The Potential Benefits of a Novel Food Supplement Based on Cannabis Sativa, Boswellia, and Fish Oil for Pain and Inflammation in Physical Activity: Unraveling the Role of Orexin-A Modulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Study Protocol
- -
- Treatment group: Fifteen participants received Flector Softgel FS Integratore for 2 weeks.
- -
- Placebo group: Ten participants received a placebo supplement identical in appearance and taste.
2.2. Physical Activity Program
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- -
- Male and female participants aged 30–60 years.
- -
- Amateur athletes with regular physical activity (>3 times/week).
- -
- A body mass index (BMI) between 22 and 30 kg/m2 (normal–overweight range).
- -
- A history of recurrent joint or musculoskeletal pain during or after physical activity.
- -
- No anti-inflammatory or joint-active medication use in the 10 days prior to enrollment.
- -
- A negative pregnancy test for women of childbearing potential.
- -
- Provision of written informed consent.
- -
- A diagnosed chronic inflammatory or autoimmune disease.
- -
- The use of corticosteroids, opioids, or immunomodulators within 30 days.
- -
- Allergies to any supplement ingredients.
- -
- Pregnancy or lactation.
- -
- Psychiatric disorders or cognitive impairments affecting compliance.
2.4. Flector Softgel FS Integratore Characteristics
- An amount of 500 mg of Cannabis Sativa L. seed oil (cannabinoid-free) (recognized by the Ministry of Health for improving joint functionality);
- An amount of 250 mg of Boswellia Serrata Roxb (supports joint functionality and helps counteract localized tension states);
- An amount of 250 mg of fish oil 33/23 Tg (related to anti-inflammatory activity);
- An amount of 160 mg of omega-3;
- An amount of 0.6 mg of collagen UC II (undenatured type II; supported by clinical studies).
2.5. Anthropometrical and Biochemical Measurements
2.6. Pain Evaluation
- 0–4 mm: No pain;
- 5–44 mm: Mild pain;
- 45–74 mm: Moderate pain;
- 75–100 mm: Severe pain.
2.7. Bioplex Assay
2.8. Description of Study Variables
- -
- Subjective pain perception, measured using the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS);
- -
- The serum orexin-A concentration;
- -
- The levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6.
- -
- Serum levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 and self-reported measures of post-exercise recovery and perceived well-being, obtained through structured questionnaires.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. The Cytokines Assay in Flector Softgel FS Group and Placebo Group
3.1. Anthropometric and Biochemical Parameters
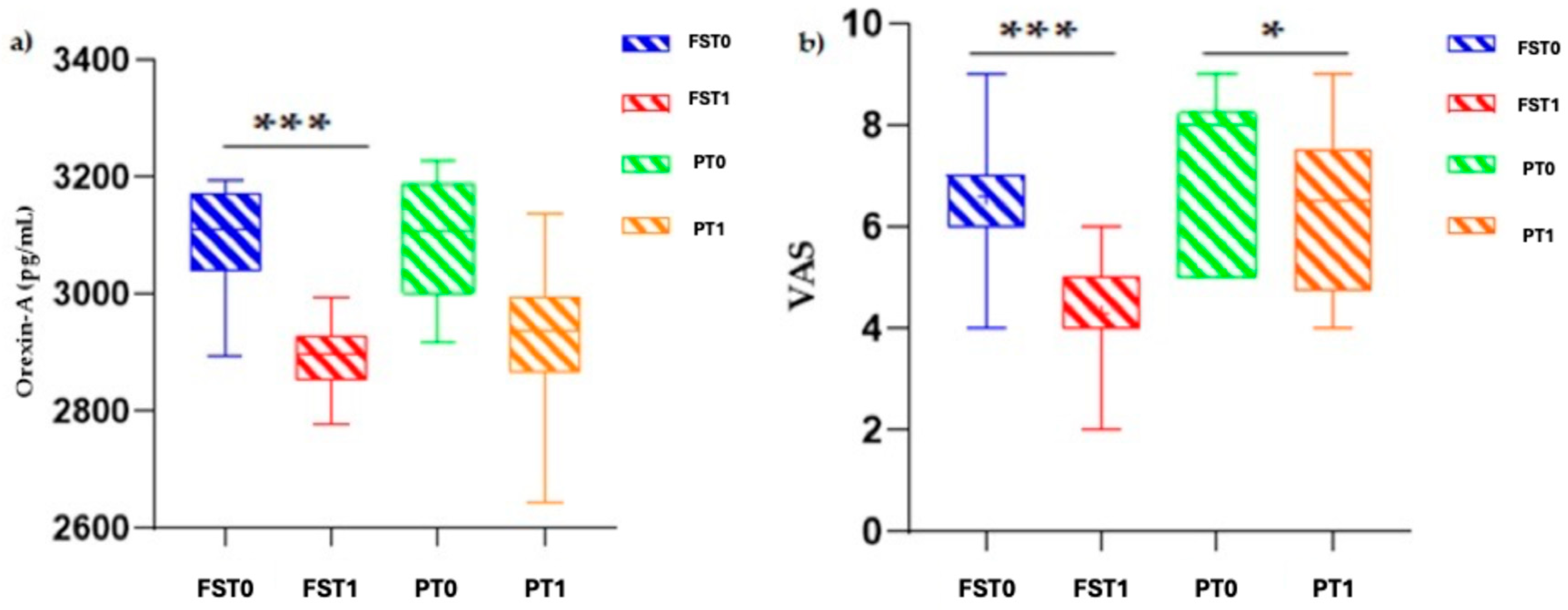
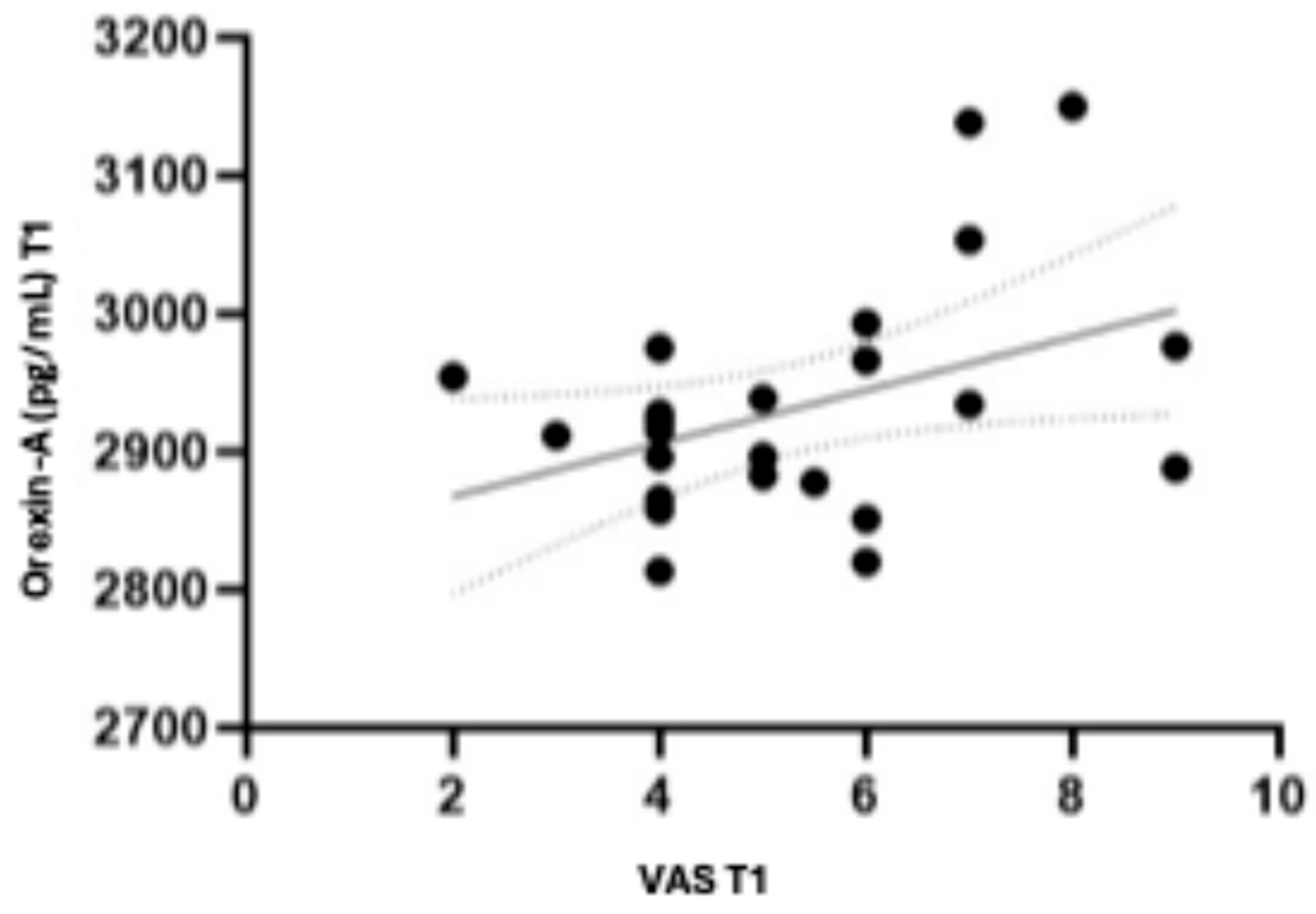
3.2. Orexin-A and VAS Profile in Flector Softgel FS Group and Placebo Group
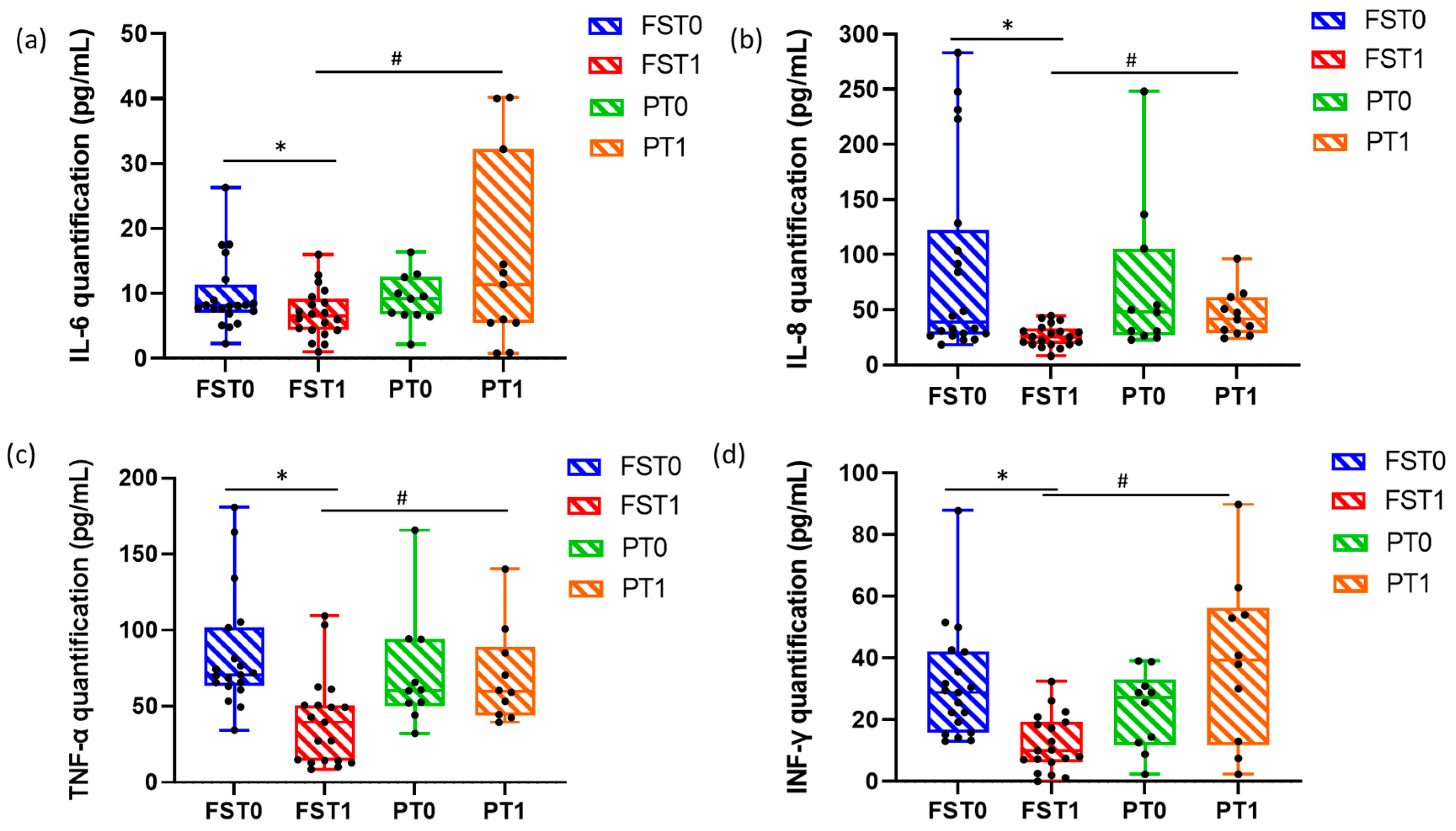
3.3. Bioplex Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adams, V.; Linke, A. Impact of Exercise Training on Cardiovascular Disease and Risk. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.G. An Evidence-Based Review of Overuse Wrist Injuries in Athletes. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 51, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feragalli, B.; Ippolito, E.; Dugall, M.; Cacchio, M.; Belcaro, G.; Cesarone, M.R.; Abdel-Tawab, M.; Riva, A.; Togni, S.; Eggenhoffner, R.; et al. Effectiveness of a Novel Boswellic Acids Delivery Form (Casperome®) in the Management of Grade II Ankle Sprains Due to Sport Trauma—A Registry Study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 4726–4732. [Google Scholar]
- Kuptniratsaikul, V.; Dajpratham, P.; Taechaarpornkul, W.; Buntragulpoontawee, M.; Lukkanapichonchut, P.; Chootip, C.; Saengsuwan, J.; Tantayakom, K.; Laongpech, S. Efficacy and Safety of Curcuma Domestica Extracts Compared with Ibuprofen in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Multicenter Study. Clin. Interv. Aging 2014, 9, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, F.; Togni, S.; Belcaro, G.; Dugall, M.; Luzzi, R.; Ledda, A.; Pellegrini, L.; Eggenhoffner, R.; Giacomelli, L. A Novel Lecithin Based Delivery Form of Boswellic Acids (Casperome®) for the Management of Osteo-Muscular Pain: A Registry Study in Young Rugby Players. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 4156–4161. [Google Scholar]
- Riva, A.; Allegrini, P.; Franceschi, F.; Togni, S.; Giacomelli, L.; Eggenhoffner, R. A Novel Boswellic Acids Delivery Form (Casperome®) in the Management of Musculoskeletal Disorders: A Review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 5258–5263. [Google Scholar]
- Nieman, D.C.; Shanely, R.A.; Luo, B.; Dew, D.; Meaney, M.P.; Sha, W. A Commercialized Dietary Supplement Alleviates Joint Pain in Community Adults: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Community Trial. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawker, G.A.; Mian, S.; Kendzerska, T.; French, M. Measures of Adult Pain: Visual Analog Scale for Pain (VAS Pain), Numeric Rating Scale for Pain (NRS Pain), McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ), Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ), Chronic Pain Grade Scale (CPGS), Short Form-36 Bodily Pain Scale (SF-36 BPS), and Measure of Intermittent and Constant Osteoarthritis Pain (ICOAP). Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, S240–S252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, A.; Hoggart, B. Pain: A Review of Three Commonly Used Pain Rating Scales. J. Clin. Nurs. 2005, 14, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hush, J.M.; Refshauge, K.M.; Sullivan, G.; De Souza, L.; McAuley, J.H. Do Numerical Rating Scales and the Roland-Morris Disability Questionnaire Capture Changes That Are Meaningful to Patients with Persistent Back Pain? Clin. Rehabil. 2010, 24, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, P.; Küçükdeveci, A.A.; Tennant, A. The Use of the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) in Rehabilitation Outcomes. J. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 44, 609–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjermstad, M.J.; Fayers, P.M.; Haugen, D.F.; Caraceni, A.; Hanks, G.W.; Loge, J.H.; Fainsinger, R.; Aass, N.; Kaasa, S. Studies Comparing Numerical Rating Scales, Verbal Rating Scales, and Visual Analogue Scales for Assessment of Pain Intensity in Adults: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2011, 41, 1073–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Merchan, C. Conservative treatment of acute knee osteoarthritis: A review of the Cochrane Library. J. Acute Dis. 2016, 5, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yu, G. Effectiveness of Boswellia and Boswellia extract for osteoarthritis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Complement. Med. Therap. 2020, 20, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, E. Frankincense: Systematic review. BMJ 2008, 337, a2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joos, E.; Peretz, A.; Beguin, S.; Famaey, J.P. Reliability and Reproducibility of Visual Analogue Scale and Numeric Rating Scale for Therapeutic Evaluation of Pain in Rheumatic Patients. J. Rheumatol. 1991, 18, 1269–1270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuettel, D.; Primdahl, J.; Weber, U.; Terslev, L.; Østergaard, M.; Petersen, R.; Pedersen, A.K.; Möller, S.; Hørslev-Petersen, K. Pain and Self-Reported Swollen Joints Are Main Drivers of Patient-Reported Flares in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from a 12-Month Observational Study. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 47, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haefeli, M.; Elfering, A. Pain Assessment. Eur. Spine J. 2006, 15, S17–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworkin, R.H.; Turk, D.C.; Farrar, J.T.; Haythornthwaite, J.A.; Jensen, M.P.; Katz, N.P.; Kerns, R.D.; Stucki, G.; Allen, R.R.; Bellamy, N.; et al. Core Outcome Measures for Chronic Pain Clinical Trials: IMMPACT Recommendations. Pain 2005, 113, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, E.J.; Liebman, M.; Bijur, P.E. Prospective Validation of Clinically Important Changes in Pain Severity Measured on a Visual Analog Scale. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2001, 38, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, A.; Monda, M.; Valenzano, A.; Messina, G.; Villano, I.; Moscatelli, F.; Cibelli, G.; Marsala, G.; Polito, R.; Ruberto, M.; et al. Functional Changes Induced by Orexin a and Adiponectin on the Sympathetic/Parasympathetic Balance. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.d.N.; Kumar, S.; Bashir, T.; Suntsova, N.; Methippara, M.M.; Szymusiak, R.; McGinty, D. GABA-mediated Control of Hypocretin- but Not Melanin-concentrating Hormone-immunoreactive Neurones during Sleep in Rats. J. Physiol. 2005, 563, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bays, H.E.; González-Campoy, J.M.; Henry, R.R.; Bergman, D.A.; Kitabchi, A.E.; Schorr, A.B.; Rodbard, H.W. Is Adiposopathy (Sick Fat) an Endocrine Disease? Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2008, 62, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puszczalowska-Lizis, E.; Flak, K.; Biskup, M.; Zak, M. Physical Activity of Women After Radical Unilateral Mastectomy and Its Impact on Overall Quality of Life. Cancer Control. 2020, 27, 1073274819900407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, V.; Stellavato, A.; Russo, R.; Cimini, D.; Valletta, M.; Alfano, A.; Pedone, P.V.; Chambery, A.; Schiraldi, C. Molecular Fingerprint of Human Pathological Synoviocytes in Response to Extractive Sulfated and Biofermentative Unsulfated Chondroitins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffner, S.M.; Ruilope, L.; Dahlöf, B.; Abadie, E.; Kupfer, S.; Zannad, F. Metabolic Syndrome, New Onset Diabetes, and New End Points in Cardiovascular Trials. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2006, 47, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P. Inflammation in Atherosclerosis. Nature 2002, 420, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Proinflammatory Cytokines. Chest 2000, 118, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkonen, J.P. Lipid Signaling Cascades of Orexin/Hypocretin Receptors. Biochimie 2014, 96, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, L.-C.; Lee, H.-J.; Ho, Y.-C.; Chen, S.-P.; Liao, Y.-Y.; Ma, C.-H.; Fan, P.-C.; Fuh, J.-L.; Wang, S.-J. Orexins/Hypocretins: Pain Regulation and Cellular Actions. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 3089–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.W.; Akladious, A.; Hu, Y.; Azzam, S.; Feng, P.; Strohl, K.P. Effects of Orexin 2 Receptor Activation on Apnea in the C57BL/6J Mouse. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2014, 200, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blake, G.J.; Ridker, P.M. Are Statins Anti-Inflammatory? Trials 2000, 1, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C.; Bosco, N.; Bourdet-Sicard, R.; Capuron, L.; Delzenne, N.; Doré, J.; Franceschi, C.; Lehtinen, M.J.; Recker, T.; Salvioli, S.; et al. Health Relevance of the Modification of Low-Grade Inflammation in Ageing (Inflammageing) and the Role of Nutrition. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 40, 95–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Piñero, S.; Muñoz-Carrillo, J.C.; Victoria-Montesinos, D.; García-Muñoz, A.M.; Andreu-Caravaca, L.; Gómez, M.; Schölzel, M.; García-Guillén, A.I.; López-Román, F.J. Efficacy of Boswellia serrata Extract and/or an Omega-3-Based Product for Improving Pain and Function in People Older Than 40 Years with Persistent Knee Pain: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, W.; Riediger, C.; McCarthy, A.L.; Isenring, E. Cannabidiol and exercise recovery: A review of potential mechanisms and safety considerations. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, R.S.; Patil, K.R.; Singh, R.N. Nutraceutical synergy: Mechanistic insights into the anti-inflammatory and metabolic effects of combined botanical compounds. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1174567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosla, S.; Farr, J.N.; Tchkonia, T.; Kirkland, J.L. The Role of Cellular Senescence in Ageing and Endocrine Disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.S.; Alvarez-Leite, J.I. Low-Grade Inflammation, Obesity, and Diabetes. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2014, 3, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraldi, S.; Lolli, A.; Pappalardo, G.; Guizzardi, F.; Prati, P.; Ferrario, P.; Magni, P. Role of Nutraceuticals and Functional Foods in Modulating the Inflammatory Response in Athletes: A Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, F.; Valette, M.; López-Ben, R.; Cormet-Boyaka, E.; Leloire, A.; Chardigny, J.M.; Guéraud, F.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Peuchant, E.; Capel, F.; et al. Nutritional Modulation of Low-Grade Inflammation via Fatty Acid Intake and Gut Microbiota in Ageing and Cardiovascular Diseases. Nutrients 2017, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Buttari, B.; Profumo, E.; Saso, L. A Perspective on the Role of Anti-Inflammatory Nutraceuticals in Preventing Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, B.M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. A Review of the Role of Orexin System in Pain Modulation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 90, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristino, L.; Luongo, L.; Imperatore, R.; Boccella, S.; Becker, T.; Morello, G.; Piscitelli, F.; Busetto, G.; Maione, S.; Di Marzo, V. Orexin-A and Endocannabinoid Activation of the Descending Antinociceptive Pathway Underlies Altered Pain Perception in Leptin Signaling Deficiency. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | Flector FS T0 | Flector FS T1 | p-Value (Flector) | Placebo T0 | Placebo T1 | p-Value (Placebo) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (kg) | 74.46 ± 2.97 | 73.65 ± 2.98 | 0.043 | 75.35 ± 2.98 | 75.55 ± 2.94 | n.s. |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.46 ± 0.63 | 23.19 ± 0.62 | 0.038 | 25.64 ± 0.83 | 25.72 ± 0.87 | n.s. |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 150.13 ± 5.77 | 140.91 ± 2.93 | 0.027 | 139.45 ± 3.50 | 137.32 ± 2.40 | n.s. |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 111.32 ± 6.48 | 90.57 ± 5.72 | 0.015 | 99.45 ± 1.20 | 98.56 ± 2.30 | n.s. |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 125.14 ± 5.27 | 73.25 ± 6.14 | 0.009 | 110.45 ± 2.60 | 111.12 ± 3.50 | n.s. |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 55.13 ± 6.14 | 53.76 ± 4.14 | n.s. | 48.24 ± 2.50 | 49.45 ± 4.60 | n.s. |
| Insulinemia (µU/mL) | 5.53 [4.10–6.75] | 3.37 [2.10–4.25] | 0.021 | 5.40 ± 3.10 | 4.67 ± 1.30 | n.s. |
| CRP (mg/mL) | 0.89 ± 0.10 | 0.48 ± 0.07 | 0.012 | 0.78 ± 0.50 | 0.77 ± 0.20 | n.s. |
| Variable | W Statistic | p-Value | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 0.974 | 0.652 | Normal |
| BMI | 0.979 | 0.734 | Normal |
| Total cholesterol | 0.966 | 0.544 | Normal |
| HDL | 0.912 | 0.043 | Non-normal |
| LDL | 0.983 | 0.782 | Normal |
| Triglycerides | 0.961 | 0.478 | Normal |
| Insulinemia | 0.894 | 0.032 | Non-normal |
| CRP | 0.927 | 0.060 | Normal |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Messina, A.; Monda, A.; Vassallo, V.; Di Maio, G.; Polito, R.; La Marra, M.; Allocca, S.; Casillo, M.; Moscatelli, F.; Scavone, C.; et al. The Potential Benefits of a Novel Food Supplement Based on Cannabis Sativa, Boswellia, and Fish Oil for Pain and Inflammation in Physical Activity: Unraveling the Role of Orexin-A Modulation. Sports 2025, 13, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13070199
Messina A, Monda A, Vassallo V, Di Maio G, Polito R, La Marra M, Allocca S, Casillo M, Moscatelli F, Scavone C, et al. The Potential Benefits of a Novel Food Supplement Based on Cannabis Sativa, Boswellia, and Fish Oil for Pain and Inflammation in Physical Activity: Unraveling the Role of Orexin-A Modulation. Sports. 2025; 13(7):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13070199
Chicago/Turabian StyleMessina, Antonietta, Antonietta Monda, Valentina Vassallo, Girolamo Di Maio, Rita Polito, Marco La Marra, Salvatore Allocca, Maria Casillo, Fiorenzo Moscatelli, Cristina Scavone, and et al. 2025. "The Potential Benefits of a Novel Food Supplement Based on Cannabis Sativa, Boswellia, and Fish Oil for Pain and Inflammation in Physical Activity: Unraveling the Role of Orexin-A Modulation" Sports 13, no. 7: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13070199
APA StyleMessina, A., Monda, A., Vassallo, V., Di Maio, G., Polito, R., La Marra, M., Allocca, S., Casillo, M., Moscatelli, F., Scavone, C., Taturi, F., Monda, V., Messina, G., Schiraldi, C., & Monda, M. (2025). The Potential Benefits of a Novel Food Supplement Based on Cannabis Sativa, Boswellia, and Fish Oil for Pain and Inflammation in Physical Activity: Unraveling the Role of Orexin-A Modulation. Sports, 13(7), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13070199












