Overuse of Short-Acting Beta-2 Agonists (SABAs) in Elite Athletes: Hypotheses to Explain It
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Shadow of Doping
2.1. Are SABAs Associated with a Doping Effect?
2.2. So, Why This Overconsumption?
3. Epidemiology
4. A Low Use of Inhaled Corticosteroids and Therefore a Greater Use of SABA
4.1. So Why the Heavy Use of Beta Agonists Instead of ICS?
4.1.1. Variable Effectiveness
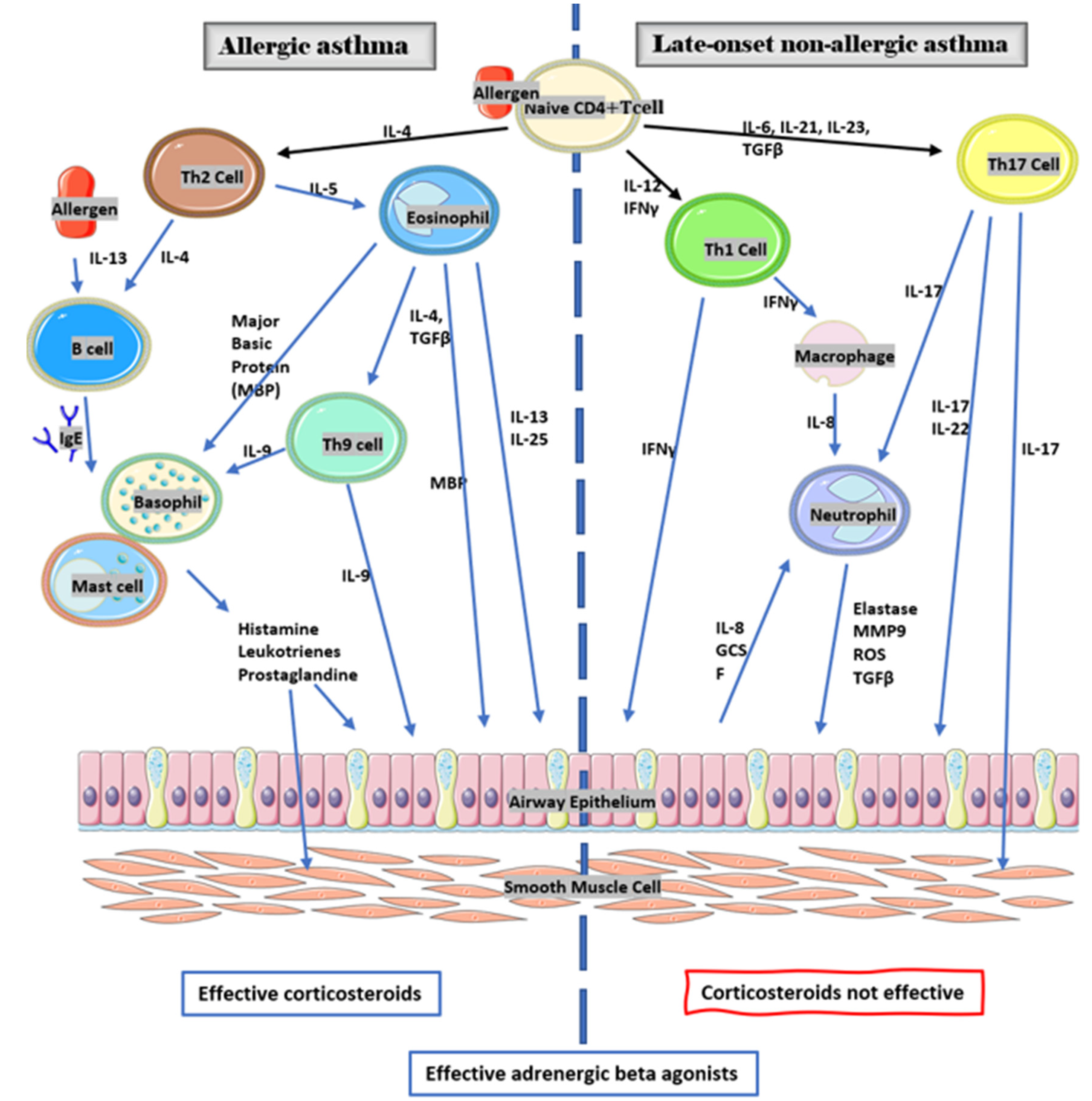
4.1.2. Immunologic Profile and Inflammatory Responses in Asthma
4.1.3. Asthma th1 and th17
4.1.4. To Which Phenotype Does an Athlete’s Asthma and EIB Asthma Belong?
4.1.5. Pathophysiology of Sports Asthma
4.1.6. Are Adrenergic Agonist Betas Effective in Mixed Asthma th2 th1–17?
5. Very High Frequency of Use in Athletes
6. Summary
7. Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alentorn-Geli, E.; Samuelsson, K.; Musahl, V.; Green, C.; Bhandari, M.; Karlsson, J. The Association of Recreational and Competitive Running With Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2017, 47, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, J.E. The impact of exercise on asthma. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 19, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.P.; Wai, J.P.M.; Tsai, M.K.; Yang, Y.C.; Cheng, T.W.D.; Lee, M.C.; Chan, H.T.; Tsao, C.K.; Tsai, S.P.; Wu, X. Minimal Amount of Exercise to Prolong Life. JACC Cardiol. 2014, 64, 482–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Eichenberger, P.A.; Diener, S.N.; Kofmehl, R.; Spengler, C. Effects of Exercise Training on Airway Hyperreactivity in Asthma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 1157–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coëtmeur, D.; Parrat, E.; Nocent-Ejnaini, C.; Magiapan, G.; Prud’homme, A.; Oster, J.-P.; Appere de Vecchi, C.; Maurer, C.; Raherison, C.; Debieuvre, D.; et al. Activité physique et asthme sévère: Résultats de l’étude FASE-CPHG. Rev. Des Mal. Respir. 2020, 37, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béta-2-agonistes|World Anti-Doping Agency. 2021. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/fr/content/liste-des-interdictions/interdites-en-permanence/bta-2-agonistes (accessed on 4 October 2021).
- Carlsen, K.H.; Anderson, S.D.; Bjermer, L.; Bonini, S.; Brusasco, V.; Canonica, W.; Cummiskey, J.; Delgado, L.; Del Giacco, S.R.; Drobnic, F.; et al. Exercise-induced asthma, respiratory and allergic disorders in elite athletes: Epidemiology, mechanisms and diagnosis: Part I of the report from the Joint Task Force of the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology (EAACI) in cooperation with GA2LEN. Allergy 2008, 63, 387–403. [Google Scholar]
- Fitch, K.D. The World Anti-Doping Code: Can you have asthma and still be an elite athlete? Breathe 2016, 12, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fitch, K.D. An overview of asthma and airway hyper-responsiveness in Olympic athletes. Br. J. Sports Med. 2012, 46, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, S.; Karacabeyli, D.; Galts, C.; Maclnnis, M.J.; Sporer, B.; Koehle, M. Effects of inhaled bronchodilators on lung function and cycling performance in female athletes with and without exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2015, 18, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlini, M.; Whyte, G.; Marcora, S.; Loosemore, M.; Chester, N.; Dickinson, J. Improved Sprint Performance With Inhaled Long-Acting Β2-Agonists Combined with Resistance Exercise. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2019, 14, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsen, A.; Hostrup, M.; Backer, V.; Bangsbo, J. Effect of formoterol, a long-acting β2-adrenergic agonist, on muscle strength and power output, metabolism, and fatigue during maximal sprinting in men. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 310, R1312–R1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Baak, M.A.; de Hon, O.M.; Hartgens, F.; Kuipers, H. Inhaled Salbutamol and Endurance Cycling Performance in Non-Asthmatic Athletes. Int. J. Sports Med. 2004, 25, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlini, M.; Beato, M.; Marcora, S.; Dickinson, J. The Effect of 1600 μg Inhaled Salbutamol Administration on 30 m Sprint Performance Pre and Post a Yo-Yo Intermittent Running Test in Football Players. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2019, 184, 716–721. [Google Scholar]
- Hostrup, M.; Kalsen, A.; Auchenberg, M.; Bangsbo, J.; Backer, V. Effects of acute and 2-week administration of oral salbutamol on exercise performance and muscle strength in athletes. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2014, 26, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helenius, I.J.; Tikkanen, H.O.; Haahtela, T. Association between type of training and risk of asthma in elite athletes. Thorax 1997, 52, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helenius, I.J.; Rytilä, P.; Metso, T.; Haahtela, T.; Venge, P.; Tikkanen, H.O. Respiratory symptoms, bronchial responsiveness, and cellular characteristics of induced sputum in elite swimmers. Allergy 1998, 53, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrite, A.; Allonier, C.; Com-Ruelle, L.; Le Guen, N. IRDES. L’asthme en France en 2006: Prévalence, Contrôle et Déterminants; Report no: 549; IRDS: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Voy, R.O. The U.S. Olympic Committee experience with exercise-induced bronchospasm, 1984. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1986, 18, 328–330, Report no: 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Wolfarth, B.; Wittmer, C.; Nowak, D.; Radon, K.; GA2LEN-Olympic study-Team. Self-reported asthma and allergies in top athletes compared to the general population—Results of the German part of the GA2LEN-Olympic study 2008. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2010, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poussel, M.; Chenuel, B. Bronchoconstriction induite par l’exercice sans asthme associé chez l’athlète: Physiopathologie, diagnostic et prise en charge spécifique. Rev. Malad. Respir. Actual 2010, 27, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.; Mulgirigama, A.; Berend, N. Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction: Prevalence, pathophysiology, patient impact, diagnosis and management. NPJ Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2018, 28, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.Y.M.; Martin, R.J.; Szefler, S.J.; Sher, E.R.; Ying, S.; Kay, A.B.; Hamid, Q. Dysregulation of interleukin 4, interleukin 5, and interferon 1 gene expression in steroid-resistant asthma. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 181, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiler, J.M.; Anderson, S.D.; Randolph, C.; Bonini, S.; Craig, T.; Pearlman, D.; Rundell, K.; Silvers, W.; Storms, W.; Bernstein, D.I.; et al. Pathogenesis, prevalence, diagnosis, and management of exerciseinduced bronchoconstriction: A practice parameter. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010, 105, S1–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, J.P.; Craig, T.J.; Stoloff, S.W.; Hayden, M.L.; Ostrom, N.K.; Eid, N.S.; Colice, G.L. Impact of exercise-related respiratory symptoms in adults with asthma: Exercise-Induced Bronchospasm Landmark National Survey. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2011, 32, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundell, K.W. High Levels of Airborne Ultrafine and Fine Particulate Matter in Indoor Ice Arenas. Inhal. Toxicol. 2003, 15, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumme, A.; Haahtela, T.; Öunap, J.; Rytilä, P.; Obase, Y.; Helenius, M.; Remes, V.; Helenius, I. Airway inflammation, bronchial hyperresponsiveness and asthma in elite ice hockey players. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 22, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2021. Available online: www.ginathma.org (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Parsons, J.P.; Hallstrand, T.S.; Mastronarde, J.G.; Kaminsky, D.A.; Kaminsky, D.A.; Rundell, K.W.; Hull, J.H.; Storms, W.W.; Weiler, J.M.; Cheek, F.M.; et al. An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline: Exercise-induced Bronchoconstriction. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 1016–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.Y.; Bloom, J.W. Update on glucocorticoid action and resistance. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, R.; Giembycz, M.A. Understanding how long-acting β2-adrenoceptor agonists enhance the clinical efficacy of inhaled corticosteroids in asthma—An update. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 3405–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, A.; Altraja, A.; Kampe, M.; Linder, M.; Virtanen, I.; Laitinen, L.A. Tenascin is increased in airway basement membrane of asthmatics and decreased by an inhaled steroid. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, T.; Minshall, E.M.; Leung, D.Y.; Laberge, S.; Ernst, P.; Martin, R.J.; Hamid, Q. Expression of IL-12 and IL-13 mRNA in asthma and their modulation in response to steroid therapy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sue-Chu, M.; Karjalainen, E.M.; Laitinen, A.; Larsson, L.; Laitinen, L.A.; Bjermer, L. Placebo-controlled study of inhaled budesonide on indices of airway infammation in bronchoalveolar lavage fuid and bronchial biopsies in cross-country skiers. Respir. Int. Rev. Thorac. Dis. 2000, 67, 417–425. [Google Scholar]
- Trigg, C.J.; Manolitsas, N.D.; Wang, J.; Calderon, M.A.; McAulay, A.; Jordan, S.E.; Herdman, S.E.; Jhalli, N.; Duddle, J.M.; Hamilton, S.A.; et al. Placebo controlled immunopathologic study of four months of inhaled corticosteroids in asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 150, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukioka, K.; Koya, T.; Ueno, H.; Hayashi, M.; Sakagami, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Arakawa, M.; Suzuki, E.; Kikuchi, T. Phenotypic analysis of asthma in Japanese athletes. Allergol. Int. 2017, 66, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, S.D.; Kippelen, P. Airway injury as a mechanism for exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in elite athletes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrant, D.M.; Metzger, D.W. Emerging Roles of T Helper Subsets in the Pathogenesis of Asthma. Immunol. Investig. 2010, 39, 526–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckheeram, R.V.; Zhou, R.; Verma, A.D.; Xia, B. CD4+T Cells: Differentiation and Functions. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 925135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, W.W.; Lemanske, R.F. Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Kolls, J. Neutrophilic Inflammation in Asthma and Association with Disease Severity. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 942–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuthota, P.; Wang, H.B.; Spencer, L.A.; Weller, P.F. Immunoregulatory roles of eosinophils: A new look at a familiar cell. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 38, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, S.E. Asthma phenotypes: The evolution from clinical to molecular approaches. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.C.; Meyers, D.A.; Wenzel, S.E.; Teague, W.G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; D’Agostino, R.; Castro, M.; Curran-Everett, D.; Fitzpatrick, A.M.; et al. Identification of Asthma Phenotypes Using Cluster Analysis in the Severe Asthma Research Program. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elenkov, I.J. Glucocorticoids and the Th1/Th2 Balance. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1024, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrigan, C.J.; Brown, P.H.; Barnes, N.C.; Szefler, S.J.; Tsai, J.J.; Frew, A.J.; Kay, A.B. Glucocorticoid Resistance in Chronic Asthma: Peripheral Blood T Lymphocyte Activation and Comparison of the T Lymphocyte Inhibitory Effects of Glucocorticoids and Cyclosporin A. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1991, 144, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitch, K.D. β2-Agonists at the Olympic Games. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2006, 31, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norqvist, J.; Eriksson, L.; Söderström, L.; Lindberg, A.; Stenfors, N. Self-reported physician-diagnosed asthma among Swedish adolescent, adult and former elite endurance athletes. J. Asthma 2015, 52, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, L.M.; Irewall, T.; Lindberg, A.; Stenfors, N. Prevalence, age at onset, and risk factors of self-reported asthma among Swedish adolescent elite cross-country skiers. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2018, 28, 180–186. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsen, K.H. Sports in extreme conditions: The impact of exercise in cold temperatures on asthma and bronchial hyper-responsiveness in athletes. Br. J. Sports Med. 2012, 46, 796–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Delgado, L.; Palmares, C.; Lopes, C.; Jacinto, T.; Rytilä, P.; Silva, J.A.; Gastel-Branco, M.G.; Haahtela, T. Competitive swimmers with allergic asthma show a mixed type of airway inflammation. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 31, 1139–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonetto, G.; Corradi, M.; Carraro, S.; Zanconato, S.; Alinovi, R.; Folesani, G.; Da Dalt, L.; Mutti, A.; Baraldi, E. Longitudinal Monitoring of Lung Injury in Children after Acute Chlorine Exposure in a Swimming Pool. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.D.; Davidson, W.J.; Wong, L.E.; Traves, S.L.; Leigh, R.; Eves, N.D. Airway inflammation, cough and athlete quality of life in elite female cross-country skiers: A longitudinal study. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 26, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karjalainen, E.M.; Laitinen, A.; Sue-Chu, M.; Altraja, A.; Bjermer, L.; Laitinen, L.A. Evidence of Airway Inflammation and Remodeling in Ski Athletes with and without Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness to Methacholine. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 2086–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, S.D.; Brannan, J.D. Methods for “Indirect” Challenge Tests Including Exercise, Eucapnic Voluntary Hyperpnea, and Hypertonic Aerosols. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2003, 24, 27–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perpiñá Tordera, M.; García Río, F.; Álvarez Gutierrez, F.J.; Cisneros Serrano, C.; Compte Torrero, L.; Entrenas Costa, L.M.; Melero Moreno, C.; Rodríguez Nieto, M.J.; Torrego Fernández, A. Guidelines for the Study of Nonspecific Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness in Asthma. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2013, 49, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterk, P.J.; Bel, E.H. Bronchial hyperresponsiveness: The need for a distinction between hypersensitivity and excessive airway narrowing. Eur. Respir. J. 1989, 2, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thornton, D.J.; Sheehan, J.K. From mucins to mucus: Toward a more coherent understanding of this essential barrier. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2004, 1, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, S.D.; Kippelen, P. Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction: Pathogenesis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2005, 5, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heir, T.; Oseid, S. Self-reported asthma and exercise-induced asthma symptoms in high-level competitive cross-country skiers. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 1994, 4, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallstrand, T.S.; Debley, J.S.; Farin, F.M.; Henderson Jr, W.R. Role of MUC5AC in the pathogenesis of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonini, M.; Gramiccioni, C.; Fioretti, D.; Ruckert, B.; Rinaldi, M.; Akdis, C.; Todaro, A.; Palange, P.; Carlsen, K.H.; Pelliccia, A.; et al. Asthma, allergy and the Olympics: A 12-year survey in elite athletes. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 15, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutau, G. Sport, asthme et allergie. Rev. Fr. Allergol. 2017, 57, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allergies|Inserm—La Science Pour la Santé. 2020. Available online: https://www.inserm.fr/information-en-sante/dossiers-information/allergies (accessed on 4 October 2021).
- OMS. Réseau International des Autorités de Sécurité Sanitaire des Aliments (INFOSAN). Available online: https://www.who.int/foodsafety/fs_management/No_03_allergy_June06_fr.pdf (accessed on 4 October 2021).
- Vermeer, P.D.; Harson, R.; Einwalter, L.A.; Moninger, T.; Zabner, J. Interleukin-9 Induces Goblet Cell Hyperplasia during Repair of Human Airway Epithelia. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 28, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäki-Heikkilä, R.; Karjalainen, J.; Parkkari, J.; Valtonen, M.; Lehtimäki, L. Asthma in Competitive Cross-Country Skiers: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2020, 50, 1963–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwaru, B.I.; Ekström, M.; Hasvold, P.; Wiklund, F.; Telg, G.; Janson, C. Overuse of short-acting β2-agonists in asthma is associated with increased risk of exacerbation and mortality: A nationwide cohort study of the global SABINA programme. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M. Mechanisms of action of b2-adrenoceptor agonists. In Asthma & Rhinitis; Busse, W.W., Holgate, S.T., Eds.; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2000; pp. 1541–1568. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, P.J. Effect of β agonists on inflammatory cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 104, S10–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perttunen, H.; Moilanen, E.; Zhang, X.; Barnes, P.J.; Kankaanranta, H. β2-Agonists Potentiate Corticosteroid-Induced Neutrophil Survival. COPD 2008, 5, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.; Theron, A.J.; Steel, H.C.; Durandt, C.; Tintinger, G.R.; Feldman, C. The Beta-2-Adrenoreceptor Agonists, Formoterol and Indacaterol, but Not Salbutamol, Effectively Suppress the Reactivity of Human Neutrophils In Vitro. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 105420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M. Molecular mechanisms of β2-adrenergic receptor function, response, and regulation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 117, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.A.; Strauss, L.; Skowronski, M.; Ciufo, R.; Novak, R.; McFadden, E.R., Jr. Effect of long-term salmeterol treatment on exercise-induced asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, S.; Swystun, V.A.; Bhagat, R.; Cockcroft, D.W. Inhaled Corticosteroids Do Not Prevent the Development of Tolerance to the Bronchoprotective Effect of Salmeterol. Chest 1996, 109, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockcroft, D.W.; Swystun, V.A.; Bhagat, R. Interaction of inhaled beta 2 agonist and inhaled corticosteroid on airway responsiveness to allergen and methacholine. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 152, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, J.; McConnell AWhyte, G. Diagnosis of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction: Eucapnic voluntary hyperpnoea challenges identify previously undiagnosed elite athletes with exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarnieri, M.; Balmes, J.R. Outdoor air pollution and asthma. Lancet 2014, 383, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vertadier, N.; Trzepizur, W.; Faure, S. Overuse of Short-Acting Beta-2 Agonists (SABAs) in Elite Athletes: Hypotheses to Explain It. Sports 2022, 10, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports10030036
Vertadier N, Trzepizur W, Faure S. Overuse of Short-Acting Beta-2 Agonists (SABAs) in Elite Athletes: Hypotheses to Explain It. Sports. 2022; 10(3):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports10030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleVertadier, Nicolas, Wojciech Trzepizur, and Sébastien Faure. 2022. "Overuse of Short-Acting Beta-2 Agonists (SABAs) in Elite Athletes: Hypotheses to Explain It" Sports 10, no. 3: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports10030036
APA StyleVertadier, N., Trzepizur, W., & Faure, S. (2022). Overuse of Short-Acting Beta-2 Agonists (SABAs) in Elite Athletes: Hypotheses to Explain It. Sports, 10(3), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports10030036