Importance of Emulsification in Calibrating Infrared Spectroscopes for Analyzing Water Contamination in Used or In-Service Engine Oil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
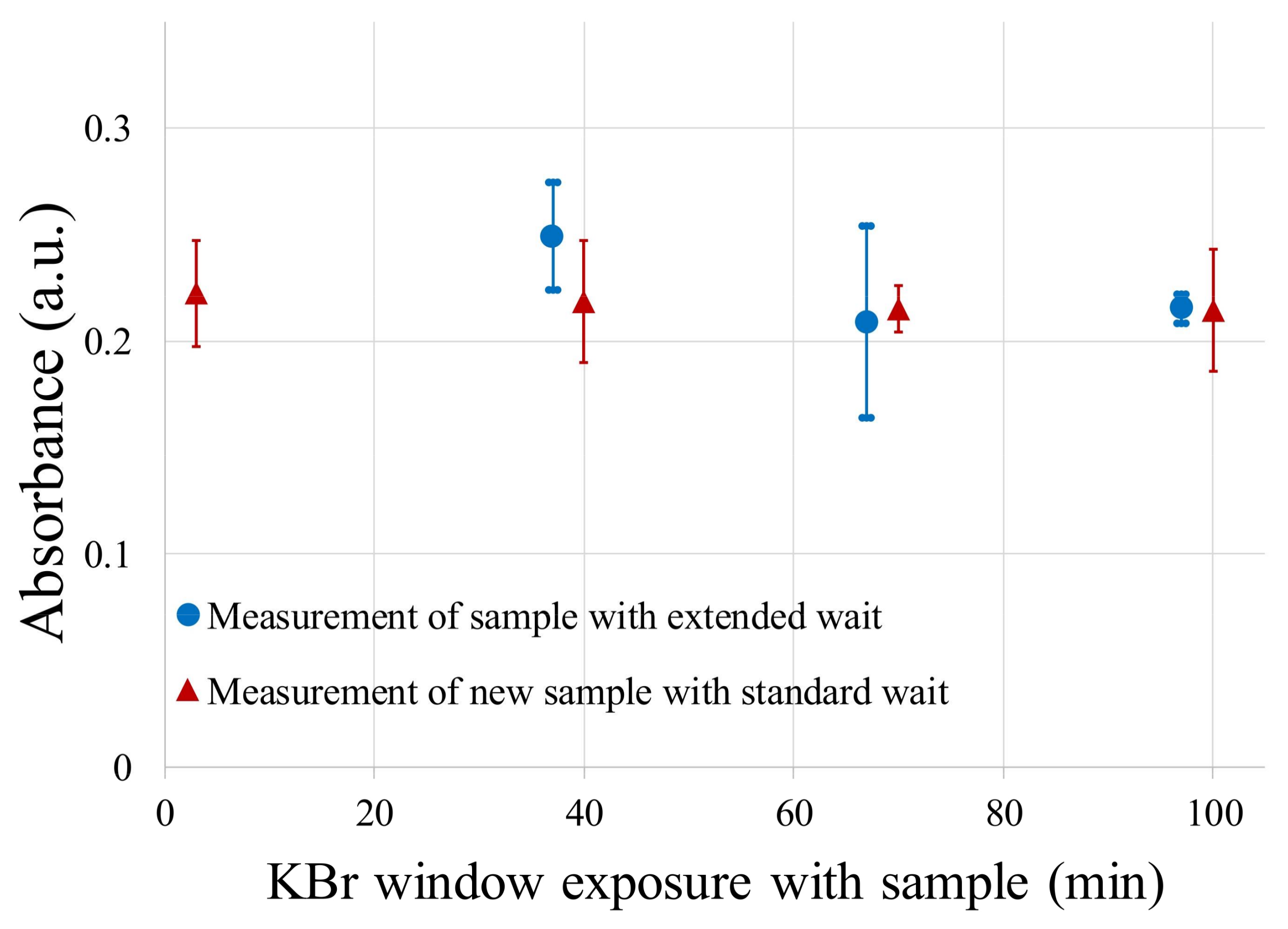
2.2. FT-IR Spectral Analysis
2.3. Data Preprocessing and Analysis
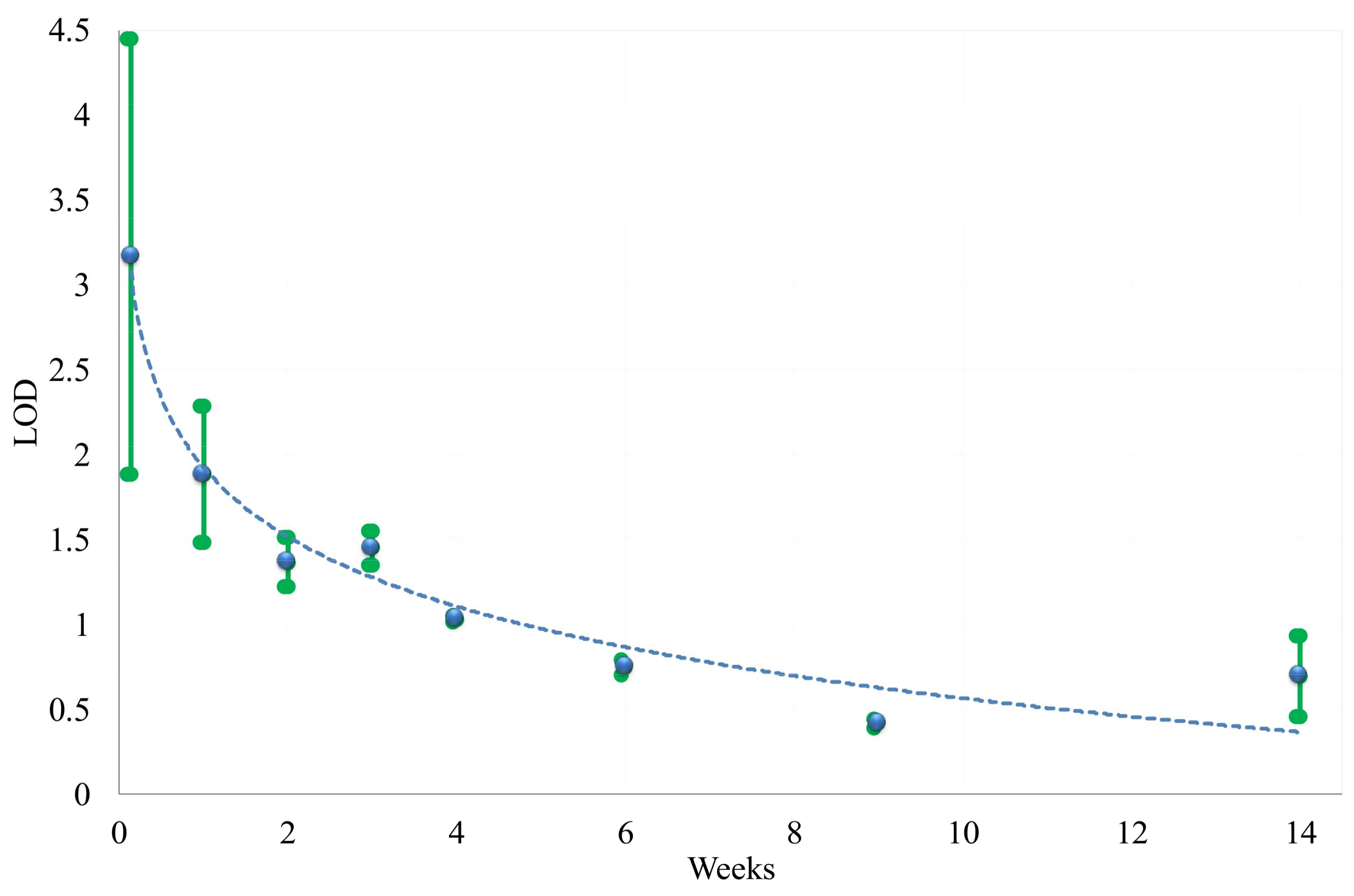
3. Results
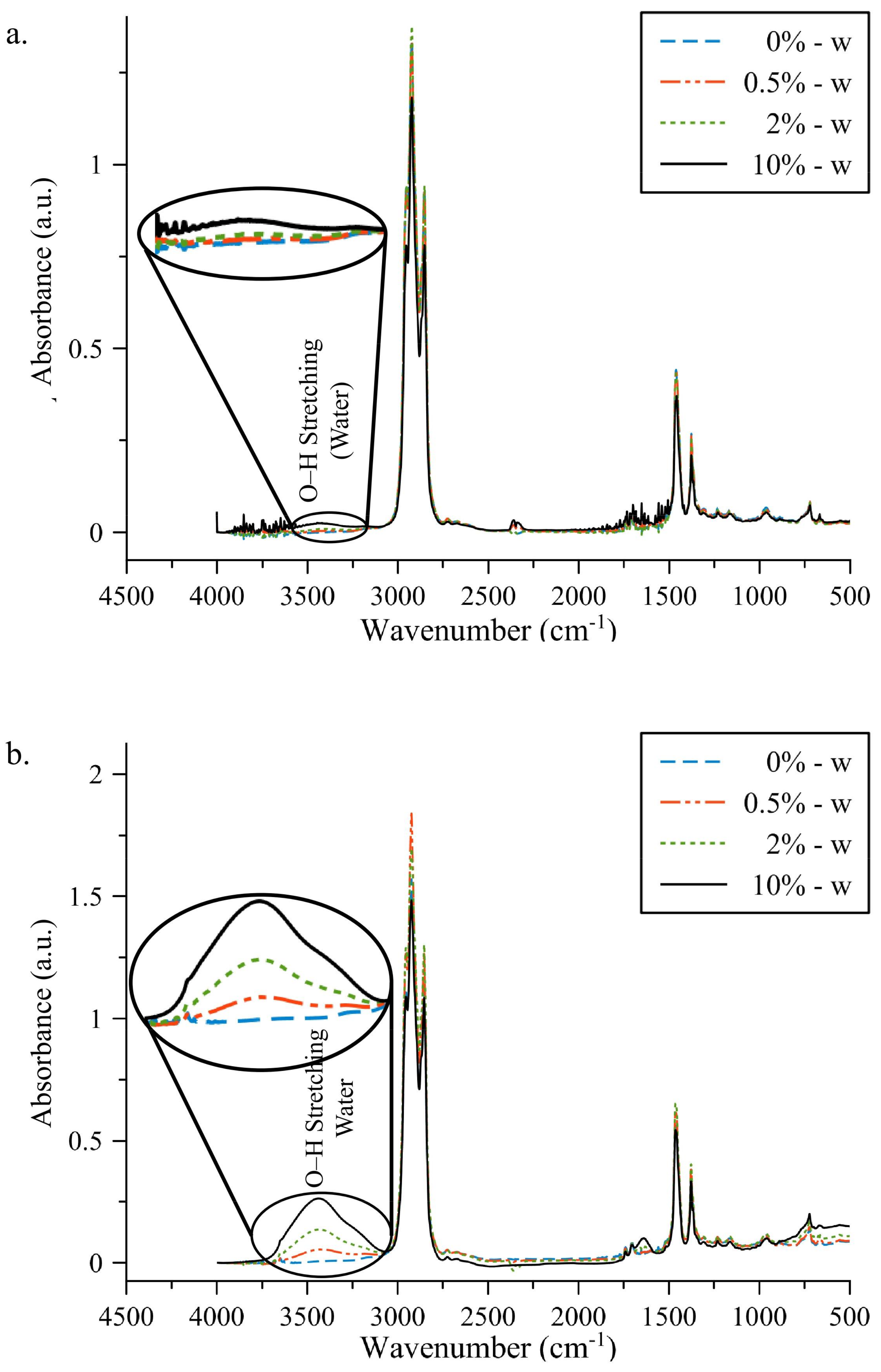
3.1. FT-IR Absorption Spectra
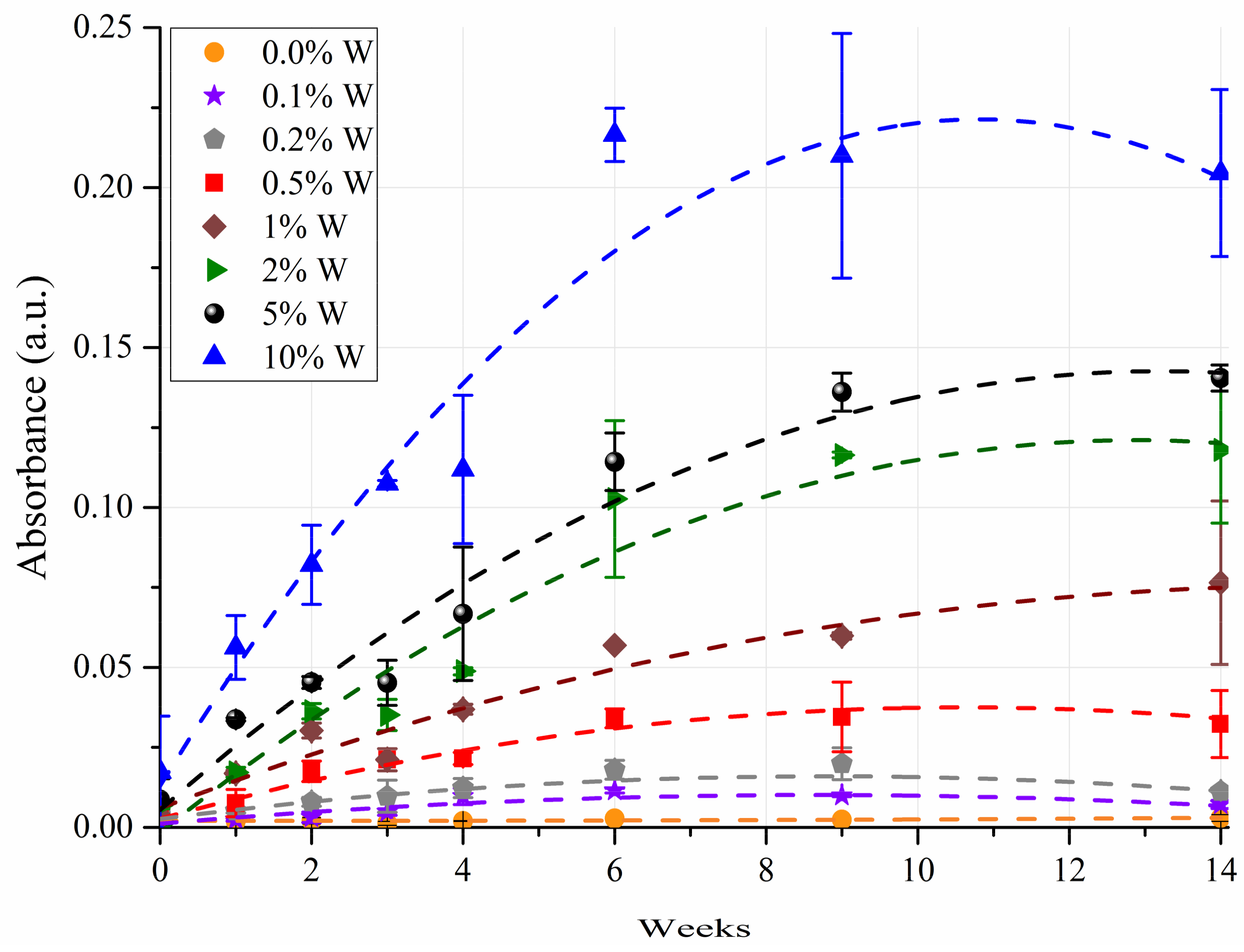
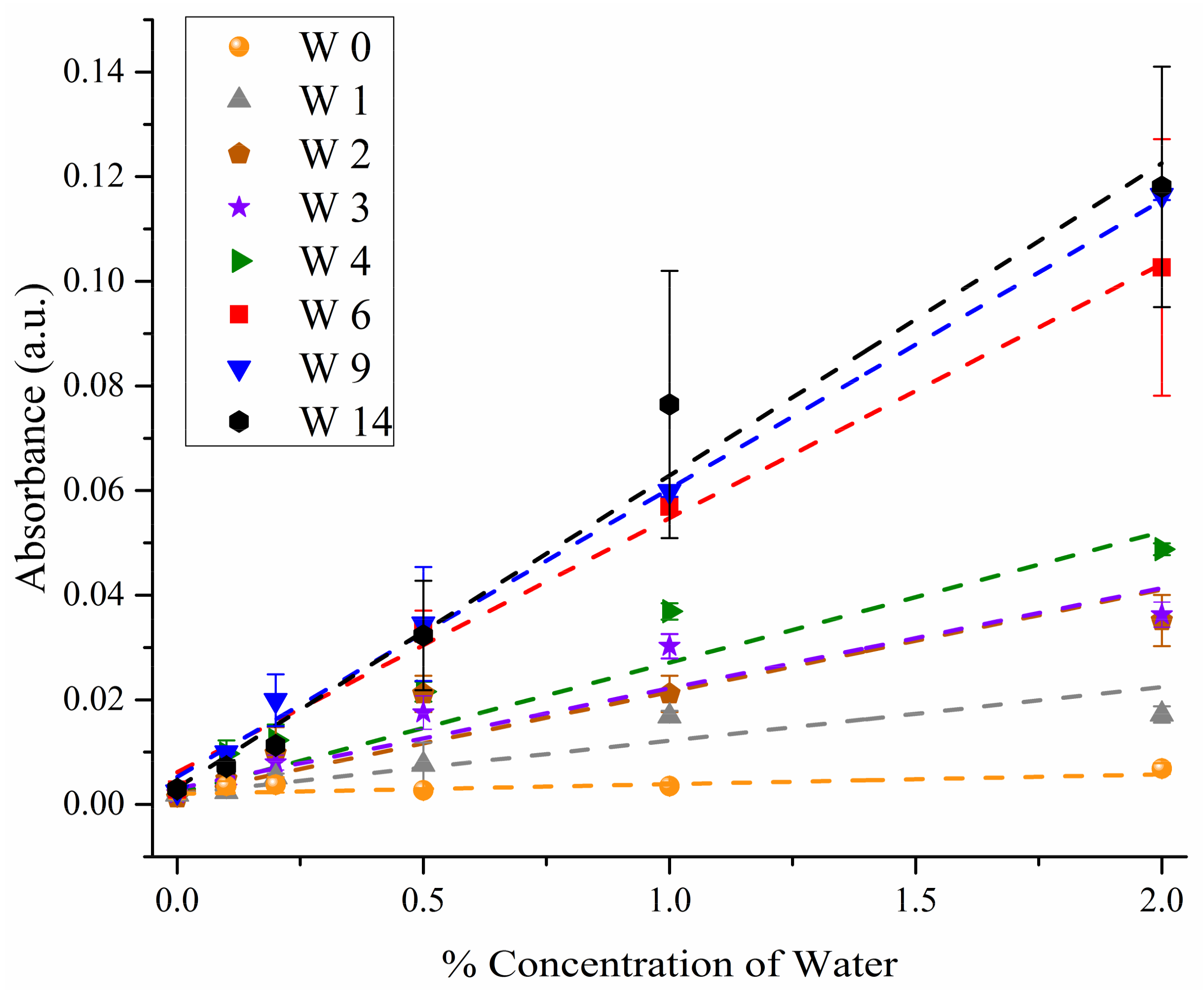
3.2. ANOVA Modeling
3.3. Predicting Water Contamination Level from FT-IR Absorption Spectra Analysis
3.4. Comparing the Modeling Techniques
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandler, D. Two faces of water. Nature 2002, 417, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eachus, A.C. The trouble with water. Tribol. Lubr. Technol. 2005, 61, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Dittes, N.J. Condition Monitoring of Water Contamination in Lubricating Grease for Tribological Contacts. Ph.D. Thesis, Lulea University of Technology, Lulea, Sweden, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hamawand, I.; Yusaf, T.; Rafat, S. Recycling of waste engine oils using a new washing agent. Energies 2013, 6, 1023–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahimi, B.; Semnani, A.; Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A.; Shakoori Langeroodi, H.; Hakim Davood, M. Monitoring of the physical and chemical properties of a gasoline engine oil during its usage. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2012, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.H. Oil-in-water Emulsion Breaking by Electrocoagulation in a Modified Electrochemical Cell. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 9634–9643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensel, J.K.; Carpenter, A.P.; Ciszewski, R.K.; Schabes, B.K.; Kittredge, C.T.; Moore, F.G.; Richmond, G.L. Molecular characterization of water and surfactant AOT at nanoemulsion surfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holloway, M. The Oil Analysis Handbook: A Comprehensive Guide to Using and Understanding Oil Analysis; NCH Corporation: Irving, TX, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y. Oil Analysis Handbook for Predictive Equipment Maintenance, 3rd ed.; Spectro Scientific: Chelmsford, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Frassa, K.A.; Siegfriedt, R.K.; Houston, C.A. Modern Analytical Techniques to Establish Realistic Crankcase Drains. SAE Trans. 1966, 74, 591–604. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, M.; Coello, J.; Iturriaga, H.; Maspoch, S.; Gonzalez, R. Determination of water in lubricating oils by mid- and near-infrared spectroscopy. Mikrochim. Acta 1998, 128, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.; Villarroya, I. NIR spectroscopy: A rapid-response analytical tool. TrAC. Trends Anal. Chem. 2002, 21, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borin, A.; Poppi, R.J. Application of mid infrared spectroscopy and iPLS for the quantification of contaminants in lubricating oil. Vib. Spectrosc. 2005, 37, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, N.S.; Amonette, J.E.; Autrey, T.; Ho, J.T. Detection of trace levels of water in oil by photoacoustic spectroscopy. Sens. Actuators B 2001, 77, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakoby, B.; Vellekoop, M.J. Physical sensors for water-in-oil emulsions. Sens. Actuators A 2004, 110, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Jin, L.; Cao, Q. Evaluation of modified used engine oil acting as a dispersant for concentrated coal-water slurry. Fuel 2016, 175, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Munaim, A.M.; Reuter, M.; Abdulmunem, O.M.; Balzer, J.C.; Koch, M.; Watson, D.G. Using Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy to Discriminate among Water Contamination Levels in Diesel Engine Oil. Trans. ASABE 2016, 59, 795–801. [Google Scholar]
- Ballari, M.; Bonetto, F.; Anoardo, E. NMR relaxometry analysis of lubricant oils degradation. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, 3746–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeleszczuk, Ł.; Pisklak, D.M.; Wawer, I. Analysis of water in the chicken eggshell using the 1H magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Avic. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, M.L; Lisabeth, K.W. Quantitative produced water analysis using mobile 1H NMR. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2016, 27, 105501. [Google Scholar]
- Margolis, S.A.; Vaishnav, K.; Sieber, J.R. Measurement of water by oven evaporation ufsing a novel oven design. 2. Water in motor oils and motor oil additives. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 380, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, A.; Quail, F. Detailed State of the Art Review for the Different On-Line/In-Line Oil Analysis Techniques in Context of Wind Turbine Gearboxes. J. Tribol. 2011, 133, 044001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, M.; Spurlock, M. Strategic oil analysis: Developing the test slates. Tribol. Lubr. Technol. 2009, 65, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Standard Practice for Condition Monitoring of Used Lubricants by Trend Analysis Using Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectrometry; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010; ASTM E2412-10.
- Sadecka, E.; Szela̧g, H. One-step synthesis of W/O and O/W emulsifiers in the presence of surface active agents. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2013, 16, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yetilmezsoy, K.; Fingas, M.; Fieldhouse, B. Modeling Water-in-Oil Emulsion Formation Using Fuzzy Logic. J. Mult. Log. Soft Comput. 2012, 18, 329–353. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Lin, Y.; Li, A.; Tarasov, V.V. Emulsification for castor biomass oil. Front. Chem. Eng. China 2011, 5, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirmizi, N.P.; Raghuraman, B.; Wiencek, J. Demulsification of Water/Oil/Solid Emulsions by Hollow-Fiber Membranes. AIChE J. 1996, 42, 1263–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajivand, P.; Vaziri, A. Optimization of demulsifier formulation for separation of water from crude oil emulsions. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, A.H.; Abu Hassan, M.A.; Yunus, R.M. Characterization and demulsification of water-in-crude oil emulsions. J. Appl. Sci. 2007, 7, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, B.M.S.; Ramalho, J.B.V.S.; Lucas, E.F. Demulsification of Water-in-Crude Oil Emulsions by Microwave Radiation: Effect of Aging, Demulsifier Addition, and Selective Heating. Energy Fuels 2012, 27, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, L.L. Petroleum Emulsions. In Advances in Chemistry; ACS: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; Chapter 1; pp. 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, F.; Seelenbinder, J. On-Site, Low Level Quantitative FTIR Analysis of Water in Oil Using a Novel Water Stabilization Technique. 2013. Available online: https://www.petro-online.com/article/analytical-instrumentation/11/a2-technologies/on-site-low-level-quantitative-ftir-analysis-of-water-in-oil-using-a-novel-water-stabilization-technique/365 (accessed on 4 April 2018).
- Al-Sabagh, a.M.; Emara, M.M.; Noor El-Din, M.R.; Aly, W.R. Formation of water-in-diesel oil nano-emulsions using high energy method and studying some of their surface active properties. Egypt. J. Pet. 2011, 20, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurlbert, S.H. Pseudoreplication and the Design of Ecological Field Experiments. Ecol. Monogr. 1984, 54, 187–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasesha, K.; De Marco, L.; Mandal, A.; Tokmakoff, A. Water vibrations have strongly mixed intra- and intermolecular character. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tholen, D.W.; Linnet, K.; Kondratovich, M.; Armbruster, D.A.; Garrett, P.E. Protocols for Determination of Limits of Detection and Limits of Quantitation. Available online: http://www.forskningsdatabasen.dk/en/catalog/2389308881 (accessed on 5 April 2018).
- Jiao, J.; Burgess, D.J. Ostwald ripening of water-in-hydrocarbon emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 264, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, A.M.; Santos, L.M.; Fortuny, M.; Melo, R.L.F.V; Coutinho, R.C.C.; Santos, A.F. Evaluation of water content and average droplet size in water-in-crude oil emulsions by means of near-infrared spectroscopy. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 3450–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, G.R.; Farias, G.B.; Braz, T.M.; Santos, L.M.; Amaral, M.J.; Fortuny, M.; Franceschi, E.; Dariva, C.; Santos, A.F. Use of near infrared for evaluation of droplet size distribution and water content in water-in-crude oil emulsions in pressurized pipeline. Fuel 2015, 147, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, W.J.; Santos, K.M.C.; Cruz, A.A.; Franceschi, E.; Dariva, C.; Santos, A.F.; Santana, C.C. Effect of water content, temperature and average droplet size on the settling velocity of water-in-oil emulsions. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klik, I.; Chang, C. Time range of logarithmic decay. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 47, 9091–9094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, D.A.; Pry, T. Limit of blank, limit of detection and limit of quantitation. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2008, 29, S49–S52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Water Contamination (%) | Week 0 | Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 6 | Week 9 | Week 14 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean * | N | Mean * | N | Mean * | N | Mean * | N | Mean * | N | Mean * | N | Mean * | N | Mean * | |
| 0.1 | 4 | −0.105 c | 3 | −1.022 e | 4 | 1.862 e | 3 | 1.080e | 4 | 3.097 e | 4 | −0.989 e | 4 | 2.893 d | 4 | −0.327 f |
| 0.2 | 4 | 0.064 bc | 2 | 1.204 de | 4 | 2.241 e | 4 | 0.703 e | 4 | 4.629 e | 4 | 1.424 e | 4 | 7.836 d | 4 | 3.635 ef |
| 0.5 | 4 | 1.603 bc | 4 | 1.380 d | 4 | 6.721 d | 4 | 4.711 d | 4 | 6.491 d | 2 | 9.020 cd | 4 | 7.646 d | 4 | 8.005 e |
| 1.0 | 4 | 3.194ab | 4 | 4.021 c | 2 | 9.708 c | 4 | 7.688 c | 4 | 10.050 cd | 3 | 15.499 c | 4 | 17.119 c | 4 | 21.587 d |
| 2.0 | 2 | 3.187abc | 2 | 5.324 c | 4 | 11.430 bc | 4 | 9.063 c | 4 | 12.476 c | 4 | 30.321 b | 4 | 33.977 b | 4 | 32.068 c |
| 5.0 | 4 | 1.724 bc | 4 | 8.638 b | 4 | 12.442 b | 4 | 11.589 b | 4 | 18.973 b | 3 | 32.941 b | 4 | 40.638 b | 4 | 39.968 b |
| 10.0 | 4 | 6.273a | 3 | 15.323a | 4 | 22.977a | 4 | 30.822a | 4 | 29.497a | 4 | 63.018a | 4 | 58.597a | 4 | 54.629a |
| Week | 0.5% | 1.0% | 2.0% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean * | N | Mean * | N | Mean * | |
| 14 | 3 | 8.005a | 4 | 21.587a | 4 | 32.068a |
| 9 | 4 | 7.646a | 4 | 17.119 b | 4 | 33.977a |
| 6 | 2 | 9.019a | 3 | 15.49 b | 4 | 30.321a |
| 4 | 4 | 6.491a | 4 | 10.050 c | 4 | 12.476 b |
| 3 | 4 | 4.711ab | 4 | 7.688 cd | 4 | 9.063 bc |
| 2 | 4 | 6.721a | 2 | 9.708 c | 4 | 11.429 b |
| 1 | 4 | 1.380 b | 4 | 4.021 de | 2 | 5.324 bc |
| 0 | 4 | 1.603 b | 4 | 3.194 e | 2 | 3.187 c |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Holland, T.; Abdul-Munaim, A.M.; Watson, D.G.; Sivakumar, P. Importance of Emulsification in Calibrating Infrared Spectroscopes for Analyzing Water Contamination in Used or In-Service Engine Oil. Lubricants 2018, 6, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6020035
Holland T, Abdul-Munaim AM, Watson DG, Sivakumar P. Importance of Emulsification in Calibrating Infrared Spectroscopes for Analyzing Water Contamination in Used or In-Service Engine Oil. Lubricants. 2018; 6(2):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6020035
Chicago/Turabian StyleHolland, Torrey, Ali Mazin Abdul-Munaim, Dennis G. Watson, and Poopalasingam Sivakumar. 2018. "Importance of Emulsification in Calibrating Infrared Spectroscopes for Analyzing Water Contamination in Used or In-Service Engine Oil" Lubricants 6, no. 2: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6020035
APA StyleHolland, T., Abdul-Munaim, A. M., Watson, D. G., & Sivakumar, P. (2018). Importance of Emulsification in Calibrating Infrared Spectroscopes for Analyzing Water Contamination in Used or In-Service Engine Oil. Lubricants, 6(2), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6020035






