Anticodon Wobble Uridine Modification by Elongator at the Crossroad of Cell Signaling, Differentiation, and Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
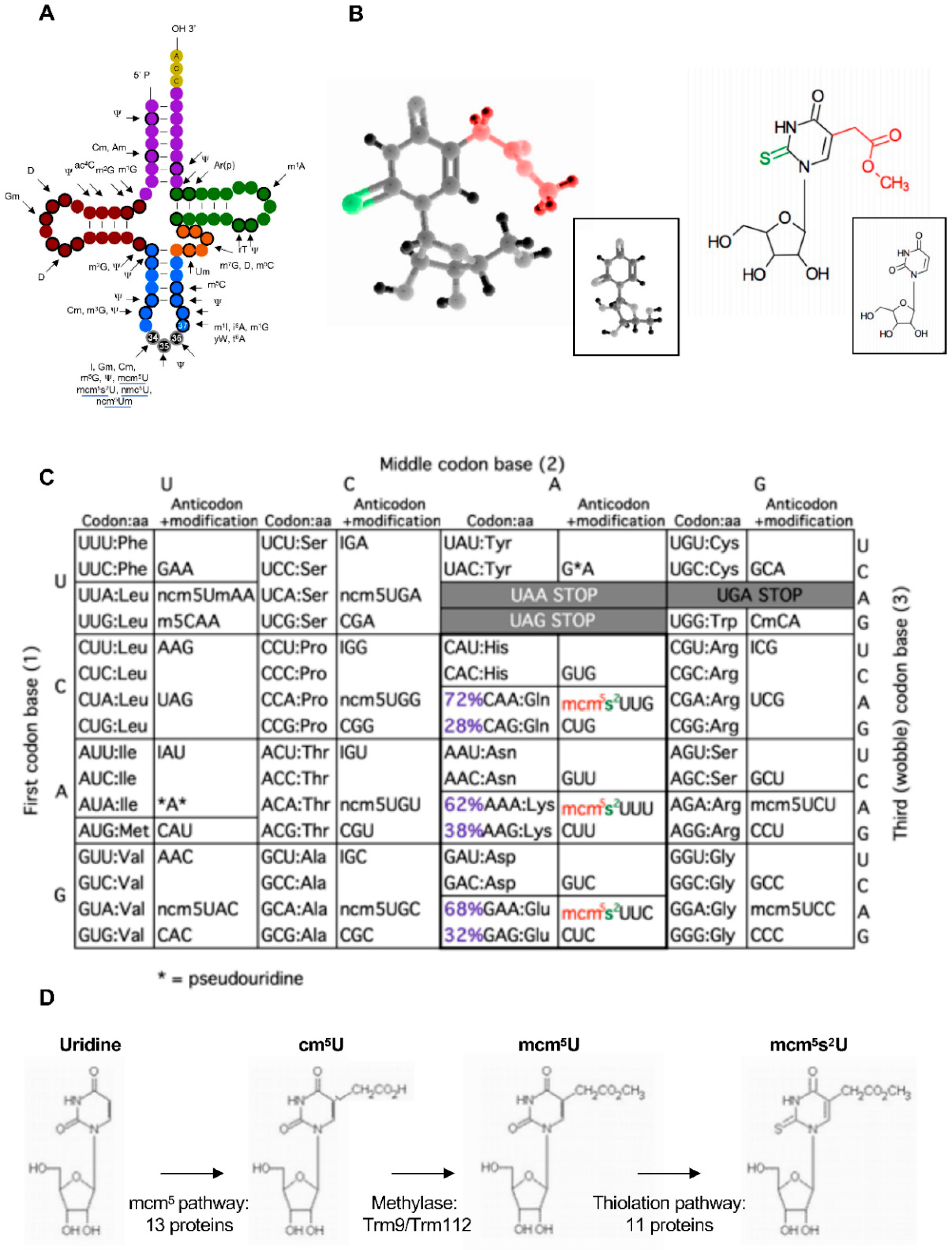
2. Codon-Based Regulation of Translation
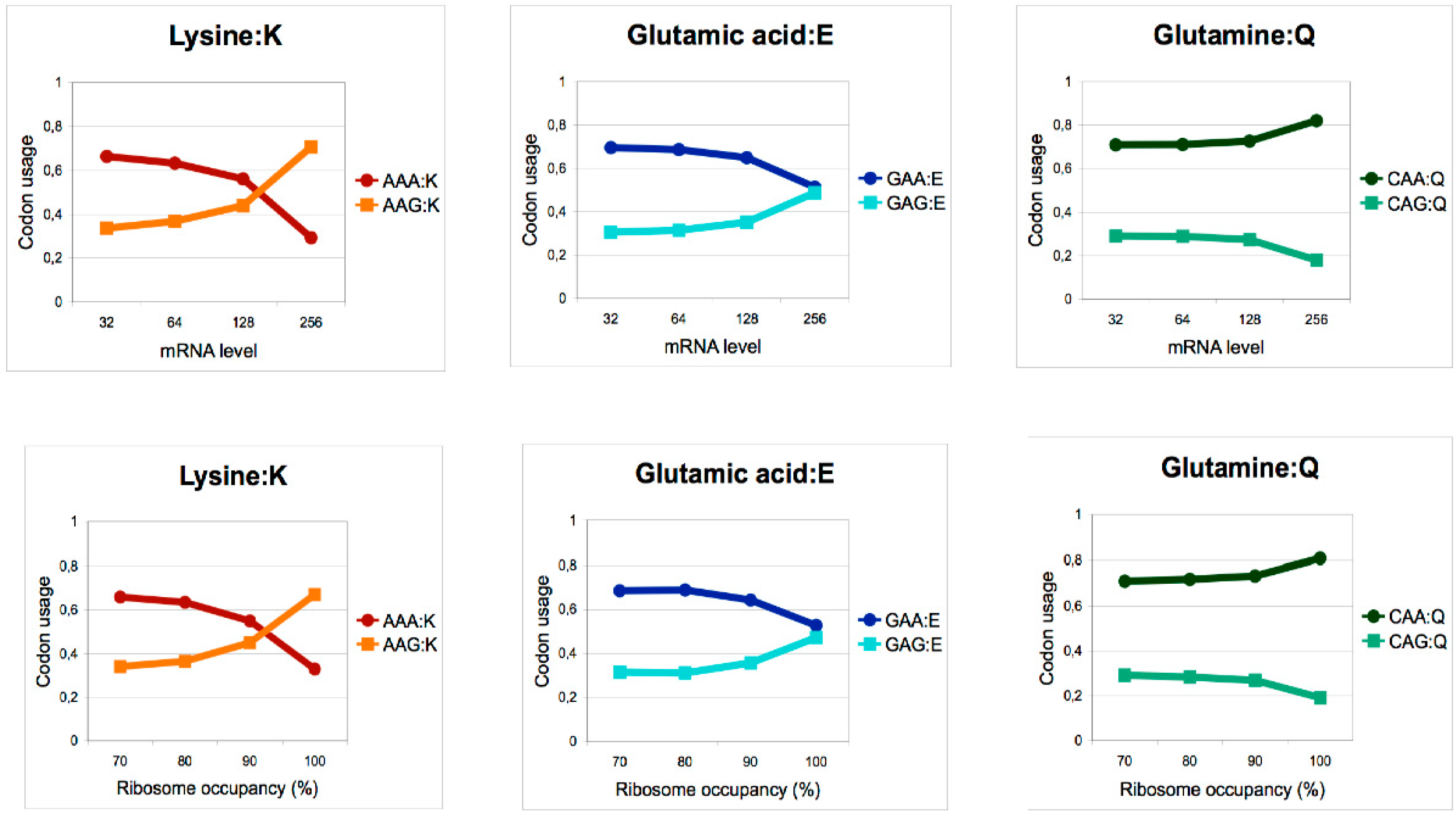
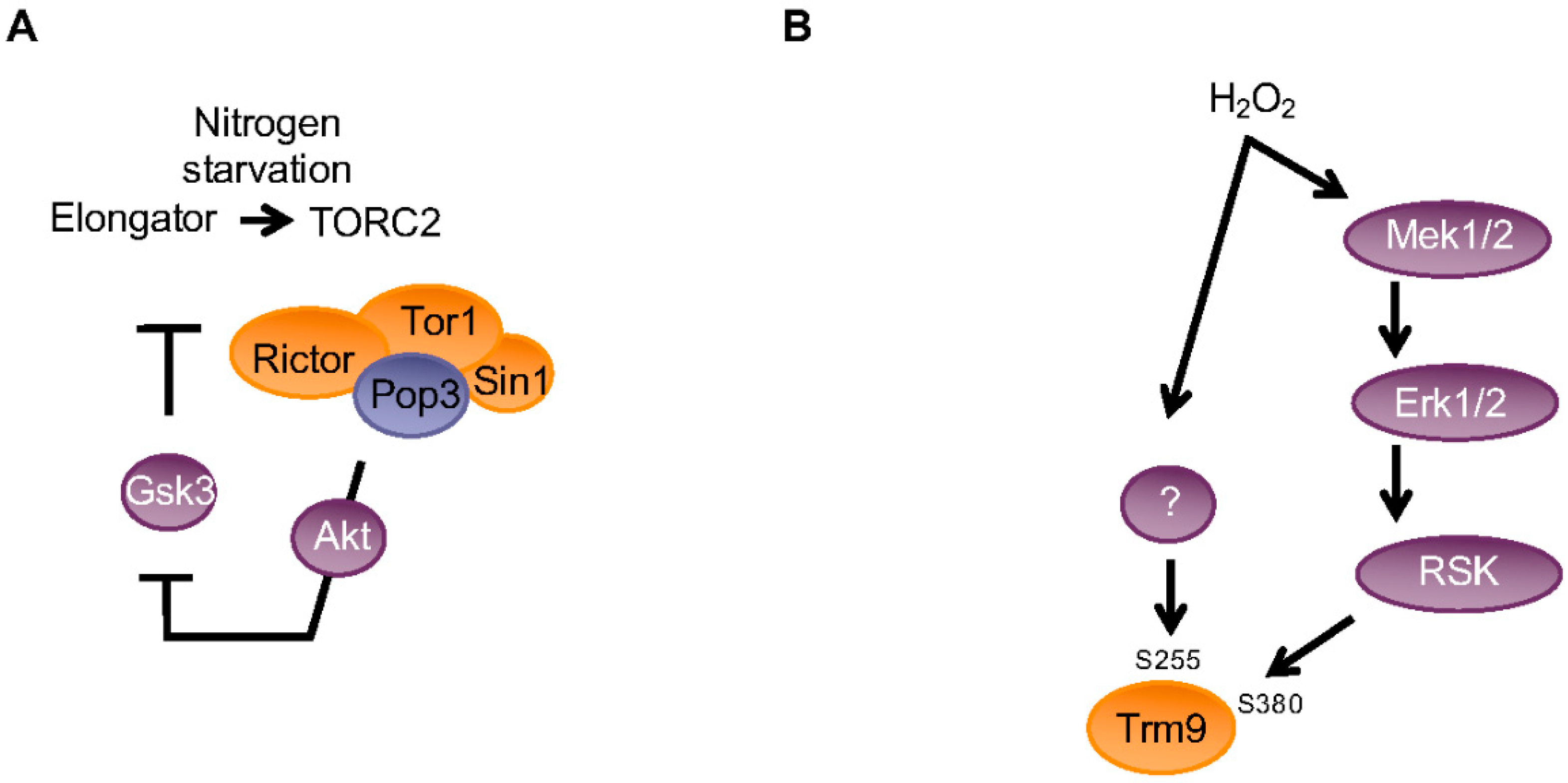
3. Reprogramming of the mcm5 Modification by Cellular Signaling Controls Codon-Biased Translation in Various Contexts
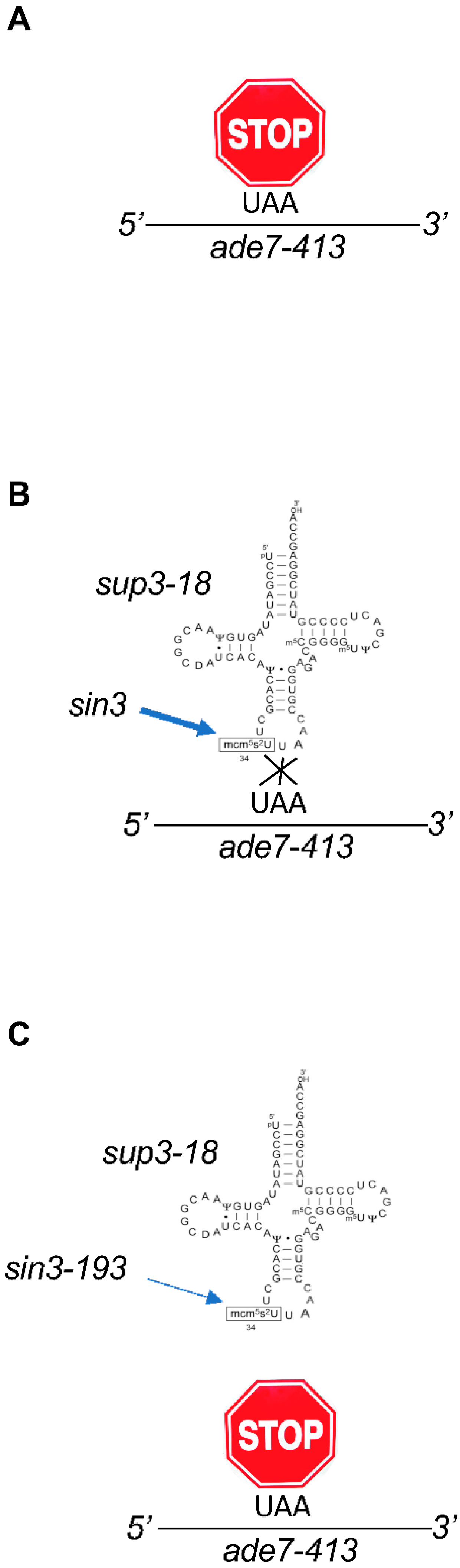
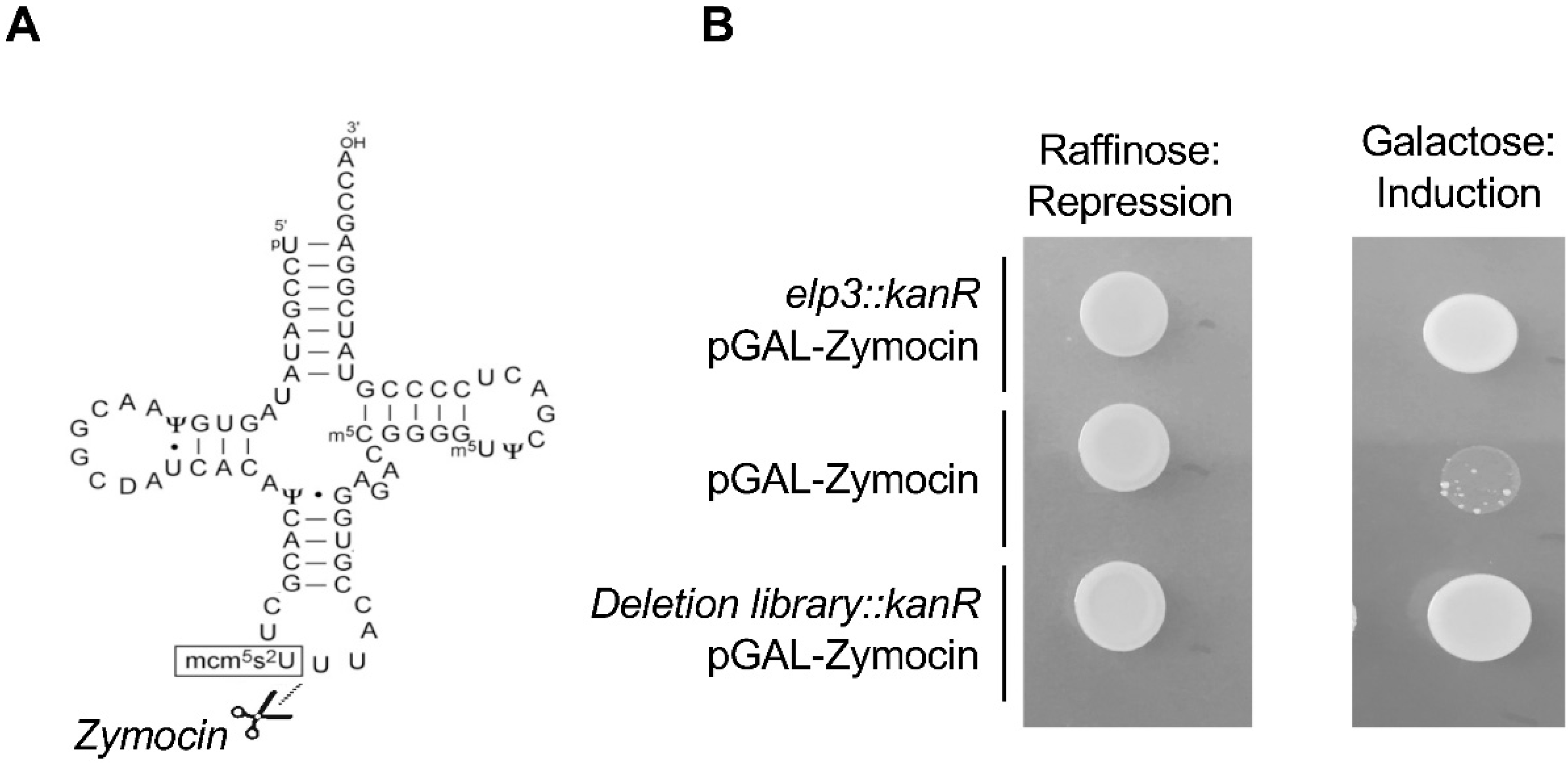
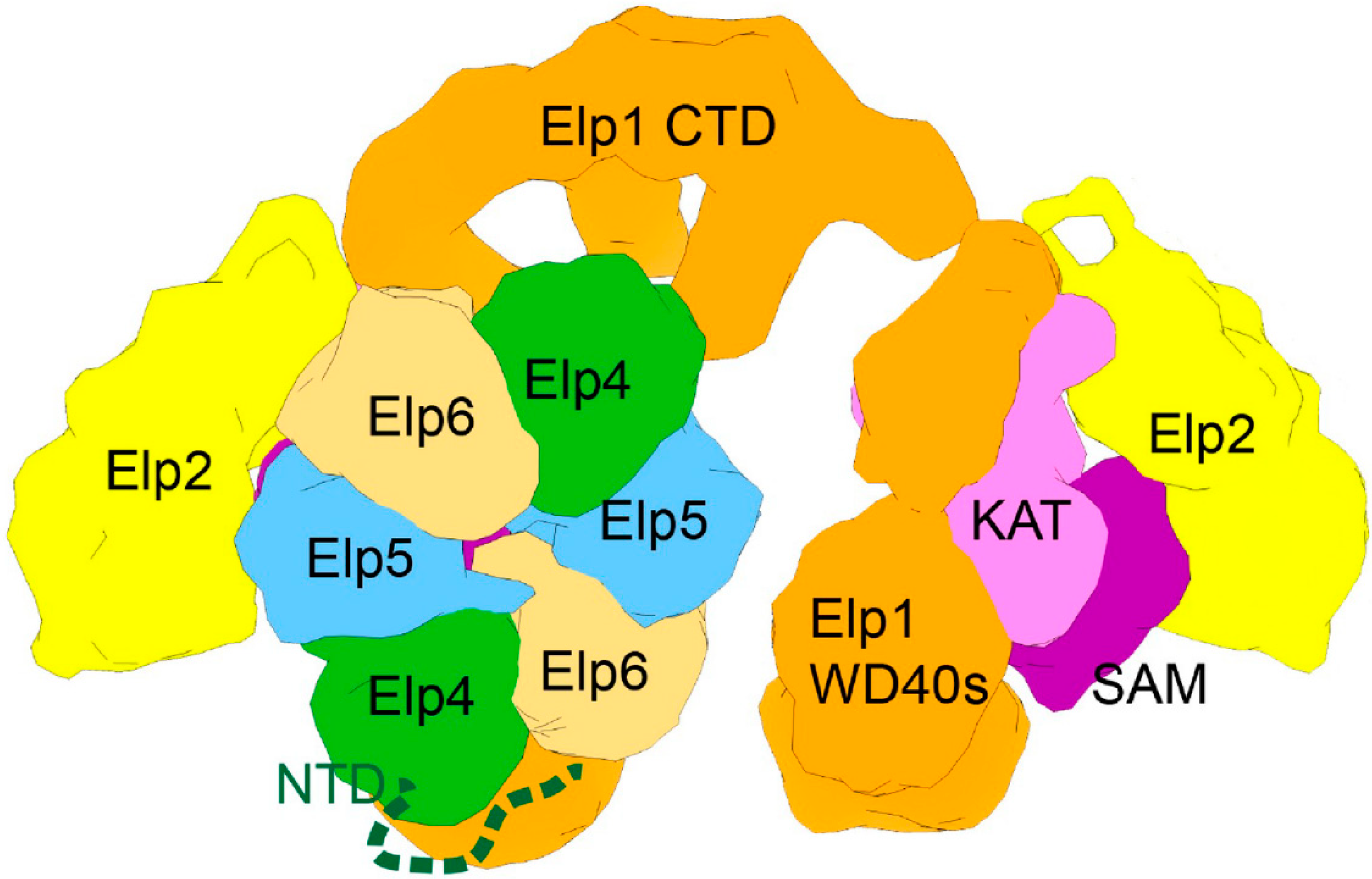
4. Elongator tRNA Modifications as a Protection from Protein Misfolding and Aggregation
5. Elongator tRNA Modification and Diseases
6. Perspectives
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Otero, G.; Fellows, J.; Li, Y.; de Bizemont, T.; Dirac, A.M.; Gustafsson, C.M.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Svejstrup, J.Q. Elongator, a multisubunit component of a novel RNA polymerase II holoenzyme for transcriptional elongation. Mol. Cell 1999, 3, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, G.S.; Petrakis, T.G.; Ethelberg, S.; Tokunaga, M.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Svejstrup, J.Q. RNA polymerase II elongator holoenzyme is composed of two discrete subcomplexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 32743–32749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogan, N.J.; Greenblatt, J.F. Characterization of a six-subunit holo-elongator complex required for the regulated expression of a group of genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 8203–8212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, G.S.; Kristjuhan, A.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Svejstrup, J.Q. Elongator is a histone H3 and H4 acetyltransferase important for normal histone acetylation levels in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3517–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittschieben, B.O.; Otero, G.; de Bizemont, T.; Fellows, J.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Ohba, R.; Li, Y.; Allis, C.D.; Tempst, P.; Svejstrup, J.Q. A novel histone acetyltransferase is an integral subunit of elongating RNA polymerase II holoenzyme. Mol. Cell 1999, 4, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittschieben, B.O.; Fellows, J.; Du, W.; Stillman, D.J.; Svejstrup, J.Q. Overlapping roles for the histone acetyltransferase activities of SAGA and elongator in vivo. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 3060–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, C.; Kristjuhan, A.; Winkler, G.S.; Svejstrup, J.Q. Elongator interactions with nascent mRNA revealed by RNA immunoprecipitation. Mol. Cell 2004, 14, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogan, N.J.; Kim, M.; Ahn, S.H.; Zhong, G.; Kobor, M.S.; Cagney, G.; Emili, A.; Shilatifard, A.; Buratowski, S.; Greenblatt, J.F. RNA polymerase II elongation factors of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: A targeted proteomics approach. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 6979–6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahl, P.B.; Chen, C.Z.; Collins, R.N. Elp1p, the yeast homolog of the FD disease syndrome protein, negatively regulates exocytosis independently of transcriptional elongation. Mol. Cell 2005, 17, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svejstrup, J.Q. Elongator complex: How many roles does it play? Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2007, 19, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Fazly, A.M.; Zhou, H.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Stillman, B. The elongator complex interacts with PCNA and modulates transcriptional silencing and sensitivity to DNA damage agents. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofia, H.J.; Chen, G.; Hetzler, B.G.; Reyes-Spindola, J.F.; Miller, N.E. Radical SAM, a novel protein superfamily linking unresolved steps in familiar biosynthetic pathways with radical mechanisms: Functional characterization using new analysis and information visualization methods. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, Y.; Yamagata, K.; Hong, K.; Wakayama, T.; Zhang, Y. A role for the elongator complex in zygotic paternal genome demethylation. Nature 2010, 463, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurse, P.; Hayles, J. Using genetics to understand biology. Heredity 2019, 123, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phizicky, E.M.; Hopper, A.K. tRNA biology charges to the front. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 1832–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agris, P.F.; Vendeix, F.A.; Graham, W.D. tRNA’s wobble decoding of the genome: 40 years of modification. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 366, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björk, G.R. Biosynthesis and Function of Modified Nucleosides. In tRNA: Structure, Biosynthesis, and Fundtion; RajBhandary, D.S.A.U., Ed.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; Volume 11, pp. 165–205. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T. Biosynthesis and function of wobble modifications. In Fine-Tuning of RNA Functions by Modification and Editing; Grosjean, H., Ed.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, F.V.T.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Malkiewicz, A.; Agris, P.F. The role of modifications in codon discrimination by tRNA(Lys)UUU. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarian, C.; Marszalek, M.; Sochacka, E.; Malkiewicz, A.; Guenther, R.; Miskiewicz, A.; Agris, P.F. Modified nucleoside dependent Watson-Crick and wobble codon binding by tRNALysUUU species. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 13390–13395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewez, M.; Bauer, F.; Dieu, M.; Raes, M.; Vandenhaute, J.; Hermand, D. The conserved Wobble uridine tRNA thiolase Ctu1-Ctu2 is required to maintain genome integrity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5459–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leidel, S.; Pedrioli, P.G.; Bucher, T.; Brost, R.; Costanzo, M.; Schmidt, A.; Aebersold, R.; Boone, C.; Hofmann, K.; Peter, M. Ubiquitin-related modifier Urm1 acts as a sulphur carrier in thiolation of eukaryotic transfer RNA. Nature 2009, 458, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noma, A.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Suzuki, T. Mechanistic characterization of the sulfur-relay system for eukaryotic 2-thiouridine biogenesis at tRNA wobble positions. Nucleic Acids Res 2009, 37, 1335–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.J.; Esberg, A.; Huang, B.; Bjork, G.R.; Bystrom, A.S. Eukaryotic wobble uridine modifications promote a functionally redundant decoding system. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 3301–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percudani, R.; Pavesi, A.; Ottonello, S. Transfer RNA gene redundancy and translational selection in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 268, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyer, W.D.; Thuriaux, P.; Kohli, J.; Ebert, P.; Kersten, H.; Gehrke, C.; Kuo, K.C.; Agris, P.F. An antisuppressor mutation of Schizosaccharomyces pombe affects the post-transcriptional modification of the “wobble” base in the anticodon of tRNAs. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 2856–2862. [Google Scholar]
- Grossenbacher, A.M.; Stadelmann, B.; Heyer, W.D.; Thuriaux, P.; Kohli, J.; Smith, C.; Agris, P.F.; Kuo, K.C.; Gehrke, C. Antisuppressor mutations and sulfur-carrying nucleosides in transfer RNAs of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 16351–16355. [Google Scholar]
- Thuriaux, P.; Minet, M.; Hofer, F.; Leupold, U. Genetic Analysis of Antisuppressor Mutants in the Fission Yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1975, 142, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Johansson, M.J.; Bystrom, A.S. An early step in wobble uridine tRNA modification requires the Elongator complex. Rna 2005, 11, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.E.; Rio, A.G.; Nicolas, A.; Kolodner, R.D. A genomewide screen in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for genes that suppress the accumulation of mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11529–11534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Huang, B.; Esberg, A.; Johansson, M.J.; Bystrom, A.S. The Kluyveromyces lactis gamma-toxin targets tRNA anticodons. Rna 2005, 11, 1648–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, M.M.; Della Seta, F.; Di Como, C.J.; Sugimoto, H.; Kobayashi, R.; Arndt, K.T. The SAP, a new family of proteins, associate and function positively with the SIT4 phosphatase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 2744–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatt, S.; Zabel, R.; Vonkova, I.; Kumar, A.; Netz, D.J.; Pierik, A.J.; Rybin, V.; Lill, R.; Gavin, A.C.; Balbach, J.; et al. Structure of the Kti11/Kti13 heterodimer and its double role in modifications of tRNA and eukaryotic elongation factor 2. Structure 2015, 23, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolaj-Robin, O.; McEwen, A.G.; Cavarelli, J.; Seraphin, B. Structure of the Elongator cofactor complex Kti11/Kti13 provides insight into the role of Kti13 in Elongator-dependent tRNA modification. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esberg, A.; Huang, B.; Johansson, M.J.; Bystrom, A.S. Elevated levels of two tRNA species bypass the requirement for elongator complex in transcription and exocytosis. Mol. Cell 2006, 24, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begley, U.; Dyavaiah, M.; Patil, A.; Rooney, J.P.; Direnzo, D.; Young, C.M.; Conklin, D.S.; Zitomer, R.S.; Begley, T.J. Trm9-Catalyzed tRNA Modifications Link Translation to the DNA Damage Response. Mol. Cell 2007, 28, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, F.; Matsuyama, A.; Candiracci, J.; Dieu, M.; Scheliga, J.; Wolf, D.A.; Yoshida, M.; Hermand, D. Translational control of cell division by Elongator. Cell Rep. 2012, 1, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, F.; Matsuyama, A.; Yoshida, M.; Hermand, D. Determining proteome-wide expression levels using reverse protein arrays in fission yeast. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1830–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, F.; Hermand, D. A coordinated codon-dependent regulation of translation by Elongator. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 4524–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Vazquez, J.; Vargas-Perez, I.; Sanso, M.; Buhne, K.; Carmona, M.; Paulo, E.; Hermand, D.; Rodriguez-Gabriel, M.; Ayte, J.; Leidel, S.; et al. Modification of tRNA(Lys) UUU by elongator is essential for efficient translation of stress mRNAs. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladang, A.; Rapino, F.; Heukamp, L.C.; Tharun, L.; Shostak, K.; Hermand, D.; Delaunay, S.; Klevernic, I.; Jiang, Z.; Jacques, N.; et al. Elp3 drives Wnt-dependent tumor initiation and regeneration in the intestine. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 2057–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapino, F.; Delaunay, S.; Rambow, F.; Zhou, Z.; Tharun, L.; De Tullio, P.; Sin, O.; Shostak, K.; Schmitz, S.; Piepers, J.; et al. Codon-specific translation reprogramming promotes resistance to targeted therapy. Nature 2018, 558, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffena, J.; Lefcort, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lehrmann, E.; Chaverra, M.; Felig, J.; Walters, J.; Buksch, R.; Becker, K.G.; George, L. Elongator and codon bias regulate protein levels in mammalian peripheral neurons. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candiracci, J.; Migeot, V.; Chionh, Y.-H.; Bauer, F.; Brochier, T.; Russell, B.; Shiozaki, K.; Dedon, P.C.; Hermand, D. Reciprocal regulation of TORC signaling and tRNA modifications by Elongator enforces nutrient-dependent cell fate. Sci. Adv. 2019. revised version resubmitted, awaiting final decision. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.T.; Pang, Y.L.; Deng, W.; Babu, I.R.; Dyavaiah, M.; Begley, T.J.; Dedon, P.C. Reprogramming of tRNA modifications controls the oxidative stress response by codon-biased translation of proteins. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.T.; Dyavaiah, M.; DeMott, M.S.; Taghizadeh, K.; Dedon, P.C.; Begley, T.J. A quantitative systems approach reveals dynamic control of tRNA modifications during cellular stress. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.; Pham, P.; Dedon, P.C.; Begley, T.J. Lifestyle modifications: Coordinating the tRNA epitranscriptome with codon bias to adapt translation during stress responses. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Ramos, J.; Begley, U.; Dedon, P.C.; Fu, D.; Begley, T.J. Phosphorylation of human TRM9L integrates multiple stress-signaling pathways for tumor growth suppression. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaas9184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolaj-Robin, O.; Seraphin, B. Structures and Activities of the Elongator Complex and Its Cofactors. Enzymes 2017, 41, 117–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauden, M.I.; Jaciuk, M.; Muller, C.W.; Glatt, S. Structural asymmetry in the eukaryotic Elongator complex. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatt, S.; Letoquart, J.; Faux, C.; Taylor, N.M.; Seraphin, B.; Muller, C.W. The Elongator subcomplex Elp456 is a hexameric RecA-like ATPase. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauden, M.I.; Kosinski, J.; Kolaj-Robin, O.; Desfosses, A.; Ori, A.; Faux, C.; Hoffmann, N.A.; Onuma, O.F.; Breunig, K.D.; Beck, M.; et al. Architecture of the yeast Elongator complex. EMBO Rep. 2017, 18, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiaputra, D.T.; Cheng, D.T.; Lu, S.; Hansen, J.M.; Dalwadi, U.; Lam, C.H.; To, J.L.; Dong, M.Q.; Yip, C.K. Molecular architecture of the yeast Elongator complex reveals an unexpected asymmetric subunit arrangement. EMBO Rep. 2017, 18, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauden, M.I.; Jaciuk, M.; Weis, F.; Lin, T.Y.; Kleindienst, C.; Abbassi, N.E.H.; Khatter, H.; Krutyholowa, R.; Breunig, K.D.; Kosinski, J.; et al. Molecular basis of tRNA recognition by the Elongator complex. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.Y.; Abbassi, N.E.H.; Zakrzewski, K.; Chramiec-Glabik, A.; Jemiola-Rzeminska, M.; Rozycki, J.; Glatt, S. The Elongator subunit Elp3 is a non-canonical tRNA acetyltransferase. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addis, L.; Ahn, J.W.; Dobson, R.; Dixit, A.; Ogilvie, C.M.; Pinto, D.; Vaags, A.K.; Coon, H.; Chaste, P.; Wilson, S.; et al. Microdeletions of ELP4 Are Associated with Language Impairment, Autism Spectrum Disorder, and Mental Retardation. Hum. Mutat. 2015, 36, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strug, L.J.; Clarke, T.; Chiang, T.; Chien, M.; Baskurt, Z.; Li, W.; Dorfman, R.; Bali, B.; Wirrell, E.; Kugler, S.L.; et al. Centrotemporal sharp wave EEG trait in rolandic epilepsy maps to Elongator Protein Complex 4 (ELP4). Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 17, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlgarten, C.; Jablonowski, D.; Breunig, K.D.; Stark, M.J.; Schaffrath, R. Elongator function depends on antagonistic regulation by casein kinase Hrr25 and protein phosphatase Sit4. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 73, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonowski, D.; Fichtner, L.; Stark, M.J.; Schaffrath, R. The yeast elongator histone acetylase requires Sit4-dependent dephosphorylation for toxin-target capacity. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, W.; Jablonowski, D.; Di Santo, R.; Thuring, K.L.; Scheidt, V.; Hammermeister, A.; Ten Have, S.; Helm, M.; Schaffrath, R.; Stark, M.J. Phosphorylation of Elp1 by Hrr25 is required for elongator-dependent tRNA modification in yeast. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1004931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvadurai, K.; Wang, P.; Seimetz, J.; Huang, R.H. Archaeal Elp3 catalyzes tRNA wobble uridine modification at C5 via a radical mechanism. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 810–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedialkova, D.D.; Leidel, S.A. Optimization of Codon Translation Rates via tRNA Modifications Maintains Proteome Integrity. Cell 2015, 161, 1606–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechmann, S.; Frydman, J. Evolutionary conservation of codon optimality reveals hidden signatures of cotranslational folding. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawer, H.; Hammermeister, A.; Ravichandran, K.E.; Glatt, S.; Schaffrath, R.; Klassen, R. Roles of Elongator Dependent tRNA Modification Pathways in Neurodegeneration and Cancer. Genes 2018, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelrod, F.B. A world without pain or tears. Clin. Auton. Res. 2006, 16, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maayan, C.; Axelrod, F.B.; Akselrod, S.; Carley, D.W.; Shannon, D.C. Evaluation of autonomic dysfunction in familial dysautonomia by power spectral analysis. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 1987, 21, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maayan, C.; Kaplan, E.; Shachar, S.; Peleg, O.; Godfrey, S. Incidence of familial dysautonomia in Israel 1977-1981. Clin. Genet. 1987, 32, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsborn, T.; Tukenmez, H.; Chen, C.; Bystrom, A.S. Familial dysautonomia (FD) patients have reduced levels of the modified wobble nucleoside mcm(5)s(2)U in tRNA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 454, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Kataoka, N.; Miyauchi, K.; Ohe, K.; Iida, K.; Yoshida, S.; Nojima, T.; Okuno, Y.; Onogi, H.; Usui, T.; et al. Rectifier of aberrant mRNA splicing recovers tRNA modification in familial dysautonomia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2764–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmens, R.; Moore, M.J.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Brown, R.H., Jr.; Robberecht, W. RNA metabolism and the pathogenesis of motor neuron diseases. Trends Neurosci. 2010, 33, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguesse, S.; Creppe, C.; Nedialkova, D.D.; Prevot, P.P.; Borgs, L.; Huysseune, S.; Franco, B.; Duysens, G.; Krusy, N.; Lee, G.; et al. A Dynamic Unfolded Protein Response Contributes to the Control of Cortical Neurogenesis. Dev. Cell 2015, 35, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edvardson, S.; Prunetti, L.; Arraf, A.; Haas, D.; Bacusmo, J.M.; Hu, J.F.; Ta-Shma, A.; Dedon, P.C.; de Crecy-Lagard, V.; Elpeleg, O. tRNA N6-adenosine threonylcarbamoyltransferase defect due to KAE1/TCS3 (OSGEP) mutation manifest by neurodegeneration and renal tubulopathy. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 25, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, R.; Abdel-Salam, G.M.; Guy, M.P.; Alomar, R.; Abdel-Hamid, M.S.; Afifi, H.H.; Ismail, S.I.; Emam, B.A.; Phizicky, E.M.; Alkuraya, F.S. Mutation in WDR4 impairs tRNA m(7)G46 methylation and causes a distinct form of microcephalic primordial dwarfism. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klassen, R.; Ciftci, A.; Funk, J.; Bruch, A.; Butter, F.; Schaffrath, R. tRNA anticodon loop modifications ensure protein homeostasis and cell morphogenesis in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 10946–10959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiaville, P.C.; Legendre, R.; Rojas-Benitez, D.; Baudin-Baillieu, A.; Hatin, I.; Chalancon, G.; Glavic, A.; Namy, O.; de Crecy-Lagard, V. Global translational impacts of the loss of the tRNA modification t(6)A in yeast. Microb. Cell 2016, 3, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaunay, S.; Rapino, F.; Tharun, L.; Zhou, Z.; Heukamp, L.; Termathe, M.; Shostak, K.; Klevernic, I.; Florin, A.; Desmecht, H.; et al. Elp3 links tRNA modification to IRES-dependent translation of LEF1 to sustain metastasis in breast cancer. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 2503–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hermand, D. Anticodon Wobble Uridine Modification by Elongator at the Crossroad of Cell Signaling, Differentiation, and Diseases. Epigenomes 2020, 4, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes4020007
Hermand D. Anticodon Wobble Uridine Modification by Elongator at the Crossroad of Cell Signaling, Differentiation, and Diseases. Epigenomes. 2020; 4(2):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes4020007
Chicago/Turabian StyleHermand, Damien. 2020. "Anticodon Wobble Uridine Modification by Elongator at the Crossroad of Cell Signaling, Differentiation, and Diseases" Epigenomes 4, no. 2: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes4020007
APA StyleHermand, D. (2020). Anticodon Wobble Uridine Modification by Elongator at the Crossroad of Cell Signaling, Differentiation, and Diseases. Epigenomes, 4(2), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes4020007




