Modelling Transitions in Regimes of Lubrication for Rough Surface Contact
Abstract
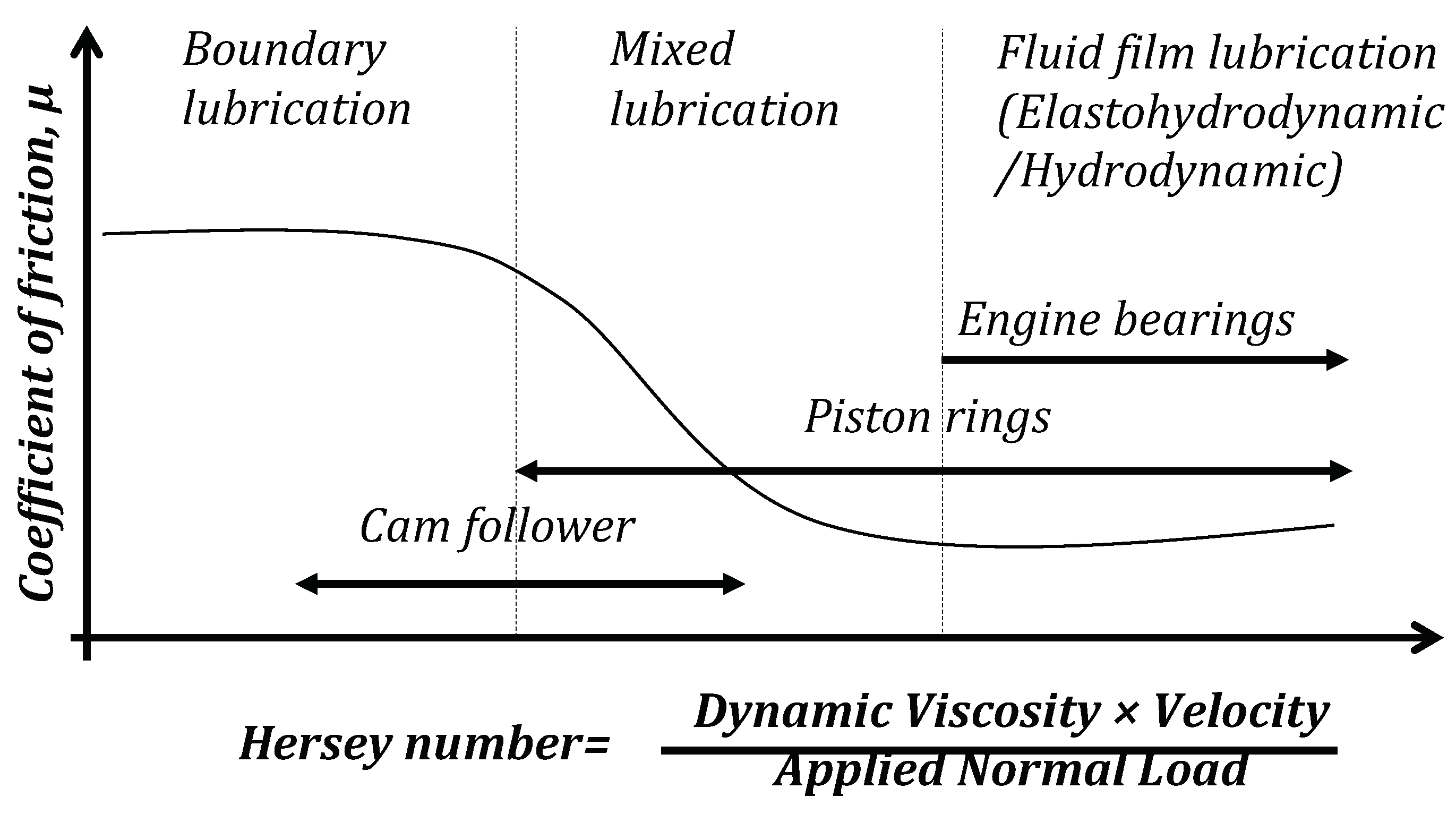
1. Introduction
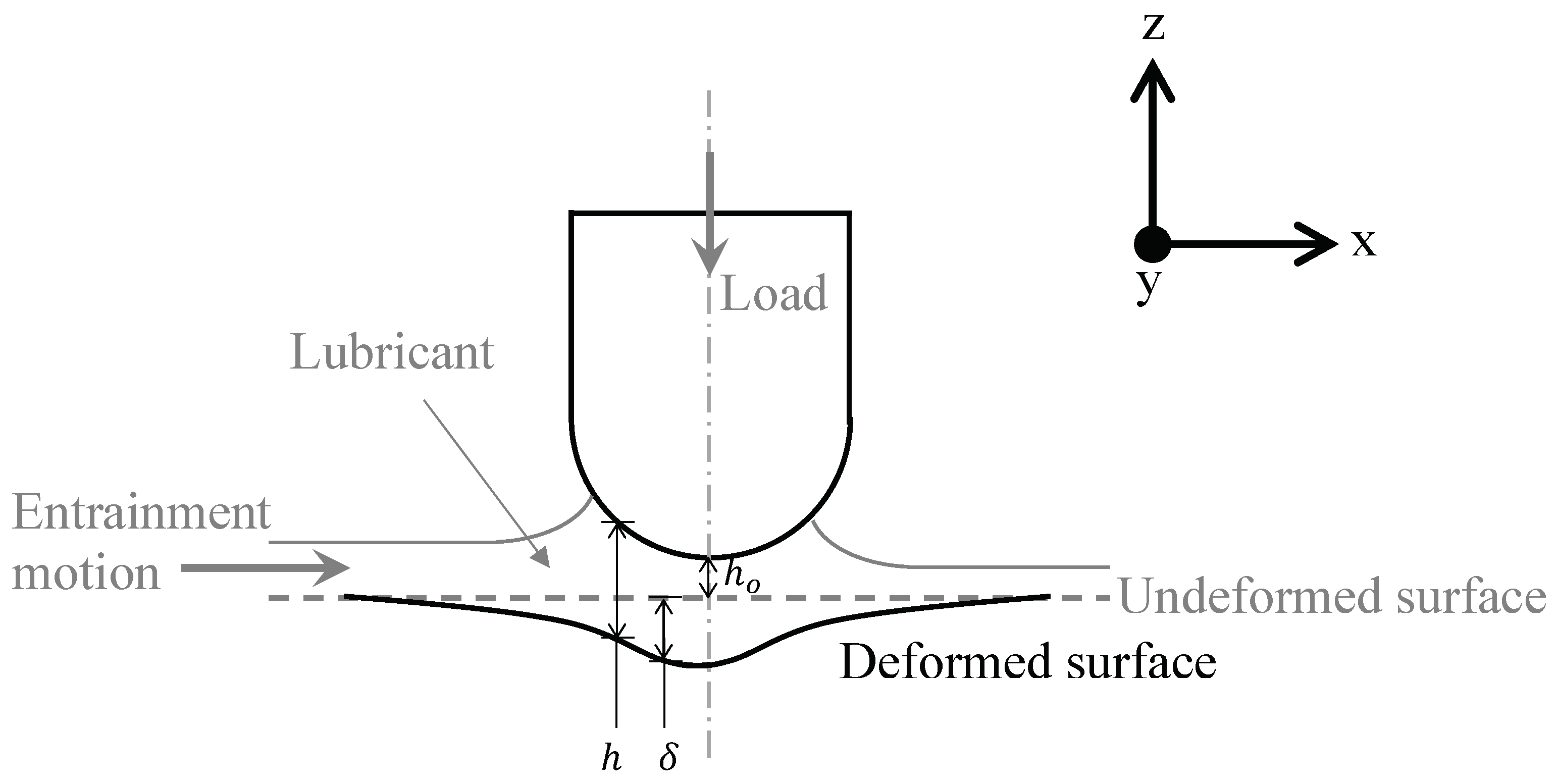
2. Mathematical Approach
2.1. Hydrodynamic Pressure
2.2. Interacting Asperity Pressure
2.3. Frictional Conjunction
2.4. Numerical Method
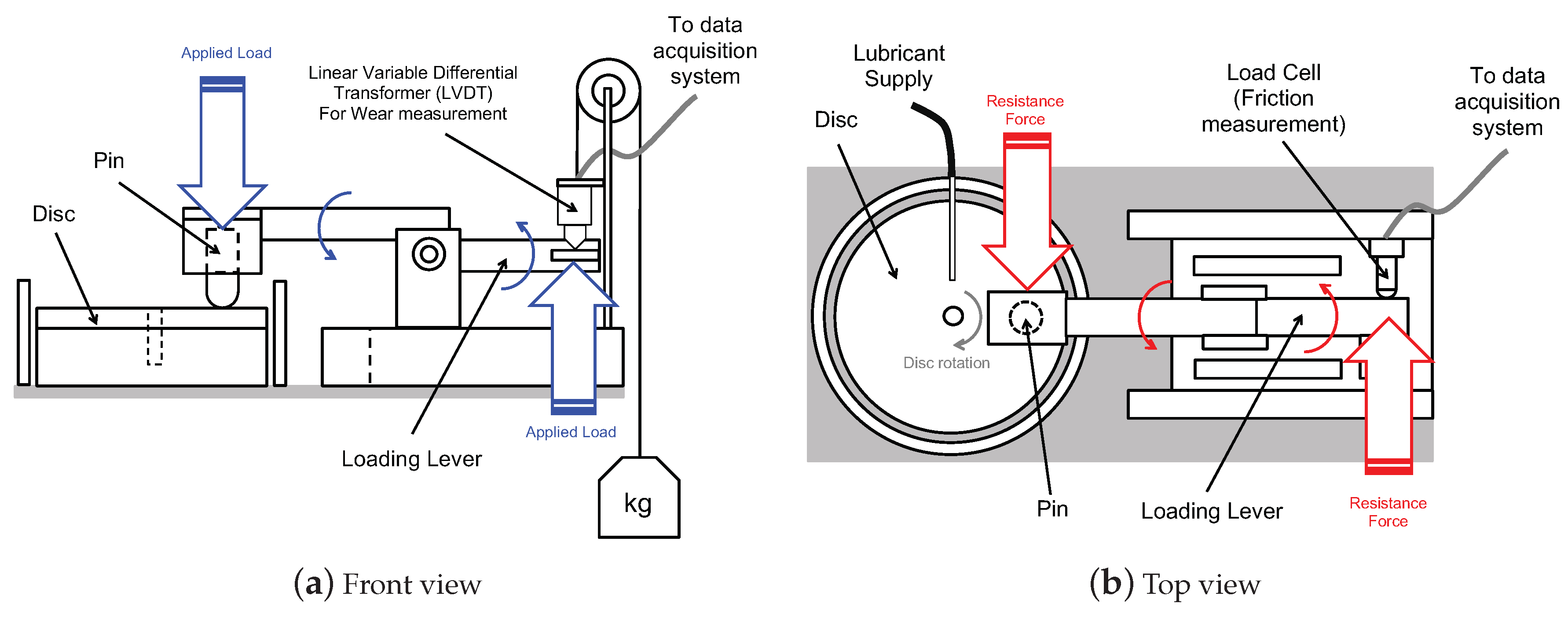
3. Experimental Approach
3.1. Friction Testing
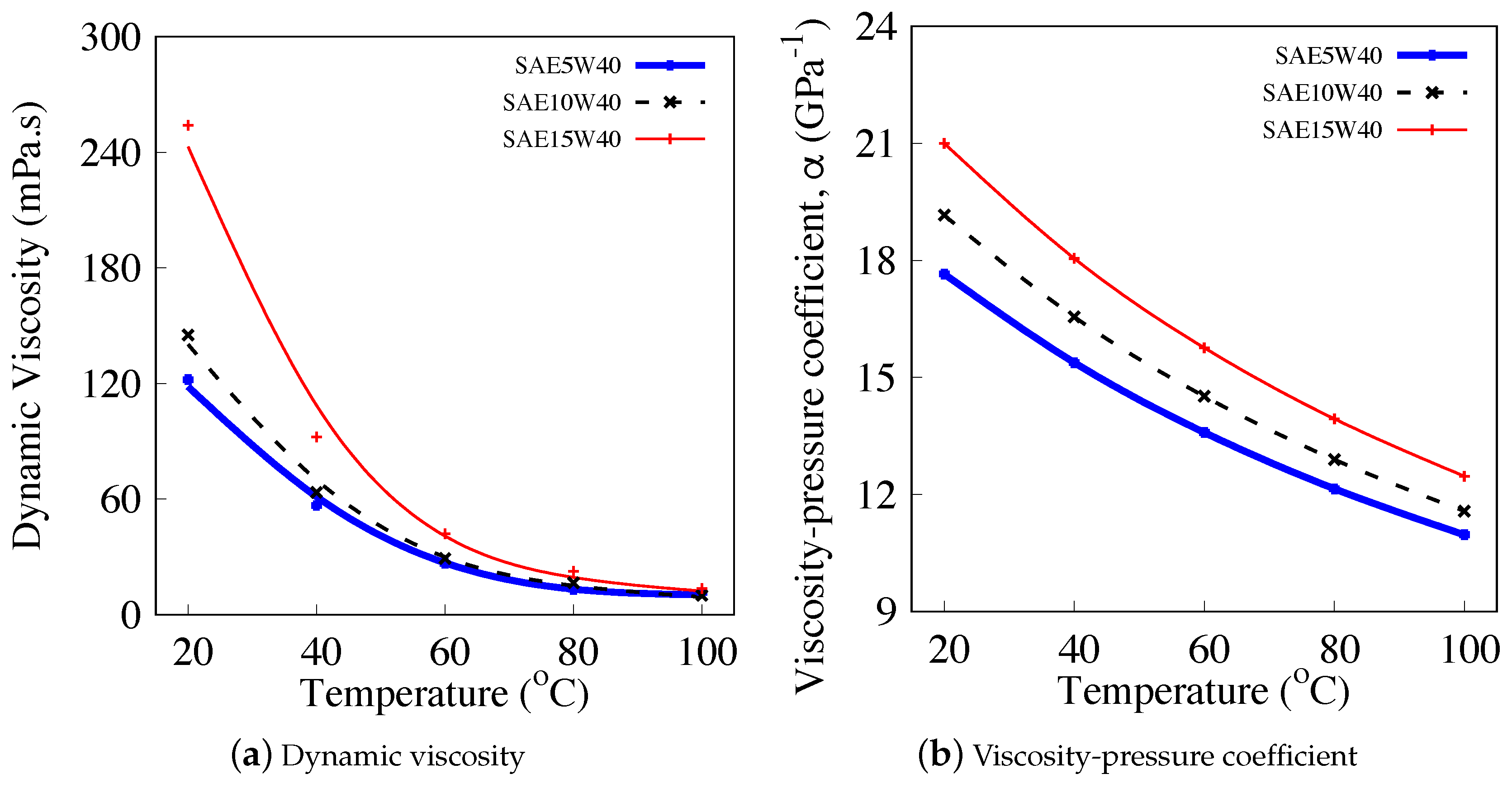
3.2. Lubricant Viscosity-Pressure Correlation
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A | Apparent contact area (m2) |
| a | Hertzian contact radius in the x-direction (m) |
| b | Hertzian contact radius in the y-direction (m) |
| D | Influence coefficient (m) |
| E | Modulus of elasticity (m) |
| Effective modulus of elasticity (m) | |
| Boundary friction force (N) | |
| Rough surface model statistical function, and (−) | |
| Viscous friction force (N) | |
| Total friction force (N) | |
| Non-dimensional material parameter (−) | |
| Non-dimensional elasticity parameter (−) | |
| Non-dimensional viscosity parameter (−) | |
| H | Non-dimensional elastic lubricant film profile (−) |
| h | Elastic lubricant film profile (m) |
| Minimum clearance (m) | |
| Local gap along conjunction (m) | |
| m | Pressure coefficient of boundary shear strength (−) |
| Slope of the logarithmic linear relationship between the lubricant (−) | |
| Dynamic viscosity and temperature (−) | |
| Interception of the logarithmic linear relationship between | |
| The lubricant dynamic viscosity and temperature (−) | |
| P | Non-dimensional hydrodynamic pressure (−) |
| Asperity interacting pressure (Pa) | |
| Hydrodynamic pressure (Pa) | |
| Maximum Hertzian pressure (Pa) | |
| R | Pin curvature radius (m) |
| T | Temperature (°C) |
| t | Time (s) |
| U | Non-dimensional average contact surface sliding speed in the x-direction (m/s) |
| Non-dimensional sliding speed parameter (−) | |
| u | Contact surface sliding speed in the x-direction (m/s) |
| Average contact surface sliding speed in the x-direction (m/s) | |
| V | Non-dimensional average contact surface sliding speed in the y-direction (m/s) |
| v | Contact surface sliding speed in the y-direction (m/s) |
| Average contact surface sliding speed in the y-direction (m/s) | |
| W | Contact load (N) |
| Reference contact load (N) | |
| Non-dimensional load parameter (−) | |
| X | Non-dimensional coordinate along the x-direction (−) |
| Coordinate along the x-direction (m) | |
| Y | Non-dimensional coordinate along the y-direction (−) |
| Coordinate along the y-direction (m) | |
| Lubricant viscosity-pressure coefficient (Pa−1) | |
| Curvature radius at the asperity peak (m) | |
| Slope of the limiting shear stress-pressure relation (−) | |
| Contact elastic deformation (m) | |
| Surface density of asperity peaks (−) | |
| Lubricant dynamic viscosity (Pa.s) | |
| Bulk lubricant dynamic viscosity at (Pa.s) | |
| Non-dimensional lubricant dynamic viscosity (−) | |
| Separation parameter (−) | |
| Poisson’s ratio (−) | |
| Lubricant density (kg/m3) | |
| Bulk lubricant density at (kg/m3) | |
| Non-dimensional lubricant density (−) | |
| Composite surface roughness (m) | |
| Boundary shear (Pa) | |
| Eyring shear stress (Pa) | |
| Viscous shear (Pa) | |
| Relaxation factor for pressure convergence loop (−) | |
| Relaxation factor for load balance loop (−) |
Appendix A
| Parameters | Non-Dimensional | Relation |
|---|---|---|
| x | X | |
| y | Y | |
| h | H | |
| p | P | |
| U | ||
| V |
Appendix B. Finite Difference Scheme
Appendix C
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pin curvature radius, R | 5 | mm |
| Wear track radius | 20 | mm |
| Young’s modulus (disk) | 210.0 | GPa |
| Young’s modulus (pin) | 110.0 | GPa |
| Poisson’s ratio (disk) | 0.27 | - |
| Poisson’s ratio (pin) | 0.21 | - |
| Eyring shear stress | 2 | MPa |
Appendix D
| Lubricant Type | Tsupply (°C) | (-) | m (-) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAE5W40 | 35 | 0.048 | 0.107 |
| SAE10W40 | 30 | 0.043 | 0.106 |
| SAE15W40 | 23 | 0.051 | 0.115 |
References
- U.S. Energy Information Administration. International Energy Outlook 2017. 2017. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/outlooks (accessed on 19 June 2018).
- Chong, W.W.F.; Ng, J.-H.; Rajoo, S.; Chong, C.T. Passenger transportation sector gasoline consumption due to friction in Southeast Asian countries. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 158, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, K.; Andersson, P.; Erdemir, A. Global energy consumption due to friction in passenger cars. Tribol. Int. 2012, 47, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stribeck, R. Die wesentlichen eigenschaften der gleit-und rollenlager. Z. Ver. Deutsch. Ing. 1902, 46, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar]
- Hersey, M.D. The laws of lubrication of horizontal journal bearings. J. Wash. Acad. Sci. 1914, 4, 542–552. [Google Scholar]
- LaFountain, A.R.; Johnston, G.J.; Spikes, H.A. The elastohydrodynamic traction of synthetic base oil blends. Tribol. Trans. 2001, 44, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-Z.; Wang, S.; Shi, F.; Wang, Y.-C.; Chen, H.-B.; Wang, H.; Hu, Y.-Z. Simulations and measurements of sliding friction between rough surfaces in point contacts: From ehl to boundary lubrication. J. Tribol. 2007, 129, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalchenko, A.M.; Erdemir, A.; Ajayi, O.O.; Etsion, I. Tribological behavior of oil-lubricated laser textured steel surfaces in conformal flat and non-conformal contacts. Mater. Perform. Charact. 2017, 6, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Zhu, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.J. Experimental and numerical investigations of the stribeck curves for lubricated counterformal contacts. J. Tribol. 2017, 139, 021505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maru, M.M.; Trommer, R.M.; Cavalcanti, K.F.; Figueiredo, E.S.; Silva, R.F.; Achete, C.A. The stribeck curve as a suitable characterization method of the lubricity of biodiesel and diesel blends. Energy 2014, 69, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, S.H.; Chong, W.W.F.; Ng, J.-H.; Ghazali, M.J.G.; Wood, R.J.K. Influence of fatty acid methyl ester composition on tribological properties of vegetable oils and duck fat derived biodiesel. Tribol. Int. 2017, 113, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patir, N.; Cheng, H.S. An average flow model for determining effects of three-dimensional roughness on partial hydrodynamic lubrication. J. Lubr. Technol. 1978, 100, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Cheng, H.S.; Hamrock, B.J. Effect of surface roughness on pressure spike and film constriction in elastohydrodynamically lubricated line contacts. Tribol. Trans. 1990, 33, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salant, R.F. An average flow model of rough surface lubrication with inter-asperity cavitation. J. Tribol. 2001, 123, 134–143. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, N.; Rahmani, R.; Rahnejat, H.; King, P.D.; Fitzsimons, B. Tribology of piston compression ring conjunction under transient thermal mixed regime of lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2013, 59, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kraker, A.; van Ostayen, R.A.J.; Rixen, D.J. Development of a texture averaged reynolds equation. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 2100–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hua, M.; Dong, G.; Zhang, D.; Chin, K. A mixed lubrication model for studying tribological behaviors of surface texturing. Tribol. Int. 2016, 93, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, N.; Rahmani, R.; Rahnejat, H.; King, P.D.; Howell-Smith, S. A numerical model to study the role of surface textures at top dead center reversal in the piston ring to cylinder liner contact. J. Tribol. 2016, 138, 021703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venner, C.H.; Napel, W.E.T. Surface roughness effects in an ehl line contact. J. Tribol. 1992, 114, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-Z.; Zhu, D. A full numerical solution to the mixed lubrication in point contacts. J. Tribol. 2000, 122, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.J. On the stribeck curves for lubricated counterformal contacts of rough surfaces. J. Tribol. 2015, 137, 021501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, A.; Tien, C.L. Fractal characterization and simulation of rough surfaces. Wear 1990, 136, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.L.; Greenwood, J.A.; Poon, S.Y. A simple theory of asperity contact in elastohydro-dynamic lubrication. Wear 1972, 19, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelinck, E.R.M.; Schipper, D.J. Calculation of stribeck curves for line contacts. Tribol. Int. 2000, 33, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.A.; Williamson, J.B.P. Contact of nominally flat surfaces. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phy. 1966, 295, 300–319. [Google Scholar]
- Popovici, R.I.; Schipper, D.J. Stribeck and traction curves for elliptical contacts: Isothermal friction model. Int. J. Sust Constr. Des. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Friction prediction of rolling-sliding contact in mixed ehl. Measurement 2017, 100, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijesh, K.P.; Khonsari, M.M. On the degradation of tribo-components in boundary and mixed lubrication regimes. Tribol. Lett. 2019, 67, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodorescu, M.; Kushwaha, M.; Rahnejat, H.; Rothberg, S.J. Multi-physics analysis of valve train systems: From system level to microscale interactions. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part K 2007, 221, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.A.; Tripp, J.H. The contact of two nominally flat rough surfaces. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1970, 185, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, W.W.F.; Teodorescu, M.; Vaughan, N.D. Cavitation induced starvation for piston-ring/liner tribological conjunction. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavos, A.; Nikolakopoulos, P.G. Tribology of new thin compression ring of fired engine under controlled conditions-a combined experimental and numerical study. Tribol. Int. 2018, 128, 214–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz, M.; Chong, W.W.F.; Teodorescu, M.; Theodossiades, S.; Rahnejat, H. Transient mixed thermo-elastohydrodynamic lubrication in multi-speed transmissions. Tribol. Int. 2012, 49, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, W.W.F.; de la Cruz, M. Elastoplastic contact of rough surfaces: A line contact model for boundary regime of lubrication. Meccanica 2014, 49, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.I. Lubrication, Tribology & Motorsport; Technical Report, SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Barus, C. Art. x.-isothermals, isopiestics and isometrics relative to viscosity. Am. J. Sci. 1893, 45, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelands, C.J.A.; Vlugter, J.C.; Waterman, H.I. The viscosity-temperature-pressure relationship of lubricating oils and its correlation with chemical constitution. J. Basic Eng. 1963, 85, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appeldoorn, J.K. A Simplified Viscosity-Pressure-Temperature Equation; Technical Report, SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Yasutomi, S.; Bair, S.; Winer, W.O. An application of a free volume model to lubricant rheology i—Dependence of viscosity on temperature and pressure. J. Tribol. 1984, 106, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.S.; Klaus, E.E.; Duda, J.L. Development of a method for the prediction of pressure-viscosity coefficients of lubricating oils based on free-volume theory. J. Tribol. 1989, 111, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bair, S.; Kottke, P. Pressure-viscosity relationships for elastohydrodynamics. Tribol. Trans. 2003, 46, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bair, S.; Yamaguchi, T. The equation of state and the temperature, pressure, and shear dependence of viscosity for a highly viscous reference liquid, dipentaerythritol hexaisononanoate. J. Tribol. 2017, 139, 011801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bair, S. A critical evaluation of film thickness-derived pressure–viscosity coefficients. Lubr. Sci. 2015, 27, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khonsari, M.M.; Hua, D.Y. Generalized non-newtonian elastohydrodynamic lubrication. Tribol. Int. 1993, 26, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bair, S.; Winer, W.O. A rheological model for elastohydrodynamic contacts based on primary laboratory data. J. Lubr. Technol. 1979, 101, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khonsari, M.M.; Hua, D.Y. Thermal elastohydrodynamic analysis using a generalized non-newtonian formulation with application to bair-winer constitutive equation. J. Tribol. 1994, 116, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masjedi, M.; Khonsari, M.M. Theoretical and experimental investigation of traction coefficient in line-contact ehl of rough surfaces. Tribol. Int. 2014, 70, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.L. Contact Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Gohar, R.; Rahnejat, H. Fundamentals of Tribology; World Scientific Publishing Company: Singapore, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, O. IV. On the theory of lubrication and its application to mr. beauchamp tower’s experiments, including an experimental determination of the viscosity of olive oil. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1886, 177, 157–234. [Google Scholar]
- Swift, H.W. The stability of lubricating films in journal bearings. (includes appendix). In Minutes of the Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers; Thomas Telford-ICE Virtual Library: London, UK, 1932; Volume 233, pp. 267–288. [Google Scholar]
- Stieber, W. Hydrodynamische Theorie des Gleitlagers das Schwimmlager; VDI: Berlin, Germany, 1933. [Google Scholar]
- Dowson, D.; Higginson, G.R. Elasto-Hydrodynamic Lubrication: The Fundamentals of Roller And Gear Lubrication; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1966; Volume 23. [Google Scholar]
- Teodorescu, M.; Taraza, D.; Henein, N.A.; Bryzik, W. Simplified Elasto-Hydrodynamic Friction Model of the Cam-Tappet Contact; Technical report, SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jalali-Vahid, D.; Rahnejat, H.; Jin, Z.M. Elastohydrodynamic solution for concentrated elliptical point contact of machine elements under combined entraining and squeeze-film motion. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. J. 1998, 212, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimble, D.W.; Theodossiades, S.; Rahnejat, H.; Wilby, M. Thin film tribology of pharmaceutical elastomeric seals. Appl. Math. Model 2013, 37, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höglund, E. Influence of lubricant properties on elastohydrodynamic lubrication. Wear 1999, 232, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgado, P.L.; Otero, J.E.; Lejarraga, J.B.S.; Sanz, J.L.M.; Lantada, A.D.; Munoz-Guijosa, J.M.; Yustos, H.L.; Wiña, L.; García, J.M. Models for predicting friction coefficient and parameters with influence in elastohydrodynamic lubrication. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. J. 2009, 223, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, E.-H.; Ma, B.; Li, H.-Y. Numerical and experimental studies on tribological behaviors of cu-based friction pairs from hydrodynamic to boundary lubrication. Tribol. Trans. 2018, 61, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.L.; Green, I. On the modeling of elastic contact between rough surfaces. Tribol. Trans. 2011, 54, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahanian, M.; Hamrock, B.J. Fluid-film lubrication regimes revisited. Tribol. Trans. 1991, 34, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrock, B.J.; Schmid, S.R.; Jacobson, B.O. Fundamentals of Fluid Film Lubrication; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ståhl, J.; Jacobson, B.O. A non-newtonian model based on limiting shear stress and slip planes—Parametric studies. Tribol. Int. 2003, 36, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
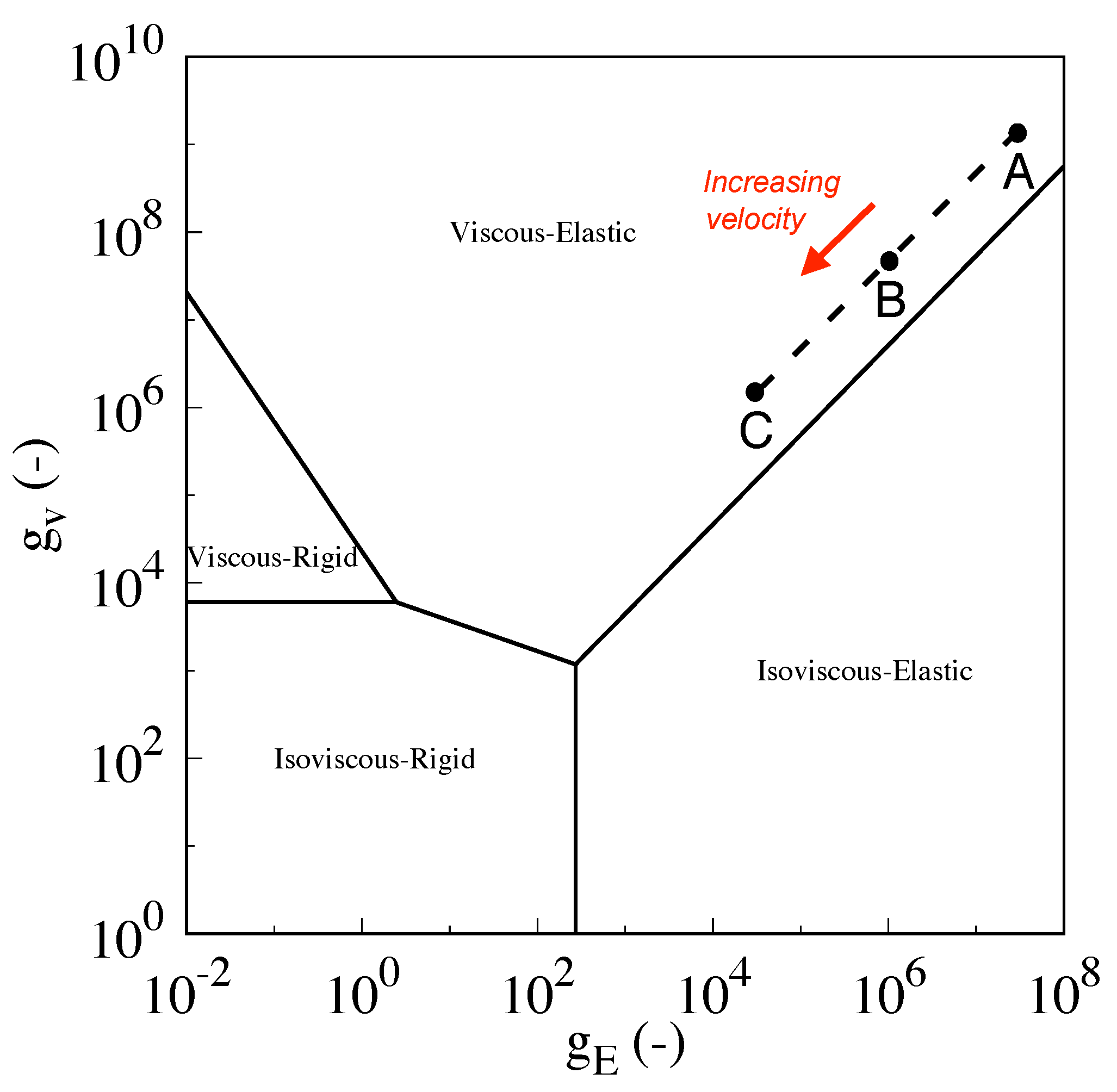
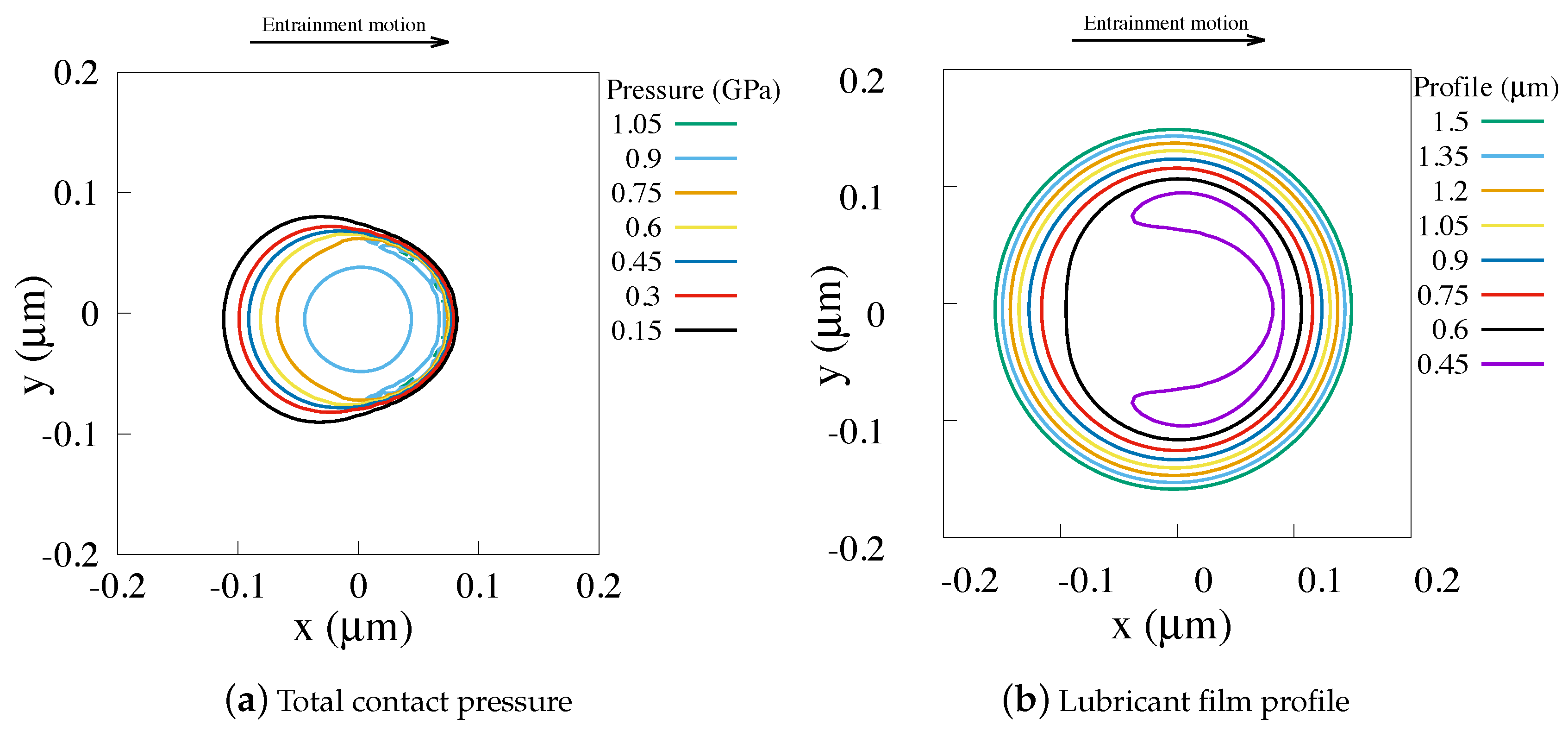
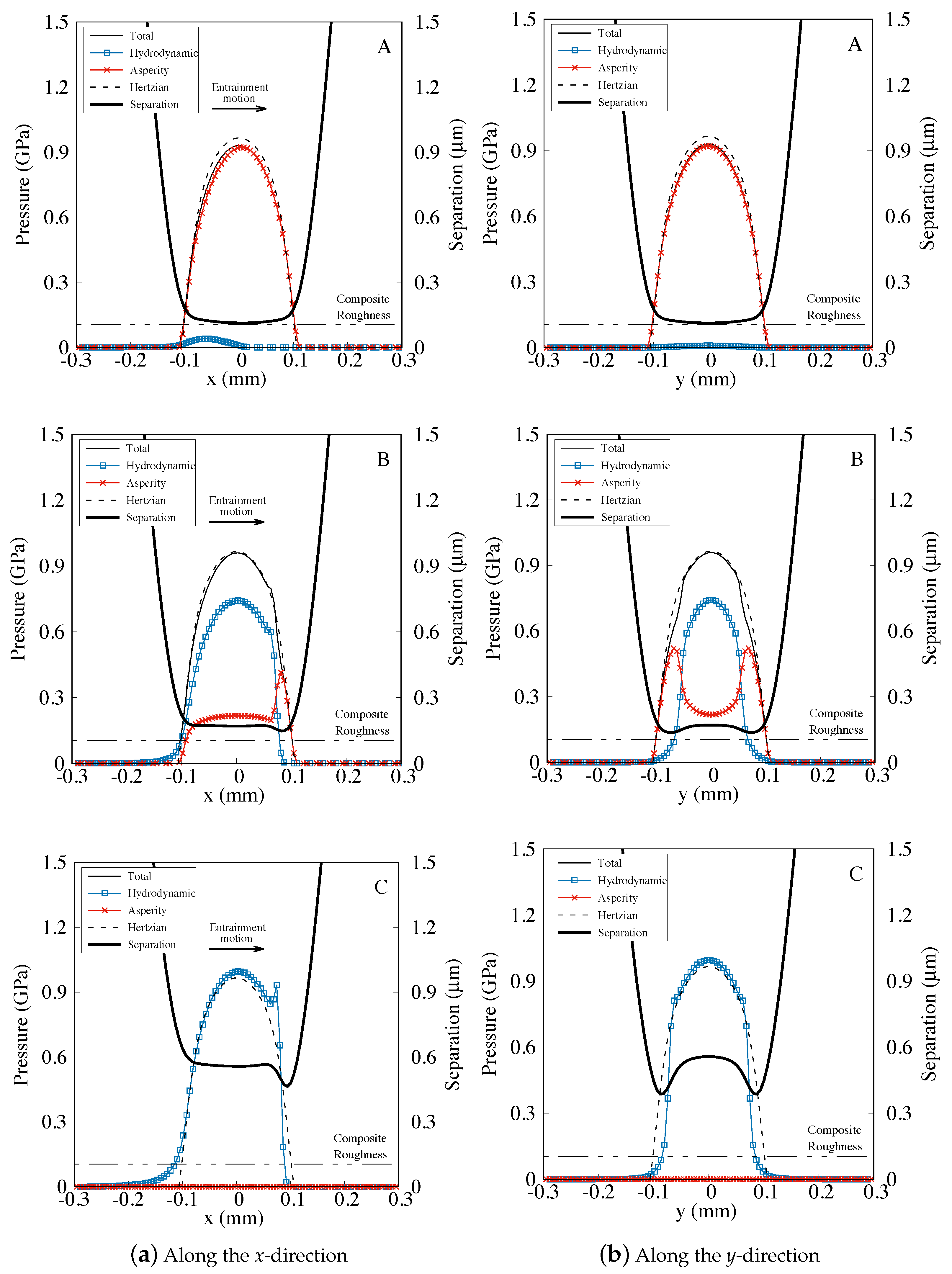
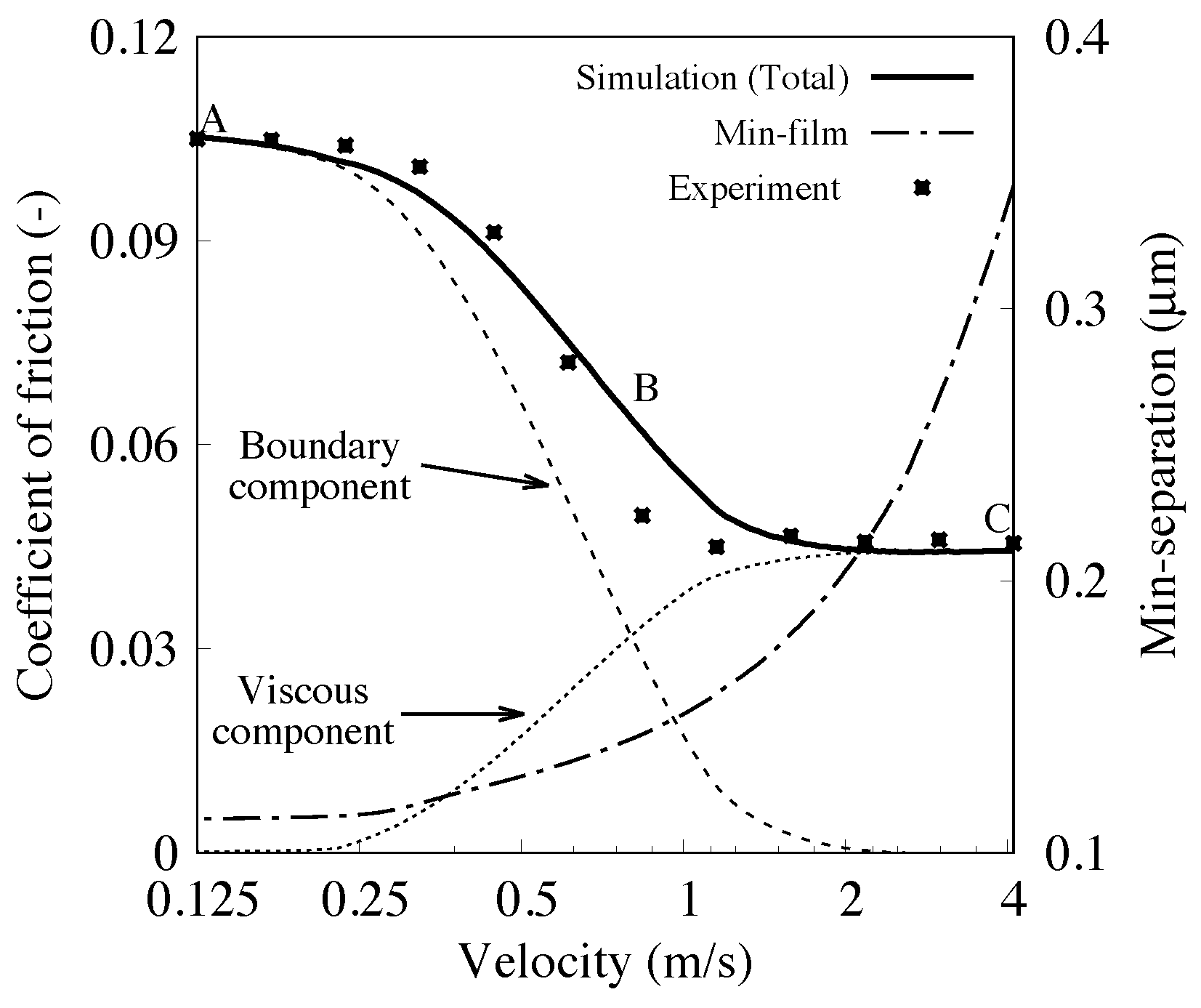
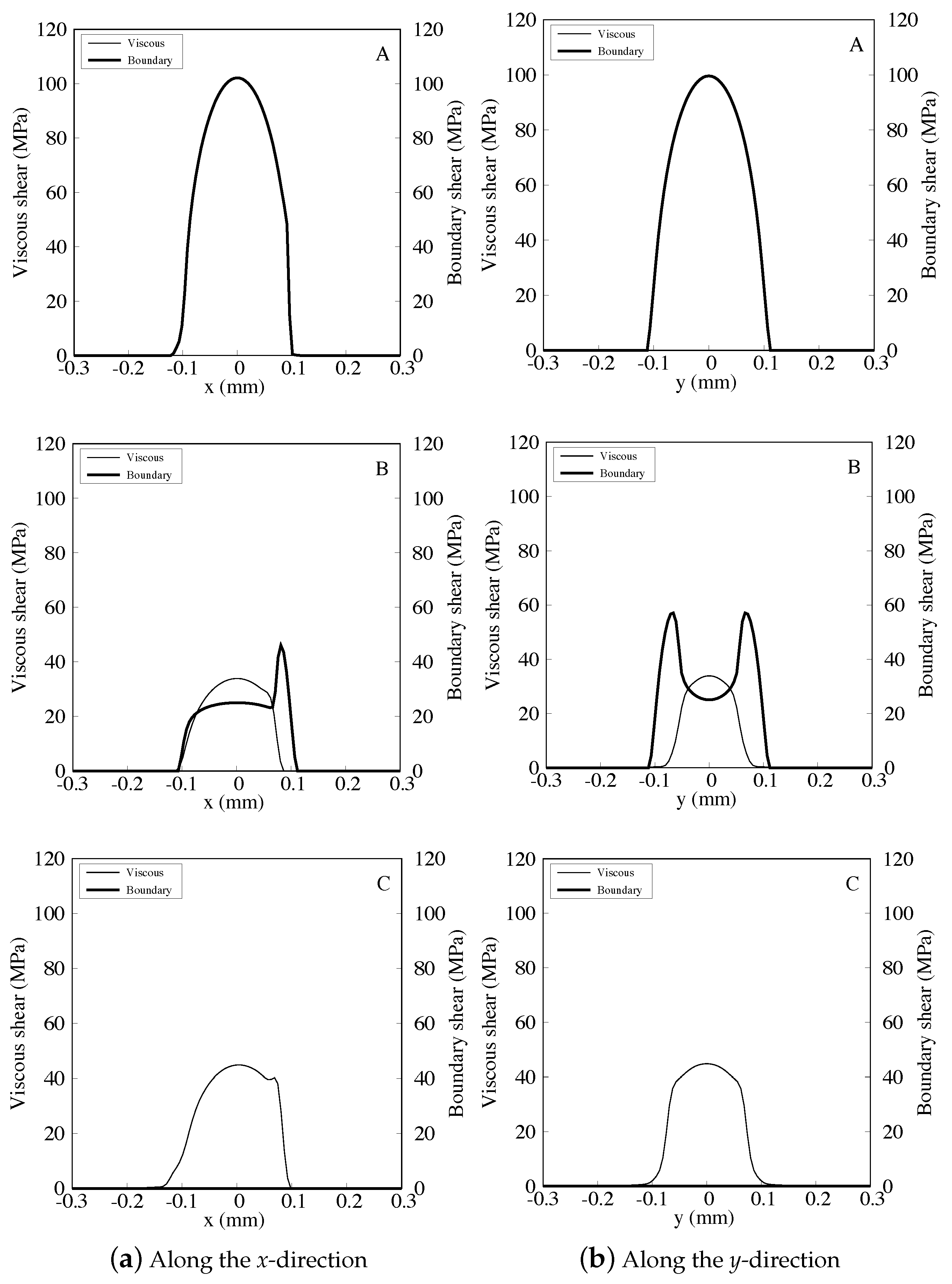
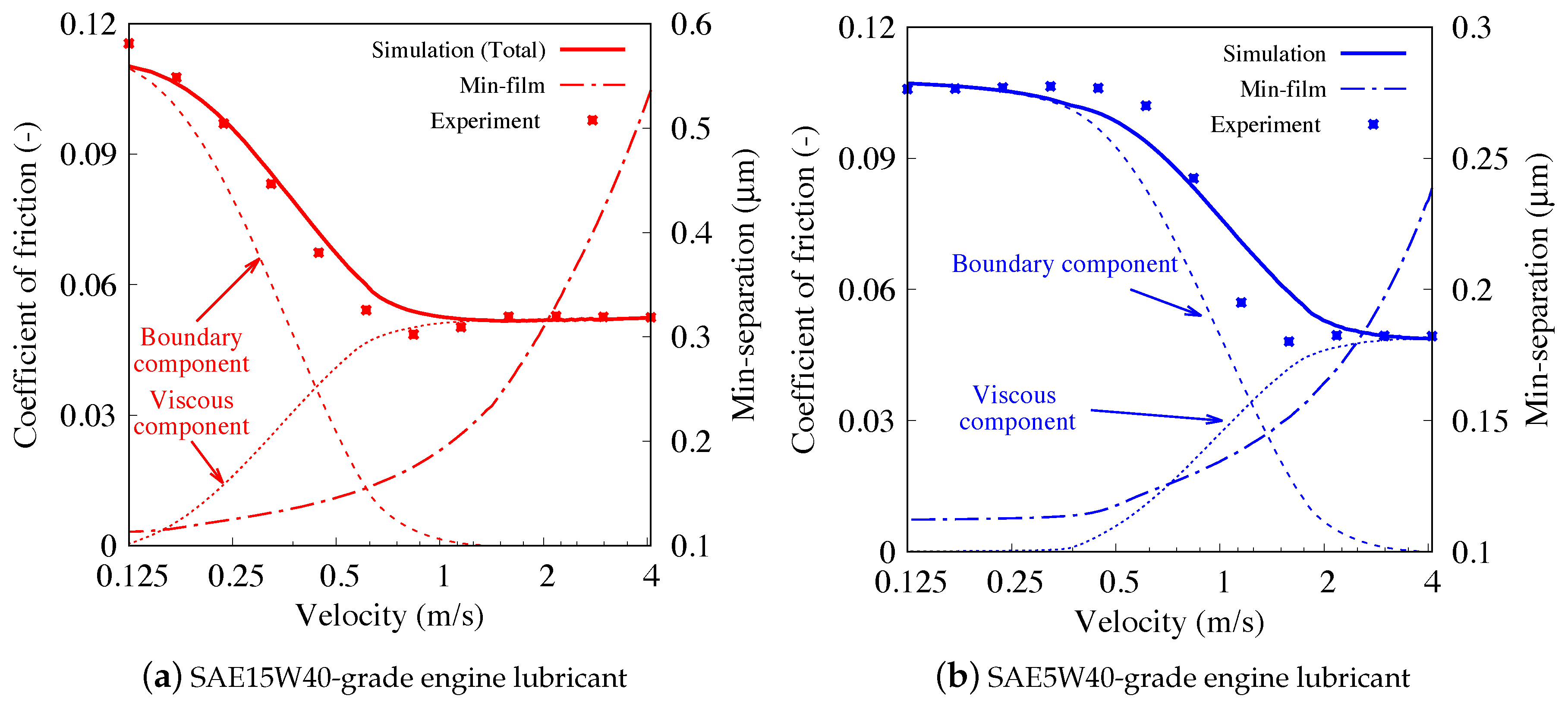
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Composite surface roughness, | 0.105 | μm |
| 0.4 | - | |
| 0.055 | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chong, W.W.F.; Hamdan, S.H.; Wong, K.J.; Yusup, S. Modelling Transitions in Regimes of Lubrication for Rough Surface Contact. Lubricants 2019, 7, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7090077
Chong WWF, Hamdan SH, Wong KJ, Yusup S. Modelling Transitions in Regimes of Lubrication for Rough Surface Contact. Lubricants. 2019; 7(9):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7090077
Chicago/Turabian StyleChong, William Woei Fong, Siti Hartini Hamdan, King Jye Wong, and Suzana Yusup. 2019. "Modelling Transitions in Regimes of Lubrication for Rough Surface Contact" Lubricants 7, no. 9: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7090077
APA StyleChong, W. W. F., Hamdan, S. H., Wong, K. J., & Yusup, S. (2019). Modelling Transitions in Regimes of Lubrication for Rough Surface Contact. Lubricants, 7(9), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7090077






