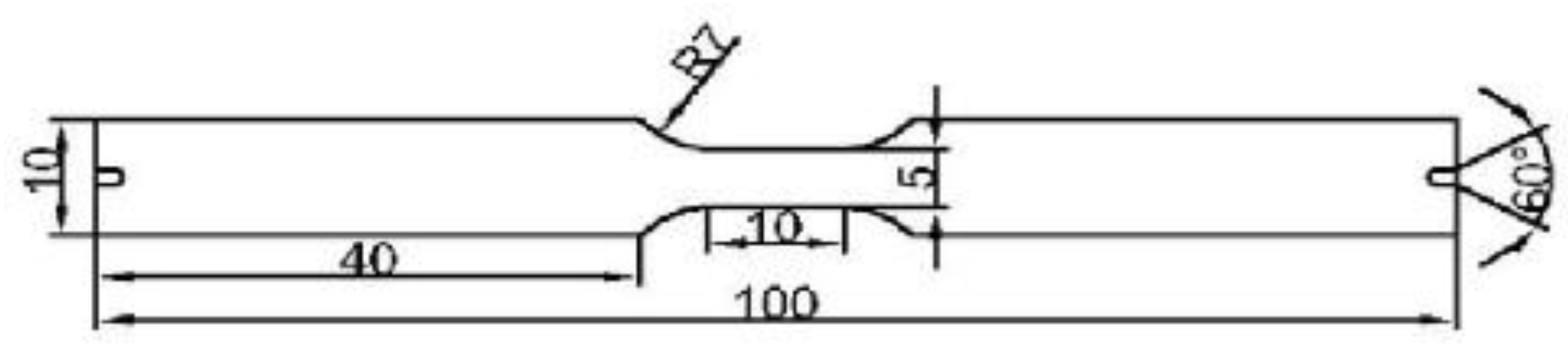
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
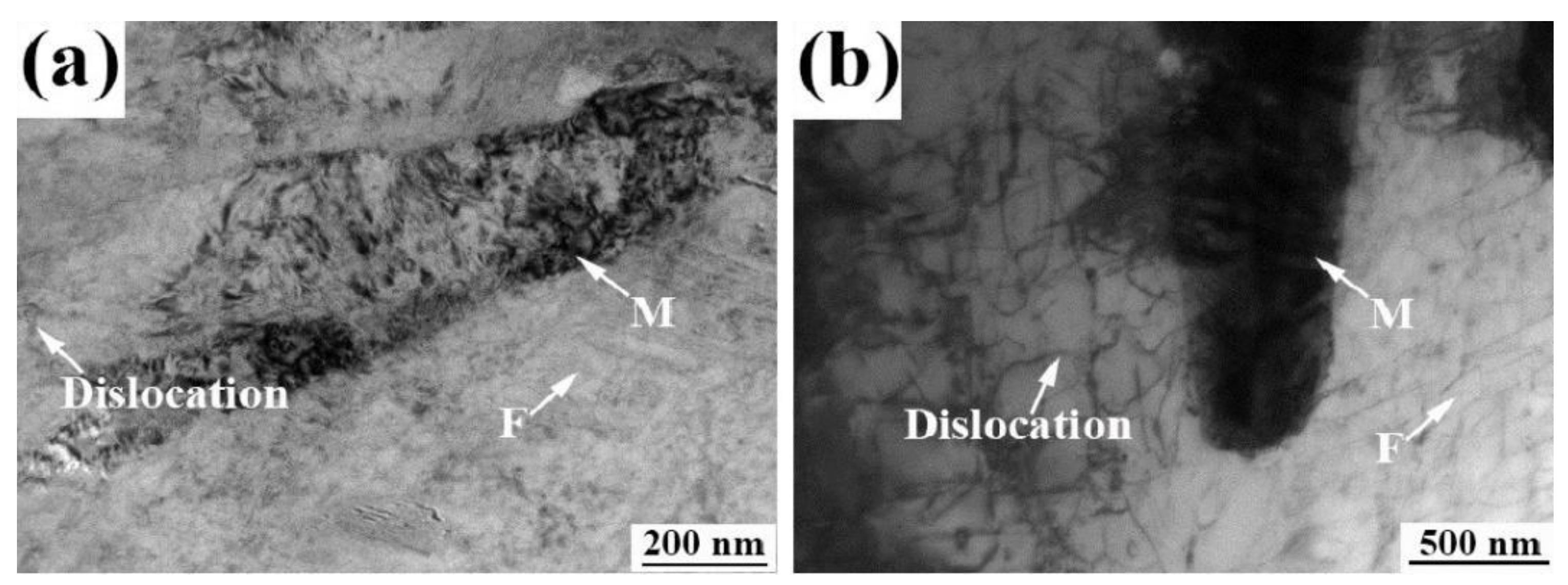
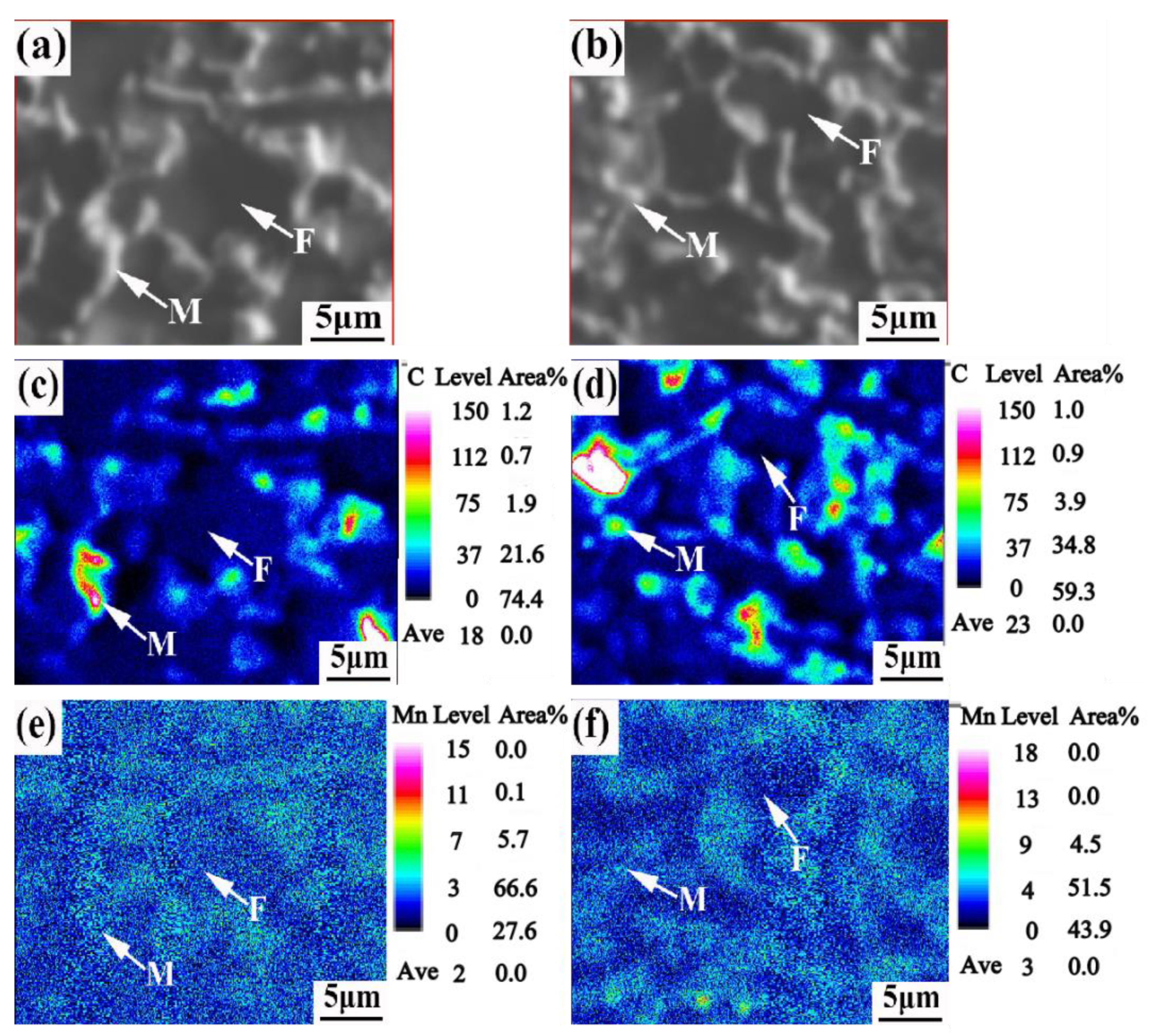
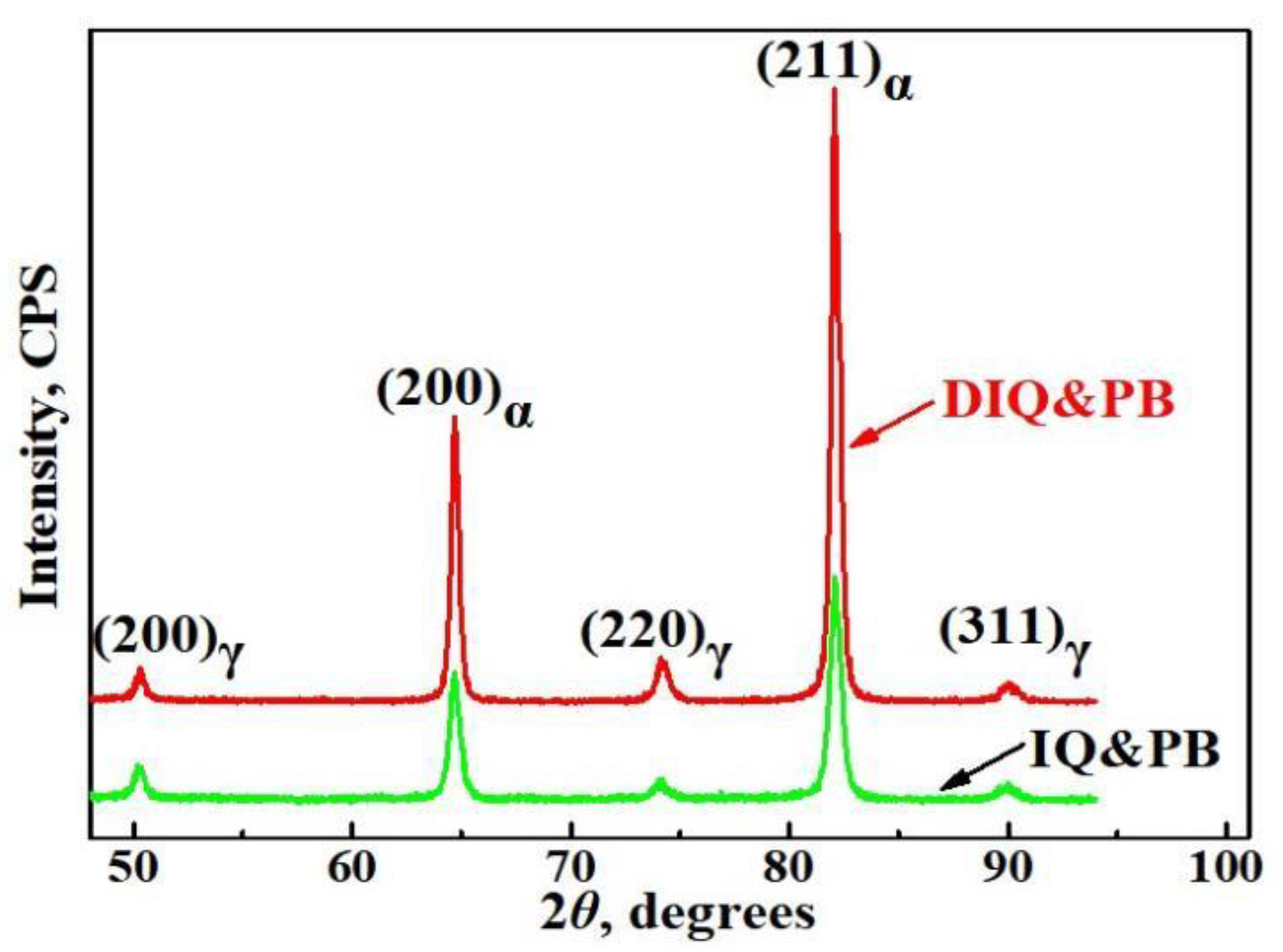
3.1. Dislocation Multiplication and C, Mn Partitioning Behavior
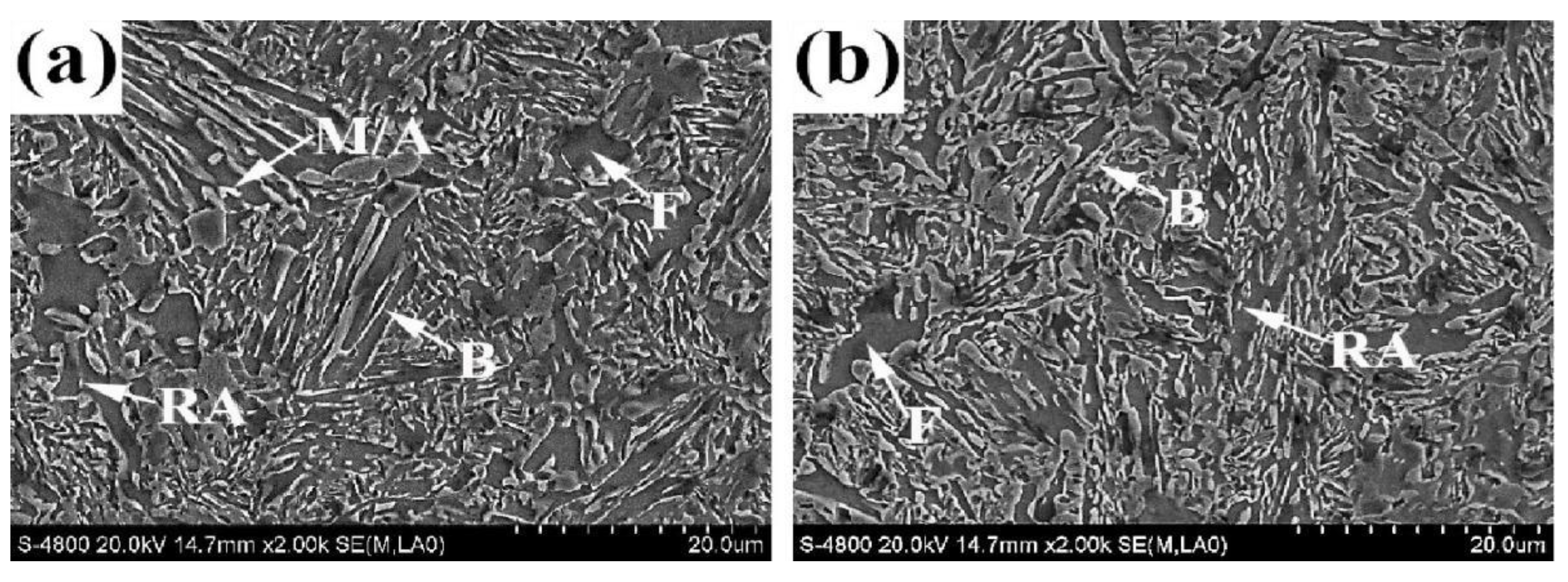
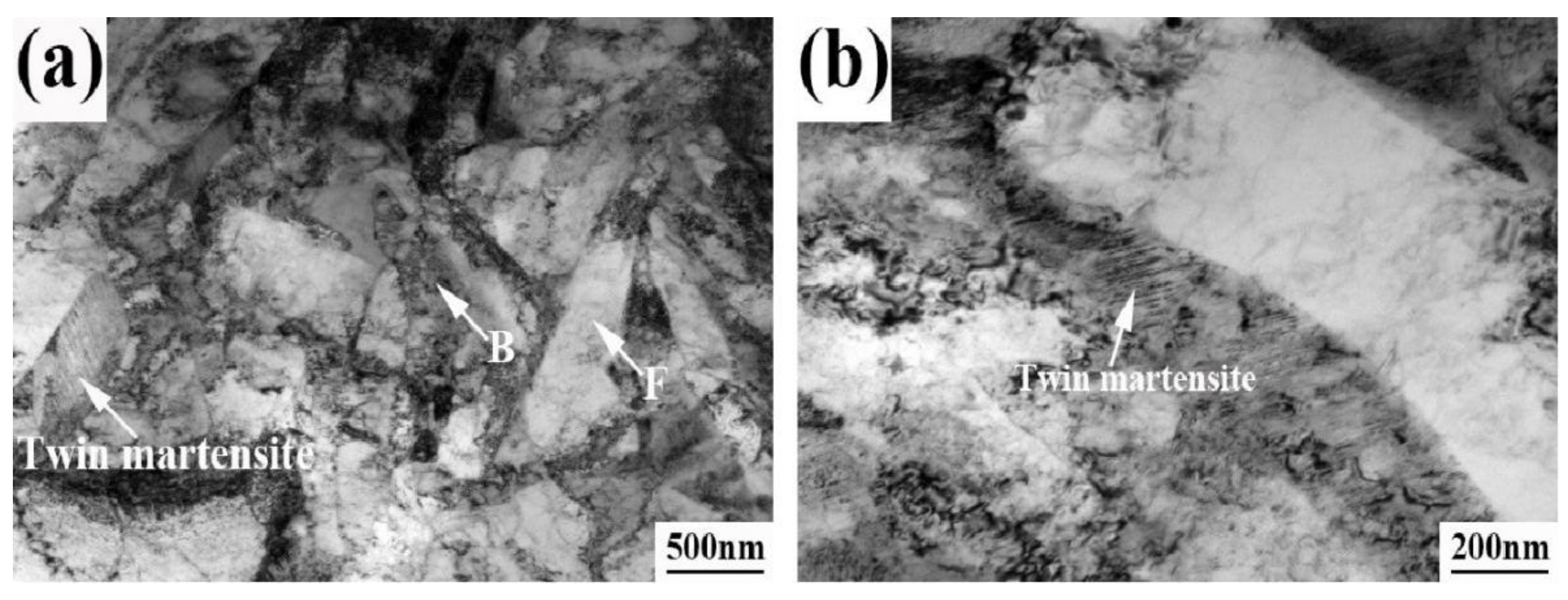
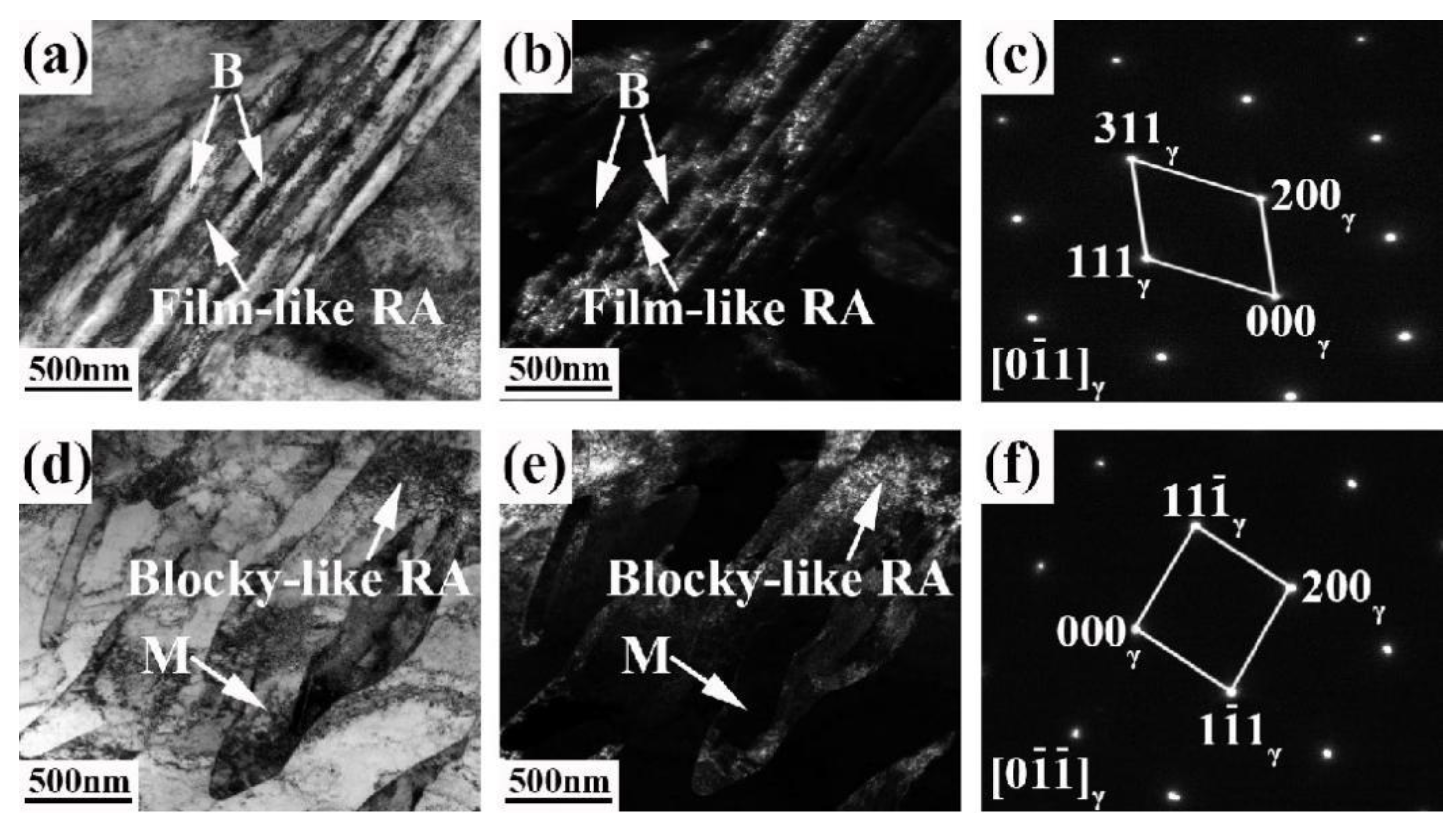
3.2. Microstructure and Retained Austenite
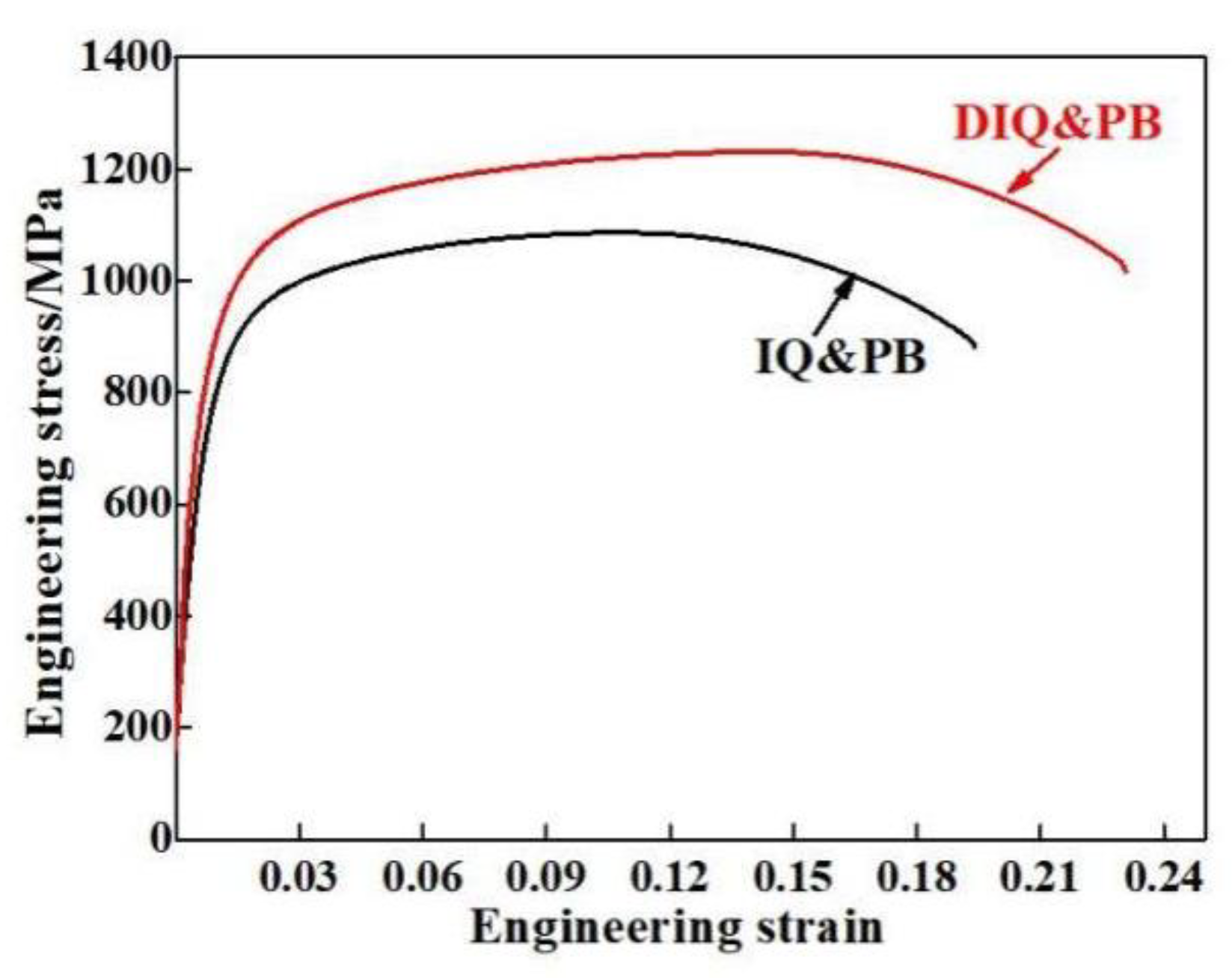
3.3. Tensile Behavior
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The intercritical compressive deformation promote the diffusion of C and Mn elements from α-phase to γ-phase. After compression deformation, the size of the bainite lath decreases from 16 μm to 8 μm and the morphology is dense and uniform. Block twin martensite distributes in the position of the adjacent ferrite.
- (2)
- The blocky and film-like retained austenite can be observed in IQ&PB and DIQ&PB samples. The film-like austenite is located between the bainite lath, the blocky austenite mainly distributes at ferrite/bainite interface. After compressive deformation treatment, the size of the blocky-retained austenite is obviously refined.
- (3)
- After the intercritical deformation, the ultimate tensile strength and elongation are improved, and the product of strength and elongation reaches 29,926.6 MPa·%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamada, A.; Khosravifard, A.; Porter, D.; Karjalainen, L.P. Physically based modeling and characterization of hot deformation behavior of twinning-induced plasticity steels bearing vanadium and niobium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 703, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, X.; Dong, C.; Zhao, X.Y.; Kang, S.X. Effect of bainitic transformation combined with hot forming on the microstructure and mechanical properties of bainite-martensite multiphase steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 731, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xiong, Z.; Yang, D.; Cheng, X. Heterogeneous quenching and partitioning from manganese-partitioned pearlite: Retained austenite modification and formability improvement. Acta Mater. 2022, 235, 118060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoel, R.H. Metallography and partitioning of alloying elements in dual-phase steels. Metallography 1984, 17, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, E.J.; Cho, L.; De Cooman, B.C. Kinetics of the partitioning of carbon and substitutional alloying elements during quenching and partitioning (Q&P) processing of medium Mn steel. Acta Mater. 2016, 107, 354–365. [Google Scholar]
- Maheswari, N.; Chowdhury, S.G.; Kumar, K.C.H.; Sankaran, S. Influence of alloying elements on the microstructure evolution and mechanical properties in quenched and partitioned steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 600, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhuang, B.; Duan, X.; Wu, Y.X.; Cai, Z.X. Element distribution and diffusion behavior in Q&P steel during partitioning. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2013, 20, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.J.; Chen, L.S.; Song, J.Y. Effect of alloy elements partitioning behavior on retained austenite and mechanical property in low carbon high strength steel. Acta Metall Sin. 2014, 50, 531–539. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.P.; Jin, X.J.; Dong, H.; Shi, J. Martensitic microstructural transformations from the hot stamping, quenching and partitioning process. Mater. Charact. 2011, 62, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Hodgson, P.D.; Wu, K.M. Acceleration of the super bainite transformation through a coarse austenite grain size. Mater. Lett. 2014, 122, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Mateo, C.; Caballero, F.G.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Development of hard bainite. ISIJ Int. 2003, 43, 1238–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.P.; Sun, H.; Liu, B.; Li, D.Z.; Sun, F.G.; Jin, X.J. An ultrahigh strength steel with ultrafine-grained microstructure produced through intercritical deformation and partitioning process. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhao, K. The combined effect of hot deformation plus quenching and partitioning treatment on martensite transformation of low carbon alloyed steel. Acta Metall Sin. 2015, 51, 913–919. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, F.; Yang, Z. Effects of high-temperature deformation and cooling process on the microstructure and mechanical properties of an ultrahigh-strength pearlite steel. Mater. Des. 2017, 114, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yan, S.; Yin, B.G.; Li, H.J.; Ran, X. Effects of temperature and strain rate on the dynamic recrystallization of a medium-high-carbon high-silicon bainitic steel during hot deformation. Vacuum 2018, 148, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.D.; Xu, Y.B.; Ponge, D.; Yang, X.L.; Hu, Z.P.; Peng, F.; Ju, X.W.; Wu, D.; Raabe, D. Effect of intercritical deformation on microstructure and mechanical properties of a low-silicon aluminum-added hot-rolled directly quenched and partitioned steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 656, 200–215. [Google Scholar]
- Basuki, A.; Aernoudt, E. Effect of deformation in the intercritical area on the grain refinement of retained austenite of 0.4 C trip steel. Scr. Mater. 1999, 40, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostash, O.P.; Kulyk, V.V.; Poznyakov, V.D.; Gaivorons’kyi, O.A.; Vira, V.V. Influence of the modes of heat treatment on the strength and cyclic crack-growth resistance of 65 G steel. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Li, X.L.; Guo, Y.; Kang, J.; Chen, D.; Wang, G.D. Microstructure and partitioning behavior characteristics in low carbon steels treated by hot-rolling direct quenching and dynamical partitioning processes. Mater. Charact. 2016, 121, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, N.D.; Chisholm, M.F.; Pennycook, S.J. Atomic-resolution chemical analysis using a scanning transmission electron microscope. Nature 1993, 366, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennycook, S.J.; David, B.; Williams, C.B. Transmission electron microscopy: A textbook for materials science. MIcrosc. Microanal. 2010, 16, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostka, A.; Tak, K.G.; Hellmig, R.J.; Estrin, Y.; Eggeler, G. On the contribution of carbides and micrograin boundaries to the creep strength of tempered martensite ferritic steels. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pešička, J.; Kužel, R.; Dronhofer, A.; Eggeler, G. The evolution of dislocation density during heat treatment and creep of tempered martensite ferritic steels. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 4847–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HajyAkbary, F.; Sietsma, J.; Petrov, R.H.; Miyamoto, G.; Furuhara, T.; Santofimia, M.J. A quantitative investigation of the effect of Mn segregation on microstructural properties of quenching and partitioning steels. Scr. Mater. 2017, 137, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, Z.Q.; Wang, X.M.; Li, X.C.; Yan, L.; Misra, R.D.K. The critical impact of intercritical deformation on variant pairing of bainite/martensite in dual-phase steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 771, 138668. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cen, Q.Y.; Wang, W.J.; Sun, X.Y. A novel process combining thermal deformation and intercritical annealing to enhance mechanical properties and avoid Lüders strain of Fe-0.2C-7Mn TRIP steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 839, 142849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.; Lawrence, B.; Boyd, J.D.; Pilkey, A.K. Effect of microstructure on retained austenite stability and work hardening of TRIP steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 4516–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.J.; Xiong, L.; Han, G.; Wang, X.L.; Shang, C.J. Thermal stability of retained austenite and properties of a multi-phase low alloy steel. Metals 2018, 8, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, W.Q.; Wang, X.D.; Hua, X.M.; Liu, H.B.; Jin, X.J. The austenite reversion and co-precipitation behavior of an ultra-low carbon medium manganese quenching-partitioning-tempering steel. Acta Mater. 2017, 146, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.G.; Miyamoto, G.; Kaneshita, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Toji, Y.; Furuhara, T. Growth model of austenite during reversion from martensite in Fe-2Mn-1.5Si -0.3C alloy: A transition in kinetics and morphology. Acta Mater. 2018, 154, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, H.; Tian, Y.; Chen, L. Effect of Intercritical Deformation on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Quenching and Partitioning Low Carbon Multiphase High-Strength Steel. Metals 2022, 12, 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122010
Yao Z, Zhang M, Zhang Y, Li H, Xu H, Tian Y, Chen L. Effect of Intercritical Deformation on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Quenching and Partitioning Low Carbon Multiphase High-Strength Steel. Metals. 2022; 12(12):2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122010
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Zhiqiang, Mingshan Zhang, Yuan Zhang, Hongbin Li, Haiwei Xu, Yaqiang Tian, and Liansheng Chen. 2022. "Effect of Intercritical Deformation on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Quenching and Partitioning Low Carbon Multiphase High-Strength Steel" Metals 12, no. 12: 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122010
APA StyleYao, Z., Zhang, M., Zhang, Y., Li, H., Xu, H., Tian, Y., & Chen, L. (2022). Effect of Intercritical Deformation on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Quenching and Partitioning Low Carbon Multiphase High-Strength Steel. Metals, 12(12), 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122010





