Abstract
Ionic liquids (ILs) are molten organic salts consisting of organic cations and weakly coordinating organic/inorganic anions at room temperature. ILs have excellent physical and chemical properties such as high thermal stability, high combustible temperature, high miscibility with organic compounds and so on, making them good candidates for high performance lubricants and lubricant additives. The functional designability of ILs makes them novel lubrication materials that can break through the bottleneck of the active control of friction and lubrication. This paper firstly briefly introduces how to design the physical and chemical properties of the ILs required for different friction conditions by bonding specific cations with anions. Then, the lubrication mechanisms of ILs as base lubricants and additives for oils and water are focused on. The correlation between the structure of ILs and the lubrication results are established, which can guide the structural design of ILs in different applications. The response behaviors of friction characteristics under external electric fields are analyzed, which can provide a theoretical basis for the intelligent control of friction based on ILs.
1. Introduction
Lubricants can significantly reduce the friction resistance and wear of friction pairs in mechanical equipment. In addition, they can also play the role in cooling, cleaning, and preventing the contamination of friction pairs. A good lubrication system can improve the stability and service life of the equipment, save energy, reduce energy loss, and save raw materials [1,2,3,4]. Meanwhile, additives are the essence of modern advanced lubricants, which can improve the physical and chemical properties of basic lubricants, give new special properties to lubricants, or strengthen their original performances to meet higher requirements.
Ionic liquids (ILs) are organic substances in the form of liquid salts. There are more than one million combinations for different types and structures of cations and anions. Some combinations can obtain important characteristics of low melting temperature, high combustible temperature, low vapor pressure, superior thermal stability, low volatility, and easy miscibility with organic substances [5,6]. Therefore, ILs have great potential to become future lubricants and lubricant additives. One of the most important advantages of ILs: they are green sustainable substances. Ye et al. reported the study of ILs as a lubricant for the first time in 2001. It was found that 1-methyl-3-hexylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate and 1-ethyl-3-hexylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate have lower friction coefficients, lower wears, and higher load carrying capacities than aviation lubricants (X-1P and PFPE) [7]. Since then, the application of ILs as lubricants and lubricant additives has aroused extensive research interests. Based on the structural designability of ILs, the concepts of proton-ILs [8,9] and polymer-ILs [10,11] have been proposed in subsequent studies. The main advantage of proton-ILs is that they have good tribological properties, and their synthesis routes are simple, which can greatly reduce the cost [9]. For polymer-ILs, some properties of IL monomers are integrated into polymers, and the polymer chains can in turn give ILs unique aggregation structures and morphologies, which are not possessed by IL monomers [10]. Compared to traditional lubricants, polymer-ILs can offer lower friction and better surface protection, enabling superlubricity [11].
Until now, more than four hundred ILs have been studied as lubricants or lubricant additives in various friction systems. In addition, ILs are also smart materials developed in recent years. The application of applied electric fields in ILs’ lubrication has been paid more and more attention [12,13,14]. In this paper, the relationship between the physical and chemical properties of ILs and their molecular structure is first briefly introduced. Then, the contributions of ILs as base lubricants and additives of lubricating oils and water to the reduction in friction are summarized from lubrication mechanisms. The frictional response behaviors of ILs induced by external electric fields are analyzed. This review establishes the correlation law between IL structures and lubrication results in different applications, which can provide theoretical guidance for the application design of ILs.
2. The Relationship between the Physical and Chemical Properties of ILs and Their Molecular Structures
The physical and chemical properties of ILs can be regulated by the ion type and ion modification. The lubrication effect of ILs as lubricants can be enhanced by the improvement of their physical and chemical properties. The flexible molecular structure of ILs is an important reason why they are candidates for future lubricants and lubricant additives. The ion type can determine certain properties of ILs. All ILs of the same type have these properties. For example, imidazolium-based ILs have low melting points and excellent chemical and electrochemical stabilities [15], fatty acid anion-based ILs have the property of being sustainable [16,17], and so on. Ion modification can improve the physical and chemical properties of ILs by changing the intermolecular forces. Typical ion modifications include the length of the regulatory chain, substituent number, C2 methylation, and functionalization. The composition of cations and anions of some typical and basic ILs are recorded in Figure 1, where Rn (n = 1, 2, 3, 4) is the modifiable part. This section mainly analyzes the correlation between four physicochemical properties (viscosity, corrosion properties, thermal stability, and conductivity) of ILs, which are closely related to lubrication results, and the types of ions and modified structures in ILs, as well as how different ion types and modifications specifically influence the physical and chemical properties of ILs.
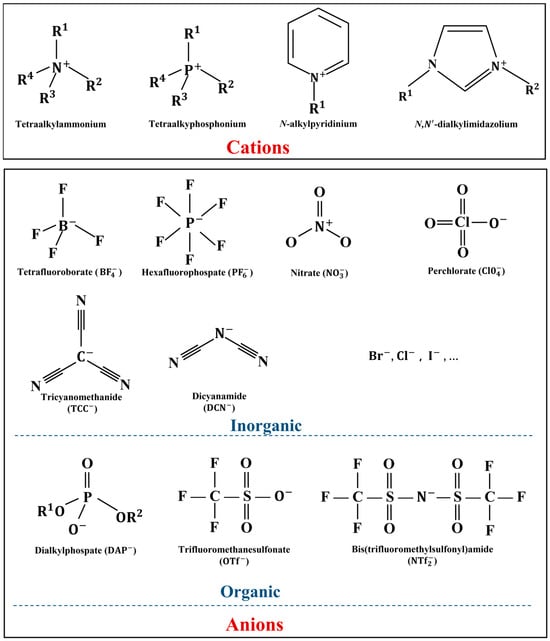
Figure 1.
Typical cations and anions of ILs.
2.1. Viscosity
Viscosity is one of the most important physical properties of a lubricant. Under certain working conditions, the viscosity of the lubricant is the main reason for determining the thickness of the lubricating film. In addition, high-viscosity lubricants will cause a lot of friction loss and heat. The difficulty of convection heat dissipation will cause the rupture of the lubrication film and surface wear, which will affect the friction force.
It is well known that the viscosity of ILs can be determined by the interaction of a cation–anion pair [18]. While the interaction between cations and anions is closely related to their structures, the difference in the number of branch chains, saturation degree, and chain length of alkyl chains all can lead to a change in an IL’s viscosity [17,19,20,21]. Among them, the influence of the number of branched chains on the viscosity of ILs is closely related to the distribution structure of branched chains. Amzad Khan et al. synthesized the bis(2-ethylhexyl)phosphate (BEHP) anion-based ammonium and phosphonium ionic liquids, as shown in Figure 2a, exhibiting significantly low viscosity. It was believed that the quaternary structure of ammonium and phosphonium cations decorated with four alkyl chains and the iso-structure of 2-ethylhexyl led to a steric hindrance and diminished the van der Waals interactions, resulting in the viscosity of these ILs being significantly lower than conventional ILs [19]. For branch chains with non-quaternary structural distributions, as shown in Figure 2b, Han et al. found that the greater the number of branch chains, the greater the viscosity of ILs. The quantitative relationship between the number of branch chains and the viscosity of ILs was almost unaffected by the temperature [20]. When studying the effect of alkyl chain length on the viscosity of ILs, taking the fatty acid anions shown in Figure 2c as an example, it was found that the viscosity of ILs increased with the increasing chain length of fatty acid anions. This was attributed to the increasing van der Waals interaction between the associated methylene units. For fatty acid anions with different unsaturation degrees, as shown in Figure 2d, it was found that the higher the unsaturation degree of the anion, the lower the viscosity of the IL. The introduction of unsaturation sites in fatty acid anions significantly diminished the van der Waals interaction, owing to the steric constraint, reducing the viscosity [17,21]. Additionally, the lighter, smaller, and highly symmetrical structures of the anion molecules contribute extra viscosity in IL systems [22].
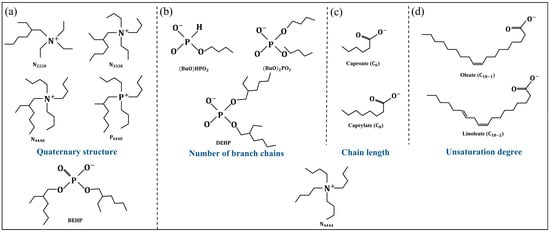
Figure 2.
Regulation of viscosity by changing the molecular structure of ILs: (a) the quaternary structure of ammonium and phosphonium cations, (b) the structure of anions containing different numbers of branched chains, (c) the structure of anions with different chain lengths, (d) the structure of anions with different unsaturation degrees. Redrawn from [19,20] with permissions (Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands).
2.2. Corrosion Property
When using ILs as lubricants, the wear volume of the surface is closely related to the corrosion property of the ILs. Most ILs used as lubricants contain halogens as a whole or as part of anions, such as X− (F−, Cl−, Br− or I−), , , , , and so on [23]. The water-sensitive halogenated ILs (X−, , , ) will release toxic corrosive gases (HF, HCl, etc.) during the hydrolysis process, and cause serious corrosion events. The copper strip test results revealed that a halogen-constituted IL () developed several corrosions, and the hydrolysis and decomposed products of halogen-constituted ILs were found to facilitate the corrosion events [24]. The corrosion effect of halogenated ILs on the surface caused by impurities such as water limits their application in the field of lubricants. Some ways to minimize impurities such as water include selecting high-quality ILs, regularly changing lubricants, cleaning lubrication systems, using filtration equipment, strengthening equipment maintenance, and controlling the use of the environment, etc. For the selection of high-quality ILs, halogen-free ILs are gaining increasing attention [24,25,26,27]. Among them, phosphonium cation and phosphonium anion ILs have been proved to be excellent lubricant additives [28,29]. In addition to halide elements, functional groups tethered to the cations or anions can change the corrosion properties of ILs as well. Han et al. synthesized four different functional alkylimidazolium dibutyl phosphate ILs to use as lubricants for a steel/Al alloy, and the structures can be seen in Figure 3. The corrosion performances of the functionalized ILs were aggravated when the carboxylic and cyano groups were tethered to cations, while the tethering of a hydroxyl or benzene ring on cations has no significant effect on the corrosion property of ILs [30].
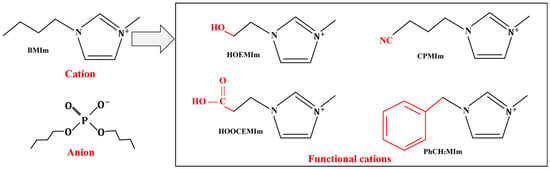
Figure 3.
Regulation of corrosion property of ILs by tethering different functional groups to cations. Redrawn from [30] with permission (Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands).
2.3. Thermal Stability
High temperature is one of the extreme conditions that ILs cannot avoid when they are used as lubricants. The decomposition temperature of ILs as lubricants can be effectively increased by changing the type and structure of the cation or anion in the ILs. The effect of the structural factors on the thermal stability of ILs can be described as follows:
- (1)
- The anion type has the greatest influence on the thermal stability of ILs, and then the cation type, while cation modification has the least effect [31,32]. Among them, the difference of nucleophilic properties caused by the anion type is an important reason for affecting the thermal stability of ILs. A nucleophilic substitution reaction is an important way of ILs’ decomposition. The stronger the nucleophilic properties of anions, the more likely a nucleophilic substitution reaction is to occur, leading to the decomposition of the IL; thus, the worse the thermal stability of the IL. The thermal stability order of common anions is as follows: [31]. Additionally, the anion type can affect the location of the nucleophilic reaction and then affect the decomposition path of the ILs, resulting in differences in the thermal stability of the ILs. Zhang et al. analyzed the short-term thermal stability and decomposition mechanism of 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazole bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imine ([BMIM][Tf2N]), 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazole acetate ([BMIM][Ac]) and 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazole tetrafluoroborate ([BMIM][BF4]. There were one and two locations for and , respectively, where nucleophilic reactions could occur, corresponding to one and two decomposition pathways. The decomposition pathway of was the most complicated. The short-term thermal stability of the three ILs followed the following order: [BMIM] [Ac] < [BMIM][BF4] < [BMIM][Tf2N]. It was proposed that the more complex the decomposition mechanism of the ILs, the better the thermal stability [33].
- (2)
- Imidazolium-based ILs exhibit higher thermal stability than tetraalkyl ammonium-, piperidinium-, and pyridinium-based ILs, owing to compact structure provided by the imidazolium ring, higher intermolecular interactions, a smaller free volume, and low steric hindrance [23,34].
- (3)
- The thermal stability of ILs can be increased by shortening the chain length, increasing the number of substituents, and replacing C2−H with a methyl group [35,36].
- (4)
- The influence of different group-functionalized cations or anions on the thermal stability of ILs is also significantly different. For example, allyl-functionalization would decrease the thermal stability of ILs. Meanwhile, for hydroxyl functionalization, the thermal stability depends on the anion type [34].
2.4. Conductivity
Conductivity is one of the unique properties of ILs that distinguishes it from other lubricants, and is the main reason why external electric fields can regulate their tribological properties. Furthermore, conductivity is inversely proportional to viscosity [37]. Therefore, it is meaningful to clarify the relationship between the conductivity and molecular structure of ILs.
Conductivity can be regulated by the number and mobility of charge carriers [38]. The number of charge carriers in ILs is closely related to the ionicity of ILs. The higher the ionicity of the IL, the higher the number of charge carriers, and the better the conductivity of the IL. The type of ions can determine their Lewis acidity and basicity, as shown in Figure 4a. ILs composed of weakly Lewis-acidic cations and weakly Lewis-basic anions have high ionicity [39]. In addition to the type of ions, functional modification can also change the Lewis basicity of ions. Guo et al. synthesized a series of three novel protic ionic liquids, 2-hydroxyethylammonium 2-ethylhexanoate (Eet), 2-hydroxymethylammonium 2-ethylhexanoate (Met), and 2-hydroxydimethylammonium 2-ethylhexanoate (Det), as shown in Figure 4b. It was found that the conductivity of Det was higher than that of Met and Eet, due to the strongest Lewis basicity of the corresponding alkanol amine [9]. The number of charge carriers per unit volume can be adjusted by changing the number of ions. Zhang et al. proposed that increasing the number of cations in ILs can reduce the electrostatic interaction and the number of ions per volume, thus reducing the intensity of the conductivity [40]. The mobility of charge carriers is related to the interaction between ions. The larger the mobility of charge carriers, the better the conductivity of the IL. Tao et al. proposed that length of alkyl chains can increase the van der Waals forces and reduce the mobility of charge carrier imidazolium nitrogen [41], and the conductivity decreased with increasing the alkyl chain length in ILs.
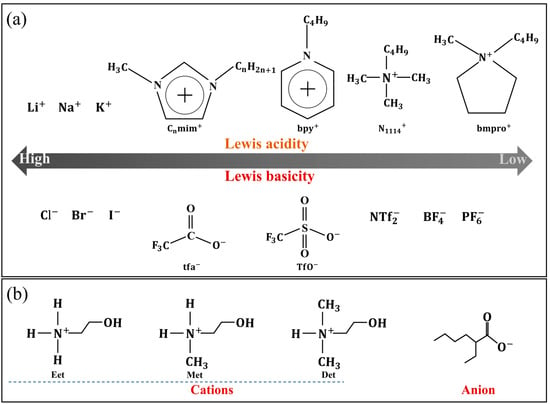
Figure 4.
(a) Schematic diagram of Lewis acidity and basicity of typical cations and anions, (b) ILs with different basicities caused by changing the functional groups. Redrawn from [9,40] with permissions (RSC, London, UK and MDPI, Basel, Switzerland).
The physical and chemical properties of ILs that meet the requirements of actual lubrication conditions can be obtained by designing the type and structure of cations and anions. This is an important reason for why ILs can be used as future lubricants and lubricant additives.
3. The Lubrication Mechanisms and Behaviors of ILs
Many studies on ILs as lubricants and lubricant additives have attempted to relate the lubrication results and wear resistance to the properties of the lubricant films formed by ILs on solid surfaces. They believed that the behaviors of ILs on solid surfaces could control the tribological properties [42,43]. This study reviews the lubrication mechanism of ILs used as a base lubricant, as oil-based lubricant additives and as water-based lubricant additives, based on the behaviors of ILs on solid surfaces. Combined with the need for intelligent friction control, the friction response behaviors of ILs induced by an external electric field are analyzed as well.
3.1. ILs Used as Base Lubricants
This section mainly analyzes the lubrication mechanism of ILs used as base lubricants from their molecular behaviors on solid surfaces.
ILs used as base lubricants can form two forms of lubrication films on the surface, which can play a role in protecting the surface and reducing friction during sliding. One is the physical adsorption film between the IL and the surface, as shown in Figure 5a. ILs could assemble near the convex points of the metal surfaces because of the attraction force from the positive charge. The polar head groups of cations adsorb on the anions while their nonpolar tail groups of an alkyl side chain stretch away from the substrate. Another group of anions are attracted by the attraction force between the different charges, and so on [44]. During this attraction and arrangement process, irregularity gradually increases, and finally the ions close to the substrate surface become more orderly arranged, and those far away from the substrate surface adopt a more irregular distribution. The length of the alkyl side chain is an important factor affecting the adsorption of ILs on the surface. Xiao et al. studied the relationship between the alkyl side chain length of three ILs (1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([OMIM][PF6]), 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([HMIM][PF6]), and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([BMIM][PF6])) and their film thicknesses. The alkyl side chain length of [OMIM]+, [HMIM]+ and [BMIM]+ were n = 8, 6, and 4, respectively. The film thickness followed the order: [OMIM][PF6] > [HMIM][PF6] > [BMIM][PF6] [45]. It is worth noting that the effect of the alkyl side chain length on adsorption appears to be limited by length. It cannot be considered that the longer the alkyl side chain length, the greater the thickness and density of the adsorption film. Tariq et al. studied the adsorption and friction of the 1-alkyl-3-methyl imidazolium family ([Cnmim][Cl] with n = 10, 12, and 14) on gold surfaces. The results showed that the longer the alkyl chain length, the smaller the adsorption mass and the higher the friction coefficient [46]. Through the analysis of the above studies, it can be speculated that for the short length of the alkyl side chain, the relationship between the length of the alkyl side chain and the quality of the film follows the rules that the longer the alkyl side chain, the thicker and denser the film. It can be believed that within a certain range, the longer the alkyl side chain, the stronger the van der Waals force between alkyl chains, the more ordered the arrangement of ions, and the better the density of the film. In the case that the side chain is perpendicular to the substrate surface, the longer chain will occupy a larger spatial distance, resulting in an increase in the thickness of the film. Smith proposed a method of controlling the thickness of ILs films in terms of the number of ion layers [47]. The functional group tethered to the cation influences the adsorption behavior of the ionic liquid on alloy surface as well, thus tailoring its lubrication performance [30]. A series of oxygen-containing ILs were synthesized by Han et al. for a magnesium alloy, and they found that the difference in the alkyl chain structure greatly influences the adsorption and lubrication performance of ILs, as shown in Figure 6. The IL with a longer linear alkyl chain and a less reactive polar group can adsorb orderly and densely on the surface to form a dense film. This dense film can reduce the oxidation of the magnesium alloy, and further prevent the hydration of the oxidation film. A thin but dense double-layer film can be formed to protect the surface effectively under friction tests. An IL with a more branched alkyl chain and a more reactive polar group can generate a sparse and active absorbed film, which accelerates the oxidation of the magnesium alloy. Thus, with friction tests being undergone, the oxidation film grew thicker, but it was hydrated easily to create porosity, which was easily destroyed under friction tests [48].
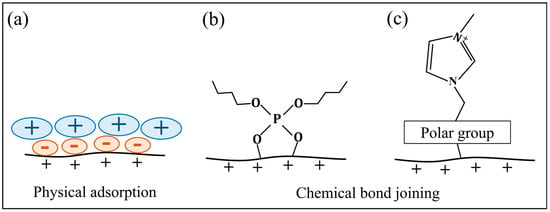
Figure 5.
The film formation modes of ILs on the surface: (a) physical adsorption, (b,c) chemical adsorption.
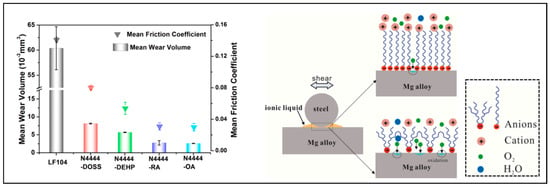
Figure 6.
Effect of alkyl chain structure on physical adsorption films. Redrawn from [48] with permission (Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands).
The lubrication film generated by the reaction between the active element in the ILs and the fresh surface is called the tribo-chemical reaction film [27,28,49]. The polar group in the molecular structure of ILs can strongly bind to the metal surface to form the chemical adsorption film [50]. Both friction heat and friction surface activation can promote the stable connection between the polar functional groups of ions in ILs and metal surfaces through chemical bonds.
The phosphate group is a typical polar group, and the binding mode of cations carrying the phosphate groups to the metal surfaces can be seen in Figure 5b [30,51,52]. The ILs, which contain fluorine and the phosphorus element in their molecular structures, exhibited anti-wear and corrosion-inhibition effects. The phosphorus elements formed the phosphate film on the sliding surface, due to the tribo-chemical reaction. The formation of the phosphate boundary layer prevented the formation of iron halide and enhanced the wear resistance. However, the friction-reduction effect was inferior to that of the phosphorus-free ILs [51]. When a polar group is introduced into the cation of ILs, the cation can also form a stable chemical bond with the positively charged surface through the polar group during friction. Taking N, N’-dialkylimidazolium as an example, the connection mode between the cation with a polar functional group and the surface is shown in Figure 5c [30].
The chemisorbed film produced by friction can more effectively protect the surface from severe wear. Han et al. found that the anti-wear performance and load-carrying capacity of ILs can be greatly improved by tethering polar groups (hydroxyl, carboxylic acid, and cyano) to the cation. However, the ILs with a benzyl group in the cation showed very poor tribological performance, which was ascribed to the steric hindrance of the benzyl group in the imidazolium cation, weakening the adsorption effect of the ILs [30]. The inherent polar nature of fatty acid anions facilitates their interaction promptly with steel surfaces under the boundary lubrication, and forms the stable tribo-chemical film of ILs. Compared with polyol ester lubricant-based oil, the fatty acid ionic liquids acting as lubricants provide 18–50% reduction in the coefficient of friction. The deposition of the tribo-chemical thin film of fatty acid ionic liquids can reduce both the friction and the wear. Gusain et al. proposed that the degree of friction reduction is largely affected by the chain length and the degree of unsaturated fatty acid anion molecules. The larger the molecular chain length and the smaller the degree of unsaturation, the better the lubrication characteristics of ILs [21]. The tribo-chemical reaction film can exist alone in the friction process or simultaneously with the physical adsorption film [52,53]. Zhang et al. evaluated the tribological properties of three novel phosphate-based ILs as lubricants for the steel–steel sliding pair by using Optimol-SRV oscillating. It was suggested that the phosphate part of the IL would decompose and react with the substrate to generate new species of FePO4. Meanwhile, an adsorbing film of alkyl imidazole formed on the surface of the FePO4, and accounted for the reduction in friction and wear [52].
ILs exhibit characteristic behavior at solid−liquid interfaces, which can influence their lubrication properties as well. To minimize the complex chemical reactions, Watanabe et al. measured the interface between a self-assembled monolayer (SAM) formed on a Au substrate and ILs by sum frequency generation (SFG) spectroscopy. Combining the calculation result of the orientation angle of the imidazolium ring with the friction test, it was found that the larger the tilt angle, the lower the friction coefficient [54], as shown in Figure 7. It is important to note that the interfacial molecular measurements and friction tests in the above study were independent. The molecular behaviors of ILs at the interface and their contribution to the frictional properties under lubrication conditions are still unclear.
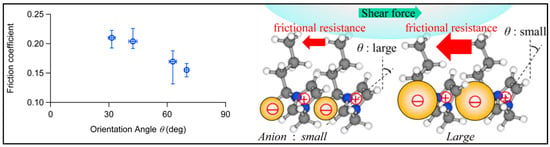
Figure 7.
Influence of ILs’ characteristic behavior on friction. Redrawn from [54] with permission (ACS, Washington, DC, USA).
To sum up, both the interface behaviors of ILs (physical adsorption, chemical reaction and the contact angle between the ions and the surface) and the materials of frictional pairs will affect the lubrication effect of ILs.
3.2. ILs Used as Oil-Based Additives
In addition to potential corrosive properties, most ILs are much more expensive to manufacture than common lubricants. The current production technology mainly reduces the reaction steps of IL synthesis by establishing effective synthesis schemes, and even realizes one-step synthesis to make ILs more economically viable [55]. Using ILs as additives is another effective strategy to make ILs more economically viable, which has received wide attention and achieved satisfactory results [56,57]. Compared with glycerol, a concentration of 2.5 wt% IL in glycerol was found to have a similar behavior in friction and wear to the corresponding neat IL, which confirmed the strong surface affinity of the IL in a mixed lubricant to the substance. A further advantage of ILs used as additives was proposed: that the surface corrosion processes, mainly by etching, disappeared when the neat IL was diluted in a base fluid [58]. Relevant research showed that although fully formulated engine oil exhibited all the required additives for its optimized performance, the 1.5% dose of ILs (bis(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate (BEHP)) could still offer significantly improved lubrication properties [19]. Researchers attributed the improvement of the lubrication properties of the mixed oils with ILs as additives to the improvement of their physicochemical properties [26,59] and the change in lubrication interface characteristics. The structure design of ILs to optimize their physical and chemical properties has been briefly introduced in the second section. This section focuses on the influence of changes in interface characteristics caused by ILs as additives to oil-based lubricants on lubrication results.
The friction properties of ILs used as additives of oil-based lubricants can be mainly attributed to the interaction between the IL and the material surface, the interaction between the IL and the base oil, and the interaction between the IL and other oil-based additives. In the mixed lubricant oil using an IL as an additive, the interaction between the IL and the material surface can be divided into the physical adsorption, the tribo-chemical reaction, and their synergistic effect [60,61,62,63,64,65,66], which is similar to ILs used as base lubricants. Some ILs exhibit poor friction and wear behaviors due to a frictional corrosion reaction when they are used as base lubricants, but they have better frictional properties when they are used as lubricant additives. Guo et al. believed that small additions of some ILs in the biodegradable oil were enough to form a protective layer that avoids detrimental tribo-corrosion reactions with the steel surface [9]. It is worth noting that some researchers only attributed the anti-friction effect of ILs as lubricant additives to the interaction between ILs and material surfaces, while ignoring the exploration of the role of other components in the mixed lubricants [17,23,24,67,68,69].
The function of ILs and base lubricants in the mixed lubricant can be divided into two kinds: synergistic and competitive. Lv et al. studied the friction-reducing properties of 23 N-containing hetero cyclic IL additives in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and proposed the mechanism of synergistic friction reduction between ILs and DMSO, as shown in Figure 8a. Intermolecular hydrogen bonds form between the ILs and the DMSO, and intramolecular hydrogen bonds exist within the anion and the cation. In this system, the alkyl chain in the cation of the IL can also interact with the methyl group in the DMSO by intermolecular van der Waals forces. Because the friction system was combined with an orderly arrangement of molecules, it had an orderly liquidity ability. The ordered small molecule system can promote a good friction-reducing performance [70]. Han et al. proposed the mechanism of competitive adsorption between IL additives and base lubricants on the surface, as shown in Figure 8b, and analyzed the effect of competitive adsorption on lubrication performance. At the beginning of the friction test, the steel surface was almost completely covered by the polar functional groups of the base oil molecules. As the friction test continued, electrons were released from the steel surface [71]. Therefore, the metal surface had more positive charges, IL could be adsorbed to the surface, and could then react with the steel surface to form a chemical reaction film. Importantly, when the addition amount was as low as 1 wt%, the IL with a high interaction with the steel surface could be adsorbed on the steel surface more quickly and effectively; the run-in period was short, and the friction coefficient was more stable [72].
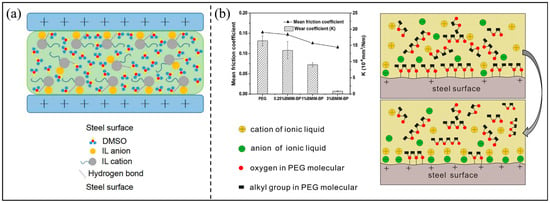
Figure 8.
(a) Synergy between ILs and base lubricant and (b) competitive adsorption of ILs and base lubricant. Redrawn from [70,71] with permissions (Taylor and Francis, Oxford, UK and Springer, Berlin, Germany).
When ILs are used as additives, the interactions between the ILs and the material surfaces, especially the formation process of the lubricating film, are influenced by the base lubricant molecules. The ILs and the base oil molecules have synergistic or competitive adsorption on the surface during the formation of the lubrication film, such that even if the content of the IL as an additive is very small, it can achieve the same anti-friction results as that of the pure IL.
If there is more than one additive in an oil-based lubricant, the effect of the interaction between additives on the lubrication result cannot be ignored [73]. Wei et al. found that the graphene could still be stably dispersed in the base oil even after 30 days by adding ILs to graphene an oil-based lubricant. A molecular simulation study showed that ILs tended to insert into graphene layers, and promoted the affinity of graphene and the base oil. At the same time, the addition of ILs improved the friction and wear properties of the mixed lubricant. The synergistic effect of ILs and graphene can broaden the application of graphene in the field of friction [74]. Zhang et al. used poly(isobutylene)-based IL (PIBIL) as an additive to some engine oils. A significant synergistic effect between the PIBIL and ZDDP was found to effectively enhance the anti-wear properties of oils, as shown in Figure 9. The tremendous decrease in WSD (Wear Scar Diameter) for the synergistic binary additive was attributed to the hybrid film formed by PIBIL and ZDDP [75].
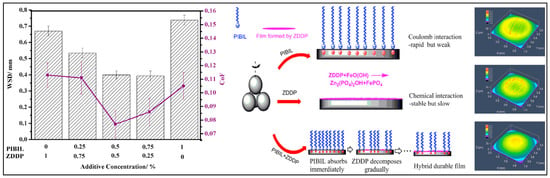
Figure 9.
Effect of interaction between ILs and other additives on friction. Redrawn from [75] with permission (Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands).
In addition to the interaction between ILs and the surface, the interaction between ILs and the base lubricant molecules and ILs and other additive molecules on the lubrication results all deserve attention when ILs are used as oil-based lubricant additives, which are of great significance for the preparation of multi-functional oil-based lubricants.
3.3. ILs Used as Water-Based Additives
In addition to oil, water is also a common lubricant. It has many advantages such as non-flammability, excellent cooling ability, good cleaning effects, good environmental compatibility, and low cost [76]. At present, low-cost water-based lubricants are more and more widely used in the metal-cutting fluids market [77]. However, compared with mineral or synthetic oils, water-based lubricants have disadvantages, such as poor perishability and poor film-forming ability [78]. These defects greatly limit the practical application of water-based lubricants in the industrial field [79]. This section mainly analyzes how ILs used as additives improve the corrosion resistance and film-forming ability of water-based lubricants.
The corrosion of water on metal surfaces is one of the main reasons limiting its application as a lubricant on metal surfaces. The film formed on the surface when an IL is used as an additive is the main reason for improving the corrosion resistance of water-based lubricants. Firstly, polar groups in the molecular structure of ILs can be preferentially adsorbed when competing with water molecules, thus forming a physical adsorption layer with high elastic modulus on the metal surface to prevent direct contact between the water and metal, thus enhancing the water corrosion resistance of the surface [80], as shown in Figure 10a. Specific types of ILs such as the seven kinds of amino acid ILs synthesized by Yang et al. [80], the five novel ILs synthesized by Xu et al. [81], the two new phosphate organic guanidine salt water-based additives (P4-G and P8-G) synthesized by Chen et al. [82], and the protone-type ILs synthesized by Dong et al. [83], as shown in Figure 10b, can preferentially form stable physical adsorption films on the surface under the condition of water-based lubrication. In addition to ILs forming physical adsorption films directly on the surface, Yu et al. proposed another method by synthesizing an IL from lignin, tetrabutylphosphorus hydroxide, and benzotriazole. Lignin can adsorb to the metal surface to form a “soft film”; the phenolic hydroxyl group present in lignin can effectively capture oxygen free radicals and form resonance-stable semi-quinone free radicals to interrupt chain reactions, leading to an excellent anticorrosion performance in cooperation with tetrabutylphosphorus hydroxide and benzotriazole [84], as shown in Figure 10c. Additionally, Aviles et al. found that there was no tribo-corrosion for a thin film obtained on the steel surface after the evaporation of water from a solution of ILs in water when using an ammonium succinate protic IL (PIL) as a water-based lubricant, as shown in Figure 10d. This means that such thin film lubricants have very good corrosion resistance [85].
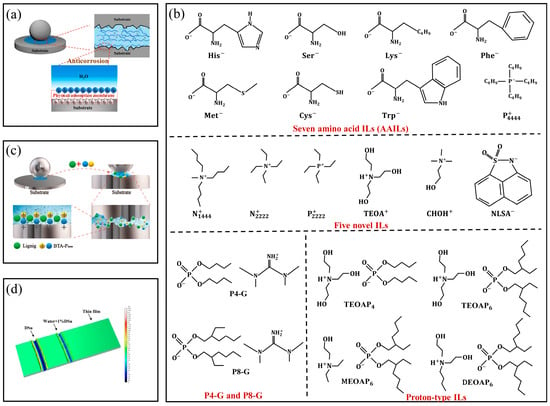
Figure 10.
(a) ILs’ physical adsorption film that prevented direct contact between water and metal. (b) Specific types of ILs, and (c) corrosion-resistant coatings based on ILs, (d) interrupt the chain reaction in which corrosion occurs. Redrawn from [80,81,82,83,84,85] with permissions (Elsevier, Amsterdam, Netherlands and ACS, Washington, USA and Springer, Berlin, Germany).
Most researchers attribute the enhancement of the film-forming ability of water-based lubricants to the physical adsorption film, the tribo-chemical reaction film, or their joint action formed by ILs on the metal surface [86,87,88,89,90]. Figure 11 shows some specific types of ILs capable of forming physical adsorption films or tribo-chemical reaction films on the surface in the water-lubricated environment. The ILs on the left of Figure 11 are more inclined to form physical adsorption films on the surface. Combined with Figure 10b, it can be inferred that fatty acid ILs (carboxylic acids, phosphoric acids, amino acids, etc.) used as additives for water-based lubricants are more conducive to the improvement of corrosion resistance and the film-forming ability of water-based lubricants. The ILs on the right of Figure 11 are more likely to form tribo-chemical reaction films during friction. When the ions contain active non-metallic elements such as fluorine and sulfur, the ILs have greater probabilities to react with the surface during the friction process, generating lubricating films.
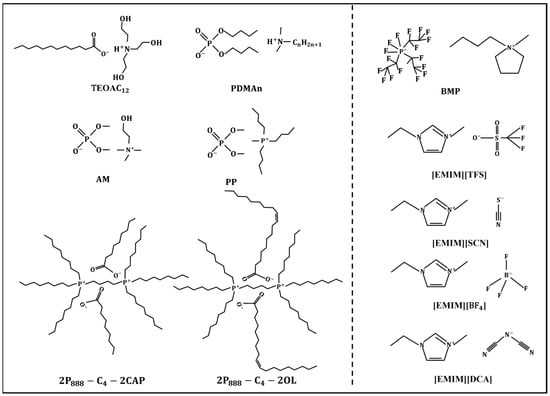
Figure 11.
Specific types of ILs capable of forming physical adsorption films or tribo-chemical reaction films on the surface in the water-lubricated environment. Redrawn from [86,87,89,90] with permissions (ACS, Washington, USA and Springer, Berlin, Germany).
It is worth noting that recent studies are more inclined to optimize the run-in process and improve the additive materials to form a more dense and stable boundary film and improve the tribological properties of the surface [91,92,93,94].
Most ILs that have been reported have complex structures that require high synthesis routes and conditions, reducing their potential for practical applications. Related research reports new routes for the in situ formation of IL additives in base lubricants without synthesis [95,96,97]. Wang et al. mixed lithium bis(trifluoromethane sulfonyl) imide (LI) and Tween-20 (TW) in a certain proportion, and the IL [LI(TW)] bis(trifluoromethane sulfonyl) imide (Li-TW) was formed in situ. A complex cation [Li(TW)]+ was obtained through the donation of lone pairs on an oxygen atom of a TW molecule to a Li+ cation. The large-size ions formed in situ had good boundary adsorption ability and could undergo physical adsorption and chemical reactions on the steel surface to form a relatively stable protective film, as shown in Figure 12a, thus showing excellent lubrication and anti-wear properties [98]. This method of the in situ formation of ILs is more convenient, environmentally protective, and cost saving, and improves the practical application potential of ILs. Preparing IL-based solid boundary films is another way to optimize the running-in process. Espinosa et al. lubricated the sapphire/AISI 316L contact with water with the protic ionic liquid (PIL) bis(2-hydroxyethylammonium) succinate (MSu), and with a 1 wt% solution of MSu in water. It was found that the use of water as a lubricant of stainless steel/sapphire gives rise to a transition to dry contact, with a sharp friction coefficient increase after the running-in period. The use of the IL eliminated the running-in period and shows an excellent lubricating performance, with low friction and mild wear. The addition to water of a single weight percentage proportion of the IL not only reduced the running-in period, but gave rise to a transition to ultralow friction due to the formation of a boundary film of the IL molecules on the wear track once the evaporation of water had taken place, as shown in Figure 12b [99].
Some ways to improve the film-forming capacity of water-based lubricants by improving additive materials include the synergistic use of multiple ILs and the interaction of ILs with other additives in water-based lubricants [85,100,101]. Zheng et al. applied two choline-based ILs as lubricants additives in glycerol solution and investigated the tribological properties of their different combinations. There was a significant synergistic lubrication effect between the two ILs, which was manifested as a dense and stable boundary film composed of a mixed adsorption layer and a complex friction film. The optimal ILs combination provided the best anti-wear and anti-friction performance [102], as shown in Figure 12c. Ammonium carboxylate IL in combination with graphene were used as additives for water-based lubricants. The thin film obtained on the steel surface after evaporation of water from a solution of the IL in water reduced wear rate and eliminated the high friction period during running-in. The dispersion of a low concentration of graphene nanoplatelets eliminated the initial high friction sliding distance, which prevented surface damage and the formation of wear debris. The combination of ILs with graphene sheets as additives enabled water-based lubricants to achieve both a low coefficient of friction and no wear [85]. Kreivaitis et al. made a hybrid water-based lubricant additive by combining silicon oxide nanoparticles with tert-octylamine oleate. The hybrid additive could form a composite tribo-film, which was composed of a tribo-chemical film, formed by ILs and nanoparticles embedded in the film on the metal surface. Compared with ILs alone, the synergistic properties of nanoparticles and the IL can further enhance the lubrication ability of the water-based lubricant [101].
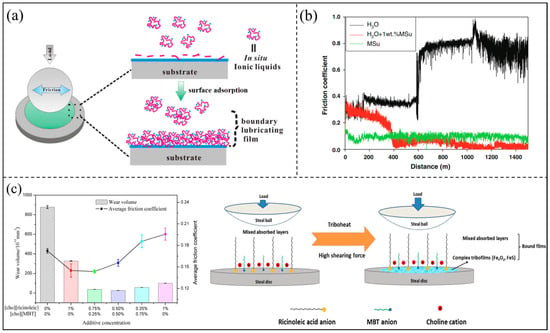
Figure 12.
(a) In situ preparation and boundary lubrication film formation of novel ILs, (b) effect of solid boundary film based on ionic liquid on friction coefficient, and (c) the synergistic action of ILs. Redrawn from [98,99,102] with permissions (Elsevier, Amsterdam, Netherlands and Springer, Berlin, Germany).
The addition of ILs to water-based lubricants can enhance the film-forming ability of water molecules as well. A superlubricity between steel surfaces lubricated by mixtures of [Choline][Proline] ([Cho][Pro]) IL and glycerol aqueous solution has been reached, which can be attributed to the formation of a stable water film. The stern layer formed by [Cho][Pro] and the hydrogen-bond network enabled a thin water layer at the interface. The addition of [Cho][Pro] can be helpful to maintain enough water in the steady period to retain a low viscosity [103]. The above researches show that choosing the appropriate IL as the additive of water-based lubricants can effectively avoid the defects of easy corrosion and film formation of water.
3.4. The Tribological Behaviors of ILs in Response to External Electric Fields
The external electric field can induce changes in the structure and properties of ILs at the lubrication interface, so as to effectively regulate the tribological properties [104,105]. The study on the external electric field regulating ILs’ lubrication is still in the preliminary stage. There are some differences in the phenomena and conclusions. In current studies, the regulation mechanisms of external electric fields on the lubrication characteristics of ILs at the lubrication interface are mainly developed from the surface arrangement of ILs, viscosity, film thickness, film breakdown characteristics, and the interaction between ILs and other materials.
When a small external voltage is applied to the IL-lubricated surface, an electric field will drive the oppositely charged ions in the IL to the solid/liquid interface, forming an ordered ion layer. The ordered arrangement of ILs at the interface may be the direct driving mechanism of friction reduction [106]. Dold et al. investigated the effect of applied voltage on the friction and anti-wear properties of steel–steel friction pairs lubricated by ILs. As the current increased, the number of cations and anions adsorbed on the friction surface increased significantly, enabling the formation of a more stable lubricating protective film [107]. The arrangement of the adsorbed ILs at the interface can be controlled by the electric field [108]. Li et al. suggested a voltage-induced interphase transition of trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium-bis(oxalato) borate ([P6,6,6,14][BOB]) from a self-assembled bilayer structure to the usual electric double-layer structure [109]. ILs at the interfaces have a higher probability of being aligned along the external electric field direction, due to dielectric polarization, which may lead to the increase in “structure” layers of ions near electrified solid surfaces, as shown in Figure 13a. The effect of external electric fields on the confined ionic liquid film with a shorter alkyl side chain is more noticeable [110]. The strength of the arrangement order of the ILs under current-carrying lubrication in many cases depends on the applied electrochemical potential [111].
The rearrangement of ILs at the interface induced by the external electric field can change the thickness of the lubrication film, which will also lead to changes in the lubrication result. According to the applied voltage, the [BMIM][PF6] IL can show a jump-like increase and decrease in the friction coefficient, as shown in the top of Figure 13b. Michalec et al. attributed such a phenomenon to changes in lubrication film thickness induced by the external electric field. It is worth noting that there was a difference between the initial and final values of the coefficient of friction. It was caused by layers of the residual alkyl chain ordered at contacting surfaces that remained even after the electric circuit was disconnected [112], as shown in the bottom of Figure 13b. When ILs were used as lubricant additives, the electric field could enhance the ionic strength of the interface and make the tribo-chemical film formed at the interface thicker, thus changing the tribological properties. The control of the external electric field on the tribological properties of ILs at the interface is also affected by the structure of the ILs. In current-carrying lubrication, the molecular structure of ions containing double bonds destroyed the symmetry of molecules and reduced the density of molecules, thus affecting the anti-wear characteristics of current-carrying lubrication [113].
The change in the viscosity of the ILs caused by the application of an external electric field is one of the important reasons for the change in interface friction. Ions could freely move originally in the area of the boundary lubrication, while, under the external electric field, the formation of the ordered boundary film adsorbed on the rubbing surfaces would lead to the entanglement of the alkyl side chains, which could increase the effective viscosity [114]. Thus, the friction coefficient increased. This ordered structure of ions will also affect the performance in the regime of the hydrodynamic lubrication. Relevant studies show that the viscosity of some ILs can be increased by several orders of magnitude under the external electric field. Combined with the relationship between viscosity and friction force, they believe that the application of an external electric field will produce a greater friction force [115,116], as shown in Figure 13c. Our previous study found that the viscosity of the IL-lubricant increased under the action of an electric current, which was mainly attributed to the aggregation of ions. An oil film resistance model was proposed to evaluate the degree of ion aggregation. The resistance of the lubricating oil film decreased with the increase in current intensity, indicating that the degree of ion aggregation increased. The viscosity and resistance of the oil film showed opposite trends [117].
Notably, the current has a tendency to break down the lubrication film, changing the lubrication mechanism of ILs [118]. Huang et al. found a step-like jump of the friction coefficient with the varied currents. It was believed that the adsorption layer of ions would first be driven away from the higher current areas with the current improved, which would increase the direct contact between tribopairs. When switching off the current, the boundary film of the ions absorbed between the tribopairs was reconstructed, and the friction coefficient returned to the initial value again [119], as shown in Figure 13d.
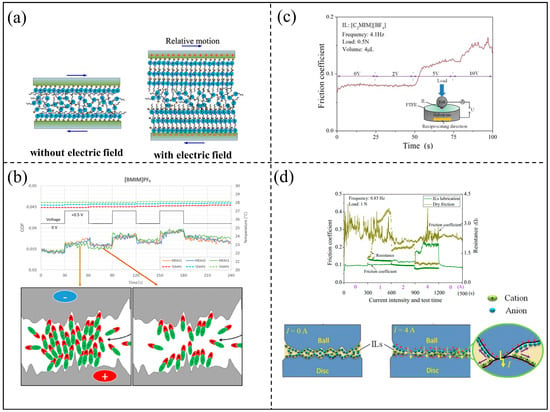
Figure 13.
(a) The arrangement of ILs confined in narrow gaps without and with external electric fields, (b) the effect of film thickness on friction performances, (c) the effect of viscosity change caused by electric field on friction performances, (d) the effect of film breakdown on friction performance. Redrawn from [111,112,116,119] with permissions (ACS, Washington, USA and Springer, Berlin, Germany and IOP, Bristol, UK).
In addition to the IL’s characteristics, the external electric field can induce ILs to have a synergistic effect with other materials, thus changing the friction. Wang et al. explored the effects of copper nanowires (Cu NWs) and an IL (1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium perchlorate ([BMIM][ClO4]) on the tribological properties of the IL under external voltages. It showed that Cu NWs would react with [BMIM][ClO4], and different products would be produced depending on the reaction days. [BMIM][ClO4] with 0.15 wt% Cu NWs after 60 days showed the best tribology property and conductivity [120]. When the substrate material has microstructures, it has a self-lubricating function, which can store the lubricant during the working process and release the lubricant under the action of external forces (friction, electricity, etc.), thereby improving its tribological properties. The frictional behaviors of porous copper matrix composites (PCMCs) with or without stored ILs under electric currents were studied. It was found that the wear rates of PCMCs with an IL lubricant is approximately one third of those without an IL lubricant, because IL stored in the composites could be released to the friction area under frictional and electrical stimulation, improving the tribological condition greatly [121].
The above studies show that the conductive properties of ILs make them a preferred candidate for electrically controlled friction, and the real-time control of friction coefficients has been successfully achieved in some studies, but there are still objections in the specific mechanism analysis.
4. Conclusions
ILs, which have controllable physical and chemical properties due to their designable structures, are important candidates for future lubricants and lubricant additives. The application advantages of ILs in lubrication have been proven by many research groups around the world. This paper reviews the friction reduction and control mechanism of ILs in four typical lubrication systems, as follows:
- (1)
- When ILs are used as base lubricants, lubrication films can form on the surface through physical adsorption and tribo-chemical reactions. Two forms of lubrication film can exist at the same time to reduce friction and wear and improve the load bearing. In addition, the material of friction pairs and the molecular inclination of the ILs on the surface cannot be ignored.
- (2)
- When ILs are used as oil-based lubricant additives, the interaction between the ILs and the material surface, the base lubricant, and the other additives can significantly improve the surface friction state. The interaction between ILs and the surface is mainly manifested as the formation of lubricating films. The interaction between ILs and the base lubricating oil or other lubricant additives is mainly in the form of coordination or competition.
- (3)
- Corrosion and poor film-forming ability are two major obstacles to the practical application of water-based lubricants. The addition of ILs can avoid the surface corrosion of water-based lubricants by forming a physical adsorption film on the surface that prevents direct contact between water molecules and the surface, forming a corrosion-resistant coating during friction and interrupting the chain reaction of corrosion. The preparation of ILs in situ and the combined use of various additives were put forward to improve the film-forming ability of water-based lubricants from the aspects of process and material.
- (4)
- The conductivity property of ILs makes them have the potential to become intelligent lubricating materials. The external electric field can change the viscosity, the arrangement order on the surface, and the film thickness of ILs, so as to realize the real-time adjustment of the friction coefficient.
ILs have been used in many different lubrication systems as lubricants and lubricant additives. It is worth noting that when ILs are used as base lubricants, there are the obvious defects of high price- and low price-performance. Halogen ILs have the risk of easy corrosion. When ILs are used as additives, the design and synthesis theories of ILs still need to be simplified. There is a lack of theoretical guidance systems for the design and synthesis of ILs according to the requirements of different working conditions. Researchers will conduct further studies on these defects in the future.
Additionally, the antifriction mechanisms of ILs have been described in detail. This situation is expected to continue in the future, especially in the study of electrically controlled friction based on ILs. More such models and formulas will be proposed to a provide theoretical basis for the accurate control of friction based on ILs. The use of ILs as smart lubrication materials is expected to expand significantly in the future.
Author Contributions
Investigation, R.W. and W.L.; resources, C.Z. and Z.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.L.; writing—review and editing, C.Z.; supervision, Q.C.; project administration, J.N.; funding acquisition, C.Z. and Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52175157), Beijing Institute of Precise Mechatronics and Controls (43001211202204), and the Tribology Science Fund of State Key Laboratory of Tribology (SKLTKF19B08).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Perez-Martinez, C.S.; Perkin, S. Interfacial Structure and Boundary Lubrication of a Dicationic Ionic Liquid. Langmuir 2019, 35, 15444–15450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghi, F.; Milani, P.; Podestà, A. Solid-Like Ordering of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids at Rough Nanostructured Oxidized Silicon Surfaces. Langmuir 2019, 35, 11881–11890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.R.; Wang, H.D.; Liu, Y.H. Adjustable superlubricity system using polyalkylene glycol with various acid aqueous solutions. Friction 2023, 11, 1138–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.J.; Song, J.; Shi, H.Y.; Wang, H.D.; Wen, S.Z.; Liu, Y.H. Hierarchical self-assembled structure and frictional response of phthalocyanine molecules. Friction 2023, 11, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Li, L. Uncovering the Underlying Mechanisms Governing the Solidlike Layering of Ionic Liquids (ILs) on Mica. Langmuir 2020, 36, 2743–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.K.; Chat, K.; Szklarz, G.; Laskowski, L.; Grzybowska, K.; Paluch, M.; Richert, R.; Adrjanowicz, K. Dynamics of Pyrroli-dinium-Based Ionic Liquids Under Confinement. II. The Effects of Pore Size, Inner Surface, and Cationic Alkyl Chain Length. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 124, 5395–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.F.; Liu, W.M.; Chen, Y.X.; Yu, L.G. Room-temperature ionic liquids: A novel versatile lubricant. Chem. Commun. 2001, 21, 2244–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, V.d.C.; Leonardo, M.d.S.; Leonardo, M.A.; Roberto, M.S.; Silvana, M.; Klester, S.S.; Marcelo, B.P.; Cleber, R.d.L.L.; Sandra, E.; Carlos, A.d.S.; et al. A Tribological and Electrochemical Study of Protic Ionic Liquid and Bentonite Particles Used as Lubricating Additives in Water-Based Lubricants. J. Bio-Tribo-Corros. 2023, 9, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Adukure, A.R.; Iglesias, P. Effect of Ionicity of Three Protic Ionic Liquids as Neat Lubricants and Lubricant Additives to a Biolubricant. Coatings 2019, 9, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedeva, O.; Kultin, D.; Kustov, L. Advanced research and prospects on polymer ionic liquids: Trends, potential and application. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 9001–9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Ripin, Z.M.; Jiang, C.; Pasang, T. Superlubricity of Materials: Progress, Potential, and Challenges. Materials 2023, 16, 5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.F.; Xia, Y.Q.; Liu, L.H.; Feng, X. Study on the conductive and tribological properties of copper sliding electrical contacts lubricated by ionic liquids. Tribol. Int. 2018, 130, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Meng, Y.G.; Tian, Y. Effect of Imidazolium Ionic Liquid Additives on Lubrication Performance of Propylene Carbonate under Different Electrical Potentials. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 56, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Wang, J.H.; Li, C.S.; Zhao, G.Q.; Wang, X.B. A study of 2,5-dimercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives as multifunc-tional additives in water-based hydraulic fluid. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2014, 66, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadanandhan, A.M.; Khatri, P.K.; Jain, S.L. A novel series of cyclophosphazene derivatives containing imidazolium ionic liquids with variable alkyl groups and their physicochemical properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 295, 111722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sernaglia, M.; Blanco, D.; Battez, A.H.; Viesca, J.L.; González, R.; Bartolomé, M. Two fatty acid anion-based ionic liquids—Part I: Physicochemical properties and tribological behavior as neat lubricants. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 305, 112827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusain, R.; Dhingra, S.; Khatri, O.P. Fatty-Acid-Constituted Halogen-Free Ionic Liquids as Renewable, Environmentally Friendly, and High-Performance Lubricant Additives. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C.; Huo, F.; Liu, X.M.; Dong, K.; He, H.Y.; Yao, X.Q.; Zhang, S.J. Influence of Microstructure and Interaction on Viscosity of Ionic Liquids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 3505–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Gusain, R.; Khatri, O.P. Organophosphate anion based low viscosity ionic liquids as oil-miscible additives for lubrication enhancement. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 272, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.Y.; Qiao, D.; Zhang, S.W.; Feng, D.P. Influence of phosphate and phosphonate ionic liquid structures on lubrication for different alloys (Mg, Al, Cu). Tribol. Int. 2017, 114, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusain, R.; Khatri, O.P. Fatty acid ionic liquids as environmentally friendly lubricants for low friction and wear. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 3462–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.K.; Dewangan, Y.; Singh, A.K.; Mishra, R.; Susan, M.A.; Salim, R.; Taleb, M.; El Hajjaji, F.; Berdimurodov, E. Ionic liquids as green and smart lubricant application: An overview. Ionics 2022, 28, 4923–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusain, R.; Gupta, P.; Saran, S.; Khatri, O.P. Halogen-Free Bis(imidazolium)/Bis(ammonium)-Di[bis(salicylato)borate] Ionic Liquids as Energy-Efficient and Environmentally Friendly Lubricant Additives. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2014, 6, 15318–15328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusain, R.; Khatri, O.P. Halogen-free ionic liquids: Effect of chelated orthoborate anion structure on their lubrication properties. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 25287–25294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Yasa, S.R.; Gusain, R.; Khatri, O.P. Oil-miscible, halogen-free, and surface-active lauryl sulphate-derived ionic liquids for enhancement of tribological properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 318, 114005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totolin, V.; Minami, I.; Gabler, C.; Döorr, N. Halogen-free borate ionic liquids as novel lubricants for tribological applications. Tribol. Int. 2013, 67, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, Y.; Koyama, T.; Tsuboi, R.; Nakano, M.; Miyake, K.; Sasaki, S. Tribological Performance of Halogen-Free Ionic Liquids as Lubricants of Hard Coatings and Ceramics. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 51, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Watanabe, N.; Inada, K.; Ishioka, A.; Hayase, S.; Kawatsura, M.; Minami, I.; Mori, S. Design of Alkyl Sulfate Ionic Liquids for Lubricants. Chem. Lett. 2009, 38, 64–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerholt, A.; Weschta, M.; Boesmann, A.; Tremmel, S.; Korth, Y.; Wolf, M.; Schluecker, E.; Wehrum, N.; Lennert, A.; Uerdingen, M.; et al. Halide-Free Synthesis and Tribological Performance of Oil-Miscible Ammonium and Phosphonium-Based Ionic Liquids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.Y.; Qiao, D.; Sun, L.M.; Feng, D.P. Functional alkylimidazolium ionic liquids as lubricants for steel/aluminum contact: Influence of the functional groups on tribological performance. Tribol. Int. 2018, 119, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maton, C.; De Vos, N.; Stevens, C.V. Ionic liquid thermal stabilities: Decomposition mechanisms and analysis tools. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5963–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siedlecka, E.M.; Czerwicka, M.; Stolte, S.; Stepnowski, P. Stability of Ionic Liquids in Application Conditions. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 15, 1974–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Liu, S.H.; Wang, Y. Exploring the influence of the type of anion in imidazolium ionic liquids on its thermal stability. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2023, 148, 4985–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.Y.; Mu, T.C. Comprehensive Investigation on the Thermal Stability of 66 Ionic Liquids by Thermogravimetric Analysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 8651–8664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.H.; Liang, Y.M.; Xia, Y.Q.; Zhou, F.; Liu, X.Q. High-Temperature Tribological Properties of 2-Substituted Imidazolium Ionic Liquids for Si3N4-Steel Contacts. Tribol. Lett. 2008, 32, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, F.; Gabler, C.; Zare, P.; Mahrova, M.; Dörr, N.; Bayon, R.; Fernandez, X.; Binder, W.H.; Hernaiz, M.; Tojo, E.; et al. Dicationic ionic liquids as lubricants. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapiot, P.; Lagrost, C. Electrochemical Reactivity in Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2238–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, S.; Masci, G.; Casciotta, F.; Caminiti, R.; Scarpellini, E.; Campetella, M.; Gontrani, L. Cholinium-amino acid based ionic liquids: A new method of synthesis and physico-chemical characterization. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 20687–20698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, K.; Tokuda, H.; Watanabe, M. Ionicity in ionic liquids: Correlation with ionic structure and physicochemical properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.G.; Shi, R.; Ma, X.Y.; Lu, L.J.; He, Y.D.; Zhang, X.H.; Wang, Y.T.; Deng, Y.Q. Intrinsic Electric Fields in Ionic Liquids Determined by Vibrational Stark Effect Spectroscopy and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Chem-Eur. J. 2012, 18, 11904–11908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, D.J.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, F.F.; Li, Z.M.; Hu, N.; Chen, X.S. Synthesis and Thermophysical Properties of Biocompatible Cho-linium-Based Amino Acid Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2013, 58, 1542–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbourne, A.; Vo Tchovsky, K.; Warr, G.G.; Atkin, R. Ion structure controls ionic liquid near-surface and interfacial nanostructure. Chem. Sci. 2014, 6, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Leonard, D.N.; Guo, W.; Qu, J. Understanding Tribofilm Formation Mechanisms in Ionic Liquid Lubrication. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, M.H.; Fan, M.J.; Liang, Y.M.; Zhou, F.; Xia, Y.Q. Imidazolium hexafluorophosphate ionic liquids as high temperature lubricants for steel–steel contacts. Wear 2010, 268, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.P.; Guo, D.; Liu, S.H.; Pan, G.S.; Lu, X.C. Film Thickness of Ionic Liquids Under High Contact Pressures as a Function of Alkyl Chain Length. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 41, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, M.; Serro, A.P.; Colaço, R.; Saramago, B.; Lopes, J.N.C.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Effect of alkyl chain length on the adsorption and frictional behaviour of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ionic liquid surfactants on gold surfaces. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 377, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.; Lovelock, K.R.J.; Gosvami, N.N.; Welton, T.; Perkin, S. Quantized friction across ionic liquid thin films. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 15317–15320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.Y.; Hao, D.; Gao, P.; Wen, P.; Fan, M.J. Tailoring an inorganic-organic double layer tribofilm for high-performance ionic liquid magnesium alloy lubricants. Tribol. Int. 2023, 179, 108197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, A.E.; Khemchandani, B.; Howlett, P.C.; Sun, J.; Macfarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. Ionic liquids as antiwear additives in base oils: Influence of structure on miscibility and antiwear performance for steel on aluminum. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 11544–11553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.Z.; Huang, P. Principles of Tribology, 2nd ed.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 305–306. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, Y.; Yagi, S.; Koyama, T.; Tsuboi, R.; Sasaki, S. Lubricity and corrosiveness of ionic liquids for steel-on-steel sliding con-tacts. P. I Mech. Eng. 2012, 226, 991–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Feng, D.P.; Xu, B. Tribological Characteristics of Alkylimidazolium Diethyl Phosphates Ionic Liquids as Lubricants for Steel–Steel Contact. Tribol. Lett. 2009, 34, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Hu, L.T.; Feng, D.P. Tribological behaviors of novel crown-type phosphate ionic liquids as lubricants for steel/aluminum contacts. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2013, 65, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Nakano, M.; Miyake, K.; Tsuboi, R.; Sasaki, S. Effect of Molecular Orientation Angle of Imidazolium Ring on Fric-tional Properties of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquid. Langmuir 2014, 30, 8078–8084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calandra, P.; Szerb, E.I.; Lombardo, D.; Algieri, V.; Maiuolo, L. A Presentation of Ionic Liquids as Lubricants: Some Critical Comments. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriuis, A. Tribological Properties of Protic Ionic Liquid as an Additive in Aqueous Glycerol Solution for Ruby-Bearing Steel Tribo-Contact. Lubricants 2023, 11, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, R.I.P. Influence of Hydrogen Bonding and Ionicity of Protic Ionic Liquids on Lubricating Steel-Steel and Steel-Aluminum Contacts: Potential Ecofriendly Lubricants and Additives. Tribol. Lett. 2020, 68, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronberger, M.; Pejaković, V.; Gabler, C.; Kalin, M. How anion and cation species influence the tribology of a green lubricant based on ionic liquids. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 933–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejaković, V.; Kronberger, M.; Mahrova, M.; Vilas, M.; Tojo, E.; Kalin, M. Pyrrolidinium sulfate and ammonium sulfate ionic liquids as lubricant additives for steel/steel contact lubrication. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, P.S.; Gusain, R.; Dhawaria, M.; Suman, S.K.; Khatri, O.P. Antimicrobial and lubrication properties of 1-acetyl-3-hexylbenzotriazolium benzoate/sorbate ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 46567–46572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejakovi, V.; Tomastik, C.; Drr, N.; Kalin, M. Influence of concentration and anion alkyl chain length on tribological properties of imidazolium sulfate ionic liquids as additives to glycerol in steel-steel contact lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2016, 97, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, S.; Sasaki, S.; Miyatake, M. In-situ observation of tribo-decomposition behavior of ionic liquids composed of phosphonium-cation and cyano-anion using quadrupole mass spectrometer. Tribol. Int. 2021, 153, 106547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Truhan, J.J.; Dai, S.; Luo, H.; Blau, P.J. Ionic liquids with ammonium cations as lubricants or additives. Tribol. Lett. 2006, 22, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viesca, J.L.; García, A.; Battez, A.H.; González, R.; Monge, R.; Fernández-González, A.; Hadfield, M. FAP- Anion Ionic Liquids Used in the Lubrication of a Steel-Steel Contact. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 52, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Battez, A.; González, R.; Viesca, J.L.; Fernández-González, A.; Hadfield, M. Lubrication of PVD coatings with ethyl-dimethyl-2-methoxyethylammonium tris(pentafluoroethyl)trifluorophosphate. Tribol. Int. 2013, 58, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejakovic, V.; Kalin, M. Frictional behaviour of imidazolium sulfate ionic liquid additives under mixed slide-to-roll conditions: Part 1 Variation of mixtures with identical weight ratio of ionic liquid additive. Lubr. Sci. 2015, 27, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, P.K.; Aathira, M.S.; Thakre, G.D.; Jain, S.L. Synthesis and tribological behavior of fatty acid constituted tetramethylguanidinium (TMG) ionic liquids for a steel/steel contact. Mat. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. 2018, 91, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.N.; Cai, T.; Zhang, Y.X.; Ye, M.T.; Shang, W.J.; Liu, D.; Tong, D.Y.; Liu, S.G. Synthesis, characterization and tribological evaluation of novel 1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane based dicationic ionic liquids as efficient antiwear lubricant additives. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2019, 62, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.L.; Wang, Y.R.; Huang, G.W.; Ma, Z.F.; Shi, Y.J.; Cai, M.R.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.M. Task-Specific Oil-Miscible Ionic Liquids Lubricate Steel/Light Metal Alloy: A Tribochemistry Study. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1800791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.C.; Chen, T.; Wang, T.T.; Li, Y.; Gao, X.L. Friction-reducing properties of N-containing ionic liquid additives by using quantitative structure tribo-ability relationship model. J. Disper Sci. Technol. 2020, 43, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Wang, H.Z.; Feng, D.P. Tribological Performance and Mechanism of Phosphate Ionic Liquids as Additives in Three Base Oils for Steel-on-aluminum Contact. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 55, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.Y.; Qiao, D.; Guo, Y.X.; Feng, D.P.; Shi, L. Influence of Competitive Adsorption on Lubricating Property of Phosphonate Ionic Liquid Additives in PEG. Tribol. Lett. 2016, 64, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheireddin, B.A.; Lu, W.; Chen, I.; Akbulut, M. Inorganic nanoparticle-based ionic liquid lubricants. Wear 2013, 303, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.X.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, L.Y.; Xi, D.Y. Effects of ionic liquid on the dispersion and tribological property of graphene lubricant. Lubr. Sci. 2020, 32, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Cai, T.; Shang, W.J.; Sun, L.W.; Liu, D.; Tong, D.Y.; Liu, S.G. Environmental friendly polyisobutylene-based ionic liquid containing chelated orthoborate as lubricant additive: Synthesis, tribological properties and synergistic interactions with ZDDP in hydrocarbon oils. Tribol. Int. 2017, 115, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.R.; Zhang, C.H.; Liu, S.H. Progress in experimental study of aqueous lubrication. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 2062–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Wang, J.H.; Li, C.S.; Zhao, G.Q.; Wang, X.B. Tribological performance of poly(sodium 4-styrenesulphonate) as additive in water-glycol hydraulic fluid. Lubr. Sci. 2012, 24, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Warneke, H.; Webbert, H.; Rodriguez, J.; Austin, E.; Tokunaga, K.; Rajak, D.K.; Menezes, P.L. Water-Based Lubricants: Development, Properties, and Performances. Lubricants 2021, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Zhang, S.M.; Yu, L.G.; Zhang, Z.J.; Wu, Z.S.; Zhang, P.Y. Preparation and tribological properties of water-soluble copper/silica nanocomposite as a water-based lubricant additive. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 259, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Q.; Sun, C.F.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhao, S.J.; Cai, M.R.; Liu, Z.L.; Yu, Q.L. Amino acid ionic liquids as anticorrosive and lubricating additives for water and their environmental impact. Tribol. Int. 2021, 153, 106663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Li, H.; Tian, B.; Cui, K.; Dong, R.; Fan, M.; Cai, M.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Achieving Greener, Super-Robust Performance Water-Based Lubrication: Obtained by a Multifunctional Ionic Liquid Aqueous System and Formation of Unique Interfacial Inter-actions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 8651–8666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Q.; Yu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Yan, X.; Wang, R.; Yu, B.; Cai, M. Novel Phosphate Organic Guan-idine Salt Water-Based Additive with Integrated Anti-Friction, Anti-Wear and Anti-Corrosion Properties. Tribol. Lett. 2022, 70, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Yu, Q.; Bai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cai, M. Towards superior lubricity and anticorrosion performances of proton-type ionic liquids additives for water-based lubricating fluids. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 383, 123201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.L.; Yang, Z.Q.; Huang, Q.; Lv, H.Y.; Zhou, K.; Yan, X.Y.; Wang, X.W.; Yang, W.F.; Zhou, C.Y.; Yu, B.; et al. Lignin composite ionic liquid lubricating material as a water-based lubricating fluid additive with excellent lubricating, anti-wear and anti-corrosion properties. Tribol. Int. 2022, 174, 107742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés, M.D.; Carrión-Vilches, F.J.; Sanes, J.; Bermúdez, M.D. Diprotic Ammonium Succinate Ionic Liquid in Thin Film Aqueous Lubrication and in Graphene Nanolubricant. Tribol. Lett. 2019, 67, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Bao, L.Y.; Yu, Q.L.; Wu, Y.; Ma, Z.F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Cai, M.R.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.M. Effect of Electric Potential and Chain Length on Tribological Performances of Ionic Liquids as Additives for Aqueous Systems and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2020, 12, 39910–39919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Liu, X.; Yu, H.; Chen, H.; Feng, D.; Qiao, D. Insight into macroscale superlubricity of polyol aqueous solution in-duced by protic ionic liquid. Friction 2022, 10, 2000–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Sharma, O.P.; Khatri, O.P. Ionic Liquids-Based Aqueous Lubricants: Emulsion Stability to Enhancement of Surface Wettability and Tribological Properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.Y.; Li, J.J.; Zhang, C.H.; Wang, Z.N.; Luo, J.B. Superlubricity of 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate Ionic Liquid Induced by Tribochemical Reactions. Langmuir 2018, 34, 5245–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanmohammadi, H.; Wijanarko, W.; Espallargas, N. Ionic Liquids as Additives in Water-Based Lubricants: From Surface Ad-sorption to Tribofilm Formation. Tribol. Lett. 2020, 68, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.M.; Ribeiro, T.; Branco, L.C.; Colaço, R.; da Silva, A.G.; Saramago, B. Hydrophobic ionic liquids at liquid and solid interfaces. Tribol. Int. 2019, 129, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreivaitis, R.; Gumbyte, M.; Kupcinskas, A.; Treinyte, J.; Sendzikiene, E. Synthesis and Tribological Properties of Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonium Erucate as a Potential Environmentally Friendly Lubricant and Lubricant Additive. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlmann, P.; Watanabe, S.; Shimpi, M.R.; Leckner, J.; Rutland, M.W.; Harper, J.B.; Glavatskih, S. Boundary lubricity of phos-phonium bisoxalatoborate ionic liquids. Tribol. Int. 2021, 161, 107075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Cai, M.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Halide-free PN ionic liquids surfactants as additives for enhancing tribological per-formance of water-based liquid. Tribol. Int. 2018, 128, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.H.; Cai, M.R.; Liang, Y.M.; Fan, M.J.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.M. In situ preparation of anti-corrosion ionic liquids as the lubricant additives in multiply-alkylated cyclopentanes. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 21715–21721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Nakamura, M.; Kazue, Y.; Tachikawa, N.; Tsuzuki, S.; Seki, S.; Dokko, K.; Watanabe, M. Oxidative-stability en-hancement and charge transport mechanism in glyme-lithium salt equimolar complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 13121–13129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.H.; Liang, Y.M.; Fan, M.J.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.M. Lithium-based ionic liquids functionalized by sym-triazine and cyclotriphosphazene as high temperature lubricants. Tribol. Int. 2014, 70, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.R.; Yu, Q.L.; Cai, M.R.; Shi, L.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.M. Synergy of lithium salt and non-ionic surfactant for significantly improved tribological properties of water-based fluids. Tribol. Int. 2017, 113, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, T.; Jiménez, M.; Sanes, J.; Jiménez, A.E.; Iglesias, M.; Bermúdez, M.D. Ultra-Low Friction with a Protic Ionic Liquid Boundary Film at the Water-Lubricated Sapphire–Stainless Steel Interface. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.D.; Zhao, Q.; Ju, C.; Wang, X.B. The interaction of two anticorrosive ionic liquid additives on the friction properties of water lubricants. Tribol. Int. 2020, 141, 105948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreivaitis, R.; Treinytė, J.; Kupčinskas, A.; Gumbytė, M.; Andriušis, A. Improving tribological properties of water/glycerol lubri-cating fluid by the synergy of nanoparticles and protic ionic liquid. Wear 2023, 534, 205133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.D.; Wang, X.B.; Zhang, M.; Ju, C. Synergistic Effects Between the Two Choline-Based Ionic Liquids as Lubricant Additives in Glycerol Aqueous Solution. Tribol. Lett. 2019, 67, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Bjrling, M.; Larsson, R.; Shi, Y.J. Controllable superlubricity achieved with mixtures of green ionic liquid and glycerol aqueous solution via humidity. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 345, 117860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.I.; Rutland, M.W.; Watanabe, M.; Atkin, R. Boundary Layer Friction of Solvate Ionic Liquids as a Function of Potential. Faraday Discuss. 2017, 199, 311–322. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, M.R.; Yu, Q.L.; Liu, W.M.; Zhou, F. Ionic liquid lubricants: When chemistry meets tribology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7753–7818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, J.; Hausen, F.; Hayes, R.; Webber, G.B.; Endres, F.; Rutland, M.W.; Bennewitz, R.; Atkin, R. Control of Nanoscale Friction on Gold in an Ionic Liquid by a Potential-Dependent Ionic Lubricant Layer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 155502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dold, C.; Amann, T.; Kailer, A. Influence of electric potentials on friction of sliding contacts lubricated by an ionic liquid. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 10339–10342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashazanusi, L.; Kristiansen, K.; Li, S.W.; Tian, Y.; Pesika, N.S. Role of Interfacial Water and Applied Potential on Friction at Au(111) Surfaces. Front. Mech. Eng. 2019, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Pilkington, G.A.; Mehler, F.; Hammond, O.S.; Boudier, A.; Vorobiev, A.; Glavatskih, S.; Rutland, M.W. Tuneable interphase transitions in ionic liquid/carrier systems via voltage control. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2023, 652, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.X.; Luo, J.B.; Guo, D.; Liu, S.H. Nanoconfined ionic liquids under electric fields. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 043112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, G.; Bennewitz, R. Molecular Rheology of a Nanometer-Confined Ionic Liquid. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 28284–28290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalec, M.; Svoboda, P.; Krupka, I.; Hartl, M.; Vencl, A. Investigation of the tribological performance of ionic liquids in non-conformal EHL contacts under electric field activation. Friction 2020, 8, 982–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Z.; Sun, C.F.; Yan, X.Y.; Guo, T.T.; Xiang, W.J.; Yang, Z.Z.; Yu, Q.L.; Yu, B.; Cai, M.R.; Zhou, F. Influence of the molecular structure on the tribological properties of choline-based ionic liquids as water-based additives under current-carrying lubrication. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 369, 120868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.B.; Shen, M.W.; Wen, S.Z. Tribological properties of nanoliquid film under an external electric field. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 96, 6733–6738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bou-Malham, I.; Bureau, L. Nanoconfined ionic liquids: Effect of surface charges on flow and molecular layering. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 4062–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.L.; Huang, W.; Wang, X.L. Ionic liquid lubrication at electrified interfaces. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 225301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.X.; Chen, J.M.; Liu, M.M.; Wang, F.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Cheng, Y.H.; Liu, Z.F. Relationship between Viscosity and Resistance of Oil Film: A New Way to Investigate the Controllable Friction between Charged Interfaces Lubricated by Ionic Lubricating Oil. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2200229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.K.; Karasawa, K.; Sawa, K. Effects on contact resistance of passing electrical current through wiping palladium contacts. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. Part A 1995, 18, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Kong, L.L.; Wang, X.L. Electrical Sliding Friction Lubricated with Ionic Liquids. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 65, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, L.N.; Si, L.N.; Ren, X.Y.; Wu, S. Study on the Friction Behaviors of Copper Nanowires in Ionic Liquids under External Voltages. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 5718–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, G.L.; Wang, W.Z.; Si, L.N.; Liu, F.B. Controlled friction behaviors of gradient porous Cu-Zn composites storing ionic liquids under electric field. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 115020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).