The Three-Month Effects of a Ketogenic Diet on Body Composition, Blood Parameters, and Performance Metrics in CrossFit Trainees: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval and Subject Recruitment and Consent
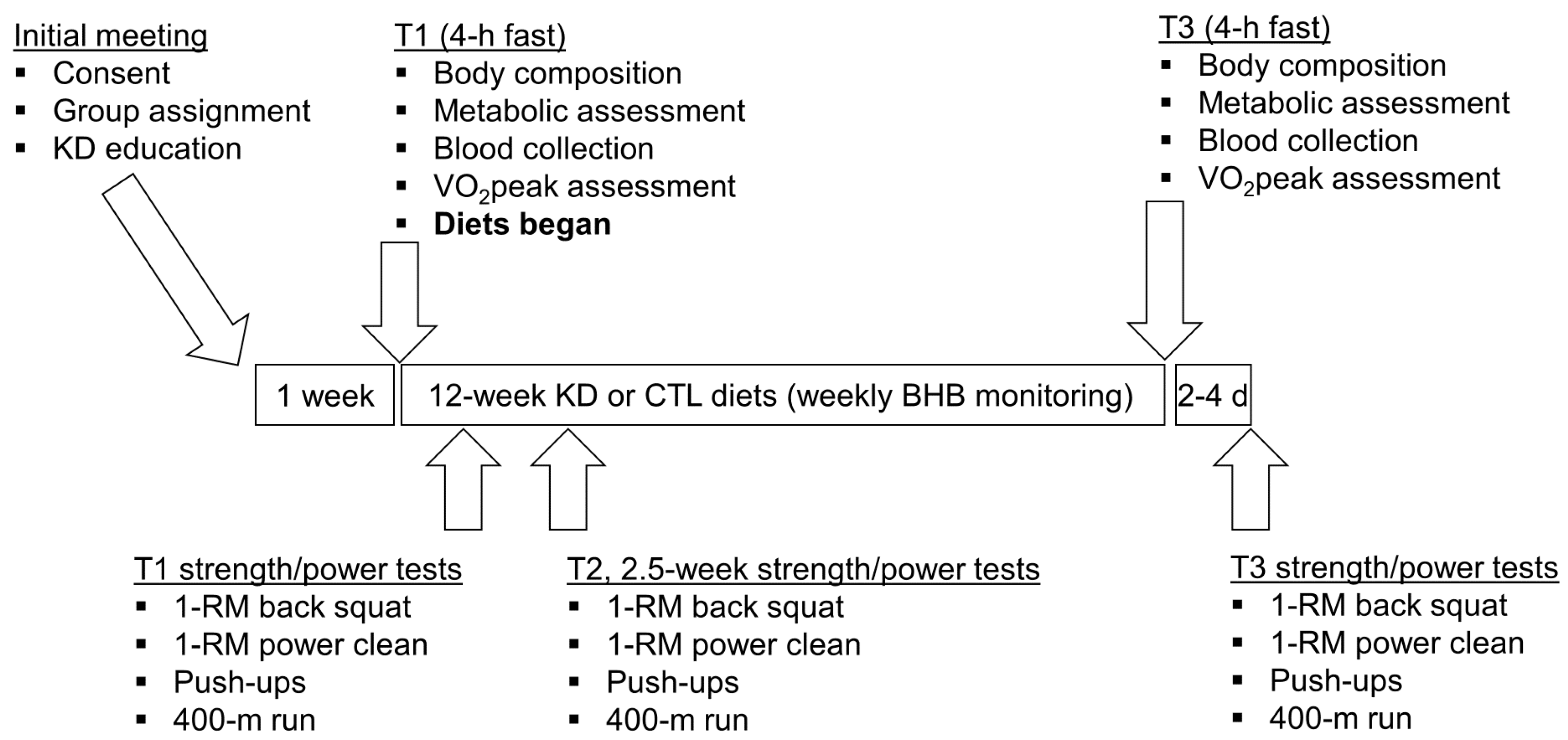
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Body Composition, Metabolic, and Aerobic Performance Assessments
2.4. Blood-Serum Collection and Analysis
2.5. Anaerobic Performance Assessments
2.6. Dietary Guidelines and Nutritional Intake Monitoring
2.7. Statistical Analyses and Data Presentation
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics between Treatments
3.2. Self-Reported Macronutrient Intakes and Workouts Completed over the Intervention
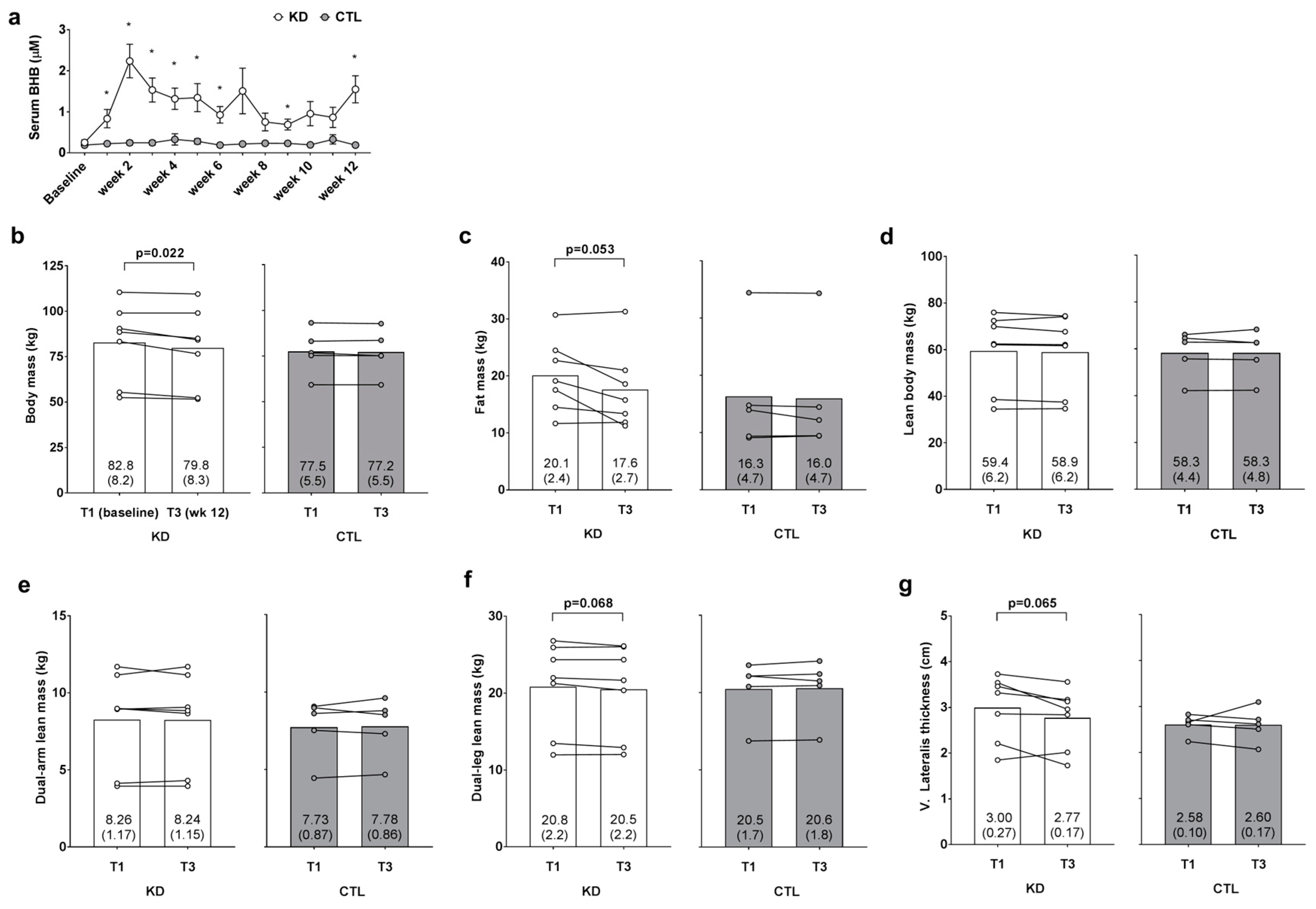
3.3. Weekly Blood Ketone Levels and Changes in Body Composition Metrics
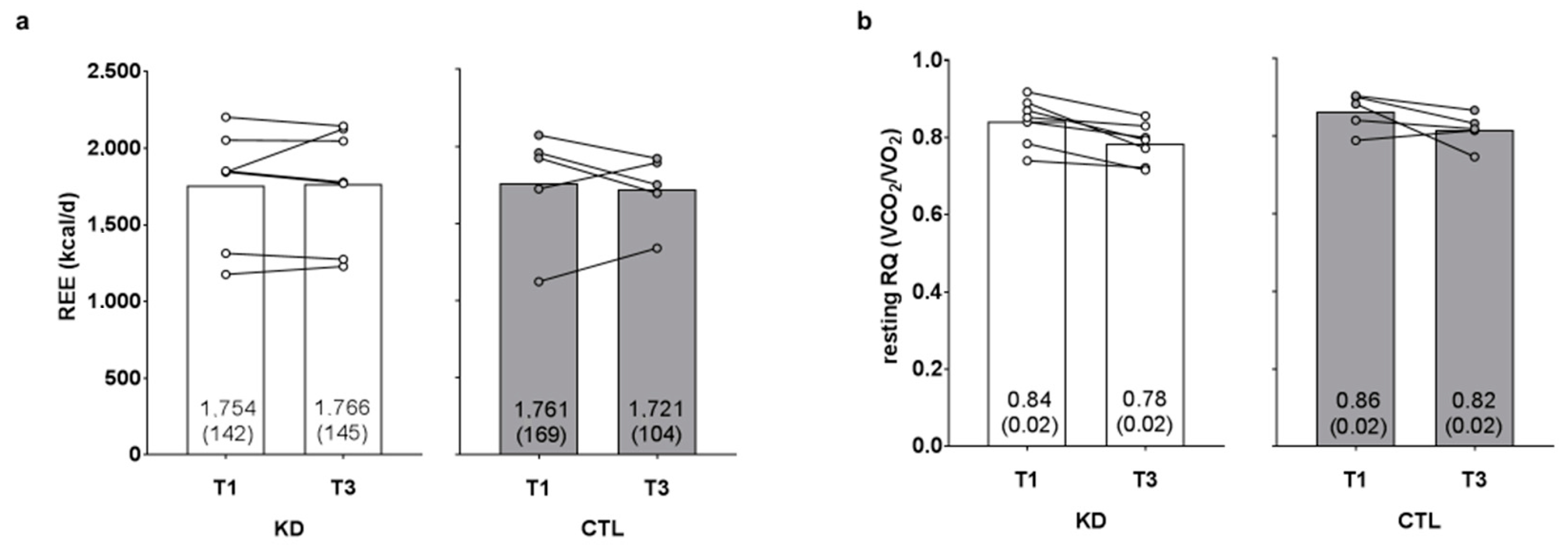
3.4. Changes in Resting Metabolic Metrics
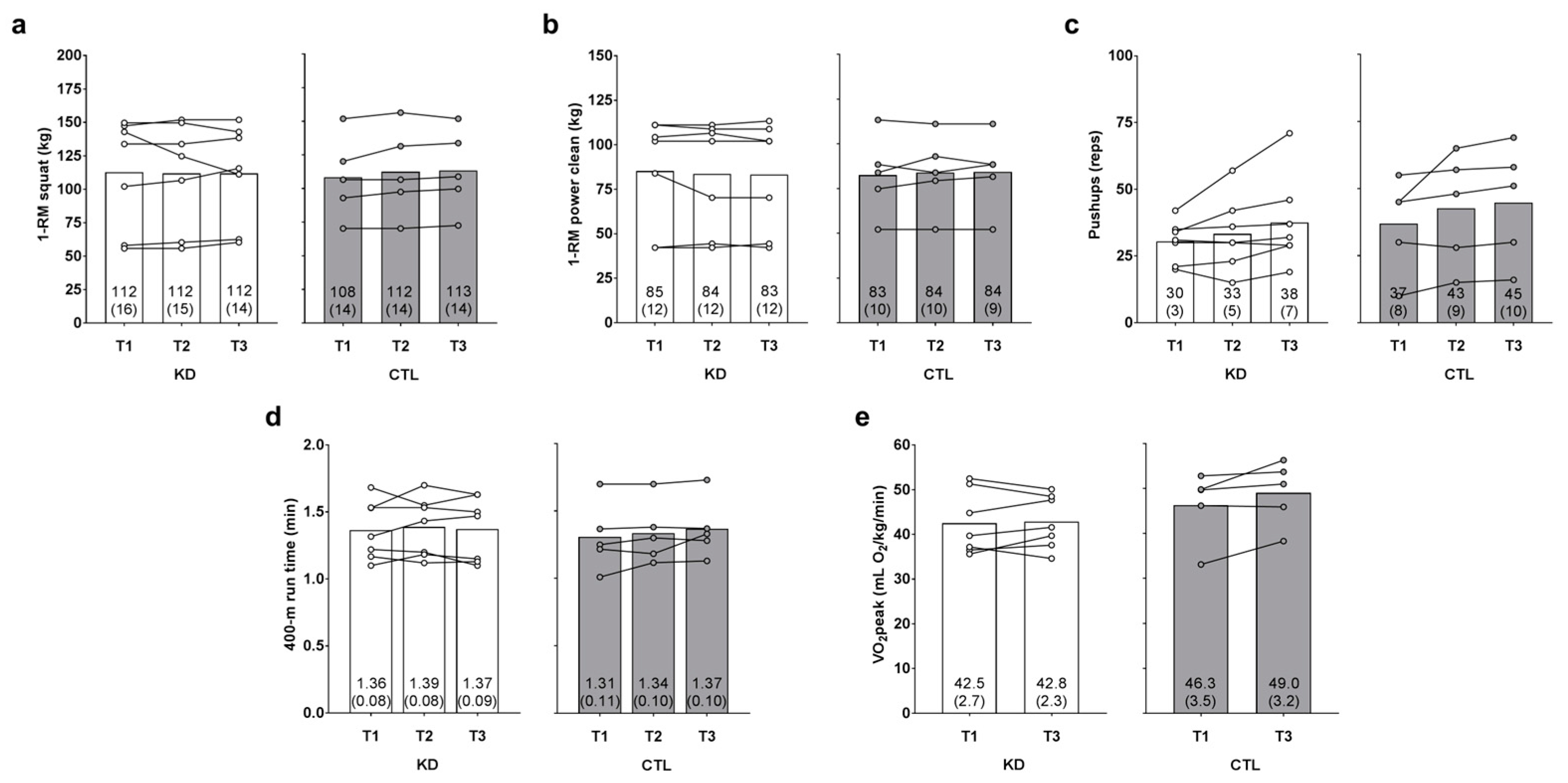
3.5. Changes in Performance Metrics
3.6. Changes in Blood-Serum Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Limitations and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Longland, T.M.; Oikawa, S.Y.; Mitchell, C.J.; Devries, M.C.; Phillips, S.M. Higher compared with lower dietary protein during an energy deficit combined with intense exercise promotes greater lean mass gain and fat mass loss: A randomized trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonio, J.; Peacock, C.A.; Ellerbroek, A.; Fromhoff, B.; Silver, T. The effects of consuming a high protein diet (4.4 g/kg/d) on body composition in resistance-trained individuals. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2014, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonio, J.; Ellerbroek, A.; Silver, T.; Orris, S.; Scheiner, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Peacock, C.A. A high protein diet (3.4 g/kg/d) combined with a heavy resistance training program improves body composition in healthy trained men and women—A follow-up investigation. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2015, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, B.; Kreider, R.B.; Ziegenfuss, T.; La Bounty, P.; Roberts, M.; Burke, D.; Landis, J.; Lopez, H.; Antonio, J.; Taylor, L.W.; et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Protein and exercise. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2007, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.D.; Holland, A.M.; Kephart, W.C.; Mobley, C.B.; Mumford, P.W.; Lowery, R.P.; Fox, C.D.; McCloskey, A.E.; Shake, J.J.; Mesquita, P.; et al. A putative low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet elicits mild nutritional ketosis but does not impair the acute or chronic hypertrophic responses to resistance exercise in rodents. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 120, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, A.M.; Kephart, W.C.; Mumford, P.W.; Mobley, C.B.; Lowery, R.P.; Shake, J.J.; Patel, R.K.; Healy, J.C.; McCullough, D.J.; Kluess, H.A.; et al. Effects of a ketogenic diet on adipose tissue, liver, and serum biomarkers in sedentary rats and rats that exercised via resisted voluntary wheel running. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 311, R337–R351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.M.; Lowery, R.P.; Roberts, M.D.; Sharp, M.H.; Joy, J.M.; Shields, K.A.; Partl, J.; Volek, J.S.; D’Agostino, D. The effects of ketogenic dieting on body composition, strength, power, and hormonal profiles in resistance training males. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, J.; Ericsson, M.; Joibari, M.M.; Anderson, F.; Carlsson, L.; Nilsson, S.K.; Sjodin, A.; Buren, J. A low-carbohydrate high-fat diet decreases lean mass and impairs cardiac function in pair-fed female C57BL/6J mice. Nutr. Metab. (Lond.) 2016, 13, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, A.R.; Pissios, P.; Otu, H.; Roberson, R.; Xue, B.; Asakura, K.; Furukawa, N.; Marino, F.E.; Liu, F.F.; Kahn, B.B.; et al. A high-fat, ketogenic diet induces a unique metabolic state in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 292, E1724–E1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoli, A.; Grimaldi, K.; D’Agostino, D.; Cenci, L.; Moro, T.; Bianco, A.; Palma, A. Ketogenic diet does not affect strength performance in elite artistic gymnasts. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2012, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, R.M.; Hamdan, H.; Torisky, D.M.; Akers, J.D. A low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet combined with 6-weeks of crossfit training improves body composition and performance. Int. J. Sports Exer. Med. 2017, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, L.M.; Ross, M.L.; Garvican-Lewis, L.A.; Welvaert, M.; Heikura, I.A.; Forbes, S.G.; Mirtschin, J.G.; Cato, L.E.; Strobel, N.; Sharma, A.P.; et al. Low carbohydrate, high fat diet impairs exercise economy and negates the performance benefit from intensified training in elite race walkers. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 2785–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kephart, W.C.; Wachs, T.D.; Mac Thompson, R.; Brooks Mobley, C.; Fox, C.D.; McDonald, J.R.; Ferguson, B.S.; Young, K.C.; Nie, B.; Martin, J.S.; et al. Ten weeks of branched-chain amino acid supplementation improves select performance and immunological variables in trained cyclists. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haun, C.T.; Mumford, P.W.; Roberson, P.A.; Romero, M.A.; Mobley, C.B.; Kephart, W.C.; Anderson, R.G.; Colquhoun, R.J.; Muddle, T.W.D.; Luera, M.J.; et al. Molecular, neuromuscular, and recovery responses to light versus heavy resistance exercise in young men. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobley, C.B.; Haun, C.T.; Roberson, P.A.; Mumford, P.W.; Romero, M.A.; Kephart, W.C.; Anderson, R.G.; Vann, C.G.; Osburn, S.C.; Pledge, C.D.; et al. Effects of whey, soy or leucine supplementation with 12 weeks of resistance training on strength, body composition, and skeletal muscle and adipose tissue histological attributes in college-aged males. Nutrients 2017, 9, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kephart, W.C.; Mumford, P.W.; McCloskey, A.E.; Holland, A.M.; Shake, J.J.; Mobley, C.B.; Jagodinsky, A.E.; Weimar, W.H.; Oliver, G.D.; Young, K.C.; et al. Post-exercise branched chain amino acid supplementation does not affect recovery markers following three consecutive high intensity resistance training bouts compared to carbohydrate supplementation. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2016, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volek, J.S.; Phinney, S.D. The Art and Science of Low Carbohydrate Performance; Beyond Obesity LLC: Miami, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Volek, J.S.; Phinney, S.D.; Forsythe, C.E.; Quann, E.E.; Wood, R.J.; Puglisi, M.J.; Kraemer, W.J.; Bibus, D.M.; Fernandez, M.L.; Feinman, R.D. Carbohydrate restriction has a more favorable impact on the metabolic syndrome than a low fat diet. Lipids 2009, 44, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noakes, M.; Foster, P.R.; Keogh, J.B.; James, A.P.; Mamo, J.C.; Clifton, P.M. Comparison of isocaloric very low carbohydrate/high saturated fat and high carbohydrate/low saturated fat diets on body composition and cardiovascular risk. Nutr. Metab. (Lond.) 2006, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brehm, B.J.; Seeley, R.J.; Daniels, S.R.; D’Alessio, D.A. A randomized trial comparing a very low carbohydrate diet and a calorie-restricted low fat diet on body weight and cardiovascular risk factors in healthy women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Arbelaez, D.; Bellido, D.; Castro, A.I.; Ordonez-Mayan, L.; Carreira, J.; Galban, C.; Martinez-Olmos, M.A.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Sajoux, I.; Casanueva, F.F. Body composition changes after very-low-calorie ketogenic diet in obesity evaluated by 3 standardized methods. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.; Rollo, I. Carbohydrate nutrition and team sport performance. Sports Med. 2015, 45 (Suppl. S1), S13–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volek, J.S.; Freidenreich, D.J.; Saenz, C.; Kunces, L.J.; Creighton, B.C.; Bartley, J.M.; Davitt, P.M.; Munoz, C.X.; Anderson, J.M.; Maresh, C.M.; et al. Metabolic characteristics of keto-adapted ultra-endurance runners. Metabolism 2016, 65, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajac, A.; Poprzecki, S.; Maszczyk, A.; Czuba, M.; Michalczyk, M.; Zydek, G. The effects of a ketogenic diet on exercise metabolism and physical performance in off-road cyclists. Nutrients 2014, 6, 2493–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McSwiney, F.T.; Wardrop, B.; Hyde, P.N.; Lafountain, R.A.; Volek, J.S.; Doyle, L. Keto-adaptation enhances exercise performance and body composition responses to training in endurance athletes. Metabolism 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | KD (n = 7) | CTL (n = 5) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Males/Females (n) | 5/2 | 4/1 | - |
| Age (years) | 32 ± 3 | 29 ± 3 | 0.592 |
| Height (m) | 1.71 ± 0.08 | 1.70 ± 0.03 | 0.954 |
| Body mass (kg) | 82.7 ± 8.2 | 76.9 ± 5.5 | 0.601 |
| DXA body fat (%) | 24.6 ± 2.2 | 20.6 ± 4.7 | 0.420 |
| Strength: mass | 1.35 ± 0.13 | 1.42 ± 0.18 | 0.736 |
| Variable | KD (n = 7) | CTL (n = 5) | Time p-Value Group × Time p-Value (ηp2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose (mg/dL) | |||
| Pre | 84.4 ± 4.3 | 79.2 ± 5.4 | 0.190 |
| Post | 76.7 ± 5.5 | 73.0 ± 7.4 | 0.881 (0.002) |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | |||
| Pre | 52.3 ± 3.2 | 56.6 ± 2.2 | 0.409 |
| Post | 51.3 ± 3.2 | 53.2 ± 3.2 | 0.649 (0.022) |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | |||
| Pre | 114.1 ± 16.2 | 88.4 ± 13.9 | 0.147 |
| Post | 153.9 ± 27.4 *,† | 79.0 ± 13.9 # | 0.029 (0.393) |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | |||
| Pre | 72.7 ± 9.5 | 56.8 ± 21.3 | 0.977 |
| Post | 65.9 ± 7.1 | 64.4 ± 20.7 | 0.585 (0.031) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kephart, W.C.; Pledge, C.D.; Roberson, P.A.; Mumford, P.W.; Romero, M.A.; Mobley, C.B.; Martin, J.S.; Young, K.C.; Lowery, R.P.; Wilson, J.M.; et al. The Three-Month Effects of a Ketogenic Diet on Body Composition, Blood Parameters, and Performance Metrics in CrossFit Trainees: A Pilot Study. Sports 2018, 6, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6010001
Kephart WC, Pledge CD, Roberson PA, Mumford PW, Romero MA, Mobley CB, Martin JS, Young KC, Lowery RP, Wilson JM, et al. The Three-Month Effects of a Ketogenic Diet on Body Composition, Blood Parameters, and Performance Metrics in CrossFit Trainees: A Pilot Study. Sports. 2018; 6(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleKephart, Wesley C., Coree D. Pledge, Paul A. Roberson, Petey W. Mumford, Matthew A. Romero, Christopher B. Mobley, Jeffrey S. Martin, Kaelin C. Young, Ryan P. Lowery, Jacob M. Wilson, and et al. 2018. "The Three-Month Effects of a Ketogenic Diet on Body Composition, Blood Parameters, and Performance Metrics in CrossFit Trainees: A Pilot Study" Sports 6, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6010001
APA StyleKephart, W. C., Pledge, C. D., Roberson, P. A., Mumford, P. W., Romero, M. A., Mobley, C. B., Martin, J. S., Young, K. C., Lowery, R. P., Wilson, J. M., Huggins, K. W., & Roberts, M. D. (2018). The Three-Month Effects of a Ketogenic Diet on Body Composition, Blood Parameters, and Performance Metrics in CrossFit Trainees: A Pilot Study. Sports, 6(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6010001






