Evolution of the Sex Pheromone Communication System in Ostrinia Moths
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
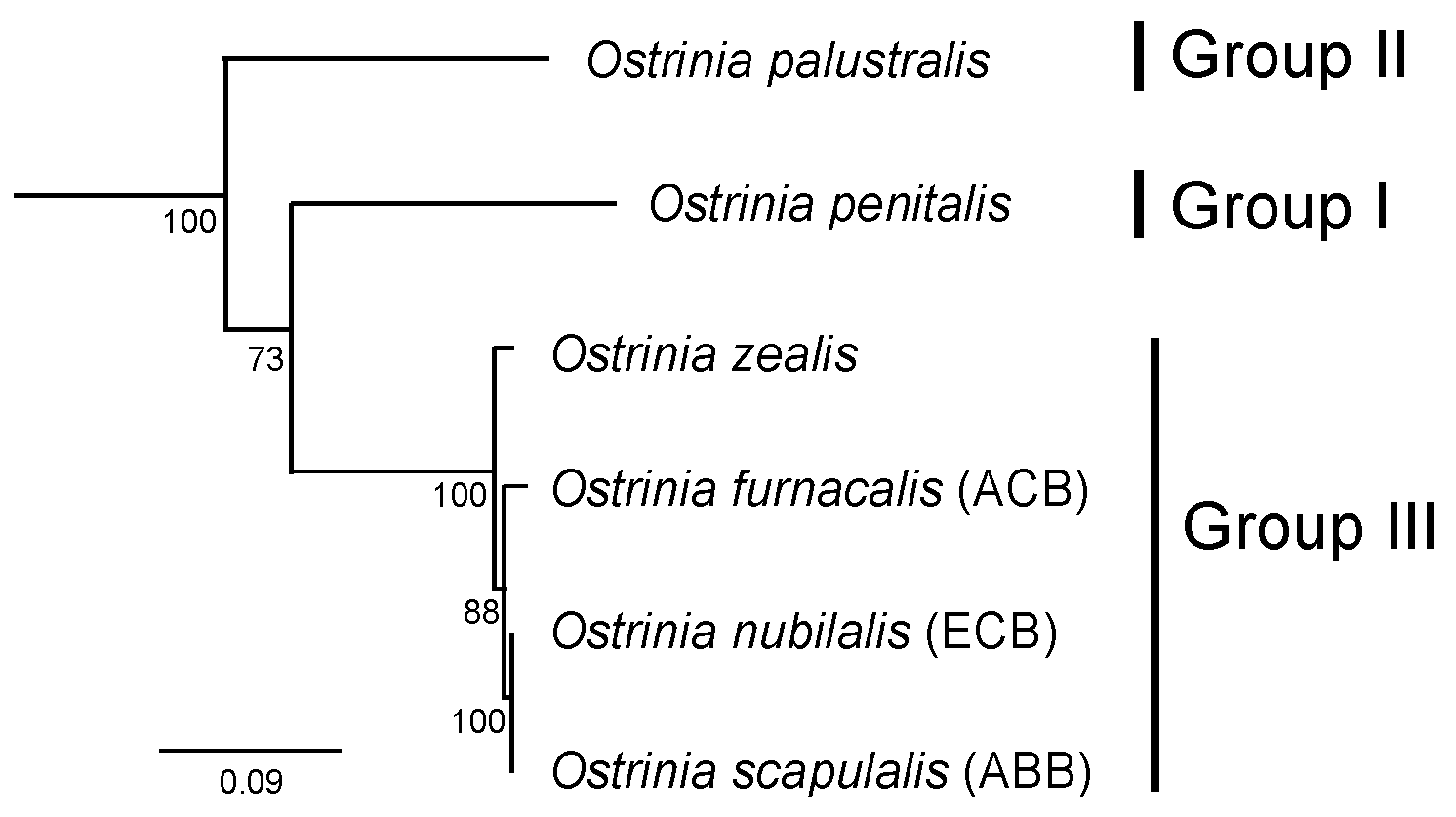
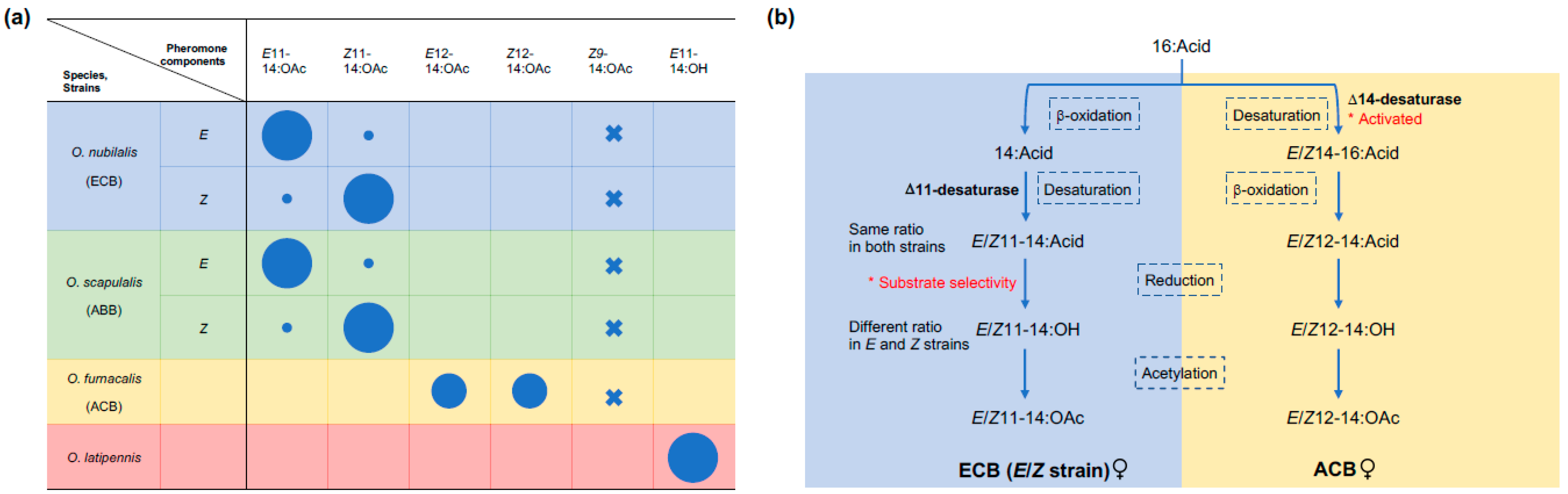
2. The Ostrinia Species and Female Sex Pheromones
3. The Molecular Basis of Pheromone Diversification
4. Male Produced Pheromones
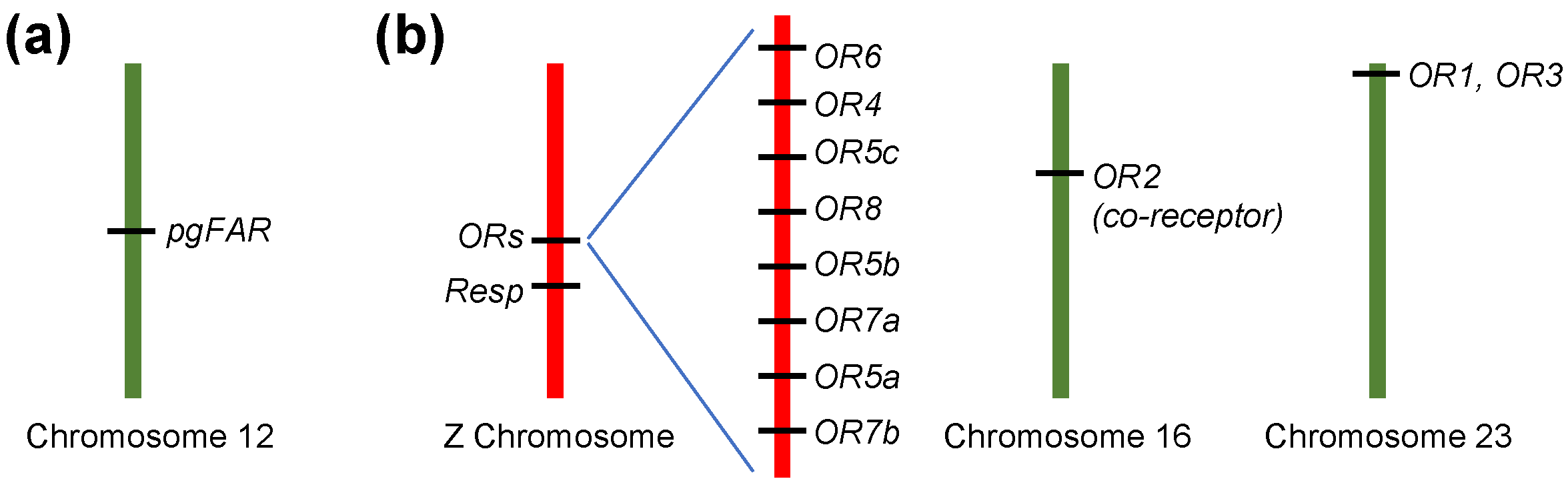
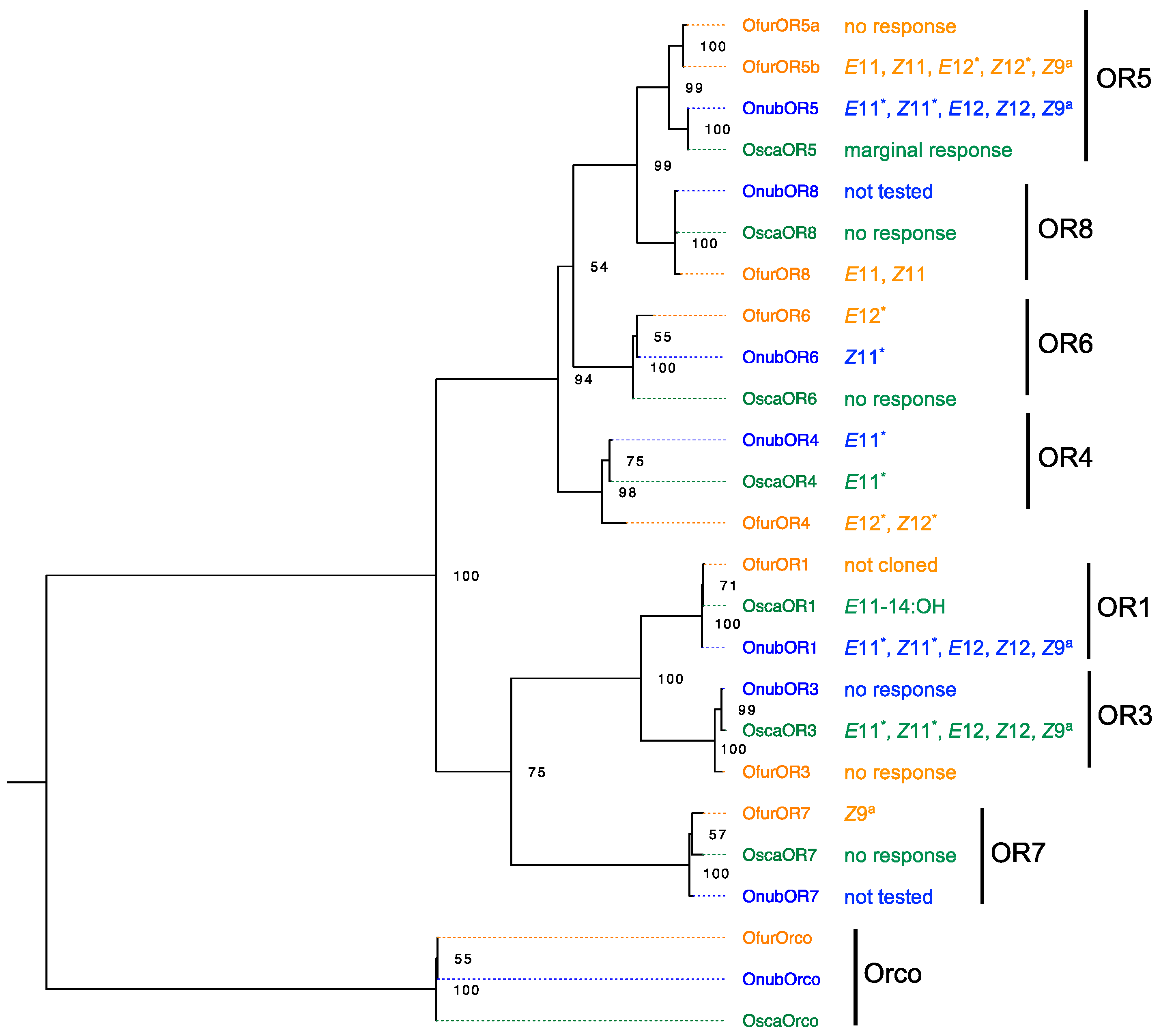
5. Ligand Profiles of Pheromone Receptor Genes in Males
6. Responses of Peripheral Olfactory Sensory Neurons to Pheromone Components
7. Antennal Lobe Projection Pattern of Pheromone Specific OSNs
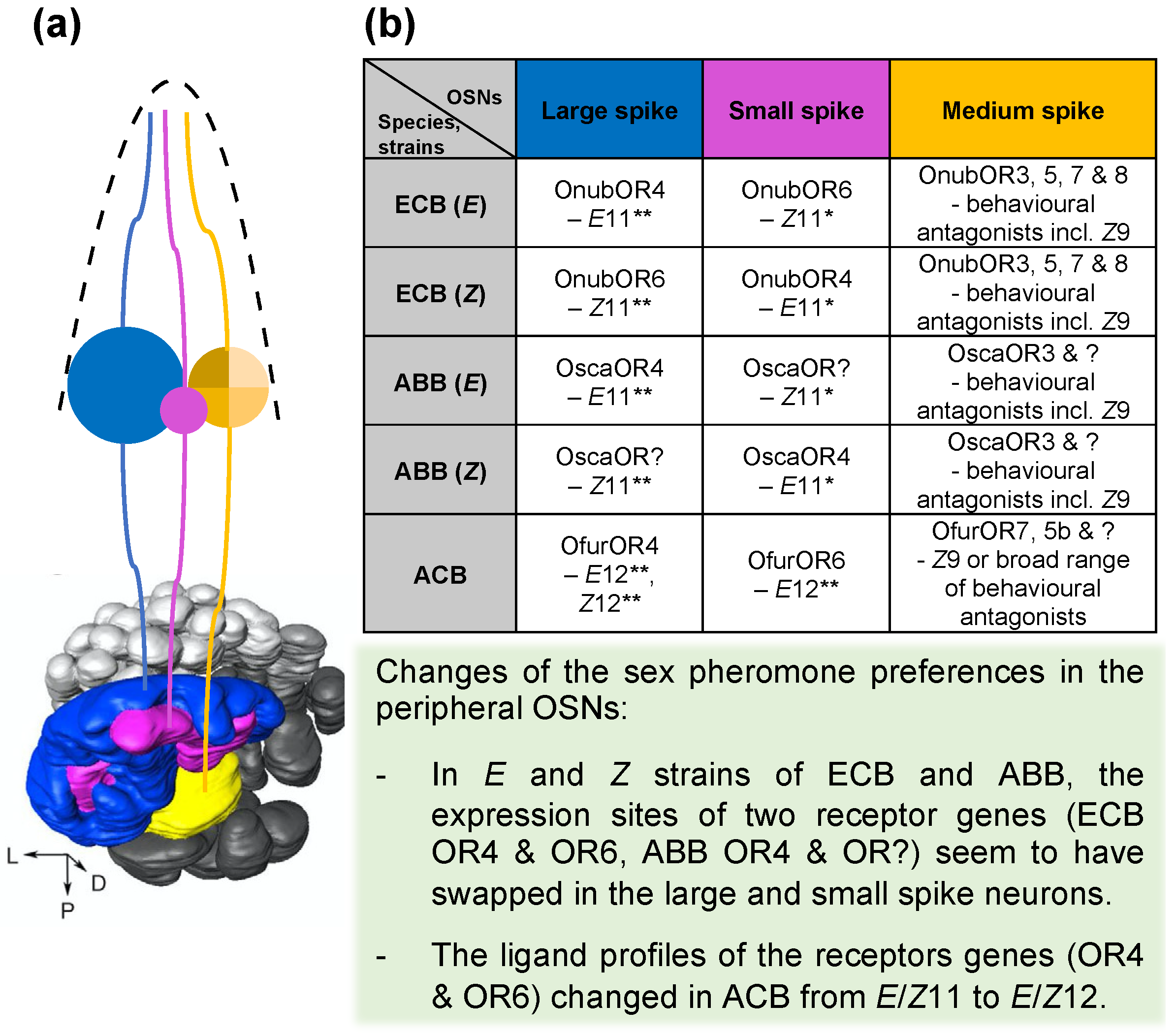
8. The Location of Pheromone Receptor Genes in OSNs
9. The Evolutionary Perspective
9.1. On the Signalers’ Side
9.2. On the Receivers’ Side
9.3. Broad Response Spectrum of Male Moths
9.4. Other Hypotheses and Forms of Selection
10. Concluding Remark
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greenfield, M.D. Signalers and Receivers: Mechanisms and Evolution of Arthropod Communication; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt, T.D. Pheromones and Animal Behavior: Chemical Signals and Signature; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Roelofs, W.L.; Liu, W.; Hao, G.; Jiao, H.; Rooney, A.P.; Linn, C.E. Evolution of moth sex pheromones via ancestral genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13621–13626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelofs, W.L.; Rooney, A.P. Molecular genetics and evolution of pheromone biosynthesis in Lepidoptera. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9179–9184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Rooney, A.P.; Kajikawa, M.; Okada, N.; Roelofs, W.L. Novel sex pheromone desaturases in the genomes of corn borers generated through gene duplication and retroposon fusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4467–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassance, J.M. Journey in the Ostrinia world: From pest to model in chemical ecology. J. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 36, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassance, J.M.; Groot, A.T.; Liénard, M.A.; Antony, B.; Borgwardt, C.; Andersson, F.; Hendeström, E.; Heckel, D.G.; Löfstedt, C. Allelic variation in a fatty-acyl reductase gene causes divergence in moth sex pheromones. Nature 2010, 466, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Liénard, M.A.; Zhao, C.-H.; Wang, C.Z.; Löfstedt, C. Neofunctionalization in an ancestral insect desaturase lineage led to rare Δ6 pheromone signals in the Chinese tussah silkworm. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.D.; Löfstedt, C. Moth pheromone receptors: Gene sequences, function and evolution. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 3, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutuura, A.; Munroe, E. Taxonomy and distribution of corn borer and allied species–genus Ostrinia (Lepidoptera-Pyralidae). Mem. Entomol. Soc. Can. 1970, 71, 1–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthrie, W.D.; Barry, D.; Huggans, J.L. Hybridization studies between Ostrinia nubilalis, Ostrinia obumbratalis and Ostrinia penitalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 1981, 54, 505–509. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.G.; Hoshizaki, S.; Huang, Y.P.; Tatsuki, S.; Ishikawa, Y. Usefulness of mitochondrial COII gene sequences in examining phylogenetic relationships in the Asian corn borer, Ostrinia furnacalis, and allied species (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1999, 34, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Frolov, A.N.; Bourguet, D.; Ponsard, S. Reconsidering the taxomony of several Ostrinia species in the light of reproductive isolation: A tale for Ernst Mayr. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2007, 91, 49–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Dong, Y.; Qiao, P.; Yang, Z. Complete mitogenomic structure and phylogenetic implications of the genus Ostrinia (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Insects 2020, 11, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malausa, T.; Dalecky, A.; Ponsard, S.; Audiot, P.; Streiff, R.; Chaval, Y. Genetic structure and gene flow in French populations of two Ostrinia taxa: Host races or sibling species? Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 4210–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streiff, R.; Courtois, B.; Meusnier, S.; Bourguet, D. Genetic mapping of two components of reproductive isolation between two sibling species of moths, Ostrinia nubilalis and O. scapulalis. Heredity 2014, 112, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cardé, R.T.; Roelofs, W.L.; Harrison, R.G.; Vawter, A.T.; Brussard, P.F.; Mutuura, A. European corn borer: Pheromone polymorphism or sibling species? Science 1978, 199, 555–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelofs, W.L.; Du, J.W.; Tang, H.X.; Robbinson, P.S.; Eckenrode, C.J. Three European corn borer populations in New York based on sex pheromones and voltinism. J. Chem. Ecol. 1985, 11, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takanashi, T.; Huang, Y.P.; Takahasi, K.R.; Hoshizaki, S.; Tatsuki, S.; Ishikawa, Y. Genetic analysis and population survey of sex pheromone variation in the adzuki bean borer moth, Ostrinia scapulalis. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2005, 84, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozsik, G.; Lakatos, A.; Szőcs, G.; Tóbiás, I. Screening some common molecular markers and a desaturase marker, linked to sex pheromone biosynthesis, in three Z-Strain and an E-strain populations of the European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis, occurring in central Europe. Acta. Phytopathol. Entomol. Hung. 2019, 54, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardé, R.; Kochansky, J.; Stimmel, J.; Wheeler, A.; Roelofs, W. Sex pheromones of the European corn borer (Ostrinia nubilalis): Cis- and trans- responding males in Pennsylvania. Environ. Entomol. 1975, 4, 413–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, A.; Arn, H.; Buser, H.-R.; Rahscher, S.; Bigler, F. Sex pheromone of European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis: Polymorphism in various laboratory and field strains. J. Chem. Ecol. 1988, 14, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pélozuelo, L.; Malosse, C.; Genestier, G.; Guenego, H.; Frérot, B. Host-plant specialization in pheromone strains of the European corn borer Ostrinia nubilalis in France. J. Chem. Ecol. 2004, 30, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klun, J.A. Insect sex pheromones: Intraspecific pheromonal variability of Ostrinia nubilalis in North America and Europe. Environ. Entomol. 1975, 4, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglade, P.; Stockel, J. Intraspecific sex-pheromone variability in the European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis Hbn (Lepidoptera, Pyralidae). Agronomie 1984, 4, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Takanashi, T.; Hoshizaki, S.; Tatsuki, S.; Ishikawa, Y. Female sex pheromone polymorphism in adzuki bean borer, Ostrinia scapulalis, is similar to that in European corn borer, O. nubilalis. J. Chem. Ecol. 2002, 28, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianchi, R.; Maini, S.; Bullini, L. Genetic distance between pheromone strains of the European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis: Different contribution of variable substrate, regulatory and non regulatory enzymes. Heredity 1980, 45, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klun, J.A.; Bierl-Leonhardt, B.A.; Schwarz, M.; Litsinger, J.A.; Barrion, A.T.; Chiang, H.C.; Jiang, Z. Sex pheromone of the Asian corn borer moth. Life Sci. 1980, 27, 1603–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Honda, H.; Yoshiyasu, Y.; Hoshizaki, S.; Tatsuki, S.; Ishikawa, Y. Sex pheromone of the butterbur borer, Ostrinia zaguliaevi. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1998, 89, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, Y.; Takanashi, T.; Huang, Y. Comparative studies on the sex pheromones of Ostrinia spp. in Japan: The burdock borer, Ostrinia zealis. Chemoecology 1999, 9, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, T.J.; Perez, N.; Roelofs, W.L. Comparative analysis of sex-pheromone-response antagonists in three races of European corn borer. J. Chem. Ecol. 1989, 15, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takanashi, T.; Ishikawa, Y.; Anderson, P.; Huang, Y.; Löfstedt, C.; Tatsuki, S.; Hansson, B.S. Unusual response characteristics of pheromone-specific olfactory receptor neurons in the Asian corn borer moth, Ostrinia furnacalis. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 4946–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Takanashi, T.; Ohno, S.; Huang, Y.P.; Tatsuki, S.; Honda, H.; Ishikawa, Y. A sex pheromone component novel to Ostrinia identified from Ostrinia latipennis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Chemoecology 2000, 10, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.W.; Zhao, C.H.; Bengtsson, M.; Löfstedt, C. Reductase specificity and the ratio regulation of E/Z isomers in the pheromone biosynthesis of the European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1996, 26, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelofs, W.L.; Glover, T.J.; Tang, X.-H.; Sreng, I.; Robbins, P.; Eckenrode, C.; Löfstedt, C.; Hansson, B.S.; Bengtsson, B.O. Sex pheromone production and perception in European corn borer moth is determined by both autosomal and sex-linked genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 7585–7589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klun, J.A.; Maini, S. Genetic basis of an insect chemical communication system: The European corn borer. Environ. Entomol. 1979, 8, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopman, E.B.; Bogdanowicz, S.M.; Harrison, R.G. Genetic mapping of sexual isolation between E and Z pheromone strains of the European corn borer (Ostrinia nubilalis). Genetics 2004, 167, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Löfstedt, C.; Bengtsson, B.O. Genetic variation in the strongly canalized sex pheromone communication system of the European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis Hübner (Lepidoptera; Pyralidae). Genetics 1996, 144, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasukochi, Y.J.; Miura, N.; Nakano, R.; Sahara, K.; Ishikawa, Y. Sex-linked pheromone receptor genes of the European Corn Borer, Ostrinia nubilalis, are in tandem arrays. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutroumpa, F.A.; Groot, A.T.; Dekker, T.; Heckel, D.G. Genetic mapping of male pheromone response in the European corn borer identifies candidate genes regulating neurogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6401–E6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unbehend, M.; Kozak, G.M.; Koutroumpa, F.; Coates, B.S.; Dekker, T.; Groot, A.T.; Heckel, D.G.; Dopman, E.B. bric à brac controls sex pheromone choice by male European corn borer moths. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthrie, W.D.; Dollinger, E.J.; Stetson, J.F. Chromosome studies of the European corn borer, smartweed borer, and lotus borer (Pyralidae). Ann. Entomol Soc. Am. 1965, 58, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassance, J.M.; Löfstedt, C. Concerted evolution of male and female display traits in the European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis. BMC Biol. 2009, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, R.G. Molecular basis of pheromone detection in insects. In Comprehensive Insect Physiology, Biochemistry, Pharmacology and Molecular Biology; Gilbert, L.I., Iatrou, K., Gill, S.S., Eds.; Elsevier Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 2005; Volume 3, pp. 753–803. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, N.; Nakagawa, T.; Touhara, K.; Ishikawa, Y. Broadly and narrowly tuned odorant receptors are involved in female sex pheromone reception in Ostrinia moths. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanner, K.W.; Nichols, A.S.; Allen, J.E.; Bunger, P.L.; Garczynski, S.F.; Linn, C.E., Jr. Sex pheromone receptor specificity in the European corn borer moth, Ostrinia nubilalis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutroumpa, F.A.; Kárpáti, Z.; Monsempes, C.; Hill, S.R.; Hansson, B.S.; Jacquin-Joly, E. Shifts in sensory neuron identity parallel differences in pheromone preference in the European corn borer. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 2, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Coates, B.S.; Ge, X.; Bai, S.; He, K.; Wang, Z. Male- and female-biased gene expression of olfactory-related genes in the antennae of Asian corn borer, Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée) (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miura, N.; Nakagawa, T.; Tatsuki, S.; Touhara, K.; Ishikawa, Y. A male-specific odorant receptor conserved through the evolution of sex pheromones in Ostrinia moth species. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2009, 5, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, G.P.; Allen, J.E.; Bunger, P.L.; Luginbill, J.B.; Linn, C.E.; Macallister, I.E.; Kavanaugh, M.P.; Wanner, K.W. Single mutation to a sex pheromone receptor provides adaptive specificity between closely related moth species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14081–14086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecher, G.; Tamura, K.; Kumar, S. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) for macOS. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1237–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, S.Q.; Gascuel, O. An Improved General Amino Acid Replacement Matrix. Mol. Biol Evol 2008, 25, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jiang, X.-C.; Cao, S.; Yang, B.; Wang, G.-R. Functional studies of sex pheromone receptors in Asian corn borer Ostrinia furnacalis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, B.S.; Löfstedt, C.; Roelofs, W.L. Inheritance of olfactory response to sex pheromone components in Ostrinia nubilalis. Sci. Nat. 1987, 74, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallberg, E.; Hansson, B.S.; Steinbrecht, R.A. Morphological characteristics of antennal sensilla in the European cornborer Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Tissue Cell 1994, 26, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, B.S.; Hallberg, E.; Löfstedt, C.; Steinbrecht, R.A. Correlation between dendrite diameter and action potential amplitude in sex pheromone specific receptor neurons in male Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Tissue Cell 1994, 26, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, B.S. Olfaction in lepidoptera. Experientia 1995, 51, 1003–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, G. Olfactory network dynamics and the coding of multidimensional signals. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, S.; Löfstedt, C.; Hansson, B.S. Central nervous processing of sex pheromone in two strains of the European corn borer Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J. Exp. Biol. 1997, 200, 1073–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpati, Z.; Dekker, T.; Hansson, B.S. Reversed functional topology in the antennal lobe of the male European corn borer. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 2841–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, B.J.; Xia, Y.H.; Wang, H.L.; Andersson, F.; Hedenström, E.; Gross, J.; Löfstedt, C. Biosynthesis of the sex pheromone component (e, z)-7, 9-dodecadienyl acetate in the European grapevine moth, Lobesia botrana, involving ∆ 11 desaturation and an elusive ∆ 7 desaturase. J. Chem. Ecol. 2021, 47, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.D.; Löfstedt, C. Functional evolution of a multigene family: Orthologous and paralogous pheromone receptor genes in the turnip moth, Agrotis segetum. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, T.; Sakano, H.; Vosshall, L.B. Topographic mapping—the olfactory system. Cold Spring Harb Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a001776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdya, P.; Benton, R. Evolving olfactory systems on the fly. Trends Genet. 2010, 26, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, F.; Estock, M.; Hillier, N.K.; Powell, B.; Groot, A.T.; Ward, C.M.; Emerson, J.L.; Schal, C.; Vickers, N.J. Sexual isolation of male moths explained by a single pheromone response QTL containing four receptor genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8660–8665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelan, P.L. Genetics and phylogenetics in the evolution of sex pheromones. In Insect Pheromone Research: New Directions; Cardé, R.T., Minks, A.K., Eds.; Chapman & Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 563–579. [Google Scholar]
- Heckel, D.G. Smells like a new species: Gene duplication at the periphery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9481–9482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linn, C., Jr.; O’Connor, M.; Roelofs, W. Silent genes and rare males: A fresh look at pheromone blend response specificity in the European corn borer moth, Ostrinia nubilalis. J. Insect Sci. 2003, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wijk, M.; Heath, J.; Lievers, R.; Schal, C.; Groot, A.T. Proximity of signallers can maintain sexual signal variation under stabilizing selection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groot, A.T.; Claβen, A.; Staudacher, H.; Schal, C.; Heckel, D.G. Phenotypic plasticity in sexual communication signal of a noctuid moth. J. Evol. Biol. 2010, 23, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfstedt, C. Moth pheromone genetics and evolution. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1993, 340, 167–177. [Google Scholar]
- Groot, A.T.; Horovitz, J.L.; Hamilton, J.; Santangelo, R.G.; Schal, C.; Gould, F. Experimental evidence for interspecific directional selection on moth pheromone communication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5858–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, D.-D. Evolution of the Sex Pheromone Communication System in Ostrinia Moths. Insects 2021, 12, 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121067
Zhang D-D. Evolution of the Sex Pheromone Communication System in Ostrinia Moths. Insects. 2021; 12(12):1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121067
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Dan-Dan. 2021. "Evolution of the Sex Pheromone Communication System in Ostrinia Moths" Insects 12, no. 12: 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121067
APA StyleZhang, D.-D. (2021). Evolution of the Sex Pheromone Communication System in Ostrinia Moths. Insects, 12(12), 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121067




