Simple Summary
Pest control primarily depends on the application of chemical insecticides. Cyclaniliprole, a novel anthranilic diamide insecticide commercially introduced in 2017, exhibits broad-spectrum activity against various pests, including Hemiptera (aphids, whiteflies), Thysanoptera (thrips), and Lepidoptera (diamondback moth), with particularly remarkable efficacy against resistant populations. Rhopalosiphum padi (Linnaeus) and Schizaphis graminum (Rondani) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) are the two primary aphid species that infest wheat crops, and these pests frequently occur simultaneously. Nevertheless, the toxicity of cyclaniliprole to R. padi and S. graminum, along with its sublethal effects on their demographic parameters, remains unclear. Our results indicate that cyclaniliprole shows significantly acute toxicity against R. padi and S. graminum. Sublethal concentrations significantly reduced adult longevity and reproductive capacity in the F0 generation of these wheat aphid species, with no observed hormetic effects in the F1 generations of either R. padi or S. graminum. These results highlight the practical application value of cyromacridine, and support the optimization of integrated wheat aphid management strategies.
Abstract
Cyclaniliprole is a novel third-generation anthranilic diamide insecticide which has broad-spectrum efficacy against various pests, including aphids. Rhopalosiphum padi and Schizaphis graminum are the two primary aphid species that infest wheat crops. This investigation evaluates cyclaniliprole’s acute toxicity and sublethal and transgenerational effects on both aphid species. The acute toxicity assessment revealed obvious insecticidal activity, with 24 h LC50 values of 38.56 mg/L for R. padi and 33.71 mg/L for S. graminum. Sublethal exposure (LC15 and LC35 in R. padi; LC35 in S. graminum) significantly reduced adult longevity and fecundity in the F0 generation. In the F1 generation, cyclaniliprole at LC35 significantly reduced the fourth nymph stage in R. padi, whereas at LC15, it shortened the third nymph stage duration in S. graminum compared to the control. Sublethal concentrations (LC15 and LC35) of cyclaniliprole significantly reduced age-stage-specific survival rate (sxj), age-specific survival rate (lx), age-specific maternity (lxmx), and age-stage life expectancy (exj) in the F1 generation of R. padi, while only LC35 decreased lx, lxmx, and exj in S. graminum. Additionally, LC35 significantly reduced the net reproductive rate (R0) in the F1 generation of R. padi compared to the control. These findings suggest that cyclaniliprole exhibit notable acute toxicity against both aphid species and that sublethal concentrations adversely affected the F0 generation, with no observed hormetic effects in the F1 generations of R. padi and S. graminum. The findings offer valuable insights for assessing the comprehensive insecticidal potential of cyclaniliprole.
1. Introduction
Cyclaniliprole is a novel anthranilic diamide insecticide that was commercially launched in 2017 and has since been registered and marketed in multiple countries, including the United States, Canada, Australia, and Brazil [1,2]. As a diamide compound and third-generation ryanodine receptor (RyR) activator, it specifically binds to RyR receptors in insect muscle cells, causing abnormal calcium ion release that leads to muscle paralysis and death [3]. This insecticide demonstrates broad-spectrum efficacy against various pests, including Hemiptera (aphids, whiteflies), Thysanoptera (thrips), and Lepidoptera (diamondback moth), with particularly outstanding performance against resistant populations [2,4]. Its systemic properties provide long-lasting protection while maintaining safety to non-target organisms, earning it classification as a reduced-risk insecticide by the U.S. EPA [5]. Currently, it is primarily used for pest control in high-value crops such as fruits, vegetables, and tea, serving as an important tool in resistance management strategies.
Wheat, a critically important global food crop, faces severe threats from wheat aphids, which rank among the most destructive agricultural pests. These insects contribute to substantial yield losses, accounting for 10–30% of annual global wheat production [6], thereby posing a serious risk to food security worldwide. Rhopalosiphum padi (Linnaeus) and Schizaphis graminum (Rondani) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) are the two primary aphid species that infest wheat crops, and these pests frequently occur simultaneously [7,8]. These insects inflict direct damage by persistently feeding on phloem sap, depleting essential nutrients and weakening host plants [9]. Beyond sap consumption, they act as vectors for plant viruses, excrete honeydew that promotes sooty mold growth, and impair photosynthetic efficiency, collectively contributing to significant reductions in wheat yield and grain quality [10,11].
The management of wheat aphids primarily relies on chemical insecticides, which are typically applied at optimal concentrations to ensure effective pest control. However, due to rapid pesticide degradation under field conditions and continuous plant growth, residual insecticide concentrations often decline to sublethal levels shortly after application [12]. A growing body of research indicates that sublethal insecticide exposure can induce significant behavioral and physiological modifications in pests, potentially triggering cascading effects on population dynamics, species interactions, and crop damage patterns [13,14,15]. While numerous studies have demonstrated that sublethal concentrations can negatively impact pest physiology by reducing survival rates, impairing growth and fecundity, and disrupting biochemical pathways [7,16], paradoxically, certain sublethal doses may inadvertently enhance pest infestations by stimulating growth and reproduction [17,18,19]. These contrasting findings underscore the critical importance of investigating both the sublethal and transgenerational effects of insecticides for developing sustainable integrated pest management strategies.
In this study, we employ the age-stage two-sex life table approach to comprehensively assess the acute toxicity, sublethal effects, and transgenerational impacts of cyclaniliprole on R. padi and S. graminum. The results provide valuable insights for evaluating the overall insecticidal potential of cyclaniliprole and optimizing integrated pest management strategies for wheat aphids.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects and Insecticides
The populations of R. padi and S. graminum were collected in April 2024 from a wheat field located in Xinxiang, Henan Province, China (35°09′12″ N, 113°39′29″ E). The aphids were maintained on wheat seedlings (Aikang 58) under controlled laboratory conditions: temperature at 19–21 °C, relative humidity at 60 ± 10%, and a 16:8 h (light–dark) photoperiod. Throughout the rearing period, no pesticide exposure occurred. Cyclaniliprole (95% active ingredient, w/w) was provided by Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha (ISK) (Osaka, Japan).
2.2. Insecticide Bioassays
The toxicity of cyclaniliprole against R. padi and S. graminum was evaluated using a leaf-dip bioassay [20]. A stock solution of cyclaniliprole (10,000 mg/L) was prepared in acetone and serially diluted with 0.1% (v/v) Tween-80 aqueous solution to obtain five test concentrations: 1, 5, 25, 125, and 625 mg/L. Wheat leaves with approximately 30 third-instar wingless aphids were immersed in each test solution for 3–5 s, transferred to a Petri dishes lined with moist filter paper, and then maintained under the aforementioned conditions. Mortality was assessed 24 h post-treatment, with aphids considered dead if they showed no more than one leg movement upon gentle prodding with a dissection needle. A 0.1% (v/v) Tween-80 aqueous solution served as the untreated control, and each concentration was replicated three times. The mortality of control in every experiment request lower than 5%. Probit analysis (PoloPlus 2.0 software, LeOra Software, USA) was used to determine LC15, LC35, and LC50 values, along with the slope and Chi-square statistic. The derived sublethal concentrations (LC15 and LC35) were then applied to evaluate the sublethal effects of cyclaniliprole on R. padi and S. graminum.
2.3. Sublethal and Transgenerational Effects of Cyclaniliprole on R. padi and S. graminum
The sublethal and transgenerational effects of cyclaniliprole on R. padi and S. graminum were evaluated using life table analysis. A cohort of third-instar nymphs was treated by immersion in LC15 and LC35 solutions, as described in the bioassay section, with 0.1% (v/v) Tween-80 in water serving as the control. After 24 h, mortality was recorded, and sixty surviving wingless aphids were randomly selected and individually transferred to a plastic Petri dishes, each containing a moistened filter paper and three wheat seedlings (5–10 cm long). Three wheat seedlings (5–10 cm long) were wrapped with water-soaked cotton before being placed in 1.5 mL microtubes. Fresh wheat seedlings were replaced every three days. The longevity of F0 adults and their daily nymph production were recorded until all aphids died. Subsequently, sixty newborn nymphs (<24 h old) from each treatment group were randomly selected as the F1 generation. Each F1 nymph was reared individually on fresh wheat seedlings under the same conditions. The developmental duration of each life stage and daily nymph production of F1 individuals were monitored, with newborn nymphs removed after counting. Observations continued until all aphids died. The collected data were used to construct age-stage-specific two-sex life tables for analysis.
2.4. Life Table Analysis
A life table analysis of R. padi and S. graminum was conducted using the TWO-SEX-MSChart software (Version 2025.03.23) [21] following the age-stage two-sex life table theory [22,23]. The evaluated parameters included the developmental duration of different life stages, adult longevity, adult pre-reproductive period (APRP), total pre-reproductive period (TPRP), reproductive days, fecundity, intrinsic rate of increase (r), finite rate of increase (λ), net reproductive rate (R0), and mean generation time (T). These parameters were compared using a paired bootstrap test based on the confidence interval of differences [21,24]. Additionally, age-stage-specific survival rate (sₓⱼ), age-specific survival rate (lx), age-specific fecundity of the total population (mx), age-specific maternity (lₓmₓ), age-stage reproductive value (vₓⱼ), and age-specific life expectancy (eₓⱼ) were computed using the TWOSEX-MSChart program (Version 2025.03.23) [25]. The variance and standard errors of the population parameters were estimated via the bootstrap procedure incorporated in TWOSEX-MSChart, with 100,000 random resamplings [26,27].
3. Results
3.1. The Toxicity and Sublethal Concentration of Cyclaniliprole on R. padi and S. graminum
The toxicity parameters of cyclaniliprole against R. padi and S. graminum are presented in Table 1. The results show that the estimated LC15, LC35, and LC50 values of cyclaniliprole against R. padi were 4.19, 16.90, and 38.56 mg/L, respectively. Similarly, the LC15, LC35, and LC50 values against S. graminum were 2.17, 12.16, and 33.71 mg/L, respectively. For R. padi, exposure to 5.00 and 17.00 mg/L of cyclaniliprole (corresponding to LC15 and LC35) resulted in 13.83% and 37.62% mortality, respectively. In the case of S. graminum, exposure to 2.50 and 12.00 mg/L of cyclaniliprole (equivalent to LC15 and LC35) led to 17.26% and 36.92% mortality, respectively.

Table 1.
The toxicity and sublethal concentration of cyclaniliprole on Rhopalosiphum padi and Schizaphis graminum (mg/L).
3.2. Sublethal Effects of Cyclaniliprole on the F0 Generation of R. padi and S. graminum
The adult longevity of the F0 generation of R. padi and S. graminum in the control group was 13.26 ± 0.97 and 8.40 ± 0.69 d, respectively (Figure 1). Compared to the control group, the adult longevity of the F0 generation of R. padi and S. graminum was reduced to 7.17 ± 1.06 d (p < 0.001) and 7.5 ± 0.55 d, 3.26 ± 0.83 d (p < 0.001), and 5.76 ± 0.46 d (p = 0.001), respectively, when treated with LC15 and LC35 concentrations of cyclaniliprole (Figure 1). The nymphs per female of the F0 generation of R. padi and S. graminum in the control group were 45.28 ± 3.93 and 20.30 ± 2.86, respectively (Figure 1). Compared to the control group, the number of nymphs per female of R. padi and S. graminum F0 generation decreased to 25.61 ± 4.47 (p = 0.001) and 17.20 ± 2.38, 11.12 ± 3.43 (p < 0.001), and 11.58 ± 2.00 (p = 0.013), respectively, after treatment with LC15 and LC35 concentrations of cyclaniliprole (Figure 1).
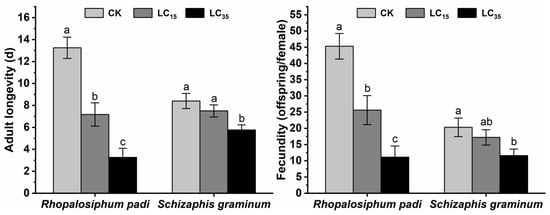
Figure 1.
The adult longevity and fecundity of Rhopalosiphum padi and Schizaphis graminum F0 generation under control conditions (CKs), treated with LC15 and LC35 concentrations of cyclaniliprole. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.3. Transgenerational Sublethal Effects of Cyclaniliprole on Developmental Time and Fecundity of R. padi and S. graminum
The developmental duration and fecundity of the F1 generation of R. padi and S. graminum, derived from parents exposed to two sublethal concentrations of cyclaniliprole, are summarized in Table 2. For the R. padi F1 generation, no significant differences were observed in the duration of the first nymph stage, second nymph stage, third nymph stage, pre-adult period, adult longevity, total longevity, APRP, and TPRP between the control and treatment groups (p > 0.05); however, the LC35 concentration of cyclaniliprole significantly reduced the fourth nymph stage (p < 0.05). Additionally, the reproductive period and nymphs per female of the R. padi F1 generation in the LC35 treatment group were significantly lower compared to the LC15-treatment group (p < 0.05). For S. graminum F1 generation, the LC15 concentration of cyclaniliprole significantly reduced the duration of the third nymph stage compared to the control group (p < 0.05), whereas no significant differences were observed in other parameters of developmental duration and fecundity (p < 0.05).

Table 2.
Sublethal effects of cyclaniliprole on the developmental duration and fecundity of Rhopalosiphum padi and Schizaphis graminum F1 generation.
3.4. Transgenerational Sublethal Effects of Cyclaniliprole on sxj, lxmx, vxj, and exj of R. padi and S. graminum
The sxj of R. padi and S. graminum F1 generation are presented in Figure 2. In the control group, the maximum sxj values for 2nd, 3rd, and 4th instar nymphs and adults were 0.73, 0.63, 0.78, and 0.93, respectively. In contrast, under the LC15 and LC35 treatments, the maximum sxj values for the corresponding stages were reduced to 0.64 and 0.64 (2nd), 0.51 and 0.49 (3rd), and 0.52 and 0.54 (4th), as well as 0.83 and 0.85 (adults), respectively, indicating that sublethal exposure (LC15 and LC35) decreased sxj of R. padi F1 generation (Figure 2). For S. graminum F1 generation, LC15 and LC35 concentrations of cyclaniliprole had no significant effects on sxj (Figure 2). Additionally, sublethal exposure (LC15 and LC35 in R. padi; LC35 in S. graminum) significantly reduced the lx and lxmx, whereas mx showed no significant difference in the F1 generation of either species (Figure 3).
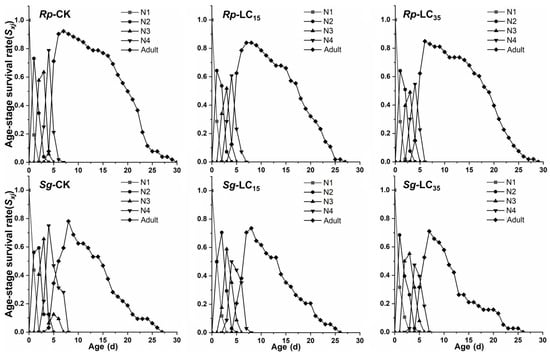
Figure 2.
Age-stage-specific survival rate (sxj) of Rhopalosiphum padi and Schizaphis graminum F1 generation under control conditions (CK) treated with LC15 and LC35 concentrations of cyclaniliprole. Rp, Rhopalosiphum padi; Sg, Schizaphis graminum; N1, first nymph stage; N2, second nymph stage; N3, third nymph stage; N4, fourth nymph stage.
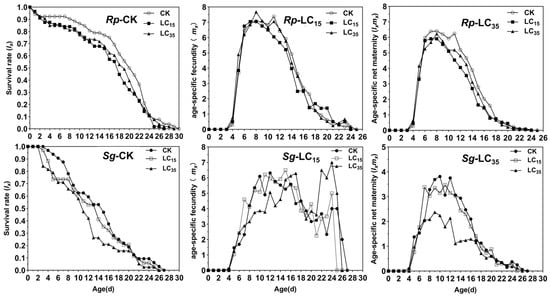
Figure 3.
Age-specific survival rate (lx), age-specific fecundity of the total population (mx), and age-specific maternity (lxmx) of Rhopalosiphum padi and Schizaphis graminum F1 generation under control conditions (CK) treated with LC15 and LC35 concentrations of cyclaniliprole. Rp, Rhopalosiphum padi; Sg, Schizaphis graminum.
The vxj did not differ significantly between treatment and control groups during the early developmental stages. However, in the later adult stages, the LC15-treated group of R. padi exhibited significantly reduced vxj compared to the control group, while the LC35-treated group of S. graminum showed significantly increased vxj relative to the control group (Figure 4). For R. padi F1 generation, the maximum exj values for the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th instar nymphs and adults in the control group were 18.63, 19.08, 18.08, 17.08, and 16.08 d, respectively. Under LC15 and LC35 treatments, these values decreased to 16.18 and 16.77 (1st instar), 16.12 and 17.43 (2nd instar), 16.23 and 17.14 (3rd instar), and 15.25 and 16.28 (4th instar), as well as 14.45 and 15.28 days (adults), respectively, indicating that sublethal exposure reduced exj in R. padi (Figure 5). Similarly, for S. graminum F1 generation, the maximum exj values declined from 13.25, 13.38, 12.19, 11.42, and 10.66 days (control group) to 12.14, 11.09, 10.00, 10.51, and 9.51 days (LC35-treated group) for the 1st through to the 4th instars and adults, respectively, indicating that LC35 exposure significantly reduced exj in S. graminum (Figure 5).
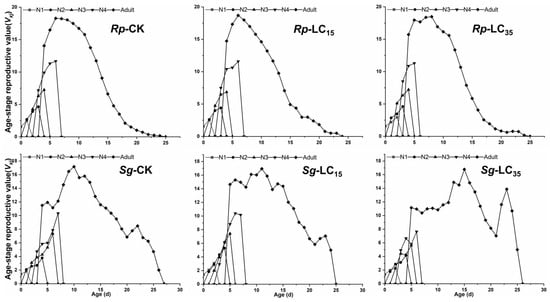
Figure 4.
Age-stage-specific reproductive rate (vxj) of Rhopalosiphum padi and Schizaphis graminum F1 generation under control conditions (CK) treated with LC15 and LC35 concentrations of cyclaniliprole. Rp, Rhopalosiphum padi; Sg, Schizaphis graminum; N1, first nymph stage; N2, second nymph stage; N3, third nymph stage; N4, fourth nymph stage.
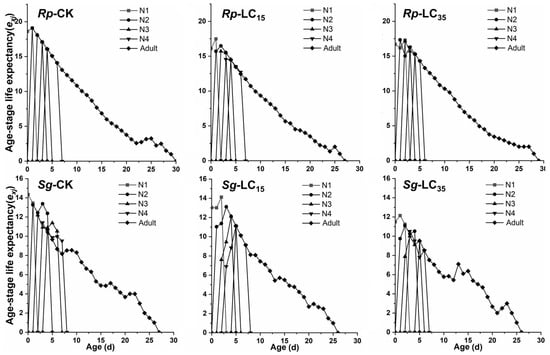
Figure 5.
Age-stage-specific life expectancy (exj) of Rhopalosiphum padi and Schizaphis graminum F1 generation under control conditions (CK), treated with LC15 and LC35 concentrations of cyclaniliprole. Rp, Rhopalosiphum padi; Sg, Schizaphis graminum; N1, first nymph stage; N2, second nymph stage; N3, third nymph stage; N4, fourth nymph stage.
3.5. The Effects of the Cyclaniliprole on Population Parameters of the R. padi and S. graminum F1 Generation
The population parameters of R. padi and S. graminum F1 generation are presented in Table 3. For R. padi F1 generation, no significant differences were observed among the CK, LC15, and LC35 groups in the r, λ, and T (p > 0.05). However, the R0 in the LC35-treated group was significantly lower than that of the control group (p < 0.05). For S. graminum F1 generation, no significant differences were detected among the CK, LC15, and LC35 groups in r, λ, R0, and T (p > 0.05).

Table 3.
Sublethal effects of cyclaniliprole on population parameters of the F1 generation of Rhopalosiphum padi and Schizaphis graminum.
4. Discussion
Chemical control remains the primary approach for managing wheat pests. Cyclaniliprole, as a novel third-generation anthranilic diamide insecticide, has demonstrated efficacy against various pests including aphids, whiteflies, thrips, and diamondback moth [2,4]. A recent study revealed that cyclaniliprole presents an exceptionally low resistance risk and shows minimal cross-resistance in Myzus persicae [28]. While these findings are promising, the toxicological effects of cyclaniliprole on wheat aphid species have not been systematically investigated. In our current study, cyclaniliprole showed pronounced acute toxicity against R. padi and S. graminum, exhibiting 24 h LC50 values of 38.56 mg/L and 33.71 mg/L, respectively. These quantitative results substantiate that cyclaniliprole serves as an effective chemical option for wheat aphid management.
Beyond their lethal effects on target pests, chemical insecticides frequently induce significant sublethal effects due to inherent field application variability and subsequent environmental degradation processes [12]. Sublethal insecticide exposures typically diminish adult longevity and reproductive output in the F0 generation of pest populations. For instance, acetamiprid sublethal concentrations were shown to significantly reduce adult lifespan and fecundity in S. graminum and Sitobion miscanthi populations [7]. Our current findings reveal that sublethal exposure (LC15 and LC35 in R. padi; LC35 in S. graminum) significantly reduced adult longevity and fecundity in the F0 generation, confirming the adverse sublethal effects on these species’ parental generations. These observations are consistent with the sub-lethal effects of most pesticides on the F0 generation of aphids. For instance, sublethal doses of flonicamid were shown to significantly decrease adult longevity and fecundity of R. padi F0 generation [29], and similarly reduced the reproductive performance of F0-generation A. gossypii [30].
Numerous studies have demonstrated that sublethal pesticide concentrations can induce transgenerational effects on insect’s development and reproductive capacity. For example, sublethal doses of pirimicarb were found to prolong the T and population doubling time while reducing the r in R. padi F1 generation [31]. Similarly, sublethal concentrations of sulfoxaflor and afidopyropen significantly extended the preadult period and TPRP, while decreasing r, R0, and λ in A. gossypii F1 generation [16,32]. In the current study, the LC35 concentration of cyclaniliprole significantly reduced duration of the fourth nymphal stage and R0 in R. padi F1 generation. And the LC15 concentration similarly shortened the third nymphal stage duration in S. graminum F1 generation. Furthermore, sublethal concentrations (LC15 and LC35) of cyclaniliprole significantly reduced sxj, lx, lxmx, and exj in the F1 generation of R. padi, while only LC35 decreased lx, lxmx and exj in S. graminum. However, other life table parameters remained unaffected in both aphid species. These findings indicate that sublethal concentrations of cyclaniliprole produce pronounced adverse transgenerational effects on R. padi populations, while exerting comparatively milder effects on S. graminum.
Certain pesticides exhibit a dose-dependent dual effect on pest toxicity, where high doses typically suppress pest population development and low dose exposures may stimulate population growth in some pest species [33]. This phenomenon, termed hormesis, has been extensively documented in previous research. Specifically, sublethal concentrations of flupyradifurone were shown to significantly increase nymph production per female and the r in M. persicae F1 generations [34], with similar enhancements of these population parameters observed in Metopolophium dirhodum following sublethal imidacloprid exposure [17]. Such insecticide-induced hormesis, which stimulates pest population growth at sublethal doses, is recognized as one of the drivers of pest resurgence [35]. Notably, our findings reveal that sublethal doses of cyclaniliprole did not significantly increase nymph production per female, r, and R0 in either R. padi or S. graminum F1 generations. These results demonstrate that the sublethal dose of cyclaniliprole has no hormesis on R. padi and S. graminum populations.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our results indicate that cyclaniliprole have an acute toxicity against R. padi and S. graminum, with a LC50 of 38.56 and 33.71 mg/L at 24 h, respectively. Sublethal exposure (LC15 and LC35 in R. padi; LC35 in S. graminum) significantly reduced adult longevity and fecundity in the F0 generation. In the F1 generation, cyclaniliprole at LC35 significantly reduced the fourth nymph stage in R. padi, whereas at LC15, it shortened the third nymph stage duration in S. graminum compared to the control. Sublethal concentrations (LC15 and LC35) of cyclaniliprole significantly reduced sxj, lx, lxmx, and exj in the F1 generation of R. padi, while only LC35 decreased lx, lxmx and exj in S. graminum. Additionally, LC35 significantly reduced the R0 in the F1 generation of R. padi compared to the control. These findings suggest that cyclaniliprole exhibit notable acute toxicity against both aphid species and that sublethal concentrations adversely affected the F0 generation, with no observed hormetic effects in the F1 generations of R. padi and S. graminum. In subsequent research, it is necessary to conduct further investigations into the control effects of cyclaniliprole on different field populations of R. padi and S. graminum and to further evaluate the resistance risks of these pest populations to cyclaniliprole. The findings will significantly enhance our knowledge of cyclaniliprole’s application value and contribute to the optimization of integrated pest management strategies for wheat aphid control.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Y. and H.W.; methodology, X.L., G.W., J.Y. and H.W.; software, X.L., G.Z., C.S. and G.W.; validation, X.L., G.W., F.W. and R.Q.; formal analysis, X.L., X.Z., W.Z., F.W. and R.Q.; investigation, G.Z., C.S., F.W., R.Q. and W.Z.; resources, X.L. and W.Z.; data curation, G.Z., C.S., F.W. and R.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, X.L., X.Z. and W.Z.; writing—review and editing, J.Y. and H.W.; visualization, X.L., G.Z., C.S., F.W., R.Q. and W.Z.; supervision, G.W., J.Y. and H.W.; project administration, J.Y. and H.W.; funding acquisition, G.W. and H.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Key Research and Development and Promotion Projects of Henan Province (No. 241111111700) and the Key Scientific and Technological Research Project of Henan Province (No. 242102110194).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Henan Province Engineering Research Center of Biological Pesticide & Fertilizer Development and Synergistic Application for providing the R. padi and S. graminum population.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sun, X.; Wei, R.; Li, L.; Zhu, B.; Liang, P.; Gao, X. Resistance and fitness costs in diamondback moths after selection using broflanilide, a novel meta-diamide insecticide. Insect Sci. 2022, 29, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Lv, H.; Tan, D.; Liang, N.; Guo, C.; Chu, D. Resistance to insecticides in the field and baseline susceptibility to cyclaniliprole of whitefly Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius) in China. Crop Prot. 2020, 130, e105065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahm, G.P.; Selby, T.P.; Freudenberger, J.H.; Stevenson, T.M.; Myers, B.J.; Seburyamo, G.; Smith, B.K.; Flexner, L.; Clark, C.E.; Cordova, D. Insecticidal anthranilic diamides: A new class of potent ryanodine receptor activators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 4898–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umetsu, N.; Shirai, Y. Development of novel pesticides in the 21st century. J. Pestic. Sci. 2020, 45, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, S.V. Repellent effects of insecticides on stephanitis pyrioides scott (Hemiptera: Tingidae) under laboratory conditions. Crop Prot. 2020, 127, e104985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.S.; Liu, Y.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X.L.; Wang, B.; Zhang, G.S.; Liu, X.F.; Hu, Z.Q.; Zhao, H.Y.; et al. Resistance of wheat accessions to the English grain aphid Sitobion avenae. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Song, C.; Zhang, P.; Li, G.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, B.; Taylor, S. The sublethal concentration of acetamiprid suppresses the population growth of 2 species of wheat aphids, Sitobion miscanthi and Schizaphis graminum (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2024, 117, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Li, Q.; Zhu, S.; Tian, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, H.; Liu, E.; Wang, L.; et al. Field-evolved sulfoxaflor resistance of three wheat aphid species in China. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furstenberg-Hagg, J.; Zagrobelny, M.; Bak, S. Plant defense against insect herbivores. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10242–10297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliephake, E.; Habekuss, A.; Scholz, M.; Ordon, F. Barley yellow dwarf virus transmission and feeding behaviour of Rhopalosiphum padi on Hordeum bulbosum clones. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2013, 146, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaris, M.; Lampert, S.; Salvadori, J.R.; Lau, D.; Pereira, P.R.V.S.; Smaniotto, M.A. Population Growth and Damage Caused by Rhopalosiphum padi (L.) (Hemiptera, Aphididae) on Different Cultivars and Phenological Stages of Wheat. Neotrop. Entomol. 2013, 42, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desneux, N.; Fauvergue, X.; Dechaume-Moncharmont, F.X.; Kerhoas, L.; Ballanger, Y.; Kaiser, L. Diaeretiella rapae limits Myzus persicae populations after applications of deltamethrin in oilseed rape. J. Econ. Entomol. 2005, 98, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Qu, Y.; Xiao, D.; Song, L.; Zhang, S.; Gao, X.; Desneux, N.; Song, D. Lethal and social-mediated effects of ten insecticides on the subterranean termite Reticulitermes speratus. J. Pest Sci. 2015, 88, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desneux, N.; Decourtye, A.; Delpuech, J.M. The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, J.D.; Banks, J.E. Population-level effects of pesticides and other toxicants on arthropods. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2003, 48, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Tang, Q.; Liang, P.; Li, J.; Gao, X. A sublethal concentration of afidopyropen suppresses the population growth of the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J. Integr. Agr. 2022, 21, 2055–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, X.; Cheng, D.; Zhang, Y. Effects of imidacloprid-induced hormesis on the development and reproduction of the rose-grain aphid Metopolophium dirhodum (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1113464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Gul, H.; Tariq, K.; Desneux, N.; Gao, X.; Song, D. Thiamethoxam induces transgenerational hormesis effects and alteration of genes expression in Aphis gossypii. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 165, 104557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Yu, W.; Yi, X.; Gao, J.; Gao, X.; Zeng, X. Sublethal effects of sulfoxaflor on the fitness of two species of wheat aphids, Sitobion avenae (F.) and Rhopalosiphum padi (L.). J. Integr. Agr. 2019, 18, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Peng, X.; Piñero, J.C.; Chen, M. Regional susceptibilities of Rhopalosiphum padi (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to ten insecticides. Fla. Entomol. 2016, 99, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H. TWOSEX-MSChart.zip. 2025. Available online: https://lifetablechi.com/software (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Chi, H.; Liu, H. Two new methods for the study of insect population ecology. Bull. Inst. Zool. Acad. Sin. 1985, 24, 225–240. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242218411 (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Chi, H. Life-table analysis incorporating both sexes and variable development rates among individuals. Environ. Entomol. 1988, 17, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.F.; Chi, H.; Guo, Y.F.; Li, X.W.; Zhao, L.L.; Ma, R.Y. Demography of Cacopsylla chinensis (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) reared on four cultivars of Pyrus bretschneideri (Rosales: Rosaceae) and P. communis pears with estimations of confidence intervals of specific life table statistics. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 2343–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuan, S.J.; Lee, C.C.; Chi, H. Population and damage projection of Spodoptera litura (F.) on peanuts (Arachis hypogaea L.) under different conditions using the age-stage, two-sex life table. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.W.; Chi, H.; Smith, C.L. Linking demography and consumption of Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) fed on Solanum photeinocarpum (Solanales: Solanaceae): With a new method to project the uncertainty of population growth and consumption. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.B.; Chi, H. Life tables of Bactrocera cucurbitae (Diptera: Tephritidae): With an invalidation of the jackknife technique. J. Appl. Entomol. 2013, 137, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Zhen, C.; Li, D.; Cheng, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, L. Risk assessment of cyclaniliprole resistance in peach-potato aphid Myzus persicae: Laboratory selection, inheritance, and cross-resistance patterns. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2025, 118, e70031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.B.; Cui, L.L.; Jiang, Y.T.; Lv, Y.P.; Li, R.J.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.A.; Zhang, B.Z.; Liu, R.Q. Sublethal effects of flonicamid on the population growth of the grain aphid Rhopalosiphum padi (L.) (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2025, 115, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Luo, C.; Lv, H.; Zhang, L.; Desneux, N.; You, H.; Li, J.; Ullah, F.; Ma, K. Impact of sublethal and low lethal concentrations of flonicamid on key biological traits and population growth associated genes in melon aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover. Crop Prot. 2022, 152, 105863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Yang, T.; Desneux, N.; Han, P.; Gao, X. Assessment of sublethal and transgenerational effects of pirimicarb on the wheat aphids Rhopalosiphum padi and Sitobion avenae. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ma, K.; Li, F.; Liang, P.; Liu, Y.; Guo, T.; Song, D.; Desneux, N.; Gao, X. Sublethal and transgenerational effects of sulfoxaflor on the biological traits of the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, R.N.; Cutler, G.C. Insecticide-induced hormesis and arthropod pest management. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Ma, K.; Chi, H.; Hou, Y.; Gao, X. Transgenerational hormetic effects of sublethal dose of flupyradifurone on the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Hemiptera: Aphididae). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0208058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, R.N.; Smagghe, G.; Stark, J.D.; Desneux, N. Pesticide-induced stress in arthropod pests for optimized integrated pest management programs. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).