Methylation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Gene in Children with Somatic Symptom Disorder: A Case-Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Participant Characteristics
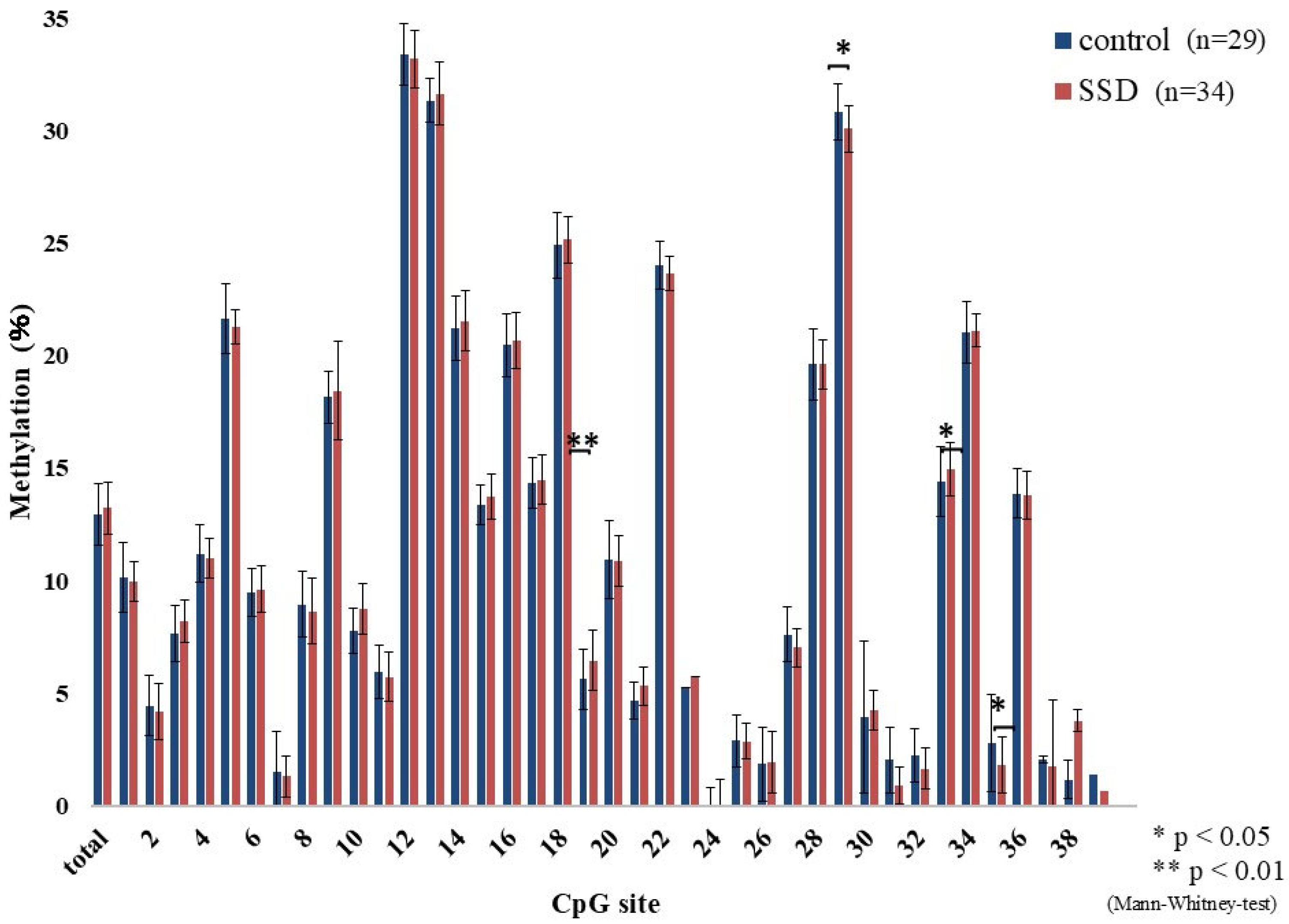
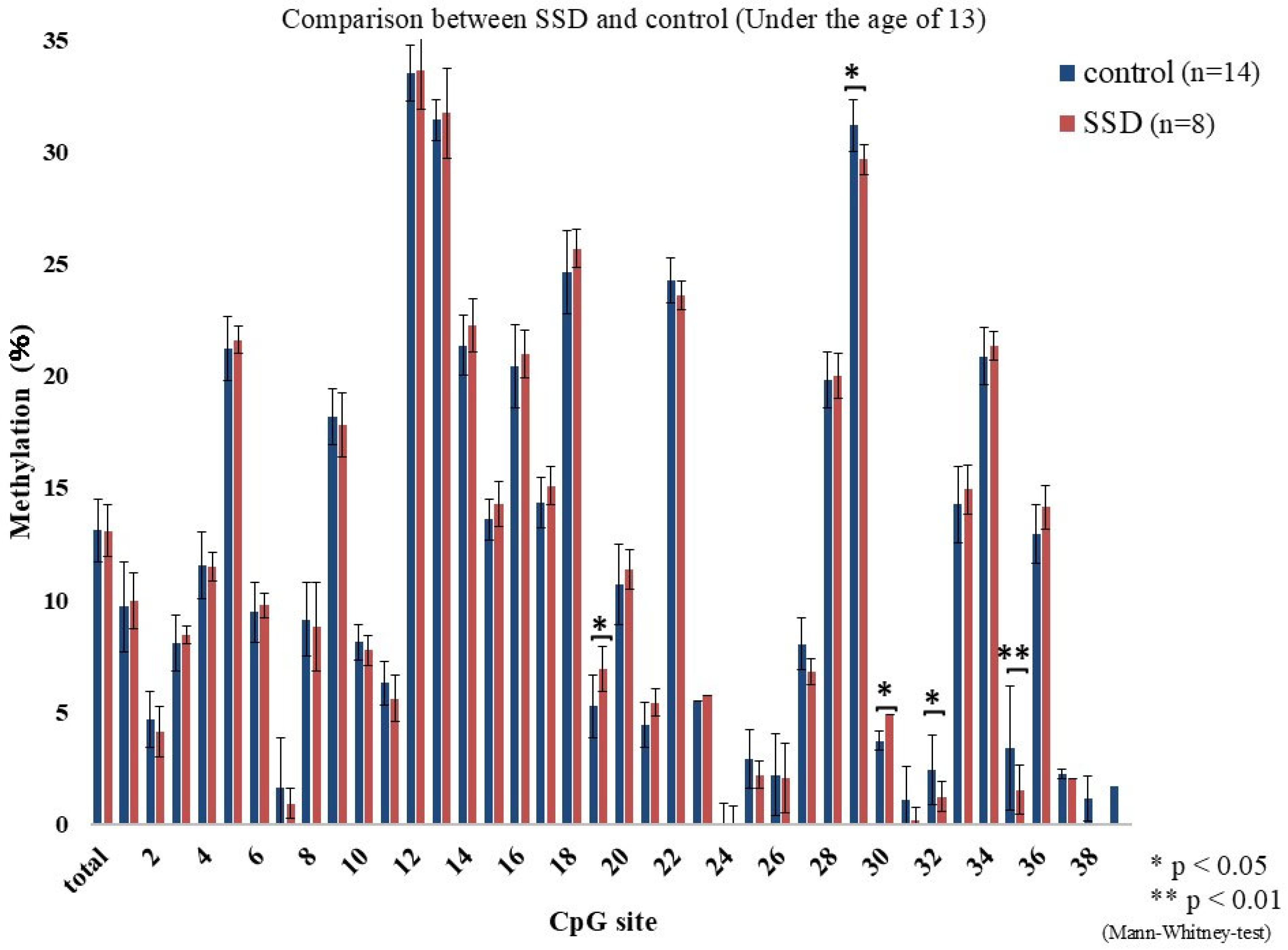
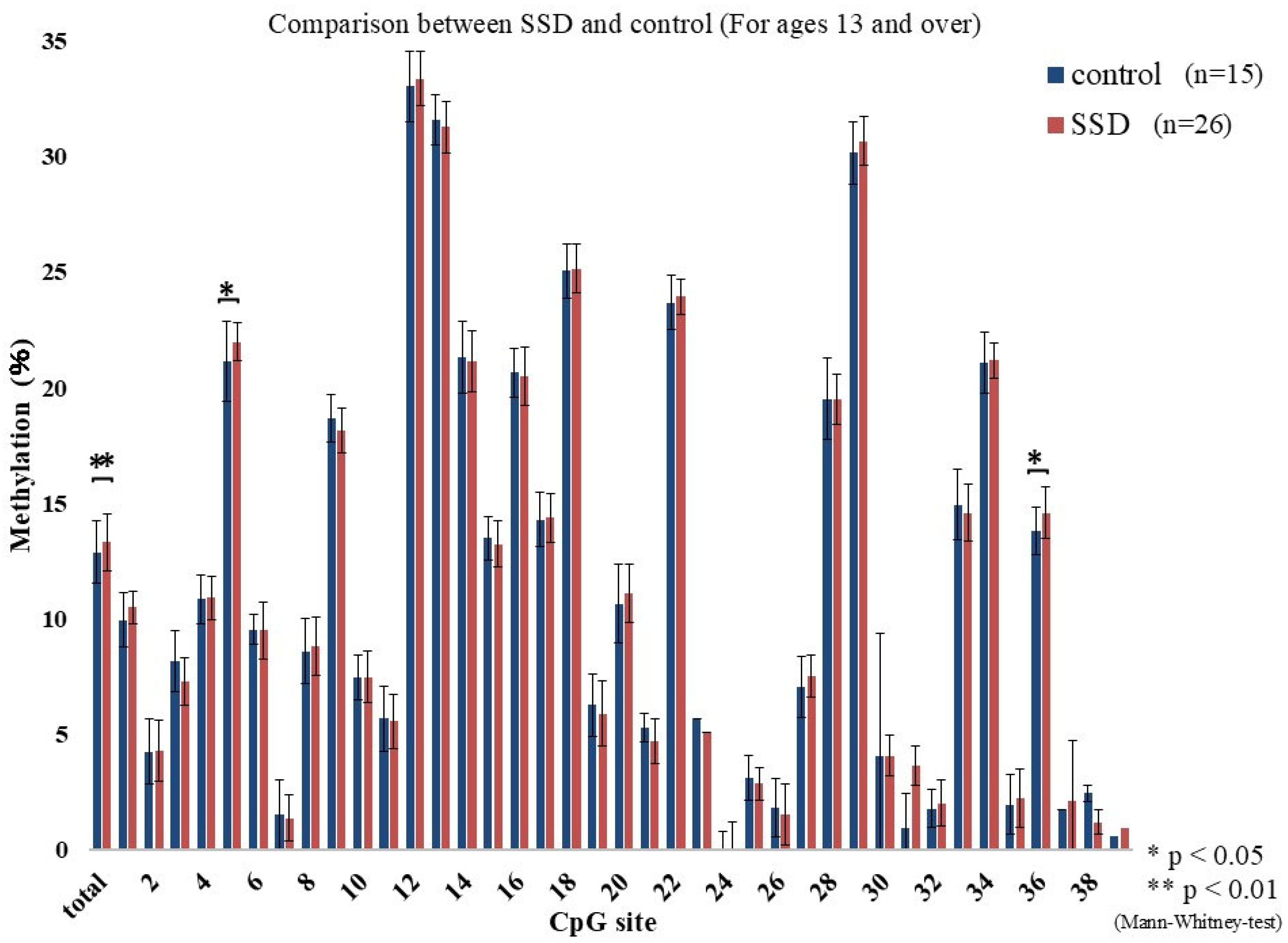
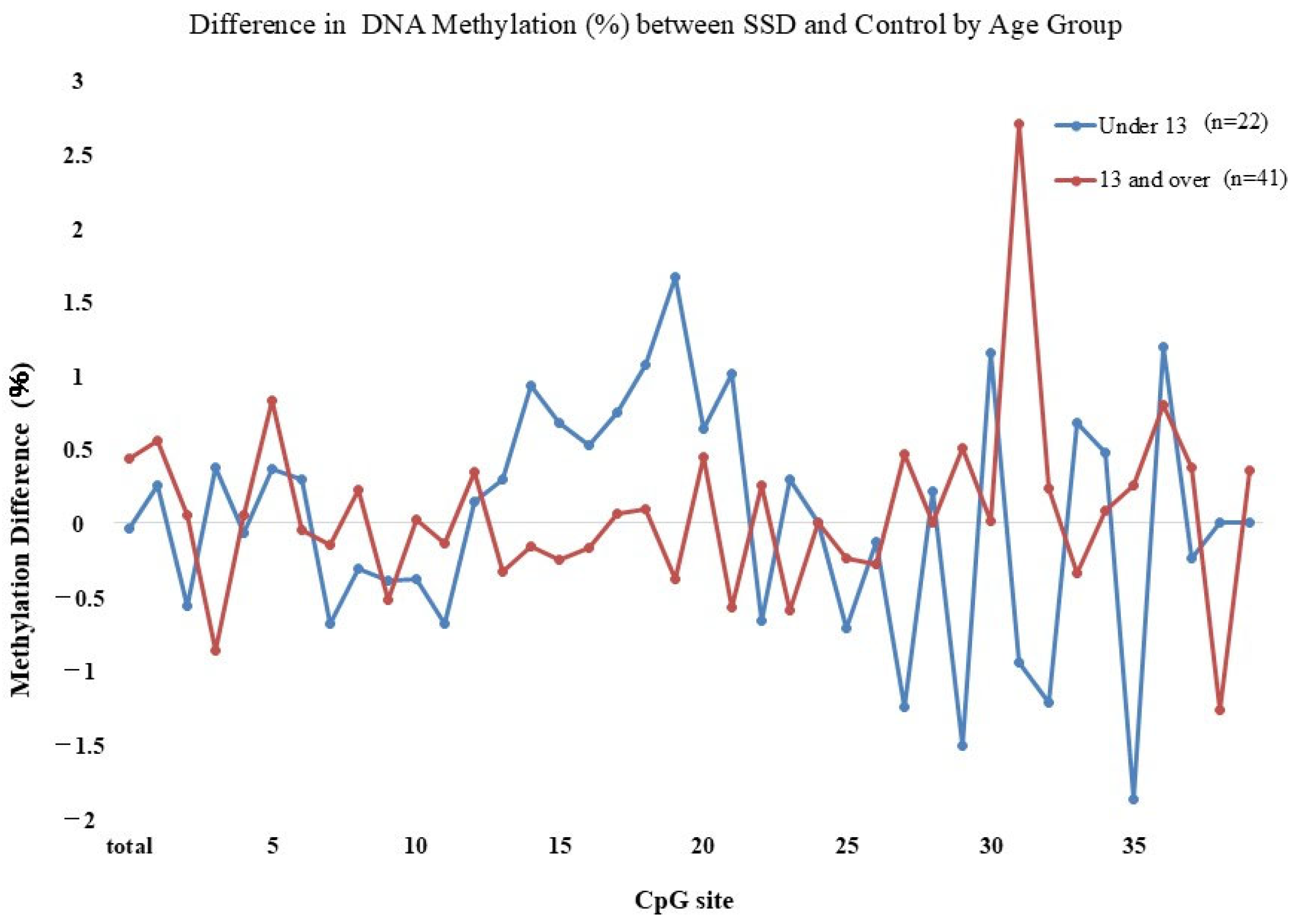
2.2. GR Gene Methylation Rate
2.3. BDI-II and KINDL Scores
2.4. Correlations Between GR Methylation Rate and Symptomatology
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Participants
3.2. Procedure
3.3. DNA Methylation Analysis
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Mahurkar, S.; Polytarchou, C.; Iliopoulos, D.; Pothoulakis, C.; Mayer, E.A.; Chang, L. Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eising, E.; Datson, N.A.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.J.M.; Ferrari, M.D. Epigenetic mechanisms in migraine: A promising avenue? BMC Med. 2013, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietjen, G.E.; Peterlin, B.L. Childhood abuse and migraine: Epidemiology, sex differences, and potential mechanisms. Headache 2011, 51, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelman, L. The triggers or precipitants of the acute migraine attack. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Gudiel, H.; Córdova-Palomera, A.; Leza, J.C.; Fañanás, L. Glucocorticoid receptor gene (NR3C1) methylation processes as mediators of early adversity in stress-related disorders causality: A critical review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 55, 520–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, I.C.; Cervoni, N.; Champagne, F.A.; D’Alessio, A.C.; Sharma, S.; Seckl, J.R.; Dymov, S.; Szyf, M.; Meaney, M.J. Epigenetic programming by maternal behavior. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parade, S.H.; Ridout, K.K.; Seifer, R.; Armstrong, D.A.; Marsit, C.J.; McWilliams, M.A.; Tyrka, A.R. Methylation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Gene Promoter in Preschoolers: Links With Internalizing Behavior Problems. Child. Dev. 2016, 87, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantake, M.; Ohkawa, N.; Iwasaki, T.; Ikeda, N.; Awaji, A.; Saito, N.; Shoji, H.; Shimizu, T. Postnatal relative adrenal insufficiency results in methylation of the glucocorticoid receptor gene in preterm infants: A retrospective cohort study. Clin. Epigenetics 2018, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradt, E.; Lester, B.M.; Appleton, A.A.; Armstrong, D.A.; Marsit, C.J. The roles of DNA methylation of NR3C1 and 11β-HSD2 and exposure to maternal mood disorder in utero on newborn neurobehavior. Epigenetics 2013, 8, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberlander, T.F.; Weinberg, J.; Papsdorf, M.; Grunau, R.; Misri, S.; Devlin, A.M. Prenatal exposure to maternal depression, neonatal methylation of human glucocorticoid receptor gene (NR3C1) and infant cortisol stress responses. Epigenetics 2008, 3, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrka, A.R.; Parade, S.H.; Eslinger, N.M.; Marsit, C.J.; Lesseur, C.; Armstrong, D.A.; Philip, N.S.; Josefson, B.; Seifer, R. Methylation of exons 1D, 1F, and 1H of the glucocorticoid receptor gene promoter and exposure to adversity in preschool-aged children. Dev. Psychopathol. 2015, 27, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perroud, N.; Paoloni-Giacobino, A.; Prada, P.; Olié, E.; Salzmann, A.; Nicastro, R.; Guillaume, S.; Mouthon, D.; Stouder, C.; Dieben, K.; et al. Increased methylation of glucocorticoid receptor gene (NR3C1) in adults with a history of childhood maltreatment: A link with the severity and type of trauma. Transl. Psychiatry 2011, 1, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melas, P.A.; Wei, Y.; Wong, C.C.; Sjöholm, L.K.; Åberg, E.; Mill, J.; Schalling, M.; Forsell, Y.; Lavebratt, C. Genetic and epigenetic associations of MAOA and NR3C1 with depression and childhood adversities. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 16, 1513–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schür, R.R.; Boks, M.P.; Rutten, B.P.F.; Daskalakis, N.P.; de Nijs, L.; van Zuiden, M.; Kavelaars, A.; Heijnen, C.J.; Joëls, M.; Kahn, R.S.; et al. Longitudinal changes in glucocorticoid receptor exon 1F methylation and psychopathology after military deployment. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaton, A.M.; Bird, A. CpG islands and the regulation of transcription. Genes. Dev. 2011, 25, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rauwerda, N.L.; Tovote, K.A.; Peeters, A.C.T.M.; Sanderman, R.; Emmelkamp, P.M.G.; Schroevers, M.J.; Fleer, J. WHO-5 and BDI-II are acceptable screening instruments for depression in people with diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2018, 35, 1678–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Gorenstein, C. Psychometric properties of the Beck Depression Inventory-II: A comprehensive review. Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2013, 35, 416–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, M.; Furukawa, T.A.; Takahashi, H.; Kawai, M.; Nagaya, T.; Tokudome, S. Cross-cultural validation of the Beck Depression Inventory-II in Japan. Psychiatry Res. 2002, 110, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, P.; Stevanovic, D.; Bagheri, Z. Cross-cultural measurement equivalence of the KINDL questionnaire for quality of life assessment in children and adolescents. Child. Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2016, 47, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, N.; Ohya, Y.; Futamura, M.; Akashi, M.; Odajima, H.; Adachi, Y.; Kobayashi, F.; Akasawa, A. Exercise-induced asthma is associated with impaired quality of life among children with asthma in Japan. Allergol. Int. 2009, 58, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, K.; Nemoto, Y.; Shibata, R. A study of the Kiddo-KINDL (Questionnaire for Measuring Health-Related Quality of Life in Children, Revised Version for 13 to 17-year-olds) in Japan. J. Jpn. Pediatr. Soc. 2007, 111, 1404–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Shibata, R.; Nemoto, Y.; Matsuzaki, K. A study of the Kid-KINDL questionnaire for measuring quality of life in elementary school children in Japan. J. Jpn. Pediatr. Soc. 2003, 107, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, T.M.; Sharfi, D.; Lee, M.; Yrigollen, C.M.; Naumova, O.Y.; Grigorenko, E.L. Comparison of whole-genome DNA methylation patterns in whole blood, saliva, and lymphoblastoid cell lines. Behav. Genet. 2013, 43, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazzari, S.; Grumi, S.; Mambretti, F.; Villa, M.; Giorda, R.; Provenzi, L. Maternal and infant NR3C1 and SLC6A4 epigenetic signatures of the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown: When timing matters. Transl. Psychiatry. 2022, 12, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leakey, T.I.; Zielinski, J.; Siegfried, R.N.; Siegel, E.R.; Fan, C.Y.; Cooney, C.A. A simple algorithm for quantifying DNA methylation levels on multiple independent CpG sites in bisulfite genomic sequencing electropherograms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Gudiel, H.; Peralta, V.; Deuschle, M.; Navarro, V.; Fañanás, L. Epigenetics-by-sex interaction for somatization conferred by methylation at the promoter region of SLC6A4 gene. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry. 2019, 89, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiopoulou, A.; Karamanolis, G.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Karatzias, G.; Gazouli, M. Molecular basis of the irritable bowel syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkeys, O.J.; Kremerskothen, K.; Quidé, Y.; Fullerton, J.M.; Green, M.J. Glucocorticoid receptor gene (NR3C1) DNA methylation in association with trauma, psychopathology, transcript expression, or genotypic variation: A systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 95, 85–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrka, A.R.; Parade, S.H.; Welch, E.S.; Ridout, K.K.; Price, L.H.; Marsit, C.; Philip, N.S.; Carpenter, L.L. Methylation of the leukocyte glucocorticoid receptor gene promoter in adults: Associations with early adversity and depressive, anxiety and substance-use disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gureje, O.; Simon, G.E.; Von Korff, M. A cross-national study of the course of persistent pain in primary care. Pain 2001, 92, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, L.S.; Garber, J.; Van Slyke, D.A.; Greene, J.W. Long-term health outcomes in patients with recurrent abdominal pain. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 1995, 20, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, L.S.; Garber, J.; Smith, C.A.; Van Slyke, D.A.; Claar, R.L. The relation of daily stressors to somatic and emotional symptoms in children with and without recurrent abdominal pain. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2001, 69, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlowska, K.; Scher, S.; Helgeland, H. Functional Somatic Symptoms in Children and Adolescents: A Stress-System Approach to Assessment and Treatment; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dempster, K.S.; O‘Leary, D.D.; MacNeil, A.J.; Hodges, G.J.; Wade, T.J. Linking the hemodynamic consequences of adverse childhood experiences to an altered HPA axis and acute stress response. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 93, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Kleinstäuber, M.; Fiori, L.M.; Turecki, G.; Wagner, J.; von Känel, R. DNA methylation signatures of functional somatic syndromes: Systematic review. Psychosom. Med. 2023, 85, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emich-Widera, E.; Kazek, B.; Szwed-Bialozyt, B.; Kopyta, I.; Kostorz, A. Headaches as somatoform disorders in children and adolescents. Ment. Illn. 2012, 4, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidetti, V.; Faedda, N.; Siniatchkin, M. Migraine in childhood: Biobehavioural or psychosomatic disorder? J. Headache Pain 2016, 17, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahgoub, M.; Monteggia, L.M. Epigenetics and psychiatry. Neurotherapeutics 2013, 10, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surdea-Blaga, T.; Baban, A.; Dumitrascu, D.L. Psychosocial determinants of irritable bowel syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tilburg, M.A.; Levy, R.L.; Walker, L.S.; Von Korff, M.; Feld, L.D.; Garner, M.; Feld, A.D.; Whitehead, W.E. Psychosocial mechanisms for the transmission of somatic symptoms from parents to children. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 5532–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitkara, D.K.; van Tilburg, M.A.; Blois-Martin, N.; Whitehead, W.E. Early life risk factors that contribute to irritable bowel syndrome in adults: A systematic review. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Indicators | SSD (n = 34) | Controls (n = 29) | p-Value (Mann–Whitney Test) (Fisher’s Exact Test) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD) years | 13.38 (1.88) | 12.71 (1.86) | 0.22 |
| Female, n (%) | 18 (52.94) | 11 (37.93) | 0.23 |
| Household income | 0.38 | ||
| JPY 0–4,999,999, n (%) | 10 (29.41) | 11 (37.93) | |
| JPY 5,000,000–10,000,000, n (%) | 11 (32.35) | 11 (37.93) | |
| JPY 10,000,000+, n (%) | 9 (26.47) | 5 (17.24) | |
| Perinatal complication, n (%) | 2 (5.88) | 6 (20.69) | 0.09 |
| Hospitalization, n (%) | 8 (23.53) | 6 (20.70) | 0.44 |
| Victim of bullying, n (%) | 8 (23.53) | 4 (13.79) | 0.33 |
| Victim of abuse, n (%) | 3 (8.82) | 2 (6.90) | 0.73 |
| Familial mental health problem, n (%) | 13 (38.24) | 3 (10.34) | <0.01 |
| Parental divorce, n (%) | 5 (14.70) | 4 (13.79) | 0.69 |
| Indicators | Under Age of 13 (n = 8) | Ages 13 and Over (n = 26) | p-Value (Fisher’s Exact Test) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Irritable bowel syndrome, n (%) | 7 (88) | 18 (69) | 0.30 |
| Orthostatic dysregulation, n (%) | 3 (38) | 22 (85) | 0.03 |
| Chronic headache, n (%) | 0 (0) | 4 (15) | 0.32 |
| Fibromyalgia syndrome, n (%) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 0.77 |
| Several somatic symptom diseases, n (%) | 2 (25) | 17 (65) | 0.08 |
| Duration of the disease more than three years, n (%) | 1 (13) | 14 (54) | 0.02 |
| CpG Site | BDI-II | KINDL Total | Physical Well-Being | Emotional Well-Being | Self-Esteem | Family | Friends | School |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSD (n = 34) | 16.69 (12.16) ** | 77.16 (12.95) ** | 11.97 (3.02) * | 14.81 (3.28) * | 9.94 (3.49) | 14.89 (3.56) | 14.19 (4.03) * | 11.41 (4.15) * |
| Controls (n = 29) | 6.70 (5.92) ** | 91.22 (11.95) ** | 16.67 (2.73) * | 16.81 (3.01) * | 11.89 (3.97) | 15.59 (3.53) | 16.85 (2.78) * | 13.41 (2.90) * |
| p-Value | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.62 | 0.02 | 0.04 |
| BDI-II | KINDL Total | Physical Well-Being | Emotional Well-Being | Self-Esteem | Family | Friends | School | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CpG 19 | 0.39 (0.09) | −0.46 (0.04) * | −0.46 (0.04) * | −0.11 (0.66) | −0.09 (0.71) | −0.19 (0.43) | −0.36 (0.12) | −0.30 (0.20) |
| CpG 29 | −0.22 (0.35) | 0.13 (0.58) | 0.49 (0.03) * | −0.25 (0.29) | −0.12 (0.61) | 0.20 (0.40) | 0.06 (0.81) | −0.14 (0.56) |
| CpG 30 | 0.37 (0.11) | −0.47 (0.04) * | −0.53 (0.02) * | 0.08 (0.75) | −0.33 (0.16) | −0.41 (0.07) | −0.14 (0.56) | −0.33 (0.16) |
| CpG 32 | −0.47 (0.04) * | 0.52 (0.02) * | 0.31 (0.20) | 0.28 (0.25) | 0.39 (0.10) | 0.37 (0.12) | 0.60 (0.008) ** | 0.31 (0.20) |
| CpG 35 | −0.63 (0.003) ** | 0.47 (0.04) * | 0.72 (0.00) ** | 0.26 (0.28) | 0.18 (0.46) | −0.03 (0.91) | 0.28 (0.23) | 0.14 (0.56) |
| BDI-II | KINDL Total | Physical Well-Being | Emotional Well-Being | Self-Esteem | Family | Friends | School | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CpG 5 | 0.08 (0.63) | −0.14 (0.40) | −0.21 (0.22) | −0.12 (0.49) | −0.08 (0.62) | −0.11 (0.51) | −0.05 (0.77) | −0.01 (0.93) |
| CpG 36 | −0.02 (0.93) | −0.09 (0.61) | −0.15 (0.39) | −0.26 (0.12) | −0.05 (0.76) | −0.20 (0.23) | 0.009 (0.96) | 0.05 (0.78) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hatta, K.; Kantake, M.; Tanaka, K.; Nakaoka, H.; Shimizu, T.; Shoji, H. Methylation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Gene in Children with Somatic Symptom Disorder: A Case-Control Study. Epigenomes 2025, 9, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9020022
Hatta K, Kantake M, Tanaka K, Nakaoka H, Shimizu T, Shoji H. Methylation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Gene in Children with Somatic Symptom Disorder: A Case-Control Study. Epigenomes. 2025; 9(2):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleHatta, Kyoko, Masato Kantake, Kyoko Tanaka, Hirofumi Nakaoka, Toshiaki Shimizu, and Hiromichi Shoji. 2025. "Methylation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Gene in Children with Somatic Symptom Disorder: A Case-Control Study" Epigenomes 9, no. 2: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9020022
APA StyleHatta, K., Kantake, M., Tanaka, K., Nakaoka, H., Shimizu, T., & Shoji, H. (2025). Methylation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Gene in Children with Somatic Symptom Disorder: A Case-Control Study. Epigenomes, 9(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9020022







