Effect of Short-Duration High-Intensity Upper-Body Pre-Load Component on Performance among High-Level Cyclists
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
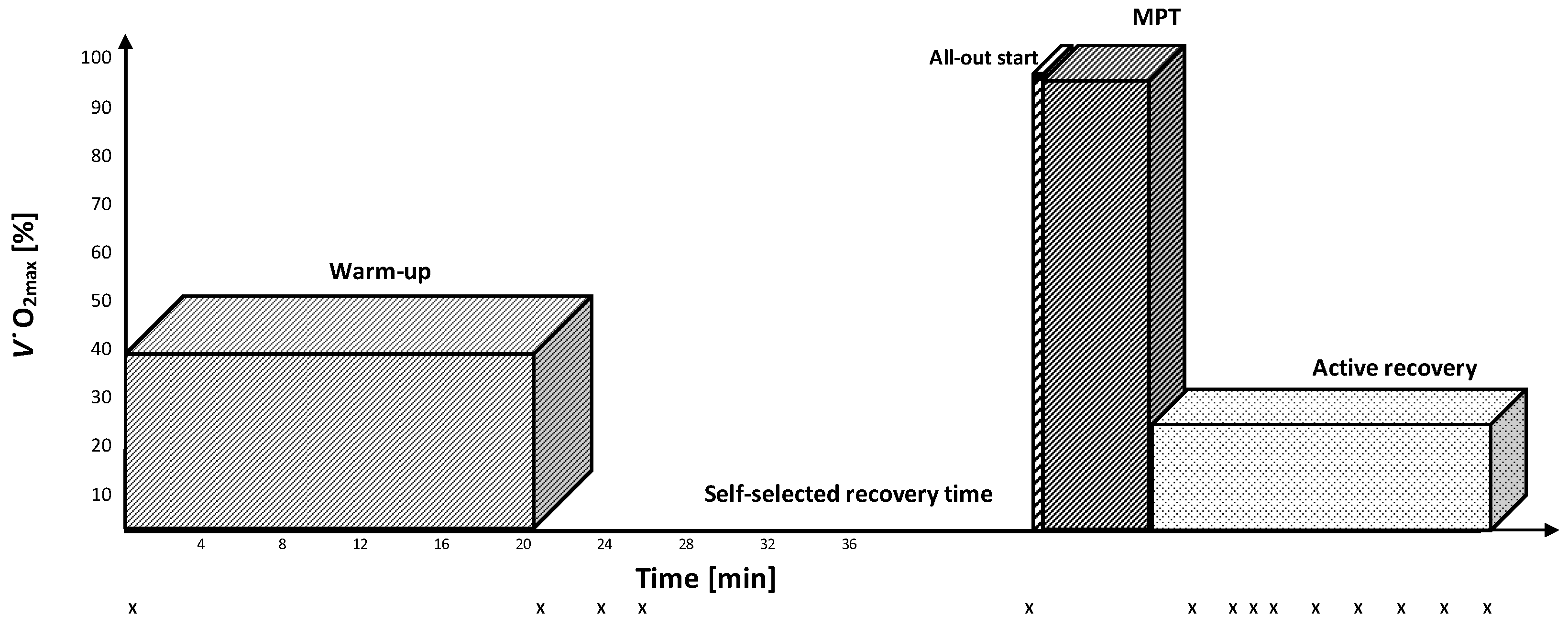
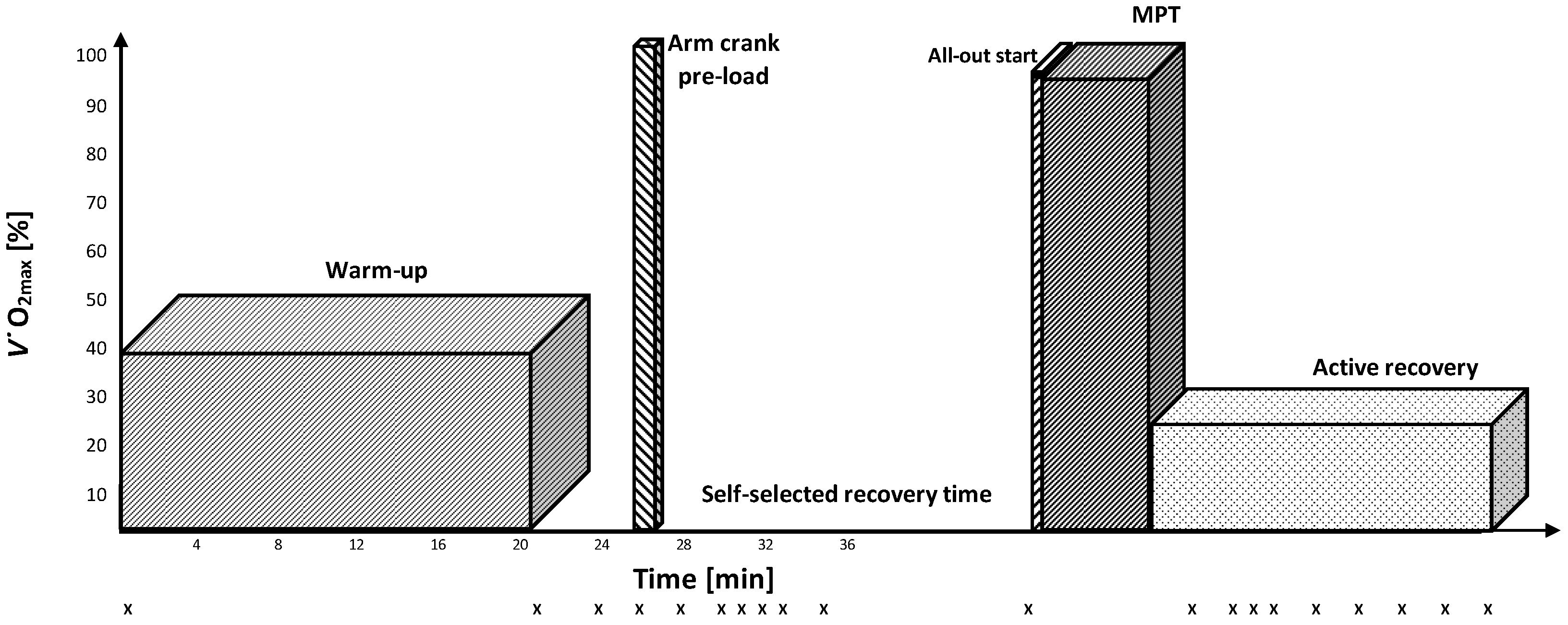
2.2. Experimental Overview
2.3. Incremental Test
2.4. Experimental Test
2.5. Measurements
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
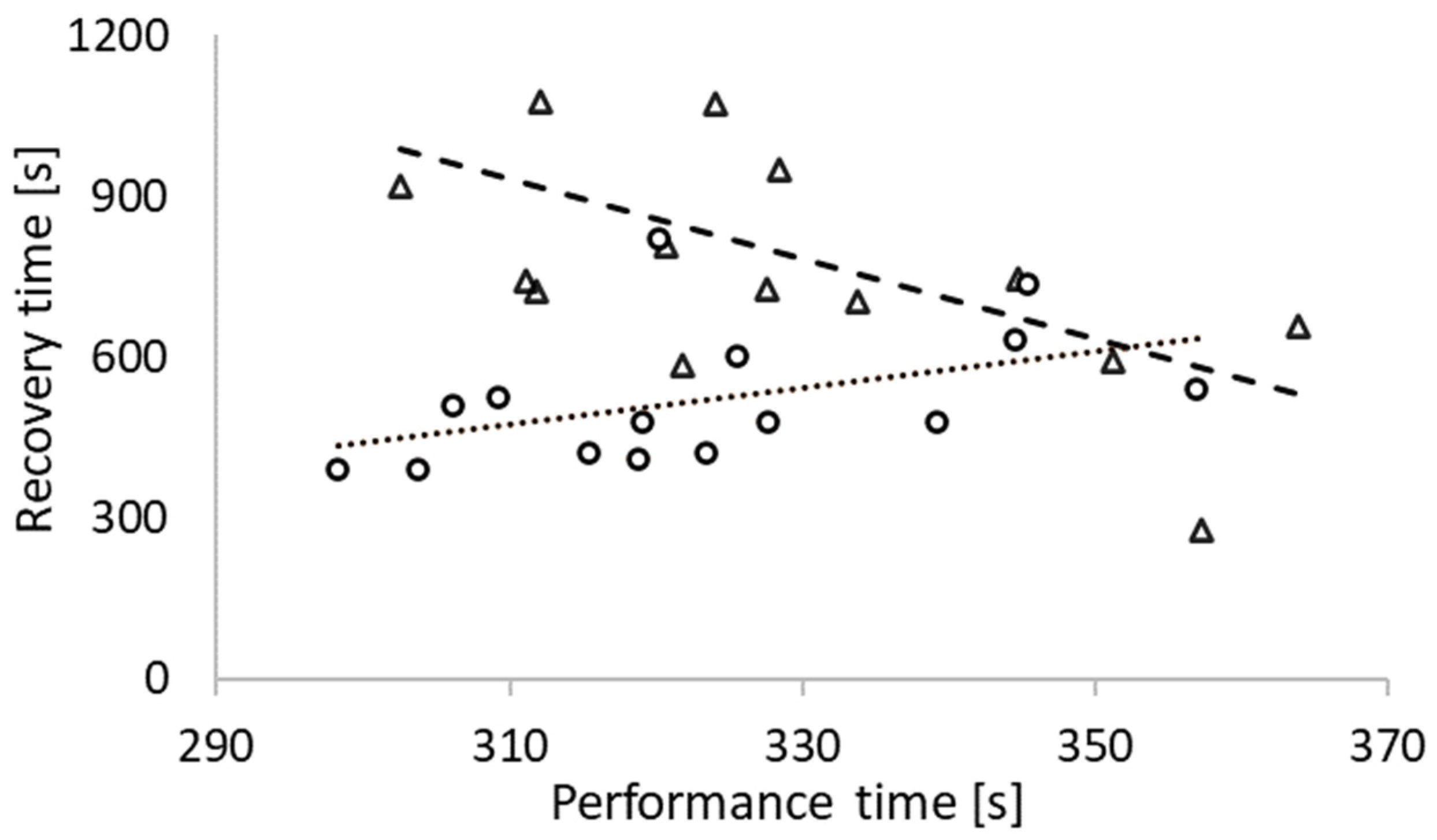
3.1. Cycling Performance
3.2. Blood Lactate Concentration
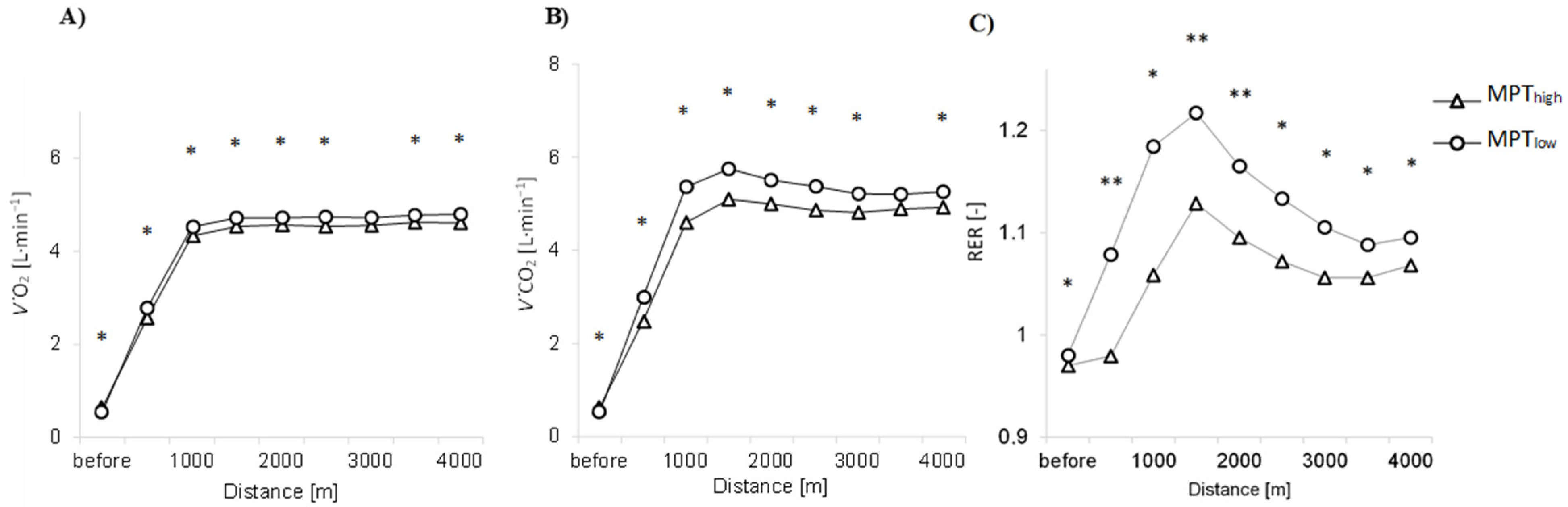
3.3. V˙O2 and V˙CO2 Kinetics
3.4. Mean Power
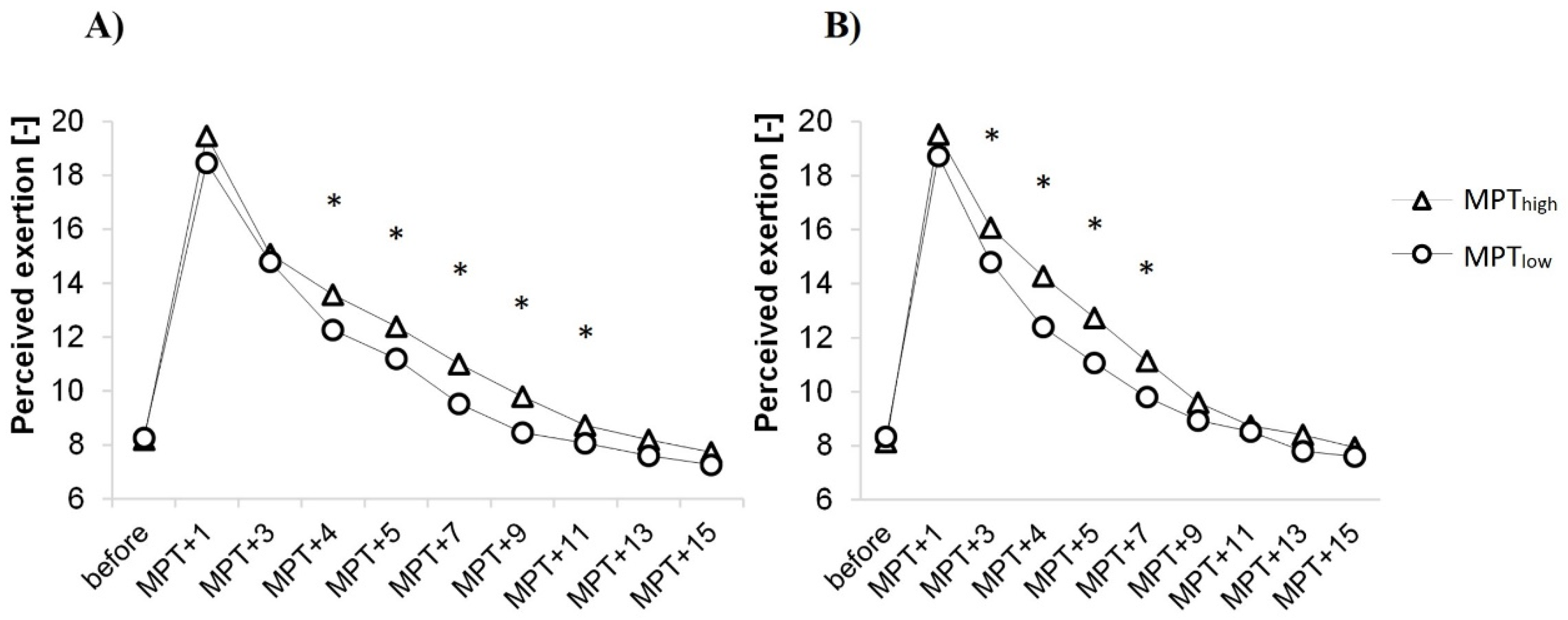
3.5. Ratings of Perceived Exertion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gladden, L.B. Lactate Metabolism: A New Paradigm for the Third Millennium. J. Physiol. 2004, 558, 5–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohnert, B.; Ward, S.A.; Whipp, B.J. Effects of Prior Arm Exercise on Pulmonary Gas Exchange Kinetics during High-Intensity Leg Exercise in Humans. Exp. Physiol. 1998, 83, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorley, A.; Lamb, K.L. The Effects of a Cycling Warm-up Including High-Intensity Heavy-Resistance Conditioning Contractions on Subsequent 4-km Time Trial Performance. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, M.; Docherty, D.; Robbins, D. Post-Activation Potentiation: Underlying Physiology and Implications for Motor Performance. Sports Med. 2005, 35, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, L.B.; Haff, G.G. Factors Modulating Post-Activation Potentiation of Jump, Sprint, Throw, and Upper-Body Ballistic Performances: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klausen, K.; Knuttgen, H.G.; Forster, H.V. Effect of Pre-Existing High Blood Lactate Concentration on Maximal Exercise Performance. Scand J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1972, 30, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, D.; Bonetti, D.; Dawson, B. The Effect of Three Different Warm-up Intensities on Kayak Ergometer Performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbino, A.; Ward, S.A.; Whipp, B.J. Effects of Prior Exercise on Pulmonary Gas-Exchange Kinetics during High-Intensity Exercise in Humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1996, 80, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Tschakert, G.; Moser, O.; Gröschl, W.; Hofmann, P. High-Intensity Exercise Warm-up, Inhibition of Glycolysis, and Its Practical Consequences. Sci. Ski. IV 2013, 224–230. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkerson, D.P.; Koppo, K.; Barstow, T.J.; Jones, A.M. Effect of Prior Multiple-Sprint Exercise on Pulmonary O2 Uptake Kinetics Following the Onset of Perimaximal Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 97, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, H.; Grice, Y.; Dekerle, J.; Brickley, G.; Hammond, A.J.P.; Pringle, J.S.M. Effect of Prior Exercise above and below Critical Power on Exercise to Exhaustion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkett, L.N.; Phillips, W.T.; Ziuraitis, J. The best warm-up for the vertical jump in college-age athletic men. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2005, 3, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajoglou, A.; Foster, C.; De Koning, J.J.; Lucia, A.; Kernozek, T.W.; Porcari, J.P. Effect of Warm-up on Cycle Time Trial Performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 1608–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richendollar, M.L.; Darby, L.A.; Brown, T.M. Ice Bag Application, Active Warm-Up, and 3 Measures of Maximal Functional Performance. J. Athl. Train. 2006, 41, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burnley, M.; Doust, J.H.; Jones, A.M. Effects of Prior Warm-up Regime on Severe-Intensity Cycling Performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purge, P.; Hofmann, P.; Merisaar, R.; Mueller, A.; Tschakert, G.; Mäestu, J.; Jürimäe, J. The Effect of Upper Body Anaerobic Pre-Loading on 2000-m Ergometer-Rowing Performance in College Level Male Rowers. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2017, 16, 264–271. [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer, P.; Müller, A.; Tschakert, G.; Sattler, M.C.; Hofmann, P. Performance Enhancing Effect of Metabolic Pre-Conditioning on Upper-Body Strength-Endurance Exercise. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bogdanis, G.C.; Nevill, M.E.; Lakomy, H.K. Effects of Previous Dynamic Arm Exercise on Power Output during Repeated Maximal Sprint Cycling. J. Sports Sci. 1994, 12, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aisbett, B.; Lerossignol, P.; Mcconell, G.K.; Abbiss, C.R.; Snow, R. Influence of All-Out and Fast Start on 5-Min Cycling Time Trial Performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 1965–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, D.; Bonetti, D.; Dawson, B. The Influence of Pacing Strategy on VO2 and Supramaximal Kayak Performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, K.; Antonellis, P.; Black, M.I.; DiMenna, F.J.; Vanhatalo, A.; Jones, A.M.; Bailey, S.J. Improvement of Oxygen-Uptake Kinetics and Cycling Performance with Combined Prior Exercise and Fast Start. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borg, G. Subjective Aspects of Physical and Mental Load. Ergonomics 1978, 21, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, J.S.; McCormick, M.C.; Robergs, R.A. Interaction among Skeletal Muscle Metabolic Energy Systems during Intense Exercise. J. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 2010, 905612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burnley, M.; Doust, J.H.; Jones, A.M. Time Required for the Restoration of Normal Heavy Exercise VO2 Kinetics Following Prior Heavy Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 101, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, A.M.; Wilkerson, D.P.; Burnley, M.; Koppo, K. Prior Heavy Exercise Enhances Performance during Subsequent Perimaximal Exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 2085–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, G.A. Intra- and Extra-Cellular Lactate Shuttles. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangsbo, J.; Michalsik, L.; Petersen, A. Accumulated O2 Deficit during Intense Exercise and Muscle Characteristics of Elite Athletes. Int. J. Sports Med. 1993, 14, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 23.3 ± 3.6 |
| Height (m) | 1.8 ± 0.1 |
| Body Mass (kg) | 76.2 ± 10.0 |
| BMI (kg·m−2) | 23.2 ± 2.0 |
| Fat (%) | 16.1 ± 3.2 |
| Body lean mass (kg) | 58.6 ± 6.8 |
| Leg lean mass (kg) | 20.5 ± 2.1 |
| V˙O2max (mL·kg−1·min−1) | 65.4 ± 6.7 |
| V˙O2max (L·min−1) | 4.9 ± 0.5 |
| Ventilatory threshold VT1 (W) | 218.7 ± 33.9 |
| Ventilatory threshold VT2 (W) | 310.8 ± 39.3 |
| Parameter | MPTlow | MPThigh | p-Value | Effect Size (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial 12 s | ||||
| Distance (m) | 198 ± 14 | 192 ± 17 | 0.133 | 0.4 (−15.3 to 2.2) |
| Average power (W·kg−1) | 10.5 ± 2.1 | 9.7 ± 2.5 | 0.104 | 0.5 (−1.6 to 0.2) |
| Peak power (W·kg−1) | 1014 ± 219 | 974 ± 221 | 0.391 | 0.2 (−139.3 to 58.0) |
| Performance | ||||
| Time (s) | 323.6 ± 16.2 | 328.9 ± 17.4 | 0.019 * | 0.7 (1.0 to 9.5) |
| Average power (W·kg−1) | 5.6 ± 0.7 | 5.3 ± 0.7 | 0.018 * | 0.7 (−0.6 to −0.1) |
| Labefore (mmol·L−1) | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 6.9 ± 2.1 | <0.001 ** | 2.5 (4.3 to 6.7) |
| Lanet (mmol·L−1) | 14.9 ± 2.2 | 11.1 ± 2.7 | <0.001 ** | 1.2 (−5.5 to −2.1) |
| Lamax (mmol·L−1) | 16.3 ± 2.2 | 17.9 ± 2.4 | 0.017 * | 0.7 (0.3 to 2.9) |
| V˙O2before (L·min−1) | 0.5 (0.47–0.66) | 0.64 (0.51–0.78) | 0.023 * | 0.4 (0.03 to 0.16) |
| V˙O2max (L·min−1) | 4.9 (4.8–5.2) | 4.6 (4.3–5.2) | 0.013 * | 0.4 (−0.4 to −0.1) |
| Recovery time (s) | 522 ± 123 | 792 ± 237 | 0.003 * | 0.9 (110.2 to 431.0) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valiulin, D.; Purge, P.; Mäestu, J.; Jürimäe, J.; Hofmann, P. Effect of Short-Duration High-Intensity Upper-Body Pre-Load Component on Performance among High-Level Cyclists. Sports 2022, 10, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports10030032
Valiulin D, Purge P, Mäestu J, Jürimäe J, Hofmann P. Effect of Short-Duration High-Intensity Upper-Body Pre-Load Component on Performance among High-Level Cyclists. Sports. 2022; 10(3):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports10030032
Chicago/Turabian StyleValiulin, Dmitri, Priit Purge, Jarek Mäestu, Jaak Jürimäe, and Peter Hofmann. 2022. "Effect of Short-Duration High-Intensity Upper-Body Pre-Load Component on Performance among High-Level Cyclists" Sports 10, no. 3: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports10030032
APA StyleValiulin, D., Purge, P., Mäestu, J., Jürimäe, J., & Hofmann, P. (2022). Effect of Short-Duration High-Intensity Upper-Body Pre-Load Component on Performance among High-Level Cyclists. Sports, 10(3), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports10030032









