Abstract
Electron beam crosslinked ultra high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) 32 mm cups with cobalt alloy femoral heads were compared with gamma-irradiation sterilized 26 mm cups and zirconia ceramic heads in a hip wear simulator. The testing was performed for a total of ten million cycles with frequent stops for cleaning and measurement of mass losses due to wear. The results showed that the ceramic on UHMWPE bearing design exhibited higher early wear than the metal on highly crosslinked samples. Once a steady state wear rate was reached, the wear rates of the two types of hip bearing systems were similar with the ceramic on UHMPWE samples continuing to show a slightly higher rate of wear than the highly crosslinked samples. The wear rates of each of the tested systems appear to be consistent with the expectations for low rates of wear in improved hip replacement systems.
1. Introduction
The wear of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene acetabular cups after total hip replacement surgery has been an issue of concern and study for many years [1,2,3,4,5,6]. After the discovery of high rates of wear of some polyethylene components in some patients, efforts began to try to improve the wear rates through design changes, polymer modification [7,8,9,10,11], or materials substitution [12,13,14]. Changes included the use of ceramic femoral head components to reduce wear, modification of the processing, packaging, and sterilization parameters of the acetabular cups, varying the molecular weight of the polyethylene or changing the additives, and modification of the polyethylene material itself.
In attempts to improve the wear resistance of the femoral head and acetabular cup bearing couple, attention has focused on both sides of the interface. Changes have been made to reduce wear of titanium alloy heads by modifying the surface [12,13] so that it would not be necessary to utilize cobalt heads on titanium alloy femoral stems. It has been suggested that the nature of the femoral head might affect the wear of the polyethylene so a change to ceramic heads [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24] was tested and has been instituted in many marketed devices. The use of ceramic-on-ceramic, in which both component materials are replaced by ceramic has also been tested and utilized in surgery [25,26,27,28] for several years. Metal-on-metal articulations initially had been used in the 1960s and 1970s [29,30] and have recently become attractive again as a possible solution to wear problems [22,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38].
This preliminary screening study compares the wear properties of an electron beam crosslinked ultra high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) when bearing against a 32 mm cobalt/chromium alloy femoral head with the properties of a gamma-irradiation-sterilized UHMWPE utilizing a 26 mm ceramic head. Previous clinical studies have shown that head size had an effect on wear rates of gamma-irradiation-sterilized UHMWPE [39,40] with larger heads exhibiting greater linear and volumetric wear rates. However, larger femoral heads have been advocated to reduce dislocation [41,42] and improve the range of motion and stability [41,43,44] of total hip replacements. Research has shown that the crosslinking of UHMWPE will reduce the wear rates in both laboratory testing [45,46,47,48,49] and in clinical experience [46,50,51,52,53]. It has been suggested that the detrimental effect of head size on wear rates may not exist for highly crosslinked UHMWPE [54,55], which may allow for the use of larger femoral heads to achieve the potential benefits. Finite element analysis modelling the predicted stresses in conventional and highly crosslinked polyethylene and Fuji film pressure analysis suggested that the stresses in highly crosslinked UHMWPE with large head sizes might be less than for 28 mm conventional polyethylene [56]. A clinical evaluation [57], with the crosslinked UHMWPE that is a part of this study, suggests that larger head sizes do produce increased wear volume over smaller heads, meaning that the use of crosslinked polyethylene, while it may reduce the wear rates over non-crosslinked material, still may suffer from the effect of increasing head size. Another clinical study showed that a wear increase due to increased head size did not appear to be significant [58].
The use of ceramic femoral heads has been suggested as a way to reduce the wear of the UHMWPE acetabular components [59,60]. Laboratory studies [15,23,61] and clinical studies [15,20,22,62] showing a wear rate improvement conflict with other clinical reports [63,64,65] suggesting no apparent difference. Recently, a matched pair analysis was reported comparing 28 mm ceramic heads with the same size metal heads [66], bearing on conventional UHMWPE and found a significant reduction in wear rate at an average of 17 years post implantation, when ceramic heads were used.
The sponsor of this study had requested the comparison of two different designs of hip replacements that he was considering using in his practice. The designs tested were the two specific designs for which he wished to compare the wear properties. The larger head and crosslinked polyethylene were available for the metal on polyethylene device and might offer advantages in reducing hip dislocation. One design utilized a large head bearing against a polyethylene that was claimed to have improved wear properties due to a crosslinking process. The other design contained a more conventional smaller head and no specific processing to enhance wear properties but the head was manufactured from a ceramic material, presumably conferring improved wear characteristics to the bearing pair.
In addition to the differences in bearing materials of the two different device designs which were tested, the head sizes were different as well. The head size for the ceramic heads was 26 mm, while that for the cobalt alloy heads was 32 mm. For one of the devices, research had shown that there might be no significant difference in the clinical wear rate for the Longevity® device when 26 mm heads were compared to 32 mm heads, although there was a trend towards a higher wear rate for the larger head [58]. For the ceramic on polyethylene, no specific study has compared the effects of head size on wear rates, although a study has been reported in which 22.25, 26, and 28 mm alumina ceramic heads from the same manufacturer were compared in a hip simulator study [40]. This study showed increases in the wear rate when head size was increased and also reviewed published literature showing that other researchers had reported studies in which larger heads had lower wear, smaller heads showed lower wear, or the wear rates were equivalent.
2. Materials and Methods
The devices tested were either 32 mm Co/Cr femoral heads bearing upon Zimmer® Longevity® polyethylene cups [67] or 26 mm Kyocera® Zirconia heads bearing upon Kyocera polyethylene cups. The 26 mm cups were manufactured from GUR 1020 resin and sterilized by gamma irradiation (4.5 MRad). The 32 mm cups were prepared and crosslinked according to a proprietary process said to reduce the wear rate between 88% and 98% over non-crosslinked polyethylene. (“Longevity™ Crosslinked Polyethylene”, Zimmer Informational Brochure).
Three of each type of cup was tested in wear and one of each type was subjected to loading, but not movement. The polyethylene cups that were subjected loading only served as soak controls in an effort to correct for the effects of fluid uptake on weight changes of the cups. The cups were mounted in a heat-softenable polyurethane resin using extra cups to avoid subjecting the test cups to the 80 °C temperatures required to cure the polyurethane.
Testing was conducted on an MTS® eight-station hip simulator, which has been customized to add load, torque, and displacement transducers on all eight stations. This simulator is of the type frequently called “Orbital Bearing”, which is the subject of ISO standard ISO 14242-3 [68]. The wear path described is the same for every loading cycle and attempts to mimic part of the normal motion of a hip in use. The devices were mounted with the head and fixture on the bottom and the cup on top (anatomic position). A Paul loading curve with a maximum load of 3000 N was used and loading synchronized with the rotation of the devices so that the same load was placed upon the same area of the cup during each cycle. The lubricant for each station was 50% bovine calf serum (Hyclone) diluted with deionized water and to which was added 20 mM Disodium EDTA Dihydrate. The EDTA was added to the deionized water and thoroughly mixed. The water/EDTA solution was filtered through 0.2 µm filter disks before being mixed with the serum.
While it was not possible to measure interface friction in these samples directly, torsional load cells were mounted on each testing station and the maximum and minimum torque measured for each sample was recorded over a total of approximately 10 cycles, periodically during testing. The difference between the highest and lowest torque was calculated and expressed as the total torsional excursion during the loading pattern applied.
Testing was conducted to a total of ten million cycles at a rate of one cycle per second (approximately 86,000 cycles per day). Measurement of weight loss during the study was conducted at every 500,000 cycles. The test was stopped and the serum removed and stored. At each cleaning interval, the cups were dismounted from the fixturing, thoroughly cleaned in accordance with internal laboratory protocols and ASTM F1714 [69], dried, and then weighed three times in a round-robin fashion to determine the weight changes which had occurred. Weight loss values were corrected for fluid uptake based upon changes in weight of the loaded soak control cups. A balance readable to 0.01 mg was used for all weighings. This method of characterizing losses due to wear is very reproducible and is consistent with the international standards [69,70].
Each polyethylene cup was inspected on a laser scanning confocal microscope (Leica SP-2, Leica Microsystems, Exton, PA, USA) and an image collected using the 10 × objective, giving a field of view of 1.5 mm × 1.5 mm (2.25 mm2). The use of the confocal microscope allowed the viewing of the non-conductive polyethylene without the charging problems that would be experienced in an electron microscope. The surface morphology of the worn cups was compared to that for the as-manufactured cups that had been subjected only to loading without oscillating movement.
3. Results
Weight losses due to wear began to occur during the first 500,000 cycles in the case of the ceramic on polyethylene samples. There was very little detectable weight loss for the crosslinked cups for the first 1,000,000 cycles but, after 1,000,000 cycles, there were losses at an average rate only slightly less than that for the ceramic on polyethylene and that average was the result of one crosslinked cup experiencing much less wear than the other two. The weight loss results over ten million cycles are shown in Figure 1 for each tested cup. In Figure 2 and Figure 3, the wear results are averaged for each type of bearing pair. The average wear rates for each type of sample are given in Table 1. In the last column, it can be seen that the average wear rate (mg/mc) for the last 8,000,000 cycles was 3.55 ± 0.55 for the ceramic on polyethylene and 3.20 ± 0.88 for the cross-linked materials. Throughout the study the average wear rate for the crosslinked polyethylene remained slightly less than that for the ceramic on polyethylene but two out of the three crosslinked cups had slightly higher wear rates than the ceramic/polyethylene bearings in the last eight million cycles. The third crosslinked cup had a much lower wear rate than the other two samples but no differences were noted in the appearance of the cup and head or the appearance of the testing lubricant. One of the ceramic-on-polyethylene had a higher total wear than the other two but the difference was not as large as that for the crosslinked cups. In these samples as well, no differences were observed that would explain the difference.
All of the tested devices were provided from inventory ready for implantation and one would assume that all devices met the manufacturer’s specifications but variations in head and cup diameters could have played a role in the observed results. The diameter data is not available for the individual samples, so this comparison was not performed.
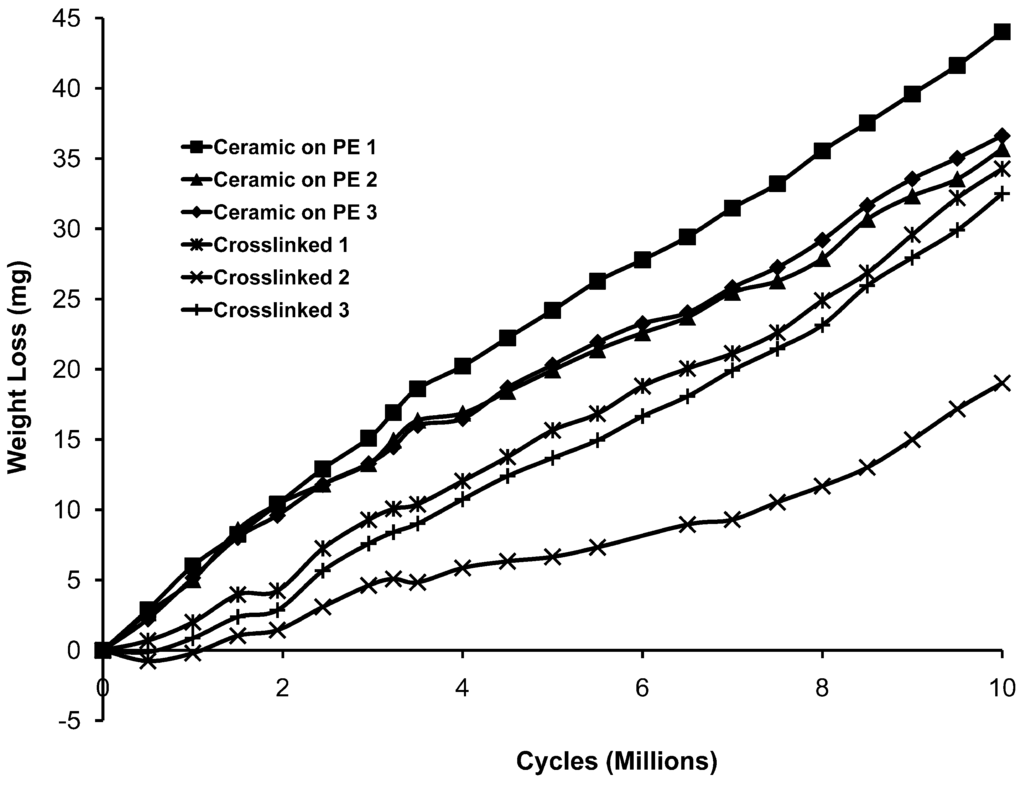
Figure 1.
Individual sample wear data (load soak corrected) for each of the six tested samples.
Figure 1.
Individual sample wear data (load soak corrected) for each of the six tested samples.
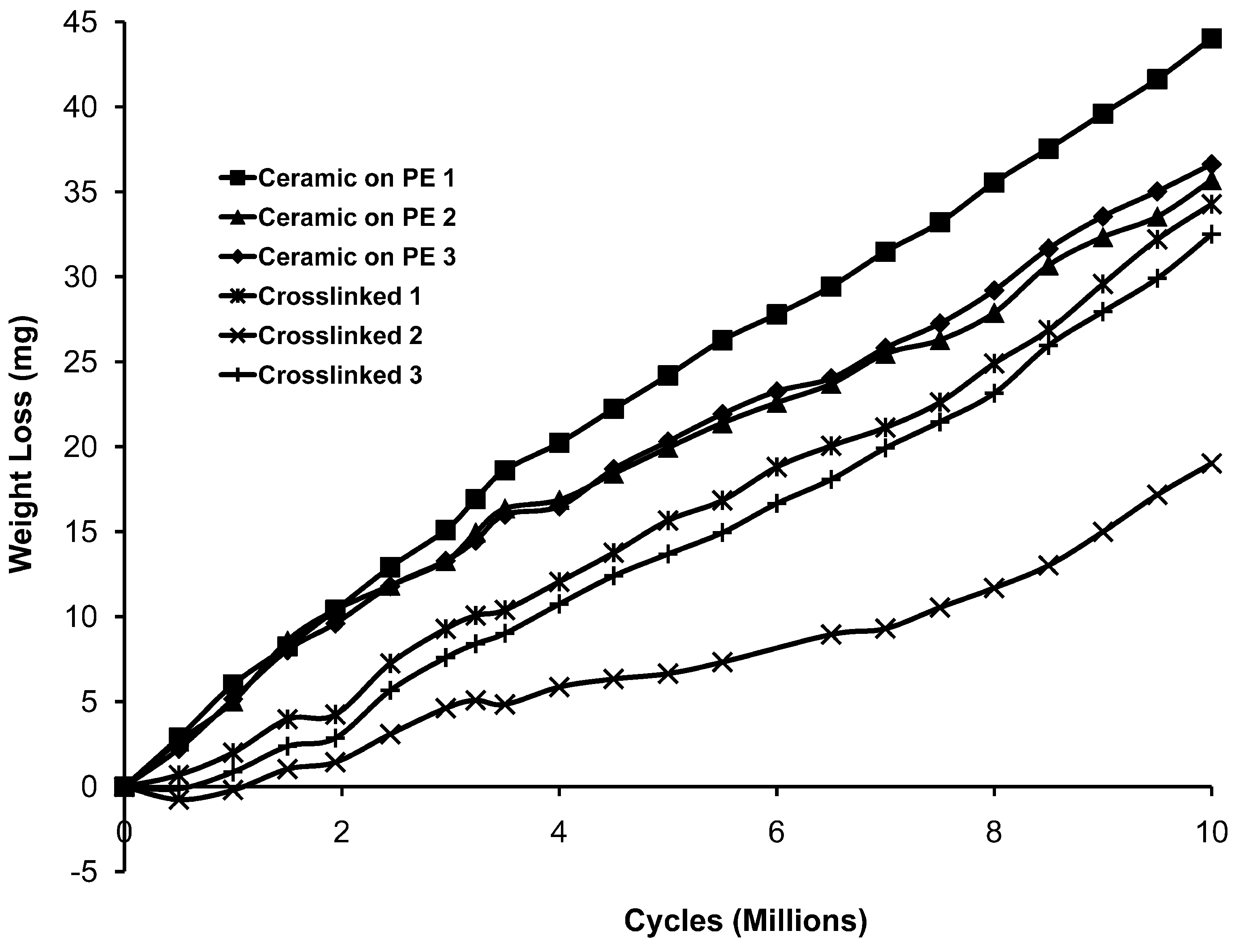
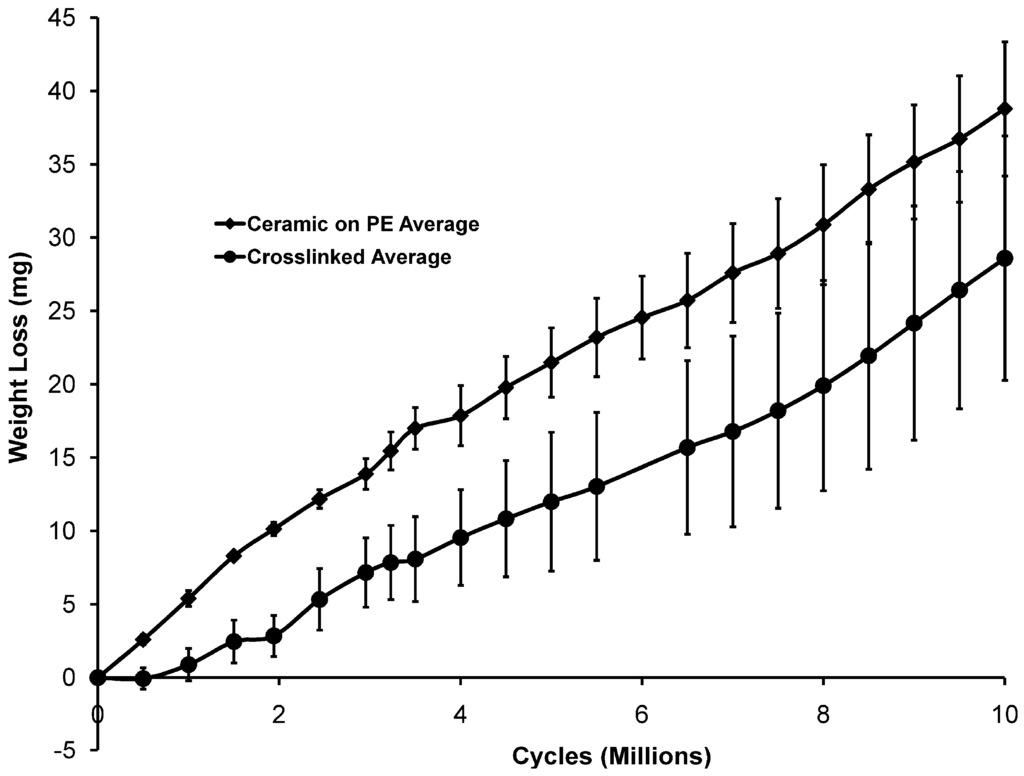
Figure 2.
Averaged wear data for each of the two sample types.
Figure 2.
Averaged wear data for each of the two sample types.
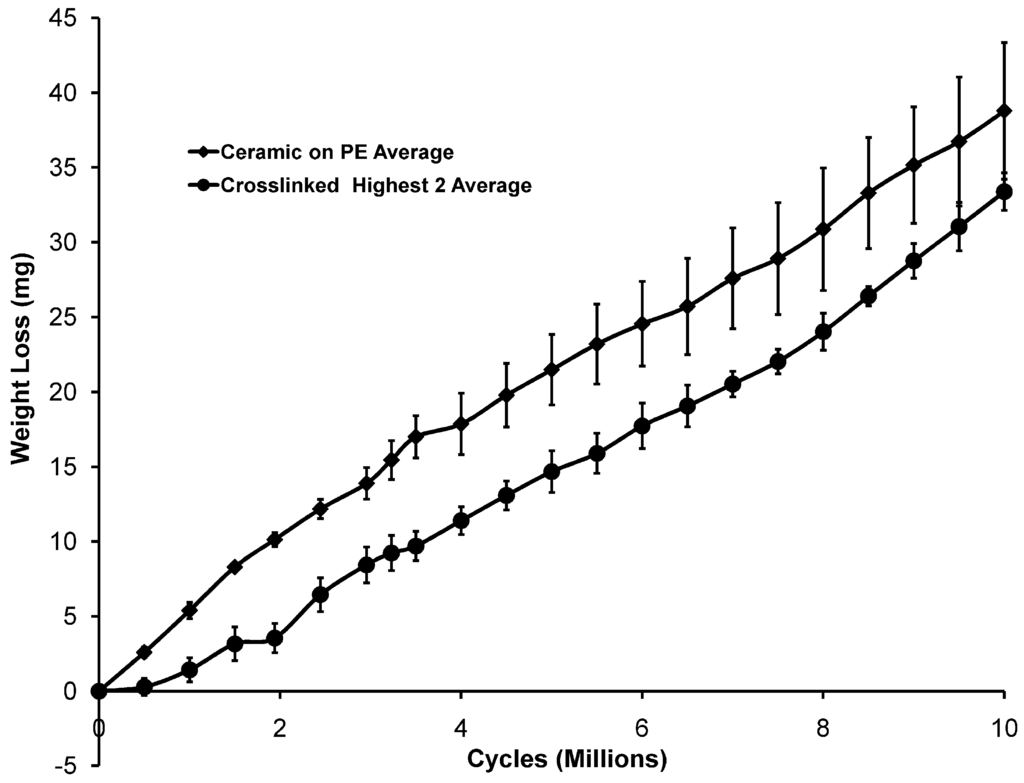
Figure 3.
Averaged wear data excluding the crosslinked polyethylene sample with the lowest wear rate.
Figure 3.
Averaged wear data excluding the crosslinked polyethylene sample with the lowest wear rate.

Table 1.
Wear rates at different points in the testing (milligrams per million cycles).
| Sample Type | First 1,000,000 | 1,000,000 to 2,000,000 | 2,000,000 to 5,000,000 | 5,000,000 to 10,000,000 | 2,000,000 to 10,000,000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic on Polyethylene | 5.40 ± 0.54 | 5.04 ± 0.59 | 3.71 ± 0.72 | 3.46 ± 0.44 | 3.55 ± 0.55 |
| Crosslinked | 0.89 ± 1.10 | 2.08 ± 0.33 | 2.99 ± 1.12 | 3.32 ± 0.73 | 3.20 ± 0.88 |
| Crosslinked (2 highest) | 1.43 | 2.26 | 3.63 | 3.74 | 3.70 |
During each loading cycle, the torque measured varied from clockwise to counterclockwise dependent upon the magnitude and direction of the loads being applied at that moment. Measurements of the torque excursion during testing showed that the friction at the bearing surfaces of the ceramic on polyethylene bearings was initially much higher than that for the metal on crosslinked polymer. This is illustrated in Figure 4. As the testing progressed, this situation was reversed and, as the wear rate of the crosslinked cups increased, the friction increased as well. From 3,000,000 cycles to 5,000,000 cycles, the torques for the two types of bearings were essentially equivalent. After 5,000,000 cycles, the average torques for the crosslinked cups were higher than for the ceramic on polyethylene bearings at all except one time point.
Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9 document the appearance of five of the eight polyethylene cups after 10,000,000 cycles of testing. Figure 6 and Figure 9 show the surface morphology of the acetabular cups that were used a soak controls for the testing, showing the machining marks that were present in all cups before any wear occurred. Manufactured polyethylene cups have residual machining marks as a result of the manufacturing process and, in most cases; the machining marks have completely disappeared by 10,000,000 cycles (Figure 5 and Figure 7). One of the tested cups (Figure 8) appears to have retained a portion of the machining marks after 10,000,000 cycles.
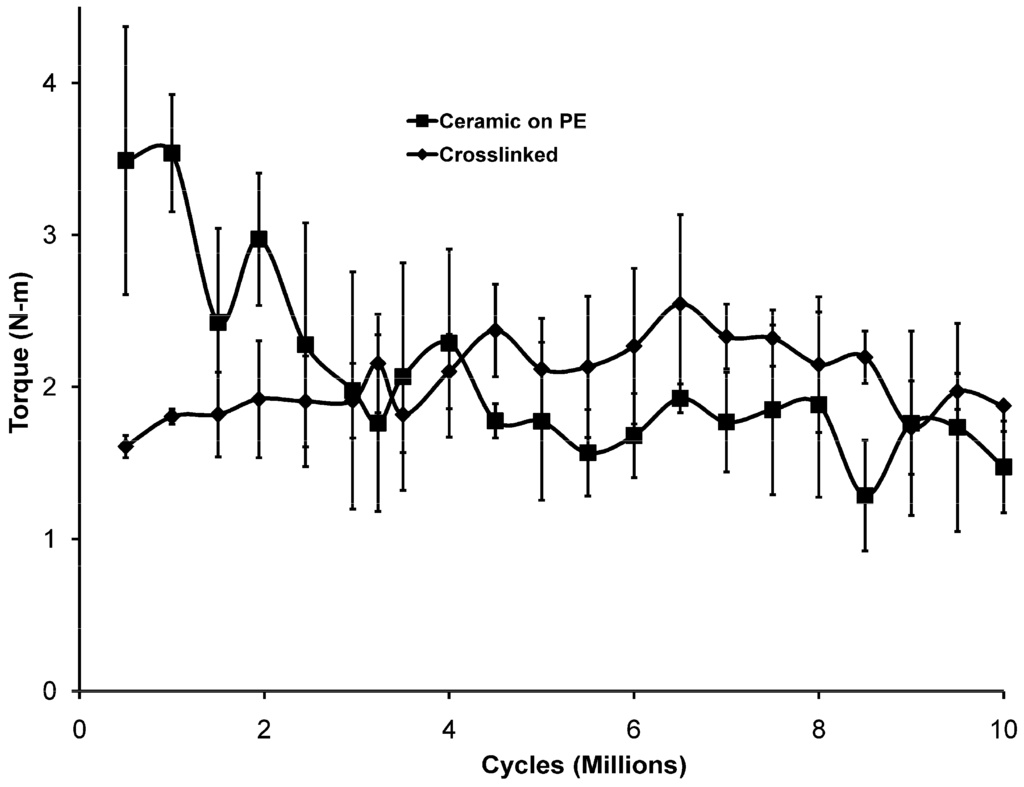
Figure 4.
Measured torque values averaged for each of the two sample types.
Figure 4.
Measured torque values averaged for each of the two sample types.
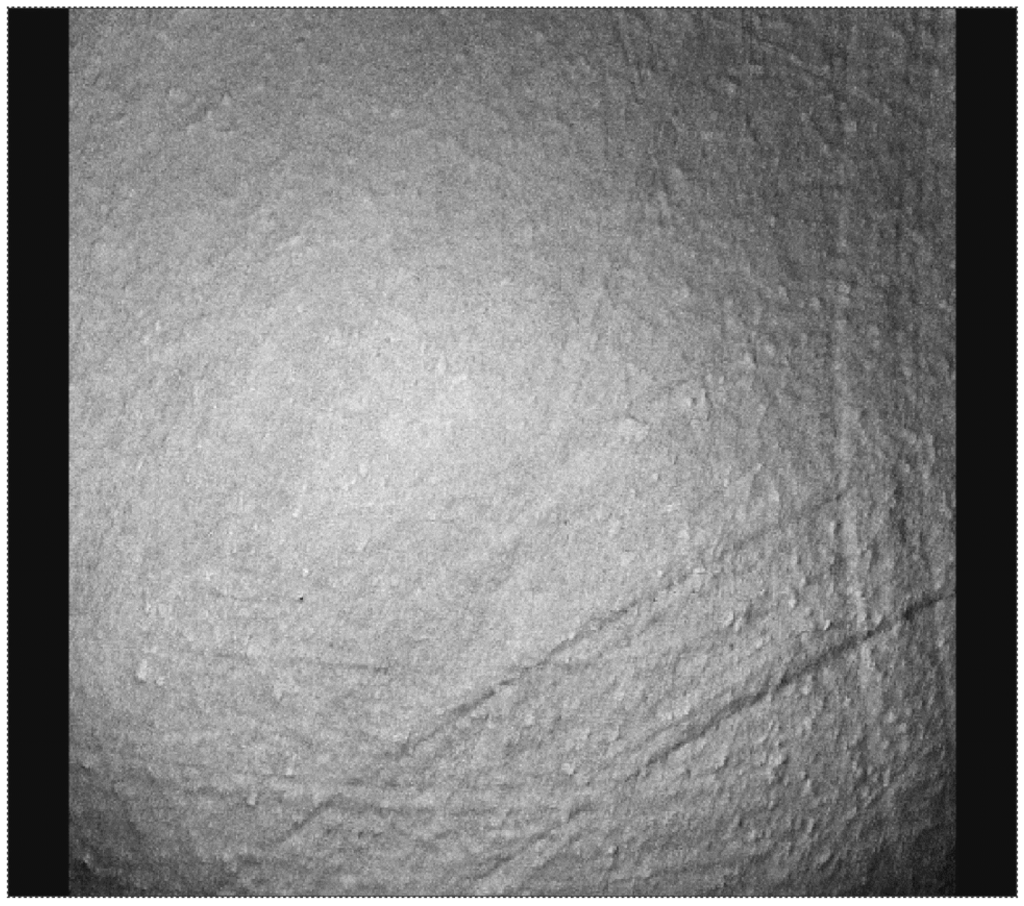
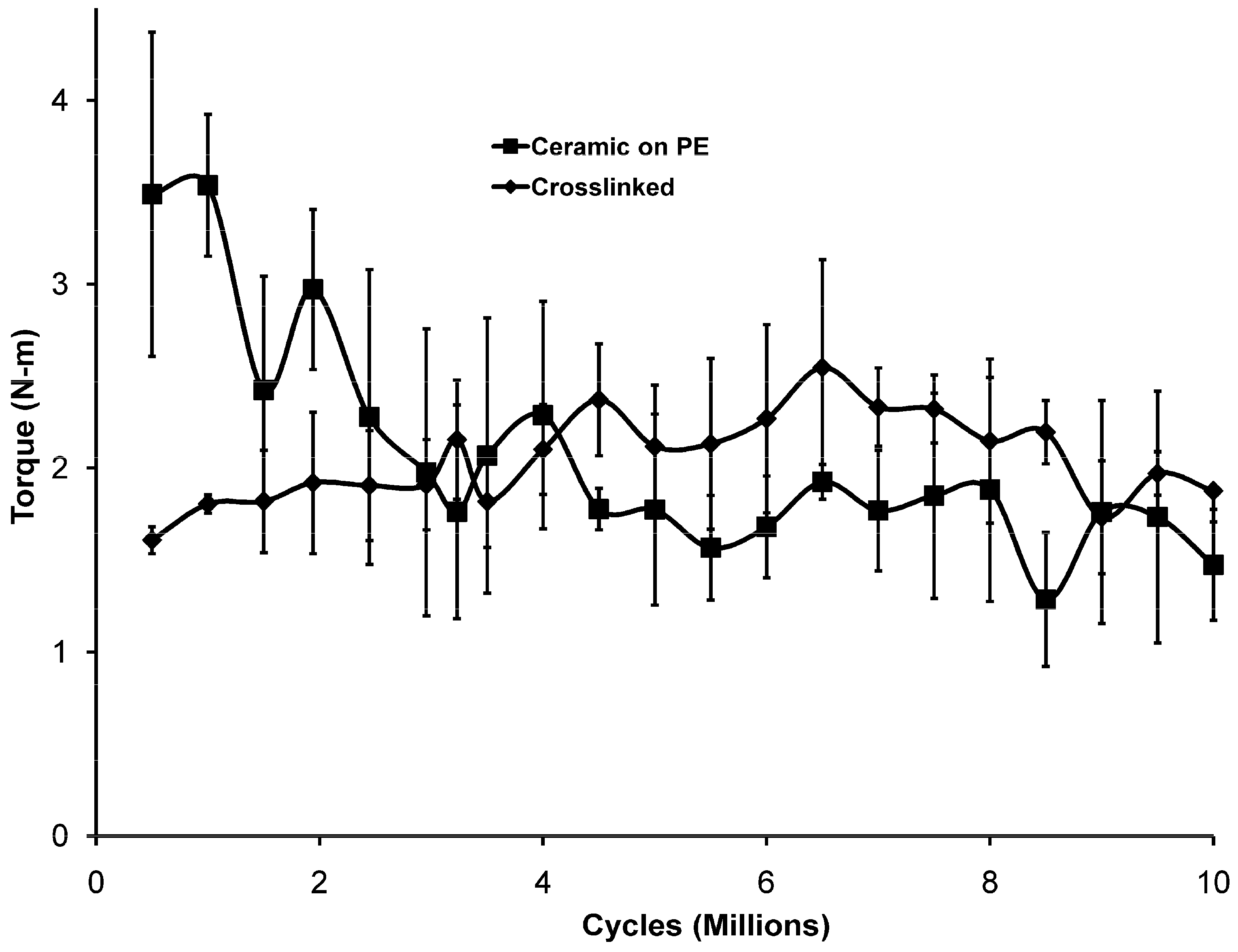

Figure 5.
Surface morphology of an acetabular cup that has been tested with a zirconia femoral head.
Figure 5.
Surface morphology of an acetabular cup that has been tested with a zirconia femoral head.
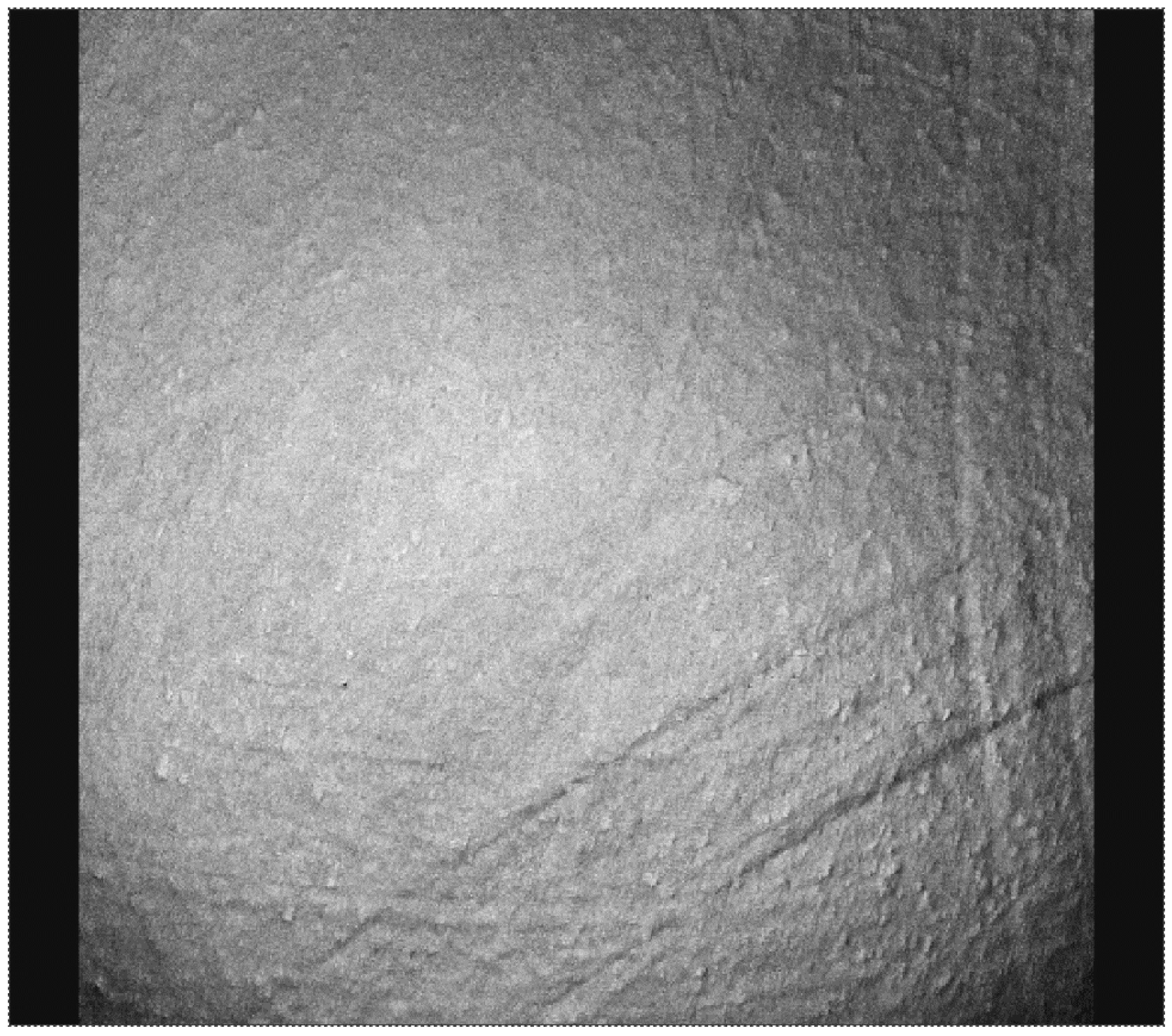
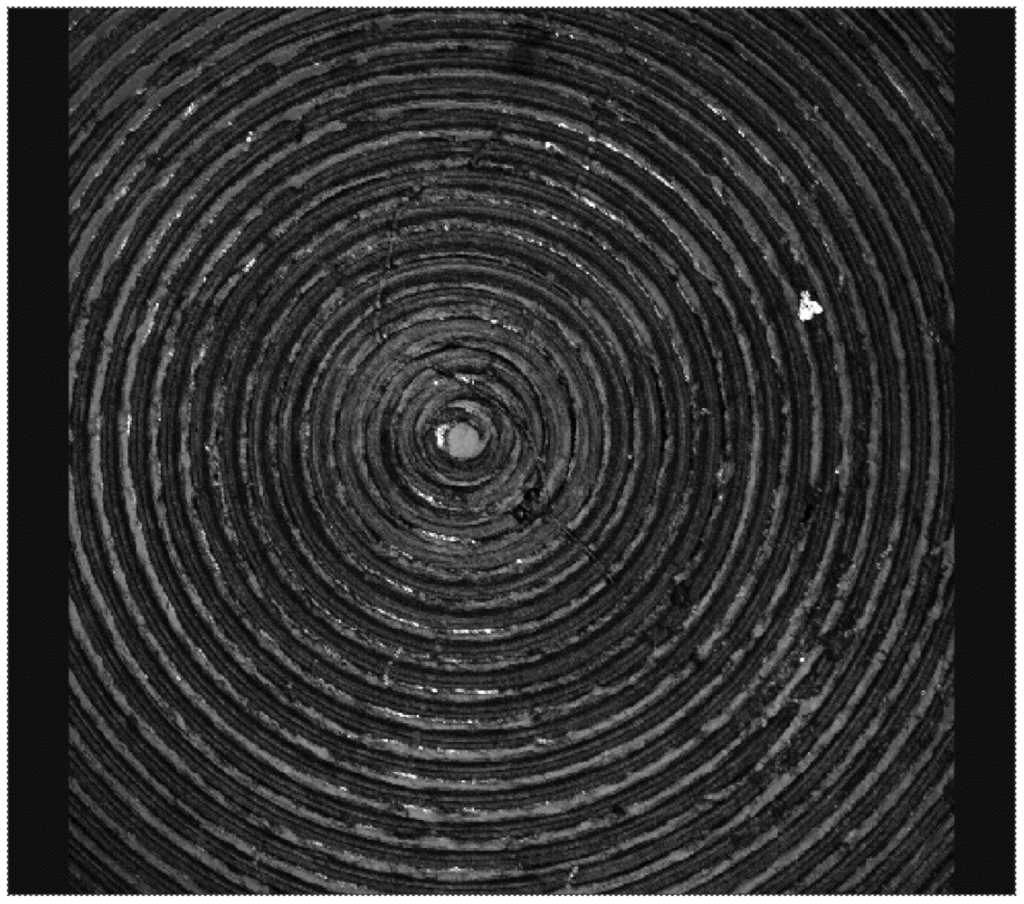


Figure 6.
Surface morphology of the same type of cup as in Figure 5 in the as-manufactured condition.
Figure 6.
Surface morphology of the same type of cup as in Figure 5 in the as-manufactured condition.
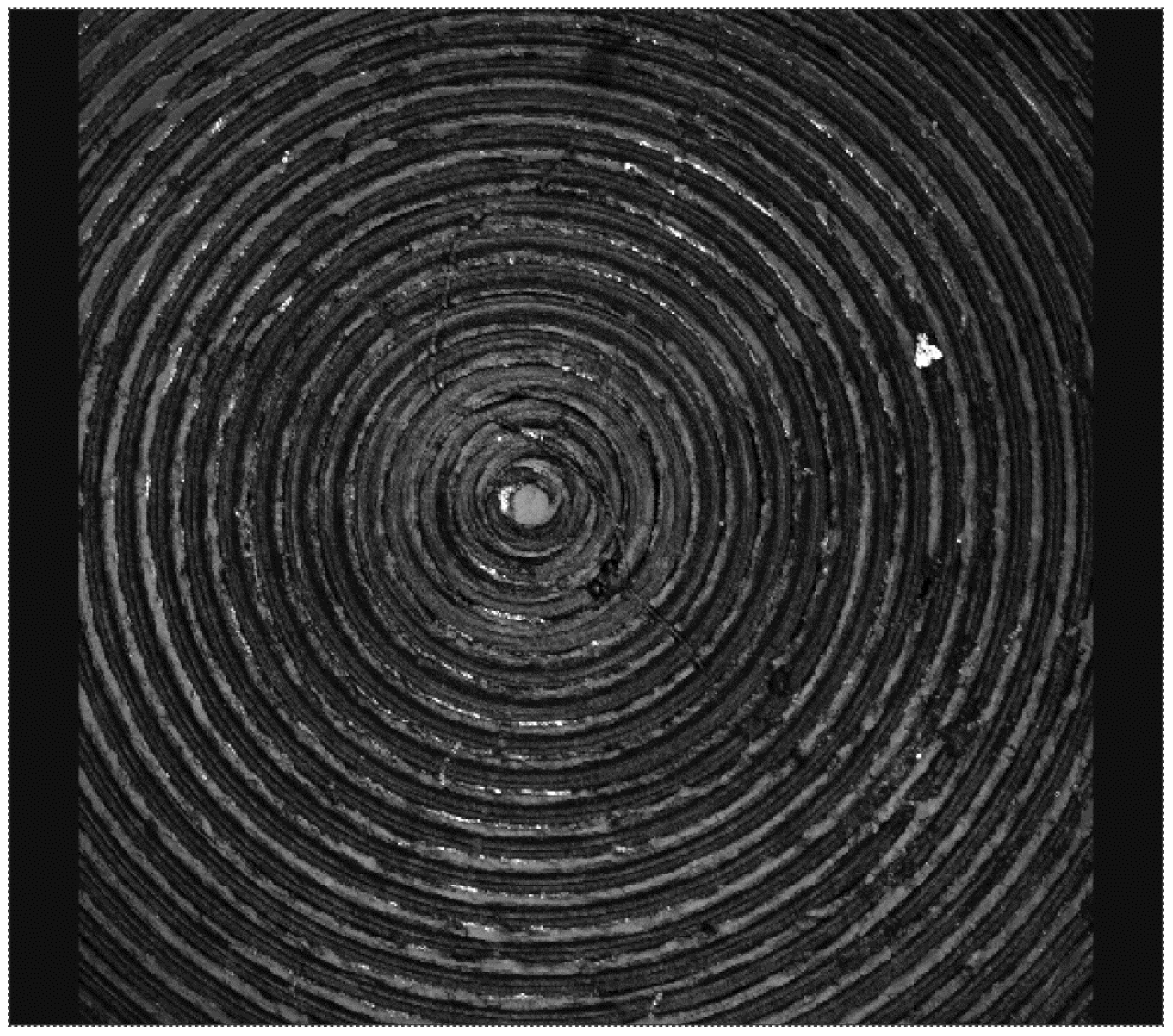

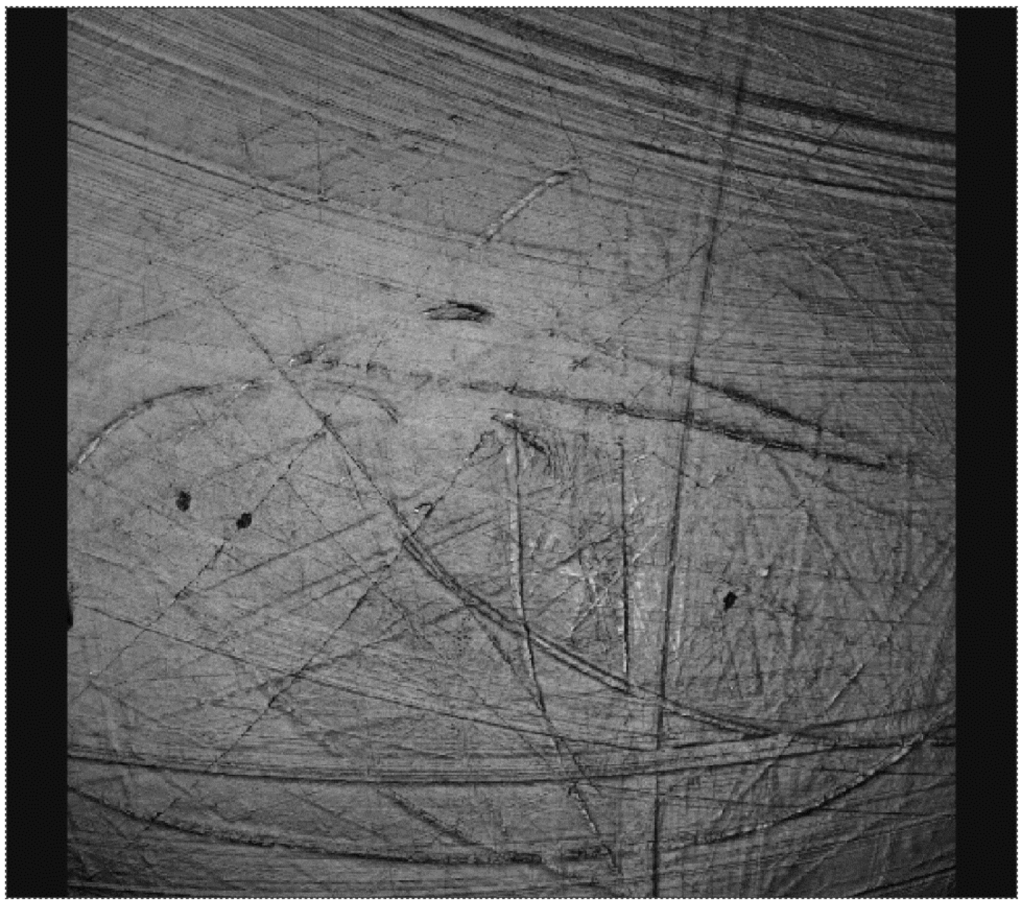
Figure 7.
Surface morphology of a crosslinked polyethylene acetabular cup that has been tested with a cobalt alloy femoral head.
Figure 7.
Surface morphology of a crosslinked polyethylene acetabular cup that has been tested with a cobalt alloy femoral head.
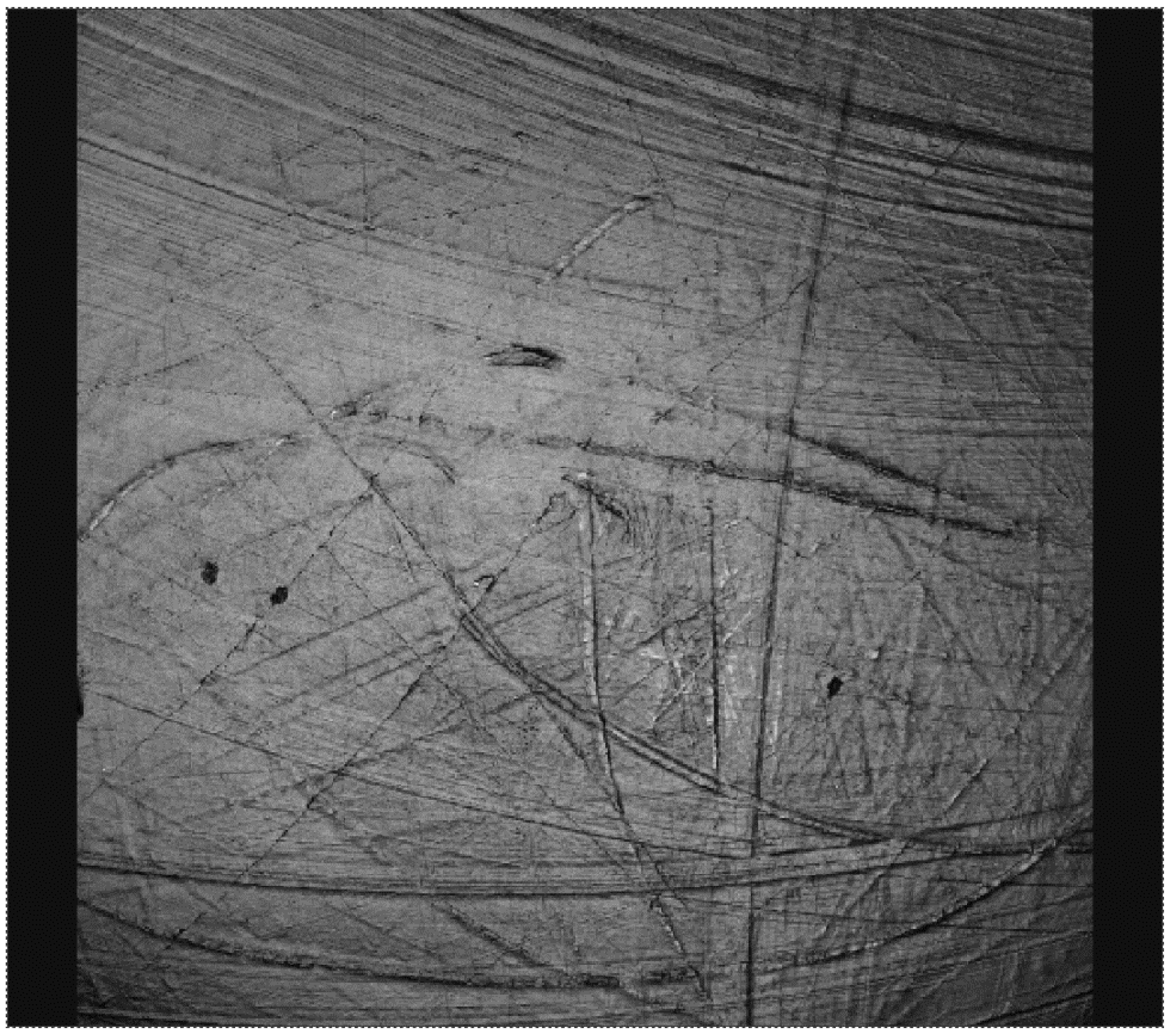
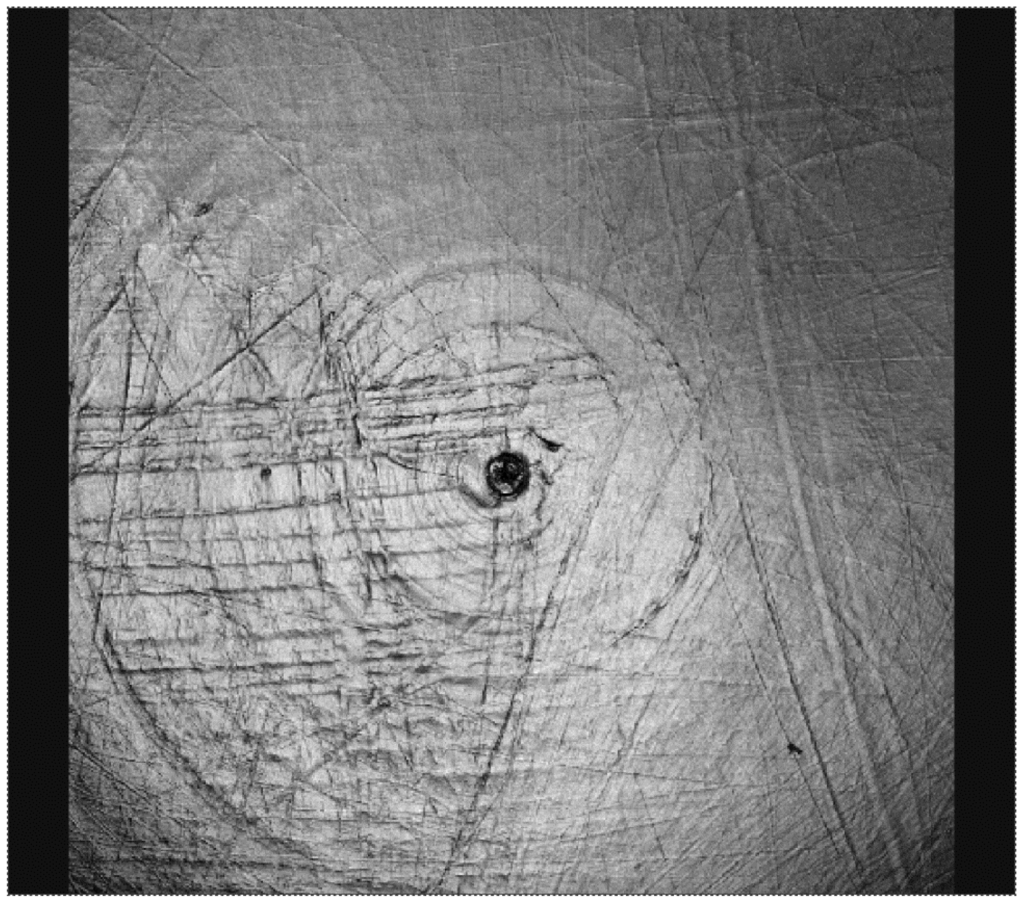
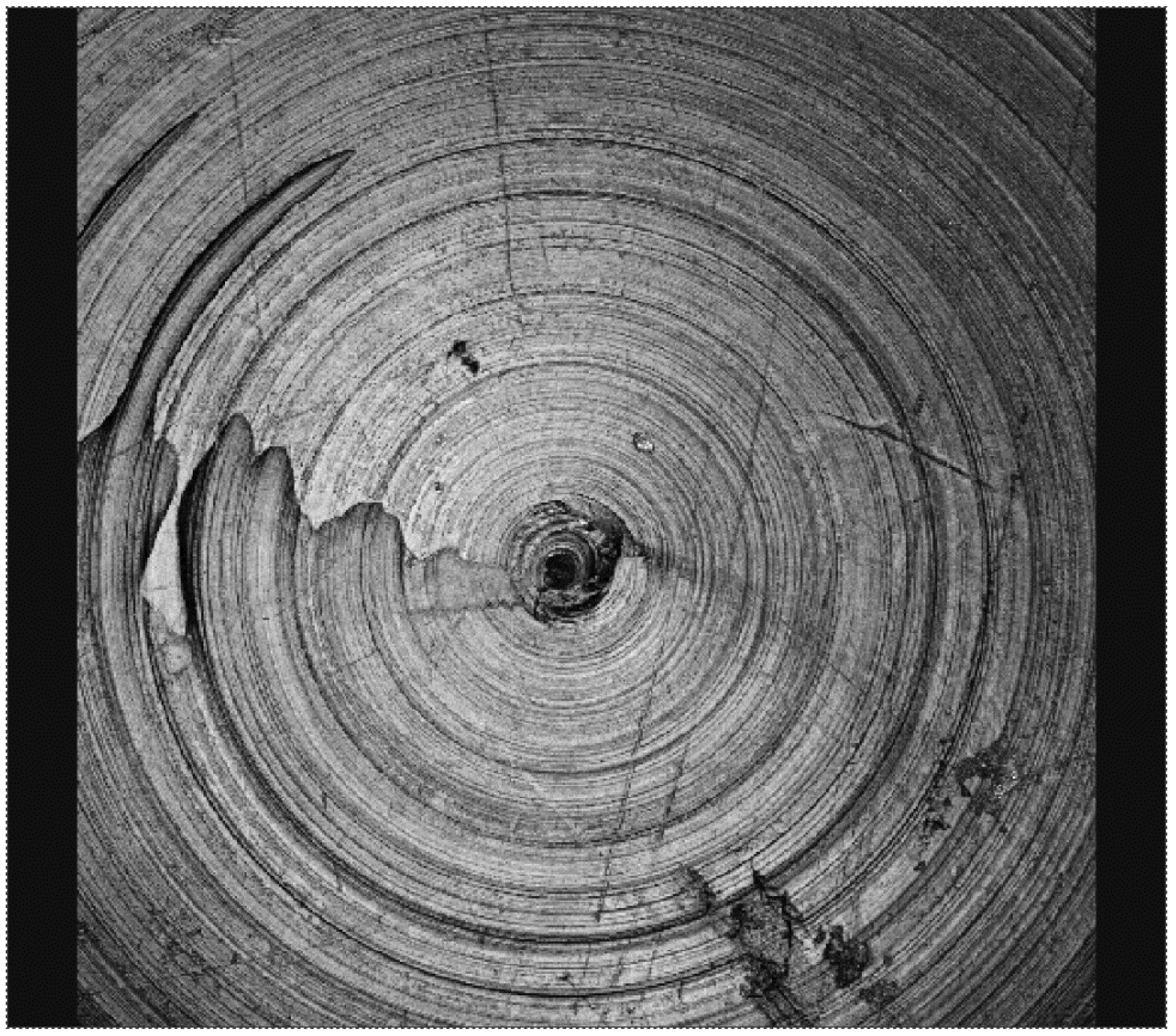
Figure 8.
Surface morphology of a crosslinked polyethylene acetabular cup that has been tested with a cobalt alloy femoral head, showing residual machining marks after 10 million wear cycles.
Figure 8.
Surface morphology of a crosslinked polyethylene acetabular cup that has been tested with a cobalt alloy femoral head, showing residual machining marks after 10 million wear cycles.
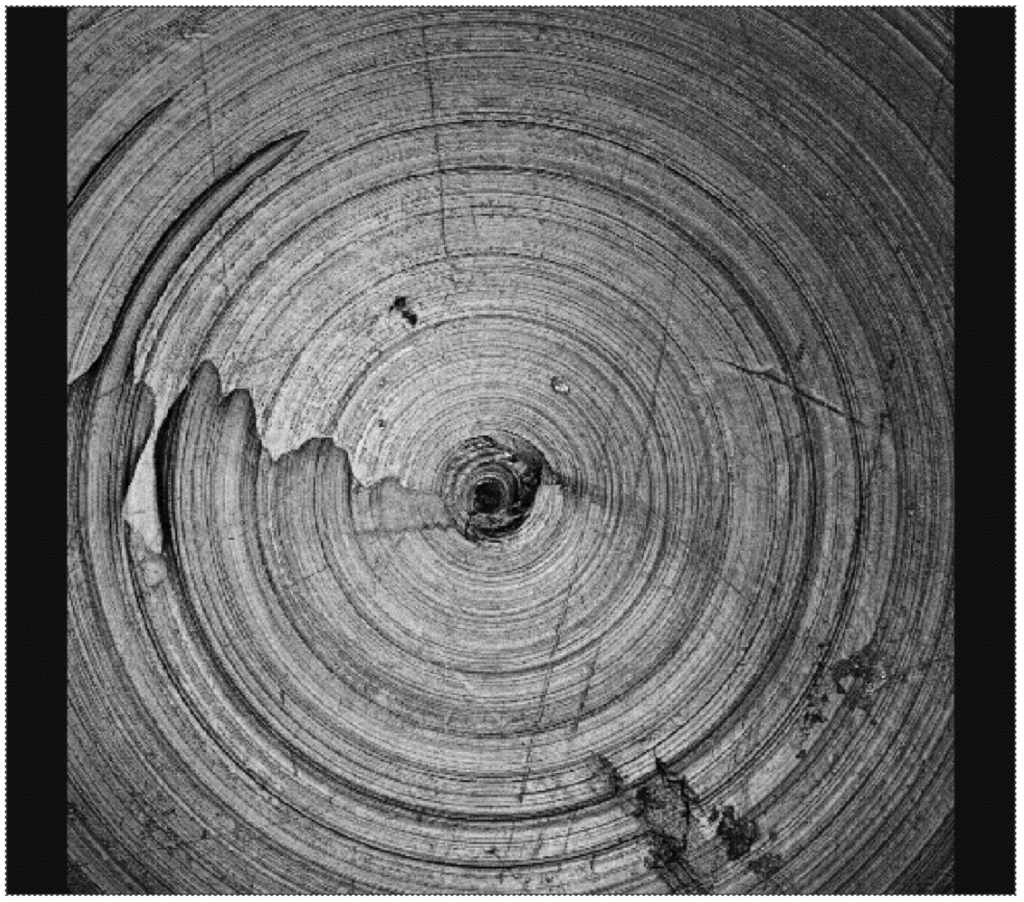
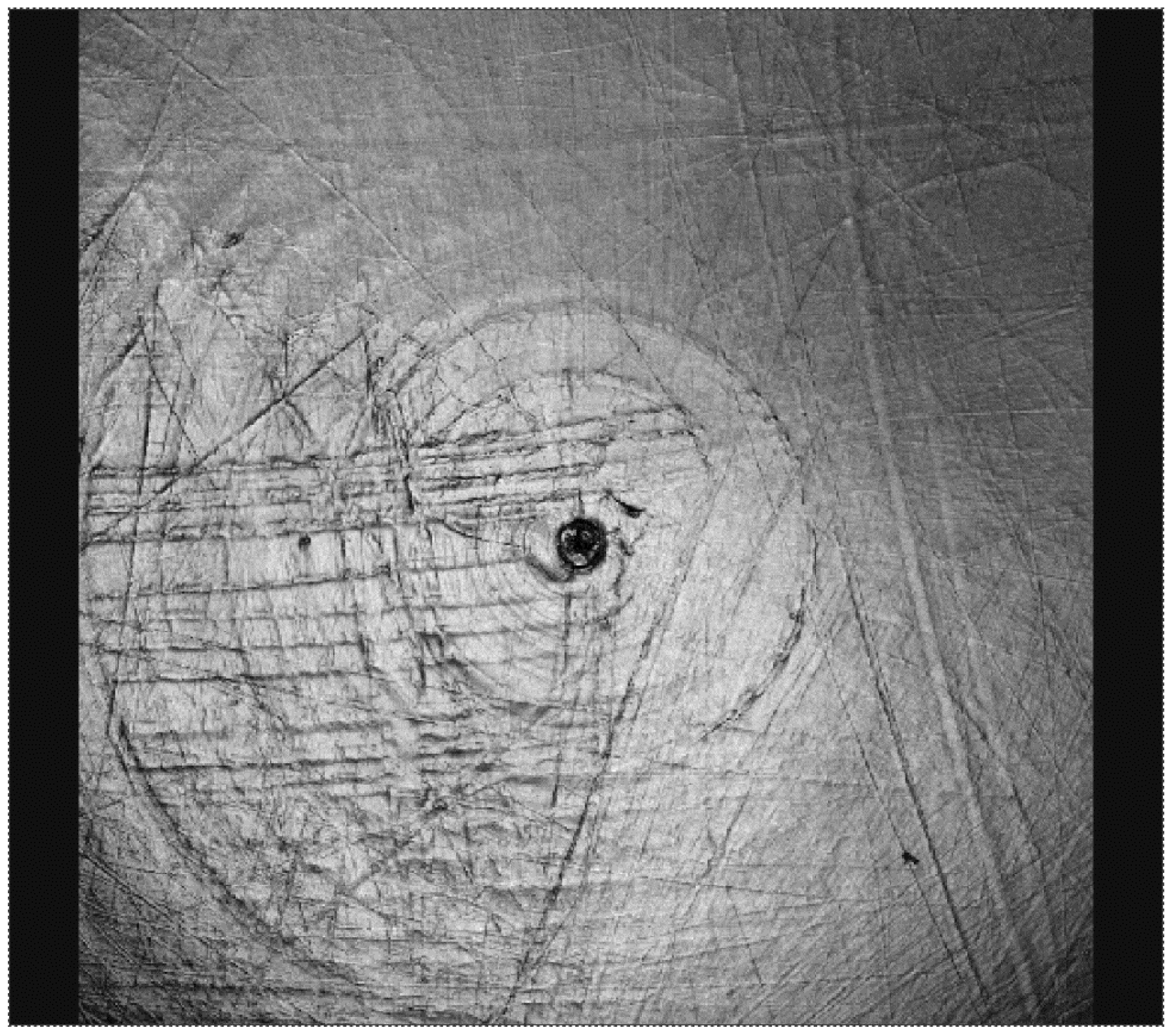

Figure 9.
Surface morphology of the same type of cup as in Figure 7 and Figure 8 in the as-manufactured condition.

The microphotography of the tester cups did not show any observable differences in surface morphology that would suggest an explanation for one of the samples with a ceramic head having higher wear results and one of the crosslinked samples having a much lower wear result.
4. Discussion
The total wear seen with the Kyocera ceramic head bearing on polyethylene was greater than that for Zimmer metal head on crosslinked polyethylene but, after about 2,000,000 cycles, the average wear rates for the two types of bearings were within one standard deviation of each other and the average wear rate of the two crosslinked cups with the highest wear rates was equivalent to the rate using ceramic heads.
The torques transmitted to the torque cells due to the movement at the bearing surfaces started out much higher for the ceramic-on-polyethylene bearings but decreased to a level slightly less than that for metal-on-crosslinked polyethylene by about 4,500,000 cycles and then remained relatively constant for the remainder of the testing period. The torques for the metal-on-crosslinked polyethylene were nearly constant throughout. This may be due to the differences in the initial surface morphology after machining or the differences in surface roughness of the head after manufacture. Over time, the two sides of the bearing couple apparently become accommodated to each other and it appears that the wear mechanism changes, perhaps to mixed mode fluid film lubrication. While this measurement is not a direct measurement of the frictional forces, the measurements are correlated with the frictional forces being experienced since the magnitude of the torque will be proportional with the force required to move the bearing surfaces past each other, which is the frictional force. As a result of the fact that the head sizes of the two devices are different, drawing conclusions about the relative friction between the two designs would be inappropriate but the conclusion can be drawn that the initial friction in the 26 mm bearing couples was much greater early in testing than after about 3 million cycles, while the friction in the 32 mm bearings was relatively constant over the entire experiment. No attempt has been made to determine the actual friction or the effect of head size on friction, although it would seem that the same frictional force at a greater distance from the center of rotation (16 mm vs. 13 mm) would yield a higher torque, which might explain the relationship between the measured torques after about 3 million cycles. Current activity in ASTM subcommittee F04.22 on Arthroplasty has included efforts to describe the relationship between measured torques and frictional forces at the bearing surface when devices are tested in hip simulators.
Researchers have reported [54,71] that the rate of wear of the electron beam crosslinked polyethylene after hip simulator testing for the equivalent of 12 years was not measurable under the conditions of their testing. In this study, two of the highly crosslinked cups did not exhibit measurable wear for the first 500,000 cycles (Figure 1) and the third almost no wear. At 1 million cycles, one was still not showing measurable wear, although all three began to show measurable wear by 1,500,000 cycles. Once the highly crosslinked cups began to show wear, the steady state wear rates for two of the samples were very similar to those for the ceramic on polyethylene tested samples. The third crosslinked cup showed much lower wear rates and still exhibited some residual machining marks after 10,000,000 cycles (Figure 8). The surface morphology of the samples after testing is very similar to that which has been previously reported [71]. Clinical results with these devices confirmed significantly reduced wear rates as compared to devices that had not received the crosslinking treatment [52,72].
The author is not aware of any other studies comparing these two designs in a single laboratory or clinical investigation. A study published in 1995 comparing the wear of highly irradiated UHMWPE with metallic heads to normally sterilized polyethylene with ceramic heads showed very similar but slightly higher wear rates for the ceramic head samples [51], which is consistent with the results of this study.
5. Conclusions
The results of hip simulator wear testing of highly crosslinked UHMWPE 32 mm cups with metallic femoral heads as compared to gamma-irradiation sterilized 26 mm cups with zirconia ceramic heads suggests that the ceramic on polyethylene devices begin to wear sooner and had higher total wear results. After the initial wearing in period, it appears that the steady state wear rates may be very similar. The wear rates of each of the tested bearing combinations is well within the rate of low wear rates that have been reported for improved hip bearing designs.
Based upon these preliminary results, either design is likely to yield acceptable rates of bearing wear when used in total joint replacement surgery.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Masaaki Matsubara, for financial support for this research and Japan Medical Materials and Zimmer Japan for donation of test specimens and fixturing.
Conflicts of Interest
The author received funding for this research from a non-commercial source (Masaaki Matsubara) and received nothing of value from any manufacturer or commercial source other than the donation of the devices tested in this study.
References
- Cates, H.E. Polyethylene wear in cemented metal-backed actabular cups. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1993, 75, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galante, J.O.; Rostoker, W. Wear in total hip prostheses. ACTA Orthop. Suppl. 1973, 145, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Jasty, M.; Goetz, D.D.; Bragdon, C.R.; Lee, K.R.; Hanson, A.E.; Elder, J.R.; Harris, W.H. Wear of polyethylene acetabular components in total hip arthroplasty. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1997, 79, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kabo, J.M. In Vivo Wear of polyethylene acetabular components. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1993, 75, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G. Polyethylene wear in total hip and knee arthroplasties. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1997, 38, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalzried, T.P.; Callaghan, J.J. Wear in total hip and knee replacements. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1999, 81, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edidin, A.A.; Herr, M.P.; Villarraga, M.L.; Muth, J.; Yau, S.S.; Kurtz, S.M. Accelerated aging studies of UHMWPE. I. Effect of resin, processing, and radiation environment on resistance to mechanical degradation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 61, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfick, A.P.D. The effect of socket design, materials and liner thickness on the wear of the porous coated anatomic total hip replacement. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2001, 215, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Z.; Wu, J.Q.; Li, J.Q.; Ren, L.Q.; Tong, J.; Arnell, A.D. Tribological behaviours of PA/UHMWPE blend under dry and lubricating condition. Wear 2006, 260, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKellop, H.; Shen, F.W.; Lu, B.; Campbell, P.; Salovey, R. Effect of sterilization method and other modifications on the wear resistance of acetabular cups made of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. A hip-simulator study. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2000, 82, 1708–1725. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McKellop, H.A.; Shen, F.-W.; Campbell, P.; Ota, T. Effect of molecular weight, calcium stearate, and sterilization methods on the wear of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene acetabular cups in a hip joint simulator. J. Orthop. Res. 1999, 17, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, C.; Bloyce, A.; Bell, T. Sliding wear behaviour of ion implanted ultra high molecular weight polyethylene against a surface modified titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. Trib. Int. 1996, 29, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostland, T.; Albrektsson, B.; Albrektsson, T.; McKellop, H. Wear of ion-implanted pure titanium against UHMWPE. Biomaterials 1989, 10, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, S.C. Compliant layer acetabular cups: Friction testing of a range of materials and designs for a new generation of prosthesis that mimics the natural joint. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2006, 220, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, I.C.; Gustafson, A. Clinical and hip simulator comparisons of ceremic-on-polyethylene and metal-on-polethylene wear. Clin. Orthop. 2000, 379, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvin, A.; Brockett, C.; Williams, S.; Hatto, P.; Burton, A.; Isaac, G.; Stone, M.; Ingham, E.; Fisher, J. Comparison of wear of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene acetabular cups against surface-engineered femoral heads. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2008, 222, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, A.A.; Dowson, D. A multi-station hip joint simulator study of the performance of 22 mm diameter zirconia-ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene total replacement hip joints. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1999, 213, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernigou, P.; Bahrami, T. Zirconia and alumina ceramics in comparison with stainless-steel heads: Polyethylene wear after a minimum ten-year follow-up. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2003, 85, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawanabe, K.; Tanaka, K.; Tamura, J.; Shimizu, M.; Onishi, E.; Iida, H.; Nakamura, T. Effect of alumina femoral head on clinical results in cemented total hip arthroplasty: Old vs. current alumina. J. Orthop. Sci. 2005, 10, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H. Comparison of polyethylene wear associated with cobalt-chromium and zirconia heads after total hip replacement. A prospective, randomized study. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2005, 87, 1769–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saikko, V.; Ahlroos, T.; Calonius, O.; Keranen, J. Wear simulation of total hip prostheses with polyethylene against CoCr, alumina and diamond-like carbon. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semlitsch, M.; Willert, H.G. Clinical wear behavior of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene cups paired with metal and ceramic ball heads in comparison to metal-on-metal pairings of hip joint replacements. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1997, 211, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.L.; Unsworth, A. A comparison between gravimetric and volumetric techniques of wear measurement of UHMWPE acetabular cups against zirconia and coblat-chromium-molybdenum femoral heads in a hip simulator. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1999, 213, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wroblewski, B.M.; Siney, P.D.; Fleming, P.A. Low-friction arthroplasty of the hip using alumina ceramic and cross-linked polyethylene. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1999, 81, 54–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affatato, S.; Ferrari, G.; Chevalier, J.; Ruggeri, O.; Toni, A. Surface characterization and debris analysis of ceramic pairings after ten million cycles on a hip joint simulator. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2002, 216, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishido, T.; Clarke, I.C.; Williams, P.; Boehler, M.; Asano, T.; Shoji, H.; Masaoka, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Imakiire, A. Clinical and simulator wear study of alumina ceramic THR to 17 years and beyond. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2003, 67, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, T.D.; Tipper, J.L.; Insley, G.; Streicher, R.M.; Ingham, E.; Fisher, J. Long-term wear of ceramic matrix composite materials for hip prostheses under severe swing phase microseparation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2003, 66, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, T.R.; Rowe, S.M.; Jung, S.T.; Seon, K.J.; Maloney, W.J. Osteolysis in association with a total hip arthroplasty with ceramic bearing surfaces. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1998, 80, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muller, M.E. The benefits of metal-on-metal total hip replacements. Clin. Orthop. 1995, 311, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walker, P.S.; Erkman, M.J. Metal-on-metal lubrication in artificial human joints. Wear 1972, 21, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.W.; Bobyn, J.D.; Medley, J.B.; Krygier, J.J.; Tanzer, M. The Otto Aufranc Award. Wear and lubrication of metal-on-metal hip implants. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1999, 369, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorr, L.D.; Wan, Z.; Longjohn, D.B.; Dubois, B.; Murken, R. Total hip arthroplasty with use of the Metasul metal-on-metal articulation. Four to seven-year results. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2000, 82, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fisher, J.; Hu, X.Q.; Stewart, T.D.; Williams, S.; Tipper, J.L.; Ingham, E.; Stone, M.H.; Davies, C.; Hatto, P.; Bolton, J.; et al. Wear of surface engineered metal-on-metal hip prostheses. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2004, 15, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, J.; Hu, X.Q.; Tipper, J.L.; Stewart, T.D.; Williams, S.; Stone, M.H.; Davies, C.; Hatto, P.; Bolton, J.; Riley, M.; et al. An in vitro study of the reduction in wear of metal-on-metal hip prostheses using surface-engineered femoral heads. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2002, 216, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, A.A.; Dowson, D.; Isaac, G.H.; Lancaster, J.G. A comparative joint simulator study of the wear of metal-on-metal and alternative material combinations in hip replacements. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2000, 214, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalzried, T.P.; Peters, P.C.; Maurer, B.T.; Bragdon, C.R.; Harris, W.H. Long-duration metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasties with low wear of the articulating surfaces. J. Arthroplast. 1996, 11, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streicher, R.M.; Semlitsch, M.; Schon, R.; Weber, H.; Rieker, C. Metal-on-metal articulation for artificial hip joints: Laboratory study and clinical results. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1996, 210, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willert, H.G.; Buchhorn, G.H.; Gobel, D.; Koster, G.; Schaffner, S.; Schenk, R.; Semlitsch, M. Wear behavior and histopathology of classic cemented metal on metal hip endoprostheses. Clin. Orthop. 1996, 329, S160–S186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livermore, J.; Ilstrup, D.; Morrey, B. Effect of femoral head size on wear of the polyethylene acetabular component. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1990, 72, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clarke, I.C.; Gustafson, A.; Jung, H.; Fujisawa, A. Hip-simulator ranking of polyethylene wear: Comparisons between ceramic heads of different sizes. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1996, 67, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaule, P.E.; Schmalzreid, T.P.; Udomkiat, P.; Amstutz, H.C. Jumbo femoral head for the treatment of recurrent dislocation following total hip replacement. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2002, 84, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kluess, D.; Martin, H.; Mittelmeier, W.; Schmitz, K.-P.; Bader, R. Influence of femoral head size on impingement, dislocation and stress distribution in total hip replacement. Med. Eng. Phys. 2007, 29, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burroughs, B.R.; Hallstrom, B.; Golladay, G.J.; Hoeffel, D.; Harris, W.H. Range of motion and stability in total hip arthroplasty with 28-, 32-, 38-, and 22-mm femoral head sizes. J. Arthroplast. 2005, 20, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, A.; Nakashima, Y.; Jingushi, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Kuraoka, A.; Iwamoto, Y. Effects of the femoral offset and the head size on the safe range of motion in total hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2009, 24, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Lima, D.D.; Hermida, J.C.; Chen, P.C.; Colwell, C.W., Jr. Polyethylene cross-linking by two different methods reduces acetabular liner wear in a hip joint wear simulator. J. Orthop. Res. 2003, 21, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerdink, C.H.; Grimm, B.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Ronduis, J.; Verberg, A.J.; Tonino, A.J. Crosslinked polyethylene compared to conventional polyethylene in total hip replacement: Pre-clinical evaluation, in vitro testing and prospective clinical follow-up study. Acta Orthop. 2006, 77, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKellop, H.; Shen, F.-W.; Lu, B.; Campbell, P.; Salovey, R. Development of an extremely wear-resistant ultra high molecular weight polyethylene for total hip replacements. J. Orthop. Res. 1999, 17, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muratoglu, O.K.; O’Connor, D.O.; Bragdon, C.R.; Delaney, J.; Jasty, M.; Harris, W.H.; Merrill, E.; Venugopalan, P. Gradient crosslinking of UHMWPE using irradiation in molten state for total joint arthroplasty. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratoglu, O.K.; Wannomae, K.; Christensen, S.; Rubash, H.E.; Harris, W.H. Ex vivo wear of conventional and cross-linked polyethylene acetabular liners. Clin. Orthop. 2005, 438, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, A.C.; D’Lima, D.D.; Colwell, C.W. Highly cross-linked polyethylene in total hip arthroplasty. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2006, 14, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oonishi, H.; Takayama, Y.; Tsuji, E. The low wear of cross-linked polyethylene socket in total hip prostheses. In Encyclopedic Handbook of Biomaterials and Bioengineering, Part A: Materials; Wise, D.L., Trantolo, D.J., Altobelli, D.F., Yaszemski, M.J., Gresser, J.D., Schwartz, E.R., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1995; Volume 1, pp. 1853–1868. [Google Scholar]
- McCalden, R.W.; MacDonald, S.J.; Rorabeck, C.H.; Bourne, R.B.; Chess, D.G.; Charron, K.D. Wear rate of highly cross-linked polyethylene in total hip arthroplasty. A randomized controlled trial. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2009, 91, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaou, V.S.; Edwards, M.R.; Bogoch, E.; Schemitsch, E.H.; Waddell, J.P. A prospective randomised controlled trial comparing three alternative bearing surfaces in primary total hip replacement. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2012, 94, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muratoglu, O.K.; Bragdon, C.R.; O’Connor, D.; Perinchief, R.S.; Estok, D.M.; Jasty, M.; Harris, W.H. Larger diameter femoral heads used in conjunction with a highly cross-linked ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene: A new concept. J. Arthroplast. 2001, 16, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermida, J.C.; Bergula, A.; Chen, P.; Colwell Jr, C.W.; D’Lima, D.D. Comparison of the wear rates of twenty-eight and thirty-two millimeter femoral heads on cross-linked polyethylene acetabular cups in a wear simulator. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2003, 85, 2325–2331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plank, G.R.; Estok, D.M., 2nd; Muratoglu, O.K.; O’Connor, D.O.; Burroughs, B.R.; Harris, W.H. Contact stress assessment of conventional and highly crosslinked ultra high molecular weight polyethylene acetabular liners with finite element analysis and pressure sensitive film. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 80, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachiewicz, P.F.; Heckman, D.S.; Soileau, E.S.; Mangla, J.; Martell, J.M. Femoral head size and wear of highly cross-linked polyethylene at 5 to 8 years. Clin. Orthop. 2009, 467, 3290–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, I.; Nakamura, N.; Takao, M.; Sakai, T.; Nishii, T.; Sugano, N. Eight-year wear analysis in Longevity highly cross-linked polyethylene liners comparing 26- and 32-mm heads. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2011, 131, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuckler, J.M.; Bearcroft, J.; Asgian, C.M. Femoral head technologies to reduce polyethylene wear in total hip arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. 1995, 317, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- D’Antonio, J.A.; Sutton, K. Ceramic materials as bearing surfaces for total hip arthroplasty. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2009, 17, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galvin, A.L.; Jennings, L.M.; Tipper, J.L.; Ingham, E.; Fisher, J. Wear and creep of highly crosslinked polyethylene against cobalt chrome and ceramic femoral heads. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2010, 224, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, J.A.; Garvin, K.L.; Boese, C.K.; Bryson, L.; Pedersen, D.R.; Callaghan, J.J.; Miller, R.K. Ceramic-on-polyethylene bearing surfaces in total hip arthroplasty. Seventeen to twenty-one year results. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2001, 83, 1688–1694. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawate, K.; Omura, T.; Kawahara, I.; Tamai, K.; Ueha, T.; Takemura, K. Differences in highly cross-linked polyethylene wear between zirconia and cobalt-chromium femoral heads in Japanese patients: A prospective, randomized study. J. Arthroplast. 2009, 24, 1221–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stilling, M.; Nielsen, K.A.; Soballe, K.; Rahbek, O. Clinical comparison of polyethylene wear with zirconia or cobalt-chromium femoral heads. Clin. Orthop. 2009, 467, 2644–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraay, M.J.; Thomas, R.D.; Rimnac, C.M.; Fitzgerald, S.J.; Goldberg, V.M. Zirconia vs. Co-Cr femoral heads in total hip arthroplasty: Early assessment of wear. Clin. Orthop. 2006, 453, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meftah, M.; Klingenstein, G.G.; Yun, R.J.; Ranawat, A.S.; Ranawat, C.S. Long-term performance of ceramic and metal femoral heads on conventional polyethylene in young and active patients: A matched-pair analysis. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2013, 95, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, M.P.; Johnson, T.S.; Crowninshield, R.D.; Blanchard, C.R.; Bambri, S.K.; Yao, J.Q. Characterization of a highly cross-linked ultrahigh molecular-weight polyethylene in clinical use in total hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2008, 23, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 14242-3-Implants for Surgery—Wear of Total Hip-Joint Prostheses—Part 3: Loading and displacement parameters for orbital bearing type wear testing machines and corresponding environmental conditions for test. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- F1714–96 (2013)-Standard Guide for Gravimetric Wear Assessment of Prosthetic Hip-Designs in Simulator Devices. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- ISO 14242-2-Implants for Surgery—Wear of Total Hip-Joint Prostheses—Part 2: Methods of measurement. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000.
- Jasty, M.; Rubash, H.E.; Muratoglu, O.K. Highly crosslinked polyethylene: The debate is over—In the affirmative. J. Arthroplast. 2005, 20, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragdon, C.R.; Barrett, S.; Martell, J.M.; Greene, M.E.; Henrik, M.; Harris, W.H. Steady state penetration rates of electron beam-irradiated, highly cross-linked polyethylene at an average of 45-month follow-up. J. Arthroplast. 2006, 21, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
