Abstract
Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS) is a neurodevelopmental disorder caused by loss of expression of the paternally inherited genes on chromosome 15q11.2-q13. However, the core features of PWS have been attributed to a critical interval (PWS-cr) within the 15q11.2-q13 imprinted gene cluster, containing the small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) SNORD116 and non-coding RNA IPW (Imprinted in Prader-Willi) exons. SNORD116 affects the transcription profile of hundreds of genes, possibly via DNA methylation or post-transcriptional modification, although the exact mechanism is not completely clear. IPW on the other hand has been shown to specifically modulate histone methylation of a separate imprinted locus, the DLK1-DIO3 cluster, which itself is associated with several neurodevelopmental disorders with similarities to PWS. Here we review what is currently known of the molecular targets of SNORD116 and IPW and begin to disentangle their roles in contributing to the Prader-Willi Syndrome phenotype.
1. Introduction
Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by hypotonia and slow growth rate in infancy, followed by severe hyperphagia throughout childhood and adulthood, often leading to obesity and associated problems. Individuals with PWS also exhibit mild to moderate learning disability and, in rare cases, psychosis and other psychiatric conditions [1]. Prader-Willi Syndrome is caused by loss of function mutations affecting the expression of genes on chromosome 15q11.2-q13. The genes in this cluster are imprinted, meaning that they are expressed only from one parental copy of the chromosome, and suppressed on the other. The imprinting of the Prader-Willi gene cluster is established during embryogenesis by a differentially methylated CpG island at the 5’ end of the bicistronic SNURF-SNRPN gene [2,3]. This CpG island is known as the imprinting center of the locus [4,5]. On the maternally inherited chromosome, the DNA in the imprinted center is methylated, which leads to the recruitment acetylation and methylation chromatin marks that repress the transcription of maternal PWS genes.
The 15q11.2-q13 region contains some paternally expressed genes, including five protein-coding genes (MKRN3, MAGEL2, NECDIN, SNURF-SNRPN), a cluster of small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs), and the non-coding RNA IPW (Figure 1). The PWS imprinted gene cluster also includes two maternally expressed protein coding genes (UBE3A and ATP10A) [6]. Loss of expression of paternally inherited genes leads to Prader-Willi syndrome, while the loss of expression of maternally inherted genes, and UBE3A in particular, leads to a distinct neurodevelopmental disorder—Angelman syndrome [7].
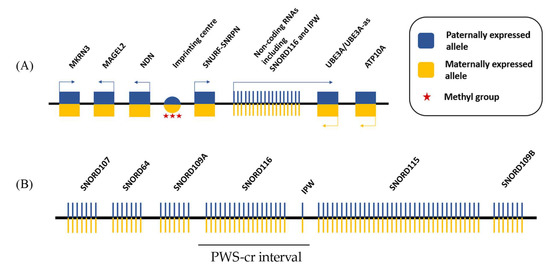
Figure 1.
Simplified schematic of the Prader-Willi syndrome locus. (A) 15q11.2-q13 imprinted region contains five paternally expressed protein-coding genes and a cluster of paternally expressed non-coding RNAs. The locus also includes two maternally expressed protein-coding genes. The imprinting of the locus is established by DNA methylation of a regulatory region upstream of the paternally expressed SNURF-SNRPN allele, which is known as the imprinting center; and (B) The non-coding RNAs in the PWS locus contain five clusters of small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) and the Imprinted in Prader Willi (IPW) exons. The SNORD116 cluster together with IPW form the PWS-cr interval.
The non-coding RNAs of the PWS cluster play an important role in the Prader-Willi syndrome phenotype by regulating the expression of other genes in a combination of epigenetic and post-transcriptional processes [8,9,10]. In particular, the Prader-Willi critical region (PWS-cr), containing the SNORD116 cluster and IPW, has been shown to contribute heavily to some of the symptoms of PWS, including the hyperphagia, metabolism, and some anxiety-related behaviors. This review aims to elucidate the current knowledge of the molecular targets of SNORD116 and IPW and how their regulatory role affects the Prader-Willi syndrome phenotype.
2. Functional Consequences of Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS)-Critical Interval Deletion
The PWS-cr interval is thought to be responsible for the majority of the symptoms associated with PWS, since deletion of the PWS-cr alone has been found sufficient to induce the core PWS phenotype [11]. Due to the high (but not complete) levels of conservation of the PWS cluster between humans and mice, mouse models have become an invaluable tool for studying the physiological and behavioral phenotypes associated with the syndrome. The knock-out of the PWS-cr interval in mice leads to a low birth weight and failure to grow in the first few weeks of life, which is comparable to the phenotype observed in humans [12,13,14,15]. Furthermore, some studies on PWS-cr deficient mice have demonstrated a replication of hyperphagia [15,16], although this behavior does not lead to obesity in these models. However, it has to be noted that other studies on this mouse model have shown no differences in the feeding behavior of mutants compared to wild type [17,18], leaving the link between the PWS-cr interval and hyperphagia in contention.
Additionally, loss of gene expression from the PWS-cr interval has been associated with a number of other phenotypes. These include disruption of circadian rhythms both in patients and mouse models, which manifest as an alteration in sleep patterns and specifically REM and Non-REM cycles, as well as a disturbance in metabolism, thermogenesis and food anticipation activity [14,19]. Due to the entanglement of the circadian clock with numerous physiological functions, it is possible that the disruption of these rhythms is at the base of a multitude of the symptoms associated with Prader-Willi syndrome [20,21,22].
However, some have questioned whether patients carrying a minimal deletion affecting the PWS-cr present with true PWS [23]. For instance, there is little evidence linking the deletion of the PWS-cr interval with the behavioral and cognitive features characteristic in PWS, although the PWS-cr interval has also been associated with anxiety and some learning disabilities [11,16,24]. Nevertheless, it still remains that deletion of the PWS-cr alone is sufficient to cause the core physiological features of PWS [11] and given this, it is critical that we examine the role of the genes within this interval.
3. SNORD116
The SNORD116 locus contains a cluster of thirty or more snoRNAs, belonging to one of the two repetitive clusters of snoRNAs in the mammalian genome [25]. All of the 15q11.2-q13 PWS region snoRNAs (SNORD64, SNORD107, SNORD109, SNORD115, SNORD116) are classified as “C/D box snoRNAs”. The C and D boxes are short conserved sequence elements, which allow snoRNAs to regulate site-specific methylation of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) [26]. This process is essential for the maintenance of proper ribosomal function, since it is thought to affect the maturity and stability of rRNA. However, none of the C/D box snoRNAs of the PWS region have a direct rRNA target [27], and studies of their functional role have given contradictory results.
Of the snoRNA clusters in the PWS locus, SNORD115 is the only one that has a clear target. SNORD115 has been demonstrated to affect the alternative splicing and A-to-I editing of the 2C serotonin receptor pre-RNA [28], which has been associated with hyperphagia and eating abnormalities, as well as with psychiatric disorders [29,30,31]. The exact mechanisms behind this regulatory effect are unknown. Interestingly, two of the snoRNAs within the SNORD116 cluster, have been shown to associate with FOX2 from the FOX family, which is a known regulator of splicing [32]. These snoRNAs are left untrimmed from long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) found between them, and bind FOX2 in a sno-lncRNA formation [17,32]. However, a recent analysis of hypothalamic transcripts indicated no differences in alternative splicing between PWS-cr deficient mice and wild type [15].
Currently, little is known about the direct molecular target(s) of SNORD116. The recognition sites of SNORD116 are not complementary to any known rRNA, tRNA or snRNA sequence. However, the SNORD116 cluster has been demonstrated to affect the expression levels of multiple genes. A study by Falaleeva et al. [33] on HEK 293T cells and post-mortem hypothalamus cells of PWS patients demonstrated that SNORD116 affects the transcription of over 200 genes. This activity was shown to be modified by SNORD115, suggesting a synergetic relationship between the two snoRNAs. Falaleeva et al. [33] hypothesize that SNORD115 and SNORD116 might form heterodimers, which is compliant with a previously proposed model of C/D box snoRNAs forming dimers [34]. Other RNA-sequencing and microarray studies have also shown that in the absence of the SNORD116 cluster, the expression of genes that play a role in feeding, skeletal development and circadian rhythm pathways are altered [15,17].
Recently, the SNORD116 cluster was also shown to potentially affect gene expression through rhythmic DNA methylation [35]. As previously mentioned, the PWS-cr interval has been associated with the regulation of circadian rhythms. This particular role of the interval has been attributed mostly to SNORD116, since the snoRNAs of the cluster are predominantly expressed in the neuropeptide Y neurons of the hypothalamus, which is where the “master” circadian molecular clock is located [15,19]. Coulson et al. [35] suggested that the SNORD116 cluster is involved in the regulation of diurnal rhythm of DNA methylation in the mouse cortex. Using whole genome bisulfite sequencing at six different time points, they demonstrated that over 23,000 CpG sites are methylated rhythmically, and that this rhythm is disrupted in the PWS-cr+/− mice. The dysregulated genes are reportedly enriched for body mass index, cholesterol and diurnal metabolism phenotypes, which are all associated with obesity and could be playing a part in the PWS phenotype.
One of the suggested mechanisms via which the SNORD116 cluster might regulate rhythmic DNA methylation is through long-noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) flanking the copies of the SNORD116 snoRNAs. These lncRNAs are spliced to form an RNA cloud, which associates with transcription factor RBBP5 and regulates the expression of circadian genes CLOCK, CRY1 and PER2. This synergetic relationship between the SNORD116 snoRNAs and their flanking lncRNAs is thought to occur independently of the sno-lncRNA-FOX2 mechanism, which might be involved in assisting alternative splicing [17].
Another possible pathway for SNORD116 mediated regulation of circadian rhythms is through A-to-I editing of methylation sites. One of the main enzymes behind A-to-I editing known as adenosine-deaminase-acting-on-RNA (ADAR2), is thought to be mediated by C/D box snoRNAs [36], with SNORD115 being a prime example of one of those snoRNAs [9,28]. ADAR2 was also recently shown to regulate the circadian clocks by performing rhythmic A-to-I editing [37]. Furthermore, elimination of circadian rhythms in mice has been associated with lower weight and less subcutaneous fat [38], which is similar to one of the phenotypes observed in PWS-cr+/− mice. However, there is no body of evidence to support this hypothesis, and although SNORD116 is now known for playing an essential role in the PWS phenotype, its exact molecular target still remains unclear and requires further studies.
4. Imprinted in Prader-Willi (IPW)
All patients carrying a mutation of the SNORD116 cluster harbor a deletion that spans the non-coding Imprinted in Prader-Willi (IPW) gene as well [11]. Similarly, the deletion of Snord116 in existing mouse models also affects the Ipw gene. Consequently, teasing apart the roles played by the Snord116 cluster and Ipw remains a key issue in understanding the neural basis of the PWS phenotype.
The molecular function of IPW was unknown until a recent study of a stem cell model of PWS showed that one of the roles of the RNA is to suppress the transcription of another cluster of imprinted genes, namely the DLK1-DIO3 locus, located on chromosome 14 (Figure 2A) [8]. The proposed mechanism for this regulation suggests that IPW is reponsible for the maintenance of repressive chromatin marks at this locus, which lowers expression of the maternally expressed genes (MEGs) in the DLK1-DIO3 region, and is suggestive of wider imprinted gene network [39]. Specfifically, Stelzer et al. [8] demonstrated that IPW interacts with G9A histone methyltransferase, which is capable of catalyzing lysine 9 histone H3 tri-methylation (H3K9me3) (Figure 2B). Pluripotent stem cells from PWS patients (PWS-iPSCs) were shown to exhibit significantly decreased levels of H3K9me3 at a region which controls the expression of the MEGs at the DLK1-DIO3 cluster. This phenotype is fully rescued by the re-introduction of IPW into the PWS-iPSCs [8], which suggests that deletion of IPW leads to overexpression of the MEGs in the locus.
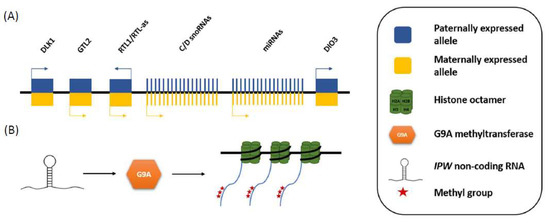
Figure 2.
Schematic of how IPW down-regulates the expression of maternally expressed genes in the DLK1-DIO3 locus. (A) The DLK1-DIO3 locus contains three paternally expressed protein coding genes, and multiple maternally expressed non-coding genes (MEGs); and (B) IPW downregulates the expression of the MEGs by recruiting G9A histone methyltransferase, which adds repressive methyl groups on lysine 9 of the amino acid tail of H3, of the nucleosomes around which the DLK1-DIO3 MEGs are wrapped.
Interestingly, very recently Coulson et al. [35] demonstrated that the maternally expressed genes of the DLK1-DIO3 locus lose diurnal DNA methylation marks in the absence of PWS-cr in mice, and hypothesized that this process is disrupted by the absence of the SNORD116 cluster. Current evidence of the role of the PWS-cr interval is suggestive of a synergetic relationship between IPW and SNORD116, which act together to regulate the expression of the DLK1-DIO3 locus MEGs through histone and DNA methylation, respectively.
Role of the DLK1-DIO3 Locus
Although the phenotypic function of IPW has not been explored experimentally, the effects of some of the genes in the DLK1-DIO3 locus have been studied extensively. The DLK1-DIO3 imprinted locus contains three paternally expressed protein-coding genes (DLK1, RTL1, DIO3) and multiple maternally expressed non-coding genes, including C/D box snoRNAs and micro-RNAs (miRNAs) (Figure 2A) [40,41]. The maternally expressed miRNAs (miR-379/miR-410) in the DLK1-DIO3 cluster are of particular importance for the understanding of the PWS phenotype and how it might be affected by IPW’s regulatory role. The DLK1-DIO3 miRNAs are known to target over 400 genes, which are collectively associated with 67 human diseases, including various physiological anomalies and learning disabilities [42].
Deletion of the miR-379/miR-410 cluster in mouse models leads to increased anxiogenic behavior, as well as with disturbances in metabolic control and homeostasis maintenance [42,43]. These phenotypic outcomes are comparable with the physiological and behavioral phenotypes observed in patients and mouse models carrying a deletion of the PWS-cr interval [8,11,16,24]. Furthermore, overexpression of the MEGs at the DLK1-DIO3 locus is known to cause Temple syndrome, which is also characterized by symptoms similar to PWS, most notably the early-age hypotonia [44]. The phenotypic overlap between a DLK1-DIO3 MEGs and the PWS-cr interval suggests that some of the core features of Prader-Willi syndrome may be caused by dysregulation of the maternal genes on the DLK1-DIO3 locus, rather than directly by (or, more likely, in addition to) the genes in the PWS locus.
Interestingly, the DLK1-DIO3 and PWS gene clusters encode the only two regions of repetitive snoRNAs in the mammalian genome. Similar to the PWS locus, the DLK1-DIO3 C/D box snoRNAs also lack well defined rRNA targets and have a very similar genomic organization to the SNORDs of the PWS locus [45,46]. These parallels have instigated the hypothesis that perhaps the two imprinted clusters may have been derived from a common ancestor during mammalian evolution [45], which offers another explanation for the similarities in the phenotypes associated with the DLK1-DIO3 and the PWS-cr interval loci.
5. Conclusions
Although generally caused by loss of paternal gene expression from 15q11-q13, the core of characteristics of Prader-Willi syndrome have been pinpointed to the PWS-cr interval containing the SNORD116 snoRNA and IPW exons. Deletion of the PWS-critical region affects the expression of hundreds of genes via a number of putative mechanisms, and to cause many of the symptoms associated with PWS. Furthermore, recent studies link the PWS-cr interval with the regulation of a distinct imprinted cluster, namely the DLK1-DIO3 imprinted locus through DNA and histone methylation. Since loss of expression from the maternal genes located in DLK1-DIO3 is also associated with aspects of the features typical of PWS, these novel discoveries have added a new layer of complexity to our current understanding of the molecular mechanisms behind this syndrome. Teasing apart the potential effects of SNORD116, IPW and the DLK1-DIO3 maternally expressed genes would inform not only our understanding of Prader-Willi syndrome, but also of multiple other pathways related to metabolical, circadian and cognitive health problems.
Funding
S.Z. is funded by the UK Medical Research Council (MRC) GW4 BioMed DTP; S.Z. and A.R.I. are members of the MRC Centre for Neuropsychiatric Genetics and Genomics (MR/L010305/1).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cassidy, S.B.; Schwartz, S.; Miller, J.L.; Driscoll, D.J. Prader-Willi syndrome. Genet. Med. 2011, 14, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenn, C.C.; Saitoh, S.; Jong, M.T.; Filbrandt, M.M.; Surti, U.; Driscoll, D.J.; Nicholls, R.D. Gene structure, DNA methylation, and imprinted expression of the human SNRPN gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1996, 58, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geuns, E.; De Rycke, M.; Van Steirteghem, A.; Liebaers, I. Methylation imprints of the imprint control region of the SNRPN-gene in human gametes and preimplantation embryos. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003, 12, 2873–2879. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kantor, B.; Kaufman, Y.; Makedonski, K.; Razin, A.; Shemer, R. Establishing the epigenetic status of the Prader–Willi/Angelman imprinting center in the gametes and embryo. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 2767–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsthemke, B.; Wagstaff, J. Mechanisms of imprinting of the Prader–Willi/Angelman region. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2008, 146A, 2041–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiveti, C.R.; Raabe, C.A.; Konthur, Z.; Rozhdestvensky, T.S. Differential regulation of non-protein coding RNAs from Prader-Willi Syndrome locus. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6445. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clayton-Smith, J.; Laan, L. Angelman syndrome: A review of the clinical and genetic aspects. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 40, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelzer, Y.; Sagi, I.; Yanuka, O.; Eiges, R.; Benvenisty, N. The noncoding RNA IPW regulates the imprinted DLK1-DIO3 locus in an induced pluripotent stem cell model of Prader-Willi syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garfield, A.S.; Davies, J.R.; Burke, L.K.; Furby, H.V.; Wilkinson, L.S.; Heisler, L.K.; Isles, A.R. Increased alternate splicing of Htr2c in a mouse model for Prader-Willi syndrome leads disruption of 5HT2C receptor mediated appetite. Mol. Brain 2016, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doe, C.M.; Relkovic, D.; Garfield, A.S.; Dalley, J.W.; Theobald, D.E.; Humby, T.; Wilkinson, L.S.; Isles, A.R. Loss of the imprinted snoRNA mbii-52 leads to increased 5htr2c pre-RNA editing and altered 5HT2CR-mediated behaviour. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 2140–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, T.; del Gaudio, D.; German, J.R.; Shinawi, M.; Peters, S.U.; Person, R.E.; Garnica, A.; Cheung, S.W.; Beaudet, A.L. Prader-Willi phenotype caused by paternal deficiency for the HBII-85 C/D box small nucleolar RNA cluster. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 719–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skryabin, B.V.; Gubar, L.V.; Seeger, B.; Pfeiffer, J.; Handel, S.; Robeck, T.; Karpova, E.; Rozhdestvensky, T.S.; Brosius, J. Deletion of the MBII-85 snoRNA Gene Cluster in Mice Results in Postnatal Growth Retardation. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, e235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, F.; Prints, Y.; Dhar, M.S.; Johnson, D.K.; Garnacho-Montero, C.; Nicholls, R.D.; Francke, U. Lack of Pwcr1/MBII-85 snoRNA is critical for neonatal lethality in Prader–Willi syndrome mouse models. Mamm. Genome 2005, 16, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassi, G.; Maggi, S.; Balzani, E.; Cosentini, I.; Garcia-Garcia, C.; Tucci, V. Working-for-Food Behaviors: A Preclinical Study in Prader-Willi Mutant Mice. Genetics 2016, 204, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Purtell, L.; Fu, M.; Lee, N.J.; Aepler, J.; Zhang, L.; Loh, K.; Enriquez, R.F.; Baldock, P.A.; Zolotukhin, S.; et al. Snord116 is critical in the regulation of food intake and body weight. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, F.; Li, H.H.; Zhang, S.; Solomon, N.; Camper, S.; Cohen, P.; Francke, U. SnoRNA Snord116 (Pwcr1/MBII-85) Deletion Causes Growth Deficiency and Hyperphagia in Mice. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, W.T.; Coulson, R.L.; Crary, F.K.; Wong, S.S.; Ach, R.A.; Tsang, P.; Alice Yamada, N.; Yasui, D.H.; LaSalle, J.M. A Prader–Willi locus lncRNA cloud modulates diurnal genes and energy expenditure. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 4318–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polex-Wolf, J.; Lam, B.Y.H.; Larder, R.; Tadross, J.; Rimmington, D.; Bosch, F.; Cenzano, V.J.; Ayuso, E.; Ma, M.K.L.; Rainbow, K.; et al. Hypothalamic loss of Snord116 recapitulates the hyperphagia of Prader-Willi syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassi, G.; Priano, L.; Maggi, S.; Garcia-Garcia, C.; Balzani, E.; El-Assawy, N.; Pagani, M.; Tinarelli, F.; Giardino, D.; Mauro, A.; et al. Deletion of the Snord116/SNORD116 Alters Sleep in Mice and Patients with Prader-Willi Syndrome. Sleep 2016, 39, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruby, N.F.; Hwang, C.E.; Wessells, C.; Fernandez, F.; Zhang, P.; Sapolsky, R.; Heller, H.C. Hippocampal-dependent learning requires a functional circadian system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15593–15598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, M.S.; Young, M.E. Circadian rhythms in the development of obesity: Potential role for the circadian clock within the adipocyte. Obes. Rev. 2006, 8, 169–181. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, R.; Sadeh, A.V.I.; Raviv, A. Instability of Sleep Patterns in Children With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2000, 39, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J. Prader-Willi and snoRNAs. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 688–689. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zieba, J.; Low, J.K.; Purtell, L.; Qi, Y.; Campbell, L.; Herzog, H.; Karl, T. Behavioural characteristics of the Prader–Willi syndrome related biallelic Snord116 mouse model. Neuropeptides 2015, 53, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.; Jiang, Y.; Bressler, J.; Armstrong, D.; Beaudet, A. Paternal Deletion from Snrpn to Ube3a in the Mouse Causes Hypotonia, Growth Retardation and Partial Lethality and Provides Evidence for a Gene Contributing to Prader-Willi Syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1999, 8, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarova, J.A.; Kramerov, D.A. Analysis of C/D box snoRNA genes in vertebrates: The number of copies decreases in placental mammals. Genomics 2009, 94, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarova, J.; Kramerov, D. SNOntology: Myriads of Novel snoRNAs or Just a Mirage? BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishore, S.; Stamm, S. The snoRNA HBII-52 Regulates Alternative Splicing of the Serotonin Receptor 2C. Science 2006, 311, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, K.N.; Lee, M.D.; Dourish, C.T.; Clifton, P.G. Serotonin 2C receptor agonists and the behavioural satiety sequence in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 71, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nonogaki, K.; Strack, A.M.; Dallman, M.F.; Tecott, L.H. Leptin-independent hyperphagia and type 2 diabetes in mice with a mutated serotonin 5-HT2C receptor gene. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, K.; Kato, T. RNA editing of serotonin 2C receptor in human postmortem brains of major mental disorders. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 346, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.-F.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, J.-F.; Wu, Y.-W.; Carmichael, G.G.; Chen, L.-L. Long Noncoding RNAs with snoRNA Ends. Mol. Cell 2012, 48, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falaleeva, M.; Surface, J.; Shen, M.; de la Grange, P.; Stamm, S. SNORD116 and SNORD115 change expression of multiple genes and modify each other’s activity. Gene 2015, 572, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleichert, F.; Gagnon, K.T.; Brown, B.A.; Maxwell, E.S.; Leschziner, A.E.; Unger, V.M.; Baserga, S.J. A Dimeric Structure for Archaeal Box C/D Small Ribonucleoproteins. Science 2009, 325, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulson, R.L.; Yasui, D.H.; Dunaway, K.W.; Laufer, B.I.; Vogel Ciernia, A.; Zhu, Y.; Mordaunt, C.E.; Totah, T.S.; LaSalle, J.M. Snord116-dependent diurnal rhythm of DNA methylation in mouse cortex. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitali, P.; Basyuk, E.; Le Meur, E.; Bertrand, E.; Muscatelli, F.; Cavaillé, J.; Huttenhofer, A. ADAR2-mediated editing of RNA substrates in the nucleolus is inhibited by C/D small nucleolar RNAs. J. Cell Boil. 2005, 169, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terajima, H.; Yoshitane, H.; Ozaki, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Shimba, S.; Kuroda, S.; Iwasaki, W.; Fukada, Y. ADARB1 catalyzes circadian A-to-I editing and regulates RNA rhythm. Nat. Genet. 2016, 49, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondratov, R.V.; Shamanna, R.K.; Kondratova, A.A.; Gorbacheva, V.Y.; Antoch, M.P. Dual role of the CLOCK/BMAL1 circadian complex in transcriptional regulation. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 530–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patten, M.M.; Cowley, M.; Oakey, R.J.; Feil, R. Regulatory links between imprinted genes: Evolutionary predictions and consequences. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2016, 283, 20152760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Rocha, S.T.; Edwards, C.A.; Ito, M.; Ogata, T.; Ferguson-Smith, A.C. Genomic imprinting at the mammalian Dlk1-Dio3 domain. Trends Genet. 2008, 24, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumamoto, S.; Takahashi, N.; Nomura, K.; Fujiwara, M.; Kijioka, M.; Uno, Y.; Matsuda, Y.; Sotomaru, Y.; Kono, T. Overexpression of microRNAs from the Gtl2-Rian locus contributes to postnatal death in mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 3653–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marty, V.; Labialle, S.; Bortolin-Cavaillé, M.; Ferreira De Medeiros, G.; Moisan, M.; Florian, C.; Cavaillé, J. Deletion of the miR-379/miR-410 gene cluster at the imprinted Dlk1-Dio3 locus enhances anxiety-related behaviour. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labielle, S.; Croteau, S.; McMurray, E.; Ruan, X.; Mousette, S.; Jonnaert, M.; Schmidt, J.; Cermakian, N.; Naumova, A. Novel imprinted transcripts from the Dlk1-Gtl2 intergenic region, Mico1 and Mico1os, show circadian oscillations. Epigenetics 2008, 3, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagami, M.; Nagasaki, K.; Kosaki, R.; Horikawa, R.; Naiki, Y.; Saitoh, S.; Tajima, T.; Yorifuji, T.; Numakura, C.; Mizuno, S.; et al. Temple syndrome: Comprehensive molecular and clinical findings in 32 Japanese patients. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 1356–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaillé, J.; Seitz, H.; Paulsen, M.; Ferguson-Smith, A.; Bachellerie, J. Identification of tandemly-repeated C/D snoRNA genes at the imprinted human 14q32 domain reminiscent of those at the Prader–Willi/Angelman syndrome region. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002, 11, 1527–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, K.N.; Vallero, R.O.; DuBose, A.J.; Resnick, J.L.; LaSalle, J.M. Imprinting regulates mammalian snoRNA-encoding chromatin decondensation and neuronal nucleolar size. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 4227–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).