Tribocorrosion Behavior of a Medium-Entropy Austenitic Stainless Steel in 3.5 wt.% NaCl: A Comparative Study with 304 and S31254 Stainless Steels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Corrosion and Tribocorrosion Tests
2.3. Microstructural Characterization and Hardness Measurements
2.4. Material Loss Rate Analysis
3. Results
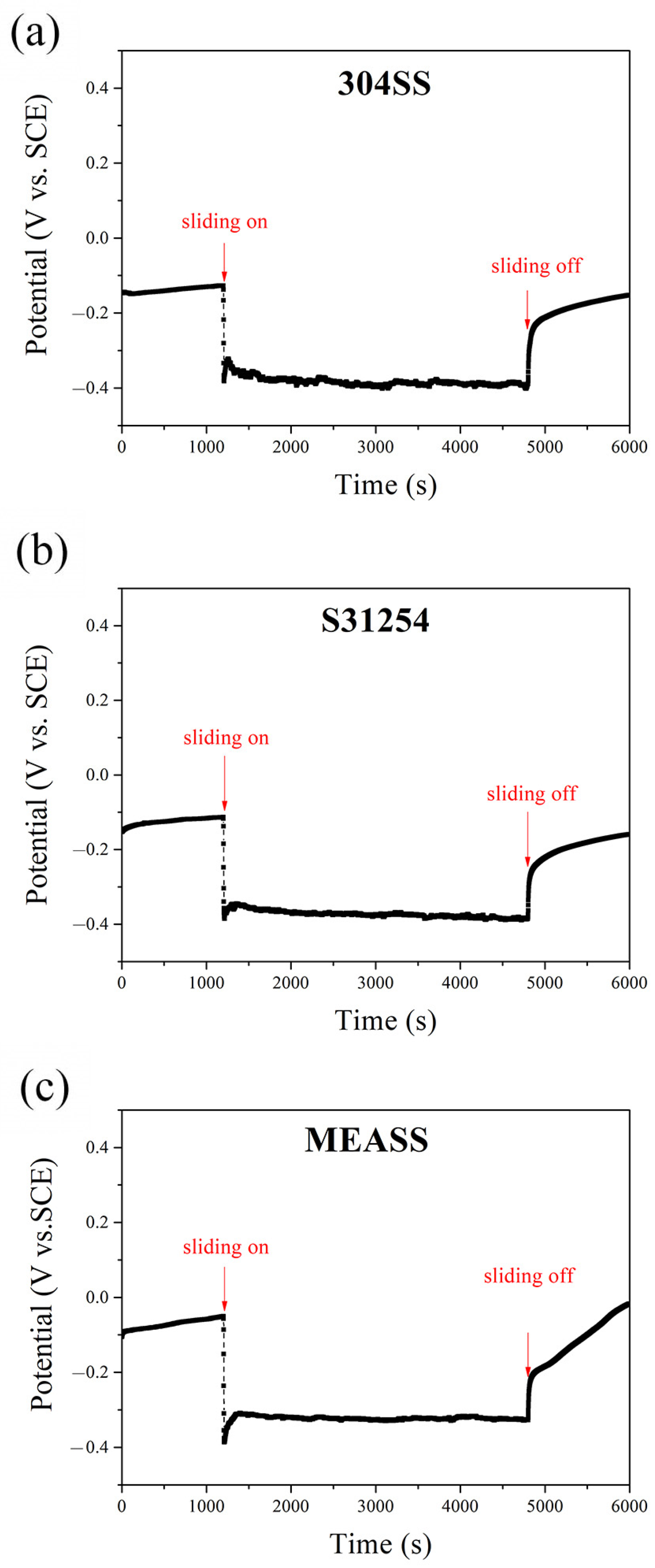
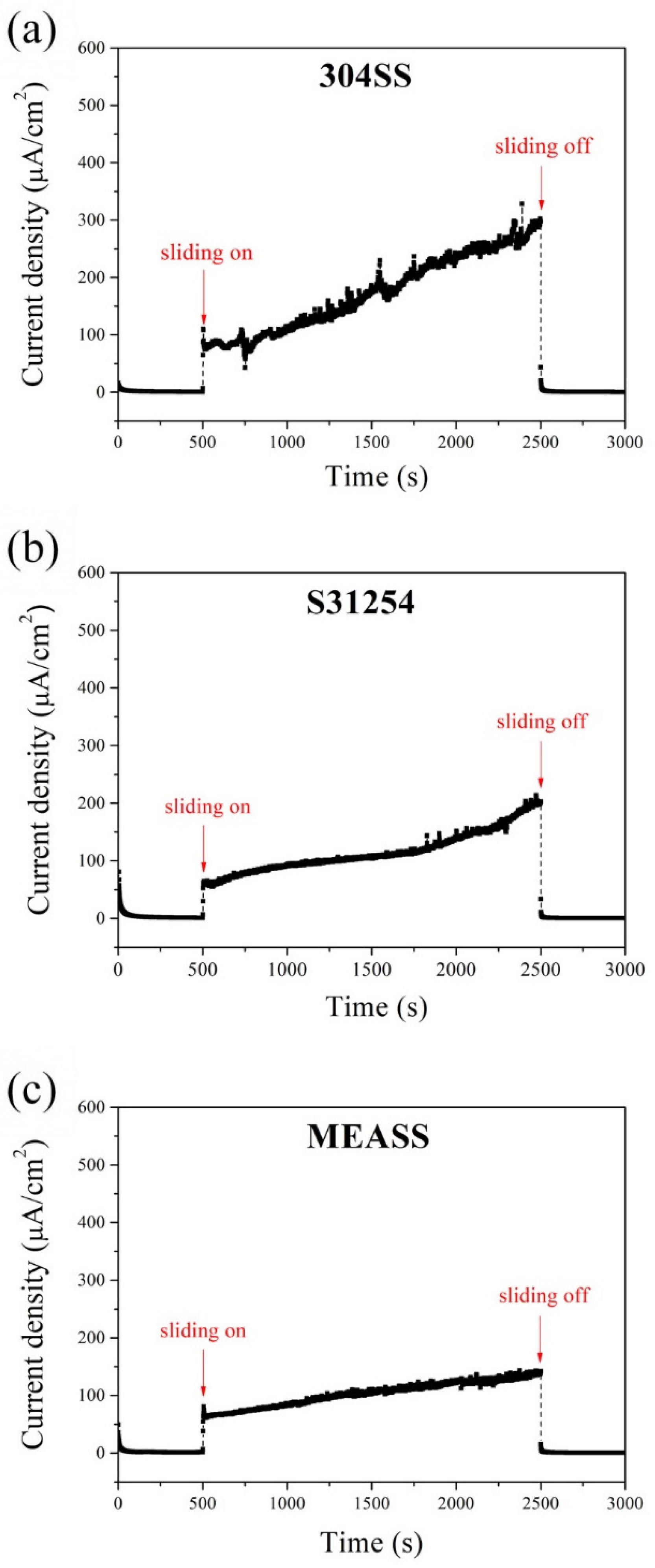
3.1. Intermittent OCP Measurements
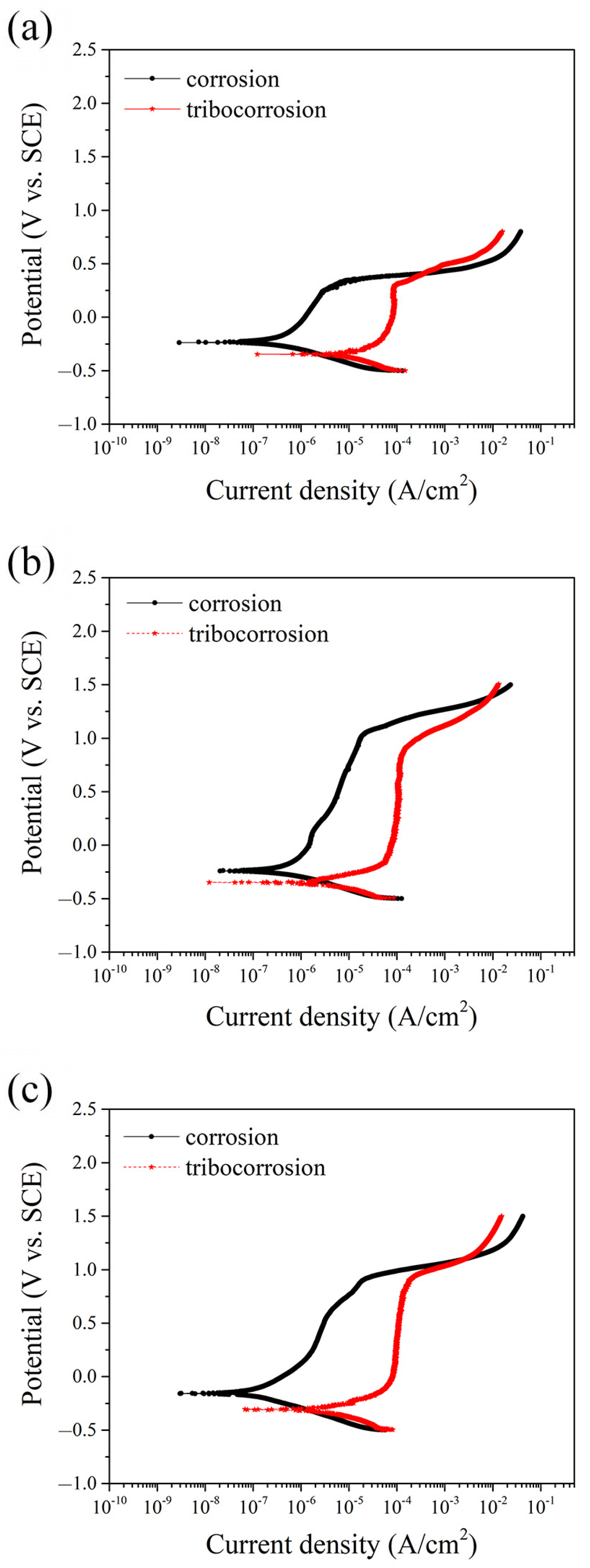
3.2. Potentiodynamic Polarization Test
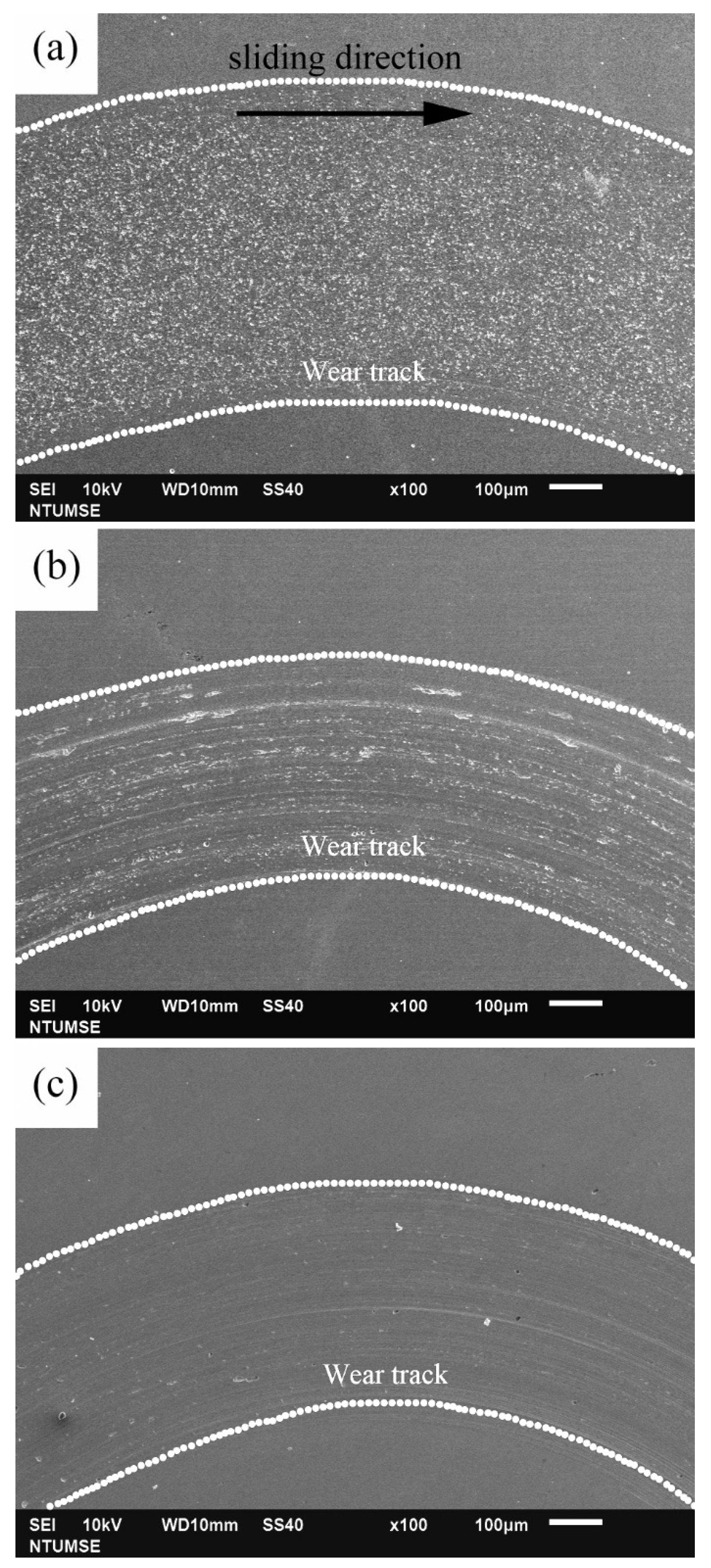
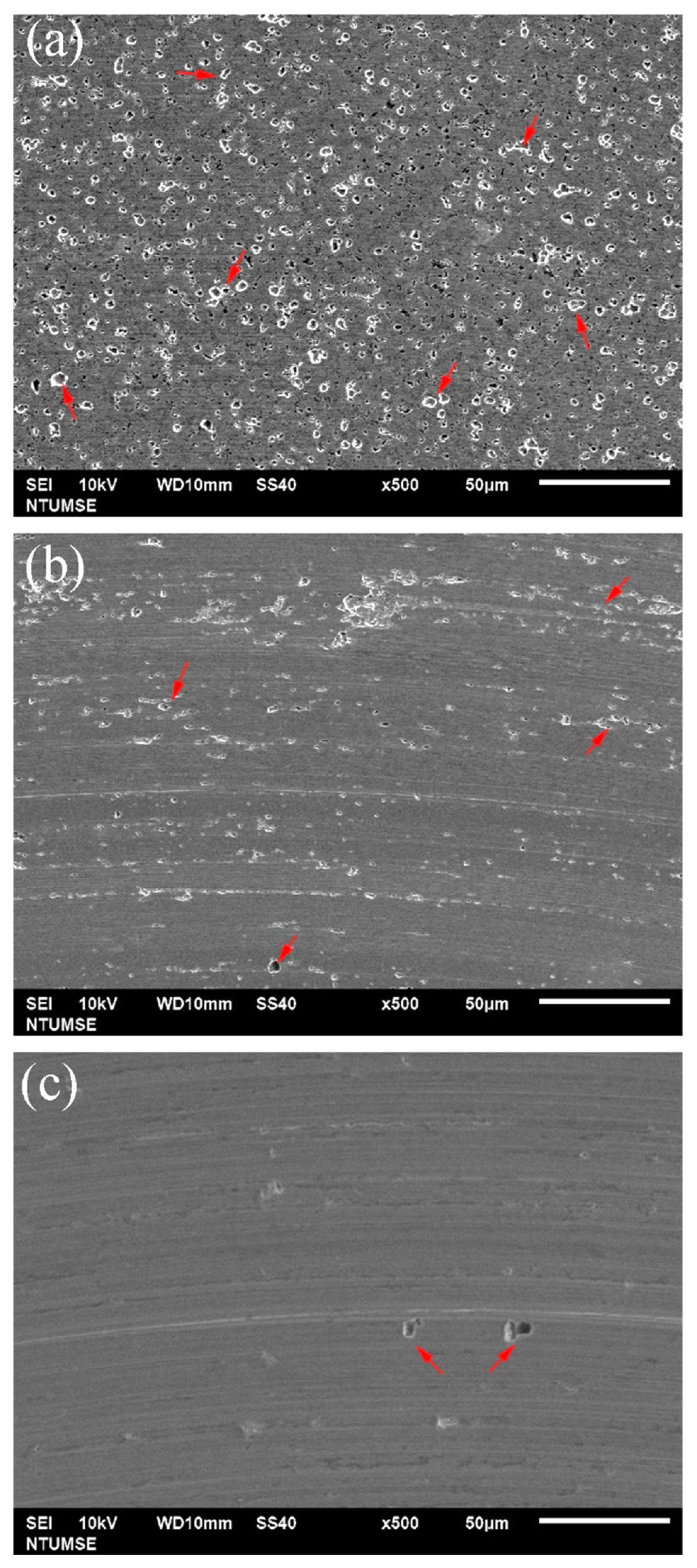
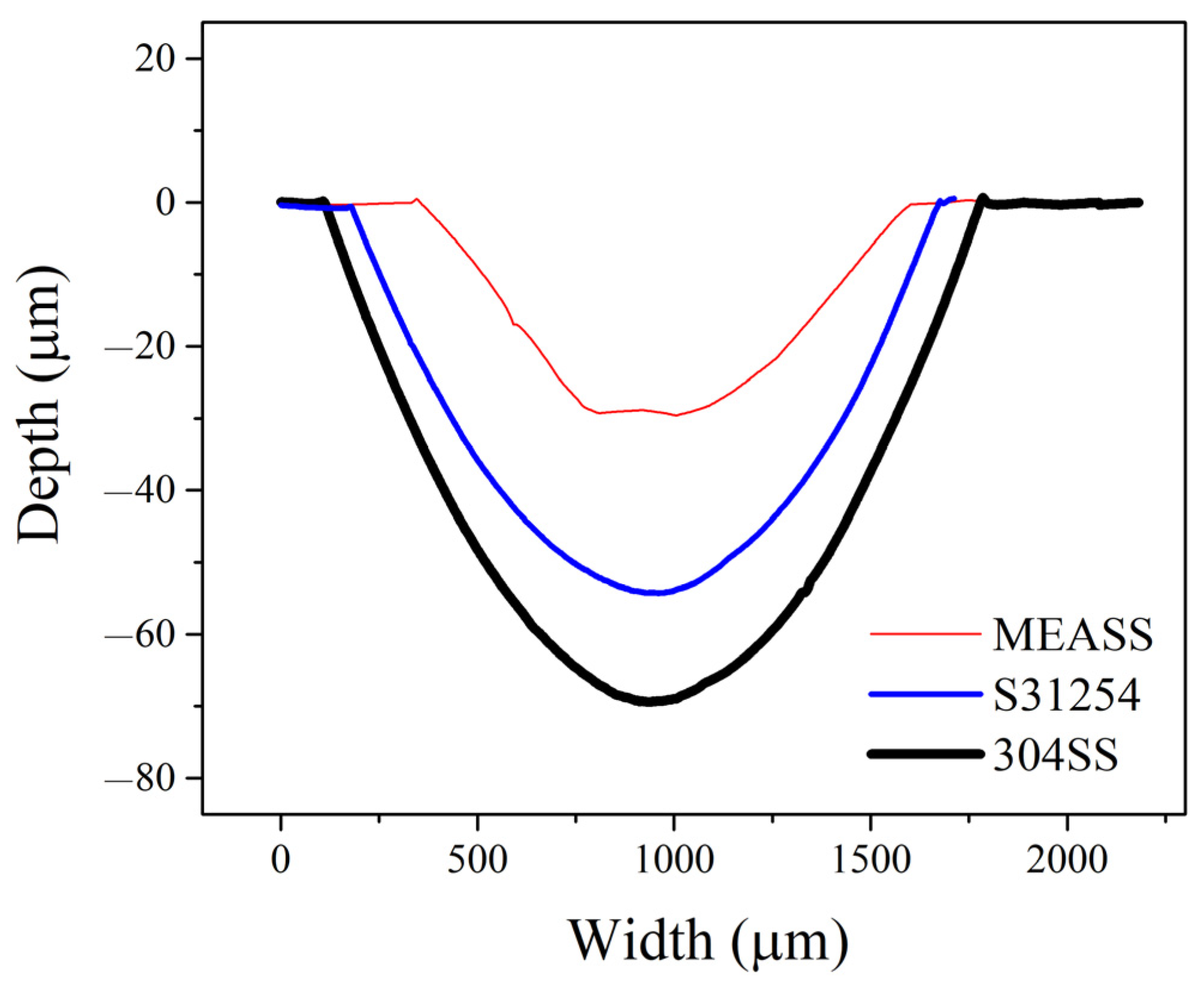
3.3. Wear Morphology and Material Loss
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Among the tested alloys, MEASS exhibited the lowest total material loss under tribocorrosion conditions. SEM analysis further confirmed minimal surface damage and pit formation in MEASS, highlighting its ability to effectively resist localized corrosion and mechanical degradation.
- Quantitative analysis revealed that corrosion-induced wear (ΔWc) was the primary contributor to total material loss, accounting for more than 80% in chloride-containing environments.
- Electrochemical tests demonstrated superior electrochemical stability and repassivation ability for MEASS, which exhibited the lowest corrosion current density (1.46 μA/cm2), representing an 83% reduction compared to 304SS under tribocorrosion conditions.
- Enhanced tribocorrosion resistance of MEASS is primarily attributed to its higher Cr and Ni contents, which strengthen the passive film, thus minimizing pit formation and subsequent mechanical degradation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melchers, R.E.; Moan, T.; Gao, Z. Corrosion of working chains continuously immersed in seawater. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2007, 12, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Luo, W.; Chen, Q.; He, X.; Liu, T. Corrosion evolution and quantitative corrosion monitoring of Q355 steel for offshore wind turbines in multiple marine corrosion zones. Ocean Eng. 2024, 311, 119044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrek-Gerstenkorn, B.; Paul, S. Metallic coatings in offshore wind sector—A mini review. NPJ Mater. Degrad. 2024, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Hernández, A.; Ellwanger, G.; Sagrilo, L. Long-term response analysis of FPSO mooring systems. Appl. Ocean Res. 2011, 33, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolt, D.; Mischler, S.; Stemp, M. Electrochemical methods in tribocorrosion: A critical appraisal. Electrochim. Acta 2001, 46, 3913–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolt, D.; Mischler, S. Tribocorrosion of Passive Metals and Coatings; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Ma, Y.; Yan, Y.; Qiao, L. Effect of frictional frequency on the subsurface evolution of 316L stainless steel in tribocorrosion and its influence on the synergistic effect between corrosion and wear. Tribol. Int. 2023, 178, 108026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Tan, W.; Bonzom, R.; Mi, X.; Zhu, G. Impact-sliding fretting tribocorrosion behavior of 316L stainless steel in solution with different halide concentrations. Friction 2023, 11, 2310–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mischler, S.; Spiegel, A.; Landolt, D. The role of passive oxide films on the degradation of steel in tribocorrosion systems. Wear 1999, 225, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obadele, B.A.; Andrews, A.; Shongwe, M.B.; Olubambi, P.A. Tribocorrosion behaviours of AISI 310 and AISI 316 austenitic stainless steels in 3.5% NaCl solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 171, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Rana, V. Tribocorrosion behaviour of AISI 304 stainless steel in 0.5 M NaCl solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 129, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, C. Tribocorrosion behaviors of Ti–6Al–4V and Monel K500 alloys sliding against 316 stainless steel in artificial seawater. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Q.-A.; Fu, S.-L.; Wang, J.-Z. Corrosion and tribocorrosion behaviors of AISI 316 stainless steel and Ti6Al4V alloys in artificial seawater. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Dalmau, A.; Richard, C.; Igual-Muñoz, A. Degradation mechanisms in martensitic stainless steels: Wear, corrosion and tribocorrosion appraisal. Tribol. Int. 2018, 121, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; An, Y.; Hou, G.; Li, S.; Deng, W.; Zhou, H.; Chen, J. Effects of loads on corrosion-wear synergism of NiCoCrAlYTa coating in artificial seawater. Tribol. Int. 2018, 118, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttunen-Saarivirta, E.; Kilpi, L.; Hakala, T.J.; Carpen, L.; Ronkainen, H. Tribocorrosion study of martensitic and austenitic stainless steels in 0.01 M NaCl solution. Tribol. Int. 2016, 95, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Liu, M.; Jiang, S.; Li, M.; Li, S.; Duan, D. Effects of different cathodic reactions on tribocorrosion behavior of AISI 430 in 0.5 mol/L sulfuric acid. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 31, 2708–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, X.-Y.; Yan, F.-Y. Tribocorrosion behaviour of type S31254 steel in seawater: Identification of corrosion–wear components and effect of potential. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 179, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwabuchi, A.; Sasaki, T.; Hori, K.; Tatsuyanagi, Y. Tribological Properties of SUS304 Steel in Seawater: Electrochemical Approach to the Wear Behaviour. JSME Int. J. Ser. 1 Solid Mech. Strength Mater. 1992, 35, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, S.; Tao, D.; Yang, J. Accelerative effect of wear on corrosion of high-alloy stainless steel. Corrosion 1993, 49, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Jiang, X.; Li, S.; Lu, X. A quantitative estimation of the synergy between corrosion and abrasion. Corros. Sci. 1994, 36, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Duan, D.-L.; Jiang, S.-L.; Li, M.-Y.; Li, S. Tribocorrosion behavior of 304 stainless steel in 0.5 mol/L sulfuric acid. Acta Metall. Sin. Engl. Lett. 2018, 31, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouknin, M.; Boumezzourh, A.; Lakbaibi, Z.; Ponthiaux, P.; Costa, J.; Majidi, L. Tribological behavior of stainless steel in sulfuric acid in the presence of Thymus zygis subsp. gracilis essential oil: Experimental and quantum chemical studies. Corros. Rev. 2021, 39, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak, A.; Zwierzycki, W. Analysis of the tribocorrosion mechanisms in a pin-on-plate combination on the example of AISI304 steel. Wear 2012, 294, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anburaj, J.; Nazirudeen, S.M.; Narayanan, R.; Anandavel, B.; Chandrasekar, A. Ageing of forged superaustenitic stainless steel: Precipitate phases and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 535, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänninen, H.; Romu, J.; Ilola, R.; Tervo, J.; Laitinen, A. Effects of processing and manufacturing of high nitrogen-containing stainless steels on their mechanical, corrosion and wear properties. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2001, 117, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaut, R.L.; Herrera, C.; Escriba, D.M.; Rios, P.R.; Padilha, A.F. A short review on wrought austenitic stainless steels at high temperatures: Processing, microstructure, properties and performance. Mater. Res. 2007, 10, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.; Bingert, J.; Rowenhorst, D.; Gupta, A.; Geltmacher, A.; Spanos, G. Two-and three-dimensional microstructural characterization of a super-austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 418, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-H.; Wu, C.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Yang, J.-R.; Chiu, P.-K.; Fang, J. Cyclic deformation and phase transformation of 6Mo superaustenitic stainless steel. Met. Mater. Int. 2007, 13, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Feng, H.; Han, P.; Dong, N.; Zhang, W.; Li, G.; Fan, G. A new insight into high-temperature oxidation mechanism of super-austenitic stainless steel S32654 in air. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 686, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malandruccolo, A. Properties of Superaustenitic Stainless Steels. In Superaustenitic Stainless Steels: A Comprehensive Overview; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 155–211. [Google Scholar]
- Jinyao, M.; Nan, D.; Zhensen, G.; Peide, H. Effect of B and Ce Micro-alloying on Secondary Phase Precipitation and Corrosion Resistance of S31254 Super Austenitic Stainless Steel. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Prot. 2024, 44, 1610–1616. [Google Scholar]
- Shockley, J.M.; Horton, D.J.; Wahl, K.J. Effect of aging of 2507 super duplex stainless steel on sliding tribocorrosion in chloride solution. Wear 2017, 380, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruman, E.; Sun, Y.; Adenan, M. A comparative study of the tribocorrosion behaviour of low temperature nitrided austenitic and duplex stainless steels in NaCl solution. Tribol. Int. 2020, 151, 106412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-C.; Huang, S.-Y.; Chu, Y.-R.; Yang, T.-H.; Yen, H.-W.; Cheng, I.-C.; Chu, P.-W.; Lee, Y.-L. Tribocorrosion Behavior of Medium-Entropy Super Austenitic Stainless Steel in Acidic Environments. Lubricants 2025, 13, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-E.; Huang, S.-Y.; Chu, Y.-R.; Chen, S.-C.; Tseng, M.-Y.; Yen, H.-W.; Lee, Y.-L. Investigating the effects of aging time on corrosion resistance and antibacterial property of newly designed medium-entropy super austenitic stainless steels. Materialia 2023, 27, 101687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G119-09; Standard Guide for Determining Amount of Synergism Between Wear and Corrosion. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009.
- Zhu, L.; Yang, P.; Lyu, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, K. Electrochemical corrosion characteristics of 316L stainless steel in simulated coastal gold mine wastewater under different pH. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2022, 17, 22099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R. Tribocorrosion response of surface-modified Ti in a 0.9% NaCl solution. Lubricants 2018, 6, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Hu, L.; Chen, M.; Sun, J.; Song, Q.; Xiao, J. Tribocorrosion behavior of aluminum alloys in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 36, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbati-Sarraf, H.; Shabani, M.; Jablonski, P.D.; Pataky, G.J.; Poursaee, A. The influence of incorporation of Mn on the pitting corrosion performance of CrFeCoNi High Entropy Alloy at different temperatures. Mater. Des. 2019, 184, 108170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Swanson, O.J.; Frankel, G.S.; Gerard, A.Y.; Lu, P.; Saal, J.E.; Scully, J. Localized corrosion behavior of a single-phase non-equimolar high entropy alloy. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 306, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Fe | Cr | Ni | Mo | Cu | Mn | N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304SS | Bal | 18 | 8 | 0.02 | 0.08 | - | - |
| S31254 | Bal | 20 | 18.31 | 6.1 | 0.73 | 0.95 | 0.21 |
| MEASS | Bal | 24.9 | 21.5 | 5.5 | 4.1 | 0.6 | 0.3 |
| Ecorr (mVSCE) | icorr (μA/cm2) | |
|---|---|---|
| 304SS_Corrosion | −233.6 ± 2.5 | 0.25 ± 0.11 |
| 304SS_Tribocorrosion | −353.3 ± 11.5 | 8.41 ± 2.59 |
| S31254_Corrosion | −223.3 ± 17.2 | 0.23 ± 0.05 |
| S31254_Tribocorrosion | −340.9 ± 6.7 | 4.92± 1.54 |
| MEASS_Corrosion | −205.6 ± 39.3 | 0.16 ± 0.04 |
| MEASS_Tribocorrosion | −314.2 ± 9.5 | 1.46 ± 0.63 |
| Specimen | Width (μm) | Maximum Depth (μm) |
|---|---|---|
| 304SS | 1702.1 ± 38.8 | 72.8 ± 2.8 |
| S31254 | 1471.8 ± 32.3 | 54.3 ± 1.7 |
| MEASS | 1206.6 ± 20.6 | 27.1 ± 0.7 |
| 304SS | Values (mg) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| T | 5.6 | 100.00 |
| C0 | 0.005 | 0.09 |
| C | 0.039 | 0.70 |
| W0 | 1.0 | 17.85 |
| W | 5.56 | 99.30 |
| S | 4.595 | 82.05 |
| ΔCW | 0.034 | 0.61 |
| ΔWC | 4.561 | 81.45 |
| S31254 | Values (mg) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| T | 4.0 | 100.00 |
| C0 | 0.0045 | 0.11 |
| C | 0.022 | 0.55 |
| W0 | 0.40 | 10.00 |
| W | 3.98 | 99.25 |
| S | 3.595 | 89.89 |
| ΔCW | 0.017 | 0.43 |
| ΔWC | 3.57 | 89.25 |
| MEASS | Values (mg) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| T | 1.8 | 100.00 |
| C0 | 0.003 | 0.17 |
| C | 0.007 | 0.39 |
| W0 | 0.30 | 16.67 |
| W | 1.79 | 99.44 |
| S | 1.50 | 83.33 |
| ΔCW | 0.004 | 0.22 |
| ΔWC | 1.49 | 82.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.-H.; Huang, S.-Y.; Chu, Y.-R.; Hsu, P.-S.; Yen, H.-W.; Cheng, I.-C.; Chu, P.-W.; Lee, Y.-L. Tribocorrosion Behavior of a Medium-Entropy Austenitic Stainless Steel in 3.5 wt.% NaCl: A Comparative Study with 304 and S31254 Stainless Steels. Lubricants 2025, 13, 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13060260
Wang C-H, Huang S-Y, Chu Y-R, Hsu P-S, Yen H-W, Cheng I-C, Chu P-W, Lee Y-L. Tribocorrosion Behavior of a Medium-Entropy Austenitic Stainless Steel in 3.5 wt.% NaCl: A Comparative Study with 304 and S31254 Stainless Steels. Lubricants. 2025; 13(6):260. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13060260
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chun-Hao, Shih-Yen Huang, Yu-Ren Chu, Peng-Shu Hsu, Hung-Wei Yen, I-Chung Cheng, Peng-Wei Chu, and Yueh-Lien Lee. 2025. "Tribocorrosion Behavior of a Medium-Entropy Austenitic Stainless Steel in 3.5 wt.% NaCl: A Comparative Study with 304 and S31254 Stainless Steels" Lubricants 13, no. 6: 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13060260
APA StyleWang, C.-H., Huang, S.-Y., Chu, Y.-R., Hsu, P.-S., Yen, H.-W., Cheng, I.-C., Chu, P.-W., & Lee, Y.-L. (2025). Tribocorrosion Behavior of a Medium-Entropy Austenitic Stainless Steel in 3.5 wt.% NaCl: A Comparative Study with 304 and S31254 Stainless Steels. Lubricants, 13(6), 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13060260






