Abstract
Evaluate the quality of finishing and degree of contamination before and after handling and surface treatment of titanium (Ti) orthodontic mini-implants (OMIs). A scanning electron microscope (SEM) study on ninety-six titanium OMIs was done. Energy-Dispersive X-ray Analysis (EDX) identified the present particles on manufactured OMIs surfaces. Then, OMIs were manipulated with gauze (dry sterile, soaked in chlorhexidine) and gloves (latex, nitrile) to evaluate the contamination of these handling materials. Finally, OMIs underwent surface treatments and were placed in bone to observe the contaminants they released. Roughness (Ra) and wettability with contact angle parameter (CA) were measured on these treated OMIs. Machined OMIs presented surface irregularities and were contaminated with manufacturing-process particles (carbon, plastic Polyvinyl Chloride PVC, aluminum). Hand-manipulated OMIs were also contaminated by the handling materials. OMIs surface characteristics were as follows: acid-etched (Ra ≈ 1.3 μm, CA ≈ 66°), machined (Ra ≈ 0.3 μm, CA ≈ 68°), SB (Ra ≈ 3.3 μm, CA ≈ 78°), and SBAO (Ra ≈ 3.1 μm, CA ≈ 92°). Bone was contaminated by OMIs surface defects and extra particles. Manufactured OMIs have surface contaminants that increase with clinical handling. Surface treatments (SBAO, a combination of sandblasting and anodic oxidation) increase the roughness and contact angle, which play an important role in osseointegration. Surface-treated OMIs leave titanium particles in the bone during their insertion-removal. The use of a gauze soaked in chlorhexidine is recommended when handling OMIs. Further investigations would be interesting to study more variables and confirm the present results.
1. Introduction
Since Costa, Raffaini and Melsen, Kanomi, and Park popularized the use of titanium mini-implants for orthodontic anchorage (OMIs), a new era of control of unwanted secondary tooth movement has begun [1,2,3]. The main advantages of these devices include ease of placement and removal by the clinician, less patient collaboration, short loading time, as well as low cost when compared to the classical dental implants [3].
Mini-implants of titanium alloy are commercially available in different packages: some are provided in blisters, while others come in plastic bags or metal boxes [4]. In several cases, the handling of OMIs before being inserted in the bone is inevitable, such as when presented in a bag, fitted on the contra-angle piece adapter, or when changing its position. In fact, sometimes, immediate OMI relocation might be needed because of its proximity to anatomical structures, persistent pain, and lack of primary stability [5,6]. These situations might cause or increase OMI surface contamination. There are several research studies concerning OMIs surface characteristics but less examine the contamination of the OMI surface when manipulated [7,8,9].
Additionally, clear information about the finishing of screw surface is lacking. Finishing is defined as the process of removing impurities or unwanted elements from a substance. Surface finishing can be appreciated with Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Analysis (EDX). SEM produces images of a sample by scanning the surface with a focused beam of electrons. The electrons interact with atoms in the sample, producing various signals that contain information about the samples’ surface topography. Ti6Al4V is the most widely used titanium alloy in OMIs because of its higher strength and clinical effectiveness compared to pure titanium [10,11]. However, the disadvantage of Ti6Al4V is its lower degree of osseointegration and greater susceptibility to corrosion in vivo, both of which may hinder stability [12]. EDX analyzes the machine-treated titanium alloy and relates its surface topography to its composition. To increase the bone/mini-implant contact, efforts are carried out to treat OMIs threads [13]. For instance, sandblasting (alumina projecting particles) and/or anodic oxidation (solution of acid agents) are two surface treatment modalities that could be done to increase the screw-bone contact surface [14,15,16]. However, these surface treatments might also increase OMIs contamination and modify their finishing quality. Again, there are few available studies evoking these OMI modifications.
The OMI surface characteristics, including its chemistry, wettability, roughness, charge, energy, zero potential, crystallinity, the nature and thickness of its oxide layer, as well as surface residual stresses, influence the osseointegration and microbiology behavior. Of all these parameters, the ones that play the most important role in improving osseointegration are roughness and wettability. Others, such as residual stresses, or surface nano-deformation, help determine the OMIs mechanical properties. Optimization of these properties is the key to success of titanium dental implant [17,18,19,20,21,22].
The aim of this SEM/EDX study is to evaluate the quality of finishing, the contamination of OMIs before and after handling, the influence of different surface treatments on roughness and wettability, and the bone contamination by surface-treated titanium OMIs.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sample
Four brands of OMIs (diameter 1.4–1.6 mm, length 6–8 mm) were used in this study: Dual Top® (Jeil Medical Corp, Seoul, Korea), Spider Screw® (HDC, Sarcedo, Italy), Absoanchor® (Dentos Inc., Daegu, Korea) and Microdent® (Implant Microdent System S.L., Barcelona, Spain).
In total, 96 mini-implants were observed with SEM and EDX (Quanta 200, FEI, Leica, Hillsboro, OR, USA) to identify surface contaminants, determine OMIs chemical composition, and spot surface irregularities that can potentially chip during OMIs insertion/removal [23].
2.2. Study Design
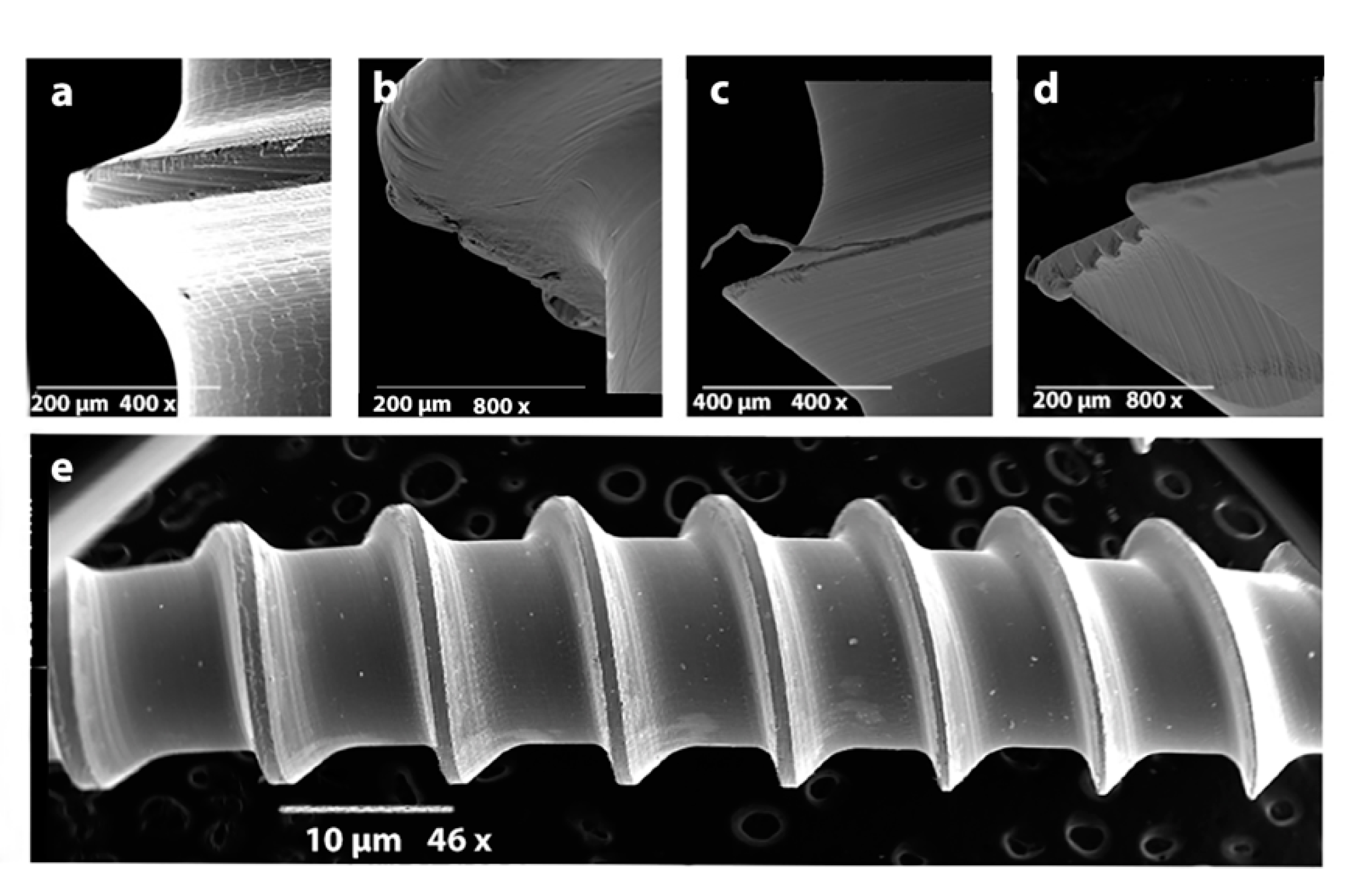
In the first part of the study, two OMIs per brand (n = 8) were observed under SEM to see the finishing of their manufacture-made surface. OMIs were handled with a tweezer from their heads to avoid any contamination of the body. Metal irregularities and other identifiable particles were visually counted in a descriptive statistic on the region of interest (ROI), which was considered as the first 6 mm threads of each OMI, starting from the tip (Figure 1a–d). These are the 6 mm that are inserted into the bone when any OMI is placed.
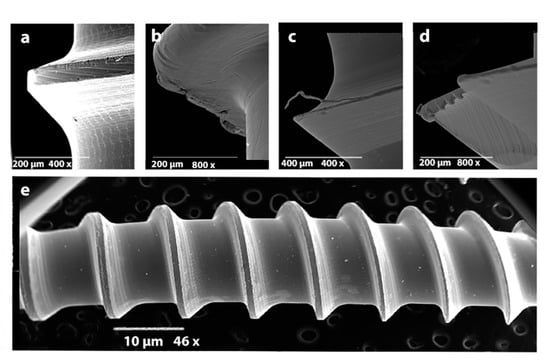
Figure 1.
(a–d): Surface irregularities and metal spikes as viewed by the Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM). From left to right: (a) Dual Top, (b) Spider®, (c) Microdent, (d) Absoanchor®. (e): Count of contaminating particles (white dots) on the body of the visible side of an orthodontic mini-implant (OMI).
In the second part, twelve OMIs per brand were used (n = 48). Every 4 OMIs (1 per brand) were handled with 4 different materials: dry sterile gauze, sterile gauze soaked in chlorhexidine 0.12%, nitrile, and latex gloves. The handling materials were also observed under SEM to identify their components and contaminating particles counted at the same ROI of the screw body shaft of the visible side of each screw (Figure 1e). EDX evaluated the composition of the contaminating particles on OMIs surfaces.
In the third part of this study, OMIs underwent two types of surface treatment: sandblasting (SB) (3 of each brand, n = 12) and a combination of sandblasting and anodic oxidation (SBAO) (3 of each brand, n = 12). Sandblasting was done by projecting 50-µm spherical alumina particles at 20 psi for 1 min with a distance of 1 cm and an angle of 45° between the screw surface and blasting tip [24,25]. Then, sandblasted OMIs were sonicated during 5 min in acetone and left to dry. Anodic oxidation involved the use of 0.1 mM/L H2SO4 at 5 V during 30 min [24].
All the surface-treated OMIs, plus one untreated OMI per brand (as control), were then inserted (at 8 mm depth, 20 Ncm torque), in vitro, into a cow rib cut in half bi-cortically [23,26]. Then, OMIs were removed. Both bone halves and the OMIs were observed under SEM and analyzed by EDX to check for potential chipped metal pieces and other contaminants from the OMIs in the cortical bone.
In the fourth part, roughness was determined by means of an optical interference profilometer (Wyko NT1100, Veeco, Tucson, AZ, USA). A Gaussian filter was used to separate waviness and shape from the roughness of the surface. Based on ISO 11562:1996 standard [14], the samples (n = 16) analyzed were as-machined (control, n = 4), anodic oxidation (AO, n = 4), sandblasted (SB, n = 4), and sandblasted and anodic oxidation (SBAO, n = 4). Measurements were made on four different surfaces after the treatments per surface treatment to characterize the amplitude and spacing roughness parameters (Sa, Sm, and SIA). Average roughness (Sa) is the average surface roughness for the length of the measurement performed; the spacing parameter is Sm (the mean spacing), and SIA is the hybrid parameter index area (real surface area/nominal surface area) [27,28,29,30,31,32].
Static contact angle (CA) was assessed using the sessile drop method. Ultrapure distilled water (Millipore) 3–6 µL drops were generated with a micrometric syringe and deposited on the substrate surface. Syringe and sample were placed inside a customized poly-methyl methacrylate (PMMA) environmental chamber, with two optical glass windows, to saturate humidity during the experiments. Tests were made at 25 °C. Wettability studies were performed with a contact angle video-based system (Contact Angle System OCA15plus, Dataphysics, Germany) and analyzed with the CA20 software 3.0 (Dataphysics, Fildestadt, Germany) [28,33,34,35].
2.3. Statistical Analyses
Statgraphics 2017 (Statpoint Technologies, Inc., The Plains, Fauquier County, VA, USA) software was used for the statistical analyses. Multivariate ANOVA evaluated the amount of particles left by the manipulation materials. Paired data analysis for small samples (Wilcoxon test) was performed to compare the number of aluminum oxide particles remaining on the OMIs after SB and SBAO protocols. Statistical significance was noted when p values were lower than 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Part 1
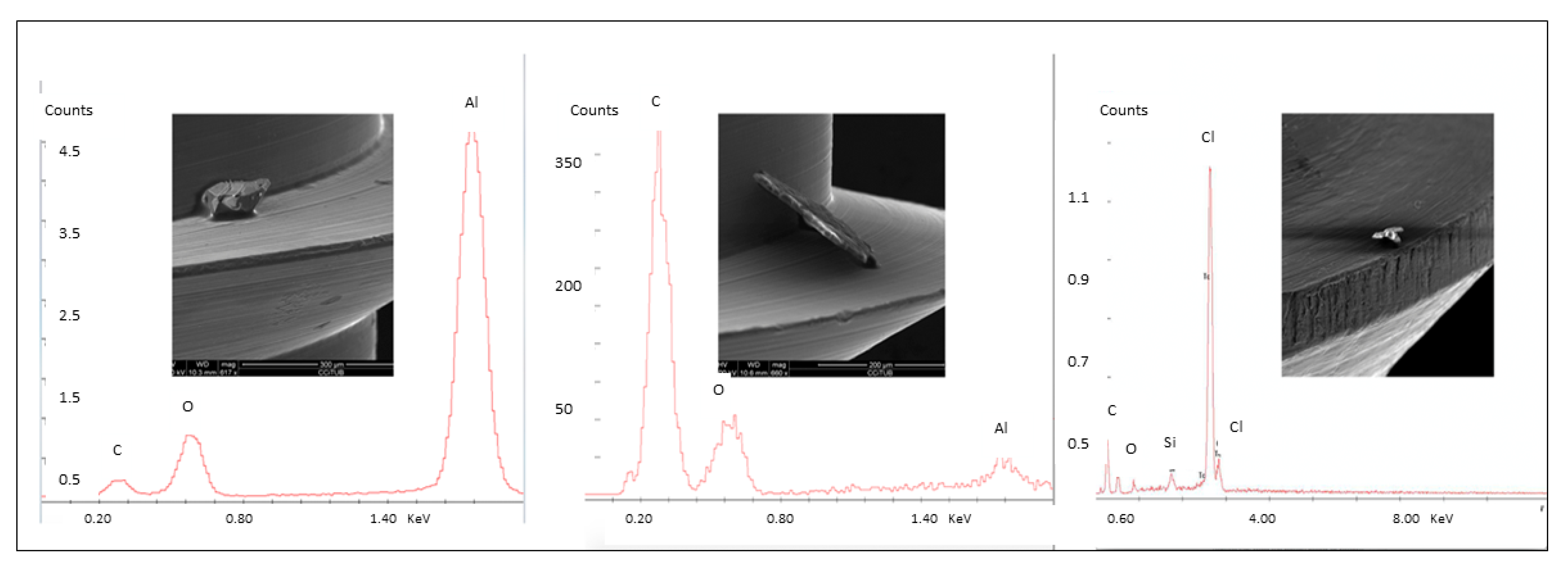
OMIs showed surface irregularities (ridges and grooves) and small metal spikes from the manufacturing process. Microdent and Spider® presented the greatest surface irregularities, followed by Absoanchor® and Dual Top. The latter was shown to have the smoothest surface with the least irregularities (Figure 1 a–d). Small plastic (PVC = polyvinyl chloride), aluminum (Al), and carbon (C) particles have also been identified on the non-manipulated machined OMIs surfaces (Figure 2).
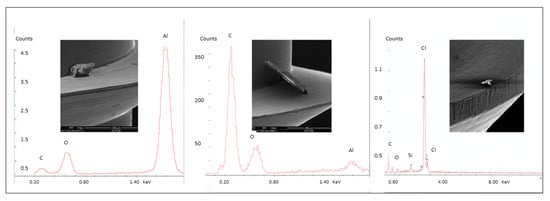
Figure 2.
Surface contamination of the machined OMIs. From left to right: aluminum particle (Al), carbon particle (C), and plastic particle (Polyvinyl Chloride PVC).
3.2. Part 2
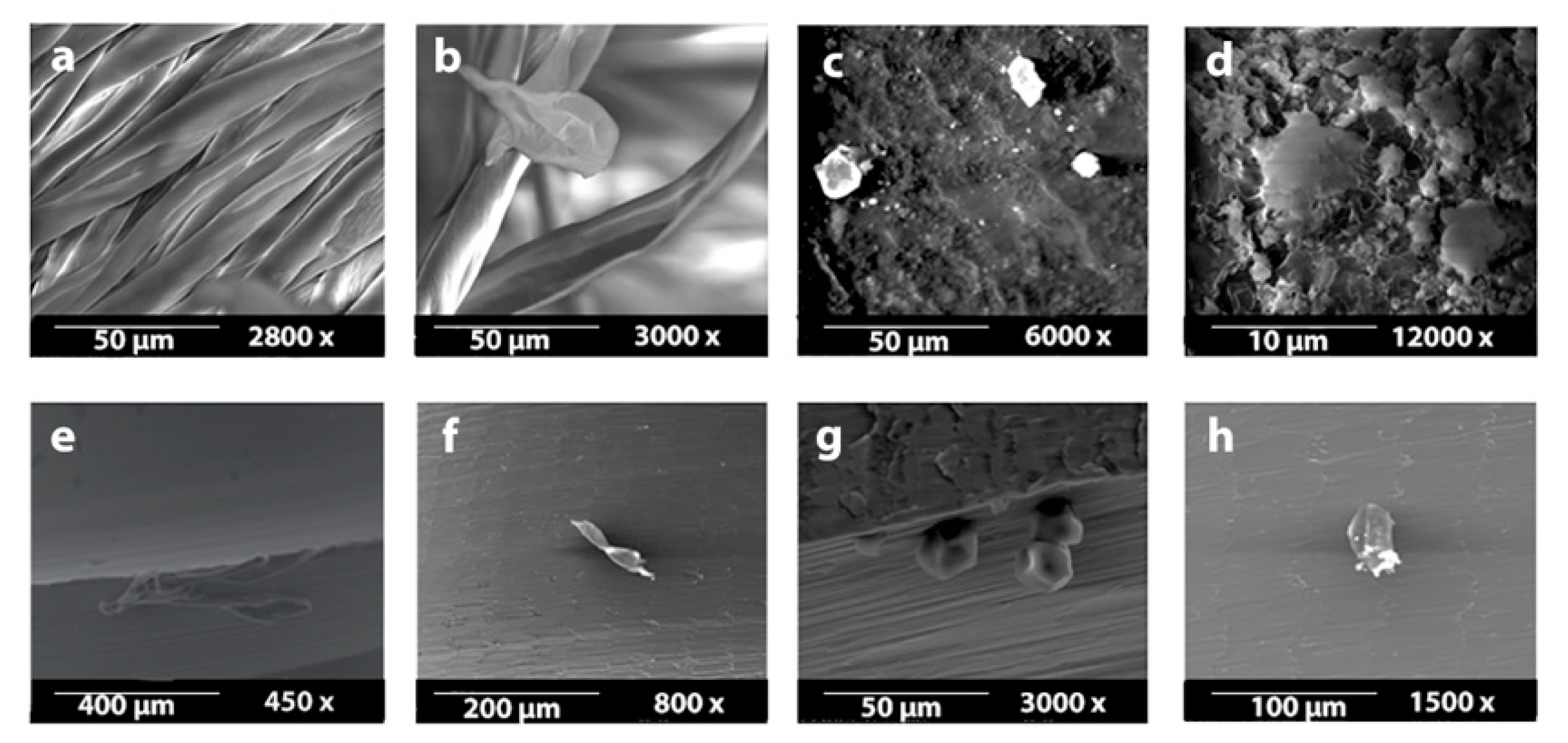
The multivariate ANOVA showed significant differences between the manipulation materials, mainly between the gauzes and the gloves (p = 0.000) (Table 1). All of the manipulated OMIs were contaminated by the material they were touched with (Figure 3).

Table 1.
Comparison of number of particles left on the region of interest (ROI) of OMIs by each of the gauzes (dry or soaked in chlorhexidine) on one hand, and the other handling materials (gauze, nitrile and latex) on the other hand. Note significant differences between the number of particles left by the nitrile glove when compared with the gauze.
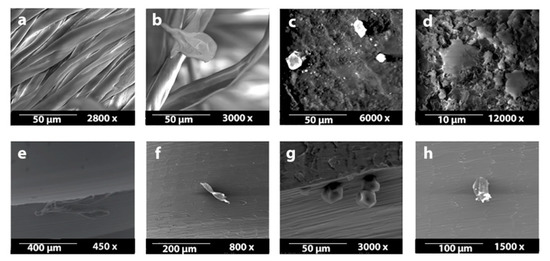
Figure 3.
(a–d): Handling materials seen under SEM (first line) and (e–h): remaining particles on the touched OMIs respectively (second line). From left to right: (a,e): sterile gauze soaked in chlorhexidine, (b,f): dry sterile gauze, (c,g): nitrile glove, (d,h): latex glove.
Gauze soaked in chlorhexidine was the least contaminating material, followed by dry sterile gauze (p = 0.014), then by latex (p = 0.000) and finally by nitrile gloves (p = 0.000) (Table 1). There was no significant difference between the OMI brand and the degree of contamination (p = 0.44). However, the most irregular screws showed the greatest contamination, especially with gauze manipulation (Table 2).

Table 2.
Number of particles left by the handling materials on the ROI of each of the OMIs brands. Note the elevated number of particles left by the nitrile glove when compared with the other materials.
3.3. Part 3
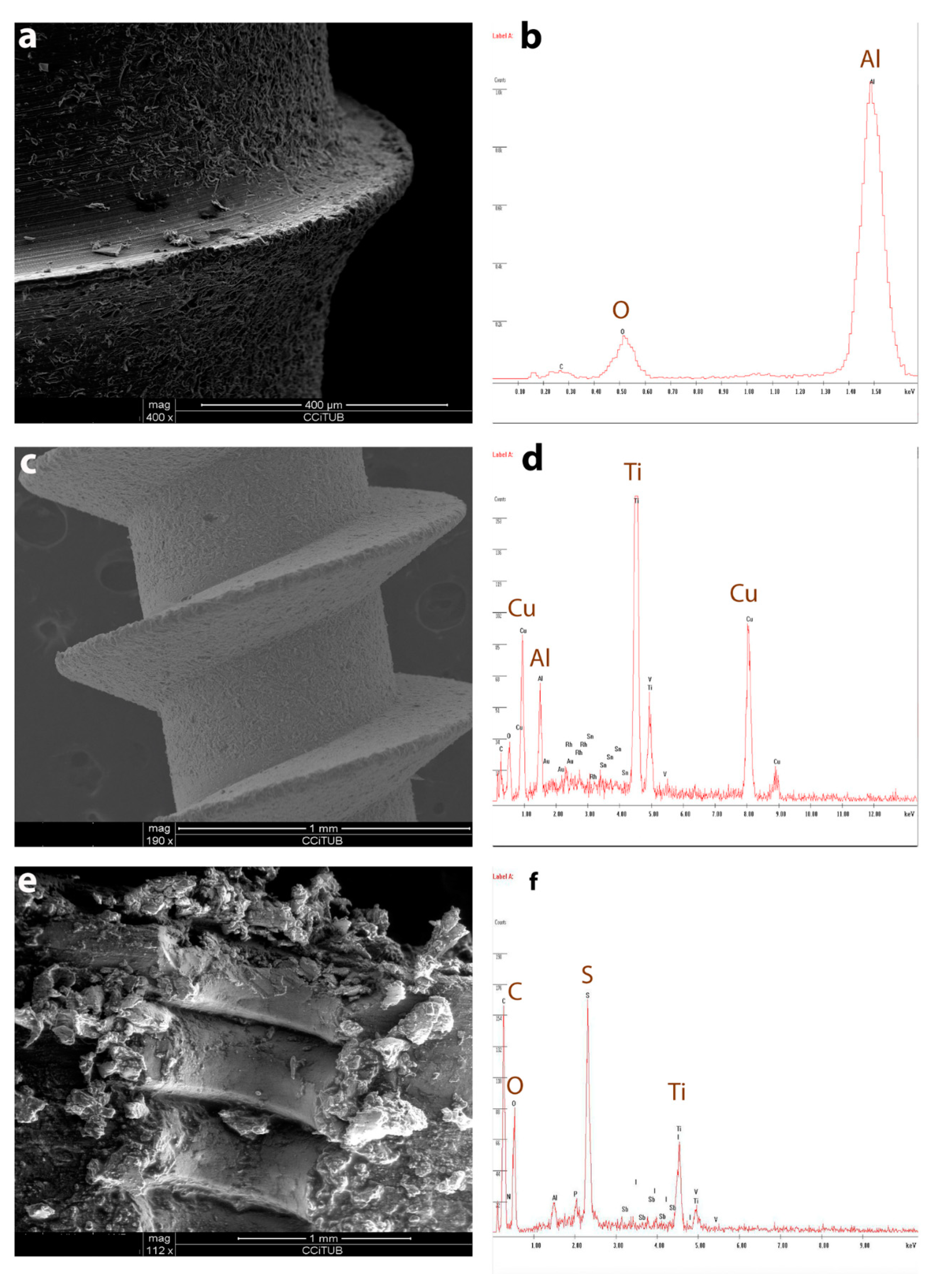
SEM showed that SB treatment contaminated OMIs surfaces with aluminum oxide particles, even after vibration in acetone, leaving the screw surface with more irregularities (Figure 4a). The EDX graph identified aluminum oxide on the sandblasted OMIs (Figure 4b).
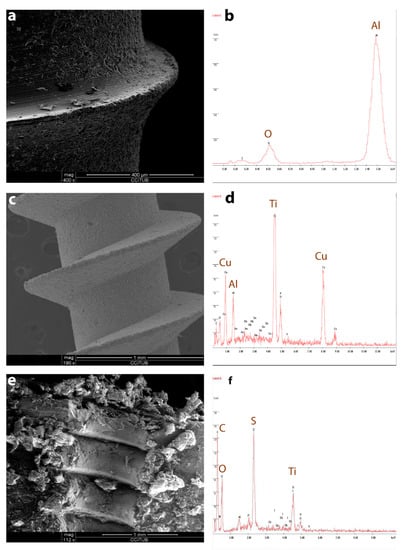
Figure 4.
(a,b): Sandblasted OMI: (a). SEM image of OMI surface, (b). Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Analysis (EDX) identification of aluminum oxide on the sandblasted OMI. (c,d): Sandblasting and anodic oxidation (SBAO) mini-implant: (c). SEM image of OMI surface, (d). EDX identification of aluminum oxide and copper molecules on the SBAO mini-implant. (e,f): Cow bone section (cortical and medullar) after OMI removal: (e). SEM image of bone surface, (f). EDX identification of titanium alloy and aluminum oxide, copper, and sulfur particles on the bone surface.
SBAO also left OMIs surfaces with similar but smaller irregularities (Figure 4c). SBAO OMIs were significantly less contaminated with aluminum oxide particles, but they had copper and sulfur particles added to their surface composition, independently of the OMIs brands (Figure 4d,f).
When OMIs were removed from the cow bone and seen under SEM, some of the irregular particles initially identified were missing from the screw surfaces and expected to be seen in the bone (Figure 1c: Microdent). However, titanium particles were not visually detected in the observed bone halves (cortical and medullar) but were identified by EDX (Figure 4e,f). Moreover, particles of aluminum oxide were found in the bone at the level of the previously inserted sandblasted OMIs (Figure 4f).
3.4. Part 4
Roughness and chemico-physical characteristics of the OMIs surfaces are the most relevant factors in improving their osseointegration. For this reason, surface topography was evaluated here by means of 3D interferometric microscope. Values obtained for surface roughness are shown in Table 3. SBAO and SB surfaces were significantly rougher than AO and Control surfaces (Table 3). AO surfaces were significantly rougher than Control surfaces according to the findings by other authors [34,35,36]. SB and SBAO surfaces did not have significantly different values of roughness.

Table 3.
Roughness and contact angles of the different mini-implants in the four OMIs groups: as-machined (Control), anodic-oxidation (AO), sandblasting (SB), and sandblasting and anodic-oxidation (SBAO). The results with the same symbol (* and &) do not present significant statistical differences (p < 0.05).
Table 3 also shows the contact angles obtained; all samples presented a hydrophobic character. However, the SB treatment increased the contact angle, thus decreasing the surface wettability [16,17].
4. Discussion
The present study aimed to evaluate the surface finishing and contamination of OMIs, on one hand, and the influence of the different surface treatments on the roughness and wettability on the other. This way, both clinicians and manufacturers could better handle OMIs and improve their success rate.
OMIs finishing varies considerably between manufacturers [36]. Surface irregularities can result from machining process, polishing defects, crystal growth deposits, and areas of detritus. Carbon particles encountered on OMIs surfaces are remainders of the grain refinement of titanium alloys [37]. The greatest amount of surface irregularities and detritus was found on the tips [38]. SEM is a useful tool to evaluate the finishing quality of manufactured OMIs [36]. However, it is difficult to establish a classification of the degree of irregularity or the quality of finishing of OMIs. Moreover, it is reported that OMIs might leave impurities or titanium particles in the bone after their removal [39] and that stress corrosion cracks might occur [40]. Therefore, SEM/EDX has been used in this study to detect the irregularities and contaminants that could have been released in the bone during OMIs placement/removal procedure. Consequently, both quality of finishing and potentially unhealthy effects of OMIs should be taken into consideration when used.
Manipulation of the OMIs simulated some situations when OMIs are touched before being placed in the bone. In fact, a significant percentage of OMIs are relocated because the orthodontic mechanics require screw repositioning on the arch [41,42]. Moreover, in some cases, OMIs packaging (small plastic bag) forces the clinician to handle the OMIs in order to fit it to the screwdriver adapter. Even though, nowadays, OMIs tend to be packaged in sterile boxes with only the head available to hold, the most appropriate way to handle OMIs is still not well-documented. Using gauze, latex and nitrile gloves, and even tweezers are the most conventional procedures in handling OMIs before their insertion or re-insertion. Latex use is limited because of the patients’ allergy to its components. Estimates of the prevalence of latex sensitivity vary from less than 1% to 6% of the general population [43,44]. However, due to repeated exposure to latex products, latex protein sensitivity is increasing [45]. This could justify the use of different glove material such as nitrile. In this study, it was demonstrated that both latex and nitrile are contaminating materials susceptible to leave behind some of their particles on the OMI surface that would be transmitted to the receiver bone site. Therefore, it would be recommended that even the chairside assistant holds the OMI with a different material (tweezer or gauze) when handing it to the practitioner. Hygroscopic chlorhexidine solution in the gauze avoids releasing fibers and other particles, as demonstrated in the present study to be the least contaminating material to hold the OMI (Table 1, p ≤ 0.014). Nevertheless, the quality of surface finishing plays an important role in avoiding the hooking of gauze fibers on the OMIs. Therefore, it could be recommended to use OMIs provided in a blister that allows the insertion of the OMI head into the handle adapter without any manual contact.
In order to increase strength and fatigue resistance of commercially pure titanium during mini-implant placement and removal, aluminum and vanadium have been added to the alloy [46]. However, this alloy may undergo corrosion in the oral environment due to its low corrosion resistance. Titanium, aluminum, and vanadium ions can be released to local and remote tissues and have been associated with side effects in the human body, particularly aluminum and vanadium [46]. Afterwards, SBAO manipulation copper and sulfurs particles were released, too, which probably could be due to the anodic-oxidation surface treatment. In order to simulate a clinical situation, OMIs with surface treatment, done to increase secondary stability [47], were inserted into cow bone of 0.5 to 1 mm cortical thickness, which is similar to the buccal cortical thickness in some anatomic regions of the human maxilla and mandible [48]. SEM observations showed that when OMIs were removed from the bone, their metal surfaces were missing metal spikes [38,40]. Even though, in some cases, the metal spikes were missing from the inserted OMIs after being removed from bone, the inability to see them in the bone halves could be due to the fact that they were pushed under a deeper bone layer while screwing the OMI. This was supported by EDX, which identified particles of titanium alloy and of aluminum from surface-treated OMIs that were released into the bone through the process of their placement and removal. Although the surface-treated OMIs are still not proven to induce bone contamination (chipping of titanium) or even local or systemic reactions in the host, caution might be needed when placing OMIs with poor finishing or surface treatment in vivo.
The other aspect of surface treatment, here studied, concerns the treated OMI-bone contact surface. The increase in roughness obtained by sandblasting and anodic oxidation increases the specific Ti surface; i.e., there is a greater surface in contact with the physiological environment, and as a consequence, there is a greater area of bone growth. The increase in roughness is mainly due to sandblasting and not to anodic oxidation, as can be seen from the results in Table 3. The anodic oxidation causes a slight increase in roughness, it is as a micro roughness in front of the macro roughness of the alumina sandblasting [33,34]. The differences between Control, AO with SB, and SBAO present significant statistical differences p < 0.005. There are no significant differences between Control and AO and between SB and SBAO. Results from in vitro studies suggested a positive correlation between surface roughness, cellular attachment, and osteoblast-like cell activity, being the blasting projection by abrasive particles (Al2O3) the one with better results [10,49,50,51]. The blasting process presents the possibility to optimize roughness. This roughness control by parameters of blasting is due to the nature and size of the abrasive particles, the projection pressure, and the distance between the gun and implant, which allow the adjustment of the desired roughness [50,51]. Furthermore, changes in roughness correlate with selective protein adsorption, collagen synthesis, and chondrocytes maturation, which all have a significant influence on OMIs osseointegration [52,53]. In a majority of those implants, the microrough surfaces are obtained by grit blasting and/or acid-etching the implant.
SB and SBAO surfaces did not have significantly different values in the number of peak-valley pairs by unit length. Since the sizes of those nano-topographic features are smaller than the lateral resolution of the technique used to measure roughness, SB and SBAO treatment produce a higher surface roughness than the samples treated with anodic oxidation. This fact and the partial hydrophilic character facilitate the development of a bioactive interface, which may improve in vitro osteoblast differentiation as well as osseointegration [15,54]. However, the mechanisms that underscore such topographical response are still poorly understood, and the role of each treatment, when the samples present a combination, is not known [16,54,55].
The influence of SBAO Ti surfaces on wettability measurements indicated an increase of surface hydrophobicity for all treated samples compared to Control (Table 3). Concerning the wettability results, some cautions must be considered, since the surface finishing tested here is far from being ideal. Rough surfaces affect the contact angles/wettability, since, for the same nominal area, the total real area is higher for rougher surfaces [56]. This means that if the surfaces were ideally plane, and nothing else other than roughness would change on that surface, the hydrophobic/hydrophilic character of the surface would be reinforced. It can be observed that all samples presented a hydrophobic character. The increase of contact angle was directly related to the increase of Ra value, and this effect was statistically significant for SB and SBAO surfaces, since higher roughness average values were obtained p < 0.005. However, sandblasting was the treatment that most decreased surface wettability. Increase of the contact angle could be due to the metastable character of the deposited water drops produced by the surface roughness features.
Further investigations would be interesting to study more variables and confirm the present results.
5. Conclusions
- OMIs have surface contaminants and irregularities from the manufacturer; the amount depends on the surface finishing.
- After clinical handling, OMIs surfaces are additionally contaminated; therefore, when handling is needed, the use of a gauze soaked in chlorhexidine is recommended.
- OMIs leave titanium particles in the bone during the procedure of insertion-removal, especially when surface-treated.
- Sandblasted and sandblasted with anodic oxidation produce an increasing of roughness and hydrophobic character of the surfaces.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.P., J.G. and T.Z.; methodology, T.Z., A.W.-S., F.d.l.I.; formal analysis, T.Z.; investigation, A.W.-S., T.Z., F.d.l.I.; resources, J.G.; data curation, E.E.; Writing—original draft preparation, T.Z., A.W.-S. Writing—review and editing, A.P., E.E.; supervision, A.P.; project administration, J.G.; funding acquisition, J.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Spanish Government and and European Union FEDER by the concession of the grant RTI2018-098075-B-C22 and the research group Generalitat de Catalunya 2017SGR708.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Costa, A.; Raffainl, M.; Melsen, B. Miniscrews as orthodontic anchorage: A preliminary report. Int. J. Adult Orthod. Orthognath. Surg. 1998, 13, 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Kanomi, R. Mini-implant for orthodontic anchorage. J. Clin. Orthod. JCO 1997, 31, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, H.S. The skeletal cortical anchorage using titanium microscrew implants. Korea J. Orthod. 1999, 29, 699–706. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgaertel-Sebastian, G.H.M.; Razavi Mohammad, R. Mini-implant anchorage for the orthodontic practi-tioner. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 133, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, S.; Yamada, K.; Deguchi, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Kyung, H.-M.; Yamamoto, T.T. Root proximity is a major factor for screw failure in orthodontic anchorage. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2007, 131, S68–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Deguchi, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Ito, M.; Kim, S. Orthodontic miniscrew failure rate and root proximi-ty, insertion angle, bone contact length, and bone density. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2013, 16, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebbar, M.; Bourzgui, F.; Aazzab, B.; Elquars, F. Anchorage miniscrews: A surface characterization study using optical microscopy. Int. Orthod. 2011, 9, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, M.; Muguruma, T.; Kawaguchi, M.; Yasuda, Y.; Mizoguchi, I. In vivo degradation of orthodontic miniscrew implants: Surface analysis of as-received and retrieved specimens. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucesoy, T.; Seker, D.E.; Arslan, E. Comparison of surface roughness and elemental analysis of different mini implant systems. Pak. Oral Dent. J. 2017, 30, 383–393. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, D.J. Principles and Practice of Variable Pressure/Environmental Scanning Electron Microscopy (VP-ESEM); John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.-C.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Jee, S.-H. Intrusion of posterior teeth using mini-screw implants. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2003, 123, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.-H.; Shotwell, J.L.; Wang, H.-L. Dental implants for orthodontic anchorage. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2005, 127, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaddad, K.; Ferreira, A.H.; Geurs, N.; Reddy, M.S. Influence of Surface Characteristics on Survival Rates of Mini-Implants. Angle Orthod. 2008, 78, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.J.; Oshida, Y.; Andres, C.J.; Barco, M.T. Surface characterizations of variously treated titanium materials. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2001, 16, 333–342. [Google Scholar]
- Yamagami, A.; Yoshihara, Y.; Suwa, F. Mechanical and histologic examination of titanium alloy material treat-ed by sandblasting and anodic oxidization. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2005, 20, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shayganpour, A.; Rebaudi, A.; Cortella, P.; Diaspro, A.; Salerno, M. Electrochemical coating of dental implants with anodic porous titania for enhanced osteointegration. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 2183–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annarelli, C.; Fornazero, J.; Cohen, R.; Bert, J.; Besse, J.-L. Colloidal Protein Solutions as a New Standard Sensor for Adhesive Wettability Measurements. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 213, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Rao, K.H. Analysis of different approaches for evaluation of surface energy of microbial cells by contact angle goniometry. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 98, 341–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teughels, W.; Van Assche, N.; Sliepen, I.; Quirynen, M. Effect of material characteristics and/or surface to-pography on biofilm development. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2006, 17 (Suppl. 2), 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgers, R.; Gerlach, T.; Hahnel, S.; Schwarz, F.; Handel, G.; Gosau, M. In vivo and in vitro biofilm formation on two different titanium implant surfaces. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2010, 21, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, F.J.; Planell, J.A.; Padrós, A. Fracture and fatigue behaviour of shot blasted titanium dental implants. Implant Dent. 2002, 11, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, C.; Gil, F.J.; Fonseca, C.; Barbosa, M.; Planell, J.A. The effect of shot blasting and heat treatment on the fatigue behavior of titanium for dental implant applications. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 486–491. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, A.; Winsauer, H.; Marcé-Nogué, J.; Mojal, S.; Puigdollers, A. Design characteristics, primary stability and risk of fracture of orthodontic mini-implants: Pilot scan electron microscope and mechanical studies. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2013, 18, e804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, M.; Benedicenti, S.; Itri, A. Hydro air abrasion on dental glass-ceramics: A direct 3D analysis by stylus profilometry. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 93, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Profile Method—Metrological Characteristics of Phase Correct Filters; ISO 11562:1996; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- Salerno, M.; Itri, A.; Frezzato, M.; Rebaudi, A. Surface Microstructure of Dental Implants Before and After Insertion: An in vitro study by means of scanning probe microscopy. Implant Dent. 2015, 24, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegueroles, M.; Gil, F.; Planell, J.; Aparicio, C. The influence of blasting and sterilization on static and time-related wettability and surface-energy properties of titanium surfaces. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 3470–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegueroles, M.; Aparicio, C.; Bosio, M.; Engel, E.; Gil, F.J.; Planell, J.A.; Altankov, G. Spatial organization of osteoblast fibronectin matrix on titanium surfaces: Effects of roughness, chemical heterogeneity and surface energy. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D.; Schenk, R.K.; Steinemann, S.; Fiorellini, J.P.; Fox, C.H.; Stich, H. Influence of surface characteristics on bone integration of titanium implants. A histomorphometric study in miniature pigs. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1991, 25, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegueroles, M.; Tonda-Turo, C.; Planell, J.A.; Gil, F.J.; Aparicio, C. Adsorption of fibronectin, fibrinogen, and albu-min on TiO2, Time-resolved kinetics, structural changes, and competition study. Biointerphases 2012, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillem-Marti, J.; Delgado, L.M.; Godoy-Gallardo, M.; Pegueroles, M.; Herrero, M.; Gil, F.J.; Herrero-Climent, M. Fibroblast adhesion and activation onto micro-machined titanium surfaces. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 24, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manero, J.M.; Gil, F.; Padrós, E.; Planell, J. Applications of environmental scanning electron microscopy (ESEM) in biomaterials field. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2003, 61, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Brånemark, P.I.; Hansson, H.A.; Lindström, J. Osseointegrated titanium implants: Requirements for ensuring a long-lasting, direct bone-to-implant anchorage in man. Acta Orthop. 1981, 52, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinar-Escalona, E.; Bravo-Gonzalez, L.A.; Pegueroles, M.; Gil, F.J. Roughness and wettability effect on histologi-cal and mechanical response of self-drilling orthodontic mini-implants. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 20, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco-Ortega, E.; Alfonso-Rodríguez, C.A.; Monsalve-Guil, L.; España-López, A.; Jiménez-Guerra, A.; Garzón, I.; Alaminos, M.; Gil, F.J. Relevant aspects in the surface properties in titanium dental implants for the cellular vi-ability. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 64, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, R.; Ghosal, P.; Muraleedharan, K.; Nandy, T.K.; Ray, K.K. Effect of boron and carbon addition on micro-structure and mechanical properties of Ti-15-3 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 4819–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmann, P.F.P.; Ruschel, H.C.; Vargas, I.A.; De Verney, J.C.K.; Kramer, P.F. Titanium alloy orthodontic mini-implants: Scanning electron microscopic and metallographic analyses. Acta Odontol. Lat. 2015, 28, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, P.; Kharbanda, O.P.; Duggal, R.; Das, T.K.; Kalyanasundaram, D. Surface deterioration and elemental compo-sition of retrieved orthodontic miniscrews. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2015, 147, S88–S100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Könönen, M.H.; Lavonius, E.T.; Kivilahti, J.K. SEM observations on stress corrosion cracking of commercially pure titanium in a topical fluoride solution. Dent. Mater. 1995, 11, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.R.; Choo, H.; Kim, S.H.; Ngan, P. Timely relocation of mini-implants for uninterrupted full-arch distali-zation. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2010, 138, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.-H.; Kim, B.-M.; Kyung, S.-H.; Lim, J.K.; Kim, Y.H. Success Rate and Risk Factors Associated with Mini-Implants Reinstalled in the Maxilla. Angle Orthod. 2008, 78, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepner, D.L.; Castells, M.C. Latex Allergy: An Update. Anesth. Analg. 2003, 96, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugut, A.I.; Ghatak, A.T.; Miller, R.L. Anaphylaxis in the United States: An investigation into its epidemiology. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, B.R. Perioperative care of patients with latex allergy. AORN J. 2000, 72, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Morais, L.S.; Serra, G.; Pelero, G.F.A.; Rodrigues, L.; Muller, C.; Meyers, A.; Elias, C.N. Systemic levels of metallic ions released from orthodontic mini-implants. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2009, 135, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.S.; Kim, S.K.; Chang, Y.I.; Baek, S.H. In vitro and in vivo mechanical stability of orthodontic mini-implants: Effect of sandblasted, large-grit, and anodic-oxidation vs. sandblasted, large-grit, and acid-etching. Angle Orthod. 2012, 82, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgaertel, S.; Hans, M.G. Buccal cortical bone thickness for mini-implant placement. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2009, 136, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deguchi, T.; Takano-Yamamoto, T.; Kanomi, R.; Hartsfield, J.K.J.; Roberts, W.E.; Garetto, L.P. The use of small titani-um screws for orthodontic anchorage. J. Dent. Res. 2003, 82, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchon, P.W.; Brenton, M.D.; Coppes, J.K.; From, A.M.; Torner, J.C. Factors Affecting the Pullout Strength of Self-Drilling and Self-Tapping Anterior Cervical Screws. Spine 2003, 28, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, P.; Gil, J.; Aparicio, C. Relevant Properties for Immobilizing Short Peptides on Biosurfaces. IRBM 2017, 38, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giner, L.; Mercadé, M.; Torrent, S.; Punset, M.; Perez, R.; Delgado, L.M.; Gil, F.J. Double acid etching treatment of dental implants for enhanced biological properties. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2017, 16, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Román, J.; Padilla, S.; Doadrio, J.; Gil, F.J. Bioactivity and mechanical properties of SiO2-CaO-P2O5 glass-ceramics. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.; Gil, F.J.; Best, S.; Ginebra, M.P.; Driessens, F.C.; Planell, J.A. The cement setting reaction in the Ca-HPO4-alpha-Ca3(PO4)2 system: An X-ray diffraction study. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 42, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, W.; Smith, R.K.; Zilberman, Y.; Mozsary, P.G.; Smith, R.S. Osseous adaptation to continuous loading of rigid endosseous implants. Am. J. Orthod. 1984, 86, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Chung, K.R. The effect of early loading on the direct bone-to-implant surface contact of the orthodontic osseointegrated titanium implant. Korean J. Orthod. 2001, 31, 173–185. [Google Scholar]
- Arciniegas, M.P.; Casals, J.; Manero, J.M.; Pena, J.; Gil, F.J. Study of hardness and wear behaviour of NiTi shape memory alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2008, 460, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).