Abstract
Three diprotic ionic liquids (PILs) containing bis(2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium cations and citrate (DCi), lactate (DL), or salycilate (DSa) hydroxy/carboxylate anions were studied as lubricants for Ti6Al4V–sapphire contact. At room temperature, the neat PILs are non-Newtonian fluids, which show up to a 70% friction coefficient reduction with respect to water. New aqueous lubricants were developed using PILs as 1 wt.% additives in water. The new (Water + 1 wt.% PILs) lubricants showed friction reductions of higher than 50% with respect to water at room temperature. The lowest friction coefficients at room temperature were achieved with thin lubricant layers deposited on Ti6Al4V using Water + 1 wt.% PIL after water evaporation. At 100 °C, the best tribological performance, with the lowest friction coefficients and wear rates, was obtained for the PILs containing aliphatic anions: DCi, and DL. The surface layers of the sapphire balls with mild adhesion and abrasion wear mechanisms were observed via scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS).
1. Introduction
The advantages of titanium alloys over other metal alloys, such as high corrosion resistance, high specific mechanical properties, good high-temperature performance, and biocompatibility, has seen their increasing use in a wide range of fields from aerospace technology to biomedicine. However, titanium alloys present relatively low hardness values and poor tribological performance. In order to decrease the friction values and increase the wear resistance of titanium alloys [1,2] and, in particular, of TI6Al4V [3,4] is a major technological challenge in critical applications, such as precision instruments, aerospace equipment, or biomedical materials.
Recent advances in titanium tribology have focused on the use of water-based lubricants, vegetable oils, and the combination of base lubricants and nanomaterials. Yang et al. [5] used 5 wt.% castor oil sodium sulfate water emulsion in the lubrication of Ti6Al4V against WC-Co under reciprocating sliding, obtaining a friction coefficient of 0.2 after a short running-in period. Adsorption of the micelles formed by the additive molecules on the titanium alloy surface was proposed as the main mechanism. The same research group described [6] the effect of the addition of amines containing hydrophilic or hydrophobic substituents on the effectiveness of castor oil sodium sulfate aqueous lubricant. The formation of ammonium salts by the reaction between the amine and carboxylate groups was proposed. Lubricating performance was related to the ability to form adsorbed layers.
A recent review [7] has analyzed the increasing need for sustainable, high-tribological performance metalworking fluids for difficult-to-cut materials, including titanium alloys. The main research lines are based on the use of additives or surfactants to modify vegetable oils or water-based biolubricants and the application of minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) to the cutting regions.
Singh et al. [8] reported a 15% friction reduction MQL with 1.5% graphene in canola oil compared to conventional flood lubrication.
Some current research lines that look at reducing energy loss and increasing the tribological performance of lubricant oils include the use of nanoadditives [9] and surface coatings [10].
Graphene nanoplatelets in palm oil [11] have also been used for Ti6Al4V MQL. Other works [12,13,14] have described the use of Al2O3, MoS2, and TiO2 [15] in different vegetable base oils.
Zn nanoparticles in polyethylene glycol have been used to lubricate the steel/Ti6Al4V pair [16]. Good lubricating performance was attributed to the formation of ZnO films on the titanium and steel surfaces under sliding conditions.
Ionic liquids (ILs) have been investigated for the last two decades as lubricants, lubricant additives, and precursors of surface coatings for a variety of materials [17,18] found among the numerous relevant industrial applications of these ordered fluids, with a unique combination of properties [19]. Although a limited number of studies have referred to titanium lubrication with ionic liquids [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27], they have shown promising potential.
Our research group has reported significant reductions in the friction coefficients and wear rates for titanium and titanium alloys using aprotic imidazolium ionic liquids with halide-containing anions [20,21]. In this line, Fan et al. [22] have described the use of perfluorosulfonate ILs as lubricants of Ti6Al4V. Phosphorus-containing ILs, such as quaternary ammonium phosphate [23], have also been studied as lubricants in titanium–steel contacts. However, the presence of the highly reactive aluminum in Ti6Al4V alloy causes tribocorrosion processes when lubricated with these ILs.
Davis et al. [24] studied the effect of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate on turning titanium grade 2, obtaining a 60% tool wear reduction with respect to unlubricated conditions and 15% with respect to lubrication without IL.
Friction and wear for pure titanium have been reduced by coating the surface with dicationic imidazolium ILs [25]. Although ILs have made a significant contribution to precision machining fluids, fluorine-containing imidazolium ILs have been shown to suffer tribochemical degradation on Ti6Al4V surfaces [26].
ILs have made recent contributions to the current need for a reduction in the quantity of lubricant used, particularly for cutting fluids and sustainable precision-machining operations [27,28].
Nontoxic, noncontaminant, sustainable, or even biodegradable lubricants could be based on water as a base fluid [29,30]. In this case, halogen-free water-soluble IL additives are needed in order to improve the poor tribological performance of water and to avoid corrosion and contamination. New aqueous water + PIL lubricants will also be analyzed in the present study. Moreover, these aqueous lubricants were used as precursors for thin-film lubricants.
Specifically, three protic ammonium carboxylate ionic liquids (PILs), namely, bis(2-hydroxydiethylammonium) salicylate (DSa), tri[bis(2-hydroxydiethylammonium)] citrate (DCi), and bis(2-hydroxydiethylammonium) lactate (DL) (Figure 1) were selected. 2-hydroxyethylammonium lactates have been shown to be nontoxic and highly biodegradable [31]. Recent studies [31,32] have also confirmed the low toxicity of PILs, including those used in the present study. Another relevant aspect is that PILs are readily available through a simple synthetic route and have shown good tribological performance in recent studies. DSa and DCi have been previously used as lubricants under various sliding conditions [33,34]. As far as the authors are aware, this is the first time that PILs have been used in the lubrication of Ti6Al4V and the first study on the tribological performance of DL, although lactate IL lubricants have been previously studied. 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium lactate has been used as a lubricant additive [35], and triethanolamine lactates have recently shown their ability to form adsorbed layers on iron surfaces [36,37]. The pin-on-disk configuration conditions selected in the present study are similar to those used in previous studies on titanium lubrication with aprotic ILs [20,21]. Although this is a fundamental study rather than an applied one, the Al2O3 counterpart was selected because it is commonly used in the cutting or machining operations of Ti6Al4V.
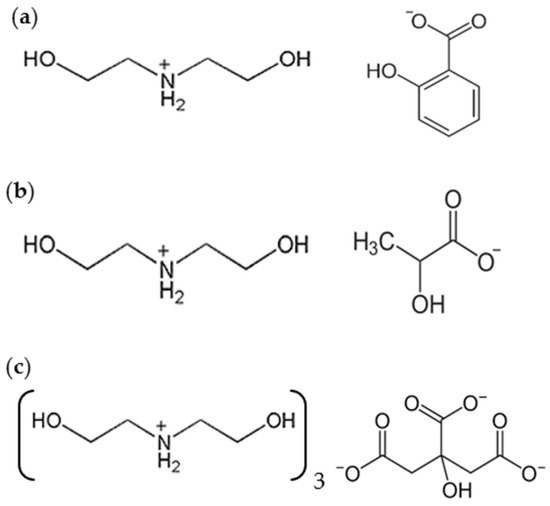
Figure 1.
PILs formulation: (a) Bis(2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium salicylate (DSa); (b) Bis(2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium lactate (DL); (c) Tri[bis(2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium citrate (DCi).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The synthesis and characterization of PIL lubricants (Figure 1) have been previously described [38,39,40].
Ti6Al4V (Ti Gr5 ASTM B348; chemical composition: 5.5% Al; 3.5% V; 1.1% Sn; 0.18% Fe; hardness: 355 HV, Young’s modulus: 115 GPa; Poisson’s ratio: 0.34) was purchased from Special Metals and Products S.L. (Barcelona, Spain). Disks 25 mm in diameter were cut and polished to an average surface roughness (Ra) < 0.20 μm, measured by a RT ALPA-SM contact profiler. 1.5 mm diameter sapphire balls (Goodfellow, Cambridge, UK) (99.9% Al2O3; hardness: 1700 HV; Young’s modulus: 370 GPa; Poisson’s ratio: 0.23) were used as counterparts.
2.2. Rheology
Viscosity measurements were performed with an AR-G2 rotational rheometer from TA Instruments (New Castle, DE, USA) using a plate–plate configuration, with temperature controlled by a Peltier system with an accuracy of 0.1 °C.
2.3. Contact Angle Measurements
A DSA 30B (Krüss, Hamburg, Germany) equipment was used to measure the contact angles on the Ti6Al4V surfaces. Instantaneous contact angles and contact angles after 5 min were determined for each lubricant.
2.4. Tribological Tests
Friction values of the sapphire balls against the Ti6Al4V disks were recorded by a pin-on-disk tribometer (Microtest, Madrid, Spain) that was equipped with an oven [21] under ambient conditions (HR 50 ± 5%) at 25 and 100 °C. To ensure reproducibility, the tribological tests were repeated at least three times under a normal load of 1N (average contact pressure: 0.99 GPa), with a sliding velocity of 0.05 ms−1, a sliding radius of 5.0 mm, a sliding distance of 200 m, and a lubricant volume of 0.2 mL. After each tribological test, the disks were cleaned with distilled water and ethanol and then dried with hot air.
2.5. Surface Analysis
Wear measurements of the Ti6Al4V disks were determined by means of a Talysurf CLI 500 (Taylor Hobson, Leicester, UK) optical profilometer. A scanning electron microscope (SEM) S3500 N (Hitachi, Chiyoda, Japan) was used to obtain the electron micrographs and energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectra of the wear tracks. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analyses were performed using K-Alpha Thermo-Scientific equipment (Waltham, MA, USA), with ±0.1 eV precision.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Viscosity Measurements
The viscosity values of some protic ionic liquids have previously been reported [41] under different conditions. We now report the influence of shear rate and temperature on their rheological behavior. It is important to notice that the protic ionic liquids used in the present study were saturated with adsorbed water, as no drying method was applied before measurements.
Figure 2 shows the variation in viscosity with shear rate for the three protic ionic liquids, both at room temperature (Figure 2a) and at 100 °C (Figure 2b).
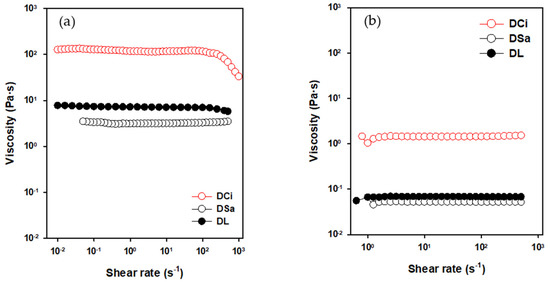
Figure 2.
Viscosity variation with shear rate for neat PILs: (a) 25 °C; (b) 100 °C.
At room temperature, the ionic liquids show non-Newtonian behavior, with a shear thinning effect. The data were fitted to the Ostwald-de Waele model, according to equation 1, and the values are shown in Table 1. Parameter n gives information about the deviation from Newtonian behavior. DCi presents a stronger shear thinning, and a lower value of n indicates the presence of reversible interactions disturbed at high shear rates [42].

Table 1.
Viscosity parameters at 25 °C.
Conversely, at 100 °C (Figure 2b), all ionic liquids show Newtonian behavior, with constant viscosity values (shown in Table 2).

Table 2.
Viscosity values at 100 °C.
As can be observed in Figure 2, DCi presents much higher viscosity values than DL and DSa, not only at room temperature, where variable water contents can influence viscosity values but also at 100 °C once the water has been removed. This is attributed to stronger anion–cation interactions in DCi due to the presence of a tricarboxylate anion and three protic ammonium cations in its molecular composition, while DSa and DL are monocationic with monocarboxylate anions.
3.2. Contact Angles
Table 3 shows the contact angle values for the neat PILs and for the Water + 1 wt.% PILs. It can be observed that DSa shows much higher wettability on Ti6Al4V than DL and DCi. This is particularly so after 5 min when DSa shows the lowest contact angle of all the lubricants. This is attributed to a strong interaction between the chelating salycilate anion and the titanium surface.

Table 3.
Contact angles on Ti6Al4V.
Due to its very high viscosity (Figure 2) and strong molecular interactions, DCi shows very low wettability, such that the contact angles, both instantaneous and after 5 min, are the highest (Table 3). As expected, the contact angles for all the water-based lubricants are very similar due to the low ionic liquid proportion.
3.3. Friction Coefficients and Wear Rates at Room Temperature
3.3.1. Neat PIL Lubricants
Figure 3 shows that after the initial period of 20 min, all ionic liquid lubricants show similar steady-state friction coefficient records along a sliding distance up to 200 m (the corresponding record for water is shown in Figure 4). The average coefficient of friction values after three tests for each lubricant, including water, are reported in Table 4.
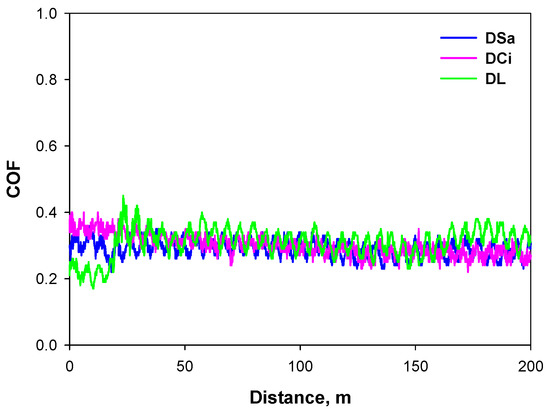
Figure 3.
Coefficient of friction (COF) sliding distance records for neat ionic liquids at room temperature.
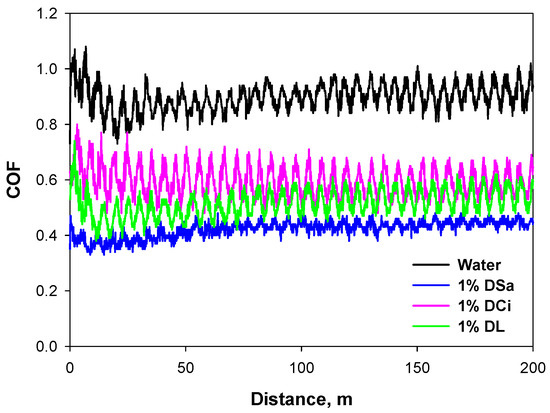
Figure 4.
Coefficient of friction records for water and the Water + 1wt.% ionic liquids at room temperature (sliding distance 200 m).

Table 4.
Coefficients of friction and wear rates for neat lubricants at room temperature.
As expected, water behaves as a very poor lubricant, with a very high friction value of 0.9. All the neat PILs show a much better friction-reducing performance, with coefficients of friction ≤0.3 and a reduction of between 67% and 70% when compared to water. The short chain, aliphatic DCi, and DL also saw reduced wear rates for Ti6Al4V. The best antiwear performance was obtained in the case of DL. In contrast, DSa produced the highest wear rate. This result could be related to the low contact angle of DSa on Ti6Al4V (Table 3) and the strong surface interactions, which could give rise to the formation of coordination compounds, thus justifying the high wear loss. Differences in viscosity and contact angles do not produce significant variations in the average friction values for PILs.
3.3.2. Water + 1 wt.% PIL
Once the efficient tribological performance of the PILs as neat lubricants was established, they were used as additives in water in order to develop new aqueous environmentally friendly lubricants. A 1 wt.% mass fraction of PIL was added to water and was selected in an attempt to obtain significant results using a low additive proportion.
Figure 4 shows that the addition of 1 wt.% ionic liquid reduces the friction coefficient of water at room temperature. Table 5 summarizes the average coefficients of friction and the wear rate values for these water-based lubricants. The average friction values (Table 5) for all water-based lubricants show that a maximum friction reduction of higher than 50% was obtained with the addition of DSa. However, Water + DL and Water + DCi showed lower friction reductions with respect to water. The order of wear rate is Water + DSa < Water + DCi < Water + DL. It is interesting to note that the wear rate for Water + DSa is not only the lowest of the three Water + PIL lubricants, but it is also lower than that obtained for neat DSa (Table 4). In this way, the dilution of DSa in water might reduce the strong surface interaction with respect to neat DSa, as we have seen via an increase in contact angle, thus reducing the amount of material loss.

Table 5.
Coefficients of friction and wear rates for the Water + 1wt.% PIL lubricants.
Previous results for similar short-chain ammonium carboxylate protic ionic liquids in water [43] have shown that, under sliding conditions (for stainless steel–sapphire contacts), water evaporates after a certain sliding distance and the thin ionic liquid film that remains at the contact is able to give ultralow friction values.
In the present case, no transition to lower friction is observed in Figure 4 over 200 m. When the sliding distance was extended to 500 m, Figure 5 shows that water maintains high friction values from 300–500 m, while the Water + PIL lubricants show transitions to lower friction values between 350–450 m. This is attributed to the formation of PIL surface layers on Ti6Al4V when water evaporates at the contact zone.

Figure 5.
Coefficient of friction records for water and Water + 1 wt.% ionic liquids at room temperature (sliding distance: 500 m).
3.3.3. Thin Lubricant Layers
In order to take advantage of this lubricating ability of the PILs, the next objectives were to eliminate the presence of water, which causes high friction coefficients, and to reduce the volume of PIL lubricant at the contact point. Following the previously described methodology [44] for other water-based lubricants and materials, the surface of the Ti6Al4V disks was covered with (Water + 1 wt.% PIL), and thin film PIL lubricants were obtained after subsequent water evaporation.
Upon the basis of these results, thin PIL layers were generated on the Ti6Al4V disks by water evaporation under mild conditions, as previously described in [44] (before the tribological tests). Figure 6 shows the coefficient of friction results for the new thin-layer lubricants.
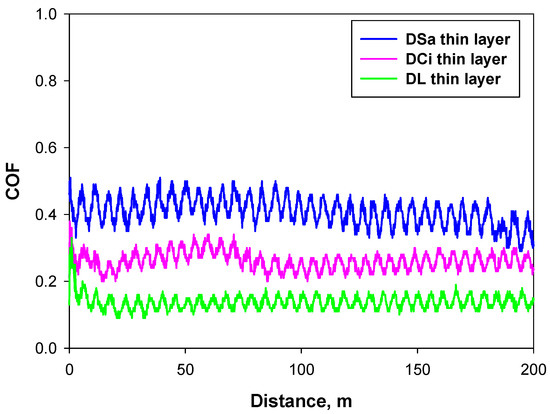
Figure 6.
Evolution of coefficients of friction with sliding distance for thin-layer PIL lubricants at room temperature (sliding distance: 200 m).
These new thin-film lubricants achieve the lowest friction coefficients (Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6), in particular, the citrate and lactate derivatives DCi and DL. It is especially relevant that the low friction coefficient obtained for the DL thin layer (0.13; Table 6) saw up to a 76% reduction, as compared to Water + DL (Table 5), and more than a 50% reduction when compared with neat DL (Table 4).

Table 6.
Coefficients of friction and wear rates for the thin-layer lubricants.
The fact that the DSa thin-layer lubricant presents a friction coefficient and wear rate values very similar to those obtained for Water + DSa (Table 5) could be attributed to the higher water content in the DSa thin layer than in the rest of the thin-layer lubricants.
The wear rate values for Ti6Al4V at room temperature (Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6) are in good agreement with the friction coefficient values. While the best performance for a water additive was found for DSa, the lowest wear rate values were obtained for DCi and DL, both as neat lubricants and as thin-film lubricants.
3.4. Wear Mechanisms and Surface Analysis at Room Temperature
3.4.1. Neat PIL Lubricants
Figure 7a shows the SEM micrograph of the wear track and the titanium element map on the sapphire ball after lubrication at room temperature with neat DCi. The scar on the sapphire ball is covered by a thin, discontinuous titanium layer adhered to the Ti6Al4V disk. As expected, the main peaks in the EDX spectrum of the sapphire ball are those of aluminum and oxygen. The presence of carbon or nitrogen peaks from the DCi lubricant was also detected on the ball’s surface (Figure 7b), which, however, was free from adhered titanium in some areas, as shown in the spectrum of Figure 7b.
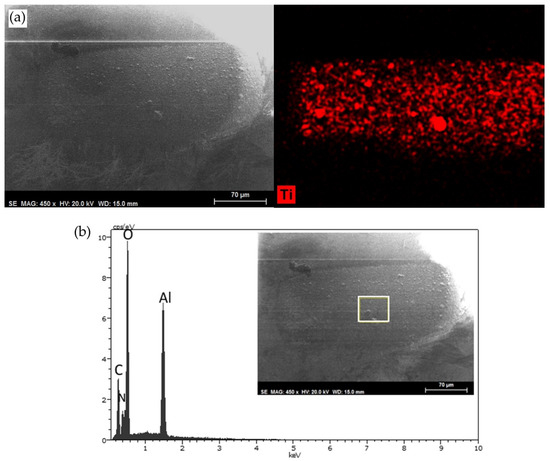
Figure 7.
Lubrication with neat DCi at room temperature: (a) SEM micrograph and titanium element map on the sapphire ball. (b) SEM micrograph and EDX spectrum of the selected (white box) region of the layer on the sapphire ball.
In contrast to neat DCi, the neat DL lubricant is able to protect the sliding contact from titanium transference at room temperature. As shown in Figure 8, in this case, the entire contact area on the sapphire ball is free from titanium and is covered by a tribolayer containing carbon and nitrogen from the DL lubricant. This is in agreement with the lowest wear rate observed in the case of neat DL (Table 4).
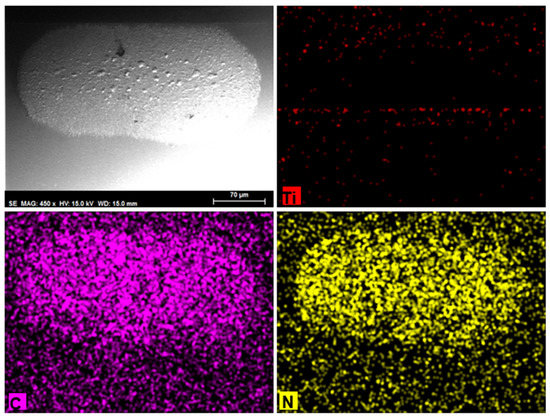
Figure 8.
SEM micrograph, and Ti, C, and N element maps of the sapphire ball after lubrication with neat DL at room temperature.
The wear track on the disk after lubrication with neat DCi (Figure 9) shows only titanium, aluminum, and vanadium peaks, corresponding to the elements present in Ti6Al4V alloy, without carbon or oxygen from the lubricant. The magnification of the SEM micrograph in Figure 9 shows parallel grooves characteristic of a mild abrasive wear mechanism.
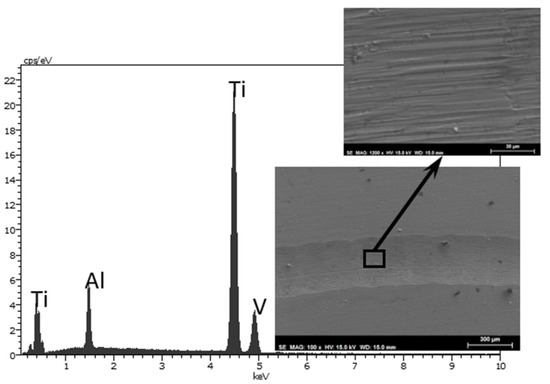
Figure 9.
SEM micrographs and EDX spectrum of Ti6Al4V disk after lubrication with neat DCi at room temperature and higher magnification of a region inside the wear track.
A similar mild abrasive wear mechanism was also observed inside the wear track of the neat DL lubricant (Figure 10).
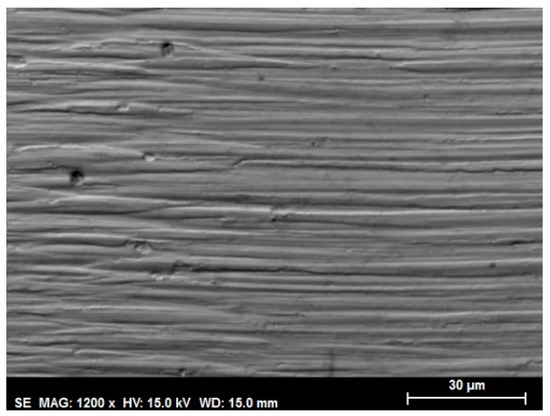
Figure 10.
SEM micrograph of the wear track on the Ti6Al4V disk after lubrication with neat DL at room temperature.
Neat DSa produces very severe abrasive surface damage (Figure 11a), with wear debris adhered to the sapphire ball, which presents a machining chip morphology. A layer of titanium adhered to the sapphire surface (Figure 11b) covers the wear scar, thus showing the adhesive wear mechanism.
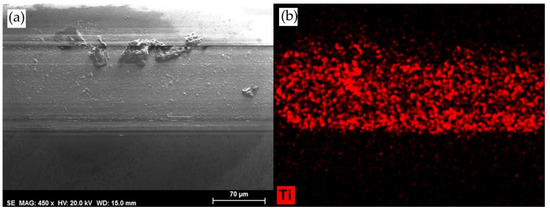
Figure 11.
(a) SEM micrograph and (b) titanium element map on sapphire ball after the test with neat DSa at room temperature.
3.4.2. Water + 1 wt.% PILs
Pure water failed to lubricate the sapphire–titanium contact. As seen in Figure 12a, the severe wear produces a flat circular wear scar on the sapphire ball surface. Figure 12b,d show the scars on the sapphire balls after lubrication with the 1 wt.% solutions of the PILs in water. The smallest wear scar area was obtained for the Water + 1%DSa lubricant. This is in agreement with the lower wear rate of Ti6Al4V after lubrication with Water + 1 wt.%DSa (Table 5) and with the variation in wear-track width and the severity of the wear damage on the Ti6Al4V disks for each water-based lubricant (Figure 13a–d).
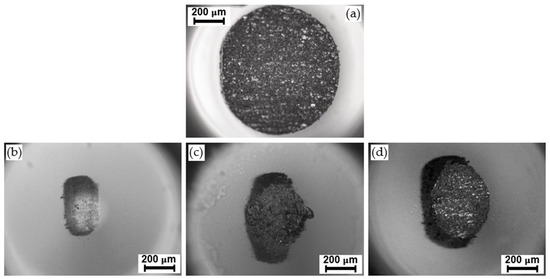
Figure 12.
Wear scars on the sapphire balls after lubrication with (a) water, (b) Water + DSa, (c) Water + DCi, and (d) Water + DL (room temperature; sliding distance: 200 m).
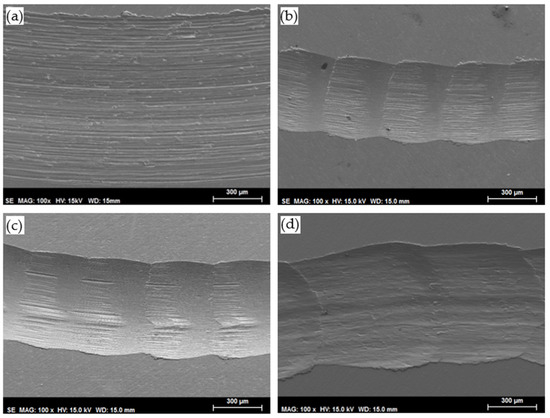
Figure 13.
Wear tracks on the Ti6Al4V disks after lubrication with (a) water, (b) Water + DSa, (c) Water + DCi, and (d) Water + DL.
3.4.3. Thin-Layer Lubricants
After lubrication with the DSa thin-layer lubricant, which was deposited onto the Ti6Al4V surface after water evaporation, the sapphire ball surface shows (Figure 14) the presence of adhered particles that do not contain titanium, as the EDX spectrum only shows Al and O from the sapphire and C and N from the lubricant. This is attributed to the strong interaction of DSa with the Ti6Al4V surface after thin-film formation, which would prevent or diminish titanium adhesion to the sapphire ball’s surface. This is in sharp contrast to the adhesive mechanism seen for neat DSa (Figure 11b).
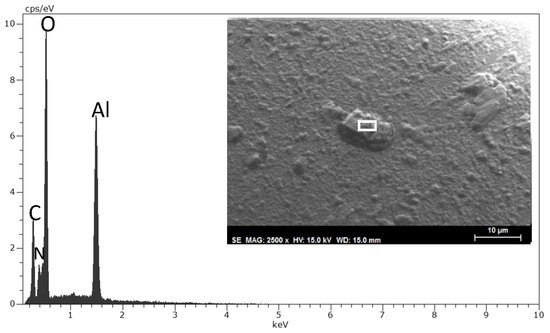
Figure 14.
SEM image and EDX spectrum of the selected region (white box) of the sapphire ball after lubrication with DSa thin layer.
Figure 15 shows that when a thin layer of DCi is deposited on Ti6Al4V before the tribological test, the wear scar on the sapphire ball (after the test) is also free from titanium adhesion. This is, again, in sharp contrast with the observation made for neat DCi (Figure 6) and could account for the lower wear rate observed for the DCi thin-layer lubricant (Table 6).
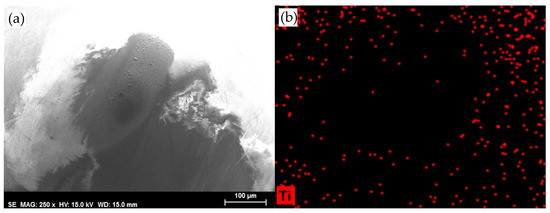
Figure 15.
(a) SEM micrograph and (b) Ti element map of the sapphire ball after lubrication with the DCi thin-lubricant layer at room temperature.
When DL is used as a thin-layer lubricant, the scar on the sapphire ball (Figure 16a) contains both titanium (Figure 16b) and carbon (Figure 16c).
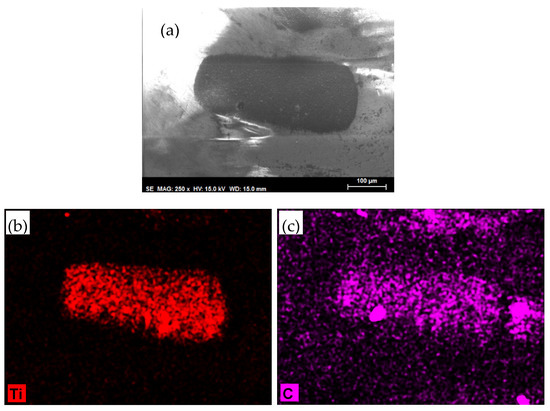
Figure 16.
Lubrication with a DL thin film at room temperature: (a) SEM micrograph of the sapphire ball; (b) titanium element map, and (c) carbon element map.
The formation of this transfer layer shows that the DL thin-film lubricant is not able to protect the Ti6Al4V alloy as efficiently as neat DL. However, the final wear rate, once the tribolayer is formed, is slightly lower than that obtained for neat DL.
Table 7 shows the XPS surface analysis results after lubrication with DL as a neat lubricant and with a DL thin-layer lubricant at room temperature. The binding energies were assigned according to the literature [21,44] and are in agreement with previous XPS results for protic ammonium carboxylate ionic liquid lubricants on different surfaces.

Table 7.
XPS results for Ti6Al4V disk after lubrication tests at room temperature.
Aliphatic or adventitious carbon is the main C1s peak at 285 eV. C1s binding energies at 286, 287, and 289 eV are assigned, respectively, to the –CH2OH, –CH2NH, and –COO functional groups, which are present in the composition of DL cations and anions (Figure 1). The three O1s binding energies at 530 eV (the most abundant), 531, and 532 eV correspond to oxide, –OH, and –CO– groups. Although the values of the O1s binding energies are the same for neat DL and thin-layer DL, the relative abundance of each peak changes. Thus, for the DL thin-layer lubricant, a higher atomic percentage is found for the peak assignable to the oxides, and a lower atomic percentage is found for the peaks at 532 eV, which could be due to a reduction in the water proportion present in the thin-layer DL with respect to neat DL.
The main N 1s peak at 400.1 eV is due to the protic ammonium –NH group present in the cation. The minor peak at 401.5 eV for neat DL and 401.8 eV for the thin-layer DL could be due to –C–N quaternary ammonium caused by surface interactions and degradation processes under sliding conditions.
A total of two Ti 2p3/2 peaks were observed: the less abundant, being assignable to titanium metal, appears at a lower binding energy, and the second, present in a much higher proportion at a higher binding energy, corresponds to titanium oxide. In a similar way, the two Al 2p3/2 binding energies correspond to metallic aluminum (the minor peak at a lower binding energy) and to aluminum oxide or hydroxide (present in a higher proportion). A third minor Al 2p3/2 peak observed in the case of lubrication with the thin-layer DL is tentatively assigned to nonstoiquiometric aluminum oxide (AlOx) [45].
3.5. Friction Coefficients and Wear Rates at 100 °C
Because the Ti6Al4V–sapphire pair is formed by materials with high-temperature applications, it was important to test the tribological behavior of the new PIL lubricants above room temperature, in particular, at 100 °C, under conditions where water cannot be used.
Table 8 shows the tribological results for the three neat PIL lubricants at 100 °C. As expected, the friction coefficients and wear rates are higher than those found at room temperature (Table 4) for all lubricants, with the highest increase observed for DSa. The salicylate derivative also presented the highest wear rate under neat lubricant at room temperature (Table 3). These results could be related to its lower viscosity at both 25 and at 100 °C (Table 1 and Table 2, respectively). The best lubricants with the lowest friction coefficients and wear rates at 100 °C are, again, as was observed at room temperature, the citrate and lactate aliphatic PILs species, DCi and DL. Here, neat DCi shows the best friction-reducing ability, probably due to a reduction in viscosity at a high temperature (Figure 2; Table 1 and Table 2).

Table 8.
Coefficients of the friction and wear rates at 100 °C.
3.6. Wear Mechanisms and Surface Analysis after Tests at 100 °C
SEM/EDX studies were carried out for the best lubricants at 100 °C; in particular, DCi and DL in the presence of adhered material from the Ti6Al4V disk to the sapphire ball were analyzed. Figure 17 shows that, after lubrication with neat DCi at 100 °C, the surface of the sapphire ball is covered by a titanium-free layer. The strong carbon and oxygen peaks in the EDX spectrum could be assigned to the presence of a DCi surface layer. A peak around 1 eV, which is assignable to sodium, could be due to sample contamination.
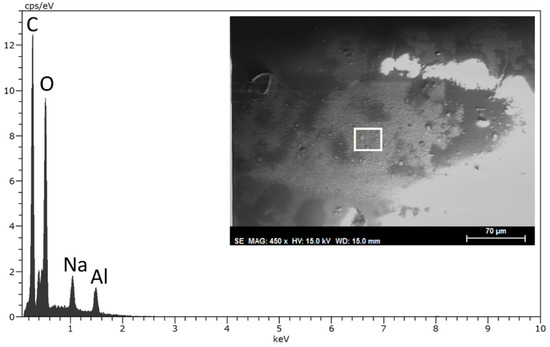
Figure 17.
SEM micrograph and EDX spectrum of the selected area (white box) on the sapphire ball after lubrication with neat DCi at 100 °C.
This result is similar to that observed for the DCi thin-layer lubricant at room temperature (Figure 15). However, under these more severe conditions, at 100 °C and in the presence of a thick layer of neat DCi lubricant, a more continuous tribolayer covers the contact region on the sapphire ball surface.
After lubrication with DL at 100 °C (Figure 18), the adhesion of some wear debris particles composed of Ti, Al, and V, from the Ti6Al4V disk to the ball’s surface took place. A lower carbon and oxygen proportion is present in this case, compared with DCi (Figure 17). This shows that in contrast to the results observed at room temperature, a more stable surface layer with the lowest friction coefficient at 100 °C (Table 8) is formed by DCi.
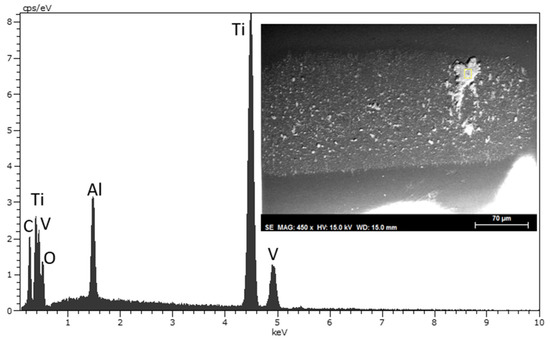
Figure 18.
SEM micrograph and EDX spectrum of wear debris on the selected area (white box) on the sapphire ball after lubrication with neat DL at 100 °C.
4. Conclusions
Three sustainable and ecofriendly protic ionic liquids containing 2-hydroxyethyl diprotic ammonium cations and carboxylate anions derived from natural products (citrate, salicylate, and lactate) were studied. The rheological study showed that the neat protic ionic liquids are non-Newtonian fluids at room temperature and present Newtonian behavior at 100 °C. The tricarboxilate citrate derivative shows higher viscosity values and lower wettability on Ti6Al4V surfaces than the monocarboxylate versions.
The three protic ionic liquids were studied as neat lubricants, as lubricant additives (in water), and as thin lubricant layers for Ti6Al4V sliding against sapphire at room temperature, as well as neat lubricants at 100 °C.
At room temperature, the neat protic ionic liquid lubricants presented maximum friction coefficient reductions of up to 70%. The new aqueous lubricants composed with the addition of 1 wt.% protic ionic liquid (to water) were also able to reduce friction and wear. The salicylate derivative showed the best tribological performance as an additive in water.
When water is removed by evaporation, protic ionic liquids are deposited as thin films on the Ti6Al4V surface. These thin-layer lubricants achieve the lowest friction coefficients, in particular, the citrate and lactate derivatives. Bis(2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium lactate thin layers are able to reduce the friction coefficient by 76%, as compared to its 1% solution in water, and by more than 50% when compared to the neat lactate lubricant.
The viscosity reduction experienced by neat DCi at 100 °C enhances its tribological performance, showing the lowest friction coefficient under these conditions.
Adhesive and abrasive wear, with the transference of the titanium alloy to the sapphire surface, and the formation of surface tribolayers on the sapphire ball from the protic ionic liquid lubricants that prevent or reduce the adhesion of the titanium alloy to the sapphire ball, are the main surface mechanisms, as evidenced by SEM/EDX.
The chemical composition of both anions and cations in the protic ionic liquids studied here allows for the formation of strong electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonds due to the presence of carboxylate and hydroxyl groups on the anions and hydroxyl groups and ammonium protons on the cations. The presence of bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonium lactate on Ti6Al4V surfaces is therefore confirmed (via XPS), both after lubrication with neat DL and with a DL thin layer, which shows the best antiwear performance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.-E.J. and M.-D.B.; methodology, A.-E.J., M.-D.A., R.P. and M.-D.B. investigation, A.-E.J. and M.-D.A.; writing—original draft preparation, M.-D.A., M.-D.B., A.-E.J. and R.P.; writing—review and editing, all authors; funding acquisition, M.-D.B., J.S. and F.-J.C.-V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Agencia Estatal de Investigación (AEI), and the European Union FEDER Program (Grants # MAT2017–85130-P and PID2021-122169NB-I00).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Long, M.; Rack, H.J. Friction and surface behaviour of selected titanium alloys during reciprocating-sliding motion. Wear 2001, 249, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.X.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.Q. Investigation on wear characteristics of a titanium alloy/steel tribo-pair. Mater. Des. 2015, 65, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, A.; Straffelini, G.; Tesi, B.; Bacci, T. Dry sliding wear mechanisms of the Ti6Al4V alloy. Wear 1997, 208, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, J.A.; Satish, V.K. Evolution of wear debris morphology during dry sliding of Ti-6Al-4V against SS316L under ambient and vacuum conditions. Wear 2020, 456–457, 203378. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.H.; Dai, Y.J.; Luo, J.B. Lubricity and adsorption of castor oil sulfated sodium salt emulsion solution on titanium alloy. Tribol. Lett. 2019, 67, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, T.T.; Dai, Y.J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.H. Effect of amines on the lubricity of castor oil-sulfated sodium salt solution for titanium alloys. Tribol. Lett. 2020, 68, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, K.C.; Sasahara, H.; Abd Rahim, E.; Perera, G.I.P. Recent advances on high performance machining of aerospace materials and composites using vegetable oil-based metal working fluids. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 310, 127459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Sharma, V.S.; Dogra, M. Exploration of graphene assisted vegetable oil based minimum quantity lubrication for surface grinding of Ti-6Al-4V-ELI. Tribol. Int. 2020, 144, 106113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Tao, D. Tribological performance of nanotin as lubrication additives used in steel-copper tribo-pair. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2011, 63, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrablewski, P. Investigation of energy losses of the internal combustion engine taking into account the correlation of the hydrophobic and hydrophilic. Energy 2023, 264, 126002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.M.M.; Li, W.; Xiao, H.; Zeng, Z.; Ren, Y.; Alsoufi, M.S. Energy conservation and environmental sustainability during grinding operation of Ti-6Al-4V alloys vis eco-friendly oil/graphene nanoadditive and minimum quantity lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2020, 150, 106308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xu, J.; Chen, M.; An, Q.; El Mansori, M.; Ren, F. Tool wear processes in low frequency vibration assisted drilling of CFRP/Ti6Al4V stacks with forced air-cooling. Wear 2019, 426–427, 1616–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yi, S.; Li, N.; Pan, W.; Wen, C.; Ding, S. Quantitative analysis of cooling and lubrication effects of graphene oxide nano fluids in machining titanium alloy Ti6Al4V. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 271, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yu, T.; Yang, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, R.; Wang, W. Parameter optimization during minimum quantity lubrication milling of TC4 alloy with graphene-dispersed vegetable oil-based cutting fluid. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 1508–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakib, S.; Ibne, Z.; Nurul, A.K.M.; Bashar, M.S.; Kabir, F.; Kamruzzaman, M. Tuning nano fluids for improved lubrication performance in turning biomedical grade titanium alloy. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 180–196. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, X.; Xie, H.M.; Xu, X.J.; Tang, J.Z. Study on the enhanced tribological performance for titanium alloys by PEG oil/Zn-nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 126502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, T.L.; Drummond, C.J. Protic ionic liquids: Evolving structure-property relationships and expanding applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11379–11448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.R.; Yu, Q.L.; Liu, W.M. Ionic liquid lubricants: When chemistry meets tribology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7753–7818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.J.; Jacquemin, J.; Hardacre, C. Industrial applications of ionic liquids. Molecules 2020, 25, 5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, A.E.; Bermúdez, M.D. Ionic liquids as lubricants of titanium-steel contacts. Part 2. Friction, wear and surface interactions at high temperature. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 33, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, A.E.; Bermúdez, M.D. Ionic liquids as lubricants of titanium-steel contact. Part 3. Ti6Al4V lubricated with imidazolium ionic liquids with different alkyl chain lengths. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 40, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Jin, Y.; Han, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, W.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. The effect of chemical structure on the tribological performance of perfluoropolysulfonate ILs as lubricants for Ti-6Al-4V tribopairs. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 321, 114286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Lu, Z.L.; Li, F.Z.; Jia, I.; Yang, Z.Q.; Chen, G.Q.; Yu, Q.L.; Dong, R.; Cai, M.R. Corrosion and lubrication properties of a halogen-free Gemini room-temeprature ionic liquid for titanium alloys. Tribol. Int. 2021, 156, 106850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.; Schueller, J.K.; Huang, Y. Study of ionic liquid as effective additive for minimum quantity lubrication during titanium machining. Manuf. Lett. 2015, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gindri, I.M.; Siddiqui, D.A.; Frizzo, C.P.; Martins, M.A.P.; Rodrigues, D.C. Improvement of tribological and anticorrosive performance of titanium surfaces coated with dicationic imidazolium-based ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 78795–78802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevshupa, M.; Conte, M.; del Campo, A.; Román, E. Analysis of tribochemical decomposition of two imidazolium ionic liquids on Ti-6Al-4V through mechanically stimulated gas emission spectrometry. Tribol. Int. 2016, 102, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.T.; Li, W.M.; Kumara, C.; Jin, Y.L.; Meyer, H.M.; Luo, H.M.; Qu, J. Ionic liquids as oil additives for lubricating oxygen-diffusion case-hardening titanium. Tribol. Int. 2019, 136, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.H.; Dai, Y.J.; Luo, J.B. Tribological properties of titanium alloys under lubrication of SEE oil and aqueous solutions. Tribol. Int. 2017, 109, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor Hamran, N.N.; Ghani, J.A.; Ramli, R.; Haron, C.H.C. A review on recent development of minimum quantity lubrication for sustainable machining. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 122165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Yu, Q.; Bai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Yu, B.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.; et al. Towards superior lubricity and anticorrosion performances of proton-type ionic liquids additives for water-based lubricating fluids. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovica, S.; Zicmanis, A.; Gzibovska, E.; Klavins, M.; Mekss, P. (2-Hydroxyethylammonium) lactates. Highly biodegradable and essentially non-toxic liquids. Green Sustain. Chem. 2011, 1, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, B.; Brasil, G.; Andrade, R.S.; Barretto, R.M.; Trovatti, E.; Galdorfini, B.; Iglesias, M. Cytotoxic effect of protic ionic liquids in HepG2 and HaCat human cells: In vitro and in silico studies. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 8, 447–458. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Iglesias, P. Tribological behavior of ammonium-based protic ionic liquid as lubricant additive. Friction 2021, 9, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Guo, H.; Iglesias, P. Study of the lubricating ability of protic ionic liquid on an aluminum-steel contact. Lubricants 2018, 6, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Chen, H.; Luo, T.; Wang, F.; Xiao, G.; Chen, Z.; Yi, M.; Sheng, C.; Xu, C. Tribological properties of 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium lactate ionic liquid as a lubricant additive. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 332, 115828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.; Akamatsu, M.; Sakai, K.; Sakai, H. Adsorption of hydrophilic amine-based protic ionic liquids on iron-based substrates. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 70, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, K.; Sakai, K.; Sakai, H. Lubrication by adsorption films of hydrophilic amine-based protic ionic liquids: Effect of anion species. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 70, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, M.; Gonzalez-Olmos, R.; Cota, I.; Medina, F. Bronsted ionic liquids: Study of physico-chemical properties and catalytic activity in aldol condensations. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, V.H.; Dosil, N.; Gonzalez-Cabaleiro, R.; Mattedi, S.; Martin-Pastor, M.; Iglesias, M.; Navaza, J.M. Bronsted ionic liquids for sustainable processes: Synthesis and physical properties. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.; Torres, D.; Ribeiro, F.R.; Chiari-Andreo, B.G.; Oshiro, J.A.; Iglesias, M. Sustainable cotton dyeing in nonaqueous medium applying protic ionic liquids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 8756–8765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, D.; Andrade, R.S.; Ferreira, G.A.; Mazzer, H.; Cardozo-Filho, L.; Iglesias, M. Investigation of the rheological properties of protic ionic liquids. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2016, 29, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rubio, P.M.; Avilés, M.D.; Arias-Pardilla, J.; Carrión-Vilches, F.J.; Sanes, J.; Bermúdez, M.D.; Pamies, R. Physicochemical characterisation of graphene-ammonium lactate ionic liquid nanofluid. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 367, 120446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, T.; Jiménez, A.E.; Sanes, J.; Jiménez, A.E.; Iglesias, M.; Bermúdez, M.D. Ultralow friction with a protic ionic liquid boundary film at the water-lubricated sapphire-stainless steel interface. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurín, N.; Avilés, M.D.; Espinosa, T.; Sanes, J.; Carrión, F.J.; Bermúdez, M.D.; Iglesias, P. Carbon nanophases in ordered nanofluid lubricants. Wear 2017, 376–377, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.D.; Naumkin, A.V.; Kraut-Vass, A.; Allison, J.W.; Powell, C.J.; Rumble, J.R., Jr. NIST Standard Reference Database (web version) 2003. Available online: http:/srdata.nist.gov/xps/ (accessed on 28 November 2022).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).