Abstract
Ecotribology focuses on both saving energy resources and reducing environmental pollution. Considering environmental concerns, water-based nanolubricants have gained significant attention over conventional oil-based ones. Non-ecotoxic and highly environmentally friendly nanoadditives were chosen for nanolubricant synthesis, especially considering their use at elevated temperatures. In this study, hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets (hBNNSs) and titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) were used to prepare water-based lubricants with glycerol and surfactant sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS) in water under ultrasonication. An Rtec ball-on-disk tribometer was used to investigate the tribological performance of the synthesised water-based lubricants containing different nano-hBN/TiO2 concentrations, with dry and water conditions used as benchmarks. The results indicated that the water-based nanolubricant containing 0.5 wt% hBN and 0.5 wt% TiO2 exhibited the best tribological performance at both ambient (25 °C) and elevated (500 °C) temperatures. This optimal concentration leads to a reduction in the coefficient of friction (COF) by 72.9% and 37.5%, wear of disk by 62.5% and 49%, and wear of ball by 74% and 69% at ambient and elevated temperatures, respectively, compared to that of distilled water. Lubrication mechanisms were attributed to the rolling, mending, tribofilm, solid layer formation, and synergistic effects of hBNNSs and TiO2 NPs.
1. Introduction
The environment is a constant resource provider; unfortunately, it is often misused as a sink for waste products, despite being a dynamic system that can be influenced by our actions and upon which our survival depends entirely [1,2,3]. Over the past 600 years, irresponsible and wasteful human action, destruction of natural resources, and environmental pollution have caused 50% of animal deaths due to the consumption of contaminated food, water, and air. In light of this, ecotribology can serve as a potential solution to minimise this environmental damage by 25% [4,5]. Ecotribology encompasses areas such as green tribology, sustainable tribology practices, energy-saving tribology, eco-compatible lubricants, renewable energy tribology, tribology for environmentally conscious applications, and tribology for enhancing quality of life [6,7]. Specifically, in production processes, sustainable manufacturing follows two key paths of development. The first path of development focuses on the use of green lubricants derived from natural materials, which can be reused and recycled. The second path focuses on the incorporation of certain lubricant additives with tribological and eco-friendly properties, which can be directly sprayed on the desired location, minimising the need for a large volume of lubricating fluid. Lubricants are generally considered environmentally acceptable when they are rapidly biodegradable and non-toxic to humans, fish, bacteria, and other living organisms [8].
For the eco-friendly and optimal performance of various mechanical parts in metalworking, aerospace, automotive applications, internal combustion engines, power generation, cutting tools, etc., the eco-tribological behaviour of lubricants at ambient and elevated temperatures is crucial. High-temperature lubrication is one of the toughest challenging aspects in the field of tribology [9,10]. In the engineering industry, many components operate beyond their normal temperature range, leading to many tribological issues that present significant challenges in terms of system reliability, cost efficiency, and environmental issues [11,12]. Sliding frictional motion occurs between these components; thus, lubrication technology is highly important for addressing the aforementioned concerns [13]. Numerous studies have been conducted on oil-based lubricants [14]. Unfortunately, conventional lubricants such as oil and oil-in-water emulsions are environmentally challenging for high-temperature applications, as they produce toxic fumes and hazardous chemical components when burned [15,16]. Scientists have been investigating methods for finding alternative lubricants that are environmentally friendly. Tomala et al. [17] used commercially available lubricants such as solid, inorganic, and water-dilutable binders to observe their tribological performance at 800 °C; these lubricants formed a sacrificial layer of ~15 ± 5 μm thickness to protect the sliding pairs from adhesive and abrasive wear. In recent years, water has been chosen as a replacement for these toxic oils and oil-based lubricants. This is because when water evaporates, it becomes water vapour, which is environmentally friendly. However, using only pure water is no longer effective, as it decomposes rapidly at high temperatures. In this context, the incorporation of new eco-friendly nanomaterials in water that are capable of handling diverse and dynamic surroundings for scientific and manufacturing applications is needed. According to the statistics of nanomaterials, researchers have used nanoadditives that included 3% metals [18,19], 18% metal oxides [20,21,22], 5% metal sulphides [23,24], 35% carbon-based materials [25,26,27], and 16% composites [28,29] as additives to increase the lubricating properties of water. Literature demonstrates that carbon-based and composite materials have the ability to improve lubrication performance by more than 80% compared to pure water lubrication among all the water-based additives [30]. At high temperatures, almost all the water in water-based lubricants is lost to the environment, leaving behind the nanoadditives on the surfaces. For this reason, toxic oil-based lubricants have been replaced by green water-based lubricants to prioritise environmental protection [31]. Moreover, the performance of water-based lubricants largely depends on the selection of nanoadditives, which can offer sufficient stability at high temperatures [32,33,34].
Developing an eco-friendly lubricant is achievable, but high-temperature applications have become challenging [35]. Since few materials perform effectively at temperatures above 250 °C, many elevated-temperature applications rely on self-lubricating materials that assist in the formation of protective tribolayers (glazes) during the sliding process [36,37,38]. For example, Li et al. [39] used graphite to investigate lubrication behaviour and tribological performance at 750 °C and reported that the addition of graphite to lubricants reduced the COF to less than 0.3, although it increased with increasing temperature. Among all the nanoadditives, ceramic materials possess qualities such as high melting points, excellent chemical inertness, wear resistance, and high hardness, making them ideal candidates for high-temperature tribological testing, often exceeding 1000 °C [40,41]. Over the past 30 years, ceramic materials such as hBN and TiO2 have gained attention because of their high load-bearing capacity, low density, and chemical resistivity [5,42]. Our previous study revealed that the tribological performance of 4.0 wt% nano-TiO2 lubricants at high temperatures presented outstanding friction-wear reduction [43]. Moreover, in many recent applications, composite materials made from ceramics have increasingly replaced traditional engineering materials, particularly where oxidation resistance, low friction, and high-temperature stability are essential [44,45,46]. In addition, nanocomposites are highly promising as nanoadditives in water-based lubricants for reducing friction and wear between sliding surfaces by adding one or more lubricating nanoadditives [47,48,49]. For example, the tribological performance of Al/graphite lubricants in oil-based and water-based lubricants was examined by Buchner et al. [50] at temperatures ranging from 250 to 450 °C for a sliding distance of approximately 14 mm, who reported that oil-based lubricants presented poorer COF and surface roughness than water-based. In our previous study, we discussed that the tribological performance of the combined effects of hBN and TiO2 was superior to their individual effects, with 17.4% COF reduction and 43.5% disk wear reduction [51]. Although there have been many investigations on the use of ceramic nanocomposites in water for room-temperature applications, very few studies have been proposed for high temperatures [52,53]. Therefore, the tribological behaviour of the combined effect of hBN and TiO2 as water-based nanoadditives at high temperatures should be investigated.
This study focuses extensively on investigating the tribological performance of environmentally compatible lubricants at elevated temperatures as a pathway toward achieving efficient ecotribology. The objective of this study was to develop hBN/TiO2 as environmentally friendly nanoadditives in water that can reduce both friction and wear in ambient air at temperatures of 25 and 500 °C. The lubrication mechanisms of the nanoadditives were understood in terms of the elemental distribution on the wear tracks, in particular, focusing on the influences of hBN/TiO2 in tribofilm formation at high temperatures.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
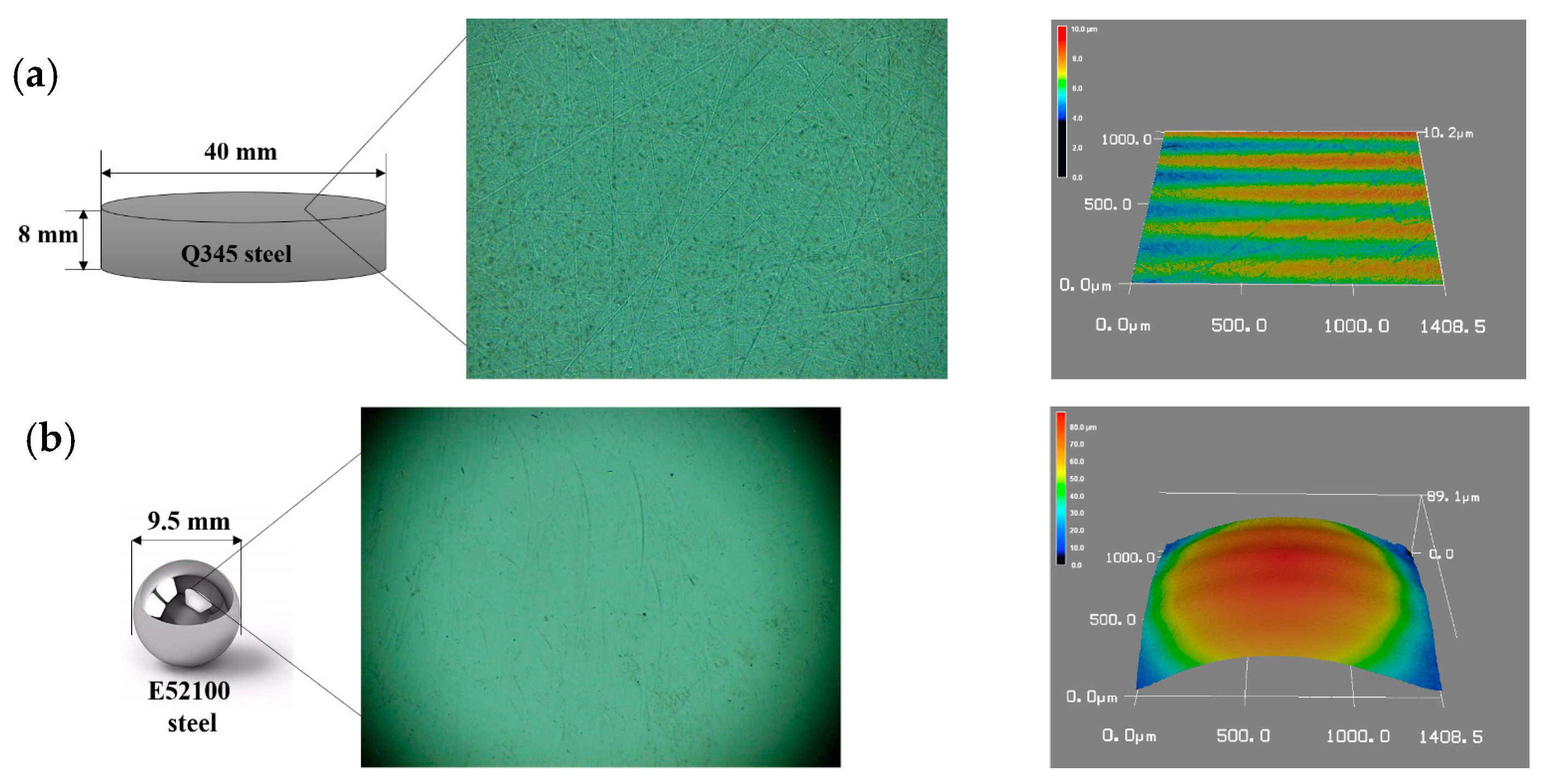
For the tribological tests, Q345 mild steel was used as the disk material, with 345 MPa yield stress and 136 HV Vickers hardness. The disk was precisely machined to 40.0 mm in diameter and 8.0 mm in thickness. Following the grinding and polishing process using a Struers Abramin Polisher (Copenhagen, Denmark) under a vertical pressure of 100 N at 300 rpm for 20 min, a surface roughness Ra of 0.5 µm was achieved (Ra measured via 3D laser microscope). The E52100 Cr steel ball was 9.5 mm in diameter with a Vickers hardness of 780 HV and a surface roughness of 0.5 µm. A schematic diagram, optical image, and 3D profile of the disk and ball are shown in Figure 1. Table 1 presents the detailed chemical compositions of the Q345 disk and E52100 ball. Prior to each tribological test, both components underwent acetone cleaning to remove machining residues.

Table 1.
Chemical compositions of the disk Q345 and ball E52100 (wt%) [54].
Table 1.
Chemical compositions of the disk Q345 and ball E52100 (wt%) [54].
| Materials | C | Si | Mn | Mo | Ni | Cr | Cu | P + S | Nb + V + Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disk | 0.16 | 0.25 | 1.5 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.02 | - | 0.019 | <0.02 |
| Ball | 1.0 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.10 | - | 1.5 | 0.03 | <0.03 | - |
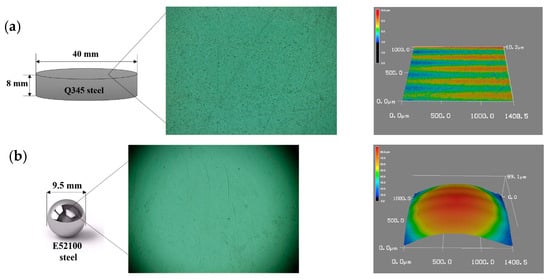
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram, optical image, and 3D profile of the (a) disk and (b) ball [55].
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram, optical image, and 3D profile of the (a) disk and (b) ball [55].
2.2. Lubricant Preparation
All nanoadditives were sourced from commercial suppliers and used as received without any additional purification. hBNNSs (98.0%), P25 TiO2 NPs (≥99.5%), glycerol (≥99.0%), and surfactant sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS) (≥99.0%) were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (Victoria, Australia). More details regarding the nanoadditives used have been provided in our previous study [51]. The water-based lubricants were prepared by first dispersing glycerol and SDBS in water via mechanical stirring, followed by hBNNSs and TiO2 NPs. The heterogeneous suspension was then uniformly mixed by ultrasonication for 30 min at a temperature of 25 °C (frequency 40 kHz, power 240 W). The lubricant compositions and nanoadditive concentrations are listed in Table 2. All the as-prepared lubricants showed good NP stability for 5 days after preparation, despite their varying concentrations in water. As observed from Figure S1, slight NP sedimentation was noticed after 7 days, and nearly all NPs settled by 30 days. For comparative analysis, dry and pure water conditions served as benchmarks.

Table 2.
Chemical compositions under different lubricating conditions.
2.3. Tribological Tests
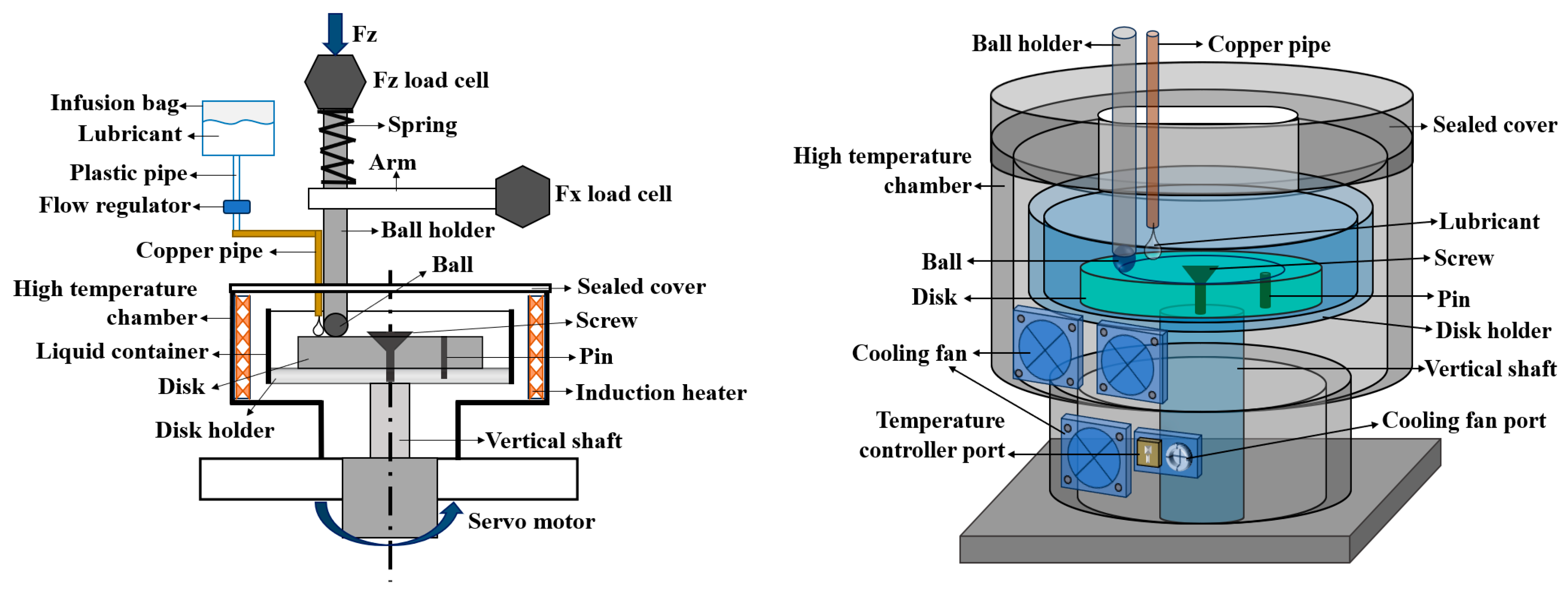
Tribological tests were performed at ambient and elevated temperatures in ambient air using an Rtec Multifunctional tribometer with a ball-on-disk configuration. The detailed working principle of the experimental apparatus was thoroughly discussed in our previous study, with a room-temperature set up [56]. Figure 2 presents the 2D and 3D schematics of the high-temperature set up used for tribological tests. The high-temperature chamber consists of upper and lower sections, which can be adjusted for sample handling. The disk was securely mounted on the disk holder, and the ball was attached to the ball holder on a load cell. The load cell, attached to the ball holder along the Z-axis, measures the in-situ friction force. A 10 mL infused bag was installed to hold the lubricants and was continuously delivered during the test into the high-temperature chamber through a copper pipe connected with the ball holder. For high temperatures, a drop-wise lubrication method was used to ensure a consistent supply of lubricant between the ball and disk.
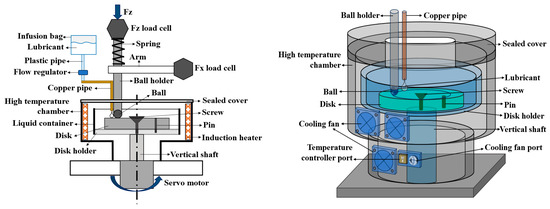
Figure 2.
The 2D and 3D schematics of the elevated temperature ball-on-disk configuration.
The load cell applied a load of 50 N vertical to the disk surface, positioned 14 mm from the disk’s centrer, and tangential to the sliding direction. The rotational speed of the disk was maintained at 50 mm/s for a test duration of 5 min. The COF was continuously recorded via MFT-16 software throughout the entire duration of each test. Each test was performed five times, and an average value was calculated. The experiments were divided into two groups based on their respective conditions. In the first group, tests were conducted at 25 °C (room temperature) in ambient air using a room-temperature set up [56]. The second group of experiments was conducted using the high-temperature set up at a constant temperature of 500 °C in ambient air.
2.4. Appraisal Techniques
A PANalytical X-ray diffraction (XRD) (Malvern Panalytical Ltd., Worcestershire, UK) with Cu-Kα radiation was used to explore the NPs’ phase characterisation. The hBNNSs and TiO2 NPs were scanned over a 2θ range of 10° to 70° using a step size of 0.043° and a scan step time of 99.44 s per step. The morphological observations of hBNNSs and TiO2 NPs were performed using the JEOL JEM-ARM200F Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). After conducting the tribological tests, the profilometry of the disk and ball wear was measured using a KEYENCE VK-X100 K 3D Laser Scanning Microscope (KEYENCE Corporation, Osaka, Japan). Five different locations were measured on the wear track of each sample, and an average value was calculated to ensure accuracy. To analyse the lubrication mechanisms of the NPs on the worn surfaces, the disk and ball surface morphologies were obtained using a JEOL JSM-6490LV Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) equipped with an energy-dispersive spectrometer (EDS) for elemental analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Nanoparticle Characterisation
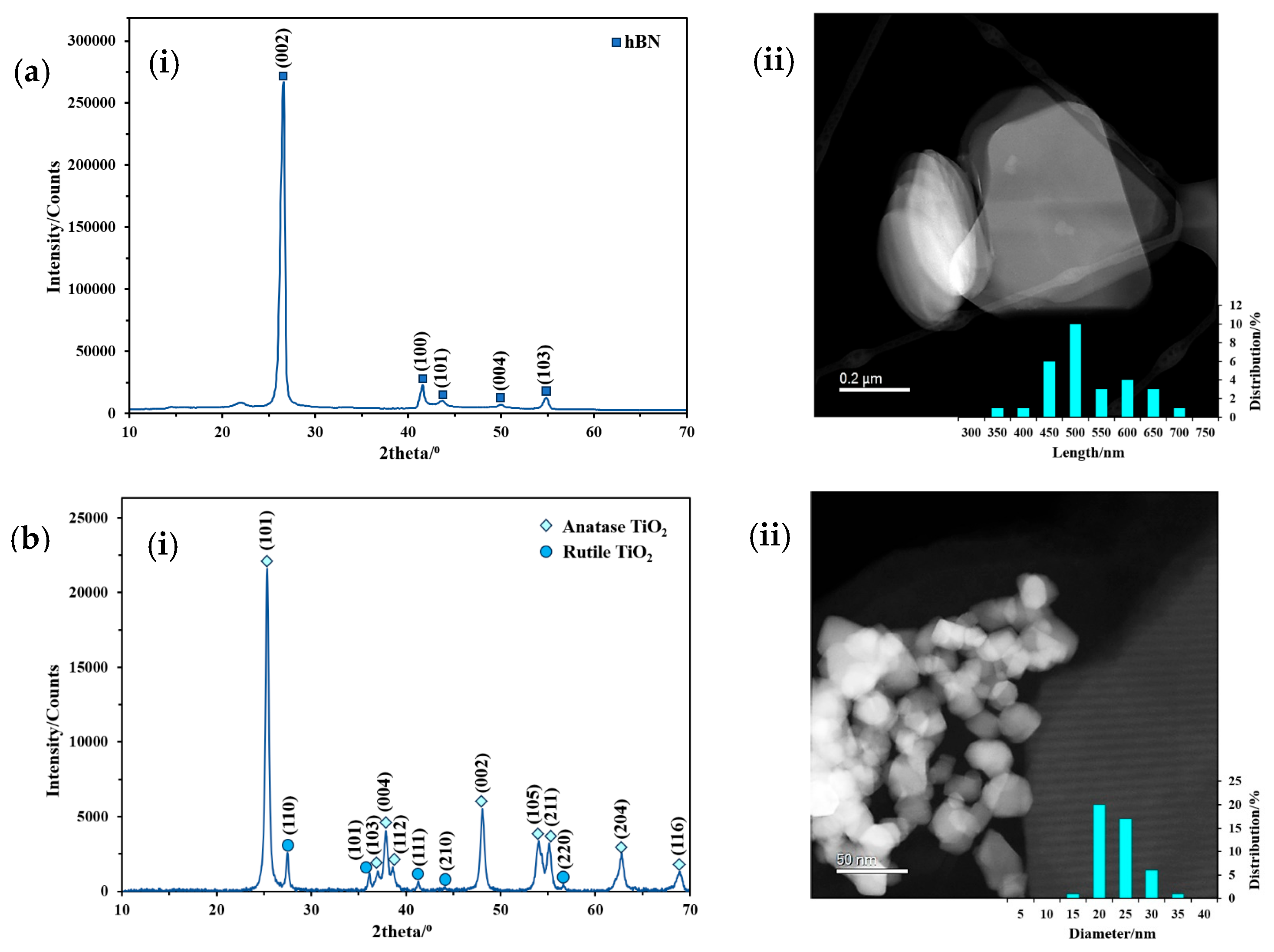
Figure 3 presents the XRD patterns and TEM images of hBNNSs and P25 TiO2 NPs. The XRD pattern of hBNNSs in Figure 3(ai) shows diffraction peaks at 2θ = 26.5°, 41.6°, 43.6°, 50.0°, and 54.8°, and the intense peak of the crystals was observed at 26.5° in the (002) direction. According to JCPDS No 034-0421 (JCPDS database), this reveals the high purity of hexagonal boron nitride. Figure 3(bi) shows the XRD pattern of P25 TiO2; the intense peaks at 2θ = 25.3°, 37.0°, 37.9°, 38.5°, 48.0°, 54.0°, 55.1°, 62.7°, and 68.9° refer to anatase (JCPDS 00-021-1272), and the peaks at 2θ = 27.5°, 36.1°, 41.2°, 44.2°, and 56.6° refer to rutile (JCPDS 01-070-7347). From the TEM images and size distributions in Figure 3(aii,bii), an average size of 500 nm in length and 50 nm in thickness was observed for hBNNSs, and an average diameter of 20 nm for was observed TiO2 NPs. More detailed characterisation has been described in our previous studies [51,56].
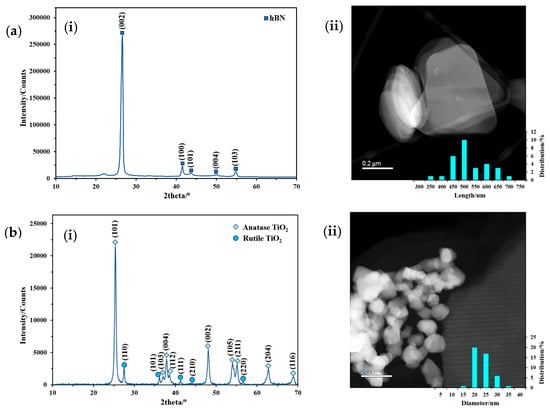
Figure 3.
(i) XRD patterns and (ii) TEM images with size distribution of (a) hBN and (b) P25 TiO2 [55].
3.2. COF
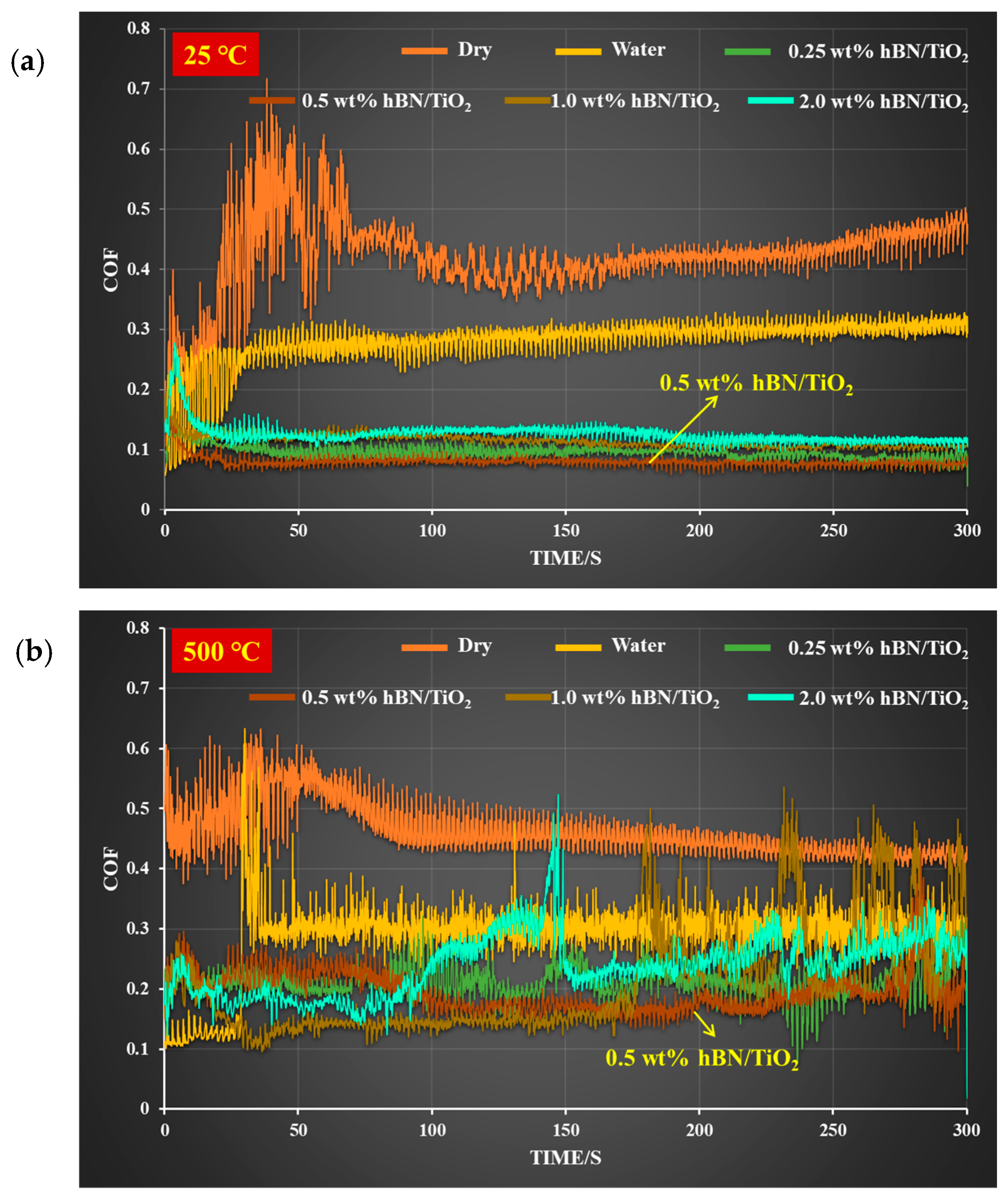
Figure 4 shows the in-situ COFs under different lubricating conditions tested at temperatures of 25 and 500 °C in ambient air. The COF was recorded in real-time by means of a load cell during each experiment, as plotted in Tables S1 and S2. At 25 °C, the COF curve initially rises abruptly during the first 50 s, then gradually stabilises, and remains almost constant throughout the rest of the test. In contrast, at 500 °C, peaks in the COF curves are observed midway through the test after a period of sliding. After the running-in period, at both 25 and 500 °C, the COF for dry conditions stabilises at approximately 0.4, and for water conditions, it stabilises at approximately 0.3. Under extreme conditions at 500 °C, pure water gradually fails after the test begins. However, a slight decrease in the COF was measured, indicating that pure water has the ability to remain on the hot surface for a short time. Continuous droplets of pure water were applied on the disk surface, and a comparatively lower COF was obtained than that under dry conditions. Under dry and pure water conditions, the COFs are relatively similar at both ambient and elevated temperatures. The COFs of the water-based lubricants with hBN/TiO2 concentrations of 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 wt% are lower than those of the dry and water conditions at both 25 and 500 °C. Following the 100 s running-in period, steady COF values of 0.09 and 0.2 for 0.25 wt% hBN/TiO2 were obtained at 25 and 500 °C, respectively, which remained nearly constant over the rest of the test. The lowest COFs exceeding 0.07 and 0.15 were obtained for the 0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2 nanolubricant at 25 and 500 °C, respectively, during the steady-state phase of the test. With the further increase in the hBN/TiO2 concentration to 1.0 wt%, the overall COF increased slightly at both 25 and 500 °C. At 25 °C, the COF stabilised at 0.12, whereas at an elevated temperature (500 °C), a few peaks were observed at certain intervals. This phenomenon occurs because, over time, as the water evaporates, the hBN/TiO2 tribofilm hardens and eventually breaks, leading to the peak appearance midway during the sliding process. The COF value for 2.0 wt% hBN/TiO2 is nearly 0.14 after the running-in period at 25 °C, while at 500 °C, the COF varies between 0.29 and 0.2, with remarkable fluctuations.
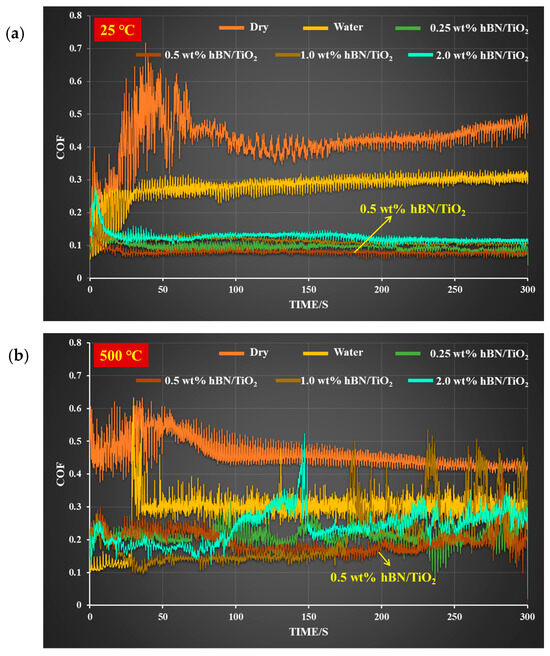
Figure 4.
In-situ COF vs. time-measured COF during tribological tests under different lubrication conditions at (a) room temperature of 25 °C and (b) high temperature of 500 °C in ambient air.
The in-situ COF at a testing temperature of 25 °C demonstrated a stable sliding process under proper lubrication in all conditions, while an elevation in temperature to 500 °C negatively affected the COF stability for all the water-based lubricants, particularly for 1.0 and 2.0 wt% hBN/TiO2. Although, the 0.5 wt% lubricants showed the lowest COFs at both 25 and 500 °C testing temperatures, the stability of its in-situ COF at 500 °C was significantly compromised. The COF using hBN/TiO2 nanolubricants varies with the testing temperature, and thus increases with increasing temperature. Additionally, the friction fluctuations are smaller at 25 °C, whereas more pronounced fluctuations are observed at 500 °C, indicating that a rise in temperature contributes to an unstable COF during sliding. Despite a few in-situ COF fluctuations, the addition of hBN/TiO2 to water led to lower COF values at all tested temperatures. Therefore, the addition of these nanoadditives resulted in a reduced COF and improved tribological performance at both ambient and elevated temperatures.
3.3. Wear of Disk
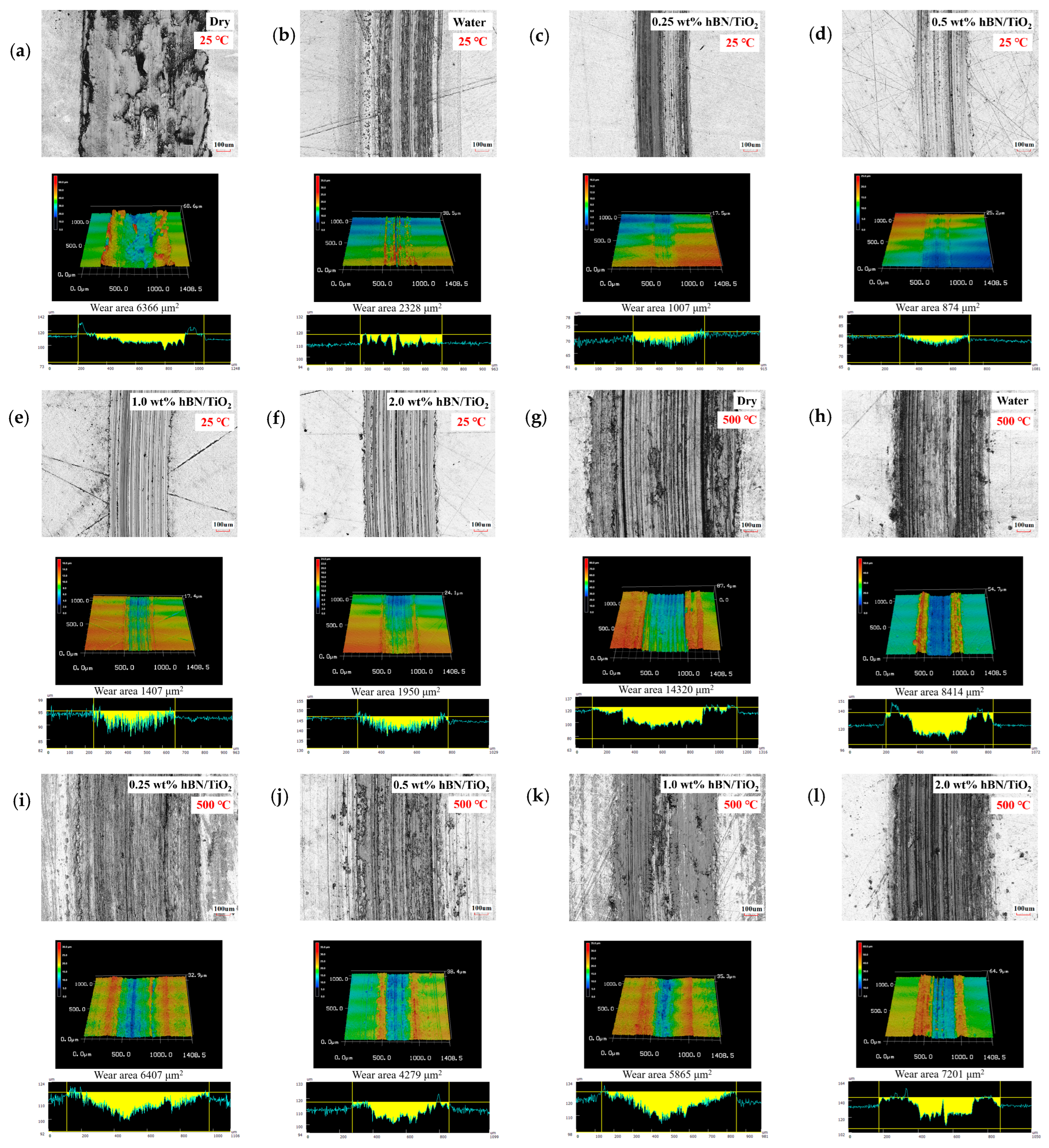
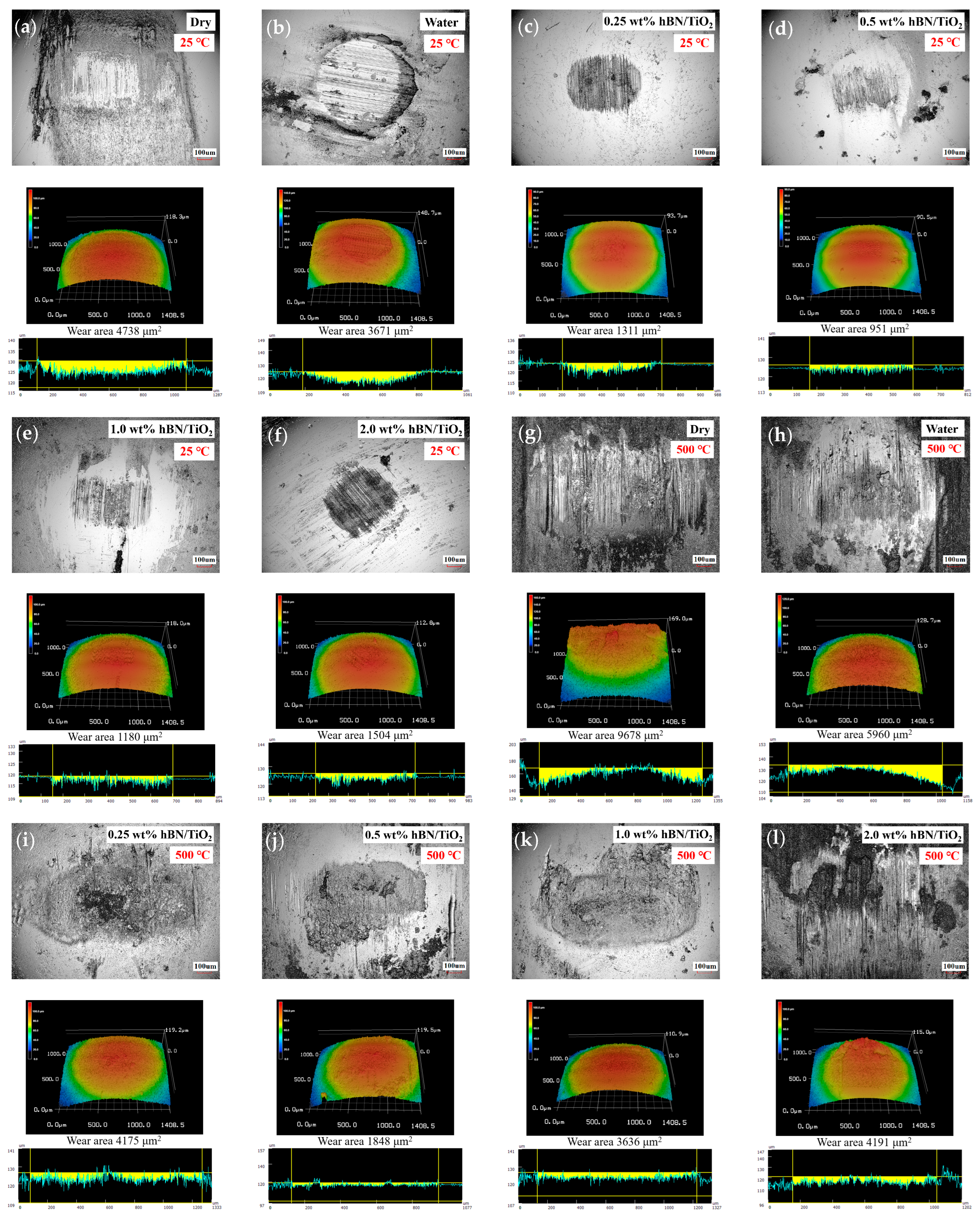
Wear micrographs were examined at testing temperatures of 25 and 500 °C to explore the influence of temperature on the wear resistance. Figure 5a–f shows the disk wear tracks under different lubricating conditions at room temperature in ambient air. The wear produced during dry sliding presented a very rough and scratchy track. Under water conditions, lubrication is poor, and the track shows no deep cracks; however, the surface finish is relatively poor with corroded edges. It can be observed that at 25 °C, the disk wear appearances for all the water-based nanolubricants are remarkably similar. hBN/TiO2 nanolubricants showed better lubricity by preventing significant metal–metal contact, as evidenced by the smaller wear area than that of dry and pure water conditions. The lowest disk wear area of 874 μm2 was achieved using 0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2, as observed from Figure 5d, and the track appearances in the optical image and 3D profile were smoother than those of the other tracks.
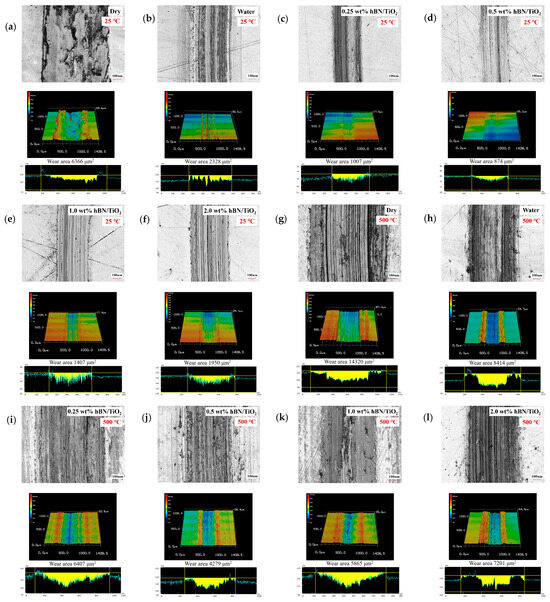
Figure 5.
Optical images and 3D profiles of disk tracks at 25 and 500 °C under different conditions: (a,g) dry, (b,h) water, (c,i) 0.25 wt% hBN/TiO2, (d,j) 0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2, (e,k) 1.0 wt% hBN/TiO2, and (f,l) 2.0 wt% hBN/TiO2.
Figure 5g–l reveal that the wear rate progressively increases as the temperature rises to 500 °C, indicating that the wear intensifies with increasing temperature. The wear tracks were significantly wider and completely covered with wear debris compared to sliding at 25 °C. Under dry sliding, the disk wear was mostly formed from grooves and scratches, resulting in an overall wear area of 14,320 μm2. The wear depth with water lubrication is also notably pronounced, exhibiting a wear area of 8414 μm2, as noted from the 3D profile in Figure 5h. When water was used at 500 °C, poor lubricity was observed in boundary lubrication. This occurs because as the temperature rises, the viscosity of water decreases, and thus, the possibility of water molecules to form thermally stable layers between sliding surfaces decreases. A decrease in wear area is detected for water-based lubricants using hBN/TiO2 concentrations up to 2.0 wt%. With the addition of hBN/TiO2, the wear area decreased to 6407 μm2 at a concentration of 0.25 wt% and further reduced to 4279 μm2 at a concentration of 0.5 wt%, as shown in Figure 5i,j. In contrast, the wear area slightly rose to 5865 and 7201 μm2 for 1.0 and 2.0 wt% hBN/TiO2, respectively. The higher wear rate at 500 °C than at 25 °C can be attributed to abrasive wear, resulting in material transfer and excessive scoring [57]. Based on the 3D profiles of the disk wear, it is clear that the average width and depth of the worn tracks increased at 500 °C compared to those at 25 °C for all the lubricating conditions. The larger wear area at 500 °C makes it clear that controlling the tribological properties at elevated temperatures is challenging. However, at both 25 and 500 °C, the optimal concentration of 0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2 has a comparatively smaller wear area.
3.4. Wear of Ball
The wear areas of balls for different lubricating conditions at 25 and 500 °C in ambient air are reported in Figure 6. A comparable appearance of the ball’s wear scar was also observed between the room- and high-temperature worn surfaces from the optical images. The wear rate calculation was challenging because minimal material removal occurred; however, it was clear that the width of the scar expanded with increasing temperature. This can be clearly seen by comparing the 3D profiles of the wear scars for all the lubricating conditions after tribological tests at 25 and 500 °C. It is worth noting that only at room temperature did the water-based lubricants significantly enhance the wear resistance, while their effectiveness in improving the wear resistance was comparatively lower at the elevated temperature. This occurred because the lubricant failed to provide enough support at high temperatures in the contact area, thus resulting in rough wear along with the formation of black iron oxides, as evident from Figure 6g–l. Severe abrasive wear occurred at 500 °C, with extensive ditches and valleys in the sliding direction, which can significantly compromise the quality of the finished product and decrease the tool lifetime due to increased surface damage [58]. However, the addition of hBN/TiO2 improved the high-temperature properties of water, and a substantial reduction in scar area was observed for all the water-based lubricants compared to that of dry and water conditions. Figure 6c,i show that when 0.25 wt% hBN/TiO2 lubricant was applied during sliding, the ball wear increased from 1311 to 4175 μm2 with the increase in temperatures from 25 to 500 °C. Compared to those of the other lubricants, the wear areas of 0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2 lubricants were the smallest at both 25 and 500 °C, reducing by up to 951 and 1848 μm2, respectively (Figure 6d,j). A further rise in hBN/TiO2 concentration to 1.0 and 2.0 wt% led to a substantial increase in ball wear area. Depending on the testing temperature, the disk and ball wear values are different but relatively similar for different conditions.
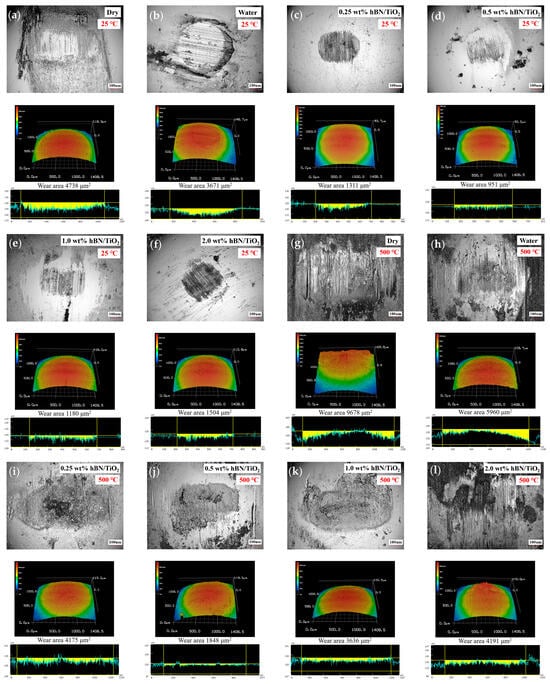
Figure 6.
Optical images and 3D profiles of ball scars at 25 and 500 °C under different conditions: (a,g) dry, (b,h) water, (c,i) 0.25 wt% hBN/TiO2, (d,j) 0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2, (e,k) 1.0 wt% hBN/TiO2, and (f,l) 2.0 wt% hBN/TiO2.
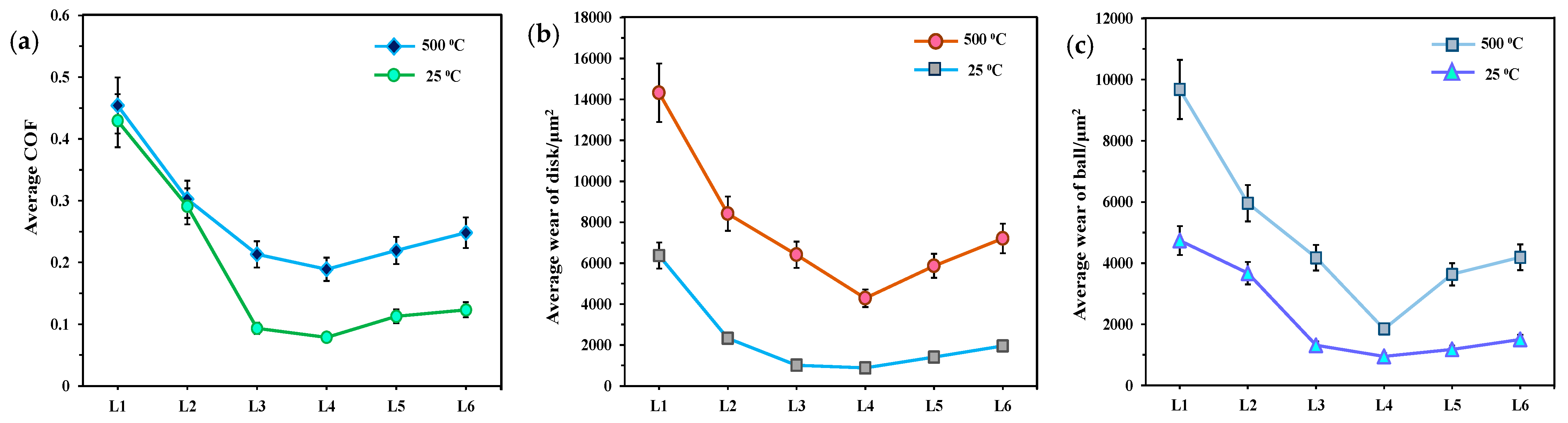
Figure 7 presents the influence of dry, water, and water-based lubrication conditions on the tribological performance at room and high temperatures. Considering the running-in period at the beginning of the test, the average COF was calculated from the stable in-situ COF value recorded after 100 s. Figure 7a indicates that the average COF increased with rising temperature across all lubricating conditions. Compared to that at 25 °C, the average COF under dry and water conditions shows minimal change when sliding at 500 °C. Although the addition of hBN/TiO2 to water reduced the average COF compared to that under dry and water conditions, the overall friction at 500 °C was consistently higher than that at 25 °C. Similarly, the disk and ball wear at 25 °C resulted in a lower wear rate with the use of water-based lubricants, while a dramatic increase in wear rate was observed at 500 °C. The anti-wear capability of both the ball and disk does not perfectly align; however, there is a noticeable correlation between them, and both exhibit a consistent trend at temperatures of 25 and 500 °C (Figure 7b,c). Overall wear rates of disks and balls for all lubricants at 500 °C are approximately 70% and 50% higher than those at 25 °C, respectively. Among all the water-based lubricants, the average COF and wear rate using 0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2 are the lowest, whereas the highest results are obtained for 2.0 wt% hBN/TiO2. At 25 and 500 °C, the optimal lubricant containing 0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2 reduced the COFs from 0.42 to 0.078 and 0.45 to 0.1889; the corresponding disk wear area decreased from 6366 μm2 to 874 μm2 and 14,320 μm2 to 4279 μm2, and ball wear from 4738 μm2 to 951 μm2 and 9678 μm2 to 1848 μm2, respectively, compared to dry conditions.
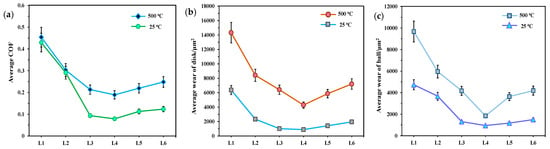
Figure 7.
Average (a) COF, (b) disk wear, and (c) ball wear under different lubricating conditions at 25 and 500 °C.
Compared to that of water, the COF reduction order for water-based lubricants at 25 °C is as follows: 0.5 wt% (72.9%) > 0.25 wt% (67.9%) > 1.0 wt% (61.2%) > 2.0 wt% hBN/TiO2 (57.6%); disk wear: 0.5 wt% (63.6%) > 0.25 wt% (56.7%) > 1.0 wt% (39.5%) > 2.0 wt% (16.2%); and ball wear: 0.5 wt% (74.1%) > 1.0 wt% (67.8%) > 0.25 wt% (64.2%) > 2.0 wt% (59%). At 500 °C, the hBN/TiO2 nanolubricants reduced the COF in the following order: 0.5 wt% (37.5%) > 0.25 wt% (29.5%) > 1.0 wt% (27.48%) > 2.0 wt% (17.9%); disk wear: 0.5 wt% (49.1%) > 1.0 wt% (30.3%) > 0.25 wt% (23.8%) > 2.0 wt% (14.4%); and ball wear: 0.5 wt% (68.9%) > 1.0 wt% (38.9%) > 0.25 wt% (29.9%) > 2.0 wt% (29.6%), compared to water conditions. Based on the above discussion, regardless of whether the testing temperature was 25 or 500 °C, 0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2 improved the tribological performance by providing sufficient lubrication between the disk and ball. Hence, hBN/TiO2 improves the high-temperature properties of water for tribological applications.
4. Discussions
4.1. Wettability
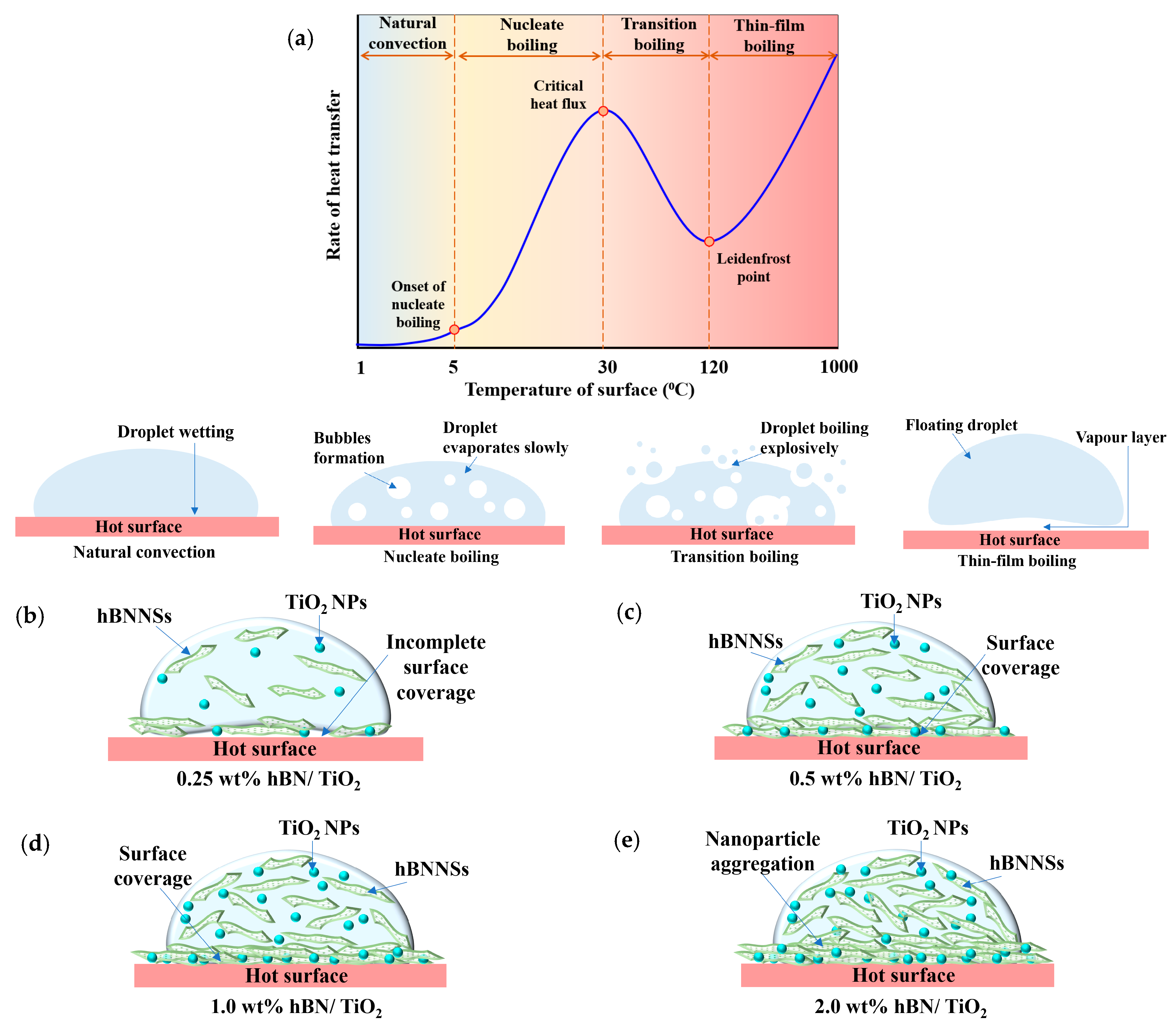
Wettability of water and water-based lubricants on the surface of Q345 steel at room temperature was discussed in our previous study [55]. At high temperatures, when liquid is dropped on a sufficiently hot surface, it evaporates in the immediate vicinity of the surface at a rate capable of sustaining the weight of the liquid; this phenomenon is known as the film boiling or Leidenfrost effect [59,60]. Under the Leidenfrost effect, the liquid fails to wet the surface when the temperature exceeds its boiling point, as a vapor layer forms between the hot surface and water, preventing direct contact [61]. Numerous studies have focused on characterising the Leidenfrost effect for water on hot surfaces [60,62,63,64,65,66]. Figure 8a presents the boiling curve of water with different boiling regimes based on the temperature of the surface; thus, when it crosses the Leidenfrost point at 120 °C, the film’s boiling regime starts. However, at a high temperature of 500 °C, the viscosity of pure water decreases, and evaporation of the floating droplet occurs, resulting in poor friction and wear properties. Limited research has been conducted on the Leidenfrost effect of lubricants with nanoadditives in water and their role in high-temperature anti-friction and anti-wear performance [67,68]. Figure 8b shows that when only 0.25 wt% hBN/TiO2 is added to water, the film boiling is not very prominent, and NPs fail to sustain a stable tribolayer, exposing the bare surfaces. Thus, the NPs are not sufficient to form a strong and consistent heat transfer pathway; these uneven distributions cause localised temperature variations that can accelerate water boiling in some areas. The tribological results indicate that 0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2 is optimal and that there is a balance between thermal stability and lubrication performance. The heat distribution is even across the surface, resulting in a uniform boiling process. This optimal amount stabilises the vapor film by reducing the fluctuations in localised boiling; thus, the film boiling is controlled by neither overheating nor rapid evaporation. At this temperature, the lubricants rest on the vapor layer, preventing the release of water onto the hot surface. This vapor layer acts as a thermal barrier, significantly reducing heat transfer between the liquid and surface. The surface of the lubricant in contact with the vapor layer consists of a combination of uniformly dispersed nanoadditives, as shown in Figure 8c. The evaporation rate and the vapor pressure just below the NPs are low and cannot support the NP load in these areas. This leads to a localised collapse of the vapour layer, enabling the NPs to wet the surface and spread across the hot surface. Under these conditions, the water phase in the lubricants evaporates with little agitation and splashes (Figure 8c). When the concentration is increased to 1.0 wt%, surface coverage with hBN/TiO2 occurs, but the coverage is not as good as that with 0.5 wt%, as each droplet contains a greater proportion of NPs than water does; thus, it experiences faster film boiling. Moreover, Figure 8d shows that the distribution of NPs is comparatively less uniform and continual. However, the solid lubricant layer after water evaporation is sufficient to provide good tribological performance. At a higher concentration of 2.0 wt%, the presence of more NPs on the hot surface facilitates more efficient heat transfer from the hot surface to water, and forms NP clusters at the liquid–solid interface (Figure 8e). Moreover, the water-to-NP ratio decreases; thus, a comparatively lower amount of water per droplet causes evaporation more quickly, leaving behind an unevenly distributed and overly dense layer of NPs. Due to these thick and brittle layers of solid-compact nanoadditives, the hBN/TiO2 tribofilm breaks down more quickly. For stable lubricants, a stable vapor layer forms, effectively allowing direct contact between lubricating NPs and the hot surface. For unstable lubricants, water is delivered to hot surfaces through agitation, splashing, and uneven boiling. As a result, unstable lubricants exhibit more irregular localised boiling compared to stable lubricants. Therefore, by using water-based nanolubricants at elevated temperatures, a thick vapor layer can be overcome by allowing contact between the NPs of lubricants and the hot steel surface.
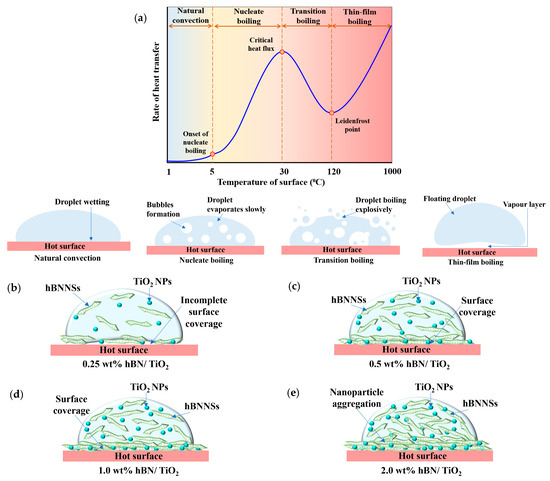
Figure 8.
(a) Boiling curve of water. Schematic of wettability of different lubricants on hot Q345 steel surface: (b) 0.25 wt% hBN/TiO2, (c) 0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2, (d) 1.0 wt% hBN/TiO2, and (e) 2.0 wt% hBN/TiO2.
4.2. Lubrication Mechanism at 25 °C
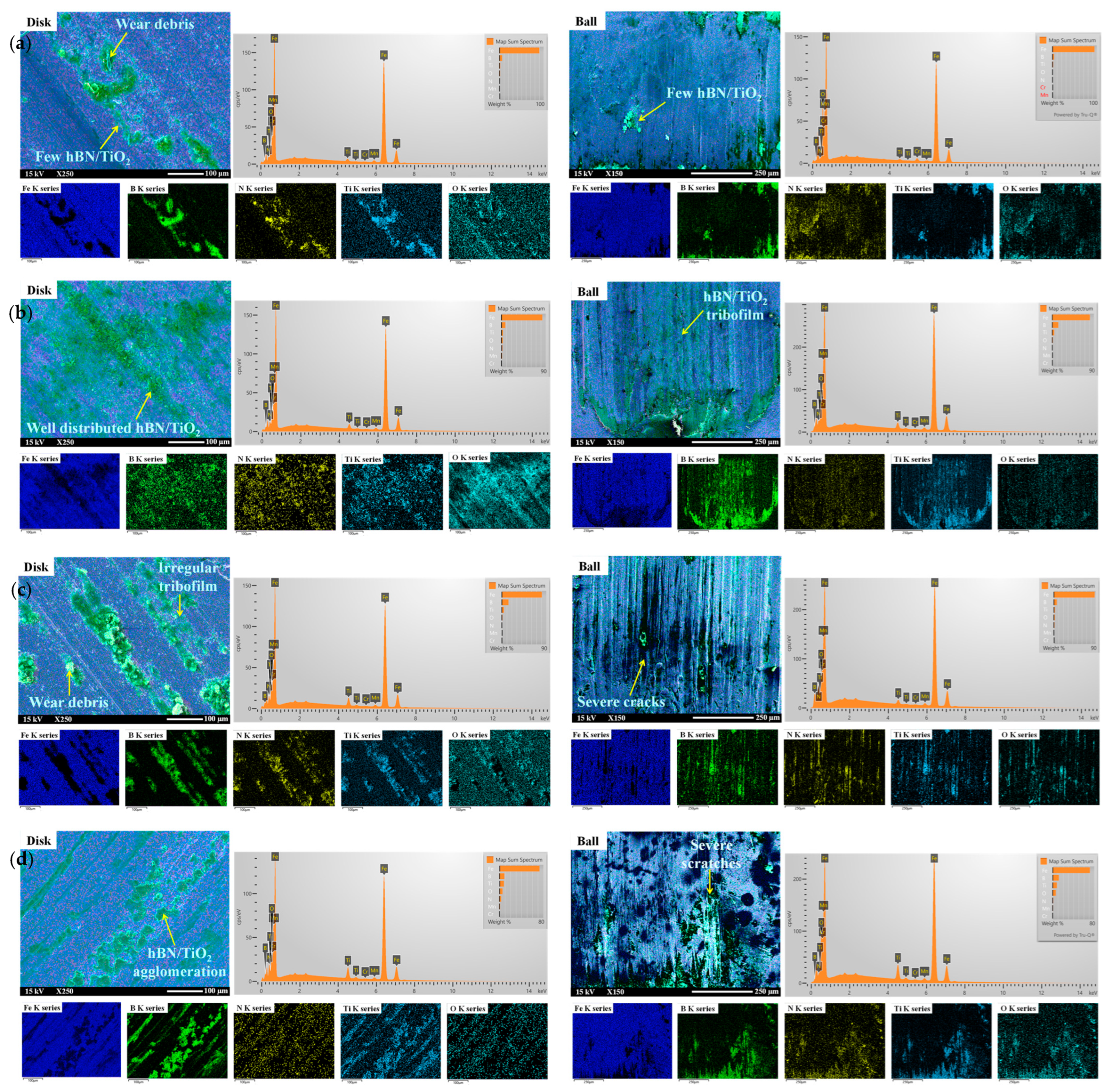
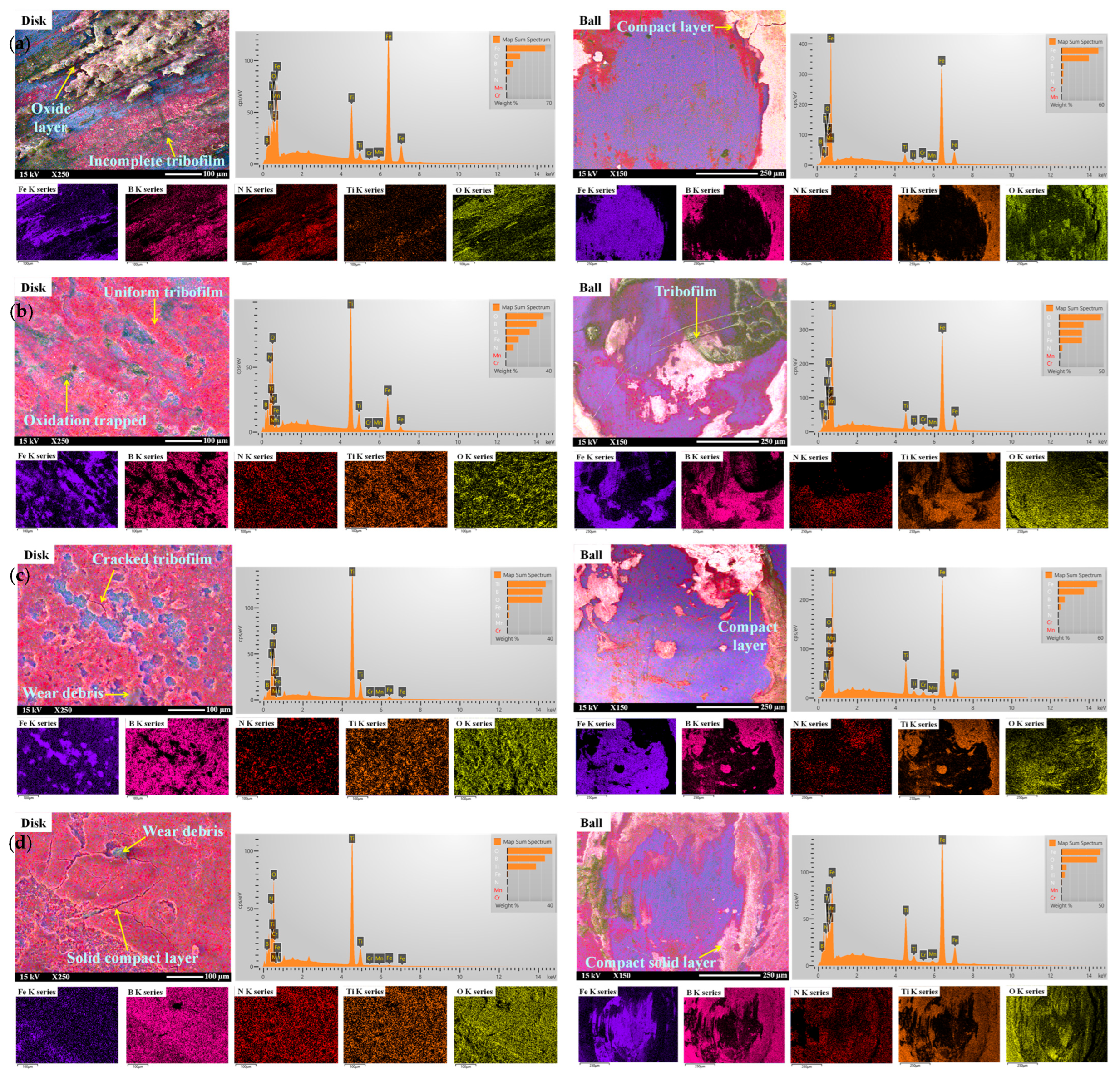
To understand the lubrication mechanism of water-based lubricants, the SEM morphologies of disk wear tracks and ball scars generated at room temperature were analysed, as presented in Figure 9. Figure 10 shows the schematics of lubrication mechanisms aligning with the SEM-EDS analysis of the disk and ball wear. With zero lubrication, the average COF at room temperature was 0.3, and it decreased to a minimum of 0.09 with the addition of hBN/TiO2 nanolubricant, suggesting tribofilm formation [69]. The wear tracks and scars generated by water-based nanolubricants appear smooth and consistently similar across all the cases, as shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6. These observations were attributed to the ability of hBN/TiO2 to maintain a more consistent lubricating film between the sliding pairs and their resistance to metal–metal contact. The formation of tribolayers on the track serves to control and stabilise friction. These tribolayers are known as glazes, which form on sliding surfaces during frictional sliding. Glazes can temporarily protect surfaces from further damage. The EDS mappings presented in Figure 9 for all the lubricating conditions confirmed that the layer was rich in B, N, Ti, and O in the brighter and darker regions. Boron and titanium are directly related to the formation of tribofilms on the wear tracks, which protect the sliding surfaces from damage, thus reducing friction and wear [70,71]. A distinctive tribofilm formed at 25 °C, and the surface coverage of the protective layer increased rapidly after a short period of sliding, causing a significant reduction in wear rate. Moreover, EDS mapping of hBN/TiO2 nanolubricants at room temperature revealed that no additional oxygen signal was detected, i.e., there was no oxide formation at 25 °C. Thus, tribo-oxidation is of minor importance at room temperature [72]. The EDS spectra in Figure 9 present a quantitative analysis of the disk tracks and ball scars with various water-based lubricants tested at 25 °C, illustrating the amount of hBN/TiO2 participating in COF and wear reduction. The 3D profiles in Figure 5 and Figure 6 clearly show that the width and depth of wear tracks and scars decrease when the water-based nanolubricants were applied.
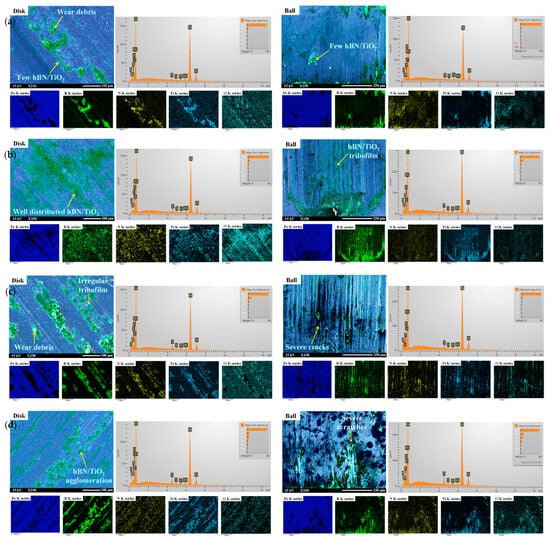
Figure 9.
SEM-EDS analysis of the disk and ball wear using water-based nanolubricants with (a) 0.25 wt% hBN/TiO2, (b) 0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2, (c) 1.0 wt% hBN/TiO2, and (d) 2.0 wt% hBN/TiO2 after sliding at ambient temperature (25 °C) in ambient air.
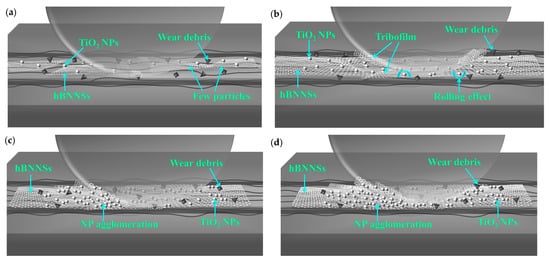
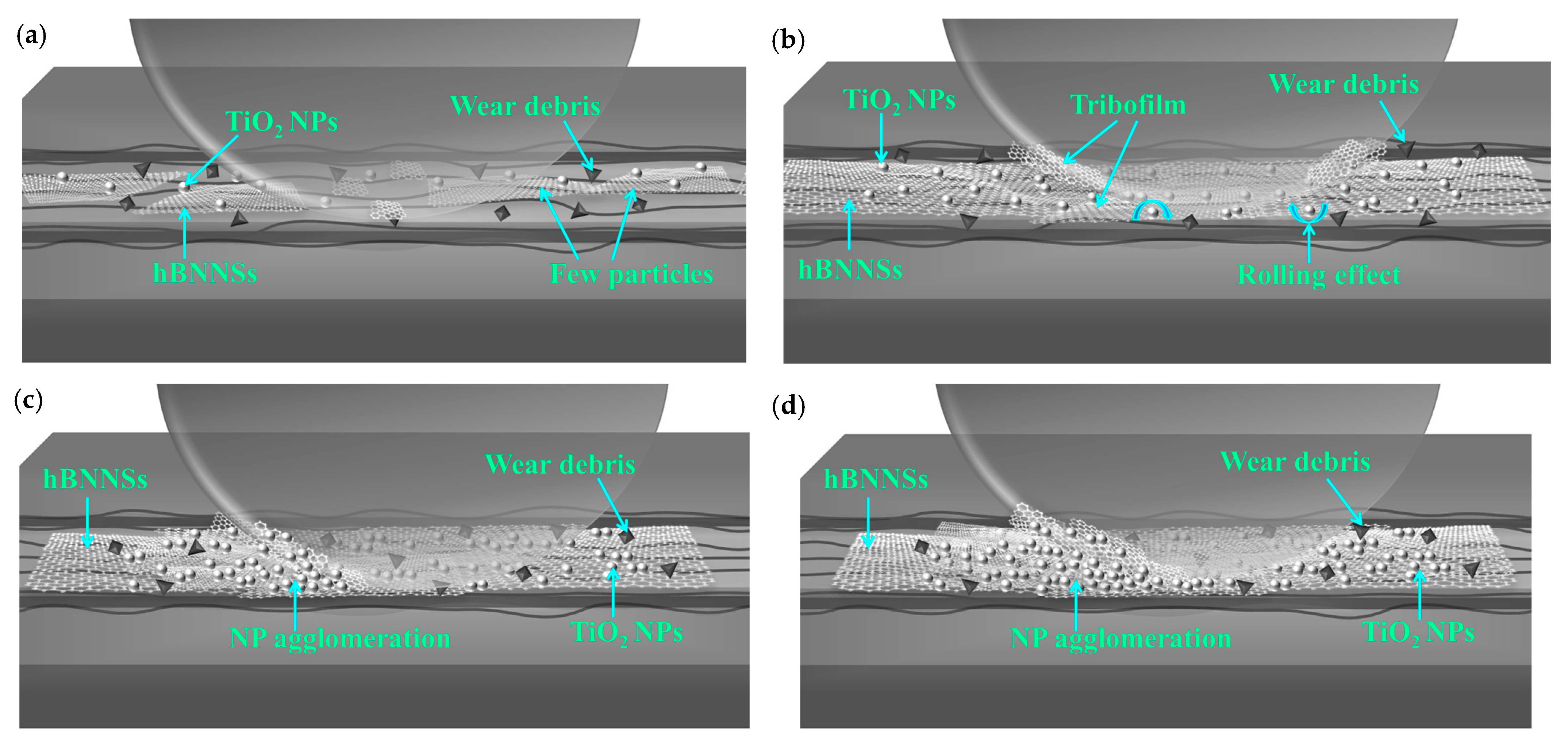
Figure 10.
Lubrication mechanisms of water-based nanolubricants using (a) 0.25 wt% hBN/TiO2, (b) 0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2, (c) 1.0 wt% hBN/TiO2, and (d) 2.0 wt% hBN/TiO2 at ambient temperature (25 °C).
As the ball hardness is much greater than the disk hardness, the degree of ball wear is negligible [73]. Under boundary lubrication, the primary lubrication mechanism for hBN/TiO2 remained unchanged, with low variations in wear rate [74]. This indicates that the concentration of hBN/TiO2 has a noticeable but limited impact on the wear rate (Figure 7). The synergistic effect of hBN and TiO2 enhanced lubrication, as shown in Figure 10b, where hBN played role in protective film formation and TiO2 facilitated the rolling effect between the sliding pairs. Figure 9b shows that the optimal concentration of 0.5 wt% provided the most effective balance and proper participation of the nanoadditive quantity in the lubricant, ensuring a well-distributed hBN/TiO2 tribofilm on the track. At 0.25 wt%, as illustrated in Figure 10a, the nanoadditives were insufficient to provide enough synergy, while higher concentrations of 1.0 and 2.0 wt% promoted agglomeration (Figure 10c,d). Thus, 1.0 and 2.0 wt% hBN/TiO2 contributed to the insignificant lubrication, which led to a rougher texture or the scratchy appearance of the worn ball surface, as shown in Figure 9c,d. In all the wear tracks, NPs are unevenly distributed along the surface, whereas the optimal lubricant (0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2) results in smoother wear surfaces. The above reasons collectively contribute to preventing metal sliding, resulting in a lower wear rate when water-based nanolubricants are used.
4.3. Lubrication Mechanism at 500 °C
SEM and EDS analyses in Figure 11 show the surface morphology of disk and ball wear after tribological testing using different water-based lubricants at 500 °C. Understanding the elevated temperature tribology of lubricants in an oxidising environment requires an interdisciplinary approach. The track changed significantly with temperature, although a major effect was observed because the temperature increased from 25 to 500 °C. The temperature at the contact area is the combination of the surrounding temperature and the heat generated by friction. Therefore, the response of metals to high-temperature sliding needs to consider these two contributions and their potential effects on the tribological development of glazes. Since water in water-based lubricants degrades quickly at high temperatures, solid particles play a role as a coating layer on the rubbing surface, thus reducing friction and wear in high-temperature environments [75,76,77]. The water acts as a medium to transfer the nanoadditives with a uniform distribution at the right spot between the sliding pairs. In addition, though glycerol (290 °C) and SDBS (360 °C) have higher boiling temperatures than water, all of them vaporise at 500 °C, leaving the wear track covered with only solid layers composed of loose hBN/TiO2 [78,79]. Water-based nanolubricants are highly resistant to oxidation and form a protective film that offers stable surface protection over time. During the initial stage of sliding, large amounts of wear debris are generated, and no apparent protective layer is formed on the surface. However, after the initial phase, the solid compact tribofilm accumulates on the sliding surfaces and repeatedly breaks down, which aligns well with the in-situ COF curve in Figure 4. To explore the protective layer composition, EDS mappings and spectra were taken, revealing the formation of BN and TiO tribofilms through the compaction of wear debris on the worn surfaces. Elemental analysis of the tribolayers and clusters formed at different test temperatures revealed that neither temperature nor wear debris compaction significantly affected the chemical composition, except for an increase in the oxygen content [80]. Thus, the EDS spectrum in Figure 11 revealed a greater trace of oxygen on the debris than that at 25 °C, as shown in Figure 9 [81]. The oxygen signals detected on the wear tracks and scars indicate slight oxidation at 500 °C. The Fe diffuses to the surface and forms FeO, as shown in the EDS maps of the worn surfaces outside the tribofilm. This clearly indicates that the worn surfaces contain oxides of Fe from the counterface material; by combining these materials, a compacted layer formed on the worn surface [82].
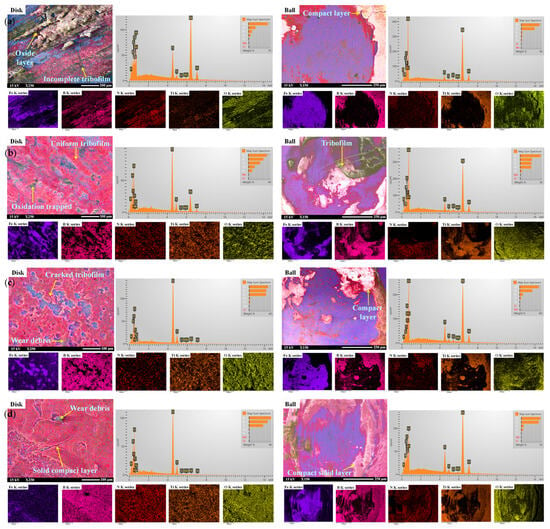
Figure 11.
SEM-EDS analysis of the disk and ball wear using water-based nanolubricants with (a) 0.25 wt% hBN/TiO2, (b) 0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2, (c) 1.0 wt% hBN/TiO2, and (d) 2.0 wt% hBN/TiO2 after sliding at elevated temperature (500 °C) in ambient air.
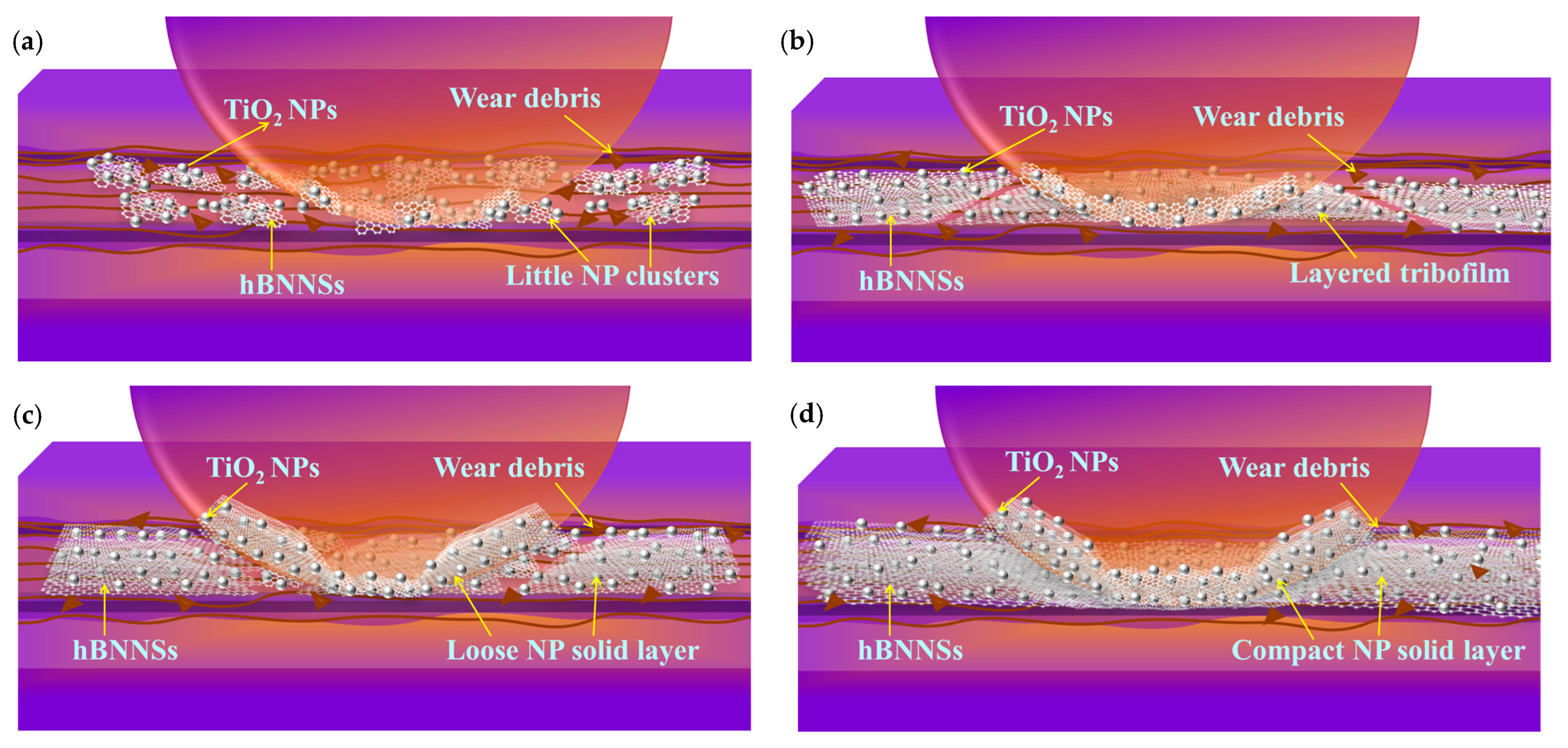
Figure 12 schematically illustrates the lubrication mechanisms involved at an elevated temperature using water-based lubricants. Under 500 °C, Figure 12a shows broken NP clusters when 0.25 wt% hBN/TiO2 was used, which aligns with the incomplete surface coverage by a few NPs during film boiling, as observed in Figure 8b. In addition, the SEM image in Figure 11a presents a non-uniform tribolayer and a broad oxide scale on the disk track, while a thick oxide layer formed on the ball scar surface near the edge of the contact area, with a few hBN/TiO2 layers present around the centre. Comparatively better lubrication was observed with 0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2 at 500 °C, as the tribofilms formed by the NPs acted as solid lubricants and trapped oxidation, thereby reducing the COF and wear (Figure 7 and Figure 11b). Moreover, a prominent glaze layer of hBN/TiO2 was observed in the EDS analysis and elemental mappings at the centre of the ball wear scars, confirming stability in the maximum contact pressure zone. Thus, an appropriate quantity of NPs could form a layered and secure tribofilm that protects the sliding surfaces (Figure 12b). In contrast, Figure 12c,d show that the incorporation of 1.0 and 2.0 wt% hBN/TiO2 resulted in a thicker and more fragile compact NP solid layer, which also did not improve the average COF and wear, as observed from Figure 7. The disk wear track in Figure 11c shows a discontinuous and cracked tribolayer with a large amount of hBN/TiO2, which is unable to trap the oxide scale, with no obvious tribofilm observed at the ball scar centre. It is important to note that the edges of the ball scars were enriched in the oxidised compact layer, indicating that the initially formed tribofilm and oxide layer gradually pushed toward the edge of the contact zone. However, increasing the concentration to 2.0 wt%, the accumulation of hBN/TiO2 on the track becomes apparent, but it prevents and traps further oxidation, as shown in Figure 11d. Interestingly, an intense pile-up of hBN/TiO2 was observed at the ball edge, where the contact pressure was expected to be minimal [83,84]. However, it is clear that the NPs resist further oxidation of the track. The EDS spectrum shows that the testing temperature has a significant effect on surface oxidation, whereas increasing the concentration of hBN/TiO2 has a relatively slight effect [72].
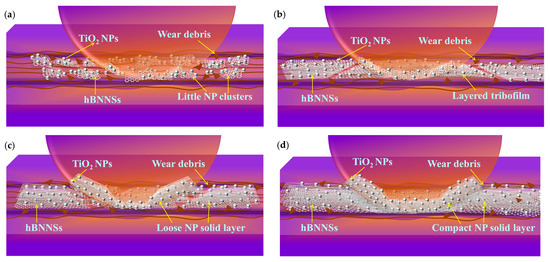
Figure 12.
Lubrication mechanisms of water-based nanolubricants using (a) 0.25 wt% hBN/TiO2, (b) 0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2, (c) 1.0 wt% hBN/TiO2, and (d) 2.0 wt% hBN/TiO2 at elevated temperature (500 °C).
From the above discussions, the lubrication mechanism at high temperatures is complex, although simple oxidation wear theory is applicable under the present conditions. According to oxidation theory, wear typically increases with rising temperature due to the accelerated oxidation rate [85]. Tribo-oxidation differs significantly from normal oxidation, suggesting that glaze formation is not only governed by the oxidation process but also influenced by the wear debris within the disk and ball wear. Thus, lubrication mechanisms at high temperatures involve the combined effects of tribofilm and oxide layer formation [86]. In summary, the results clearly highlight the remarkable performance of 0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2 through tribofilm formation rich in B, N, Ti, and O at both 25 and 500 °C.
5. Conclusions
In this study, the tribological performance of water-based lubricants with modified hBN (hBN/TiO2) at ambient and elevated temperatures was explored. The results indicate that the incorporation of hBN/TiO2 as nanoadditives in water can be a promising solution at both ambient and elevated temperatures. Combined with the influence of the NP concentration and the temperature on the tribological behaviour of hBN/TiO2 water-based lubricants, the following conclusions can be drawn:
1. hBN/TiO2 are designed to provide considerable high-temperature stability as nanoadditives in water-based lubricants. The COFs and wear of the water-based lubricants varied with respect to the test temperatures, i.e., increased with increasing temperature.
2. Among all the water-based lubricants, the optimal 0.5 wt% hBN/TiO2 one showed the best lubrication performance at both room and high temperatures, as it reduced the COFs and disk and ball wear by (81.2% and 58.4%), (86.7% and 70.11%), and (79.9% and 80.9%), respectively, compared to dry conditions.
3. The lubrication mechanism of hBN/TiO2 was governed by the synergistic effect of hBN and TiO2, leading to the formation of a BN/TiO-rich protective film between the sliding pairs. During sliding at 500 °C, the water undergoes the Leidenfrost effect and evaporates, and nano-hBN/TiO2 serves as a solid lubricant by tribofilm formation. Hence, hBN and TiO2 can effectively reduce friction and wear via in-situ tribofilm formation, which enhances the lubrication performance at even higher temperatures.
Therefore, for high-temperature lubrication systems, hBN/TiO2 nanolubricants offer a promising approach for developing responsive nanoadditives. Based on the above conclusions, hBN/TiO2 as a water-based nanoadditive has the potential to replace toxic and harmful lubricants commonly used in industry. At an industrial scale, the application of these hBN/TiO2 lubricants can be further supported by conducting life cycle assessments to determine their usage and disposal processes, thereby contributing to environmental sustainability.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/lubricants13080344/s1, Figure S1: Dispersion stability of different concentrations of nano-hBN/TiO2 in water observed for certain standing times: (a) 0 days, (b) 1 day, (c) 3 days, (d) 5 days, (e) 7 days, (f) 9 days, (g) 10 days, (h) 13 days, (i) 15 days, (j) 20 days, (k) 25 days, and (l) 30 days; Table S1: In-situ coefficients of friction (COF) under six lubricating conditions at ambient temperature (25 °C) under 50.0 N load at 50 mm/s speed; Table S2: In-situ coefficients of friction (COF) under six lubricating conditions at elevated temperature (500 °C) under 50.0 N load at 50 mm/s speed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.J., S.J., H.W. and Z.X.; methodology, A.M., H.W. and F.L.; formal analysis, A.M.; investigation, A.M. and F.L.; resources, S.J. and Z.X.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M.; writing—review and editing, Z.J. and A.M.; visualization, S.J.; supervision, Z.J.; project administration, H.W. and Z.X.; funding acquisition, Z.J. and H.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Baosteel-Australia Joint Research and Development Centre (No. BA23005).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article and Supplementary File. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support from Baosteel-Australia Joint Research & Development Center (BAJC) under the project of BA23005. The authors wish to thank the technicians in the workshop of the SMART Infrastructure Facility at the University of Wollongong for their great support in machining samples.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Zhao Xing and Sihai Jiao were employed by the company Baosteel Research Institute (R&D Centre), Baoshan Iron & Steel Co., Ltd., Shanghai 200431, China. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Barnosky, A.D.; Hadly, E.A.; Bascompte, J.; Berlow, E.L.; Brown, J.H.; Fortelius, M.; Getz, W.M.; Harte, J.; Hastings, A.; Marquet, P.A. Approaching a state shift in Earth’s biosphere. Nature 2012, 486, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnosky, A.D.; Matzke, N.; Tomiya, S.; Wogan, G.O.; Swartz, B.; Quental, T.B.; Marshall, C.; McGuire, J.L.; Lindsey, E.L.; Maguire, K.C. Has the Earth’s sixth mass extinction already arrived? Nature 2011, 471, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, J.C.; Gordon, T.J.; Florescu, E. 2013-14 State of the Future; The Millennium Project: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bartz, W.J. Ecotribology: Environmentally acceptable tribological practices. Tribol. Int. 2006, 39, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S. Environmentally friendly tribology (Eco-tribology). J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2010, 24, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebeshuber, I.C. Ecotribology: Development, Prospects, and Challenges. In Ecotribology: Research Developments; Davim, J.P., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Stojilković, M.; Golubović, D.; Ješić, D. Ecotribology aspects in the lubricants application. EXPRES 2014, 2014, 124. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.-C.; Huang, T.-F. Self-Healing Materials for Ecotribology. Materials 2017, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Cheng, J.; Qiao, Z.; Yang, J. High temperature solid-lubricating materials: A review. Tribol. Int. 2019, 133, 206–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdemir, A. A crystal-chemical approach to lubrication by solid oxides. Tribol. Lett. 2000, 8, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, A.P. Tribology at high temperatures. Tribol. Int. 1995, 28, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohda, K.; Boher, C.; Rezai-Aria, F.; Mahayotsanun, N. Tribology in metal forming at elevated temperatures. Friction 2015, 3, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Tieu, A.K.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, H.; Tran, B.H.; Cui, S. An overview of inorganic polymer as potential lubricant additive for high temperature tribology. Tribol. Int. 2016, 102, 620–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, N.W.M.; Kalam, M.A.; Masjuki, H.H.; Al Mahmud, K.A.H.; Yunus, R. The Effect of Temperature on Tribological Properties of Chemically Modified Bio-Based Lubricant. Tribol. Trans. 2014, 57, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duntu, S.H.; Ahmad, I.; Islam, M.; Boakye-Yiadom, S. Effect of graphene and zirconia on microstructure and tribological behaviour of alumina matrix nanocomposites. Wear 2019, 438–439, 203067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ürdem, Ş.; Duru, E.; Algül, H.; Uysal, M.; Akbulut, H. Evaluation of high temperature tribological behavior of electroless deposited NiB–Al2O3 coating. Wear 2021, 482–483, 203960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomala, A.; Hernandez, S.; Rodriguez Ripoll, M.; Badisch, E.; Prakash, B. Tribological performance of some solid lubricants for hot forming through laboratory simulative tests. Tribol. Int. 2014, 74, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, P. Synthesis of water-soluble Cu nanoparticles and evaluation of their tribological properties and thermal conductivity as a water-based additive. Friction 2019, 7, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Song, S.; Yang, G.; Yu, L.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, P. Preparation and Tribological Properties of Surface-Capped Copper Nanoparticle as a Water-Based Lubricant Additive. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 54, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Huang, S.; Yun, J.-H.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Stokes, J.; Jiao, S.; Wang, L.; Huang, H. Tribological Performance and Lubrication Mechanism of Alumina Nanoparticle Water-Based Suspensions in Ball-on-Three-Plate Testing. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 65, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.X.; Sun, J.L.; Wei, H.R.; Niu, T.L.; Zhu, Z.L. Research on Lubrication Behaviors of Nano-TiO2 in Water-Based Hot Rolling Liquid. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 643, 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.; Sun, J.; Bao, Y.; Meng, Y. Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on wettability and tribological performance of aqueous suspension. Wear 2017, 376–377, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanan, M.; Jianlin, S.; Jiaqi, H.; Xudong, Y.; Yu, P. Recycling prospect and sustainable lubrication mechanism of water-based MoS2 nano-lubricant for steel cold rolling process. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; Deng, J.; Wang, Z. Friction reduction of water based lubricant with highly dispersed functional MoS2 nanosheets. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 562, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, J.; Lu, X.; Mao, C.; Chen, S.; Mao, J.; et al. One-pot pyrolysis preparation of carbon dots as eco-friendly nanoadditives of water-based lubricants. Carbon 2019, 152, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Shen, Z.; Yi, M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Ma, S. In-situ exfoliated graphene for high-performance water-based lubricants. Carbon 2016, 96, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Yue, W.; Zhang, H. Bioinspired Surface Functionalization of Nanodiamonds for Enhanced Lubrication. Langmuir 2018, 34, 12436–12444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Geng, Z.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, G. Enhanced Tribological Performance of Aminated Nano-Silica Modified Graphene Oxide as Water-Based Lubricant Additive. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 6444–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Sun, J.; Wu, P. Preparation, characterization and lubrication performances of graphene oxide-TiO2 nanofluid in rolling strips. Carbon 2018, 140, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, A.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. A Comprehensive Review of Water-Based Nanolubricants. Lubricants 2021, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, C. Insight into the tribological performance of polyurethane composites under high temperature water lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2021, 155, 106784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Xie, X.; Yuan, C.; Bai, X. Study on influence of micro convex textures on tribological performances of UHMWPE material under the water-lubricated conditions. Wear 2019, 426–427, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yuan, C.; Liu, A.; Jiang, S. Study on tribological properties of novel biomimetic material for water-lubricated stern tube bearing. Wear 2017, 376–377, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Guler, S.I.; Gayah, V.V. An equitable traffic signal control scheme at isolated signalized intersections using Connected Vehicle technology. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2020, 110, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Izawa, M.; Nakanishi, T.; Tsubouchi, K. Tribological Properties of Water Glass Lubricant for Hot Metalworking. Tribol. Trans. 2009, 52, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, F.H.; Lin, D.S.; Wood, G.C. The structure and mechanism of formation of the ‘glaze’ oxide layers produced on nickel-based alloys during wear at high temperatures. Corros. Sci. 1973, 13, 449–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, F.H. The role of oxidation in the wear of alloys. Tribol. Int. 1998, 31, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, F.H.; Lin, D.S.; Wood, G.C. “Glazes” produced on Nickel-base Alloys during High Temperature Wear. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1973, 242, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.X.; Peng, D.S.; Liu, J.A.; Liu, Z.Q. An experiment study of the lubrication behavior of graphite in hot compression tests of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2001, 112, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianxin, D.; Hui, Z.; Ze, W.; Yunsong, L.; Youqiang, X.; Shipeng, L. Unlubricated friction and wear behaviors of Al2O3/TiC ceramic cutting tool materials from high temperature tribological tests. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2012, 35, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, G. Ceramic cutting tools, state of the art and development trends. Mater. Technol. 1999, 14, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.L.; Xu, F.M.; Zhang, Z.J.; Dong, Y.L.; Tan, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.M. Mechanical properties of hot-pressed Al2O3/SiC composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 4646–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Jia, F.; Zhao, J.; Huang, S.; Wang, L.; Jiao, S.; Huang, H.; Jiang, Z. Effect of water-based nanolubricant containing nano-TiO2 on friction and wear behaviour of chrome steel at ambient and elevated temperatures. Wear 2019, 426–427, 792–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, G.; Staia, M.H. High-temperature tribological characterization of zirconium nitride coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 2092–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.G.; Yoon, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Song, K. High temperature wear resistance of (TiAl)N films synthesized by cathodic arc plasma deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1996, 86–87, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrovskaya, Y.L.; Strel’nitskij, V.E.; Kuleba, V.I.; Gamulya, G.D. Friction and wear behaviour of hard and superhard coatings at cryogenic temperatures. Tribol. Int. 2001, 34, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, D.S.; Migas, J.; Martini, A.; Smith, T.; Muratore, C.; Voevodin, A.A.; Aouadi, S.M. Adaptive NbN/Ag coatings for high temperature tribological applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 4316–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouadi, S.M.; Luster, B.; Kohli, P.; Muratore, C.; Voevodin, A.A. Progress in the development of adaptive nitride-based coatings for high temperature tribological applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 204, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore, C.; Voevodin, A.A. Chameleon Coatings: Adaptive Surfaces to Reduce Friction and Wear in Extreme Environments. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2009, 39, 297–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchner, B.; Maderthoner, G.; Buchmayr, B. Characterisation of different lubricants concerning the friction coefficient in forging of AA2618. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 198, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, A.; Wu, H.; Ren, M.; Xing, Z.; Jiao, S.; Jiang, Z. A Study of Water-Based Nanolubricants Using Hexagonal Boron Nitride (hBN)-Based Nanocomposites as Lubricant Additives. Lubricants 2024, 12, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Chen, Y.K.; Ren, G. A Study of Tribological Properties of Water-Based Ceria Nanofluids. Tribol. Trans. 2013, 56, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, B. Tribological Behaviors and Lubrication Mechanism of Water-based MoO3 Nanofluid during Cold Rolling Process. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 61, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Jia, F.; Li, Z.; Lin, F.; Huo, M.; Huang, S.; Sayyar, S.; Jiao, S.; Huang, H.; Jiang, Z. Novel water-based nanolubricant with superior tribological performance in hot steel rolling. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2020, 2, 025002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, A.; Lin, F.; Wu, H.; Xing, Z.; Jiao, S.; Hasan, M.M.; Jiang, Z. hBN/TiO2 water-based nanolubricants: A solution for stick-slip mitigation in tribological applications. Nanoscale Adv. 2025, 7, 1972–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, J.; Xia, W.; Cheng, X.; He, A.; Yun, J.H.; Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Jiao, S.; Huang, L.; et al. A study of the tribological behaviour of TiO2 nano-additive water-based lubricants. Tribol. Int. 2017, 109, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.J.; D’Oliveira, A.S.C.M. NiCrSiBC coatings: Effect of dilution on microstructure and high temperature tribological behavior. Wear 2016, 350–351, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, H.; Rodríguez Ripoll, M.; Prakash, B. Tribological behaviour of self-lubricating materials at high temperatures. Int. Mater. Rev. 2018, 63, 309–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.; McHale, G. Leidenfrost Effect and Surface Wettability. In The Surface Wettability Effect on Phase Change; Marengo, M., De Coninck, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 189–233. [Google Scholar]
- Baumeister, K.J.; Hamill, T.D.; Schoessow, G.J. A generalized correlation of vaporization times of drops in film boiling on a flat plate. In Proceedings of the International Heat Transfer Conference 3, Chicago, IL, USA, 7–12 August 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Januszkiewicz, K.R.; Riahi, A.R.; Barakat, S. High temperature tribological behaviour of lubricating emulsions. Wear 2004, 256, 1050–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamberger, M.; Jeschar, R.; Prinz, B. Untersuchung des Wärmeübergangs beim Kühlen von Nichteisenmetallen durch Wasser. Int. J. Mater. Res. 1979, 70, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizikar, E. Spray cooling investigation for continuous casting of billets and blooms. Iron Steel Engng. 1970, 6, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Grissom, W.M.; Wierum, F. Liquid spray cooling of a heated surface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1981, 24, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunihide, M.; Itaru, M. The behavior of a water droplet on heated surfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1984, 27, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senda, J. Experimental studies on the behavior of a small droplet impinging upon a hot surface. ICLASS-82 1982, 397. https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1573105974496862208.
- Kwon, M.J.; Park, I.S. Numerical Study of the Effect of Nozzle Arrangement on Cooling Process in Running Hot Steel Strip after Hot Rolling. ISIJ Int. 2013, 53, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zabala, B.; Igartua, A.; Scarpis, V.; Timelli, G.; Girot, F.; Nevshupa, R. Multiparametric study of Leidenfrost point and wettability of lubricants on high-pressure die-casting dies. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2018, 125, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, A.; Wu, C.; Li, W. Tribological performance of silicone oil based Al2O3 nano lubricant for an Mg alloy subjected to sliding at elevated temperatures. Tribol. Int. 2022, 175, 107779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancroft, G.M.; Kasrai, M.; Fuller, M.; Yin, Z.; Fyfe, K.; Tan, K.H. Mechanisms of tribochemical film formation: Stability of tribo- and thermally-generated ZDDP films. Tribol. Lett. 1997, 3, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, A.; Morina, A.; Haque, T.; Voong, M. Compatibility between tribological surfaces and lubricant additives-How friction and wear reduction can be controlled by surface/lube synergies. Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 1680–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birol, Y. In situ processing of TiCp-Al composites by reacting graphite with AI-Ti melts. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 1653–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, L.; Qu, P.; Li, S.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y. Effects of lubrication and temperature on the tribological behavior of a magnesium alloy under contact sliding. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Proceedings of the International Deep-Drawing Research Group (IDDRG 2020), 26–30 October 2020, Seoul, South Korea; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; p. 012018. [Google Scholar]
- Paramsothy, M.; Chan, J.; Kwok, R.; Gupta, M. Al2O3 Nanoparticle Addition to Commercial Magnesium Alloys: Multiple Beneficial Effects. Nanomaterials 2012, 2, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M.B.; Murray, S.F.; Florek, J.J. Consideration of Lubricants for Temperatures above 1000 F. A S L E Trans. 1959, 2, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliney, H.E. Solid lubricant materials for high temperatures—A review. Tribol. Int. 1982, 15, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, I. Solid lubricants for applications at elevated temperatures: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 1991, 26, 3977–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Jérôme, F. Glycerol as a sustainable solvent for green chemistry. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemicalinfo Chemical Industry Information. Sodium Dodecylbenzene Sulfonate–C18H29SO3Na. Available online: https://kemicalinfo.com/chemicals/sodium-dodecylbenzene-sulfonate-c18h29so3na/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Jerome, S.; Ravisankar, B.; Kumar Mahato, P.; Natarajan, S. Synthesis and evaluation of mechanical and high temperature tribological properties of in-situ Al–TiC composites. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 2029–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia-Cancino, J.A.; Ramezani, M.; Álvarez-Ramos, M.E. Effect of degradation on tribological performance of engine lubricants at elevated temperatures. Tribol. Int. 2018, 124, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Stott, F.; Stack, M. The role of triboparticulates in dry sliding wear. Tribol. Int. 1998, 31, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, S.S.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Yaqub, T.B.; Cavaleiro, A.; Fernandes, F. Room and high temperature tribological performance of CrAlN(Ag) coatings: The influence of Ag additions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 450, 129011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Lou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W. Wear mechanism of Ag as solid lubricant for wide range temperature application in micro-beam plasma cladded Ni60 coatings. Tribol. Int. 2022, 167, 107402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Stott, F.; Stack, M. A mathematical model for sliding wear of metals at elevated temperatures. Wear 1995, 181, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woydt, M.; Habig, K.H. High temperature tribology of ceramics. Tribol. Int. 1989, 22, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).