How Does Dissipation Affect the Transition from Static to Dynamic Macroscopic Friction?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model
2.1. Model Derivation
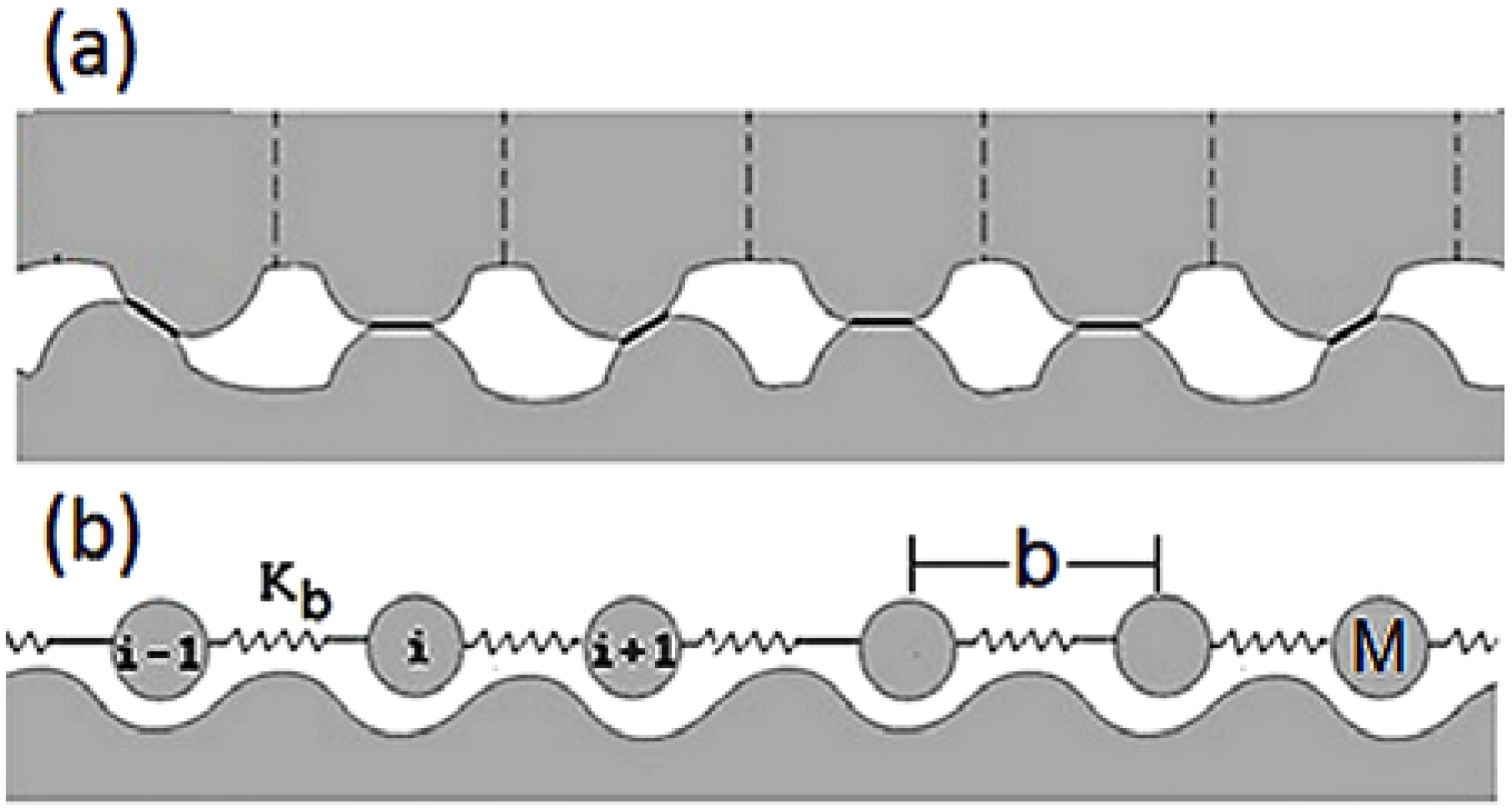
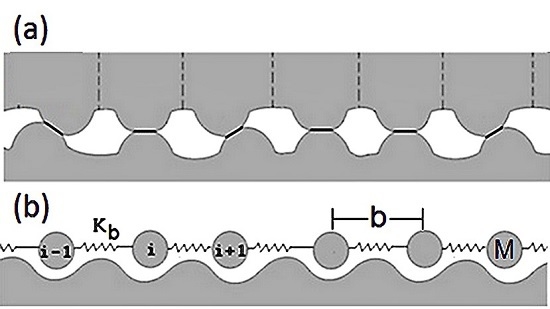
2.2. Uniform Sliding Motion
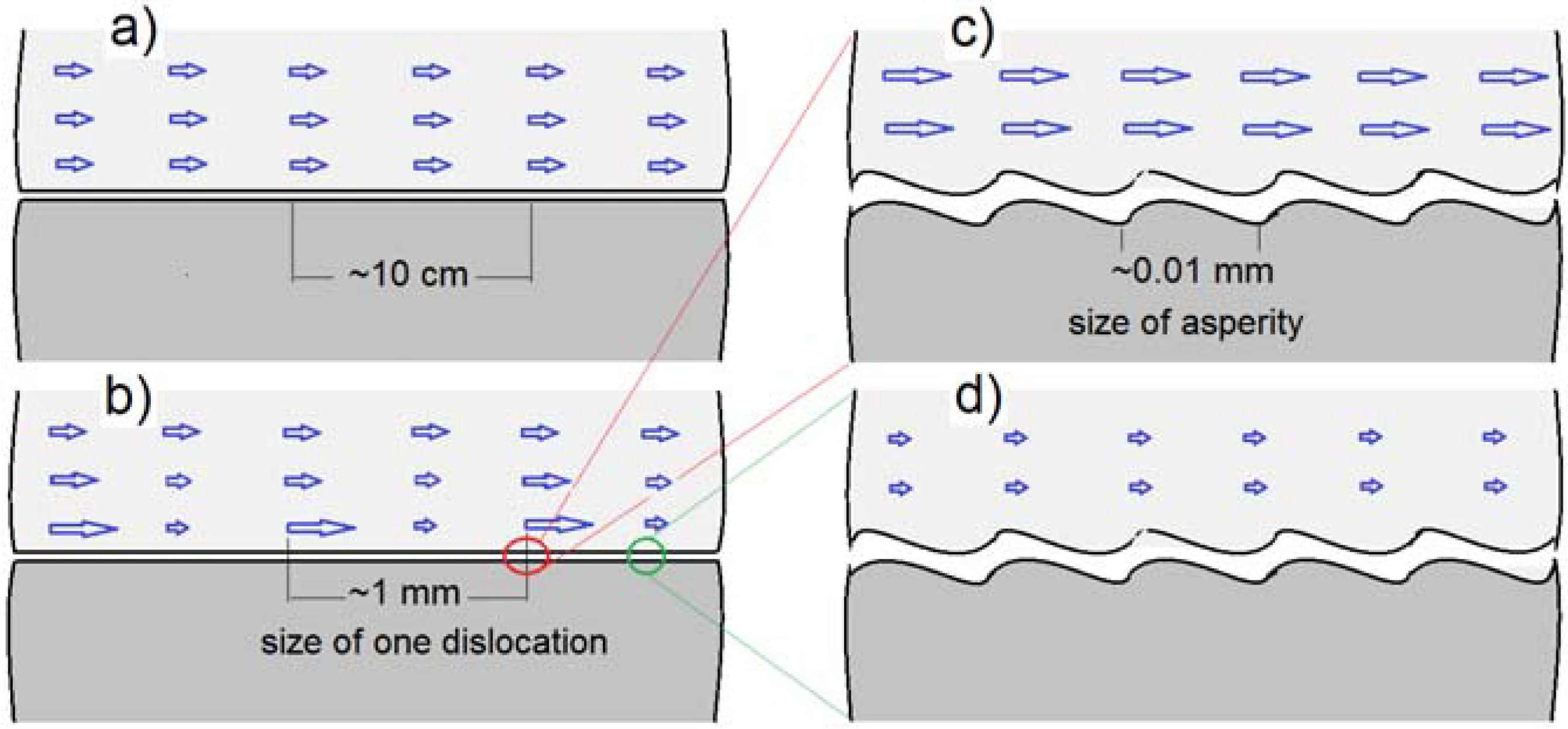
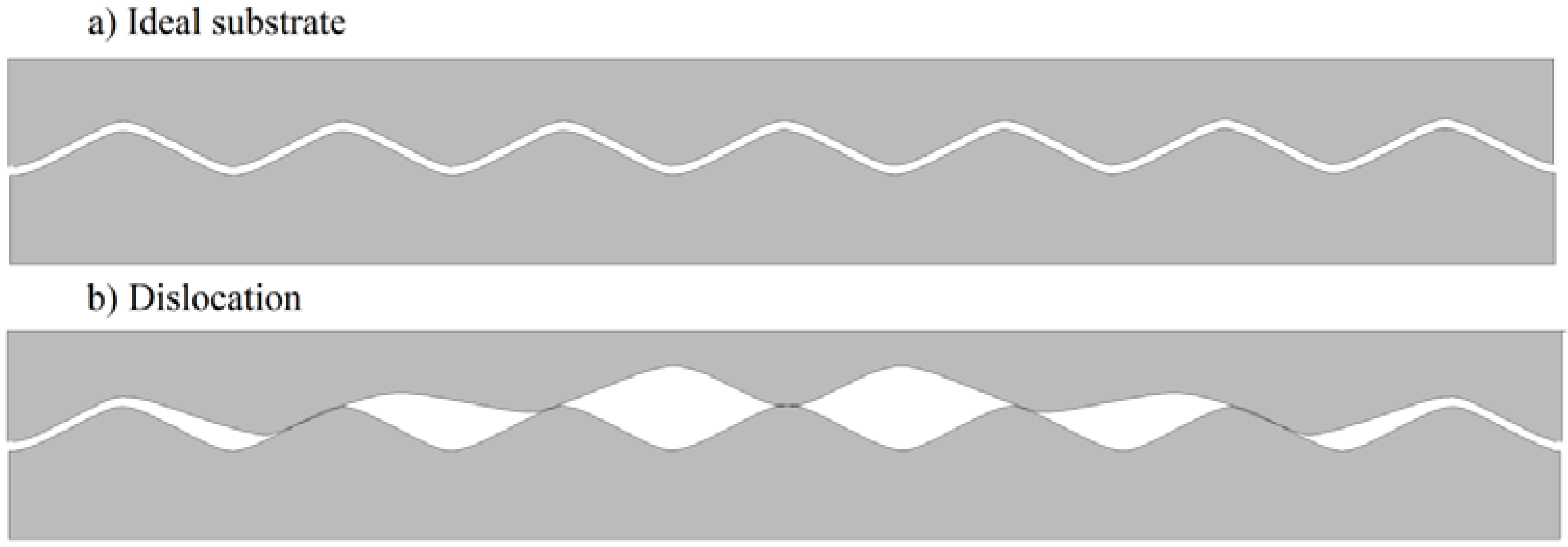
2.3. Non-Uniform Sliding Motion
3. Results
3.1. Analytical Solution (No Dissipation)
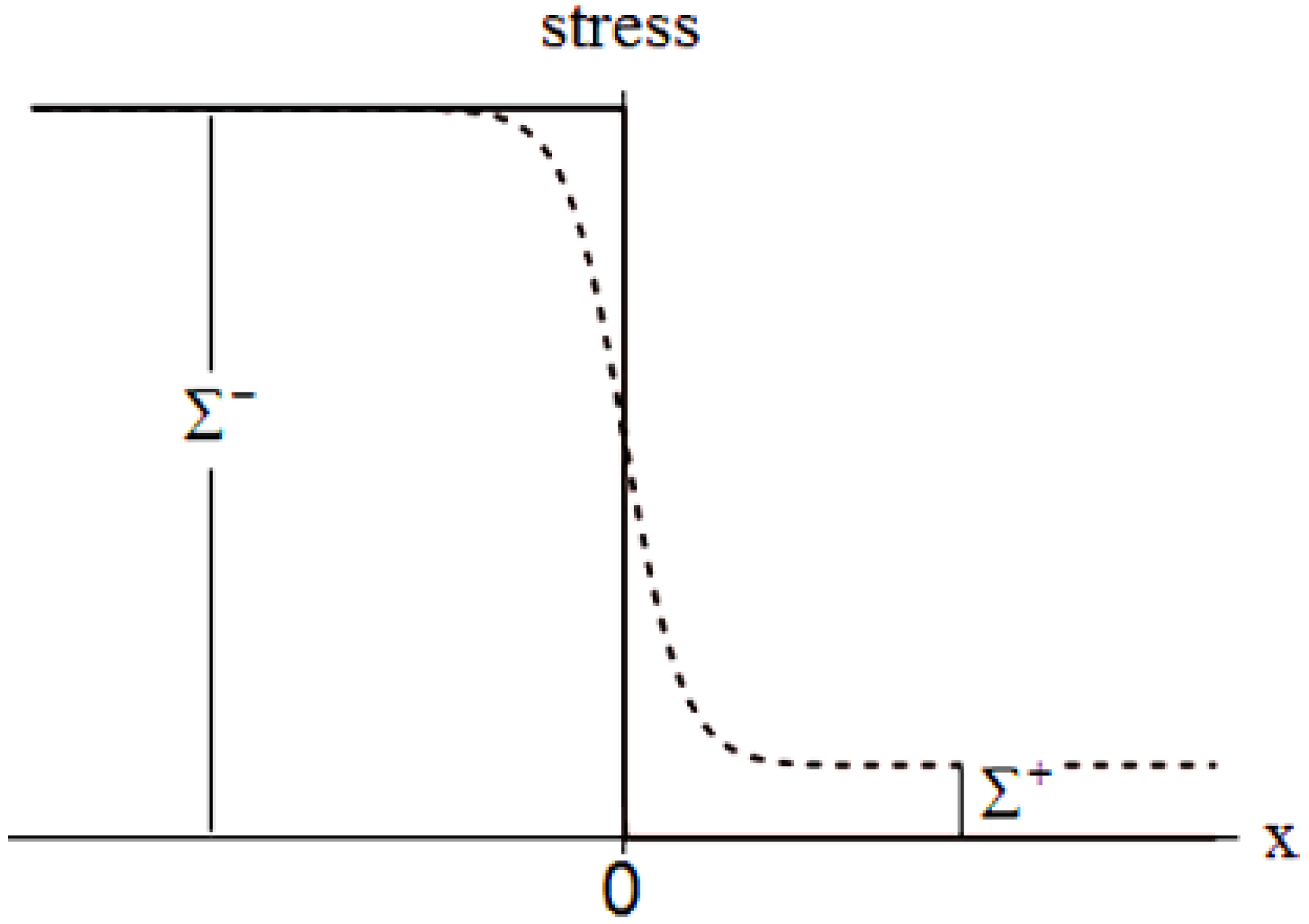
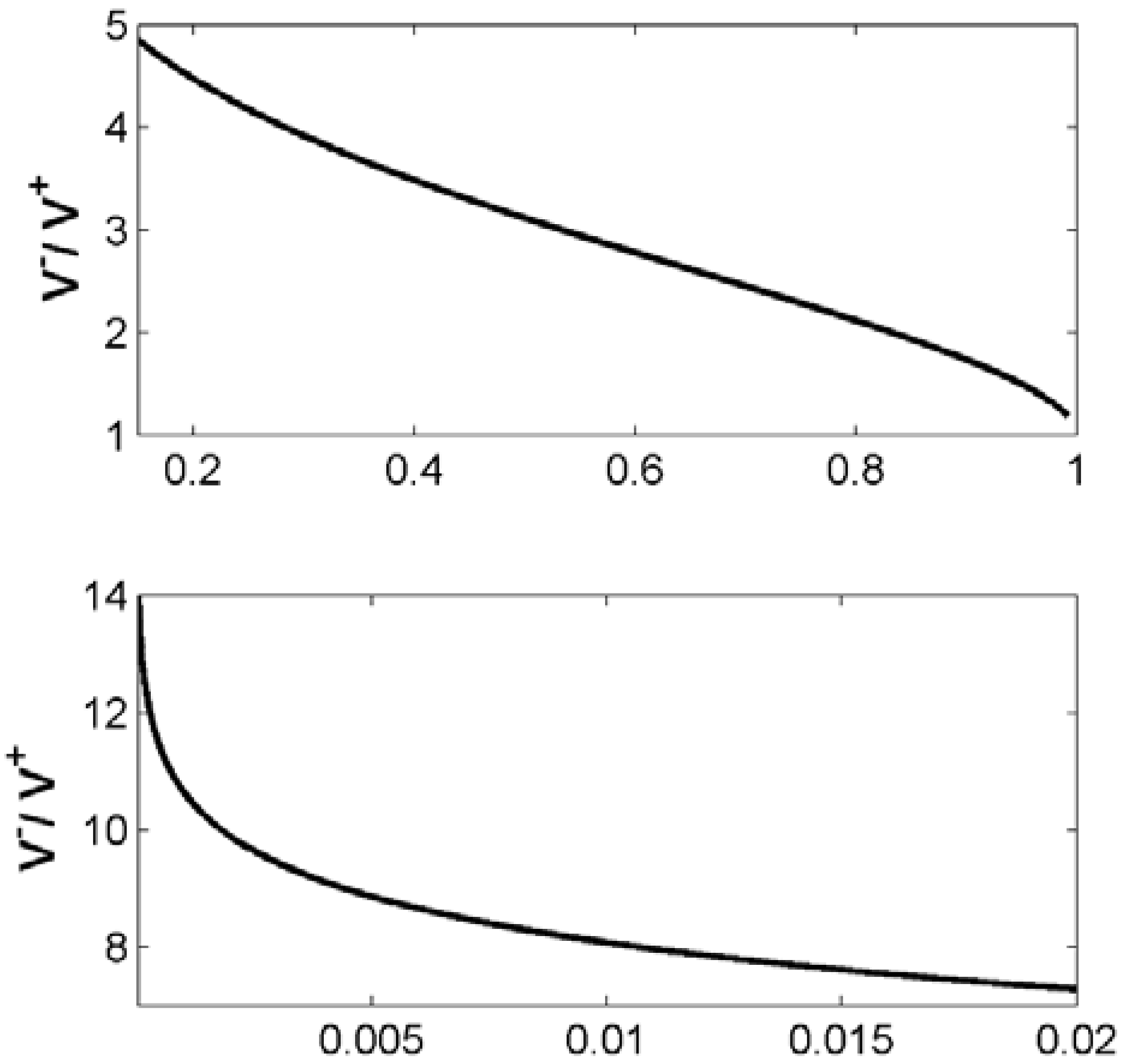
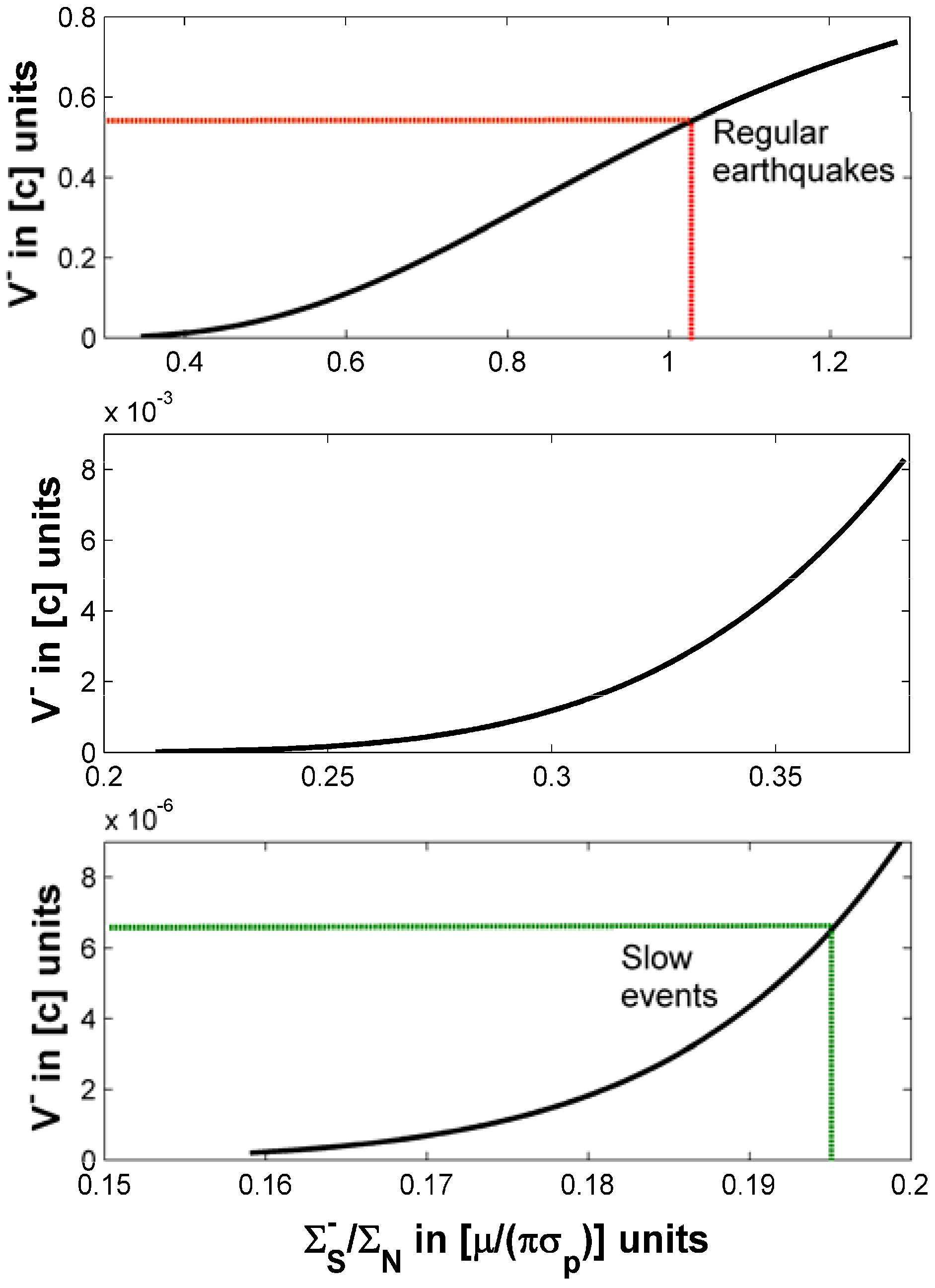

3.2. Solution with Dissipation
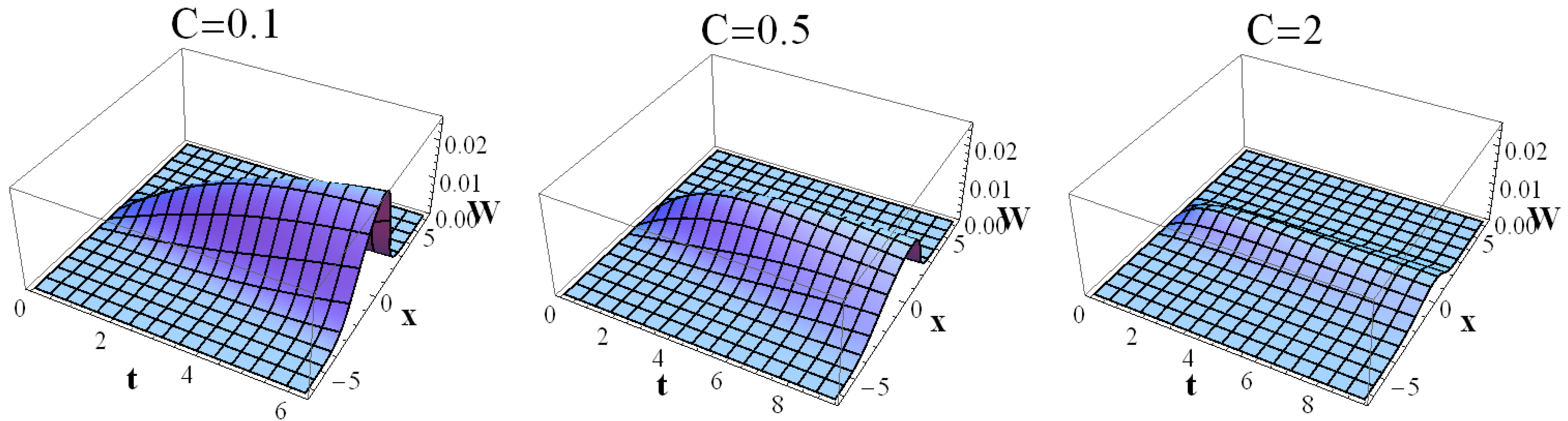
3.3. Influence of Initial Stress Σ+
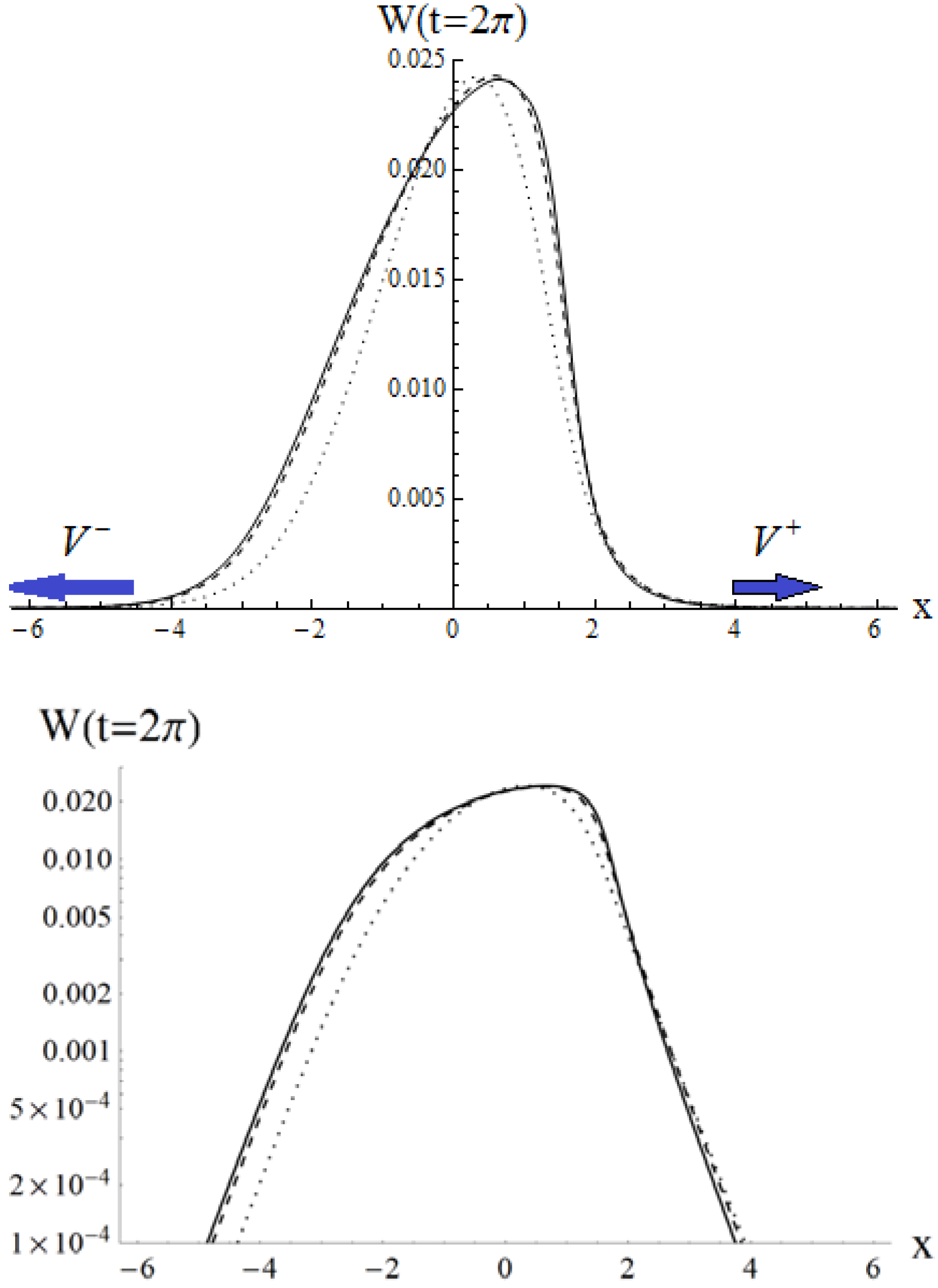
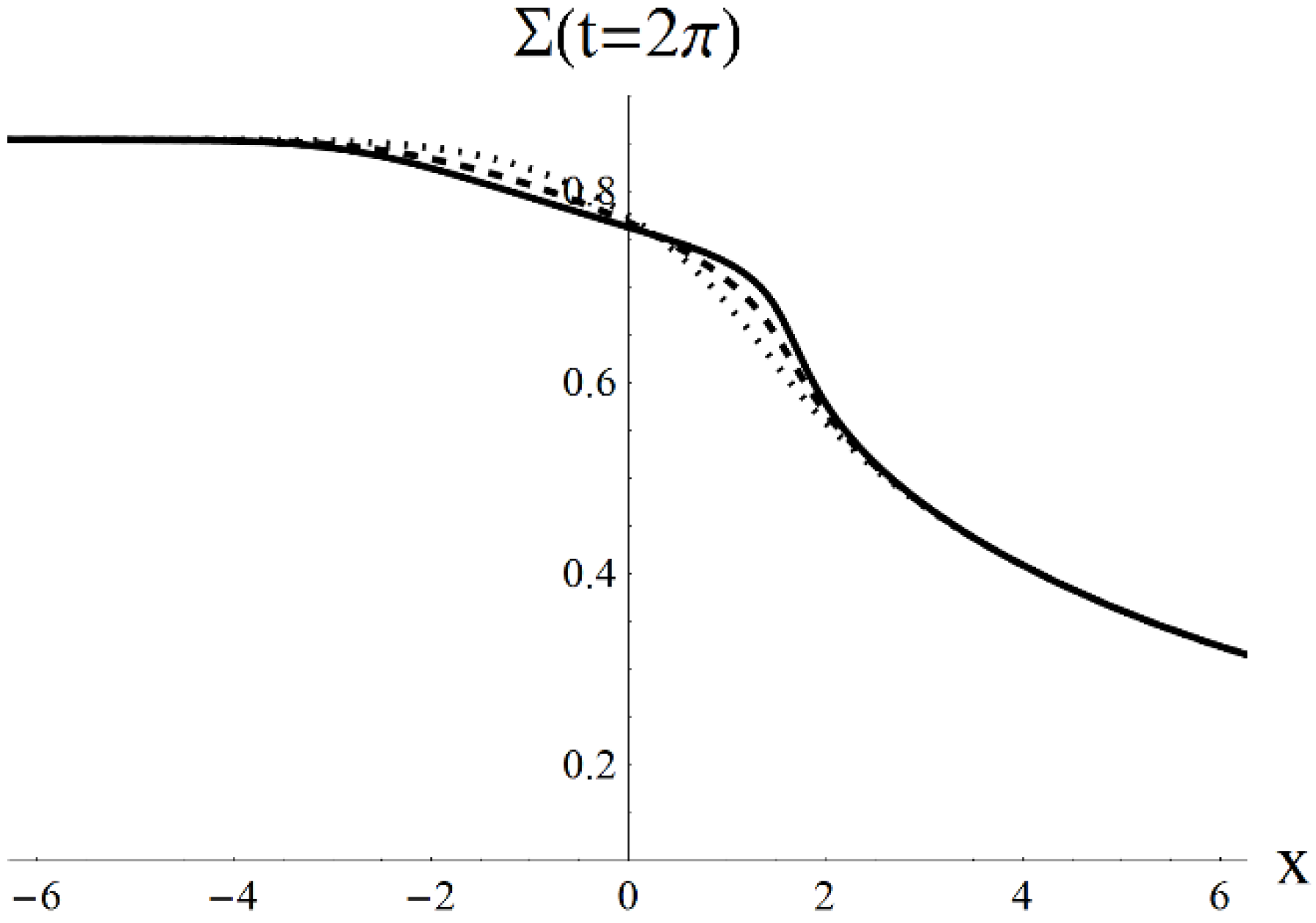
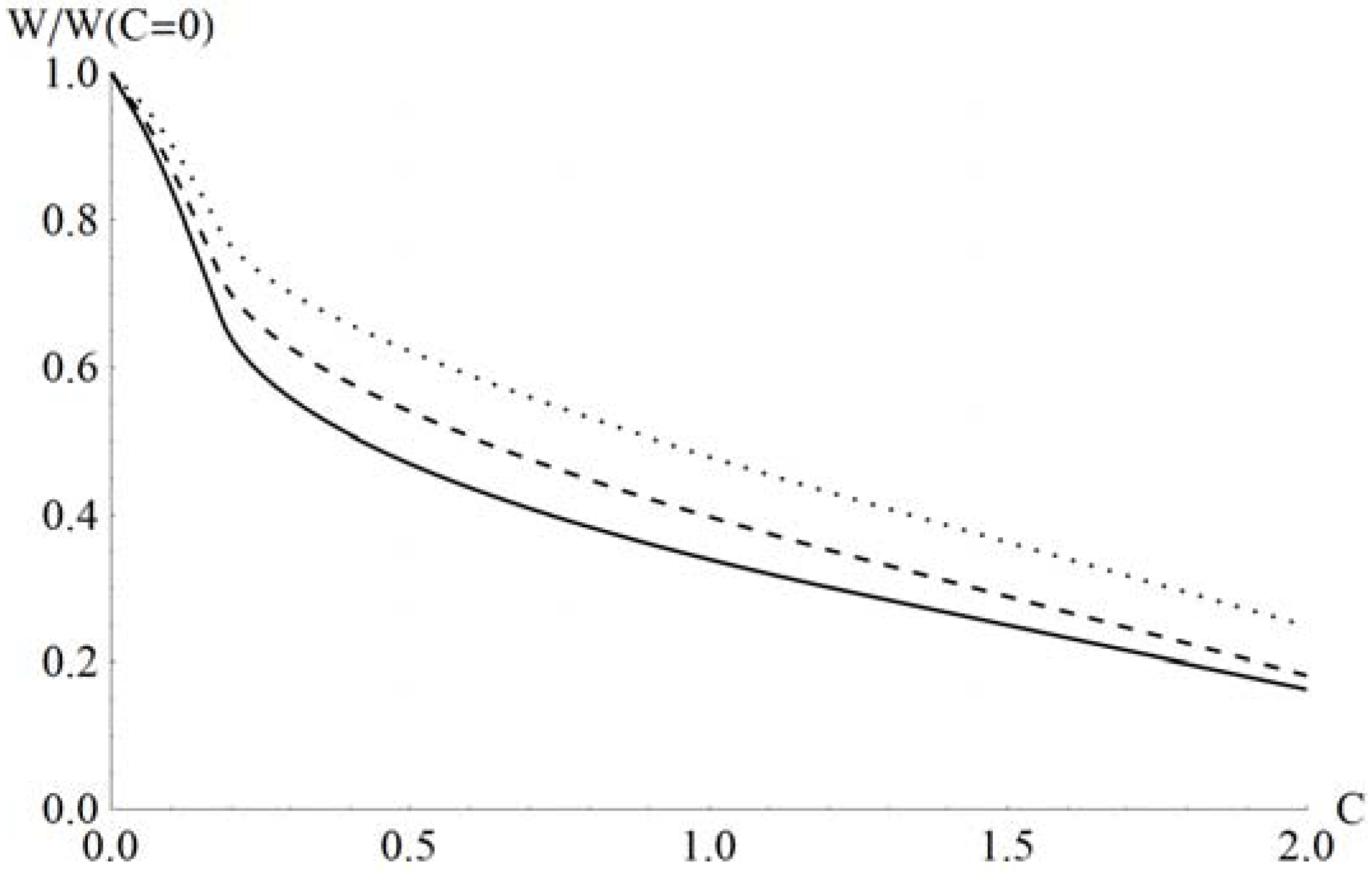
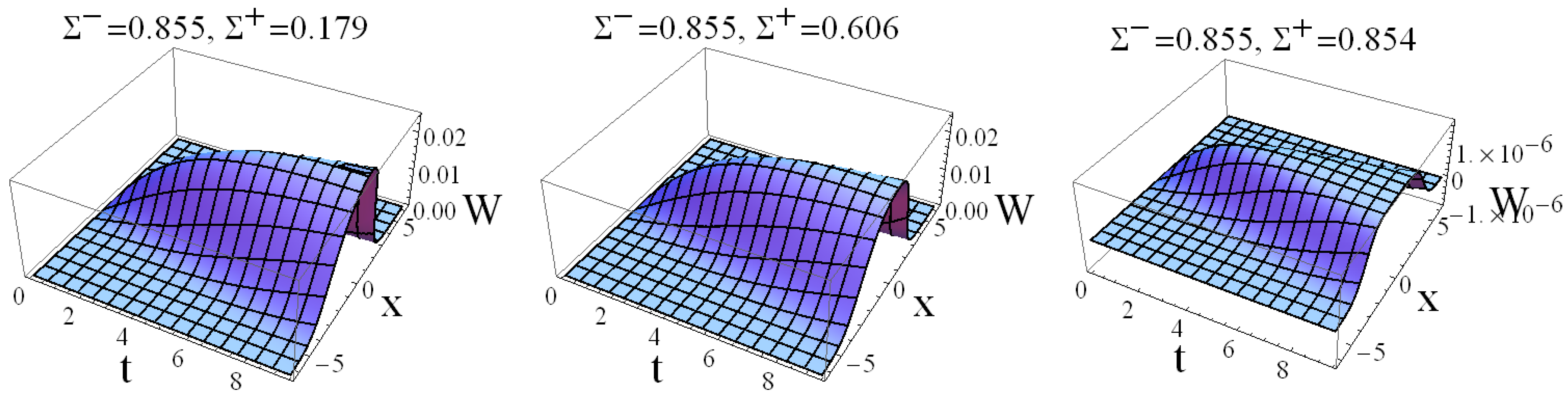
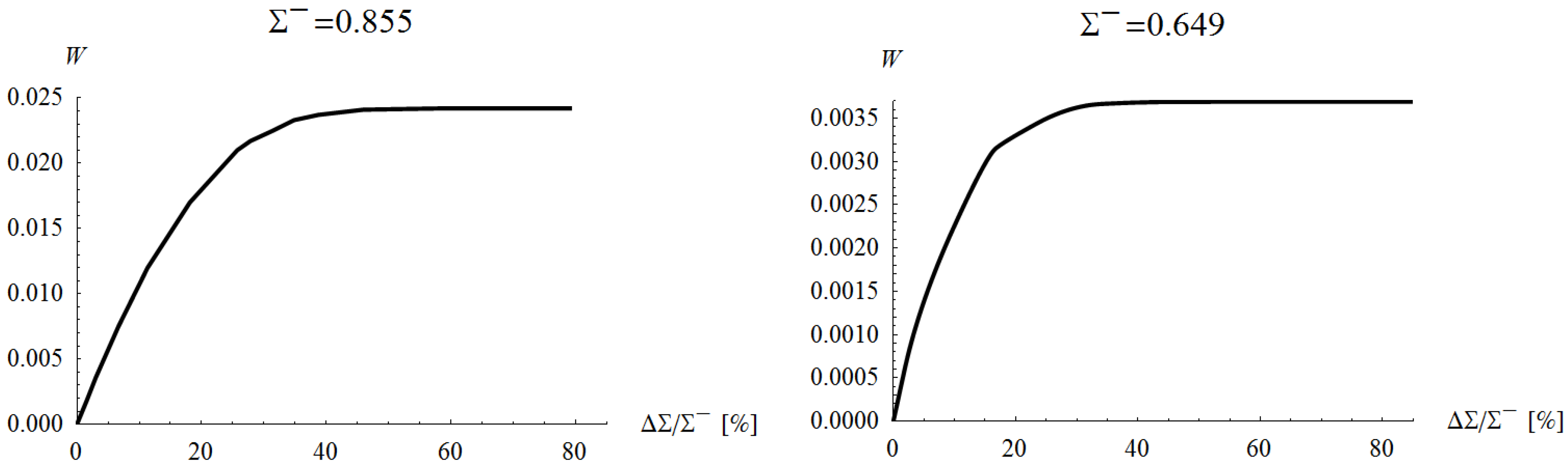
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The FK model has been modified and adapted to the case of non-lubricant macroscopic friction by introducing a parameter A which is the ratio between the real and nominal area of the frictional surfaces;
- (2)
- In the model proposed, sliding occurs due to movement of a certain type of defect, a “macroscopic dislocation” (or area of localized stress), which requires much less shear stress than uniform displacement of frictional surfaces.
- (3)
- To describe measureable macroscopic parameters, we use the Whitham modulation equations applied to the SG equation rather than the SG equation itself which applies to details at the scale of individual dislocations.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bowden, F.P.; Tabor, D. Friction and Lubrication; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowicz, E. Friction and Wear of Materials; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Marone, C. Laboratory-Derived Friction Laws and Their Application to Seismic Faulting. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1998, 26, 643–696. [Google Scholar]
- Baumberger, T.; Caroli, C. Solid friction from stick-slip down to pinning and aging. Adv. Phys. 2006, 55, 279–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, J.H. Applications of rate- and state-dependent friction to models of fault slip and earthquake occurrence. In Treatiseon Geophysics; Kanamori, H., Schubert, G., Eds.; Earthquake Seismology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 4, p. 6054. [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein, S.M.; Cohen, G.; Fineberg, J. Detachment fronts and the onset of dynamic friction. Nature (London) 2004, 430, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, S.M.; Cohen, G.; Fineberg, J. Dynamics of Precursors to Frictional Sliding. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-David, O.; Rubinstein, S.M.; Fineberg, J. Slip-stick and the evolution of frictional strength. Nature 2010, 463, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-David, O.; Cohen, G.; Fineberg, J. The Dynamics of the Onset of Frictional Slip. Science 2010, 330, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burridge, R.; Knopoff, L. Model and theoretical seismicity. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1967, 57, 341–371. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, J.; Langer, J.S. Mechanical model of an earthquake fault. Phys. Rev. A 1989, 40, 6470–6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, B.A.H.; Fasolino, A. Transition to strictly solitary motion in the Burridge-Knopoff model of multicontact friction. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielov, A.; Keilis-Borok, V.I.; Pinsky, V.; Podvigina, O.M.; Shapira, A.; Zheligovsky, V.A. Fluid migration and dynamics of a blocks-and-faults system. Tectonophysics 2007, 429, 229–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, O.M.; Peyrard, M. Modeling Friction on a Mesoscale: Master Equation for the Earthquake-like Model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, O.M.; Barel, I.; Urbakh, M. Dynamics of Transition from Static to Kinetic Friction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchbinder, E.; Brener, E.; Barel, I.; Urbakh, M. Slow cracklike dynamics at the onset of frictional sliding. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trømborg, J.; Scheibert, J.; Amundsen, D.; Thøgersen, K.; Malthe-Sørenssen, A. Transition from static to kinetic friction: Insights from a 2D model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieterich, J.H. Constitutive properties of faults with simulated gouge. In Mechanical Behavior of Crustal Rocks; Carter, N.L., Friedman, M., Logan, J.M., Sterns, D.W., Eds.; Geophysical Monograph Series; Am. Geophys. Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1981; Volume 24, pp. 103–120. [Google Scholar]
- Ruina, A.L. Slip instability and state variable friction laws. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 10359–10370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, J.H. Earthquake nucleation on faults with rate and state-dependent strength. Tectonophysics 1992, 211, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.R. Spatio-temporal complexity of slip on a fault. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 9885–9907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, J.H. A constitutive law for rate of earthquake production and its application to earthquake clustering. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 2601–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Zion, Y.; Rice, J.R. Dynamic simulations of slip on a smooth fault in an elastic solid. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Rice, J. Spontaneous and triggered aseismic deformation transients in a subduction fault model. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampuero, J.-P.; Rubin, A.M. Earthquake nucleation on rate and state faults: Aging and slip laws. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, J.H.; Richards-Dinger, K.B. Earthquake Recurrence in Simulated Fault Systems. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2010, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.-A.; Ampuero, J.-P.; Dalguer, L.A.; Mai, P.M. The transition of dynamic rupture styles in elastic media under velocity-weakening friction. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawthorne, J.C.; Rubin, A.M. Laterally propagating slow slip events in a rate and state friction model with a velocity-weakening to velocity-strengthening transition. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2013, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, P.; Rice, J.R. Dilatancy, compaction, and slip-instability of a fluid-penetrated fault. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleep, N.H. Frictional dilatancy. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2006, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, P.; Rubin, A.M.; Bradley, A.M.; Rice, J.R. Dilatant strengthening as a mechanism for slow slip events. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleep, N.H. Sudden and gradual compaction of shallow brittle porous rocks. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleep, N.H. Microscopic elasticity and rate and state friction evolution laws. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontorova, T.A.; Frenkel, Y.I. On the theory of plastic deformation and twinning. Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 1938, 8, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Vanossi, A.; Braun, O.M. Driven dynamics of simplified tribological models. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2007, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, C.L.; Duan, W.S.; Chen, J.M.; Yang, L. Lubricated friction in Frenkel-Kontorova model between incommensurate surfaces. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 2015, 20, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershenzon, N.I.; Bykov, V.G.; Bambakidis, G. Strain waves, earthquakes, slow earthquakes, and afterslip in the framework of the Frenkel-Kontorova model. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershenzon, N.I.; Bambakidis, G. Transition from static to dynamic macroscopic friction in the framework of the Frenkel-Kontorova model. Tribol. Int. 2013, 61, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershenzon, N.I.; Bambakidis, G. Model of Deep Nonvolcanic Tremor Part I: Ambient and Triggered Tremor. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2014, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, A.; Esposito, F.; Magee, C.J.; Scott, A.C. Theory and Applications of the Sine-Gordon Equation. Riv. Nuovo Cimento 1971, 1, 227–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, D.; Scott, A.C. Perturbation Analysis of Fluxon Dynamics. Phys. Rev. A 1978, 18, 1652–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, G.L. Elements of Soliton Theory; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Gurevich, A.V.; Gershenzon, N.I.; Krylov, A.L.; Mazur, N.G. Solutions of the sine-Gordon Equation by the Modulated-Wave Method and Application to a Two-State Medium. Sov. Phys. Dokl. 1989, 34, 246–248. [Google Scholar]
- Hirth, J.P.; Lothe, J. Theory of Dislocations, 2nd ed.; Krieger Publishing Company: Malabar, FL, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Gershenzon, N.I. Interaction of a group of dislocations within the framework of the continuum Frenkel-Kontorova model. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 13308–13314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitham, G.B. Linear and Nonlinear Waves; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Custo’dio, S.; Liu, P.; Archuleta, R.J. The 2004 Mw6.0 Parkfield, California, earthquake: Inversion of near source ground motion using multiple data sets. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custo’dio, S.; Archuleta, R.J. Parkfield earthquakes: Characteristic or complementary? J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Dreger, D.S. Rupture process of the 2004 Parkfield earthquake from near-fault seismic waveform and geodetic records. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custo’dio, S.; Page, M.T.; Archuleta, R.J. Constraining earthquake source inversions with GPS data: 2. A two-step approach to combine seismic and geodetic data sets. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Custo’dio, S.; Archuleta, R.J.; Liu, P. Dynamic modelling of the 2004 Mw 6.0 Parkfield, California earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, T.; Shimamoto, T. Growth of a molten zone as a mechanism of slip weakening of simulated faults in gabbro during frictional melting. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeler, N.M.; Tullis, T.E.; Goldsby, D.L. Constitutive relationships and physical basis of fault strength due to flash heating. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, H.; Dunham, E.M.; Rice, J.R. Earthquake ruptures with thermal weakening and the operation of major faults at low overall stress levels. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obara, K. Nonvolcanic deep tremor associated with subduction in southwest Japan. Science 2002, 296, 1679–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, G.; Dragert, H. Episodic tremor and slip on the Cascadia subduction zone: The chatter of silent slip. Science 2003, 300, 1942–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obara, K. Inhomogeneous distribution of deep slow earthquake activity along the strike of the subducting Philippine Sea Plate. Gondwana Res. 2009, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, H.; Shan, S.-J.; Dragert, H.; Rogers, G.; Cassidy, J.F.; Wang, K.; James, T.S.; Ramachandran, K. Spatial-temporal patterns of seismic tremors in northern Cascadia. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Vidale, J.E.; Sweet, J.R.; Creager, K.C.; Wech, A.G.; Houston, H. Tremor bands sweep Cascadia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gershenzon, N.I.; Bambakidis, G.; Skinner, T.E. How Does Dissipation Affect the Transition from Static to Dynamic Macroscopic Friction? Lubricants 2015, 3, 311-331. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants3020311
Gershenzon NI, Bambakidis G, Skinner TE. How Does Dissipation Affect the Transition from Static to Dynamic Macroscopic Friction? Lubricants. 2015; 3(2):311-331. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants3020311
Chicago/Turabian StyleGershenzon, Naum I., Gust Bambakidis, and Thomas E. Skinner. 2015. "How Does Dissipation Affect the Transition from Static to Dynamic Macroscopic Friction?" Lubricants 3, no. 2: 311-331. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants3020311
APA StyleGershenzon, N. I., Bambakidis, G., & Skinner, T. E. (2015). How Does Dissipation Affect the Transition from Static to Dynamic Macroscopic Friction? Lubricants, 3(2), 311-331. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants3020311