Effect of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Metastable Dual-Phase High Entropy Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Alloy Processing
2.2. Friction Stir Processing
2.3. Micro Tensile Test
2.4. Microstructural Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Composition and Microstructure of the Cold-Rolled and Annealed Sample
3.2. Friction Stir Processed Samples: Microstructural Evolution
3.3. Friction Stir Processed Samples: Changes in Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
- Friction stir processing significantly reduced the grain size of the material. The samples subjected to one-pass and two-pass FSP showed around 22% and 48% reduction in grain size, respectively.
- Severe plastic deformation during FSP results in a strain induced FCC-to-HCP transformation. The amount of deformation induced HCP phase in the microstructure increases with an increase in the number of FSP passes.
- The evolution of the dual-phase microstructure into a fully martensitic microstructure during tensile testing of annealed and FSPed samples indicates strain induced martensitic transformation is the dominant mode for plasticity.
- Compared to the annealed sample, the samples subjected to one-pass and two-pass FSP showed 90% and 100% increase in yield strength and 12% and 28% decrease in ductility, respectively.
- One-pass FSPed material exhibits a higher work hardening rate and a higher UTS value, as compared to both annealed and two-pass FSPed material. This is due to a combination of two factors, viz., a small grain size and a large fraction of metastable FCC phase in the microstructure of the one-pass material.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Pradeep, K.G.; Deng, Y.; Raabe, D.; Tasan, C.C. Metastable high-entropy dual-phase alloys overcome the strength-ductility trade-off. Nature 2016, 534, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miracle, D.; Majumdar, B.; Wertz, K.; Gorsse, S. New strategies and tests to accelerate discovery and development of multi-principal element structural alloys. Scr. Mater. 2017, 127, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.-J.; Gan, J.-Y.; Chin, T.-S.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Raabe, D. Strong and Ductile Non-equiatomic High-Entropy Alloys: Design, Processing, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties. JOM 2017, 69, 2099–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Tasan, C.C.; Springer, H.; Gault, B.; Raabe, D. Interstitial atoms enable joint twinning and transformation induced plasticity in strong and ductile high-entropy alloys. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaysultanov, D.; Raimov, K.; Stepanov, N.; Zherebtsov, S. Friction Stir Welding of a TRIP Fe49Mn3Crr10Co10C1 High Entropy Alloy. Metals 2021, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nene, S.; Frank, M.; Liu, K.; Sinha, S.; Mishra, R.; McWilliams, B.; Cho, K. Reversed strength-ductility relationship in microstructurally flexible high entropy alloy. Scr. Mater. 2018, 154, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Fujii, H.; Tsumura, T.; Kitagawa, Y.; Nakata, K.; Ikeuchi, K.; Matsubayashi, K.; Michishita, Y.; Fujiya, Y.; Katoh, J. Friction stir processing of 316L stainless steel plate. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2009, 14, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.G.; Ravi, K.R.; Ramakrishnarao, B.; Deshmukh, V.P.; Sharma, A.; Prabhu, N.; Kashyap, B.P. Recrystallization phenomena during friction stir processing of hypereutectic aluminum-silicon alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2013, 44, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.K.; Gunasekaran, G.; Rao, A.G.; Kashyap, B.P.; Prabhu, N. Effect of Multipass Friction Stir Processing on Mechanical and Corrosion Behavior of 2507 Super Duplex Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Komarasamy, M.; Nelaturu, P.; Tang, Z.; Liaw, P.K.; Mishra, R.S. Friction Stir Processing of a High Entropy Alloy Al0.1CoCrFeNi. Min. Met. Mater. Soc. 2015, 67, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarasamy, M.; Kumar, N.; Tang, Z.; Mishra, R.; Liaw, P. Effect of microstructure on the deformation mechanism of friction stir-processed Al0.1CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Mater. Res. Lett. 2014, 3, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Shukla, S.; Komarasamy, M.; Liu, K.; Mishra, R.S. Towards heterogeneous Al x CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy via friction stir processing. Mater. Lett. 2019, 236, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Jia, C.-L.; Wang, Z.-W.; Wu, L.-H.; Ni, D.-R.; Li, Z.-K.; Fu, H.-M.; Xue, P.; Xiao, B.-L.; Ma, Z.-Y.; et al. Achieving a High–Strength CoCrFeNiCu High–Entropy Alloy with an Ultrafine–Grained Structure via Friction Stir Processing. Acta Metall. Sin. Engl. Lett. 2020, 33, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Nene, S.S.; Frank, M.; Mishra, R.S. Effect of Strain Rate on Deformation Response of Metastable High Entropy Alloys Upon Friction Stir Processing. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2020, 51, 5043–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittiho, A.; Bhattacharyya, M.; Graves, J.; Nene, S.S.; Mishra, R.S.; Charit, I. Friction stir processing of a high entropy alloy Fe42Co10Cr15Mn28Si5 with transformative characteristics: Microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 28, 102635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nene, S.S.; Liu, K.; Frank, M.; Mishra, R.S.; Brennan, R.E.; Cho, K.C.; Li, Z.; Raabe, D. Enhanced strength and ductility in a friction stir processing engineered dual phase high entropy alloy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Raabe, D. Influence of compositional inhomogeneity on mechanical behavior of an interstitial dual-phase high-entropy alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 210, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Raabe, D.; Li, Z. Hierarchical microstructure design to tune the mechanical behavior of an interstitial TRIP-TWIP high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2018, 163, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muribwathoho, O.; Mabuwa, S.; Msomi, V. Review on Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing of Aluminium Alloys. Preprint 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Cao, G.; Zhang, W.; Qiu, C.; Zhang, D. Ductility improvement of an AZ61 magnesium alloy through two-pass submerged friction stir processing. Materials 2017, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauri, R.; Yadav, D.; Suhas, G. Effect of friction stir processing (FSP) on microstructure and properties of Al-TiC in situ composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 4732–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tasan, C.C.; Pradeep, K.G.; Raabe, D. A TRIP-assisted dual-phase high-entropy alloy: Grain size and phase fraction effects on deformation behavior. Acta Mater. 2017, 131, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Zeng, L.; Du, H.; Wang, Q.; Fan, Z.; Liu, X. Combined effects of solute drag and Zener pinning on grain growth of a NiCoCr medium-entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2021, 136, 107271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Nene, S.S.; Frank, M.; Sinha, S.; Mishra, R.S. Metastability-assisted fatigue behavior in a friction stir processed dual-phase high entropy alloy. Mater. Res. Lett. 2018, 6, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, E. Effect of multi-pass friction stir processing on mechanical properties for AA2024/Al2O3 nanocomposites. Materials 2017, 10, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rayes, M.M.; El-Danaf, E.A. The influence of multi-pass friction stir processing on the microstructural and mechanical properties of Aluminum Alloy 6082. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Rao, A.; Balasundar, I.; Kashyap, B.; Prabhu, N. On the microstructure evolution in friction stir processed 2507 super duplex stainless steel and its effect on tensile behaviour at ambient and elevated temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 719, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Wang, B.; An, X.; Ni, D.; Xiao, B.; Ma, Z. Improved cyclic softening behavior of ultrafine-grained Cu with high microstructural stability. Scr. Mater. 2019, 166, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yan, D.; Gan, K.; Lu, W.; Li, Z. Awakening the metastability of an interstitial high entropy alloy via severe deformation. Scr. Mater. 2021, 191, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nene, S.S.; Frank, M.; Liu, K.; Mishra, R.S.; McWilliams, B.A.; Cho, K.C. Extremely high strength and work hardening ability in a metastable high entropy alloy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, J.A.; Bolmaro, R.E.; Jorge, A.M.; Zhilyaev, A.; Cabrera, J.M. Prediction of Generation of High- and Low-Angle Grain Boundaries (HAGB and LAGB) During Severe Plastic Deformation. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2020, 51, 4674–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadmanjiri, J.; Berndt, C.C.; Kapoor, A.; Wen, C. Development of Surface Nano-Crystallization in Alloys by Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment (SMAT). Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2015, 40, 164–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starink, M.; Wang, S. A model for the yield strength of overaged Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 5131–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD) Analysis of Cracking in Polycrystalline Materials. Technical Note. AMETEK Mater. Anal. Div. 2015, pp. 85–90. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/41845100/Electron_Backscatter_Diffraction_in_Materials_Science_Second_Edition (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Huo, S.H.; Qian, M.; Schaffer, G.B.; Crossin, E. Fundamentals of Aluminium Metallurgy: Production, Processing and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, S.; Mirshams, R.A.; Wang, T.; Nene, S.S.; Frank, M.; Liu, K.; Mishra, R.S. Nanoindentation behavior of high entropy alloys with transformation-induced plasticity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Jia, N.; Ma, D.; Yan, H.; Li, Z.; Raabe, D. Joint contribution of transformation and twinning to the high strength-ductility combination of a FeMnCoCr high entropy alloy at cryogenic temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 759, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Li, D.; Yang, C.; Fu, L.; Kong, D.; Lu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, D.; Guan, P.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Direct Atomic-Scale Observation of Ultrasmall Ag Nanowires that Exhibit fcc, bcc, and hcp Structures under Bending. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 128, 015701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, E.C. The Nature of Martensite. Trans. AIME 1924, 70, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Thomas, S.L.; Srolovitz, D.J. Grain-boundary kinetics: A unified approach. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 98, 386–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Zhou, H.; He, J.; Liu, P.; Chen, M.; Han, J.; Srolovitz, D.J.; Teng, J.; et al. Tracking the sliding of grain boundaries at the atomic scale. Science 2022, 375, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NaghiZadeh, M.; Mirzadeh, H. Effects of Grain Size on Mechanical Properties and Work-Hardening Behavior of AISI 304 Austenitic Stainless Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2019, 90, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehetbauer, M.J.; Zhu, Y.T. (Eds.) Bulk Nanostructured Materials; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dieter, G.E.; Bacon, D. Mechanical Metallurgy; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Qiu, L.; Sun, X.; Zuo, L.; Liaw, P.; Raabe, D. Effects of retained austenite volume fraction, morphology, and carbon content on strength and ductility of nanostructured TRIP-assisted steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 636, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.; Lawrence, B.; Boyd, J.; Pilkey, A. Effect of microstructure on retained austenite stability and work hardening of TRIP steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 4516–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
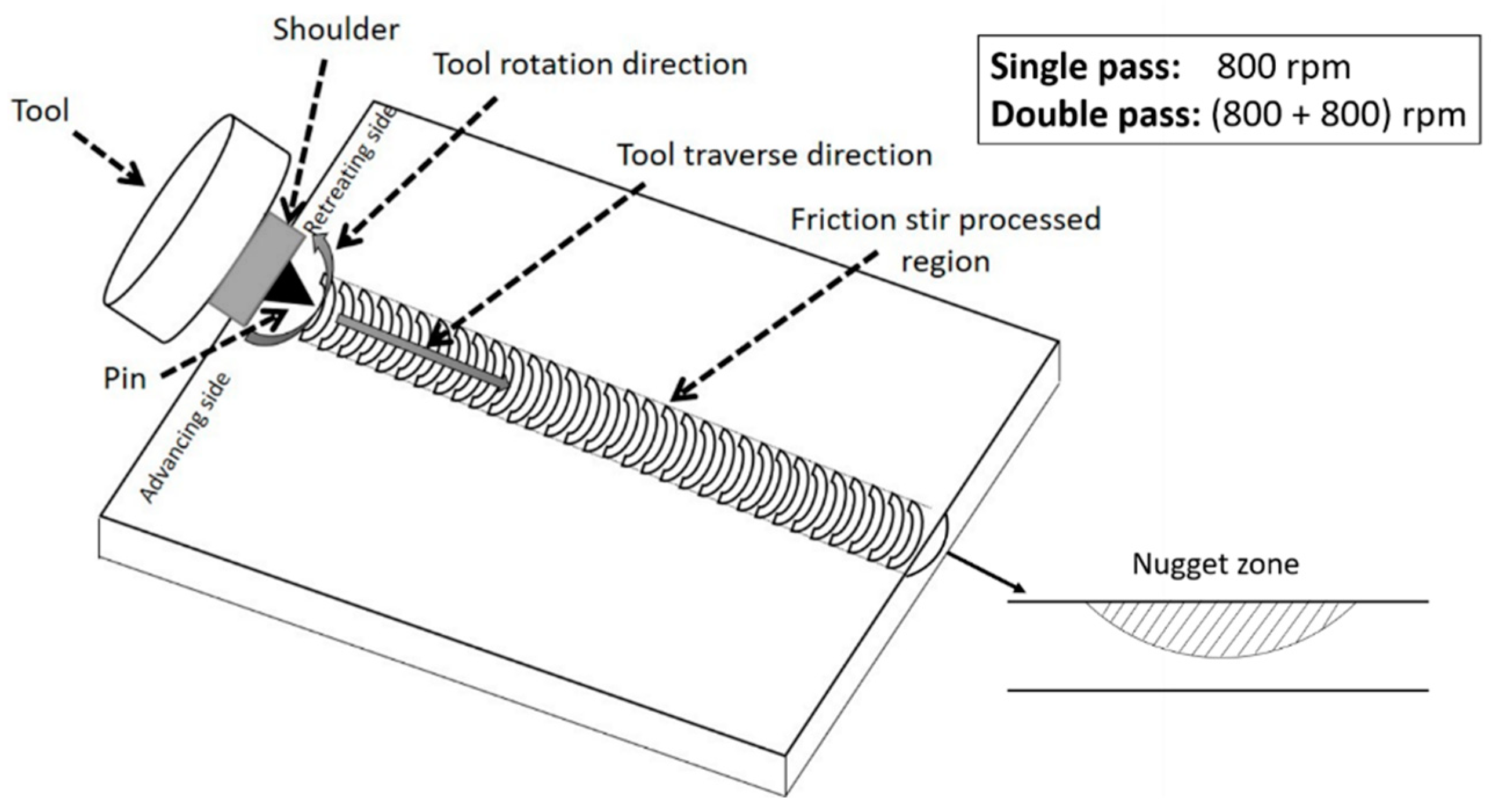













| Tool material | W-La2O3 |
| Plate thickness | 5 mm |
| Tool rotation speed | 800 rpm |
| Tool traverse speed | 50 mm/min |
| Shoulder dia. | 22 mm |
| Pin dia. | 14 mm |
| Pin length | 4 mm |
| Fe | Mn | Co | Cr | C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wt.% | 49 ± 0.94 | 30 ± 0.80 | 9 ± 0.28 | 10 ± 0.64 | 0.11 ± 0 |
| At.% | 48 ± 0.93 | 30 ± 0.45 | 9 ± 0.47 | 10 ± 0.67 | 0.51 ± 0 |
| Yield Strength, MPa | Ultimate Tensile Strength, MPa | Elongation, % | Strain-Hardening Exponent, n | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annealed | 291 ± 23 | 710 ± 30 | 63% ± 3 | 0.36 |
| One-pass | 415 ± 9 | 818 ± 18 | 55% ± 4 | 0.38 |
| Two-pass | 437 ± 21 | 768 ± 21 | 45% ± 7 | 0.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meena, N.; Rao, A.G.; Dommeti, S.G.; Prabhu, N. Effect of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Metastable Dual-Phase High Entropy Alloy. Lubricants 2023, 11, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11010002
Meena N, Rao AG, Dommeti SG, Prabhu N. Effect of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Metastable Dual-Phase High Entropy Alloy. Lubricants. 2023; 11(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeena, Neelam, Ardula Gourav Rao, Satya Gowtam Dommeti, and Nithyanand Prabhu. 2023. "Effect of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Metastable Dual-Phase High Entropy Alloy" Lubricants 11, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11010002
APA StyleMeena, N., Rao, A. G., Dommeti, S. G., & Prabhu, N. (2023). Effect of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Metastable Dual-Phase High Entropy Alloy. Lubricants, 11(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11010002





