Abstract
Boron-containing compounds are one of the lubricant additive options due to their suitable properties for additives and have been used as commercial lubricant additives. In the present study, the impact of a boron-containing lubricant oil additive, AR9100 (BR), on Pd/Rh-based three-way catalyst (TWC) performance is investigated, and the results are compared with the baseline no-additive (NA) case and the industry standard zinc dialkyl-dithiophosphate (ZDDP) results. Accelerated engine aging is performed using a genset to expose the catalysts to lubricant additives at high temperatures. All aged TWC samples are investigated for reactivity in a bench-flow reactor and characterized using a variety of analytical techniques. Compared with the no-additive case, the temperatures of 90% conversion (T90) of NO, CO, C3H6, and C3H8 for the ZDDP-aged TWC sample increased by 34, 30, 37, and 48 °C. However, the T90 of all gas species for the BR-aged TWC sample are similar to the NA-aged TWC sample. Additionally, a significant decrease in water–gas shift reactivity and oxygen storage capacity is observed in the ZDDP-aged sample, but not in the BR-aged sample. Inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) analysis and electron probe microanalysis (EPMA) maps of accelerated engine aging samples show the presence of phosphorus and boron in ZDDP- and BR-aged TWC samples, respectively. However, no boron-related peaks are observed in the X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of the BR-aged TWC sample, which may exist in the form of an amorphous phase.
1. Introduction
Automobiles are an important means of transportation worldwide, but air pollutants emitted from exhaust gases adversely affect the environment and are strictly regulated. Thus, efforts are being made to reduce air pollutants emitted from automobiles by installing an emission control system. A three-way catalyst (TWC) is commonly used to convert NOx, CO, and HCs contained in the exhaust gas of gasoline engines into CO2, H2O, and N2 and release them to the atmosphere [1]. The TWCs use platinum group metals (PGM), e.g., Pt, Pd, and Rh, as an active component, Al2O3 as a PGM support with high surface area, and Ce–Zr mixed oxide to improve catalytic activity and provide oxygen storage for perturbations from stoichiometric operation. Additionally, considerable efforts have been attempted to stabilize the catalyst and minimize performance degradation by adding various promoters [2,3,4,5,6].
The latest EPA standard requires catalyst durability from 120,000 miles to 150,000 miles, so research on improvements is needed through understanding the main causes of catalyst deactivation. The deactivation process of the catalyst is a complex phenomenon and has several causes. Sintering is the process of deactivation due to prolonged high temperature exposure to catalysts during vehicle operation [7]. The catalytically active surface exposed to high temperatures for long periods of time is lost due to crystal growth of the support or active phase due to agglomeration of the catalyst particles. Another cause of catalyst deactivation is catalyst poisoning, which occurs when impurities contained in exhaust gases are strongly adsorbed on the catalyst surface, blocking the catalytic sites from reactions [7]. In particular, ZDDP has long been used as an anti-wear, antioxidant, and anti-corrosion lubricant additive in most current engine oils, but components of Zn, S, and P contained in ZDDP have been studied to affect catalyst performance degradation. Due to lubricant loss in the exhaust gases, the formation of Zn2P3O7 [8,9] and cerium orthophosphate (CePO4) [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18] has been identified on the washcoat surface and within the catalyst washcoat, which causes site deactivation of the TWCs. For this reason, considerable efforts have been made in recent years to develop lubricant additives that increase the performance of lubricants and have less adverse effects on the catalyst. Recently, a new generation of AW additives, fully oil-miscible ionic liquids (IL), has been developed and found to effectively reduce friction and wear when used in blends with conventional ZDDP [19]. A recent study investigated the combined effects of ZDDP and a novel IL-based lubricant additive on the physicochemical properties and the performance of a Pd/Rh-based TWC [15]. They observed that the addition of the IL anti-wear additive did not have a more negative effect, but deactivation was similar, primarily because the IL also contained P. In addition, IL mixed with primary ZDDP showed less severe TWC performance degradation than IL mixed with secondary ZDDP because the S, Zn, and P contents of primary ZDDP were smaller than those of secondary ZDDP [17].
Boron (B)-containing compounds have a unique combination of tribological properties, such as self-lubrication, wear resistance, good film strength, and high temperature resistance, and are more environmentally friendly [20,21,22,23,24,25]. Therefore, B-containing compounds have been developed and studied as commercial lubricant additives. Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), the softest and most lubricious polymorph of BN, is widely used as a solid lubricant and an additive to lubricants [26,27]. Boric acid (H3BO3) has been used as a solid lubricant because it provides good lubricating properties due to its lamellar structure [20]. Recently, oil-soluble organic borate esters have been studied as promising anti-wear additives for friction modifiers, corrosion inhibitors, antioxidants, and extreme pressure performance [21,22,28,29,30,31,32,33].
The effect of B-containing additive on the Pt/Rh TWC was studied by Twigg et al. [34]. They used ZDDP and B-based engine lubricant additives to investigate engine wear and Pt/Rh TWC durability. Reported results show that the B-based lubricant additive has little difference in terms of engine wear and clean performance compared with ZDDP and has little effect on Pt/Rh TWC durability. They claimed that the B-containing lubricant additive had less of an effect on Pt-based TWC degradation than P-containing lubricant additives with respect to CO conversion performance. However, except for Twigg’s paper, there is no further study on the effect of B-based additives on the performance of catalysts and, in particular, no studies on the effect on the Pd/Rh-based TWCs and surface characterization studies. Based on Twigg's research, B-containing lubricant additive is expected to have less of an effect on the Pd/Rh-based TWC than ZDDP, but which aspects of TWC reactivity and physicochemical characterization are affected is not well understood. This lack of understanding provides the impetus for the current investigation, and the results will provide further insight into the effects of B-containing lubricant additive on Pd/Rh-based TWC.
In the present study, a novel AR9100 (B-containing) lubricant additive was added to the fuel and exposed to a Pd/Rh-based TWC with exposure levels approximating the full useful life of a vehicle while also going to elevated temperatures periodically. For a comparison with conventional non-wear additives, ZDDP (P-containing) was introduced in a subsequent exposure. The performance of each accelerated engine-aged TWC sample was evaluated on a bench-flow reactor (BFR) using the protocols developed and reported by an industry/national laboratory consortium [35]. Specifically, measurements for catalytic light-off, water–gas shift (WGS) reactivity, and oxygen storage capacity (OSC) were performed. Additionally, surface characterization studies, including N2 physisorption, X-ray diffraction (XRD), inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), and electron probe microanalysis (EPMA), were employed to identify the mechanisms of catalyst deactivation and morphological changes associated with catalyst poisoning from lubricant additives in the accelerated engine-aged TWCs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Lubricant Additives
In the present study, the industry standard ZDDP (provided by Lubrizol) and B-containing oil additive (Archoil AR9100) were used to investigate the effect of oil lubricant additives on Pd/Rh-based TWCs. The P and Zn content of ZDDP is 10% and 11% by weight, respectively (disclosed by our industrial partner). In addition, according to the material safety data sheet (MSDS) of AR9100, the concentration of potassium tetraborate (B4K2O7) is 1–10% [36]. The content of B in the AR9100 was 0.57% by weight as measured using Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) with PCA (Principal Components Analysis); this was repeated 4 times to improve confidence in measurement.
2.2. Three-Way Catalyst
The monolithic Pd/Rh-based TWCs obtained from a local dealership were used to evaluate the lubricant impact on reactivity. The dimensions of the full-size TWC are 105 mm in diameter and 85 mm in length. This TWC consists of γ-Al2O3 and CeO2 (oxygen storage material) along with stabilizers/promoters such as BaO, La2O3, and ZrO2. The ratio of Pd and Rh is 8:1 (total PGM loading is 0.6%), and cell density of the TWC is 600 cpsi (cells per square inch). For accelerated engine aging, the full-size TWCs were cored with a diameter of 42 mm and a length of 85 mm to fit the size of the exhaust manifold of the genset and wrapped in insulation (3M™ Interam™ Mat Mount 1600HT).
2.3. Accelerated Engine Aging
The Pd/Rh-based TWC was exposed to the additives using a 3.5 kW Westerbeke SBCG single-phase 60 Hz gasoline generator or genset consisting of a 0.35 L water-cooled two-cylinder gasoline engine. The genset operates at 2200 revolutions per minute (RPM) and has an electric fuel injection system controlled by a universal exhaust gas oxygen (UEGO) sensor or lambda sensor. To elevate the catalyst temperature, oxygen was injected after the combustion chambers upstream of the lambda sensor. The additional injected O2 is detected by the lambda sensor and the engine control system introduces more fuel, and the unburned fuel reacts with the additional O2 on the catalyst surface, increasing the catalyst temperature. In this manner, the target aging temperature of 700 °C can be reached in the midbed of the catalyst. Detailed process descriptions were provided in previous studies [15,17,18].
To expose the lubricant additives to the TWC, the lubricant additive was mixed with gasoline (E10) to generate exhaust gases containing the decomposition products of the lubricant additive during engine combustion. The specific exposures were performed in three different scenarios: neat gasoline (no additive or NA), gasoline mixed with conventional ZDDP (ZDDP), and gasoline mixed with the boron-based additive (BR). A study by West et al. [37] measured lubricant consumption rates of several vehicles using standard road cycles, and they reported a “high normal” lubricant consumption rate of 90 kg/km for a 2.4 L gasoline vehicle, and thus this rate, normalized to our 0.35 L genset, was used in this study based on a worst-case scenario. A vehicle must now maintain TWC functionality up to 150,000 miles or 241,000 km, and thus a 2.4 L engine, as referenced above, would consume 22 kg of oil in its lifetime; thus, our 0.35 L genset would be expected to consume 3.2 kg of oil. A typical level of anti-wear additive employed in lubricants is 1% [15,17,18,19], and thus 32 g of ZDDP was exposed to the TWC in this study. For the B-based additive, we exposed an equivalent molar dose of B as P. Accounting for the different atomic weights and B/P content in the additives, 150 g of B-based AR9100 additive was introduced to the gasoline. The genset was operated at a catalyst temperature of 700 °C for approximately 24 h over 4 days of operation to expose the TWC to the required additive dose of 32 or 150 g.
2.4. TWC Performance Evaluation Protocols
After accelerated engine aging, core samples were removed with a diameter of 2.2 cm and a length of 2.5 cm to fit the size of the quartz tube. Since more lubricant additive components were deposited in the front of the TWC in a previous study [38], the performance evaluation is performed using the first 2.5 cm portion of the catalyst inlet. Three type-K thermocouples were used to measure the catalyst's inlet and outlet gas temperatures and midbed temperature of the catalyst. A MIDAC Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) analyzer was used to measure the gaseous concentrations of NO, CO, C3H6, C3H8, CO2, NH3, and N2O at the inlet and exit of the catalyst. In this study, the simulated gas composition of the Stoichiometric Gasoline Direct Injection (S-GDI) combustion mode is specified by a protocol prescribed by an earlier report [35], and a more detailed description of the evaluation protocols is provided in previous studies [15,17,39]. In the BFR, all TWC performance evaluations were performed at a gas hourly space velocity (GHSV) of 60,000 h-1. Prior to performance evaluation of all accelerated engine-aged TWC samples, a desulfation process consisting of several 2 min lean and 2 min rich cycles was carried out at a gas inlet temperature of 700 °C for a total of 2 h. The gas composition during the desulfation process consists of 0.3% O2, 0.2% H2, 13% H2O, and N2 balanced in a lean cycle and 0.3% O2, 1.0% CO, 13% H2O, and N2 balanced in a rich cycle. After desulfation, an O2 sweep experiment was carried out to determine the optimal concentration of O2 for the TWC reactions. In the present study, the optimal condition is indicated by an abrupt increase in NO concentration between stoichiometric and fuel-lean conditions. Variation of the O2 concentration between 0.4 and 0.8% was performed on all TWC samples at an inlet gas temperature of 500 °C to precisely identify the optimal concentration. The simulated exhaust gas composition for the S-GDI combustion mode consisted of 850 ppm C3H6, 100 ppm C3H8, 0.5% CO, 0.1% NO, 0.167% H2, 13% H2O, 13% CO2, and balanced N2.
To evaluate the effect of lubricant additives on TWC reactivity, a temperature programmed reaction was performed by increasing the furnace temperature from 100 °C to 600 °C at a rate of 5 °C/min. In this experiment, the conversion of NO, CO, C3H6, and C3H8 as a function of temperature was obtained in the form of the light-off curve from which the 50% (T50) and 90% (T90) conversion temperatures were determined. The simulated exhaust gas consisted of 850 ppm C3H6, 100 ppm C3H8, 0.5% CO, 0.1% NO, 0.167% H2, 13% H2O, 13% CO2, and N2 balanced with O2 concentration corresponding to optimal conditions obtained from O2 sweep experiments. Another assessment of TWC reactivity, the WGS reaction (CO + H2O → H2 + CO2) experiment, was performed in a temperature range between 200 °C and 550 °C in 50 °C increments. The gas composition of WGS reaction consisted of 0.5% CO, 13% H2O, and balanced N2. Additionally, the oxygen storage capacity (OSC) of the TWC was performed to assess the impact of lubricant additives on the OSC of ceria (CeO2/Ce2O3). The OSC experiment was carried out in a temperature range between 300 and 550 °C in 50 °C increments using lean (0.72% O2 and N2 balance) and rich (0.5% CO and N2 balance) of 2 min each for a total of 4 cycles.
2.5. Surface Characterization Studies
Surface characterization techniques, including inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) analysis, N2 physisorption analysis, electron probe microanalysis (EPMA), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, were used to identify and elucidate the deactivation mechanisms and morphological changes of the accelerated engine-aged TWC samples. To minimize the effect of cordierite on the characterization results, the TWC washcoat was separated from the cordierite substrate and used in XRD and N2 physisorption analysis.
Electron probe microanalysis (EPMA) was used to identify structural damage of the alumina washcoat and to obtain qualitative elemental maps of P and B at a cross-section of the washcoat. EPMA was performed using a JXA-8200 (JEOL) microprobe equipped with a backscatter detector and five wavelength-dispersive spectrometers (WDS).
Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was used to detect the physicochemical properties of the washcoat components due to thermal aging, such as the average PGM crystal size; phase transition of γ-Al2O3. XRD analysis was also used to identify compounds formed on the washcoat due to exposure to lubricant additives. The XRD patterns were scanned from 5 to 90° with a CuKα radiation source (λ = 1.540598 Å) in a scan mode of 0.02° in 2 s using the PANalytical X’Pert diffractometer. All scans used a 10 mm mask (beam length) coupled with 1/4° fixed slits, a 1/2° anti-scatter slit, and a 0.02 rad soller slit. A search match was performed using Jade software and powder diffraction files (PDF) from the International Center for Diffraction Data (ICDD) database for the phase identification procedure.
Inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) was used to quantitatively measure the total concentration of P and B in accelerated engine-aged TWC samples. The ICP-OES analysis conducted by Galbraith Laboratories was performed by fusing TWC powder samples in a Bunsen burner with sodium peroxide (Na2O2) and then dissolving the product in water.
N2 physisorption analysis was performed to measure the BET surface area, pore size distribution, and pore volume of accelerated engine-aged TWC samples using a Quantachrome gas sorption system (Autosorb iQ). In this study, the degassing process was carried out for 3 h at 180 °C while flowing a mixture of He and N2. Pore size distribution and pore volume were calculated from the desorption isotherms by the Barrett, Joyner, and Halenda (BJH) method.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance Evaluation on Bench-Flow Reactor (BFR)
The O2 sweep experiment was performed at an inlet gas temperature of 500 °C to determine the optimal concentration of O2 based on the sudden increase in NO concentration. This is a critical step due to the sensitivity of the stoichiometric reactions to oxygen concentrations, and even minor errors in the mass flow controllers can lead to significant losses in either CO/THC or NO conversions in the TWC evaluation. Of these, NO is the most sensitive to O2 concentration, and thus its concentration will sharply increase as soon as there is excess oxygen available. Figure 1 shows the effect of O2 on the concentration of NO for NA-, ZDDP-, and BR-aged TWC samples. As seen in Figure 1, a drastic increase in NO concentration was observed at an O2 concentration of 0.73%, indicating an experimentally determined optimal O2 concentration for all TWC samples. This value/mass flow controller setting is used in the subsequent TWC evaluations.
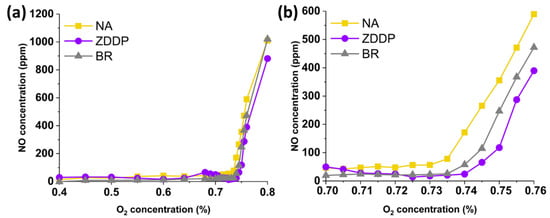
Figure 1.
Effect of O2 concentration on the concentration of NO for NA-, ZDDP-, and BR-aged TWC samples at 500 °C with O2 concentration varying between (a) full scale and (b) zoomed in.
Figure 2a–d show light-off curves for NO, CO, C3H6, and C3H8 of NA-, ZDDP-, and BR-aged TWC samples. Additionally, the formation of the byproducts NH3 and N2O is shown in Figure 2e,f, respectively. The sensitivity of the NO reaction to local conditions at the catalyst surface makes it difficult to fully assess the impact of the additives on its reactivity (Figure 2a); however, as seen in Figure 2b–d, for the ZDDP-aged TWC sample, the conversion of CO, C3H6, and C3H8 occurs at higher temperatures as compared with the NA-aged (thermal aging only) TWC sample, whereas the NA- and BR-aged TWC samples are similar. This means that a significant reduction of reactivity is observed due to the ZDDP lubricant additive, but the B-containing lubricant additive (BR) had little impact on the performance of the TWC.
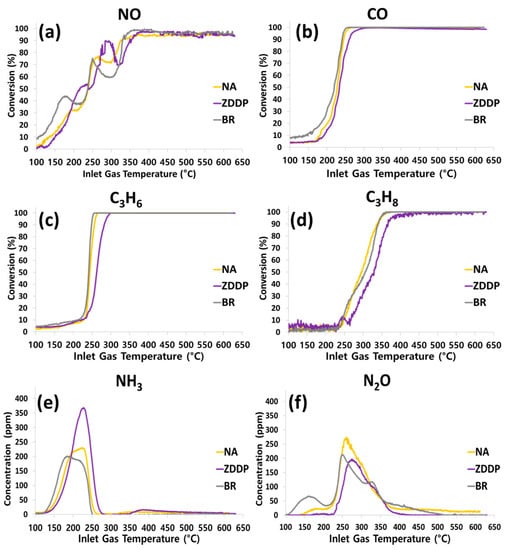
Figure 2.
Effect of inlet gas temperature on the conversion of (a) NO, (b) CO, (c) C3H6, and (d) C3H8 and on the formation of (e) NH3 and (f) N2O for NA-, ZDDP-, and BR-aged TWC samples at 0.73% O2.
From the light-off curves, the temperatures of 50% (T50) and 90% (T90) conversion of NO, CO, C3H6, and C3H8 for all TWC samples are given in Figure 3a,b, respectively. The error bars shown indicate the variances from three repeated runs and are generally less than 5 °C across each sample evaluated. As shown in Figure 3, the T50 for the ZDDP-aged TWC sample increases by 17, 28, and 31 °C for CO, C3H6, and C3H8, respectively, as compared with the NA-aged TWC sample; the T90 indicates even higher increases of 34, 30, 37, and 48 °C for NO, CO, C3H6, and C3H8, respectively. However, in the case of the BR-aged TWC sample, the T50 and T90 of all gas species are comparable to the NA-aged TWC sample. These results are generally consistent with the previous vehicle-based study [34] and indicate that our accelerated aging approach reasonably reproduces the unaccelerated study. To better understand this impact, both the individual reactions and the material characterization studies will help to elucidate the effect of two different lubricant additives on the light-off temperatures of engine-aged TWCs.
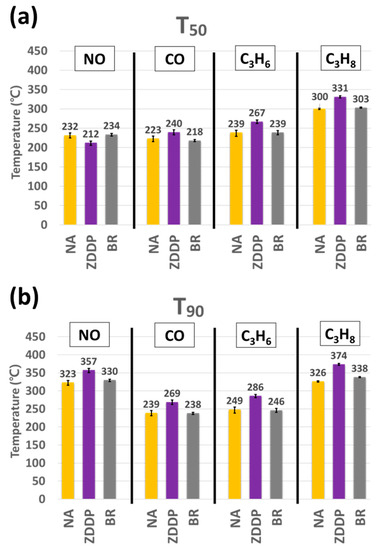
Figure 3.
(a) T50 and (b) T90 of NO, CO, C3H6, and C3H8 for NA-, ZDDP-, and BR-aged TWC samples.
Figure 4 shows the water–gas shift (WGS) reaction for NA-, ZDDP-, and BR-aged TWC samples between 200 and 550 °C at 50 °C increments. This reaction is one of the most important reactions over the TWC under fuel-rich conditions, in which CO and H2O in the exhaust gas are converted to CO2 and H2, thus allowing more margin for NOx reduction while still maintaining low CO emissions. As seen in Figure 4, the degradation of the WGS reactivity for the ZDDP-aged TWC sample is significantly degraded compared with the NA case above 350 °C. However, the WGS reactivity observed in the BR-aged TWC sample is similar to or better than that observed in the NA-aged TWC sample. This further illustrates that the lack of impact from B-based additives can have broad benefits in TWC chemistry.
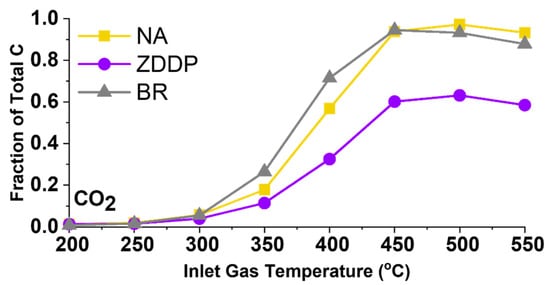
Figure 4.
Formation of CO2 in water–gas shift (WGS) reaction for NA-, ZDDP-, and BR-aged TWC samples at inlet gas temperatures between 200 °C and 550 °C.
The oxygen storage capacity (OSC) measurements were performed to probe the interactions of the lubricant additives on ceria functionality. Cerium oxide (CeO2/Ce2O3) is an important component of TWCs, which improves the conversion of CO, HC, and NOx by storing and releasing oxygen according to Ce4+/Ce3+ redox reactions [40]. Additionally, this redox functionality allows fluctuations around stoichiometric operation since the stored oxygen can be used when there is insufficient gas phase O2, or it can store oxygen and remove it from the active surface when excess O2 is in the exhaust. It is well known that poisoning from components such as P, S, and Zn in ZDDP lubricant additive adversely affects the OSC of ceria and degrades catalytic performance, but issues with boron have not been reported [10,11,12,13,14,15,17,18]. Figure 5 shows that the OSC for the ZDDP-aged TWC sample is 25 to 40% lower compared with NA case or BR-aged TWC samples. The overall OSC trend of increasing with temperature before leveling off above 450 °C is consistent with prior reports of potential oxygen storage limitations as a result of bulk diffusion above 450 °C [41].
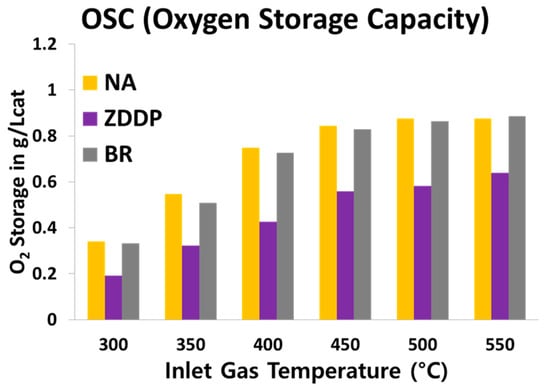
Figure 5.
Oxygen storage capacity (OSC) for NA-, ZDDP-, and BR-aged TWC samples at inlet gas temperatures between 300 °C and 550 °C in a 50 °C increment.
3.2. Characterization Studies
The notable lack of impact from boron may be due to it passing through the TWC without sticking, so further investigations were performed to measure the amount of boron, zinc, and phosphorous that accumulated in the TWC. ICP-OES was employed to quantify the total concentrations of P and Zn in each TWC sample. Figure 6a,b show the weight percentages for P and Zn, respectively, in each TWC sample. As expected, the ZDDP-aged TWC sample has the highest concentration of P and Zn with the amount of 1.38 wt% and 0.06 wt%, respectively. A small amount of P is still detected in the NA- and BR-aged TWC samples since a small amount of ZDDP-containing lubricant used in the genset is consumed during the 24-hour run. Zn accumulation is consistently lower even though it is present in equimolar amounts as P, and it has a higher molecular weight of 65 g/mol compared with the 31 g/mol weight of P. This is consistent with prior studies which show the Zn presence is notably lower in emissions control devices [15,17,18,42,43]. ICP-OES results for boron are shown in Figure 7, and its accumulation falls between Zn and P, as only 0.22 wt% boron is observed in the BR-aged TWC sample; its molecular weight is the lowest of all the elements investigated at 11 g/mol, which is approximately three times lower than P. Since B was introduced at an equivalent molar basis as P, it would be expected to accumulate on a weight basis that is also three times lower than P, but it is instead six times lower than P. Thus, P is two times more likely to adsorb in the TWC compared with B, and when P does adsorb, it significantly impacts reactivity.
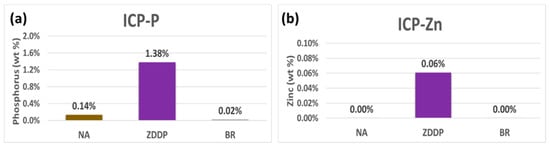
Figure 6.
ICP-OES results of (a) P and (b) Zn in weight percent for NA-, ZDDP-, and BR-aged TWC samples.

Figure 7.
ICP-OES results of B in weight percent for NA- and BR-aged TWC samples.
Once establishing the presence of the additives and how they affect the reactivity of the TWCs, it was important to probe the material properties further. To probe the crystalline phases present in the TWCs, XRD patterns were recorded after trying to remove the washcoat from the highly crystalline cordierite substrate. The results in Figure 8 show largely similar peaks for each sample, with two critical differences relating to the (♠) CePO4 and (○) cordierite phases. CePO4 is clearly more prevalent in the ZDDP-aged sample, which is consistent with the lack of ceria-based OSC in the ZDDP-aged sample. Moreover, although there is a trace amount of CePO4 in both the NA- and BR-aged TWCs, it is significantly muted. The presence of cordierite is expected, as it is difficult to remove the washcoat cleanly from the substrate despite using the techniques. Unfortunately, there is a disproportionate amount in the ZDDP-aged sample, which will have to be taken into consideration in subsequent characterizations. Although large amounts of B were identified in the ICP-OES result (see Figure 7), no peaks associated with boron are observed in the BR-aged TWC sample XRD pattern, which may present in the form of an amorphous phase.

Figure 8.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns for NA-, ZDDP-, and BR-aged TWC samples.
Maintaining a large surface area is important to allow high dispersion of the Pd/Rh active sites and thus maintain high reactivity of the catalyst. Therefore, N2 physisorption analysis, from which the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area measurement and the Barrett, Joyner, and Halenda (BJH) method for pore volume and pore size distribution are obtained, was used to investigate if the lubricant additives accelerated surface area losses. The results of the BET surface area, pore volume, and pore size distribution of each sample are given in Table 1, and indicate similar surface areas of each aged sample, 81–88 m2/g, although the ZDDP-aged sample is the lowest measured surface area which may be due to the additional cordierite in the sample. Further measurements show a clearer picture of the impact though, as the total pore volume is significantly lower in the ZDDP-aged TWC at 0.34 cm3/g vs. 0.42–0.44 cm3/g, although the average pore size is identical at 17.0–17.2 nm for each sample. Such results not only indicate that the compounds produced by the ZDDP components accumulate in the pores without clogging them but that boron does not significantly impact pore access or volume.

Table 1.
BET surface areas (SBET), pore volumes, and average pore sizes of NA-, ZDDP-, and BR-aged TWC samples.
EPMA analysis was performed to obtain a cross-sectional microscopic map of each TWC sample and detect the presence of P and B in the washcoat. The images in Figure 9 show four partial channels of the washcoated substrate with the cordierite material forming a cross shape in the middle (+); the washcoat is a rounded arc filling the corners. The color bar, according to the element wt% intensity, is displayed in the lower left corner of the figures. Elemental maps of P for NA-, ZDDP-, and BR-aged TWC samples are shown in Figure 9. As expected, the ZDDP-aged TWC sample has a large amount of P on the washcoat, and P penetrates into the washcoat but does not saturate the entire catalyst layer. Only a low concentration of P is seen in the NA- and BR-aged TWC samples, and it is solely on the surface of the washcoat. As mentioned earlier, the presence of P in the NA- and BR-aged TWC samples is due to ZDDP-containing lubricant consumption during engine operation and is consistent with the ICP-OES results (Figure 6a). Figure 10 presents EPMA micrographs of B in the washcoat of NA- and BR-aged TWC samples. The sensitivity to low molecular weight B makes the EPMA analysis more difficult, but the similarity between the NA- and BR-aged samples indicates that B is distributed evenly throughout the sample, is not present in an overlayer like P, and is present in low levels, which is also consistent with ICP results. Since there is significant TWC material in the corner, as evidenced in the figure, this technique is a clear indicator of how P can interact with a portion of the TWC, but not shut down all functionality.
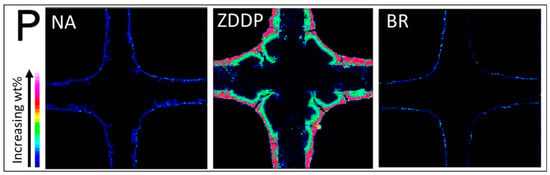
Figure 9.
EPMA elemental maps of P at the inlet of for NA-, ZDDP-, and BR-aged TWC samples.
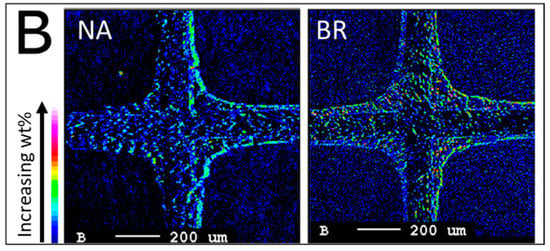
Figure 10.
EPMA elemental maps of B at the inlet of NA- and BR-aged TWC samples.
4. Conclusions
Among commercially used lubricant additives, many studies have been conducted on the effect of ZDDP on TWCs, but verification of B-based lubricant additives is insufficient. Therefore, the effects of the B-containing lubricant additive (AR-9100) on Pd/Rh-based TWC performance and the physicochemical properties were investigated and compared with a no-additive base case (NA) and ZDDP-aged TWC samples. The following results highlight the differences observed:
- Reactivity of the B-exposed samples was minimally affected and compared favorably with the no-additive case (NA).
- ○
- This was demonstrated with light-off temperatures (T50 and T90), WGS reaction, and OSC measurements.
- ○
- Conversely, ZDDP-exposed samples had a significant degradation.
- B is more likely to pass through the TWC without depositing compared with P.
- ○
- ICP-OES confirmed the presence of B on the TWC samples, but the amount collected on the TWC was notably smaller than the P amount in the ZDDP-exposed TWCs.
- ○
- After correcting for molecular weights, P was two times more likely to stick to the TWC compared with B.
- B does not form a detectable crystalline phase on the TWC, unlike the notable presence of CePO4 peaks when P is used.
- ○
- XRD confirmed the presence of CePO4, but no B-related peaks were observed.
- Finally, neither B nor P affect the overall surface area or pore size of the TWC; however, the ZDDP-aged TWC sample pore volume reduced by more than 20%.
In conclusion, since the B-containing lubricant additive (AR-9100) used in this study has little effect on a Pd/Rh-based TWC, it should be strongly considered as a ZDDP replacement for enhanced catalyst durability for vehicle applications, especially if its anti-wear properties can be fully validated.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.K., K.N. and T.J.T.; methodology, D.K., T.J.T., M.J.L. and J.Q.; validation, K.N. and T.J.T.; formal analysis, D.K. and M.J.L.; investigation, D.K.; resources, T.J.T. and J.Q.; data curation, D.K.; writing—original draft preparation, D.K.; writing—review and editing, D.K., K.N. and T.J.T.; visualization, D.K. and M.J.L.; supervision, K.N. and T.J.T.; project administration, T.J.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Vehicle Technologies Office (VTO). The authors gratefully acknowledge the support and direction of Kevin Stork, Siddiq Khan, Mike Weismiller, and Gurpreet Singh.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Twigg, M.V. Progress and Future Challenges in Controlling Automotive Exhaust Gas Emissions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 70, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, P.; Lamonier, J.F.; Sergent, N.; Aboukais, A.; Leclercq, L. Investigation of the Intrinsic Activity of ZrxCe1-xO2 Mixed Oxides in the CO+ NO Reactions: Influence of Pd Incorporation. Top. Catal. 2001, 16, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, R.M.; Farrauto, R.K.; Gulati, S. Catalytic Air Pollution Control: Commercial Technology. Platin. Met. Rev. 2010, 54, 180–183. [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa, M.; Kimura, M. Effect of Cerium Addition on the Thermal Stability of Gamma Alumina Support. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1990, 9, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtin, P.; Brunelle, J.P.; Pijolat, M.; Soustelle, M. Influence of Surface Area and Additives on the Thermal Stability of Transition Alumina Catalyst Supports. I: Kinetic Data. Appl. Catal. 1987, 34, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beguin, B.; Garbowski, E.; Primet, M. Stabilization of Alumina toward Thermal Sintering by Silicon Addition. J. Catal. 1991, 127, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulijn, J.A.; van Diepen, A.E.; Kapteijn, F. Catalyst Deactivation: Is It Predictable?: What to Do? Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 212, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, H.S.; Wlliamson, W.B.; Bomback, J.L. Deactivation of Three-Way and Oxidation Catalyst Dual Bed Emission Control Systems: Catalyst Post Mortem Analyses from Methanol-Fueled Vehicles. Appl. Catal. 1982, 3, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, W.B.; Perry, J.; Goss, R.L.; Gandhi, H.S.; Beason, R.E. Catalyst Deactivation Due to Glaze Formation from Oil-Derived Phosphorus and Zinc. SAE Tech. Pap. 1984, 841406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokosz, M.J.; Chen, A.E.; Lowe-Ma, C.K.; Kucherov, A.V.; Benson, D.; Paputa Peck, M.C.; McCabe, R.W. Characterization of Phosphorus-Poisoned Automotive Exhaust Catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2001, 33, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Guo, G.; Uy, D.; O’Neill, A.E.; Weber, W.H.; Rokosz, M.J.; McCabe, R.W. Cerium Phosphate in Automotive Exhaust Catalyst Poisoning. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2004, 50, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larese, C.; Cabello Galisteo, F.; López Granados, M.; Mariscal, R.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Furió, M.; Fernández Ruiz, R. Deactivation of Real Three Way Catalysts by CePO4 Formation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 40, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uy, D.; O’Neill, A.E.; Xu, L.; Weber, W.H.; McCabe, R.W. Observation of Cerium Phosphate in Aged Automotive Catalysts Using Raman Spectroscopy. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 41, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidis, T.N.; Sklavounos, S.A. A SEM-EDS Study of New and Used Automotive Catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1995, 133, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Toops, T.; Nguyen, K.; Brookshear, D.; Lance, M.J.; Qu, J. Impact of Lubricant Oil Additives on the Performance of Pd-Based Three-Way Catalysts. Emiss. Control. Sci. Technol. 2020, 6, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Nam, J. Impact of High-Temperature Desulfation on the Performance of Pd-Based TWC. J. Adv. Mar. Eng. Technol. 2021, 45, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Toops, T.J.; Nguyen, K.; Lance, M.J.; Qu, J. Impact of Primary and Secondary ZDDP and Ionic Liquid as Lubricant Oil Additives on the Performance and Physicochemical Properties of Pd-Based Three-Way Catalysts. Catalysts 2021, 11, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Toops, T.J.; Lance, M.J.; Qu, J.; Viola, M.B.; Lewis, S.A.; Leonard, D.N.; Hagaman, E.W. Impact of Lubricant Additives on the Physicochemical Properties and Activity of Three-Way Catalysts. Catalysts 2016, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Barnhill, W.C.; Luo, H.; Meyer III, H.M.; Leonard, D.N.; Landauer, A.K.; Kheireddin, B.; Gao, H.; Papke, B.L.; Dai, S. Synergistic Effects between Phosphonium-alkylphosphate Ionic Liquids and Zinc Dialkyldithiophosphate (ZDDP) as Lubricant Additives. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4767–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, F.U.; Glavatskih, S.; Antzutkin, O.N. Boron in Tribology: From Borates to Ionic Liquids. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 51, 281–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, B.A. Relative Antiwear Efficiency of Boron and Sulfur Surface Species. Wear 1977, 45, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jin, Z.; Xue, Q. The Performance and Antiwear Mechanism of S-containing Organic Borate as an Oil Additive. Lubr. Sci. 1994, 7, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junbin, Y. Antiwear Function and Mechanism of Borate Containing Nitrogen. Tribol. Int. 1997, 30, 387–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdemir, A.; Bindal, C.; Zuiker, C.; Savrun, E. Tribology of Naturally Occurring Boric Acid Films on Boron Carbide. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1996, 86, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuz, K.L.; Fein, R.S.; Dundy, M. EP Films from Borate Lubricants. Asle Trans. 1967, 10, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.M.; Mogne, T.L.; Chassagnette, C.; Gardos, M.N. Friction of Hexagonal Boron Nitride in Various Environments. Tribol. Trans. 1992, 35, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskilinna, J.O.; Linnolahti, M.; Pakkanen, T.A. Friction Coefficient for Hexagonal Boron Nitride Surfaces from Ab Initio Calculations. Tribol. Lett. 2006, 24, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.S.; Yie, Y.; Wang, L.G.; Chen, G.X.; Dong, J.X. Synthesis and Tribological Properties of Ferrous Octoxyborate as Antiwear and Friction-Reducing Additive of Lubricating Oil. Tribol. Lett. 2000, 8, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdan, J.M. Friction Modifiers in Engine and Gear Oils. Lubr. Sci. 2000, 12, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; Xue, Q. The Tribological Properties of the Heterocyclic Compound Containing S, N, O, and B as Additive in Liquid Paraffin. Wear 1999, 224, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Zheng, Z.; Wan, Y.; Xu, X.; Cao, L.; Yue, Q.; Sun, T. Synergistic Lubricating Effects of Borate Ester with Heterocyclic Compound. Wear 2000, 246, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Tan, Y.; Dong, J.; Chen, B. Tribological Properties of the Film Formed by Borated Dioctyl Dithiocarbamate as an Additive in Liquid Paraffin. Tribol. Int. 2002, 35, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, L.; Xue, Q. Tribological Properties and Action Mechanism of N,N-Dialkyl Dithiocarbamate-Derived S-Hydroxyethyl Borate Esters as Additives in Rapeseed Oil. Wear 2009, 266, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twigg, M.V.; Collins, N.R.; Morris, D.; O’Connell, T.J.; Ball, I.K.; Arrowsmith, S.; Cassidy, L.; Wrench, P. The Effect of Phosphorus and Boron Lubricant Oil Additives on Catalyst and Engine Durability. SAE Trans. 2004, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappé, K.G.; DiMaggio, C.; Pihl, J.A.; Theis, J.R.; Oh, S.H.; Fisher, G.B.; Parks, J.; Easterling, V.G.; Yang, M.; Stewart, M.L.; et al. Aftertreatment Protocols for Catalyst Characterization and Performance Evaluation: Low-Temperature Oxidation, Storage, Three-Way, and NH3-SCR Catalyst Test Protocols. Emiss. Control. Sci. Technol. 2019, 5, 183–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friction Modifier, SDS No. AR9100 1. 2. 0. Archoil: Norfolk, UK, 23 February 2012. Available online: https://oil-club.de/wcf/index.php?attachment/22403-sds-ar9100-nlen-pdf/ (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- West, B.; Sluder, C.S. Lubricating Oil Consumption on the Standard Road Cycle. In Proceedings of the SAE World Congress, Detroit, UM, USA, 16 April 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culley, S.A.; McDonnell, T.F.; Ball, D.J.; Kirby, C.W.; Hawes, S.W. The Impact of Passenger Car Motor Oil Phosphorus Levels on Automotive Emissions Control Systems. SAE Tech. Pap. 1996, 105, 1216–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D. Effect of Analyzer Scan Time on the Oxygen Storage Capacity Performance in Pd-Based TWCs. J. Adv. Mar. Eng. Technol. 2021, 45, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Hu, Z.; Yao, M.; Li, Y. A Review on the Pd-Based Three-Way Catalyst. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 2015, 57, 79–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedrane, S.; Descorme, C.; Duprez, D. Investigation of the Oxygen Storage Process on Ceria- and Ceria–Zirconia-Supported Catalysts. Catal. Today 2002, 75, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, S.J.; Bunting, B.G.; Toops, T.J.; Nguyen, K. The Role of Phosphorus and Soot on the Deactivation of Diesel Oxidation Catalysts. J. Soc. Automot. Eng. Jpn. 2009, 1, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunting, B.G.; More, K.; Lewis, S.; Toops, T. Phosphorous Poisoning and Phosphorous Exhaust Chemistry with Diesel Oxidation Catalysts. SAE Tech. Pap. 2005, 1, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).