Abstract
Water-based lubricants (WBLs) have been at the forefront of recent research, due to the abundant availability of water at a low cost. However, in metallic tribo-systems, WBLs often exhibit poor performance compared to petroleum-based lubricants. Research and development indicate that nano-additives improve the lubrication performance of water. Some of these additives could be categorized as solid nanoparticles, ionic liquids, and bio-based oils. These additives improve the tribological properties and help to reduce friction, wear, and corrosion. This review explored different water-based lubricant additives and summarized their properties and performances. Viscosity, density, wettability, and solubility are discussed to determine the viability of using water-based nano-lubricants compared to petroleum-based lubricants for reducing friction and wear in machining. Water-based liquid lubricants also have environmental benefits over petroleum-based lubricants. Further research is needed to understand and optimize water-based lubrication for tribological systems completely.
1. Introduction
The reduction of friction and wear is a significant challenge for researchers in tribology. In order to minimize friction and wear, a wide variety of lubricants have been developed; including solid (e.g., grease, molybdenum disulfide, polymers, soft metals) [1], gaseous (e.g., air, steam, liquid metal vapor), and liquid (e.g., petroleum oil, bio-derived oils) lubricants [2]. Similarly, a wide variety of lubricant additives have been explored [3].
Liquid lubricants have many advantages over solid or gaseous lubricants for industrial applications. Industrial-scale machines often run under extreme pressure and temperature conditions and may experience tribological failure, due to improper lubrication [4]. Therefore, the use of effective liquid lubricants is essential to minimize energy consumption in such conditions. Liquid lubricants play a significant role in heat removal, corrosion prevention, transfer of wear debris, mechanical noise reduction, and act as a liquid seal between contacts [5]. Therefore, liquid lubricants are typically used in industrial machinery.
The origin of liquid lubricants was probably led by the ancient Egyptians and Sumerians in 3500 B.C.E. [6]. It is believed that to extend the life of wooden axles and wheels, they used a viscous liquid form of petroleum called bitumen. Moreover, animal and vegetable oils and water were utilized as lubricants very often. During this period, water was used as a lubricant by the Chinese as well. However, petroleum-based lubricants always outcompeted water, and therefore, over the centuries, petroleum-based oils had been the most common lubricant in the marketplace.
According to the current reserve to production ratio of fossil-based oil, the world oil reserve might end within the next 50 years [7]. Moreover, fossil fuels generally release toxic materials to the environment, which is a threat to sustainability. Therefore, researchers have realized the need for a cheaper, safer, more eco-friendly, and efficient alternative to petroleum oils for machine lubrication in recent years. Thus, the focus has shifted to water as an alternative lubricant. It is known that water alone is a poor lubricant compared to petroleum oils, firstly due to the low viscosity of water. Moreover, water may accelerate corrosion that is unwanted in metal surfaces. Therefore, researchers have mixed water with different additives to obtain improved tribological performance [8].
Numerous additives could be chosen along with water, based on different applications. In general, the additives could act as antioxidants, anti-foaming agents, corrosion inhibitors, detergents, friction modifiers, wear improvers, metal deactivators, and/or viscosity index improvers [2,9] Also, some additives can support extreme pressure and extreme temperature conditions. Water miscible petroleum oils are generally a common choice to develop WBLs [10]. However, in recent years, some alternative additives received researcher’s attention. Some examples of these additives are nanoparticles, such as TiO2 nano-additive, polyethyleneimine-reduced graphene oxide (PEI-RGO) nanosheets, etc. [11,12]. Moreover, room temperature ionic liquids and bio-derived oils were added to water by researchers to develop WBLs [10]. By using such additives with water, tribological performances were improved. As a result, the overall lifetime of both the lubricant and the tribo-pair could be enhanced [2].
Studies have shown that some WBLs improved the tribological performance compared to petroleum-based lubricants, which resulted in a decrease in the amount of power necessary to run a machine [13]. Their performance was also outstanding as cutting fluids and hydraulic fluids [14]. Moreover, WBLs showed excellent cooling capabilities and environmentally benign attributes [15]. These diversified qualities have made WBLs a promising industrial choice.
Some challenges are evident for the water-based lubricants in their industrial applications. For example, WBLs within gearboxes or metallic machinery could experience an increased risk of corrosion [10,16]. Currently, this issue is being mitigated substantially by incorporating additives. Another potential method of reducing corrosion using WBLs is through galvanic couplings, which provide an electric charge that can further protect against corrosion [16,17]. The other main concerns facing WBLs are their viscosity and the low operating temperature range. This is a downside for applications that experience high friction causing high temperatures, damaging the contact pair. To minimize such problems, water-miscible ionic liquids have played a significant role, as shown in research.
Moreover, recent research shows that petroleum-based oils could be replaced by bio-based oils in many instances [18,19]. Moreover, bio-derived oils have demonstrated superior performance as additives to WBLs [10]. In this review, the state of the art of water-based lubricant additives has been summarized, including solid nanoparticles, ionic liquids, and other oil additives. Besides, the possible challenges of WBLs and their future advancements have been projected and elaborated.
2. Development of Water-Based Lubricants with Different Additives
Water-based liquid lubricants have good thermal conductivity and are environmentally friendly compared to petroleum-based liquid lubricants [20]. Issues, however, revolve around the use of water-based liquid lubricants for metal surfaces, including rusting and corrosion of the metal that the aqueous solution can create within the tribo-system [20]. Therefore, additives are needed to improve the tribological performance of the lubricant in terms of friction, wear, oxidation resistance, corrosion resistance, and anti-foaming, to name a few [21].
There are two general categories of additives: Water-soluble organic compounds and solid particles [20]. Water-soluble organic compounds work well with polar lubricants, such as WBLs [20]. This is because the additive creates a lubrication film on the surfaces involved in the tribo-pair. This film is produced from the organic compound molecules interacting with the polarity or electrostatic attraction of the surface materials [20]. One such example of water-soluble organic compounds includes ionic liquids. Besides, bio-based oils also have potential applications in WBLs. In recent years, solid nanoparticles were also observed as improving the lubrication performance in WBLs. Figure 1 illustrated the overall scenario of water-based lubricant additives and their common advantages.
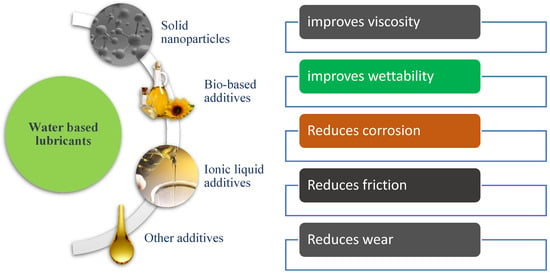
Figure 1.
Water-based lubricant additives and their advantages.
2.1. Water-Based Lubricants with Ionic Liquids Additives
Ionic liquids are salts made of cations and anions, with melting points lower than 100 °C. If their melting points are lower than room temperature (25 °C), then they are called room-temperature ionic liquids (RTILs) [22]. Most frequently used cations include imidazolium, pyridinium, ammonium, and phosphonium, while the choice of anions could vary because there are thousands of options available. The most commonly used anions for WBLs were tetrafluoroborate and hexafluorophosphate, as observed in the literature [23]. These anions are often categorized as hydrophobic with weak hydration capacity [23]. However, various combinations of anion and cations are possible to form a particular ionic liquid, and therefore, theoretically, there are 1018 different ionic liquids possible to produce through synthesis [24].
Ionic liquid lubricants have gained growing interest among scientists and engineers in the field of tribology within the past two decades [25,26,27]. This is because the unique properties of ionic liquids can be utilized for creating advanced lubricants for a variety of needs. Moreover, they can improve the lubricant to handle severe conditions, including extreme pressure and extreme temperature, where oils, greases, and solid lubricants fail [22]. The unique properties that make ionic liquids an ideal additive include thermal stability, nonflammability, high conductivity, high polarity, negligible vapor pressure, and good miscibility with water and organic solvents [20,21,22,23,28,29]. In short, they can function within a wide temperature range and can form strong and effective adsorption films, due to their highly polar nature [23].
On the other hand, current lubricants are not highly versatile. For instance, lubricants that are used for one type of contact surface material may not be suitable for another (i.e., lubricants for steel-on-steel contact versus lubricants for aluminum-on-ceramics contact) [29]. This is because the material properties of the surface and the lubricant properties are unique to how they behave together under specific applications. Ionic liquids, in comparison, stride ahead, due to versatility. The synthesis of Ionic liquids is also straightforward compared to many petroleum-based lubricant additives [28,30]. This makes the use of ionic liquids potentially more desirable for WBLs.
WBLs could introduce rust on the metal in a harsh environment, due to the corrosive nature of some ionic liquids [20]. This corrosive nature becomes functional within the tribo-system through the hydrolysis between the water and the ionic liquids [23]. The ionic liquid itself can decompose in the presence of water [28]. It was found in the literature that the halogen-containing anions contribute to hydrolysis, and therefore, increases the corrosion rate [23]. Hydrolysis and corrosion could be partially avoided for water-based ionic liquids in a few different ways. The anions in the ionic liquids can be replaced with those that are halogen-free, reducing hydrolysis within the tribo-system [23,31]. In terms of lubricant stability, hydrophobic anions over hydrophilic anions could increase stability and ensure a good lubrication film between the tribo-pair. Lastly, anti-corrosive additives, such as benzotriazole (tetrabutylphosphonium benzotriazole, for example), could help alleviate the corrosive environment [23,32]. Benzotriazole is well miscible with many ionic liquids [23]. The use of benzotriazole is limited, however, because it does not work well for high temperature or low-pressure environments [23]. However, at room temperature application, benzotriazole can play a significant role. More investigations on ionic liquids are needed to enhance high-pressure, high-temperature (<100 °C) performance of WBLs.
Researchers have explored the effects of specific ionic liquids as additives for water-based liquid lubricants. Tang et al. [33] discussed the use of carbon dots that were synthesized with ionic liquids to create a carbon dot ionic liquid (CDs-IL) additive for WBLs. In the investigation, ionic liquids, CDs, and CDs-IL were tested as water-based liquid lubricant additives in universal friction and wear tester (four balls, steel-on-steel) to determine the wear and friction reduction of the lubricants. It was determined by comparing ionic liquids, CDs, and CDs-IL as additives that CDs-IL presented the best results in friction and wear performances [33]. The tribological performance of the CDs-IL was much better than that of the ionic liquids and CDs alone, due to the synergistic effect between the CDs and ionic liquid [33].
Aviles et al. [34] experimented with the use of diprotic and triprotic ammonium ionic liquid crystals as additives for water for a sapphire-stainless steel material contact [34]. It was found that, when compared to water, the addition of additives in the lubricant reduced the friction coefficient by as much as 80% [34]. The authors described the additives’ advantages as being able to initially reduce the friction coefficient and maintain the reduced friction after the water has evaporated from the solution. The additive, palmitate derivative, presented the best performance by preventing iron oxidation from occurring when in contact with water [34]. Overall, the authors expressed that these findings could help to formulate environmentally friendly water-based liquid lubricants. Zhou et al. [35] discussed ionic liquids as lubricant additives for different types of lubricants. For water-based liquid lubricants, the authors’ research observed that 0.25 wt.% [phosphazene][Tf₂N] and 2.0 wt.% [1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium][BF₄] used in water-based liquid lubricants significantly reduced the friction of a Si₃N₄-Si₃N₄ material contact [35]. [1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium ][PF₆] also showed reduced friction for both Si₃N₄-Si₃N₄ material contact (2% in water) and steel-steel material contact (2–14.4% in a water solvent) [35]. Imidazolium] [BF₄] was also tested with water for SiO₂ on Si₃N₄, poly-Si on Si₃N₄, and Si₃N₄-Si₃N₄ tribo-pairs [35]. The inclusion of ionic liquids to water-based liquid lubricants does reflect a significant reduction in friction of the rubbing surfaces; more examples are discussed in Section 4.1.
2.2. Water-Based Lubricants with Bio-Derived Additives
Lubricant demand is on the rise from a global perspective. Many lubricants on the market today are petroleum-based. Petroleum-based lubricants can be harmful to the environment and can cause safety hazards for people, animals, and the overall environment. In recent history, government officials have incentivized manufacturing companies to use biodegradable lubricants that are more eco-friendly [36]. One way to reduce the negative impact of lubricants on the ecosystem is to replace petroleum-based lubricants with biodegradable lubricants. Bio-lubricants can reduce environmental impact by providing a renewable source of lubrication that promotes sustainability. Bio-lubricants have evolved, since the push for an eco-friendly alternative to oil-based lubricants. Bio-lubricants were first made with oils found naturally in the environment. These oils have beneficial tribological properties, due to the high lubricity that leads to a reduction in friction and wear [37].
Water-based bio-lubricants could be a sustainable source of lubrication. However, water alone is a poor lubricator, due to the low viscosity of water. Water has also been shown to have corrosive properties. Research has revealed that the addition of certain additives to water could be used to create a lubricant better than water alone [8]. Naturally found oils and fats extracted from biological sources have been used as additives to WBLs to better control tribological properties of WBLs [38]. The transition from traditional petroleum-based lubricants to more modern bio-lubricants involves the integration of chemistry, biology, and engineering.
Nowadays, bio-lubricants are made from materials found naturally in the world, such as biomass [18]. These materials include soybeans, sunflowers, coconuts, plants, to name a few [37]. Table 1 exemplifies a comparison of the factors contributing to the differences in fossil-derived lubricants and biomass-based lubricants [37]. There are many advantages associated with biomass-based lubricants. Bio-lubricants are produced from renewable resources, using the pyrolysis process, and the produced oils contain a significant amount of water. This water content comes from the moisture present in the biomass [39]. For fuel up-gradation, the water needs to be separated [40]; however, the separation step is not essential in water-based lubricants. Ji et al. [41] developed water-based lubricants using biomass-derived levulinic acid (LA) and polyols, such as ethylene glycol and glycerol. The process of how to create these lubricants is shown in Figure 2

Table 1.
Comparison of fossil-derived lubricants and biomass-based lubricants.
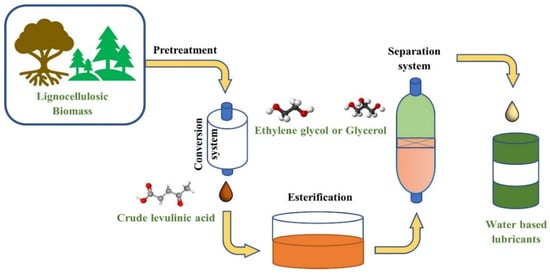
Figure 2.
Outline of the processes to create the biomass-derived water-based lubricant. Adapted from [41].
The primary source of water-based bio-lubricants is biomass, which is universally available and cheap. This means the water-based bio-lubricants are widely available and can be implemented effectively at both local and global scales. Moreover, the solutions of bio-lubricants are water-rich, meaning they will produce less harmful pollutants. Since water is renewable, recyclable, and disposable; therefore, water-based bio-lubricants could become a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based lubricants in the future [37]. However, there are some limitations of water-based bio-lubricants as well. The negative impacts include the need for technological advancements, complex logistical planning, and high-level chemistry. These drawbacks require research and development to make the end product better.
There are several potential applications of water-based bio-lubricants. One of such applications could be observed in the automobile industry. The safe and effective use of automobiles requires effective lubrication of all parts to keep the machines operating smoothly. Effective lubrication of all parts that rub together in an automobile decreases energy loss in the entire system. Mineral oils have been used heavily in the past to provide lubrication to automotive machines. However, the world is running out of crude oil, and prices are increasing, making this method of lubrication unsustainable. Therefore, water-based bio-lubricants could be an effective alternative. These additives to water include sunflowers, soybeans, coconut, palm, and other crops. Table 2 exemplifies the oil content presented in plant species found around the world [42].

Table 2.
The oil content of plants that can be added to water-based bio-lubricants [43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50]. Reproduced with permission from [42]. Copyright, Elsevier, 2014.
Vegetable oils exhibit similar properties to traditional mineral-based oils [51]. Vegetable oils can even sometimes produce better lubricity properties than standard mineral oils. Moreover, vegetable oil’s performance was increased by adding boron [52,53] or carbon [54,55,56], based on solid lubricant additives. An analysis of the properties of vegetable oils and mineral oils was conducted assessing density, viscosity index, shear stability, pour point, clod flow behavior, miscibility with mineral oils, solubility in water, oxidation stability, hydrolytic stability, sludge forming tendency, and seal swelling tendency [42]. From this study, the advantages of vegetable oils over mineral oils as additives to WBLs became evident. Some key advantages of the bio-lubricants were higher lubricity, lower friction losses, decreased automotive emissions, and less toxic environmental effects. On the other hand, one disadvantage of vegetable oil versus standard mineral oils is that they lack adequate oxidative stability for lubrication. Vegetable oils also have low thermal stability, limiting the versatile application of vegetable oils for additives to WBLs [42]. One suggestion for future study is to combine water, vegetable oils, and other additives to make a mixture ideal enough to minimize oxidation effects and make the mixture withstand higher temperatures. Such a mixture could provide an environmental advantage by replacing a significant number of petroleum-based lubricants with bio-based oils and water.
The development of water-based bio-lubricants still has a long way to go to compete with the mineral-based lubricants commonly found today. Current applications are limited, and research and development need to be performed to create new combinations of water-based bio-lubricants that can be used in more processes. With the push for more environmentally friendly manufacturing techniques, water-based bio-lubricants will continue to be developed to promote sustainability.
2.3. Water-Based Lubricants with Solid Nanoparticles
WBLs are low-cost lubricants for metalworking processes. Not only acting as a lubricant, but also as a coolant, WBLs could provide a longer tool life, reduced thermal deformation, and lower friction. However, the lubricant suffers from a low viscosity and corrosive properties that make it unviable for many tribological applications [9]. To counteract the disadvantages of WBLs, the integration of additives is used to improve the properties and performance. In some cases, additives within the lubricant allow for many increased advantages, such as further reduced tool wear and the prevention of corrosion. Furthermore, research into water-based lubricant additives can inhibit fungal or microbial growth [9]. Additives within a water-based lubricant are often used as a surface-active molecule that reduces friction, wear, and corrosion. Some examples of solid nanoparticle additives are graphene, copper, titanium-di-oxide, and many others [9,12,57,58,59,60].
One of the most common additives used in oil-based lubricants that are being implemented into WBLs is titanium-based nano-additives. The additive is used to combat the low viscosity and corrosive properties found in WBLs. Specifically, TiO2 is the most used additive in oil-based lubricants that are beginning to be implemented into WBLs more frequently [12]. The additive TiO2 has been shown to improve properties overall, such as nontoxicity, low density, friction, and wear [57]. An experiment done by Gu et al. [57] using dual-coated TiO2 nanoparticles observed friction and wear reduction under an MSR-10D four-ball tribotester at a speed of 1440 rpm at applied loads of 140 N for 10 min. After each test, scanning electron microscope (SEM), atomic force microscope (AFM), and energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS) were used to analyze the wear scars [57]. The team concluded that at low concentrations of TiO2, the additive improved the anti-wear properties of the lubricant and reduce wear scar diameter. Furthermore, the wear scars became less prominent as the concentrations increased, as well as the coefficient of friction decreased, being able to achieve a minimum value of 0.04 during testing [57].
Another study was done by Wu et al. [12], who tested TiO2 nano-additive properties using a ball-on-disk tribometer. The experiment consisted of additives at various concentrations during two different methods of testing: One method involving adding the lubricant at set time intervals and the second method involving the lubricant being continuously present throughout the test. The results of each method concluded that the addition of the additive reduced the coefficient of friction and ball wear by 49.5% and 97.8% accordingly [12]. Furthermore, they concluded that the optimal concentration of the TiO2 additive was 0.8 wt.% at room temperature.
Another water-soluble additive being tested for the lubricant are graphene-based nanoparticles. Testing done on graphene quantum dots (GQDs) additives on steel-to-steel contact proved to have enhanced tribological properties at a concentration of 4 mg/mL. The additive decreased the wear rate by 58.5% and the coefficient of friction by 42.5%. GQDs at lower concentrations were more effective at improving tribological properties than other graphene-based additives [61]. The additive has proven to be one of the most promising advancements within the graphene field.
Nanostructured borates are another additive being created by synthesizing the mixture with magnesium, zinc, aluminum, and titanium particles [62]. The additive could be added to water-based drilling fluids to improve tribological performance. The additive significantly decreased the coefficient of friction by producing a tribo-film on both surfaces [62]. Furthermore, the additive maintained stability during high pressure and temperature conditions.
2.4. Other Water-Based Lubricant Additives
There are many other potential additives for water-based lubricants. One promising additive to be used with WBLs is a water-soluble, rubber seed oil-based sulfonate. Through testing, the rubber seed oil-based sulfonate copolymer noticeably improved the anti-wear, anti-corrosion, and frictional properties of the lubricant. Furthermore, the additive was also able to improve the nonseizure load (PB value) of the water. At concentrations of 0.5%, the PB value reached 431 N, which was three times greater than the water-based lubricant without the additive, and such conditions offered a coefficient of friction of 0.085 and a wear scar diameter of 0.78 mm [60]. Rubber seed oil-based sulfonate is becoming a great candidate for additive implementation within WBLs, allowing the lubricant to maintain environmentally friendly attributes and increasing its capabilities for extreme applications.
Furthermore, an ester-based lubricant SMJH-1 was tested for its tribological performances with water-based drilling fluids and was compared to sodium montmorillonite (Na-MMT) base mud. The additive was tested at varying concentrations, while testing the lubricants before and after an aging process. The additive at 1.0% concentration reduced the lubricity coefficient (µ) by 91.4% before aging and 90.7% after the aging process [63]. It was also found that due to the aging process, this would result in increased friction, which they concluded could be the result of increased surface roughness. It was found that SMJH-1 at higher concentrations, the formation of a C=S metal film would be present, which would decrease the average roughness, as well as decrease the lubricity coefficient [63].
3. Properties of Water-Based Lubricants
Properties of the water-based lubricants could be significantly improved by using the above-mentioned additives. Some of the important properties of water-based lubricants are solubility, viscosity, density, atomic structure, wettability. These properties have a crucial effect on the tribological performance of water and are discussed below.
3.1. Viscosity
Viscosity is a measurable physical property that can translate information about the liquid’s hydration, solvation, the shape of the infused particles, and the forces acting between the particles [64]. It can also be defined as the internal resistance that a fluid has to flow. Viscosity is an important parameter in Hersey number Equation (1), that is used to define different lubrication regime in the horizontal axis of the Stribeck curve. In the equation, corresponds to the viscosity, v corresponds to the entrainment speed, and the P is the normal load. Stribeck curve is a popular diagram and could be found in the literature [65,66].
Water has a low viscosity which is one quality that makes it a poor lubricant [8]. Additives are usually added to water to improve the viscosity, therefore improving the tribological properties that are needed for lubricants [64,67,68]. For example, the TiO2 nano-additive increased the overall viscosity of the lubricant and decreased the amount of contact between the metal surfaces [58]. The effect of the viscosity of a lubricant can be seen in:
- Cavity formation
- Decreasing friction
- Film thickness
- Thermal behavior
According to a study performed by Nouri et al. [64], cavity formation was observed using high-resolution images taken throughout a timed interval to view the gradual development of cavities on a single piston-ring assembly. The cavitation was then quantified using a MATLAB program, and it was found that with a decreasing viscosity of the lubricant, the length of the cavities was also decreased. These results were consistent throughout their study, demonstrating viscosity’s effect on cavity formation [64].
As per Marx et al. [67], a reduced strain rate curve can be seen when viscosity modifiers are added to lubricants. The viscosity modifiers reduced the amount of friction and power loss at high shaft speeds, due to shear thinning. Their study also addressed film thickness, which is another quality factor that can be altered by viscosity. Film thickness is defined as the layer that is created by a lubricant between the two surfaces in contact [69]. The target thickness can vary depending on the needs of the machine. When a higher-ordered degree of molecule interacts with a surface, a thicker film develops [70]. This aligns with the idea that viscosity is directly linked to the internal properties of a liquid. This is also understandable from the stribeck curve, as increased viscosity increases the film thickness values. Therefore, in the case of water-based lubricants, an increase in the film thickness could be achieved by incorporating suitable additives to increase the viscosity.
Finally, the viscosity of a lubricant used in machines will affect the thermal behavior and heat transferability [71]. Thermal behavior is an important consideration when discussing the type of environment that is encountered by lubricants. A lubricant that heats up with little friction could cause adverse effects to the equipment and the product. The ability to distribute heat to the environment or the product is an additional consideration that must be observed. Depending on the desired requirements of the machines and products being manufactured, the rate at which heat is dissipated by the lubricant will change. The magnitude of change in the viscosity of a lubricant will depend on the additives, the size of the particles, and the percent or fraction of the additives to the solution [71]. Hajmohammadi et al. [72] observed that the viscosity of the Al2O3 diathermic oil nanofluids improved with the increase in volume fraction. Moreover, the dynamic viscosity of lubricants increased as the diameter of the nanoparticle decreased [73].
3.2. Density
Density is a property determined by the ratio of the mass of the liquid relative to the volume and can be affected by temperature. Water has a density of 1.00 g cm−3. The density of the liquid additives to water will change the density of the water-based lubricant. While adding solid nanoparticles, density will also be affected by the size and shape of the nanoparticles being used, as well as the concentration of the nanoparticle in the water [74]. For example, the density of a phosphazene-based ionic liquid additive ranges from 1.63–1.65 g cm−3 [75]. When added to WBLs, it will have an increased density with the addition of the phosphazene-based ionic liquid. This increase in density demonstrated thicker film formation, making the liquid’s suspension of the nanoparticles harder to settle. WBLs containing TiO2 are found to have a lower density than that of water [58]. Even with a lower density than water, this additive demonstrated friction reduction and a decrease in the amount of required power during the study’s drilling process.
3.3. Wettability
Surface wettability is defined by a liquid’s ability to maintain contact with a surface through adhesive and cohesive forces [76]. A common method to measure wettability is contact angle. The value of the contact angle determines how the liquid is defined. A contact angle over 150° is superhydrophobic. 90° to 150° is hydrophobic, and 10° to 90° is hydrophilic [77]. Lastly, super hydrophilic is less than 10° [77]. Increased wettability is defined by a smaller contact angle [78], which has been associated with creating a film between surfaces [13]. Water has a reported contact angle of 73.6° [13]. The wettability of water can be increased with the addition of nanoparticles [79]. When TiO2 nanoparticles of various sizes are added to water as a suspension medium, the contact angle of the mixture decreased from 73.6 to 55.22 with an increasing concentration of TiO2. The contact angle was further decreased by adding sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate (SDBS) [13]. The dissociation of SDBS in water provides phenyl sulfonic groups. These phenyl sulfonic groups get adsorbed around the nanoparticles and increase the amount of net negative charge of the nanoparticle surface. Therefore, the repulsive forces between TiO2 nanoparticles increase, and the dispersion stability gets improved [80]. Moreover, added SBDS restricts the agglomeration of nanoparticles which enhances the wettability [13].
Graphene and graphene oxides (GO) demonstrate a reduction in the friction coefficient between magnesium alloy and steel contact, ultimately reducing the wear rate [79]. The GO had a decreased contact angle of 46.5° of water [79]. Compared to graphene, GO is more effective when creating a thin layer used to protect the surfaces in contact [79]. This is further supported by the tribological properties found in the study. The GO lubricant had a more pronounced positive effect on load-carrying capacity and lubrication film endurance [79]. Alkyl polyglucosides (APGs) are another type of additive that can be added to increase the wettability of water [81]. The magnitude of the concentrations will result in either micelles or lyotropic liquid crystals forming. Micelle is formed when molecules are aggregated in a colloidal solution, like that of detergents. On the other hand, lyotropic liquid crystal is formed if an amphiphilic mesogen (a compound that portrays a liquid crystal state) is dissolved in a suitable solvent. There was a decrease in surface tension and contact angle with the addition of APGs [81]. At lower concentrations of APGs, there is a significant decrease in the contact angle [81]. At higher concentrations, there are no significant changes between the measured contact angle values [81]. Another difference was seen between the different types of APGs tested [74]. APGs with 8–10 alkyl groups decrease the contact angle to 41–50°, which is 1.7–1.8 times higher than the contact angle for pure water [81]. The wear is lower in multiple friction couples when APGs are present in the water, acting as a lubricant [81].
1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate ionic liquid was used for wettability test in literature [82]. With the addition of water, the interfacial structure of ILs was changed [82]. Differing alkyl chain lengths at different concentrations, the wettability was evaluated [82]. There was no significant difference between the different lengths, but there was a decrease in contact angle with an increase in the molar fraction of 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium ILs in the liquid [82].
Marine biofouling is an alarming phenomenon that has drawn much attention recently. It is defined as an accumulation of organisms on a submerged surface where they are not wanted. The current solution to this problem is to make: Slippery Liquid Infused Porous Surfaces (SLIPS) [83]. SLIPS are commonly formed using lubricants that are based on silicone or fluorine; neither are well-suited for marine usage [83]. A bio lubricant created using oleic acid, and methyl oleate was suggested to be a substitute for SLIPS being used [83]. Confocal microscopy could be used to observe the wetting state of the gels used to absorb the bio lubricant for testing under ultraviolet (UV) lights [83]. In such conditions, the contact angles before and after UV irradiation for the oleic acid were found to be 57° and 42° accordingly [83]. For the case of methyl oleate, the contact angles were found to be 29° and 7° [83]. Nonionic monoglyceride surfactant and xanthan gum are other additives that have been observed to be substituted for drilling wells [84]. Monoglycerides were observed with varying carbon chain lengths, ranging from 6,8, 10, and 12 [84]. Triglycerides chains were studied at 6, 8, and 10 [84]. The contact angles of each of the aqueous solutions and xanthan gum suspension solutions are displayed in Table 3 [84]. The solution that had the lowest contact angle was the monoglyceride with a carbon chain of 10 added with the xanthan gum [84].

Table 3.
The measured contact angle of aqueous solutions and xanthan gum suspensions. Reproduced with permission from [84]. Copyright John Willey and Sons, 2014.
A novel polytetrafluoroethylene with a SiO2 layer (PTFE@SiO2) is a composite nanoparticle studied in the literature [85]. The successful creation of the nanoparticle was confirmed by a change in the contact angle (using the DSA100 contact angle goniometer) observed. When the nanoparticles were partially developed through the synthesis process, there was a slight increase in the contact angle, going from 35° to 50° [85]. On the other hand, once the SiO2 completely enveloped the PTFE, then the wettability got improved, and the contact angle decreased to 32° [85].
Coconut diethanol amide (CDEA) and Tween 85 (T-85) are triazine-based covalent organic framework nanomaterial (TriC) that work as additives for WBLs [86]. The wettability test used to observe the contact angle was found by placing droplets on a steel disk that were then recorded using an optical contact angle goniometer [86]. Pure water was found to be 73.3°, while the CDEA and T-85 were 26.5° and 58.6°, respectively [86]. The addition of the additives decreased the contact angle. The difference between the additives could be explained by the polar groups that allowed hydrogen bonding between the CDEA and the water molecules. The T-85 molecules also have groups that are weakly polar, resulting in a weakening of hydrogen bonding [86].
3.4. Solubility and Other Properties
Water is a low-cost liquid that has many useful properties that make it a promising lubricant. It has a high cooling capacity. In contrast, water also has low viscosity and corrosive properties that make it undesirable as a lubricant in its standard form. To remedy these downsides, additives are mixed with distilled water through various processes to create a water-based lubricant that applies to industry. These lubricants are often used in processes, such as cooling or rolling and even metalworking. WBLs have the distinct advantage of being a coolant and a lubricant. Moreover, the following advantages could be observed: Flushing debris, thermal deformation reduction, surface finish improvements, extended tool life, and lower friction. Nanoparticles and additives are common in creating these effects with WBLs, but their efficacy is often dependent on their solubility in water.
Zhang et al. [87] investigated the feasibility of using metallic nanoparticles as an additive to water. This application is not well studied, due to a few complications with the solubility of the substance with water. The nanoclusters of the compound easily aggregate which hinders their compatibility with water. This issue was resolved using surface-modification techniques for the encapsulations. Such a technique allowed researchers to prevent aggregation and allow for compatibility with lubricants. The nanocomposite material additive that was chosen by Zhang et al. [87] was Cu/SiO2, and after surface-capping with 3-mercaptopropyl-trimethoxysilane (MPTS), oxidation was entirely prevented, as well as the nanocomposite being compatible with distilled water. The study recommended this water-based lubricant as an effective steel-on-steel solution under moderate loads. Another approach to nanocomposite additives to create WBLs was made by Pei et al. [88]. Their composite of interest was carbon nanotubes or CNT. CNTs are exceptionally strong and possess the abilities of a great WBL additive. However, CNTs are not water-soluble, which poses a problem for researchers. There have been many strategies for this solubility issue, and some will be discussed here.
Polymer chains can be covalently attached to the surfaces of CNTs which gives them improved properties. Linear polymers, copolymers, dendritic, and hyperbranched polymers have been successfully grafted to CNTs through a series of reaction methods [89]. These methods include atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP), reversible addition and fragmentation chain transfer polymerization (RAFT), and ring-opening polymerization (ROP) [90,91,92,93,94,95]. Pei et al. [88] ventured to develop a new method of creating water-soluble CNTs. Their approach was to graft water-soluble polymer chains from the surface of MWCNTs. This process was followed by the surface-initiated radical graft polymerization of acrylamide using a redox system consisting of ceric ion and reducing groups (amino) on the surface of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) as initiators [88,89]. This process is shown in Figure 3.
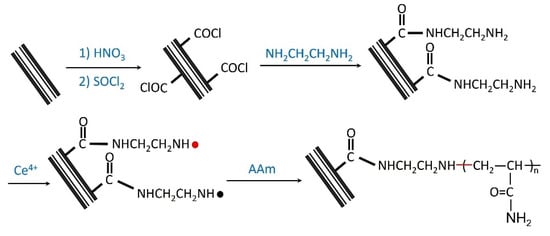
Figure 3.
Surface-initiated redox polymerization of acrylamide from MWCNTs. Reproduced with permission from [88]. Copyright Elsevier, 2008.
Pei et al. [88] observed that the load-carrying capacity of the lubricant significantly raised with MWCNTs, while the friction coefficient decreased. They attributed the success of the MWCNTs to their function as nano-ball bearings under moderate load. These results support the further investigation of other related super materials being made compatible with distilled water to be further made into a high-performance water-based lubricant. Solubility in WBLs, as discussed in studies mentioned previously, is an important and challenging task to work around when designing additives to create WBLs.
Sol et al. [14] investigated ionic liquid additives to water as a viable industrial cutting fluid. Their interest in synthesizing an effective water-based lubricant came from their dry machining operations in which high temperatures and contact angles led to excessive tool wear. Ionic Liquids, having high thermal stability, were a great candidate for reducing the tool wear in this case [14]. Sol et al. [14] were very successful in their pursuits of viable water-based cutting fluids. The halogen-free aprotic ionic fluid [THTDP][Deca] was an efficient lubricant for aluminum machining operations. The friction coefficient was reduced by over 70% when compared to water and exhibited minimal aluminum wear [14]. Another successful aspect was the fluid improved the surface finish inside the wear track, as well as reducing adhesion in the pin.
As discussed previously, one of the most interesting current fields of study in tribology is nanoparticles, and their application to WBLs as an additive is no exception. They possess phenomenal wear and friction reduction properties, which makes them a viable candidate for WBLs. One major issue with these nanoparticles is that they are not often water-soluble. Solving this issue has been approached differently by different research groups.
Cui et al. [96] synthesized nanoparticles of different materials and then tested them for their tribological properties as a water-based lubricant additive. Their motivation for this pursuit was that water-lubricated ceramics that could have friction coefficients of less than 0.01 after the running-in process, which is known as superlubricity. The term superlubricity is vague, but it describes a situation in which friction vanishes or nearly vanishes. In addition to these beneficial tribological properties, ceramics are environmentally friendly and economically favorable. Their study used SiO2, TiO2, and ZnO nanoparticles and was prepared and tested using a ball-on-plate tribometer [96]. They discovered that the friction reduction capabilities of SiO2 were much superior to that of the other two additives, although all test subjects showed viability. Additionally, the exceptional compatibility of silica gel and SiO2 was observed and was shown to be a key factor in its success.
4. Performance of Water-Based Lubricants
One of the most important functions of any lubricant is the reduction of friction between moving components. This reduction also prevents the formation of wear particles in the lubricant. While this effect not only lengthens the life of the parts involved, it also increases the efficiency of the overall system by allowing it to operate at manufactured dimensions for a longer duration. The friction and wear reduction reported in the literature for WBL is summarized in Section 4.1. Moreover, in Table 4, some of the important recent studies have been tabulated, summarizing their key properties, advantages, challenges, and mechanism behind their good performance.

Table 4.
Summary of important water-based lubricant additives with their advantages, mechanisms, and challenges.
4.1. Friction and Wear Reduction
To absolve the inherent tribological issues of water and to synthesize a high-quality lubricant, high-quality additives are mixed in. Many different groups of additives significantly improve the tribological performance of water. Multiple attempts have been made with countless materials to find the superior lubricant. Oftentimes, the improvement of one aspect of the water-based lubricant happens to the detriment of another property. The best way to utilize additives is to assess the application and choose the best compound for the task. Corrosion inhibitors, for example, prevent corrosion to both the tool and the surface in the system requiring lubrication. The task is done by sometimes creating a protective coating and other times by neutralizing corrosive contaminants in the system depending on the application. Another interesting type of additive is reserve alkalinity additives which regulate the pH of the system which neutralizes any acidic contaminants. Some examples include alkanolamines like monoethanolamine, triethanolamine, and aminomethyl propanol [9]. Emulsifiers are interesting in that they stabilize oil-soluble additives by mitigating tension between incompatible components. The phenomenon that makes this possible is its property to form micelles which are a microscopic aggregation of molecules, as a droplet in a colloidal system [97]. Examples include sodium petroleum sulfonate and alkanol amine salts of fatty acids. Finally, couplers stabilize water dilutable metalworking fluids in the concentrate. This helps stop the separation of components in the system. Some examples are propylene glycol, glycol ethers, and nonionic alkoxylates. Sulfur, phosphorus, and nitrogen are commonly used as additives to water lubricants when applied to ferrous-based equipment, as they were very effective in minimizing friction and wear in these systems [98]. For hydraulic applications, glycols are more commonly used and exhibit successful friction and wear behaviors. As shown by Tomala et al. [98], most additives reduce the coefficient of friction in numerous environments and stresses.
Ethanolamine additives, which are commonly utilized for their corrosion protection and lubrication properties, are often poor at reducing the friction coefficient from that of pure water, and in some cases, even increase it, as can be seen in Figure 4 [9]. Although this can be seen as a disadvantage, ethanolamine additives protect steel surfaces from corrosion effectively. Glycols exhibit some of the best tribological properties regarding wear and friction reduction, which agrees with many published studies [99]. A particularly significant combination of Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) and a water-soluble EP additive to reduce friction and wear was discovered by Yong et al. [99].
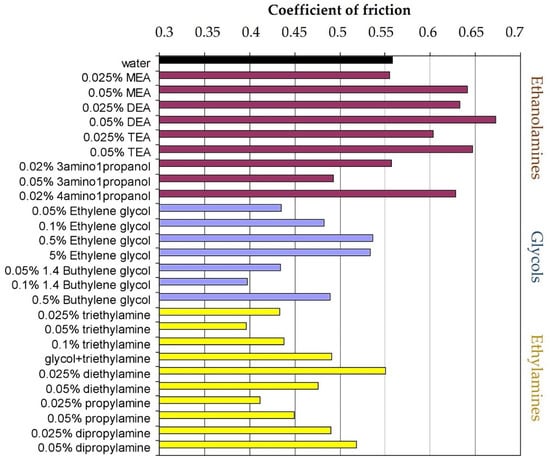
Figure 4.
Friction results for chosen additives in different concentrations. Reproduced with permission from [9]. Copyright Elsevier, 2010.
Dong et al. [100] tested the viability of proton-type ionic liquids additives for water-based lubricating fluids in several scenarios. Proton-type ionic liquids (PILs) have many advantages over other methods of water-based lubrication. For example, PILs have a very simple synthesis in which they are prepared through a proton transfer reaction between the Bronsted acids and bases, with the advantage of a low-cost, no impurity, and facile approach [101]. Another advantage is their solubility stability. Previous studies that have used WBL additives have had lubricity success, although their synthesis was complicated and costly. Zheng et al. [102] synthesized and experimented with two new water-soluble IL additives in water-glycol and found that these solutions had drastically improved lubricity and extreme pressure properties. These promising results were diminished when it was discovered that the solutions had poor solubility in water and the industrial preparation process was tedious [102].
PILs were adsorbed on the friction pair and then formed a double-layer structure on the surface, which together with the formed tribochemical reaction films on the surface effectively buffered the direct contact and collision from micro-convex bodies contributing to the friction reduction and anti-wear properties. Overall, this study further reinforces the capabilities of friction and anti-wear resistance of WBLs. Some additives and techniques create very effective WBLs. As shown in Figure 2, Ji et al. [41] developed a water-based lubricant. Their approach sought to solve common issues with other lubricants. These include properties of nonrenewability and nonbiodegradability, posing a constant threat to ecology and groundwater reserves, with a large proportion of current lubricants being released into the environment. Their results indicated that their most successful lubricant, glycerol ester of levulinic acid (LAGLE), exhibited superior lubricant properties, strong resistance to hydrolytic degradation, and excellent anti-wear performance, implying that the biomass-derived LAGLE was a potential water-based lubricant [41]. Both the LAEGE and another lubricant: Ethylene glycol ester of levulinic acid (LAGLE), showed significant friction and wear resistance abilities. Between LAEGE and LAGLE, LAGLE showed higher resistance to hydrolytic degradation, which would make it a more promising candidate in hydraulic applications.
Another method of improving the tribological performance of water lubricants is utilizing graphene oxide additives. Guo et al. [103] improved the tribological performance of water by adding nanomaterials as a water-based lubricant additive. This synthesis has generated interest in many applications, due to its tribological potential. In their study, they invented a novel nanomaterial named aminated silica-modified graphene oxide (SAG), which combines the layered nanomaterial graphene oxide (GO) and the nanoparticles hydrophilic nano-silica (SiO2) by 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES). Their use of the SAG nanomaterial in DI water dramatically reduced the wear rate of the lubricant in their tests, in addition to producing a very low friction coefficient. The SAG nanomaterial also outperformed the individual GO and nano-silica in improving wear resistance [103].
4.2. Corrosion Reduction
One of the biggest and most prominent drawbacks of WBLs is the increased potential of the lubricant causing corrosion to the machine or machinery. The concern is very prominent, especially for applications that involve gearboxes or bearings [9]. With this problem being one of the main setbacks for WBLs, research and development are ongoing for the best solution to the problem. Research has been carried out to find the optimal percentage of additives and ILs that can provide maximum performance and property improvements.
Additives, such as ionic liquids, have shown significant potential to improve corrosion reduction properties in WBLs. They offer a wide range of variations to test and produce superior water-based lubricants [9,11,81,104,105,106,107,108]. Within this section, ILs and other additives will be analyzed for their anti-corrosion capabilities. An additive with superior corrosion resistance is amino acid ionic liquids (AAILs) by Yang et al. [108]. Corrosion testing was done by using one of the seven types of AAILs that were synthesized by neutralizing acid and alkali. Testing involved the use of low carbon steel pieces in water at 18 mL and 1% [P4444][Trp] (18 mL) within a dry box at 55° C for 24 h. To evaluate the corrosion level properly, the authors used GB6144-85 as the reference standard. They were able to conclude that the inclusion of the additive resulted in weak corrosion with no visible rust that can be observed under normal seeing conditions. Using a scanning electron microscope (SEM), the surface of the piece did not show any significant differences from before the immersion. In comparison, the pieces that were immersed in pure water showed a substantial amount of corrosion, with the surface being covered in black iron oxide. Due to this corrosion, the surface had noticeably many wide and deep grooves on the surface. With additives, the corrosion resulted with grade B, and pure water resulted with grade D; Proving the AAILs increased the corrosion resistance overall [108].
Another additive with corrosion resistance properties is bio-inspired graphene-based coatings done by Chu et al. [107]. Due to the cross-linking effect within the microstructure of the hybrid coating, the additive generated densely stacked lamellar coating, which resulted in increased corrosion resistance. This was concluded through the following testing method–the authors did an electrochemical test using a classical three-electrode cell made up of a platinum plate as a counter electrode, a saturated calomel electrode (SCE) as a reference, and the sample. With the experiment being carried within ambient temperatures within a 3.5 wt.% NaCl electrolyte solution and corrosion parameters being determined using the Tafel extrapolation method. The most significant results were from the addition of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) within the solution. They determined the additives less than 15 wt.% had weak corrosion resistance and at values greater than 50 wt.% demonstrated very significant corrosion resistance [107]. An additive studied by Liu et al. [11] was PEI-RGO nanosheet that was made into a nano additive for WBLs [11]. The additive was able to double anti-wear and anti-corrosion properties, specifically for WBLs used for steel materials. The results were found from testing 201 stainless steel with 18 wt.% chromium. After stabilizing the austenite phase with manganese at 7 wt.% and decreasing nickel from 8 wt.% to 3 wt.%, it was sanded with sandpaper then washed with water and ethanol. During the use of a water-based solution, the steel was prone to corrosion, due to the oxide layer being constantly deteriorating during the wearing process [11]. Due to this process, iron atoms in the steel were being separated, which would cause iron oxide to continuously form, causing the steel to be under constant corrosion. Though the testing of the additive, PEI-RGO, combatted this process by creating a protective deposited film. The additive was able to stop oxygen molecules from entering the wear scars that would form during the wear process. Demonstrating an additive that so far can be applicable for steel materials that would suffer from corrosion with further testing being planned for nonsteel materials [11].
Furthermore, through an in-situ preparation, many multifunctional additives can be created with significant tribological properties and corrosion-resistant capabilities [105,106]. Important additives that were prepared in-situ are benzotriazole tetrabutyl phosphonium [P4444][BTA], and benzotriazole tetrabutylammonium [N4444][BTA]. Benzotriazole is a corrosion inhibitor for metals that helps increase the corrosion-resistant ability. The additives were able to create adsorption protective film on the iron surface consisting of nitrogen, which would result in no visible corrosion on the surface, outperforming the pieces being exposed to pure water and a Benzotrazole/H2O solution that had visible and substantial corrosion on the surface.
Another important additive that has been created through an in-situ preparation is [Li(nonionic surfactant)]TFSI [105]. Testing determined that the additive could increase the kinematic viscosity of the WBLs better than others at 25 °C. The additive achieved similar anti-corrosion properties as the ones made of benzotriazole, though it was created using a lithium salt and a nonionic surfactant. Another ionic liquid (IL) synthesized and tested by the same research group is [Li(nonionic surfactant)]TFSI; an Ibuprofen-based (L-Ibu) halogen-free ionic liquid [104]. The additive has resulted in greater friction-reducing, extreme pressure, anti-wear properties than commercial additives. The corrosion test consisted of the Ibuprofen IL L-Ibu106, and L-Ibu108 at 2% concentrations within the water. A copper strip and cast-iron strip were soaked independently within each lubricant [104]. After testing, the surfaces of the strips showed no discoloration compared to the strips soaked in water and a water–ethylene glycol solution (W-EG) which showed major discoloration, due to substantial corrosion. Due to this significant anti-corrosion property, the additives were able to achieve a grade A according to GB6144-85, meaning there was no rust, while looking new [104]. Additives and ionic liquids are becoming prime candidates for WBLs to implement to achieve better corrosion-resistant capabilities. Many of the additives and ILs discussed within these sections were able to increase resistance significantly. Often being able to create a protective film along the surface of the metal that would protect any formed wear scars from possible corrosion. In cases where the corrosion testing was evaluated using the GB6144-85 scale, the additives and ILs were able to achieve grade B or A (very little/no rust); Compared to a grade D in base water or another water-based solution/lubricant, which indicated severe/noticeable corrosion.
5. Recent Advancement and Challenges of Water-Based Lubricants
WBLs field has experienced significant development in recent years. Environmental concerns with oil-based lubricants have accelerated the amount of research being performed on WBLs. Petroleum-based lubricants can be toxic and are typically nonbiodegradable. This generates excess waste that can be problematic with the high volume of oil-based lubricants being used. The need for a cleaner, more efficient lubricant to replace traditional oil-based lubricants has driven researchers to develop a more sustainable option. This section will discuss recent advancements in water-based lubrication and the challenges that come along with developing new WBLs. In industrial production, a large percentage of energy loss results from friction and wear [113].
As the world population continues to rise, the need for production also rises. This means that more machines need to be used to satisfy the needs of production. The amount of crude oil the world has available is declining rapidly. In the early 2000s, there were huge efforts to find plant-based lubrication alternatives to reduce the environmental impact of machining. In more recent years, scientific research has been conducted on water-based lubrication options. Water alone cannot be used as a lubricant. Additives must be incorporated with the water to make it suitable to reduce frictional effects caused by machining. This has been one challenge water-based lubrication has presented. Many additives have been tested, but only a few can make a solution that is comparable to an oil-based lubricant. There is a rising need for better lubrication in the metal forming process, due to the high friction created by materials in contact [114]. The excessive amount of friction can lead to several negative effects, including the reduced life cycle of parts, deformation, and heat generation.
Recent research has pointed towards the use of nanoparticles as additives for lubricants. They are small, have no harmful emissions, and are chemically stable [109]. Graphene as a nanoparticle additive has been the focus of researchers recently. The research conducted by the Northwest Normal University indicated that the tribological properties of graphene as an additive decreased wear by nearly four orders of magnitude and friction coefficient by a factor of six [115]. Further, research conducted by the Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics found that graphene as a water additive for steel-on-steel contact offers 81.3% friction reduction [116]. The use of graphene has been highly efficient and is continually being implemented for more machining processes. Another nanoparticle that has been widely accepted as an efficient additive to WBLs is SiO2. SiO2 is advantageous, due to the low-cost nature of adding this nanoparticle to water. SiO2 creates a rolling action between surfaces in contact, which leads to a reduction in friction [109]. Nanoparticles can also be combined to make new additives in the ideal combinations. Recent research suggests that the lubricity of WBLs has been enhanced with the introduction of nanoparticles to the water. Water-based nanolubricants are one of the ideal formulations of WBLs, due to their eco-friendliness and overall simplicity. Another added benefit is the low-cost nature of producing this type of formulation. This advancement on the lubrication front has been applied to the industrial scale hot steel rolling process. Water-based nanolubricants that contain TiO2 have reduced the rolling force that is present in the hot rolling process. The nanoparticles took the places between the oxide layers on the workpiece surface, while the rolling process was carried out (Figure 5) [117]. Therefore, a stronger film was formed. Moreover, the friction reduction was facilitated by the wettability of the TiO2 [117]. However, more studies are needed to completely understand the mechanism of such nanolubricants.
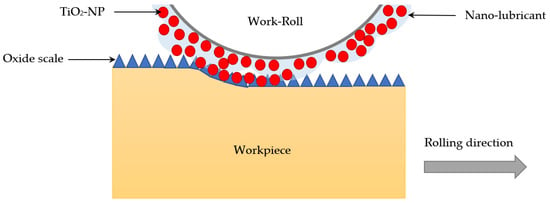
Figure 5.
Schematic illustration of lubrication mechanisms using water-based nanolubricants containing TiO2 nanoparticles during hot steel rolling. Adopted from [117].
At present, several studies have been focused on using WBLs to achieve superlubricity or very low friction. To achieve superlubricity, the frictional coefficient needs to be lower than 0.01 at the nanoscale [118]. Experimentation supported by the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC), revealed that using the running-in process on WBLs with sulfuric acid can generate super low friction. In the process, a silica layer forms from a tribochemical process and allows the surfaces to glide over one another more easily [118]. This process, as a result, reduces the coefficient of friction between surfaces.
Overall, water-based lubrication is at the forefront of technological advancement to meet the world’s desire for methods that promote sustainable manufacturing. The new type of lubricant has presented many challenges; however, research has overcome some of the challenges, and scientists have been able to produce several WBLs in large quantities. The governmental push for more environmentally friendly lubricants has quickly accelerated the advancements of water-based lubricant technologies around the world. As time goes on, manufacturing demand and capabilities will continue to rise. This will result in a greater demand for eco-friendly lubricants. Water-based lubrication is one method of machine lubrication that promotes environmental awareness and sustainable growth. Recently, the use of additives in combination with water has provided the world with a positive outlook on the lubrication front. Nanoparticles are generally cheap and easily accessible, making them an ideal additive for lubrication.
6. Conclusions
Water-based lubricants could be an environmentally friendly alternative to petroleum-based lubricants. However, the issue with WBLs is that they have poor tribological properties: Poor friction reduction, high corrosiveness, and low viscosity. Additives have shown great potential for improving the nature of WBLs. Utilizing additives with WBLs is gaining interest among scientists and engineers, not only because of the potential for being environmentally friendly, but also because there is a potential for a reusable liquid lubricant. Further exploring the use and development of additives also creates lubricants that can be used for multiple purposes. Additives can change the properties and behavior of the lubricant, resulting in high-performance liquid lubricants designed for specific tribo-systems. Properties include a higher viscosity and density to improve the thermal behavior and create thicker fluid films within the lubricant. There are also improved friction, wear, and corrosion performance for water-based liquid lubricants. The atomic structure of the lubricant changes based on the type of additive that is used. Ionic liquids, bio-additives, titanium-based nano-additive, water-soluble rubber seed oil-based sulfonate, graphene-based nanoparticles, and nanostructured borates are all potential additives that can be used with water-based liquid lubricants to improve the behavior and properties of the lubricant. A potential challenge for WBLs is that the manufacturing demand and capabilities will increase over time as additives used for water-based liquid lubricants become a viable option. Current research is focusing on the advancement and development of additives. Therefore, continuing the research and development for additives used in combination with water-based liquid lubricants is important. This will further expand the usage of water-based lubricants over petroleum-based lubricants as an eco-friendly alternative.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.H.R. and P.L.M.; Methodology, M.H.R., H.W. (Haley Warneke), H.W. (Haley Webbert), J.R., E.A., K.T.; Writing-original draft, H.W. (Haley Warneke), H.W. (Haley Webbert), J.R., E.A., K.T., M.H.R.; writing—review and editing, M.H.R., D.K.R., P.L.M.; visualization, M.H.R.; supervision, M.H.R.; project administration, P.L.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We acknowledge the support and facilities from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at the University of Nevada at Reno.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the technical help of Ashish Kasar during this review.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Scharf, T.; Prasad, S. Solid lubricants: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 511–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, P.L.; Ingole, S.P.; Nosonovsky, M.; Kailas, S.V.; Lovell, M.R. Tribology for Scientists and Engineers; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bart, J.; Gucciardi, E.; Cavallaro, S. Advanced lubricant fluids. In Biolubricants: Science and Technology; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 824–846. [Google Scholar]
- Panja, S.K. Tribological Properties of Ionic Liquids. In Tribology; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, M.; Yu, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhou, F. Ionic liquid lubricants: When chemistry meets tribology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch, J. The History of Lubrication. Available online: https://www.machinerylubrication.com/Read/579/lubrication-genesis (accessed on 7 April 2021).
- Ritchie, H. How Long before We Run Out of Fossil Fuels? Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/how-long-before-we-run-out-of-fossil-fuels (accessed on 7 April 2021).
- Wei, C.; Tobias, A.; Andreas, K.; Jurgen, R. Macroscopic Friction Studies of Alkylglucopyranosides as Additives for Water-Based Lubricants. Lubricants 2020, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomala, A.; Karpinska, A.; Werner, W.S.M.; Olver, A.; Stori, H. Tribological Properties of Additives for Water-Based Lubricants. Wear 2010, 296, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagraloff, N.; Dobler, A.; Tobie, T.; Stahl, K.; Ostrowski, J. Development of an Oil Free Water-Based Lubricant for Gear Applications. Lubricants 2019, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Guo, Y.; Wang, D. PEI-RGO Nanosheets as a Nano-Additive for Enhancing the Tribological Properties of Water-Based Lubricants. Tribol. Int. 2019, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, J.; Xia, W.; Cheng, X.; He, A.; Yun, J.H.; Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Jiao, S.; Huang, L.; et al. A study of the tribological behaviour of TiO2 nano-additive water-based lubricants. Tribol. Int. 2017, 109, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Jia, F.; Li, Z.; Lin, F.; Huo, M.; Huang, S.; Sayyar, S.; Jiao, S.; Huang, H.; Jiang, Z. Novel water-based nanolubricant with superior tribological performance in hot steel rolling. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Sol, I.; Gámez, A.; Rivero, A.; Iglesias, P. Tribological performance of ionic liquids as additives of water-based cutting fluids. Wear 2019, 426, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Ma, T.; Eryilmaz, O.L.; Shi, Y.; Erdemir, A. Superlubricity of polyalkylene glycol aqueous solutions enabled by ultrathin layered double hydroxide nanosheets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 20249–20256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailer, A.; Amann, T. Development of Water-Based Lubricants. Available online: https://www.iwm.fraunhofer.de/en/services/tribology/wear-protection-advanced-ceramics/development-of-water-based-lubricants.html (accessed on 2 February 2021).
- Supekar, S.D.; Graziano, D.J.; Skerlos, S.J.; Cresko, J. Comparing energy and water use of aqueous and gas-based metalworking fluids. J. Ind. Ecol. 2020, 24, 1158–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Bhoi, P.R.; Saha, A.; Patil, V.; Adhikari, S. Thermo-catalytic co-pyrolysis of biomass and high-density polyethylene for improving the yield and quality of pyrolysis liquid. Energy 2021, 225, 120231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H. Catalytic Co-pyrolysis of Pinewood and Waste Plastics for Improving the Selectivity of Hydrocarbons and the Quality of Pyrolysis Oil; Georgia Southern University: Statesboro, GA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Tang, W.; Liu, X.; Huang, Z. Synthesis of ionic liquid decorated muti-walled carbon nanotubes as the favorable water-based lubricant additives. Appl. Phys. A 2017, 123, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanmohammadi, H.; Wijanarko, W.; Espallargas, N. Ionic Liquids as Additives in Water-based Lubricants: From Surface Adsorption to Tribofilm Formation. Tribol. Lett. 2020, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrion, F.-J.; Sanes, J.; Bermudez, M.-D.; Jimenez, A.-E. Ionic Liquids as Advanced Lubricant Fluids. Molecules 2009, 14, 2888–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Liang, Y.; Liu, W. Ionic Liquid Lubricant: Designed Chemistry for Engineering Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Applications of ionic liquids in the chemical industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, C.J.; Siddaiah, A.; Menezes, P.L. Tribological study of imidazolium and phosphonium ionic liquid-based lubricants as additives in carboxylic acid-based natural oil: Advancements in environmentally friendly lubricants. J. Clean Prod. 2018, 176, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, C.J.; Siddaiah, A.; Menezes, P.L. Friction and Wear Behavior of Environmentally Friendly Ionic Liquids for Sustainability of Biolubricants. J. Tribol. 2019, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, C.J.; Kasar, A.K.; Menezes, P.L. Tribological performance of environmental friendly ionic liquids for high-temperature applications. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 279, 123666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rensselar, J. Unleashing the potential of ionic liquids. Tribol. Lubr. Technol. 2010, 66, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, C.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L. Room-temperature ionic liquids: A novel versatile lubricant. Chem. Commun. 2001, 2244–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserscheid, P.; Welton, T. Ionic Liquids in Synthesis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Westerholt, A.; Weschta, M.; Bosmann, A.; Tremmel, S.; Korth, Y.; Wolf, M.; Schlücker, E.; Wehrum, N.; Lennert, A.; Uerdingen, M. Halide-free synthesis and tribological performance of oil-miscible ammonium and phosphonium-based ionic liquids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, L.; Dong, R.; Zhang, C.; Sun, W.; Fan, M.; Yang, D.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Study on the synthesis and tribological properties of anti-corrosion benzotriazole ionic liquid. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 11030–11040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, W.; Wang, B.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, H.; Huang, Z. Facile Pyrolysis Synthesis of Ionic Liquid Capped Carbon Dots and Subsequent Application as the water-Based Lubricant Additives. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Xu, J.; Jin, Z.; Prakash, B.; Hu, Y. A review of recent advances in tribology. Friction 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Qu, J. Ionic Liquids as Lubricant Additives: A Review. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3209–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremmer, B.; Plonsker, L.; Martin, J. Bio-Based Lubricants; United Soybean Board: Chesterfield, MO, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Reeves, C.; Siddaiah, A.; Menezes, P. Ionic Liquids: A Plausible Future of Bio-lubricants. J. Bio Tribo Corros. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gucciardi, E.; Bart, J.; Cavallaro, S. Biolubricants: Science and Technology; Woodhead Publishing Limites: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bhoi, P.; Ouedraogo, A.; Soloiu, V.; Quirino, R. Recent advances on catalysts for improving hydrocarbon compounds in bio-oil of biomass catalytic pyrolysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 121, 109676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindfors, C.; Kuoppala, E.; Oasmaa, A.; Solantausta, Y.; Arpiainen, V. Fractionation of bio-oil. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 5785–5791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Zhang, X.; Tan, T. Preparation of a Water-Based Lubricant from Lignocellulosic Biomass and Its Tribological Properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobarak, H.; Mohamad, N.; Masjuki, H.; Kalam, M.; Mahmud, K.; Habibullah, M.; Ashraful, A. The prospects of biolubricants as alternatives in automotive applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.; Singh, B. An ideal feedstock, kusum (Schleichera triguga) for preparation of biodiesel: Optimization of parameters. Fuel 2010, 89, 1470–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaosmanoglu, F.; Tuter, M.; Gollu, E.; Yanmaz, S.; Altintig, E. Fuel properties of cottonseed oil. Energy Sources 1999, 21, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usta, N.; Aydoğan, B.; Çon, A.; Uğuzdoğan, E.; Özkal, S. Properties and quality verification of biodiesel produced from tobacco seed oil. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 2031–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Singh, S. Low cost production of ester from non edible oil of Argemone mexicana. Biomass Bioenergy 2010, 34, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hanna, M.A.; Zhou, W.-W.; Bhadury, P.S.; Chen, Q.; Song, B.-A.; Yang, S. Production and selected fuel properties of biodiesel from promising non-edible oils: Euphorbia lathyris L., Sapium sebiferum L. and Jatropha curcas L. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, X.-Y.; Li, Z.-L.; Wang, Y.-D.; Wang, C.-Y.; Shi, H.; Wang, F. Enzymatic production of biodiesel from Pistacia chinensis bge seed oil using immobilized lipase. Fuel 2012, 92, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhou, W.-W.; Hanna, M.A.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Bhadury, P.S.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.-A.; Yang, S. Biodiesel preparation, optimization, and fuel properties from non-edible feedstock, Datura stramonium L. Fuel 2012, 91, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofijur, M.; Masjuki, H.; Kalam, M.; Hazrat, M.; Liaquat, A.; Shahabuddin, M.; Varman, M. Prospects of biodiesel from Jatropha in Malaysia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 5007–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, C.J.; Menezes, P.L.; Jen, T.-C.; Lovell, M.R. The influence of fatty acids on tribological and thermal properties of natural oils as sustainable biolubricants. Tribol. Int. 2015, 90, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, M.R.; Kabir, M.; Menezes, P.L.; Higgs III, C.F. Influence of boric acid additive size on green lubricant performance. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2010, 368, 4851–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reeves, C.J.; Menezes, P.L.; Lovell, M.R.; Jen, T.-C. The size effect of boron nitride particles on the tribological performance of biolubricants for energy conservation and sustainability. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 51, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrani, E.; Siddaiah, A.; Moghadam, A.D.; Garg, U.; Rohatgi, P.; Menezes, P.L. Ball Milled Graphene Nano Additives for Enhancing Sliding Contact in Vegetable Oil. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omrani, E.; Menezes, P.L.; Rohatgi, P.K. Effect of micro-and nano-sized carbonous solid lubricants as oil additives in nanofluid on tribological properties. Lubricants 2019, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddaiah, A.; Kasar, A.K.; Manoj, A.; Menezes, P.L. Influence of environmental friendly multiphase lubricants on the friction and transfer layer formation during sliding against textured surfaces. J. Clean Prod. 2019, 209, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Lv, Y. Preparation and Tribological Properties of Dual-Coated TiO2 Nanoparticles as Water-Based Lubricant Additives. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 785680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.T.C.K.-H. Assessment of Tribological Properties of Ti3C2 as a Water-Based Lubricant Additive. Materials 2020, 13, 5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhou, C.; Gao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, S. Preparation of Cu@SiO2 composite nanoparticle and its tribological properties as water-based lubricant additive. Lubr. Sci. 2020, 32, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wang, M.; Li, M.; Huang, K.; Li, S.; Xu, L.; Yang, X.; Xia, J. Synthesis of a water-soluble, rubber seed oil–based sulfonate and its tribological properties as a water-based lubricant additive. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, R.; Hu, L.; Hou, K.; Wang, J.; Yang, S. Water-Soluble Graphene Quantum Dots as High-Performance Water-Based Lubricant Additive for Steel/Steel Contact. Tribol. Lett. 2019, 67, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffari, H.R.M.; Soltani, R.; Alaei, M.; Soleymani, M. Tribological properties of water-based drilling fluids with borate nanoparticles as lubricant additives. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 171, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Lin, Y.; Xue, Y. Effect of ester based lubricant SMJH-1 on the lubricity properties of water based drilling fluid. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 135, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, J.M.; Vasilakos, I.; Yan, Y.; Reyes-Aldasoro, C.-C. Effect of Viscosity and Speed on Oil Cavitation Development in a Single Piston-Ring Lubricant Assembly. Lubricants 2019, 7, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamrock, B.J.; Dowson, D. Ball Bearing Lubrication: The Elastohydrodynamics of Elliptical Contacts; ASME: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Menezes, P.L.; Kailas, S.V. Effect of roughness parameter and grinding angle on coefficient of friction when sliding of Al–Mg alloy over EN8 steel. J. Tribol. 2006, 128, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, N.; Fernández, L.; Barceló, F.; Spikes, H. Shear Thinning and Hydrodynamic Friction of Viscosity Modifier-Containing Oils. Part II: Impact of Shear Thinning on Journal Bearing Friction. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacConochie, I.O.; Newman, W.H. The effect of lubricant viscosity on the lubrication of gear teeth. Wear 1961, 4, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, R. EHL Film Thickness Behavior. In Encyclopedia of Tribology; Wang, Q.J., Chung, Y.-W., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 817–827. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M.; Luo, J.; Wen, S.; Yao, J. Nano-tribological properties and mechanisms of the liquid crystal as an additive. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2001, 46, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanizadeh, M.; Ahmadi, M.H.; Nazari, M.A.; Sadeghzadeh, M.; Chen, L. A review on the utilized machine learning approaches for modeling the dynamic viscosity of nanofluids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 114, 109345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajmohammadi, M.R. Assessment of a lubricant based nanofluid application in a rotary system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 146, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcione, M. Empirical correlating equations for predicting the effective thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of nanofluids. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najiha, M.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Kadirgama, K. Performance of water-based TiO2 nanofluid during the minimum quantity lubrication machining of aluminium alloy, AA6061-T6. J. Clean Prod. 2016, 135, 1623–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omotowa, B.A.; Phillips, B.S.; Zabinski, J.S.; Shreeve, J.n.M. Phosphazene-Based Ionic Liquids: Synthesis, Temperature-Dependent Viscosity, and Effect as Additives in Water Lubrication of Silicon Nitride Ceramics. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 5466–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldoveanu, S.C.; David, V. (Eds.) Chapter 7—RP-HPLC Analytical Columns. In Selection of the HPLC Method in Chemical Analysis; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 279–328. [Google Scholar]
- Cabezudo, N.; Sun, J.; Andi, B.; Ding, F.; Wang, D.; Chang, W.; Luo, X.; Xu, B.B. Enhancement of surface wettability via micro- and nanostructures by single point diamond turning. Nanotechnol. Precis. Eng. 2019, 2, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, Z.; Urbaniak, W.; Oloyede, A. The relationship between friction and wettability in aqueous environment. Wear 2011, 271, 1745–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Zhao, H.; Ge, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, L.; Xue, Q. PEGlated graphene as nanoadditive for enhancing the tribological properties of water-based lubricants. Carbon 2018, 137, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-J.; Zhu, D.-S. Investigation of pH and SDBS on enhancement of thermal conductivity in nanofluids. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2009, 470, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sułek, M.W.; Ogorzałek, M.; Wasilewski, T.; Klimaszewska, E. Alkyl Polyglucosides as Components of Water Based Lubricants. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2013, 16, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Chakraborty, D.; Khan, S. Wetting behavior of aqueous 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate {[Cn MIM][BF4] (n = 2, 4, 6)} on graphite surface. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 229, 116078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Hanh, B.M.; Isaiah Chua, J.Q.; Daniel, D.; Ismail, M.H.; Marchioro, M.; Amini, S.; Rice, S.A.; Miserez, A. Green biolubricant infused slippery surfaces to combat marine biofouling. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 568, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, D.G.; da Silva, A.d.P.M.; Cajaiba, J.; Pérez-Gramatges, A.; Lachter, E.R.; Nascimento, R.S.V. Influence of glycerides–xanthan gum synergy on their performance as lubricants for water-based drilling fluids. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, R.V.; Bera, P.; Anandan, C.; Basu, B.J. Effect of the size of silica nanoparticles on wettability and surface chemistry of sol–gel superhydrophobic and oleophobic nanocomposite coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 320, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Lei, Y.; Li, W.; Fan, M. Synergy between Covalent Organic Frameworks and Surfactants to Promote Water-Based Lubrication and Corrosion Resistance. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 1400–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. Preparation and Tribological Properties of Water-Soluble Copper/Silica Nanocomposite as a Water-Based Lubricant Additive. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Hu, L.; Liu, W.; Hao, J. Synthesis of Water-Soluble Carbon Nanotubes via Surface Initiated Redox Polymerization and Their Tribological Properties as Water-Based Lubricant Additive. Eur. Polym. J. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, M. Dispersing multi-walled carbon nanotubes with water soluble block copolymers and their use as supports for metal nanoparticles. Carbon 2007, 45, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Braidy, N.; Botton, G.A.; Adronov, A. Polymerization from the surface of single-walled carbon nanotubes-preparation and characterization of nanocomposites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Huang, S.; Dai, L.; Wallace, G.; Gao, R.; Wang, Z. Aligned coaxial nanowires of carbon nanotubes sheathed with conducting polymers. Zuschriften 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Gao, C.; Yan, D. Functionalization of multiwalled carbon nanotubes by atom transfer radical polymerization and defunctionalization of the products. Macromolecules 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.X.; Tong, R.; Qiu, X.Q.; Yang, H.F.; Lin, Y.H.; Cai, R.F.; Qian, S.X. Functionalization of multiwalled carbon nanotubes with polystyrene under atom transfer radical polymerization conditions. Carbon 2007, 45, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Wang, W.; You, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, P. Functionalization of multiwalled carbon nanotubes by reversible addition fragmentation chain-transfer polymerization. Polymer 2004, 45, 8717–8721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Bhoi, P.R. An Overview of Non-biodegradable Bioplastics. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 126218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Ding, M.; Sui, T.; Zheng, W.; Qiao, G.; Yan, S.; Liu, X. Role of Nanoparticle Materials as Water-Based Lubricant Additives for Ceramics. Tribol. Int. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresham, R.M. The Mysterious World of MWF Additives. Available online: https://www.stle.org/images/pdf/STLE_ORG/BOK/OM_OA/Friction_Tribology/The%20Mysterious%20World%20of%20MWF%20Additives_tlt%20article_Sept06.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2021).
- Ma, H.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Zuo, G.; Yu, Y.; Ren, T.; Zhao, Y. XPS and XANES characteristics of tribofilms and thermal films generated by two P- and/or S-containing additives in water-based lubricant. Tribol. Int. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, W.; Qunji, X.; Lili, C. Tribological properties of some water-based lubricants containing polyethylene glycol under boundary lubrication conditions. J. Synth. Lubr. 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Yu, Q.; Bai, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Yu, B.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.; Cai, M. Towards Superior Lubricity and Anticorrosion Performances of Proton-Type Ionic Liquids Additives for Water-Based Lubricating Fluids. Chem. Eng. J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, T.; Sanes, J.; Jiménez, A.E.; Bermúdez, M.D. Bermúdez. Protic ammonium carboxylate ionic liquid lubricants of OFHC copper Wear. Wear 2013, 303, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Zhang, G.; Ding, T.; Xiang, X.; Li, F.; Ren, T.; Liu, S.; Zheng, L. Tribological properties and surface interaction of novel water-soluble ionic liquid in water-glycol. Tribol. Int. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.L.T.; Tsao, C.-Y.A. Tribological Behavior of Self-Lubricating Aluminium/SiC/Graphite Hybrid Composites Synthesized by the Semi-Solid Powder-Densification Method. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Cai, M.; Shi, L.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Ibuprofen-Based Ionic Liquids as Additives for Enhancing the Lubricity and Antiwear of Water–Ethylene Glycol Liquid. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 65, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Cai, M.; Shi, L.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Synergy of lithium salt and non-ionic surfactant for significantly improved tribological properties of water-based fluids. Tribol. Int. 2017, 113, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Du, X.; Ma, L.; Wen, P.; Zhang, S.; Dong, R.; Sun, W.; Yang, D.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. In situ preparation of multifunctional additives in water. Tribol. Int. 2019, 130, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.H.; Tong, L.B.; Zhang, J.B.; Kamado, S.; Jiang, Z.H.; Zhang, H.J.; Sun, G.X. Bio-inspired graphene-based coatings on Mg alloy surfaces and their integrations of anti-corrosive/wearable performances. Carbon 2019, 141, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, S.; Cai, M.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Q. Amino acid ionic liquids as anticorrosive and lubricating additives for water and their environmental impact. Tribol. Int. 2021, 153, 106663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Dang, S.; Xiang, L.; Jiang, B.; Zhou, S.; Sheng, H.; Yang, T.; Pan, F. Tribological performances of SiO2/graphene combinations as water-based lubricant additives for magnesium alloy rolling. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 475, Fusheng. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietsch, J.-C.; Brender, P.; Dentzer, J.; Gadiou, R.; Vidal, L.; Vix-Guterl, C. Evidence of water chemisorption during graphite friction under moist conditions. Carbon 2013, 55, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés, M.; Carrión, F.; Sanes, J.; Bermúdez, M. Bio-based ionic liquid crystal for stainless steel-sapphire high temperature ultralow friction. Wear 2021, 204020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, B.; Zabinski, J. Ionic liquid lubrication effects on ceramics in a water environment. Tribol. Lett. 2004, 17, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, S.S.; Tysoe, W.T. Frontiers of fundamental tribological research. Tribol. Lett. 2005, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selvam, B.; Marimuthu, P.; Narayanasamy, R.; Senthilkumar, V.; Tun, K.S.; Gupta, M. Effect of temperature and strain rate on compressive response of extruded magnesium nano-composite. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berman, D.; Erdemir, A.; Sumant, A. Few layer graphene to reduce wear and friction on sliding steel surfaces. Carbon 2013, 54, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Yi, M.; Shen, Z.; Liu, L.; Ma, S.; Zhang, X. In-situ exfoliated graphene for high-performance water-based lubricants. Carbon 2016, 96, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Kamila, H.; Huo, M.; Lin, F.; Huang, S.; Huang, H.; Jiao, S.; Xing, Z.; JIang, Z. Eco-friendl water-based nanolubricants for industrial-scale hot steel rolling. Lubricants 2020, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Ren, J.; Zhou, N.; Luo, J. Investigation of running-in process in water-based lubrication aimed at achieving super-low friction. Tribol. Int. 2016, 102, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).