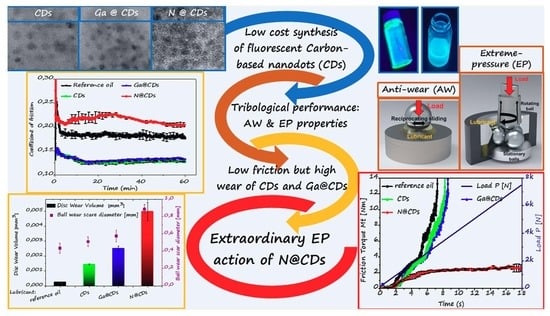
Tribological Anti-Wear and Extreme-Pressure Performance of Multifunctional Metal and Nonmetal Doped C-based Nanodots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization CDs, Ga@CDs, and N@CDs
2.3. Tribological Materials and Methods Selected for Testing CDs, Ga@CDs, and N@CDs
3. Results and Discussion
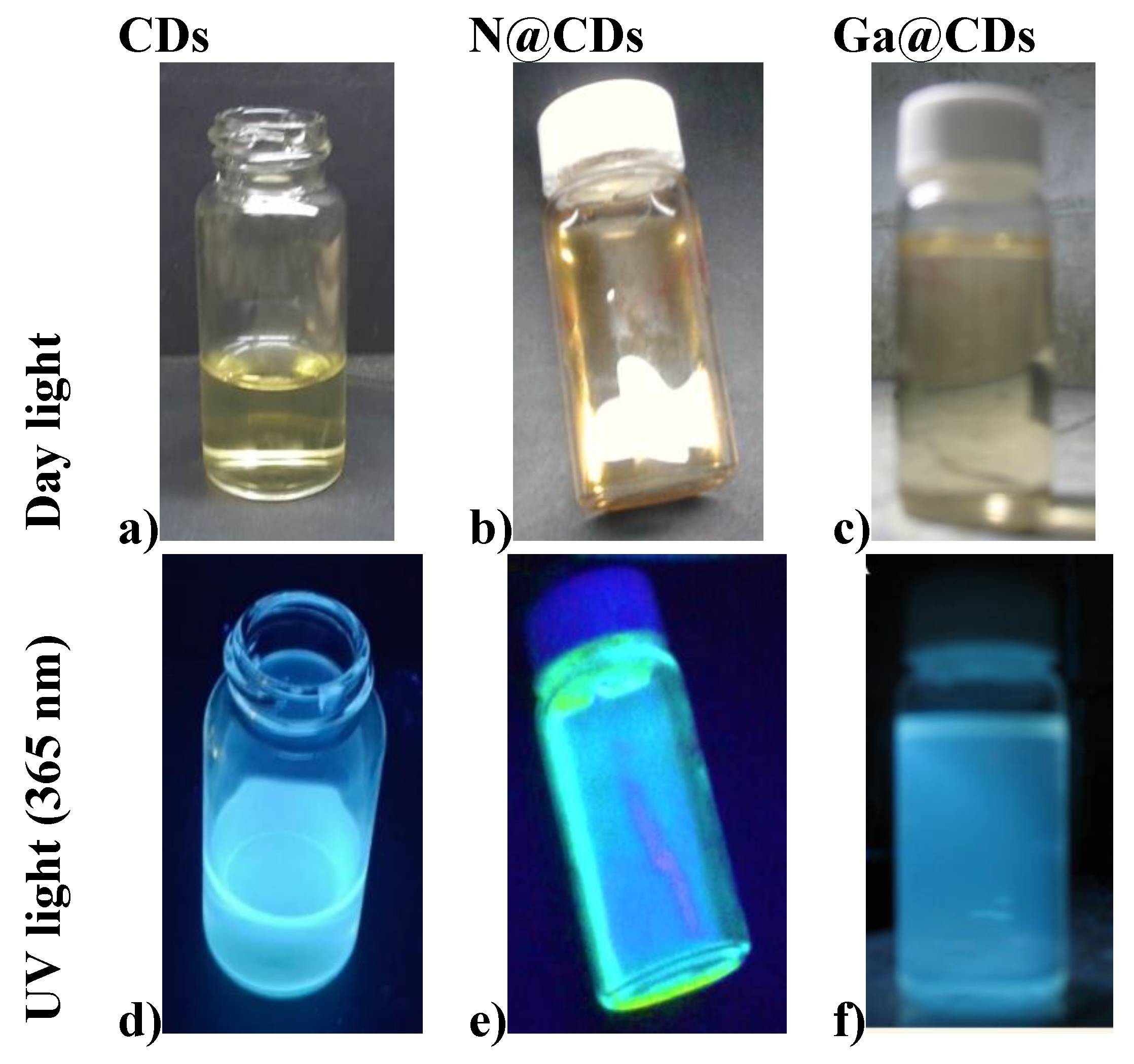
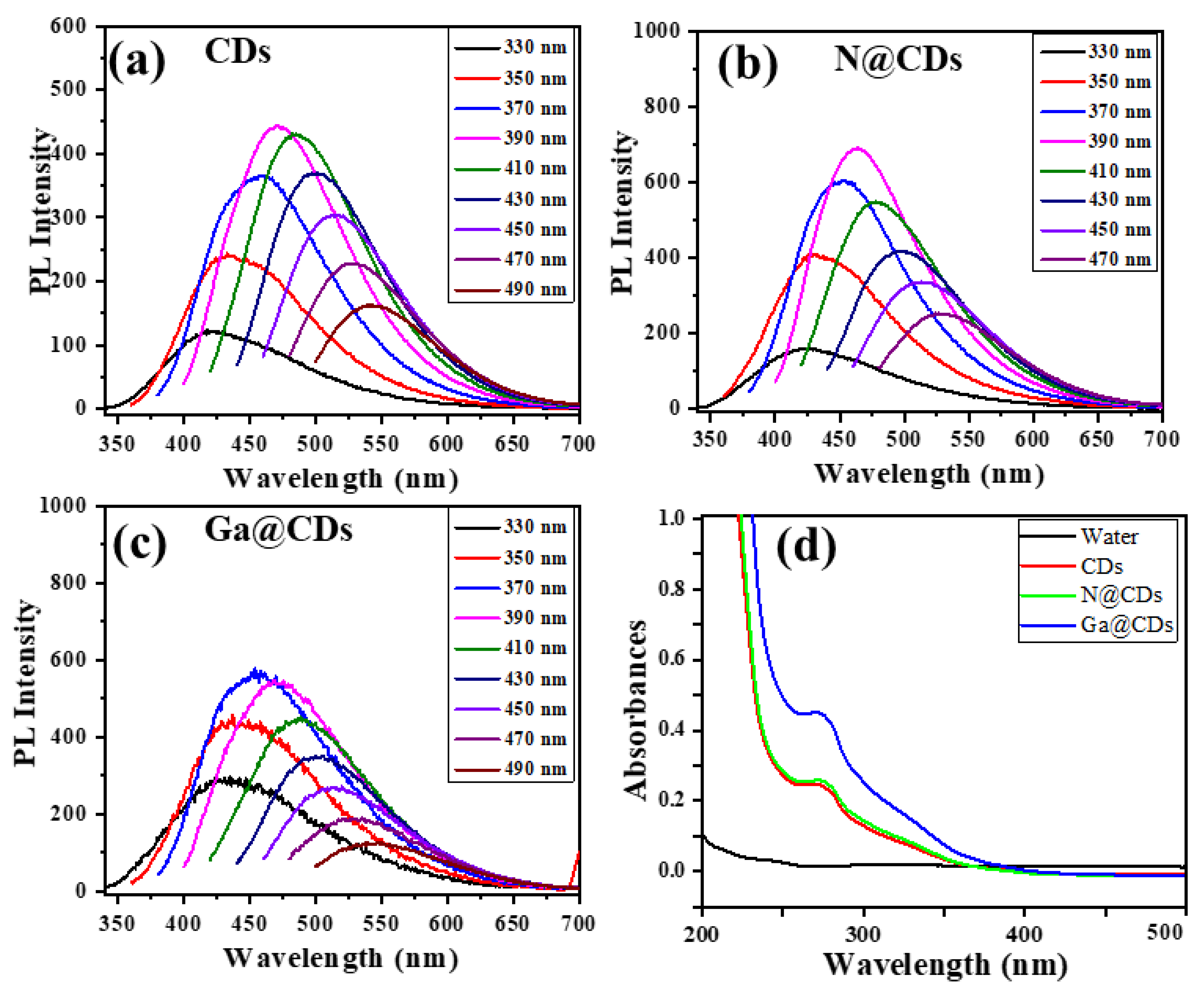
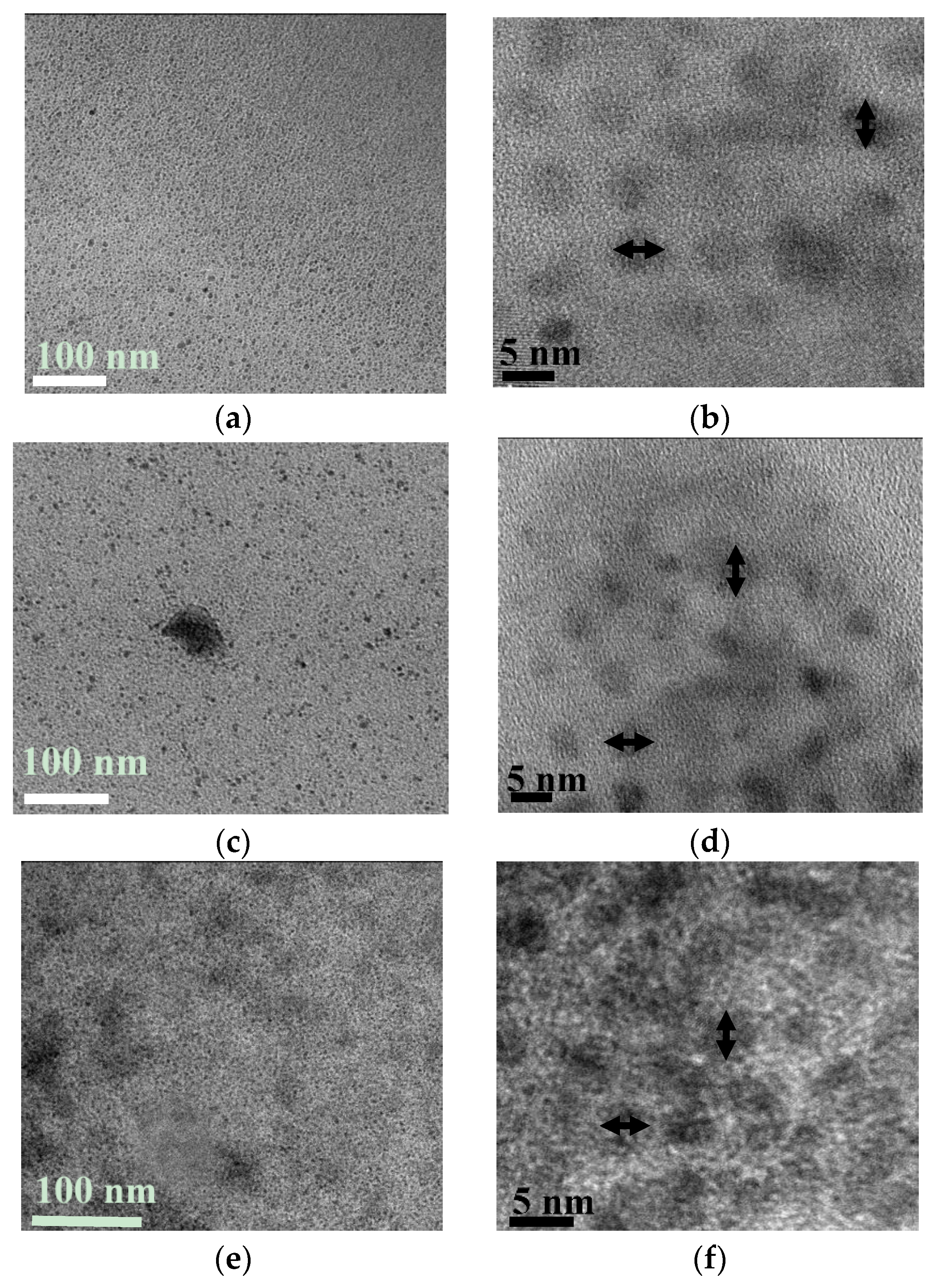
3.1. Characterization of CDs, N@CDs and Ga@CDs
3.2. Tribological Performance of CDs, N@CDs, and Ga@CDs
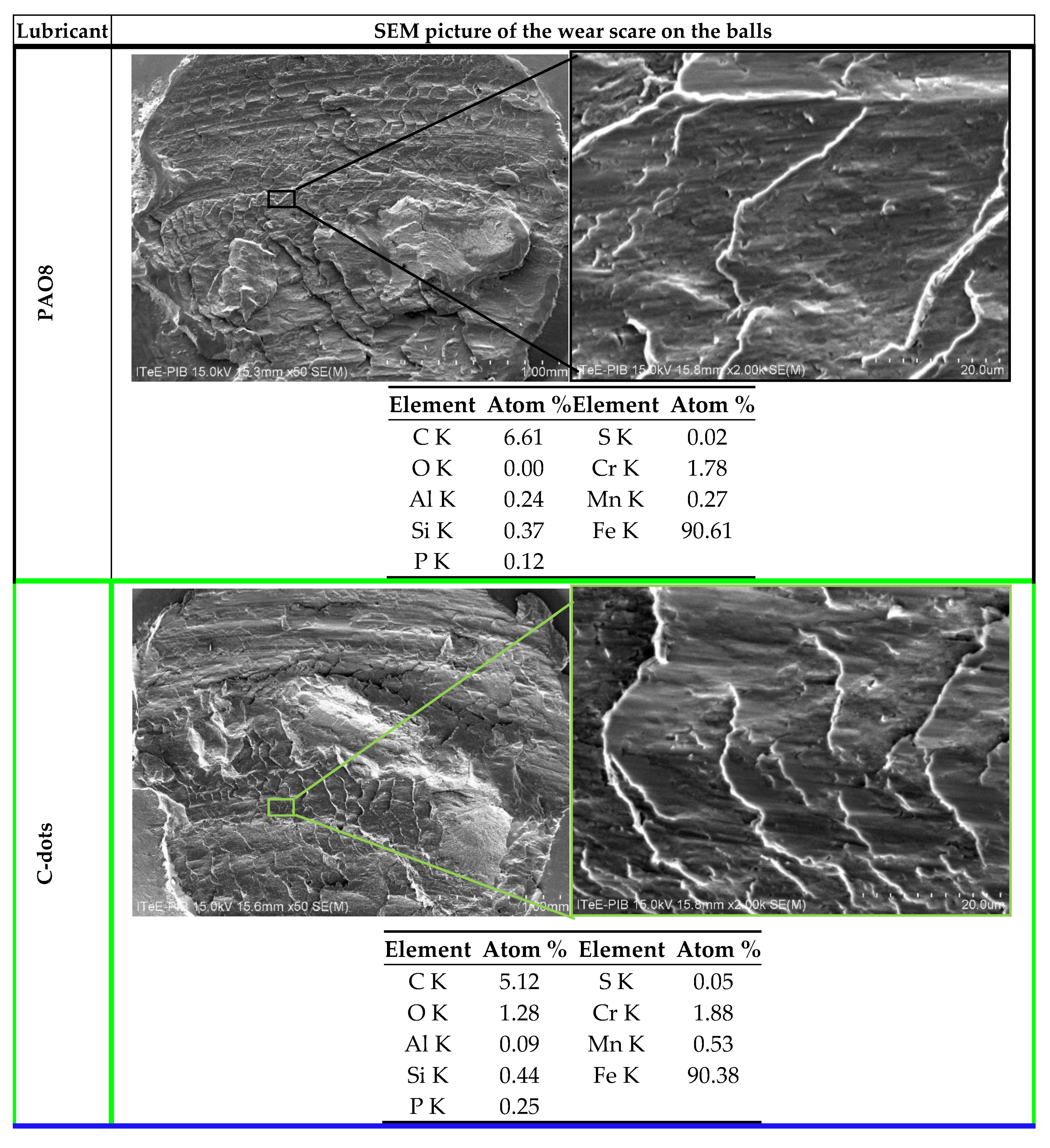
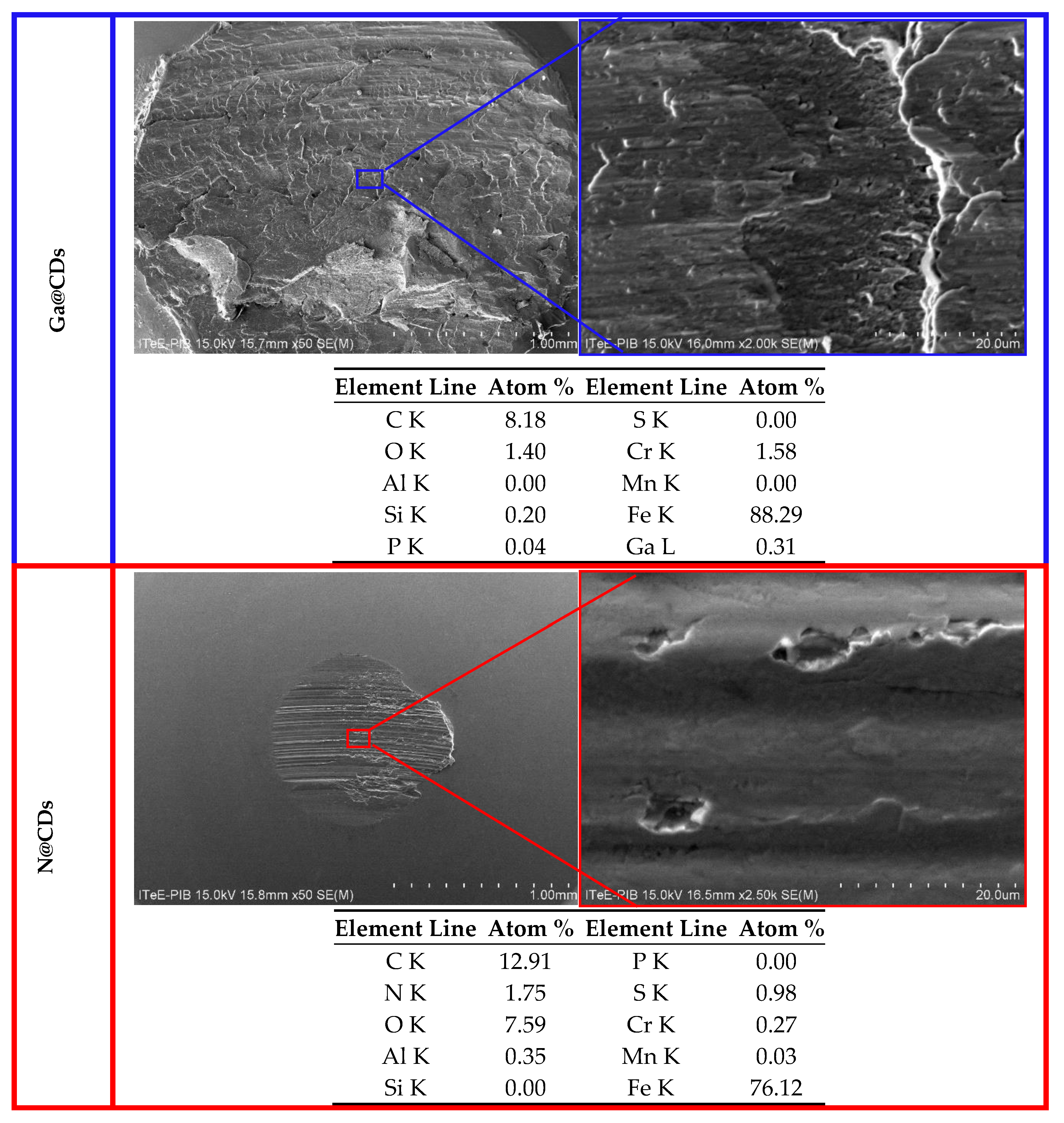
3.2.1. Anti-Wear (AW) Properties According to SRV Linear Oscillation Test Method
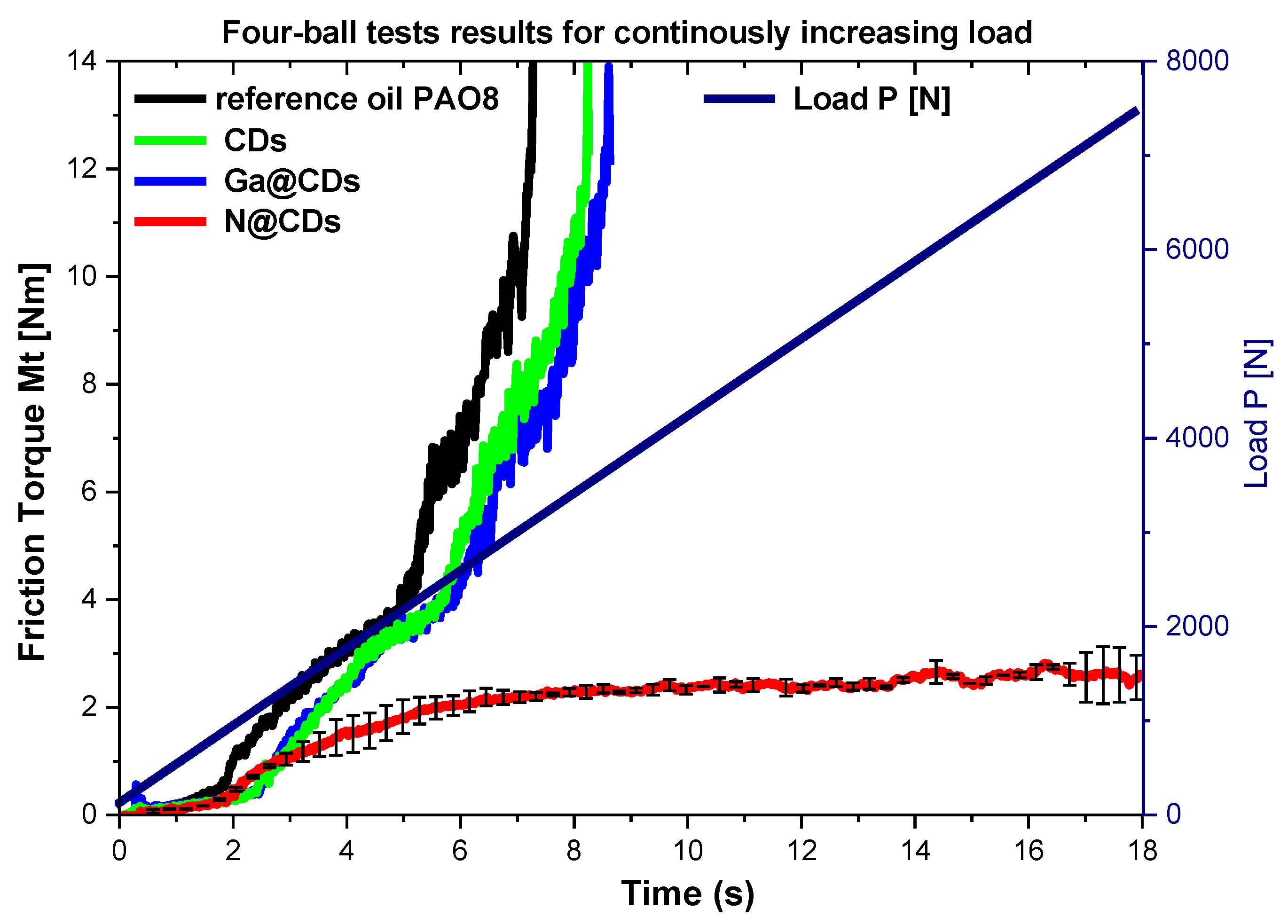
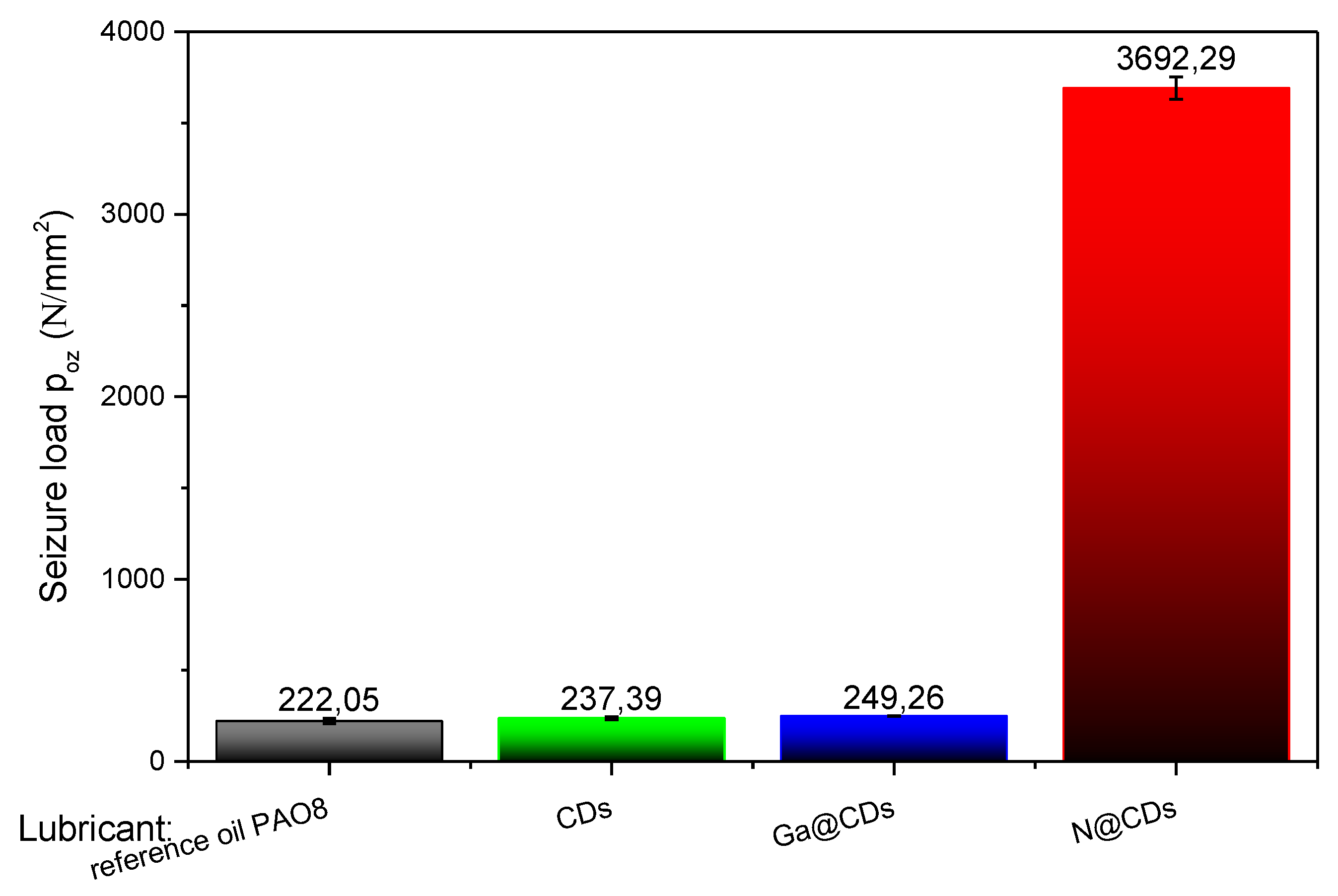
3.2.2. Extreme Pressure (EP) Properties According to T-02 Four-Ball Tester
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding

Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDs | carbon-dots |
| N@CDs | nitrogen-doped carbon-dots |
| Ga@CDs | gallium-doped carbon-dots |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| FWHM | full-width at half-maximum |
| HR-TEM | high-resolution transmission electron microscope |
| SRV | linear oscillation test machine |
| T-02 | four ball tester |
| CoF | coefficient of friction |
| AW | anti-wear |
| EP | extreme pressure |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| EDX | Energy Dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
References
- Jariwala, D.; Sangwan, V.K.; Lauhon, L.J.; Marks, T.J.; Hersam, M.C. Carbon Nanomaterials for Electronics, Optoelectronics, Photovoltaics, and Sensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2824–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.B.; Porat, Z.; Gedanken, A. Facile One-Step Sonochemical Synthesis of Ultrafine and Stable Fluorescent C-Dots. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 28, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.B.; Sahu, A.K.; Mohsin, A.S.M.; Li, X.; Gedanken, A. Refractive-Index Tuning of Highly Fluorescent Carbon Dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28930–28938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangy, A.; Kumar, V.B.; Pulidindi, I.N.; Kinel-Tahan, Y.; Yehoshua, Y.; Gedanken, A. In-Situ Transesterification of Chlorella Vulgaris Using Carbon-Dot Functionalized Strontium Oxide as a Heterogeneous Catalyst under Microwave Irradiation. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 10602–10610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himaja, A.L.; Karthik, P.S.; Singh, S.P. Carbon Dots: The Newest Member of the Carbon Nanomaterials Family. Chem. Rec. 2015, 15, 595–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Li, X.; Ma, H. A Tunable Ratiometric Ph Sensor Based on Carbon Nanodots for the Quantitative Measurement of the Intracellular PH of Whole Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6432–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Gao, Z.; Gao, G.; Wo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, G.; Cui, D. Systematic Safety Evaluation on Photoluminescent Carbon Dots. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.T.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Lu, F.; Luo, P.G.; Cao, L.; Meziani, M.J.; Liu, J.H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; et al. Carbon Dots as Nontoxic and High-Performance Fluorescence Imaging Agents. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 18110–18114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, L.; Chusuei, C.C.; Suarez, V.M.; Blackwelder, P.L.; Micic, M.; Orbulescu, J.; Leblanc, R.M. Nontoxic Carbon Dots Potently Inhibit Human Insulin Fibrillation. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 1764–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissan, I.; Kumar, V.B.; Porat, Z.; Makovec, D.; Shefi, O.; Gedanken, A. Sonochemically-Fabricated Ga@C-Dots@Ga Nanoparticle-Aided Neural Growth. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.B.; Natan, M.; Jacobi, G.; Porat, Z.; Banin, E. Ga@C-Dots as an Antibacterial Agent for the Eradication of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 400, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomala, A.; Vengudusamy, B.; Rodríguez Ripoll, M.; Naveira Suarez, A.; Remškar, M.; Rosentsveig, R. Interaction Between Selected MoS2 Nanoparticles and ZDDP Tribofilms. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 59, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveira-Suarez, A.; Tomala, A.; Pasaribu, R.; Larsson, R.; Gebeshuber, I.C. Evolution of ZDDP-Derived Reaction Layer Morphology with Rubbing Time. Scanning 2010, 32, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomala, A.; Ripoll, M.R.; Gabler, C.; Remškar, M.; Kalin, M. Interactions between MoS2 nanotubes and Conventional Additives in Model Oils. Tribol. Int. 2017, 110, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomala, A.; Ripoll, M.R.; Kogovšek, J.; Kalin, M.; Bednarska, A.; Michalczewski, R.; Szczerek, M. Synergisms and Antagonisms between MoS2 nanotubes and Representative Oil Additives under Various Contact Conditions. Tribol. Int. 2019, 129, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Ripoll, M.; Tomala, A.; Gabler, C.; Dražić, G.; Pirker, L.; Remškar, M. In Situ Tribochemical Sulfurization of Molybdenum Oxide Nanotubes. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 3281–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Kong, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, W. Material and Optical Properties of Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots Fabricated from Lemon Juice via Hydrothermal Reaction. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Gong, Z.; Gao, K.; Qiang, L.; Zhang, J.; Yu, S. Superlubricity Achieved by Carbon Quantum Dots in Ionic Liquid. Mater. Lett. 2017, 195, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, A. Carbon Quantum Dots: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 6921–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saur, N.; Sanes, J.; Carri, F. Ionanocarbon Lubricants. The Combination of Ionic Liquids and Carbon Nanophases in Tribology. Lubricants 2017, 5, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Tang, W.; Lu, H.; Huang, Z. Ionic Liquid Capped Carbon Dots as a High-Performance Friction-Reducing and Antiwear Additive for Poly(Ethylene Glycol). J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 7257–7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, Z.; Tang, W.; Wang, B. Remarkable Lubricating Effect of Ionic Liquid Modified Carbon Dots as a Kind of Water-Based Lubricant Additives. Nano 2017, 12, 1750108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Ren, S.; Zhang, P.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Dong, G. Laser-Textured Surface Storing a Carbon Dots/Poly(Ethylene Glycol)/Chitosan Gel with Slow-Release Lubrication Effect. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 21600–21606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.B.; Perelshtein, I.; Lipovsky, A.; Porat, Z.; Gedanken, A. The Sonochemical Synthesis of Ga@C-Dots Particles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 25533–25540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.B.; Sheinberger, J.; Porat, Z.; Shav-Tal, Y.; Gedanken, A. A Hydrothermal Reaction of an Aqueous Solution of BSA Yields Highly Fluorescent N Doped C-Dots Used for Imaging of Live Mammalian Cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 2913–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piekoszewski, W.; Szczerek, M.; Tuszynski, W. The Action of Lubricants under Extreme Pressure Conditions in a Modified. Wear 2001, 249, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Parás, L.; Taha-Tijerina, J.; Garza, L.; Maldonado-Cortés, D.; Michalczewski, R.; Lapray, C. Effect of CuO and Al2O3 Nanoparticle Additives on the Tribological Behavior of Fully Formulated Oils. Wear 2015, 332–333, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.B.; Dolitzky, A.; Michaeli, S.; Gedanken, A. Antiparasitic Ointment Based on a Biocompatibile Carbon Dot Nanocomposite. ACS Appl. Nano. Mater. 2018, 1, 1784–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.; Diao, S.; Antaris, A.L.; Dai, H. Carbon Nanomaterials for Biological Imaging and Nanomedicinal Therapy. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10816–10906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yin, Y.; Jain, A.; Zhou, H.S. Aqueous Phase Synthesis of Highly Luminescent, Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots and Their Application as Bioimaging Agents. Langmuir 2014, 30, 14270–14275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
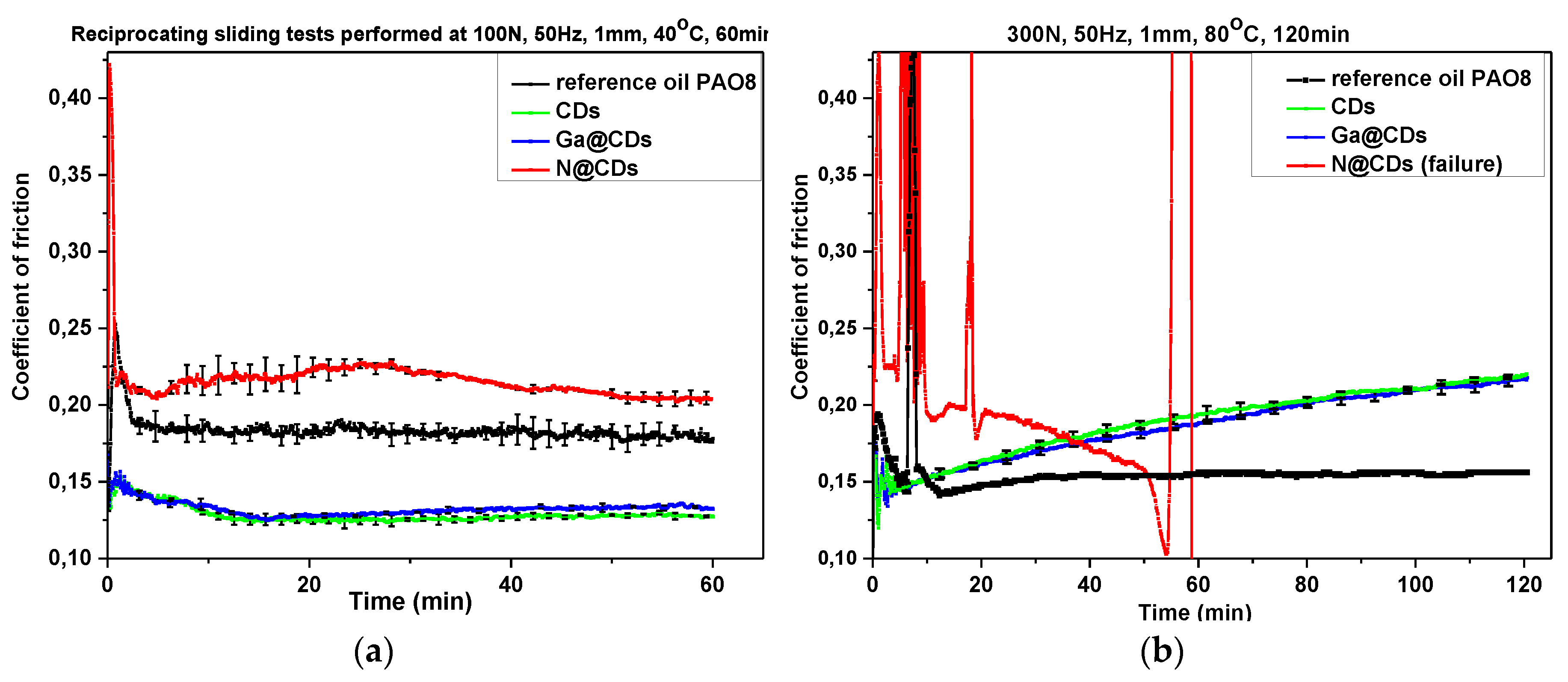
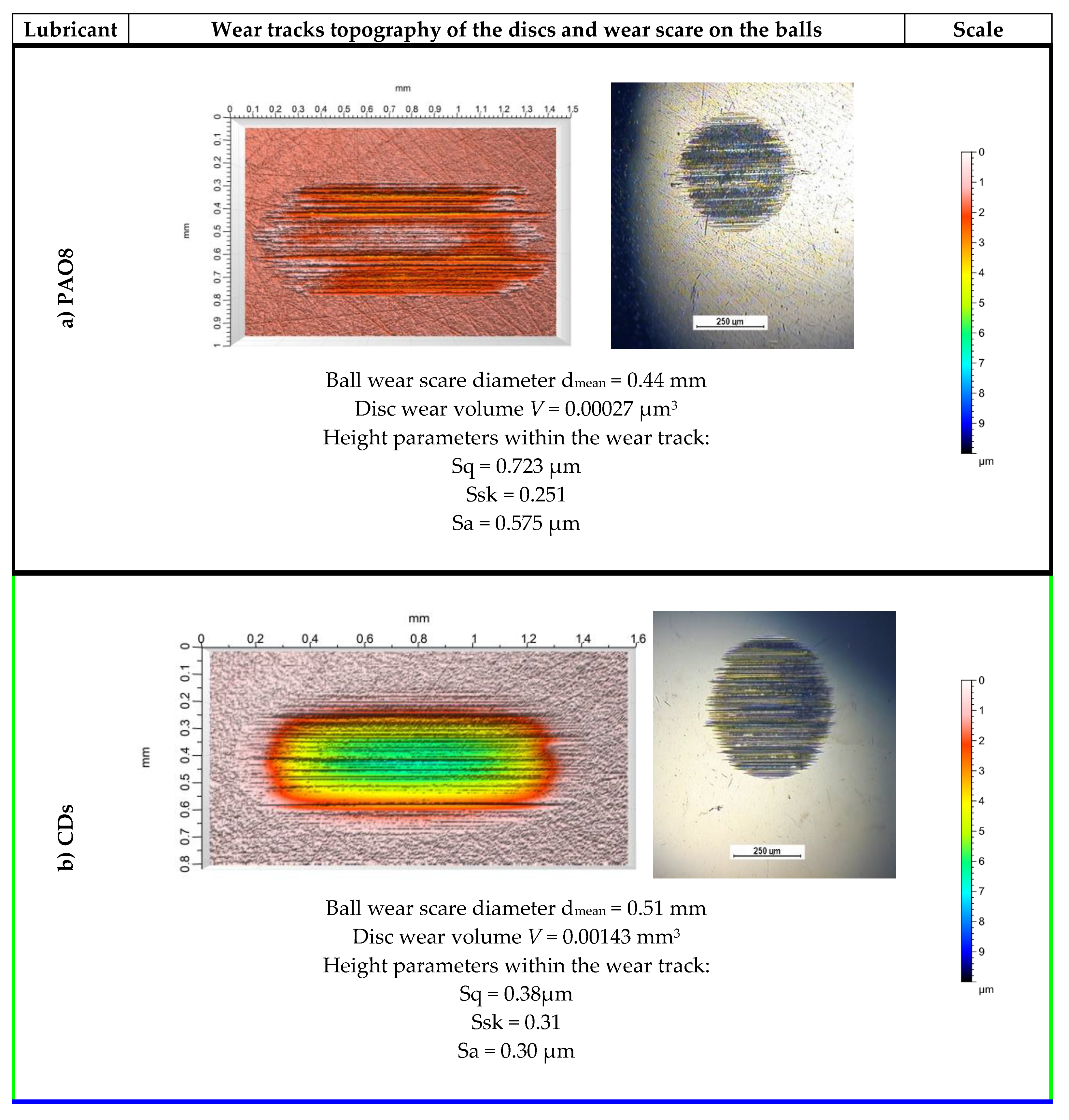
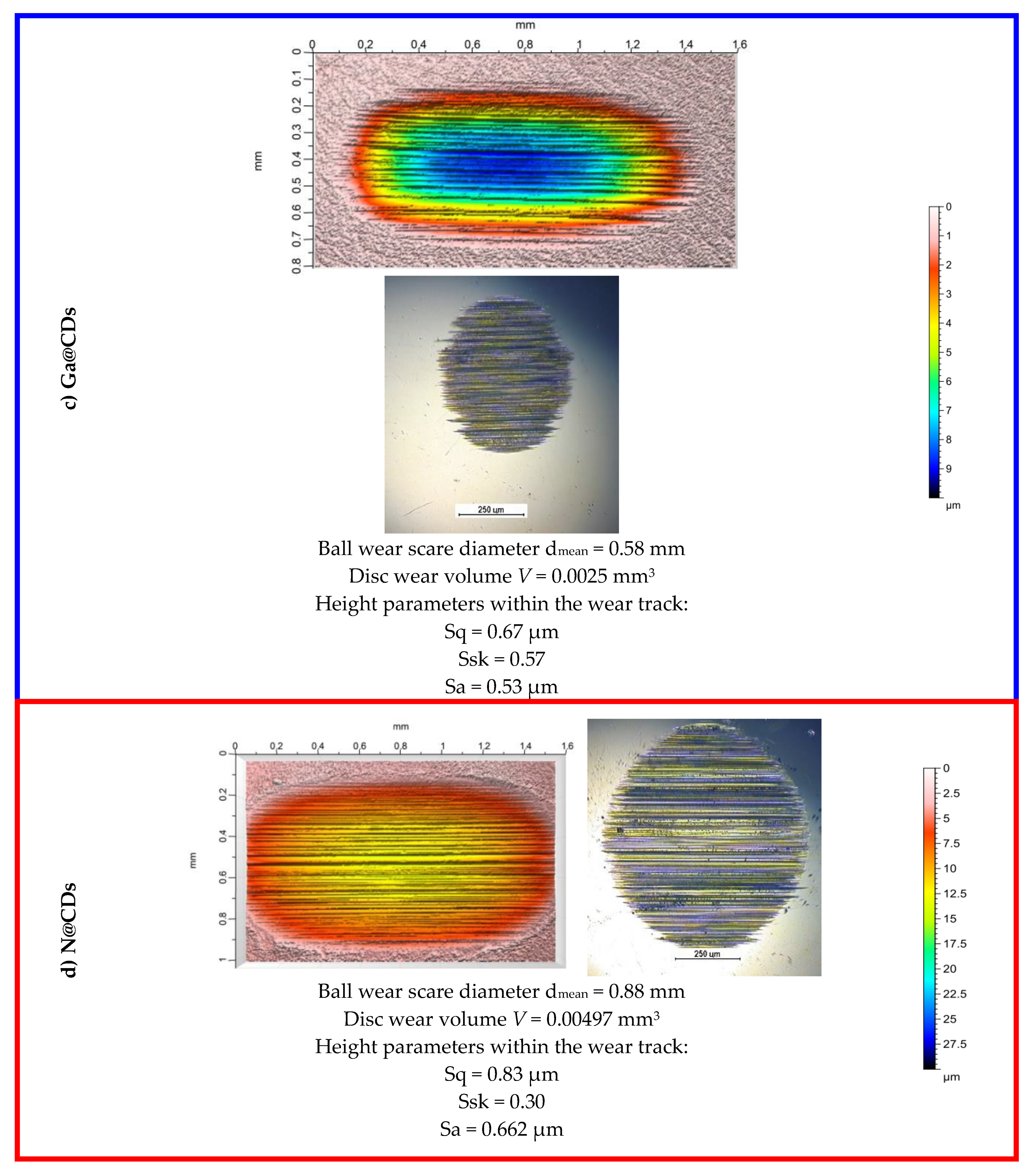
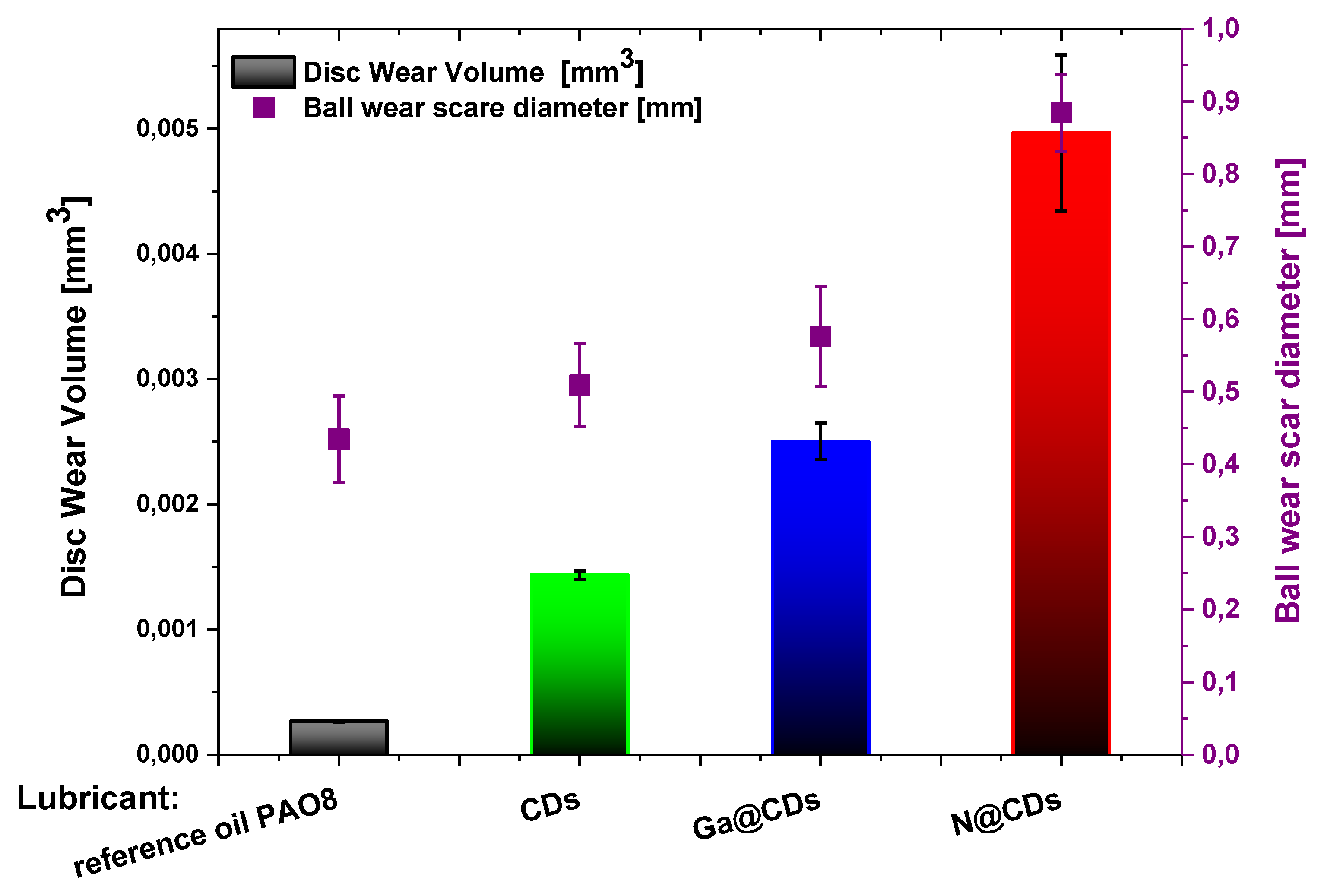
| Tribological Test Set-up | 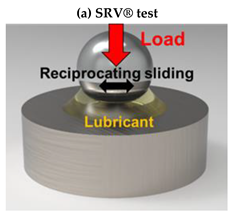 | 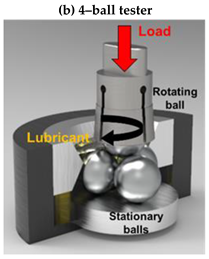 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contact Conditions | Point contact, reciprocating sliding | Point contact, rotating sliding | |
| Track Length | 1 mm | 20 mm | |
| Tested Materials | Steel–steel (100Cr6) | ||
| Speed | 0.1 m/s (50 Hz) | 500 rpm | |
| Normal Load | 300 N | 100 N | Increasing 0–7200 N |
| Mean Contact Pressure | 2.1 GPa | 1.46 GPa | Increasing 0–2.8 GPa |
| Test Duration | 120 min | 60 min | 18 sec |
| Temperature | 80 °C | 40 °C | 25 °C |
| Lubricant Blends | PAO8 reference oil, CDs, Ga@CDs, and N@CDs | ||
| Measured Parameters | The coefficient of friction, wear rate on discs and balls wear area | Friction torque, seizure load (load carrying capacity) | |
| Property Determination | Anti-wear (AW) properties | Extreme pressure (EP) properties | |
| Property: | CDs | N@CDs | Ga@CDs |
|---|---|---|---|
| QY (%) | 16 | 44 | 1.8 |
| Size (nm) | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| Doping level (ppm) | - | 13 wt % | 340 (ppm) |
| Zeta potential (mV) | −19.4 | −22.1 and +23.5 | +20.1 |
| Stability | High | High | High |
| Toxicity | Low | Low | Low |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomala, A.M.; Bhooshan Kumar, V.; Porat, Z.; Michalczewski, R.; Gedanken, A. Tribological Anti-Wear and Extreme-Pressure Performance of Multifunctional Metal and Nonmetal Doped C-based Nanodots. Lubricants 2019, 7, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7040036
Tomala AM, Bhooshan Kumar V, Porat Z, Michalczewski R, Gedanken A. Tribological Anti-Wear and Extreme-Pressure Performance of Multifunctional Metal and Nonmetal Doped C-based Nanodots. Lubricants. 2019; 7(4):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7040036
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomala, Agnieszka Maria, Vijay Bhooshan Kumar, Ze’ev Porat, Remigiusz Michalczewski, and Aharon Gedanken. 2019. "Tribological Anti-Wear and Extreme-Pressure Performance of Multifunctional Metal and Nonmetal Doped C-based Nanodots" Lubricants 7, no. 4: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7040036
APA StyleTomala, A. M., Bhooshan Kumar, V., Porat, Z., Michalczewski, R., & Gedanken, A. (2019). Tribological Anti-Wear and Extreme-Pressure Performance of Multifunctional Metal and Nonmetal Doped C-based Nanodots. Lubricants, 7(4), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7040036