The Reduction of Static Friction of Rubber Contact under Sea Water Droplet Lubrication
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
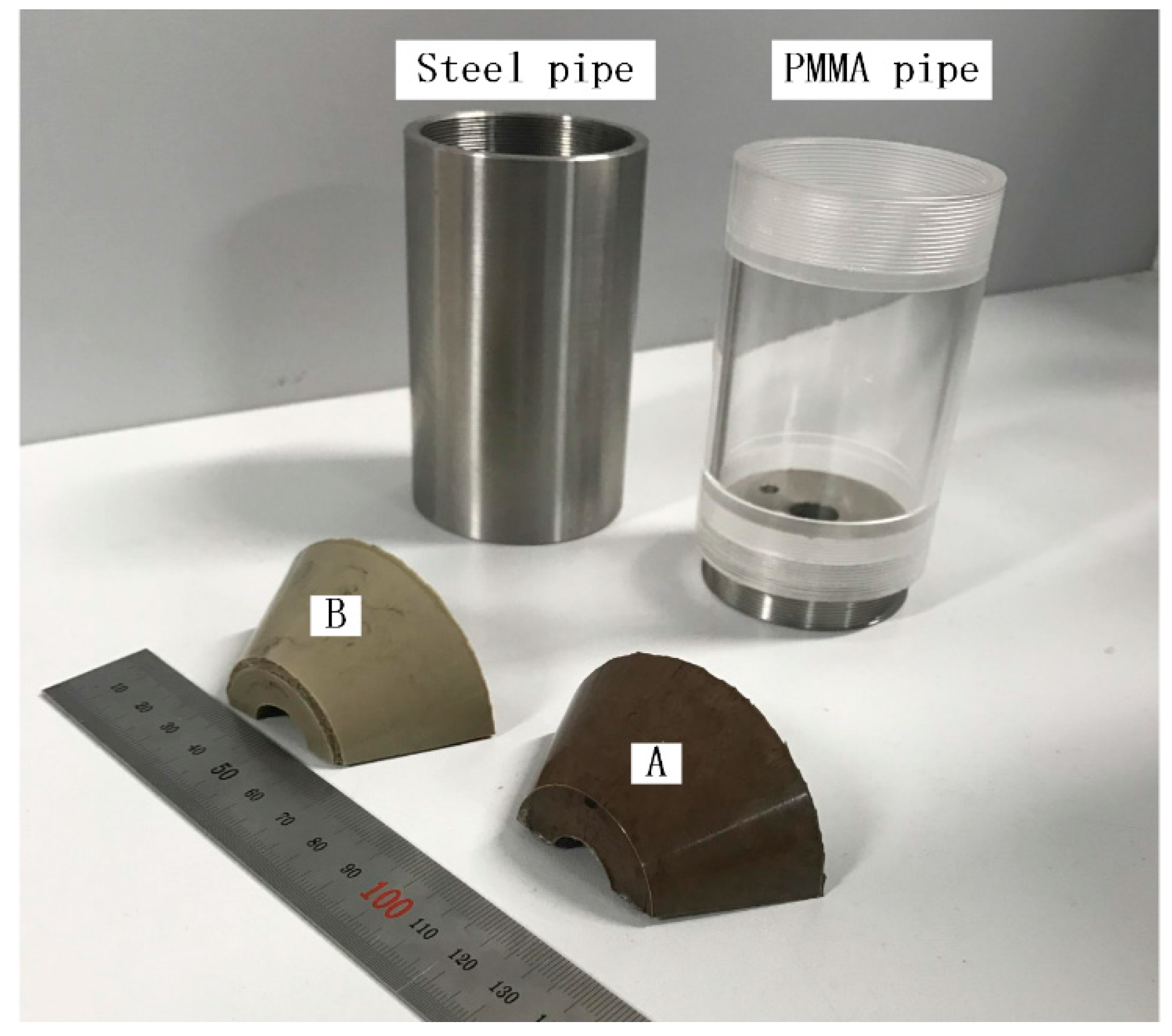
2.1. Samples
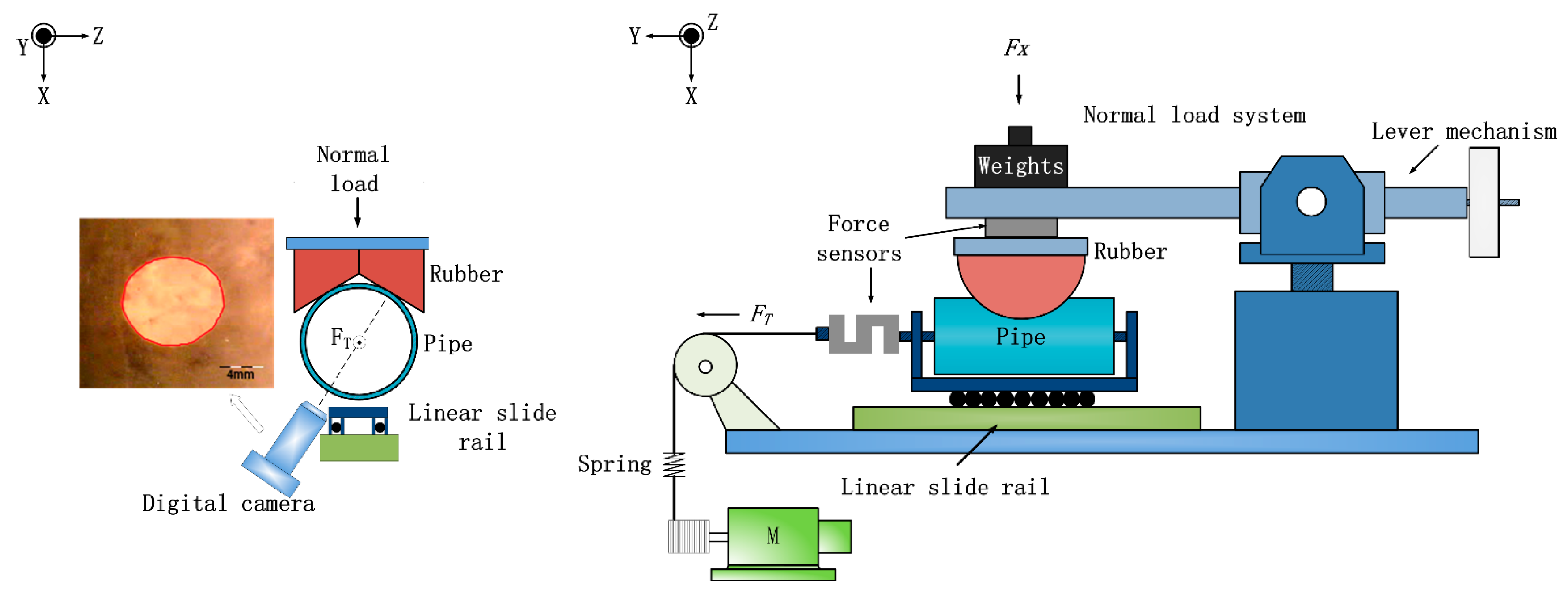
2.2. Tribological Instrument
2.3. Experimental Procedures
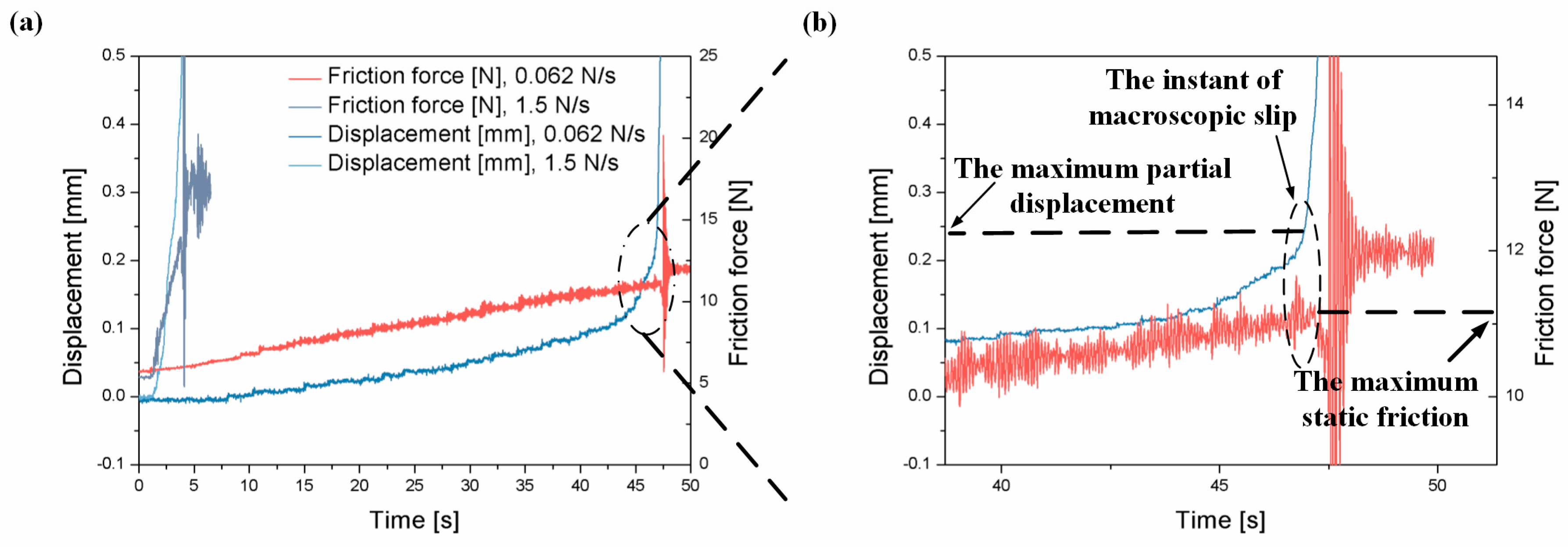
2.4. Confirmation of the Maximum Static Friction
3. Results
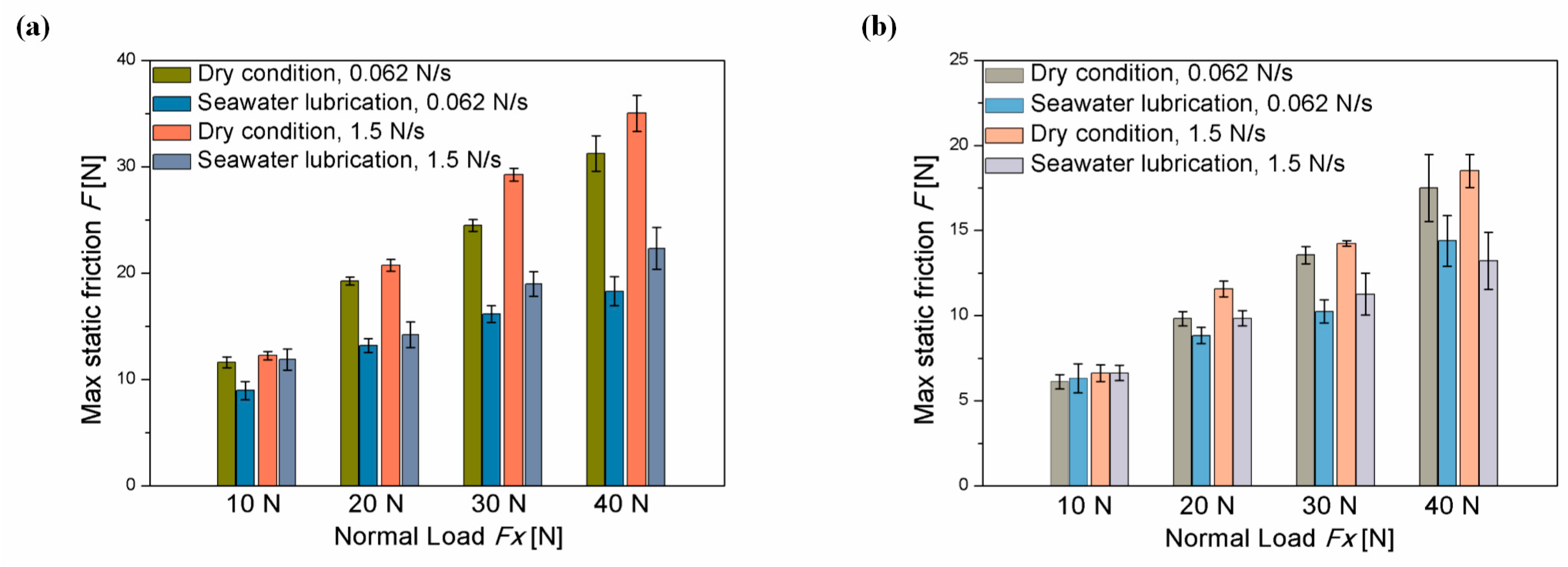
3.1. The Maximum Static Friction
3.2. Efficiency of Lubrication
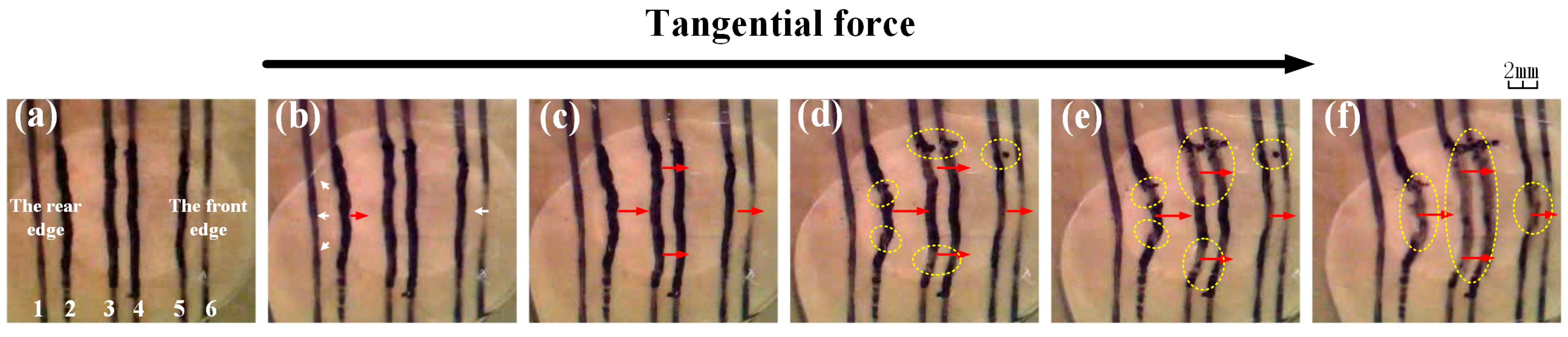
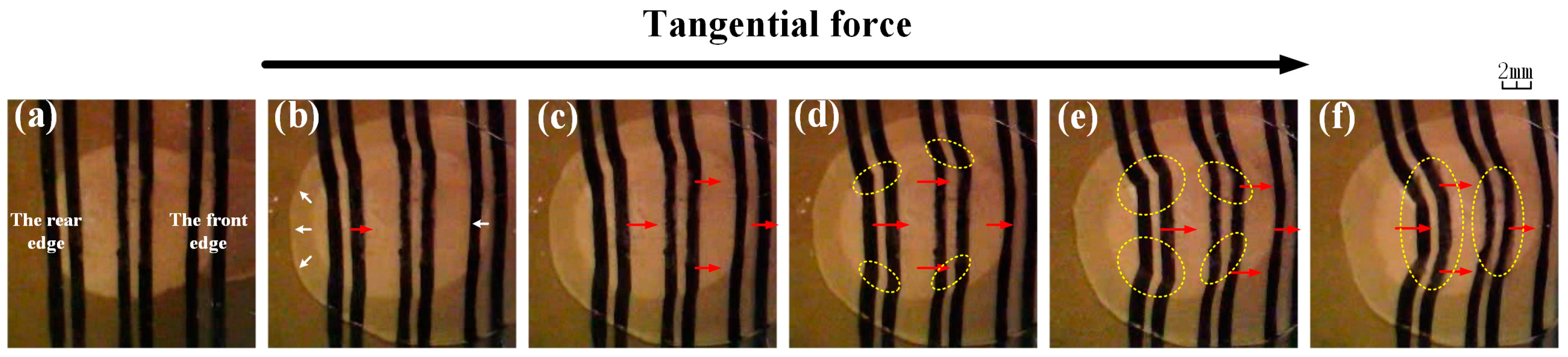
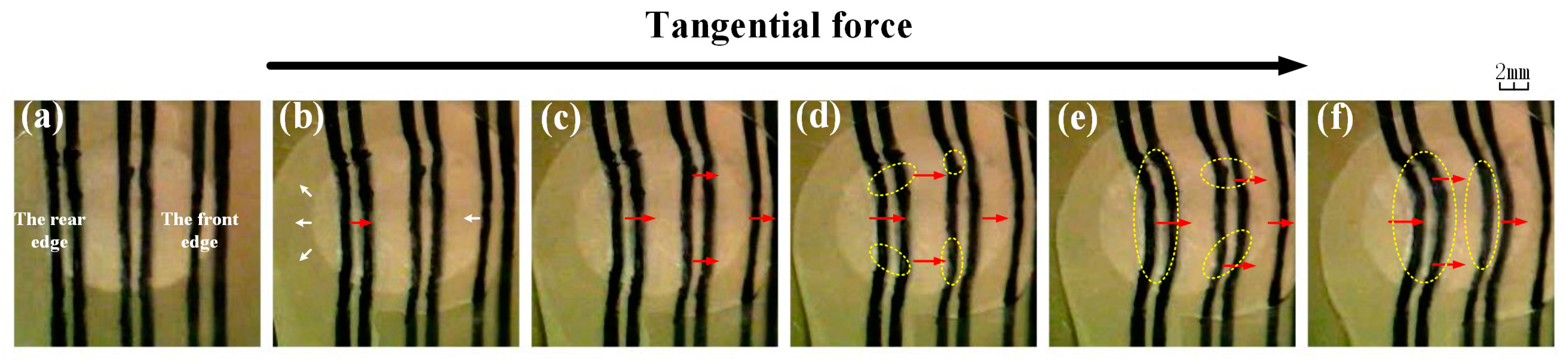
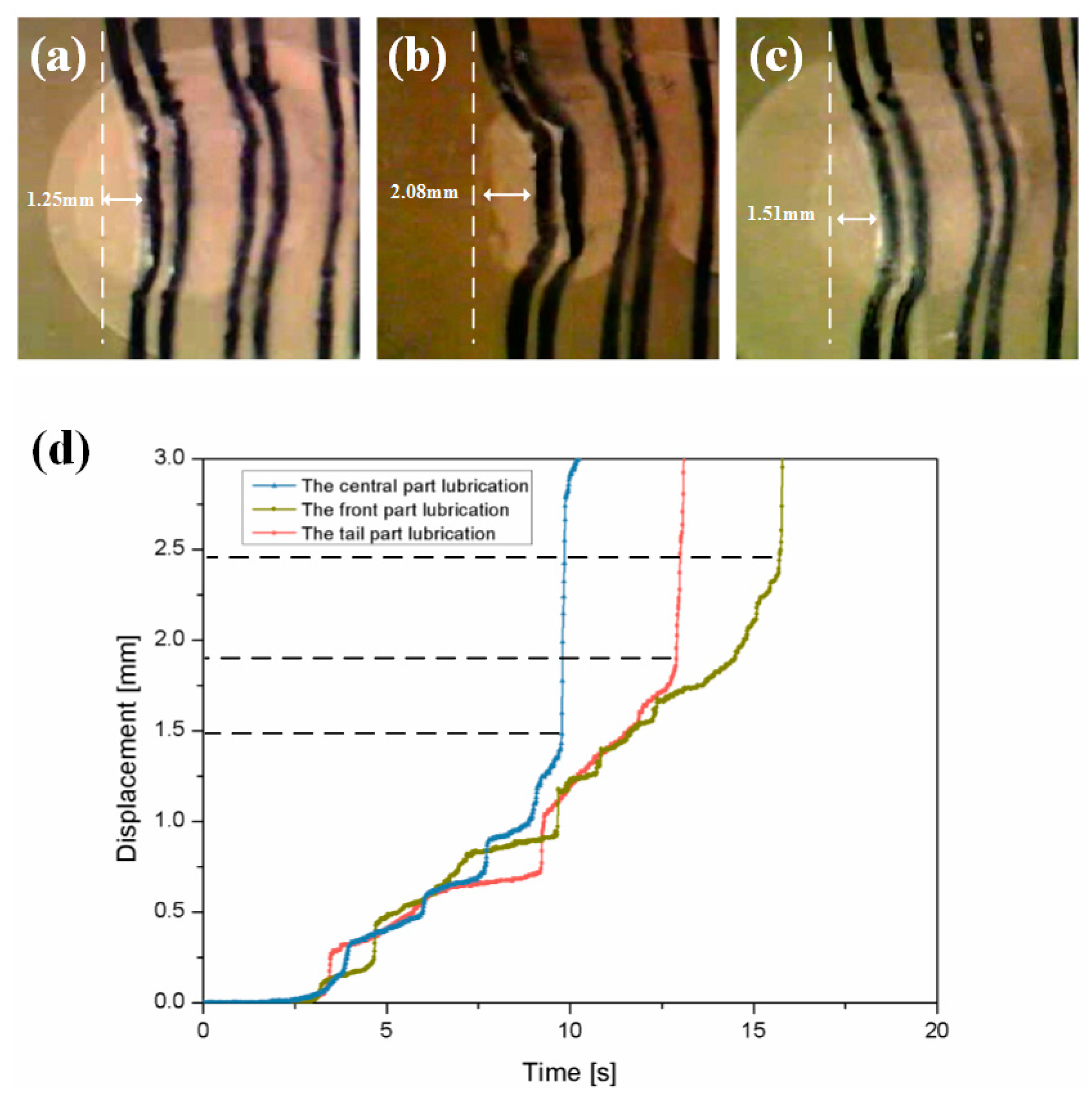
3.3. Deformation of Contact
4. Discussion
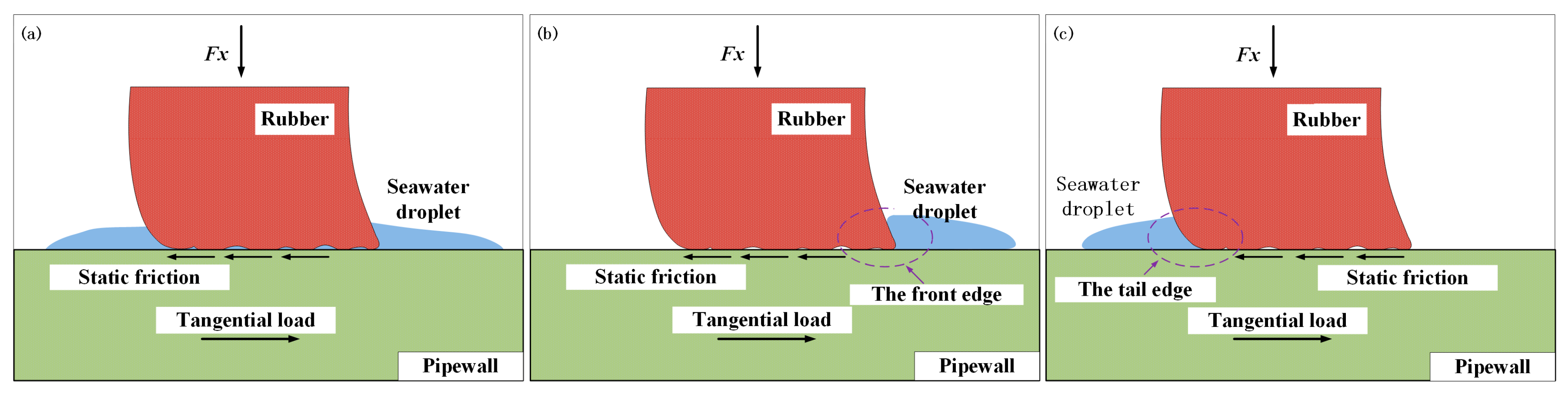
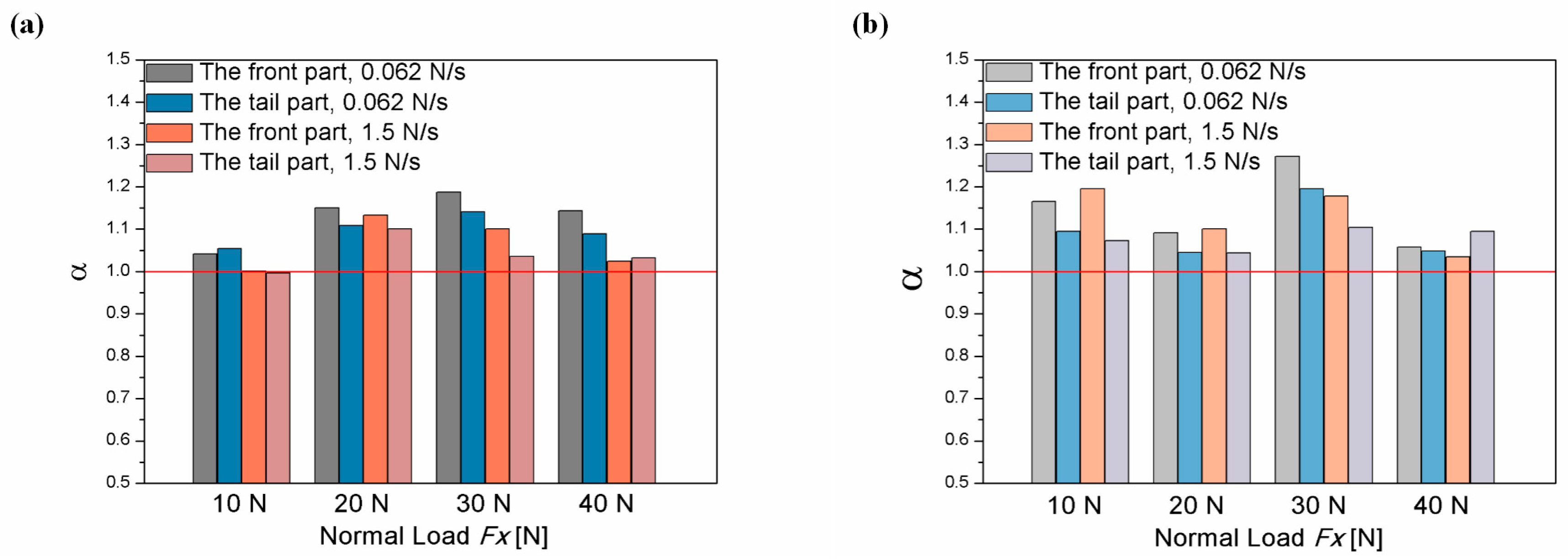
4.1. The Central Part Lubrication
4.2. Comparison of the Two Side Parts of Lubrication
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Persson, B.N.; Albohr, O.; Tartaglino, U.; Volokitin, A.I.; Tosatti, E. On the nature of surface roughness with application to contact mechanics, sealing, rubber friction and adhesion. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2004, 17, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W. Study on properties of recycled tire rubber modified asphalt mixtures using dry process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Kan, C.; Shen, Z.; Shi, Z. Experimental research on fatigue property of steel rubber vibration isolator for offshore jacket platform in cold environment. Ocean Eng. 2009, 36, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Cao, Z.; Wang, D.; Liu, S. Improving the friction and abrasion properties of nitrile rubber hybrid with hollow glass beads. Tribol. Int. 2016, 101, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitaki, A.; Briscoe, B.J.; Adams, M.J.; Johnson, S.A. The friction and lubrication of elastomers. Tribol. Ser. 1995, 30, 503–511. [Google Scholar]
- Persson, B.N. Theory of rubber friction and contact mechanics. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 3840–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallamach, A. How does rubber slide? Wear 1971, 17, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barquins, M.; Courtel, R. Rubber friction and the rheology of viscoelastic contact. Wear 1975, 32, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.L.; Greenwood, J.A. An adhesion map for the contact of elastic spheres. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 192, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, U.D. A generalized analytical model for the elastic deformation of an adhesive contact between a sphere and a flat surface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 261, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galligan, J.M.; McCullough, P. On the nature of static friction. Wear 1985, 105, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.D.; Thomas, A.G. Static friction of smooth clean vulcanized rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1977, 50, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeve, A.J.; Krijger, T.; Mugge, W.; Breedveld, P.; Dodou, D.; Dankelman, J. Static friction of stainless steel wire rope-rubber contacts. Wear 2014, 319, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deladi, E.L.; De Rooij, M.B.; Schipper, D.J. Modelling of static friction in rubber-metal contact. Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barquins, M. Adherence, friction and wear of rubber-like materials. Wear 1992, 158, 87–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barquins, M. Influence of dwell time on the adherence of elastomers. J. Adhes. 1982, 14, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savkoor, A.R.; Briggs, G.A.D. The effect of tangential force on the contact of elastic solids in adhesion. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1977, 336, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savkoor, A.R. Mechanics of sliding friction of elastomers. Wear. 1986, 113, 37–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trømborg, J.; Scheibert, J.; Amundsen, D.S.; Thøgersen, K.; Malthe-Sørenssen, A. Transition from static to kinetic friction: Insights from a 2D model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 074301. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Paolino, P.; Audry, M.C.; Chateauminois, A.; Fretigny, C.; Chenadec, Y.L.; Portigliatti, M.; Barthel, E. Surface pressure and shear stress fields within a frictional contact on rubber. J. Adhes. 2011, 87, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenen, A.; Sanon, A. Tribological and vibroacoustic behavior of a contact between rubber and glass (application to wiper blade). Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 1484–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagger, E.T.; Walker, P.S. Second paper: Further studies of the lubrication of synthetic rubber rotary shaft seals. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1966, 181, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.W. State of the art of polymer tribology. Tribol. Int. 1998, 31, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, S.; Takahashi, H.; Oya, T. Clarification of the mechanism of wiper blade rubber squeal noise generation. JSAE Rev. 2001, 22, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelinck, E.R.M.; Schipper, D.J. Calculation of Stribeck curves for line contacts. Tribol. Int. 2000, 33, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, J.K. A review of the influence of environmental humidity and water on friction, lubrication and wear. Tribol. Int. 1990, 23, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.D. Squeeze films between rubber and glass. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1971, 4, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B.N.; Tartaglino, U.; Albohr, O.; Tosatti, E. Rubber friction on wet and dry road surfaces: The sealing effect. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 035428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleau, F.; Mazuyer, D.; Koenen, A. Sliding friction at elastomer/glass contact: Influence of the wetting conditions and instability analysis. Tribol. Int. 2009, 42, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, A.; Ahmed, S.U.; Schaefer, J.A.; Scherge, M. Friction of thin water films: A nanotribological study. Surf. Sci. 2002, 504, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauss, G.F.; Weede, H.; Riekert, T. Offshore pipe laying operations-Interaction of vessel motions and pipeline dynamic stresses. Appl. Ocean Res. 1992, 14, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarracino, F.; Mallardo, V. A refined analytical analysis of submerged pipelines in seabed laying. Appl. Ocean Res. 1999, 21, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenci, S.; Callegari, M. Simple analytical models for the J-lay problem. Acta Mech. 2005, 178, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiazzo, G.; Mauro, S.; Guinzio, P.S. A tensioner simulator for use in a pipelaying design tool. Mechatronics 2009, 19, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.Q.; Wang, D.G.; Cong, C.B.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhou, Q. Dependence of abrasion behavior on cross-linked heterogeneity in unfilled nitrile rubber. Tribol. Int. 2014, 69, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yan, F.; Xue, Q. Tribological behavior of PTFE sliding against steel in sea water. Wear 2009, 267, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H.; Radok, J.R.M. The contact problem for viscoelastic bodies. J. Appl. Mech. 1960, 27, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukahori, Y.; Gabriel, P.; Busfield, J.J.C. How does rubber truly slide between Schallamach waves and stick–slip motion? Wear 2010, 269, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skouvaklis, G.; Blackford, J.R.; Koutsos, V. Friction of rubber on ice: A new machine, influence of rubber properties and sliding parameters. Tribol. Int. 2012, 49, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.D. A guide to estimating the friction of rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1992, 65, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.H.; Zhou, H.D.; Gao, S.Q.; Chen, J.M. A comparative investigation of the friction and wear behavior of polyimide composites under dry sliding and water-lubricated condition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 356, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedo, E.; Lévy, F.; Brune, H. Kinetics of capillary condensation in nanoscopic sliding friction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 185505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Rubber Type | Mechanical Properties | |||
| Elastic Modulus [MPa] | Tensile Strength [MPa] | Shore Hardness | Roughness [Ra] | |
| A | 2.26 | 13.2 | 37 | 3.1 |
| B | 3.7 | 12.79 | 51 | 3.2 |
| Pipe Type | Mechanical Properties | |||
| Elastic Modulus [MPa] | HRC | Roughness [Ra] | ||
| Steel | 2.1 × 105 | 80 | 1.7 | |
| PMMA | 3 × 103 | 99 | 1.6 | |
| Compound | NaCl | Na2SO4 | MgCl2 | CaCl2 | SrCl2 | KCl | NaHCO3 | KBr | H3BO3 | NaF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (g/L) | 24.53 | 4.09 | 5.20 | 1.16 | 0.025 | 0.695 | 0.201 | 0.101 | 0.027 | 0.003 |
| Rubber | Pipe | Normal Load [N] | Increasing Rate of Tangential Load [N/s] |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Steel, PMMA | 10, 20, 30, 40 | 0.062, 1.5 |
| B | Steel, PMMA |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.-J.; Wang, D.-G.; Guo, Y.-B. The Reduction of Static Friction of Rubber Contact under Sea Water Droplet Lubrication. Lubricants 2017, 5, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants5020012
Zhou Y-J, Wang D-G, Guo Y-B. The Reduction of Static Friction of Rubber Contact under Sea Water Droplet Lubrication. Lubricants. 2017; 5(2):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants5020012
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yong-Jie, De-Guo Wang, and Yan-Bao Guo. 2017. "The Reduction of Static Friction of Rubber Contact under Sea Water Droplet Lubrication" Lubricants 5, no. 2: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants5020012
APA StyleZhou, Y.-J., Wang, D.-G., & Guo, Y.-B. (2017). The Reduction of Static Friction of Rubber Contact under Sea Water Droplet Lubrication. Lubricants, 5(2), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants5020012





