Effects of Tool Plunging Path on the Welded Joint Properties of Pinless Friction Stir Spot Welding
Abstract
1. Introduction
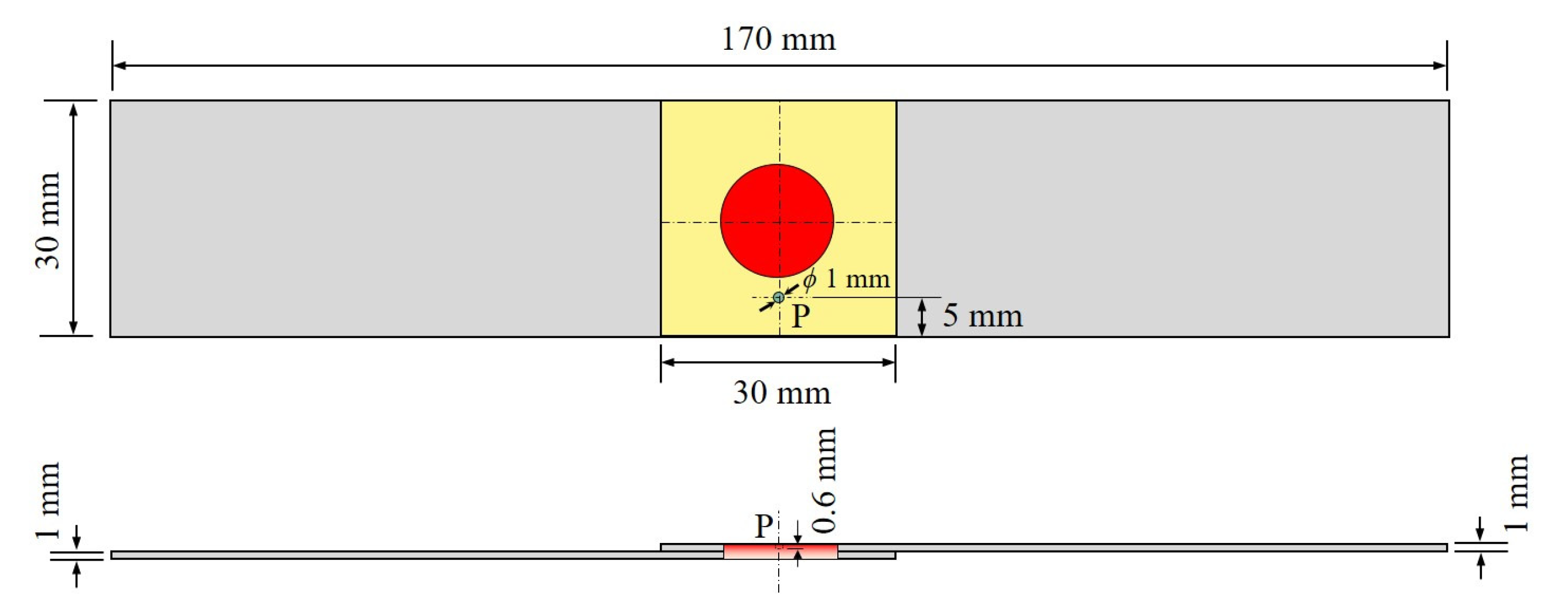
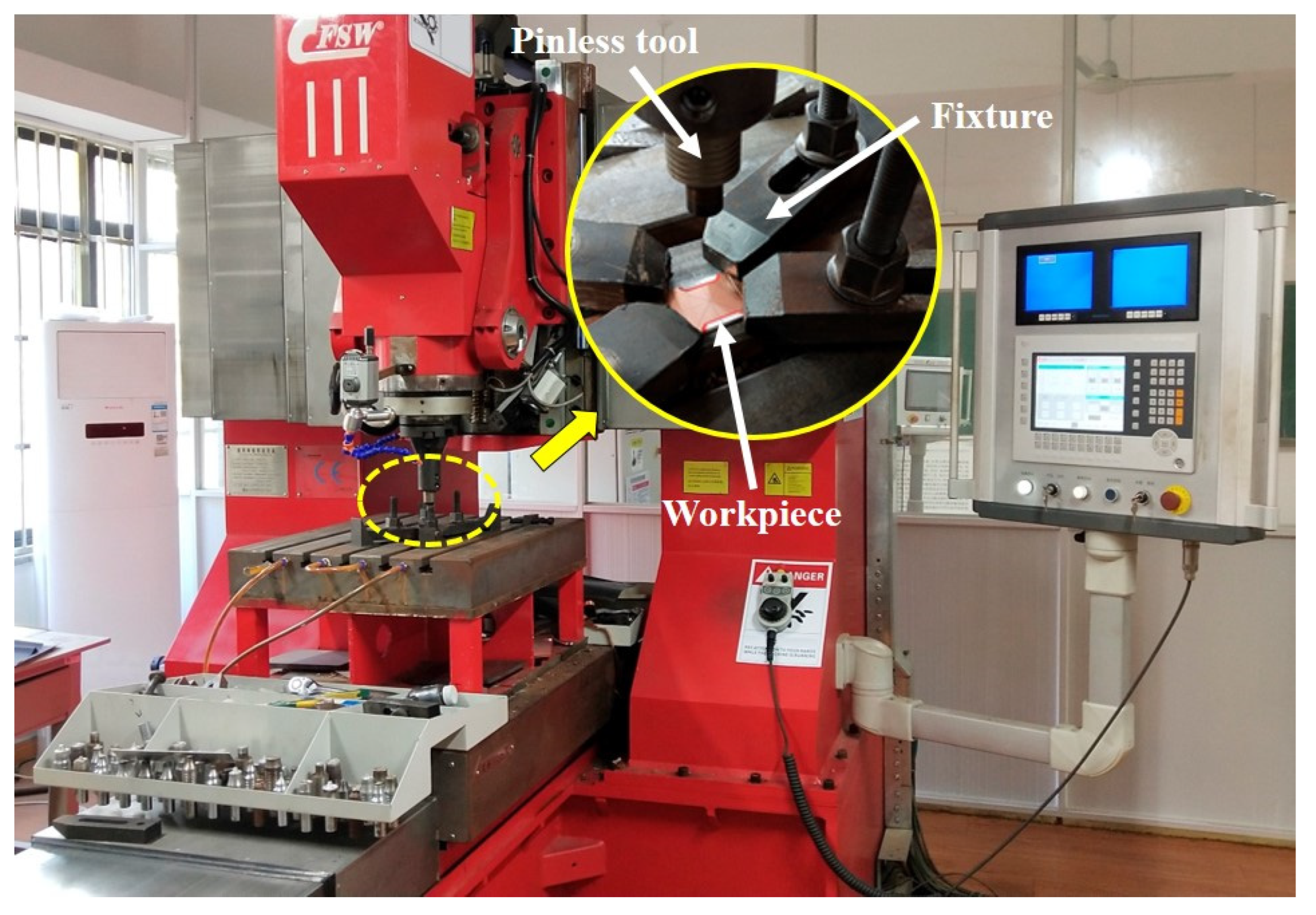
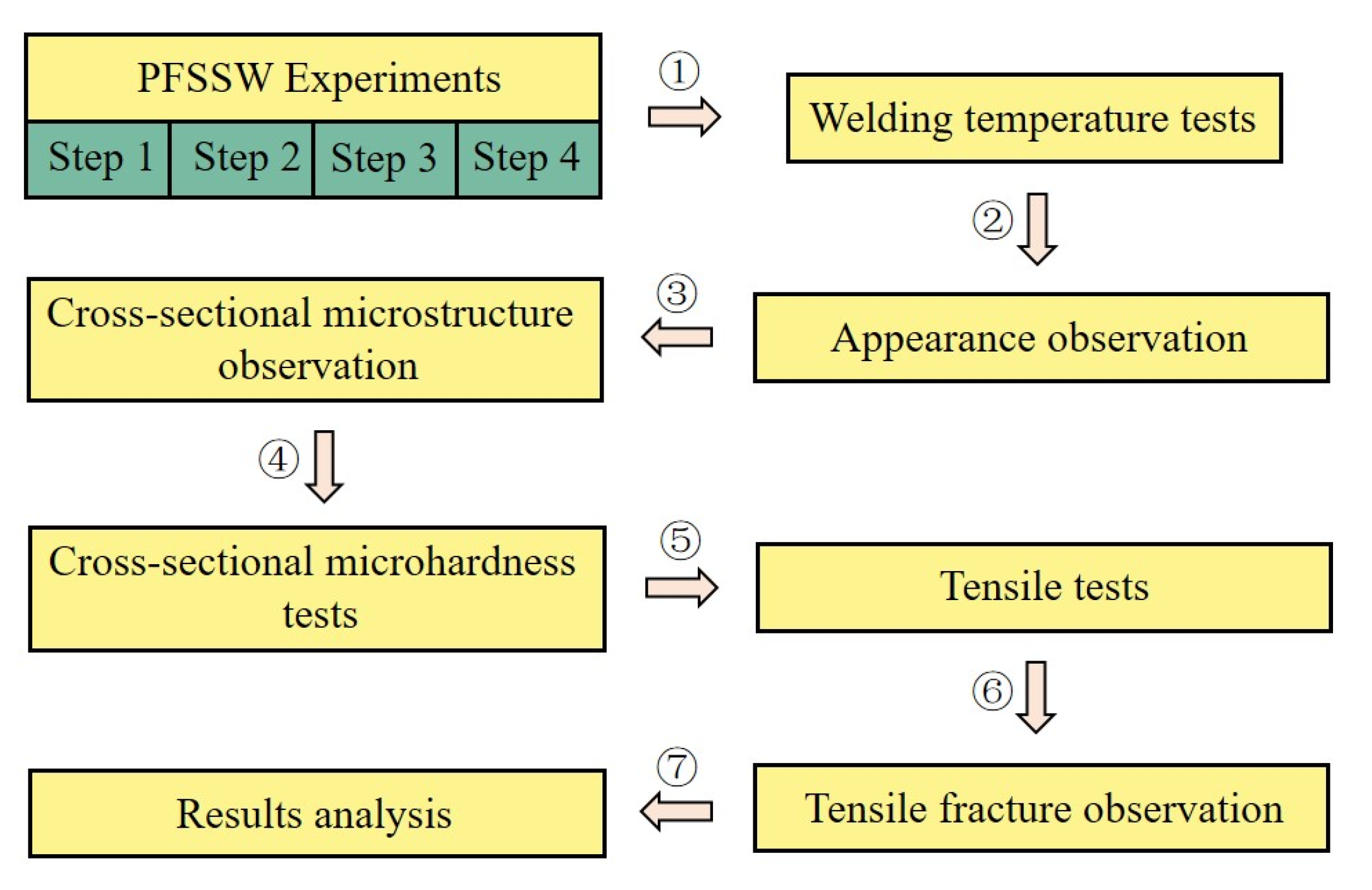
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Appearance Features
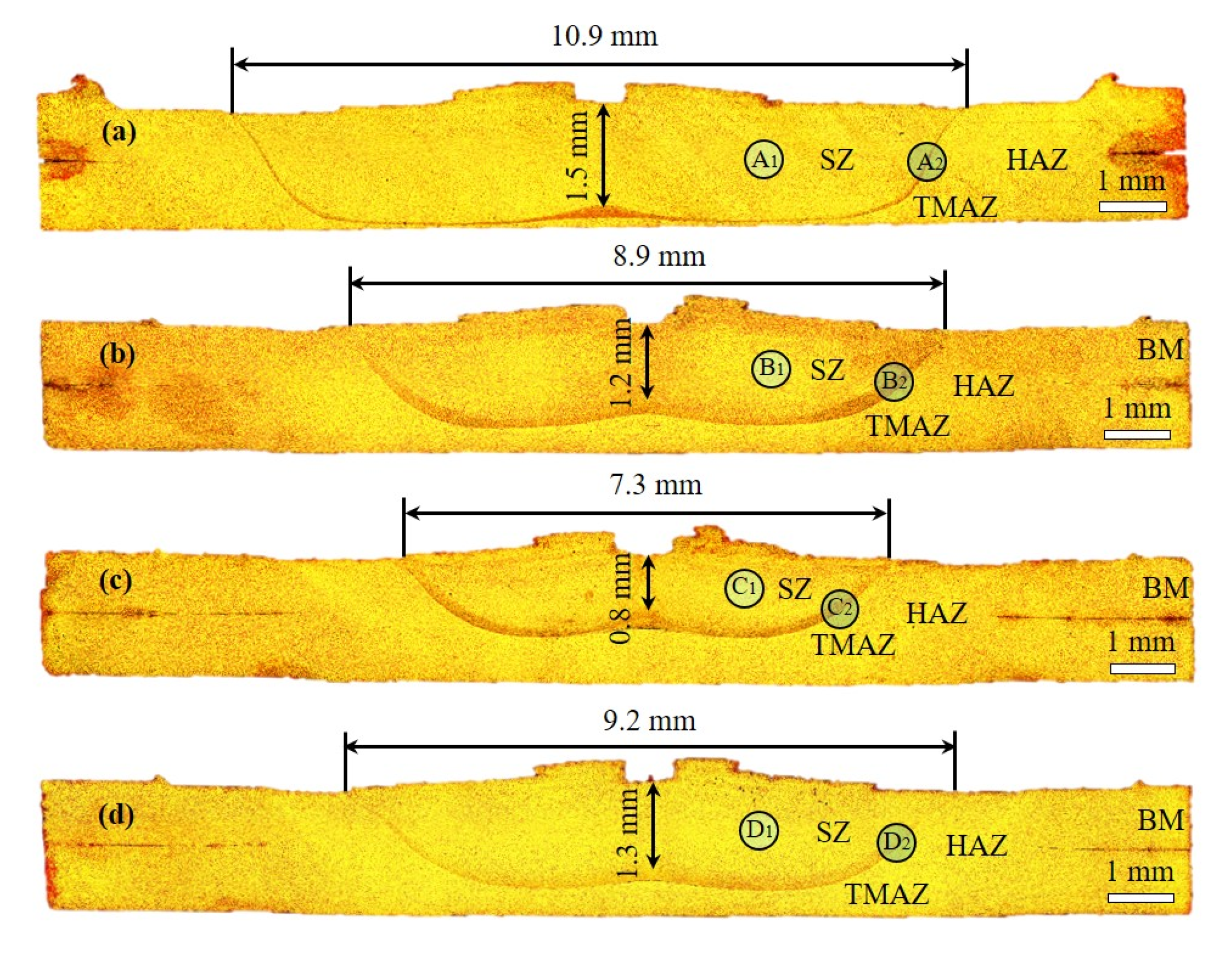
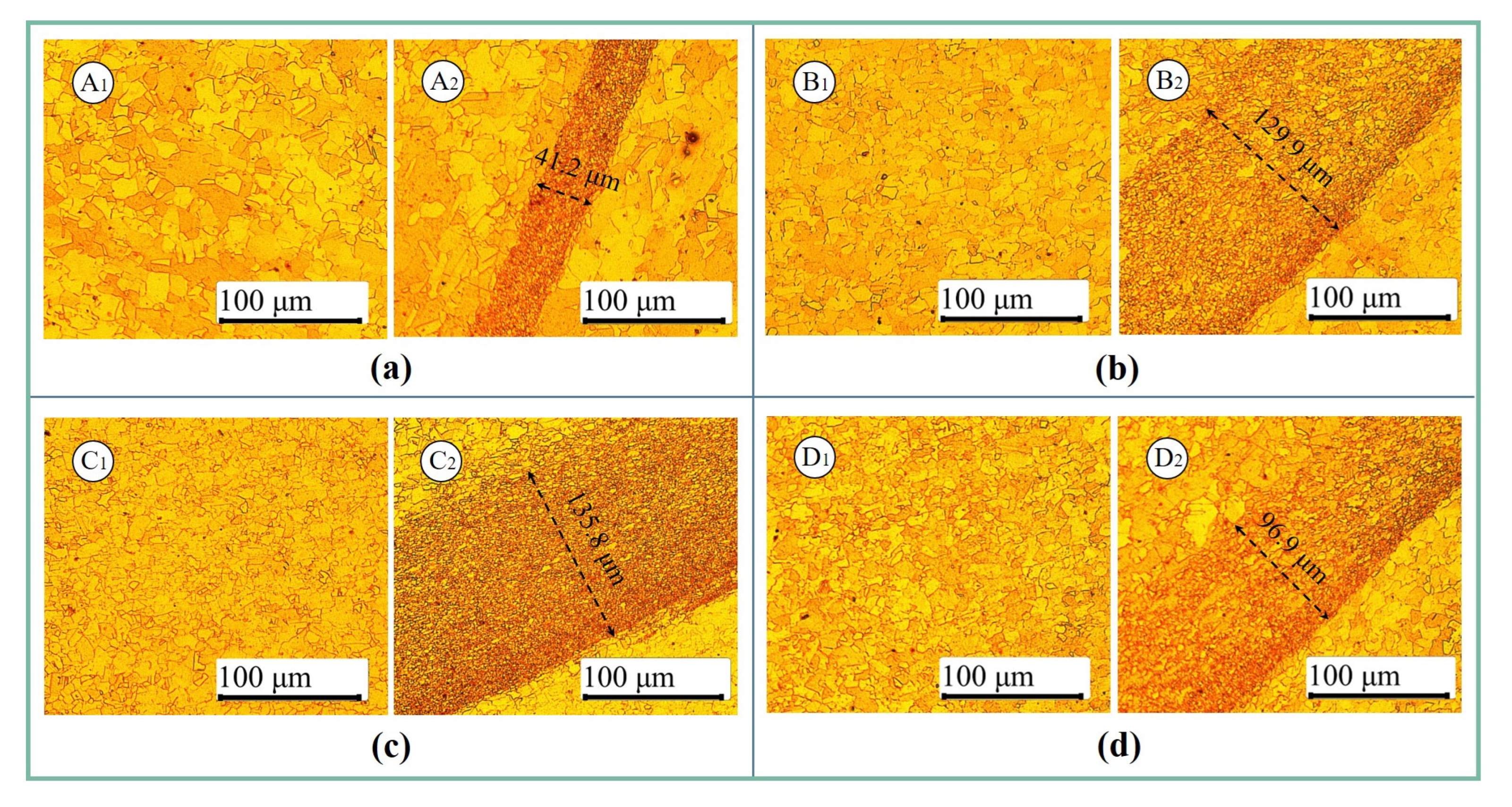
3.2. Macroscopic Morphology and Microstructure
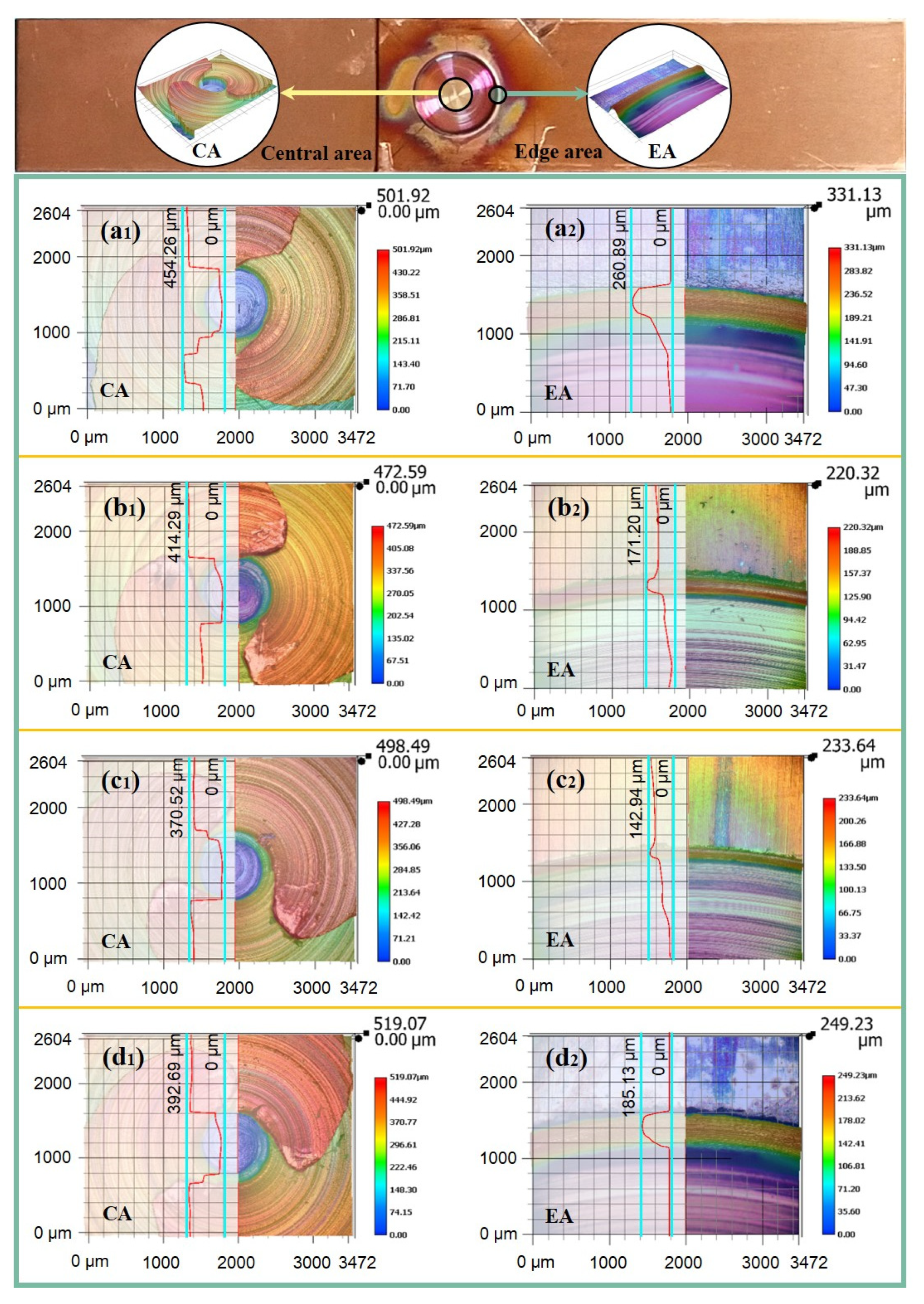
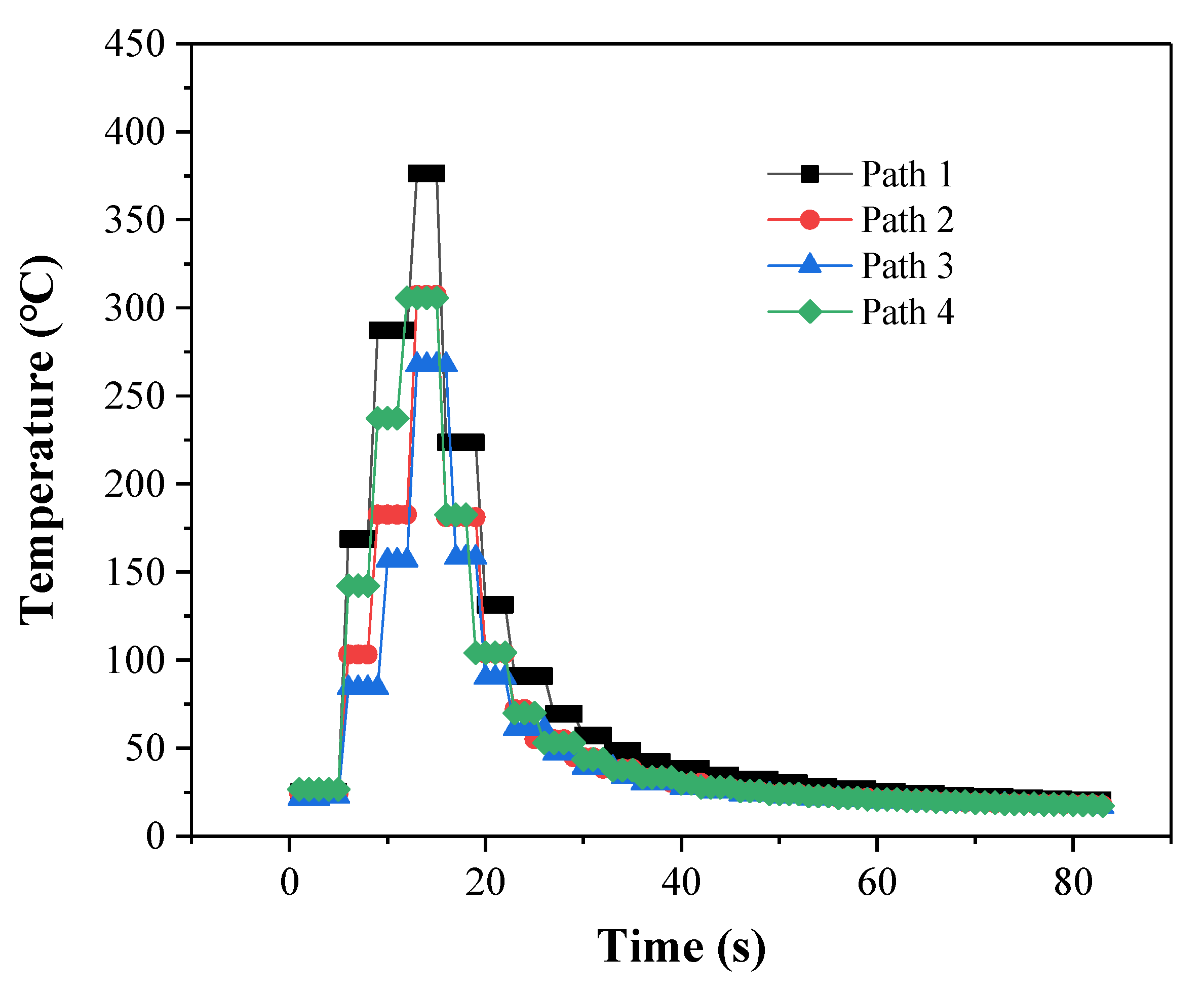
3.3. Welding Temperature
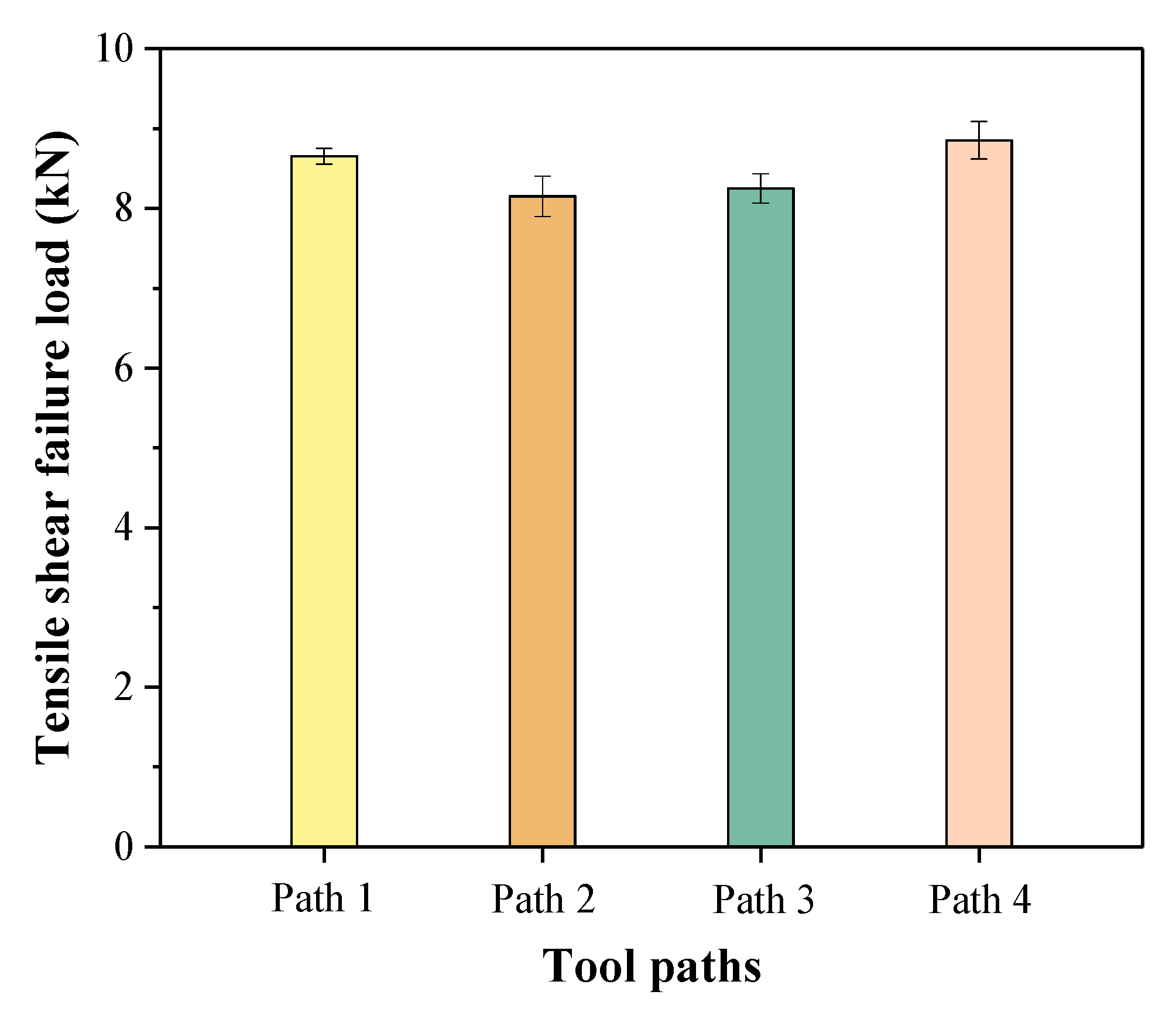
3.4. Mechanical Properties
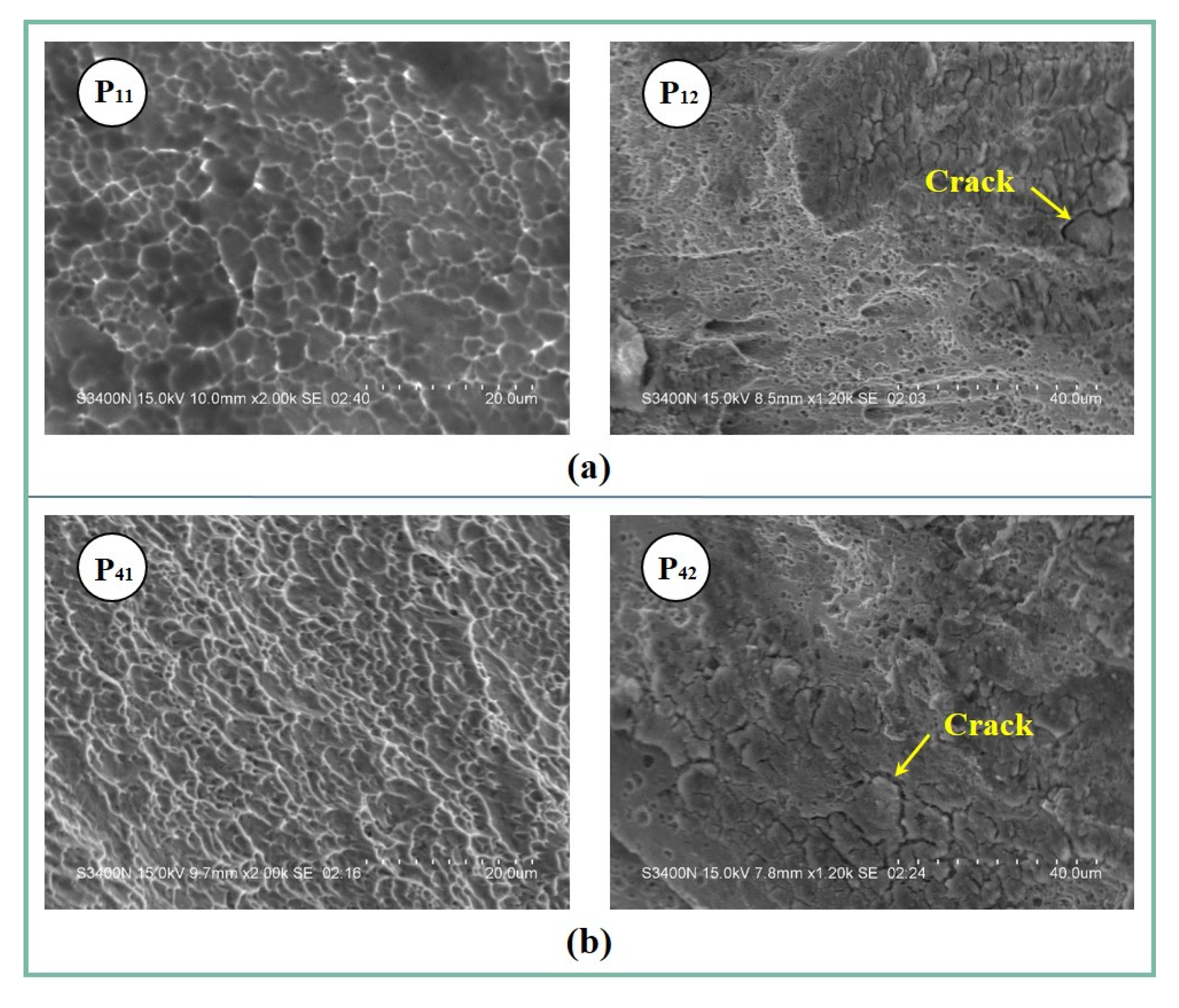
3.5. Fracture Mode
4. Conclusions
- The range of stirring zone generated by path 1 (one-time plunging: 0.3 mm) was the largest, while the range of stirring zone formed by path 3 (step-by-step plunging: 0.1 mm + 0.2 mm) was the smallest. The grains in the stirring zone of a step-by-step plunging path were smaller than those of the one-time plunging path. The width of the thermal-mechanical affected zone generated by the one-time plunging path was the smallest.
- Path 1 obtained the highest peak temperature, and path 3 gained the lowest peak temperature. The greater the initial plunging amount of the tool, the faster the temperature rise rate during the tool plunging and dwell stages.
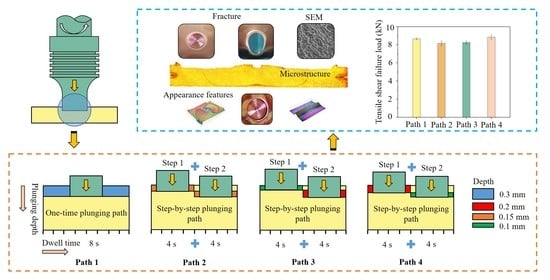
- The tensile shear failure loads of path 1, path 2 (step-by-step plunging: 0.15 mm + 0.15 mm), path 3, and path 4 (step-by-step plunging: 0.2 mm + 0.1 mm) were 8.65 kN, 8.15 kN, 8.25 kN, and 8.85 kN, respectively. The tensile shear failure load of path 4, with a step-by-step plunging path, was 2.3% higher than that of the one-time plunging path 1. The step-by-step plunging path is favorable for increasing the microhardness in the stirring zone.
- The fracture modes of the welded joints under different tool plunging paths were all nugget pullout fracture, and the fracture types of path 1 and path 4 were both ductile fracture.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, W.T.; Ding, Y.Q.; Huang, G.Q.; Huda, N.; Ahmad Shah, L.H.; Piao, Z.Y.; Shen, Y.F.; Shen, Z.K.; Gerlich, A. The role of pin eccentricity in friction stir welding of Al-Mg-Si alloy sheets: Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 121, 7661–7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzbanrad, J.; Akbari, M.; Asadi, P.; Safaee, S. Characterization of the influence of tool pin profile on microstructural and mechanical properties of friction stir welding. Metall. Mater. Trans. B-Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2014, 45, 1887–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulo Davim, J. Welding Technology, 1st ed.; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.H.; Wang, C.M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D.B.; Wang, F.F.; Ji, Y.J.; Chen, G.Q. Microstructure and corrosion behavior of bobbin tool friction stir welded 2219 aluminum alloy. Mater. Charact. 2022, 192, 112178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, W.F.; Lu, H.J.; Liu, Y.L. Effect of microstructure inhomogeneity on creep behavior of friction stir welding 7B50-T7451 aluminum alloy thick plate joint. Mater. Charact. 2022, 193, 112292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.K.; Zhang, M.T.; Li, D.X.; Liu, X.Y.; Chen, S.L.; Hou, W.T.; Ding, Y.Q.; Sun, Z.G.; Su, Y.; Li, W.Y.; et al. Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties of AlMg alloy fabricated by additive friction stir deposition. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 125, 2733–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.W.; Xiao, X.; Zhu, X.Y.; Fan, Y.X.; Jiang, C.; Song, Y.L. Influence mechanism of pin thread in friction stir welding of magnesium alloys based on the relationship between microstructure and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2023, 312, 117870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiuzuli, F.R.; Batistão, B.F.; Bergmann, L.A.; Alcântara, N.G.D.; Santos, J.F.D.; Klusemann, B.; Gargarella, P. Effect of the gap width in AZ31 magnesium alloy joints obtained by friction stir welding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 5297–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.C.; Sun, Y.F.; Nagira, T.; Ushioda, K.; Fujii, H. Strain rate dependent micro-texture evolution in friction stir welding of copper. Materialia 2019, 6, 100302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashazadeh, H.; Teimournezhad, J.; Masoumi, A. Numerical investigation on the mechanical, thermal, metallurgical and material flow characteristics in friction stir welding of copper sheets with experimental verification. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Dai, X.; Tian, C.Y.; Wu, C.S. Effect of splat cooling on microstructures and mechanical properties of friction stir welded 2195 Al-Li alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 858, 144169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasvand, A.; Ranjbarnodeh, E.; Mirsalehi, S.E. The microstructure and mechanical properties of single-pass and double-pass lap joint of Al 5754H-11 and Mg AZ31-O alloys by friction stir welding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 6023–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajeh, R.; Jafarian, H.R.; Jabraeili, R.; Eivani, A.R.; Seyedein, S.H.; Park, N.; Heidarzadeh, A. Strength-ductility synergic enhancement in friction stir welded AA2024 alloy and copper joints: Unravelling the role of Zn interlayer’s thickness. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 16, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhang, M.; Farahani, M. Experimental correlation between microstructure, residual stresses and mechanical properties of friction stir welded 2024-T6 aluminum alloys. Int. J. Adv. Des. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozaki, Y.; Uematsu, Y.; Tokaji, K. A newly developed tool without probe for friction stir spot welding and its performance. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2010, 210, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prangnell, P.B.; Bakavos, D. Novel approaches to friction spot welding thin aluminium automotive sheet. Mater. Sci. Forum 2010, 638, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, T.; Wang, P.Z.; Chu, Q.; Li, W.Y. Materials flow behavior during probeless friction stir spot welding and its correlation with macroscopic morphology and grain characteristics of joints. Jixie Gongcheng Xuebao 2020, 56, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.W.; Fu, T.; Li, W.Y. Friction stir spot welding: A review on joint macro- and microstructure, property, and process modelling. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 697170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayanan, R.; Sridhar, V.G. Studies on the influence of process parameters in friction stir spot welded joints—A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 37, 2695–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsström, A.; Bossuyt, S.; Yagodzinskyy, Y.; Tsuzaki, K.; Hänninen, H. Strain localization in copper canister FSW welds for spent nuclear fuel disposal. J. Nucl. Mater. 2019, 523, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ólafsson, D.; Vilaça, P.; Vesanko, J. Multiphysical characterization of FSW of aluminum electrical busbars with copper ends. Weld. World. 2020, 64, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiao, K.X.; Zhang, J.L.; Liu, J.P. Experimental and numerical investigations of interface characteristics of copper/steel composite prepared by explosive welding. Mater. Des. 2018, 154, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, M. Elucidating of rotation speed in friction stir welding of pure copper: Thermal modeling. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2014, 81, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarzadeh, A.; Jabbari, M.; Esmaily, M. Prediction of grain size and mechanical properties in friction stir welded pure copper joints using a thermal model. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 77, 1819–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakavos, D.; Chen, Y.C.; Babout, L.; Prangnell, P. Material interactions in a novel pinless tool approach to friction stir spot welding thin aluminum sheet. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 1266–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.Z.; Ni, D.R.; Yang, Q.; Liu, C.Z.; Ma, Z.Y. Pinless friction stir spot welding of Mg-3Al-1Zn alloy with Zn interlayer. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, S.R.; Beidokhti, B.; Haddad-Sabzevar, M. Pinless tool for FSSW of AA 6061-T6 aluminum alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 267, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.; Seyyed Ehsan, M.; Eslam, R. Pinless FSSW of DP600/Zn/AA6061 dissimilar joints. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Y.; Li, J.F.; Zhang, Z.H.; Gao, D.L.; Wang, W.B.; Dong, C.L. Improving mechanical properties of pinless friction stir spot welded joints by eliminating hook defect. Mater. Des. 2014, 62, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgül, H.G.; Dedeoğlu, O. Investigations of the mechanical and microstructural effects of pinless tool geometry on friction stir spot welding process. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2020, 73, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayanan, R.; Sridhar, V.G. Effect of process parameters in pinless friction stir spot welding of Al 5754-Al 6061 alloys. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2020, 9, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, B.H.; Salih, O.S.; Sowoud, K.M. Pinless friction stir spot welding of aluminium alloy with copper interlayer. Open Eng. 2020, 10, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Yang, X.; Li, W.; Li, Y. Microstructure and mechanical behaviour of pinless friction stir spot welded AA2198 joints. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2016, 21, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchouaha Tankoua, A.; Köhler, T.; Bergmann, J.P.; Grätzel, M.; Betz, P.; Lindenau, D. Tool downscaling effects on the friction stir spot welding process and properties of current-carrying welded aluminum-copper joints for e-mobility applications. Metals 2021, 11, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H. Pinless Friction Stir Spot Welding of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy for Aerospace Application. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, USA, May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Q.; Yang, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Vairis, A.; Wang, W.B. Numerical analysis of material flow in the probeless friction stir spot welding based on Coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian approach. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 36, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedrasiak, P.; Shercliff, H.R.; Reilly, A.; McShane, G.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, L.; Robson, J.; Prangnell, P. Thermal modeling of Al-Al and Al-Steel friction stir spot welding. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 4089–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.W.; Feng, W.Y.; Li, W.Y.; Xu, Y.X.; Chu, Q.; Ma, T.J.; Wang, W.B. Numerical modelling and experimental investigation of thermal and material flow in probeless friction stir spot welding process of Al 2198-T8. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2018, 23, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariia, R.; Nicola, C.; Giuseppe, C. Modeling of probeless friction stir spot welding of AA2024/AISI304 steel lap joint. Materials 2022, 15, 8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, P.S.; Nguyen, V.-T.; Nguyen, V.T.; Uyen, T.M.T.; Do, T.T.; Nguyen, V.T.T. Study on the fatigue strength of welding line in injection molding products under different tensile conditions. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Tran, V.T.; Pham, T.H.N.; Nguyen, V.-T.; Thanh, N.C.; Thi, H.M.N.; Duy, N.V.A.; Thanh, D.N.; Nguyen, V.T.T. Influences of material selection, infill ratio, and layer height in the 3D printing cavity process on the surface roughness of printed patterns and casted products in investment casting. Micromachines 2023, 14, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciemiorek, M.; Morawiński, Ł.; Jasiński, C.; Orłowska, M.; Chmielewski, T.; Olejnik, L.; Lewandowska, M. Characterization of ultrafine-grained copper joints acquired by rotary friction welding. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2022, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhang, M.; Sam-Daliri, O.; Farahani, M.; Vatani, A. Effect of friction stir welding parameters on the residual stress distribution of Al-2024-T6 alloy. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2021, 15, 7684–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Hao, S.J.; Li, W.Y.; Yang, X.W.; Zou, Y.F.; Wu, D.; Vairis, A. On the association between microhardness, corrosion resistance and microstructure of probeless friction stir spot welded Al-Li joint. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 2394–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murr, L.E.; Liu, G.; McClure, J.C. A TEM study of precipitation and related microstructures in friction-stir-welded 6061 aluminum. J. Mater. Sci. 1998, 33, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, B.; Skrotzki, B. Characterization of a friction-stir-welded aluminum alloy 6013. Metall. Mater. Trans B 2002, 33, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.S.; Chen, X.; Wu, Z.T.; Chen, Y.X.; Zhang, G.C. Analysis of microstructure and mechanical properties of probeless friction stir spot welding joint in AA6061-T6 aluminum alloy. Jilin Daxue Xuebao (Gongxueban), 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.Q.; Gong, W.B.; Fan, J. Influence of needleless stir friction head welding on micro-structure and properties of aluminum alloy lapping. J. Changchun Univ. Technol. 2016, 37, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Xie, J.N.; Liu, L.; Chang, G.; Ojo, O.O. Microscopic appraisal and mechanical behavior of hybrid Cu/Al joints fabricated via friction stir spot welding-brazing and modified friction stir clinching-brazing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 13239–13249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
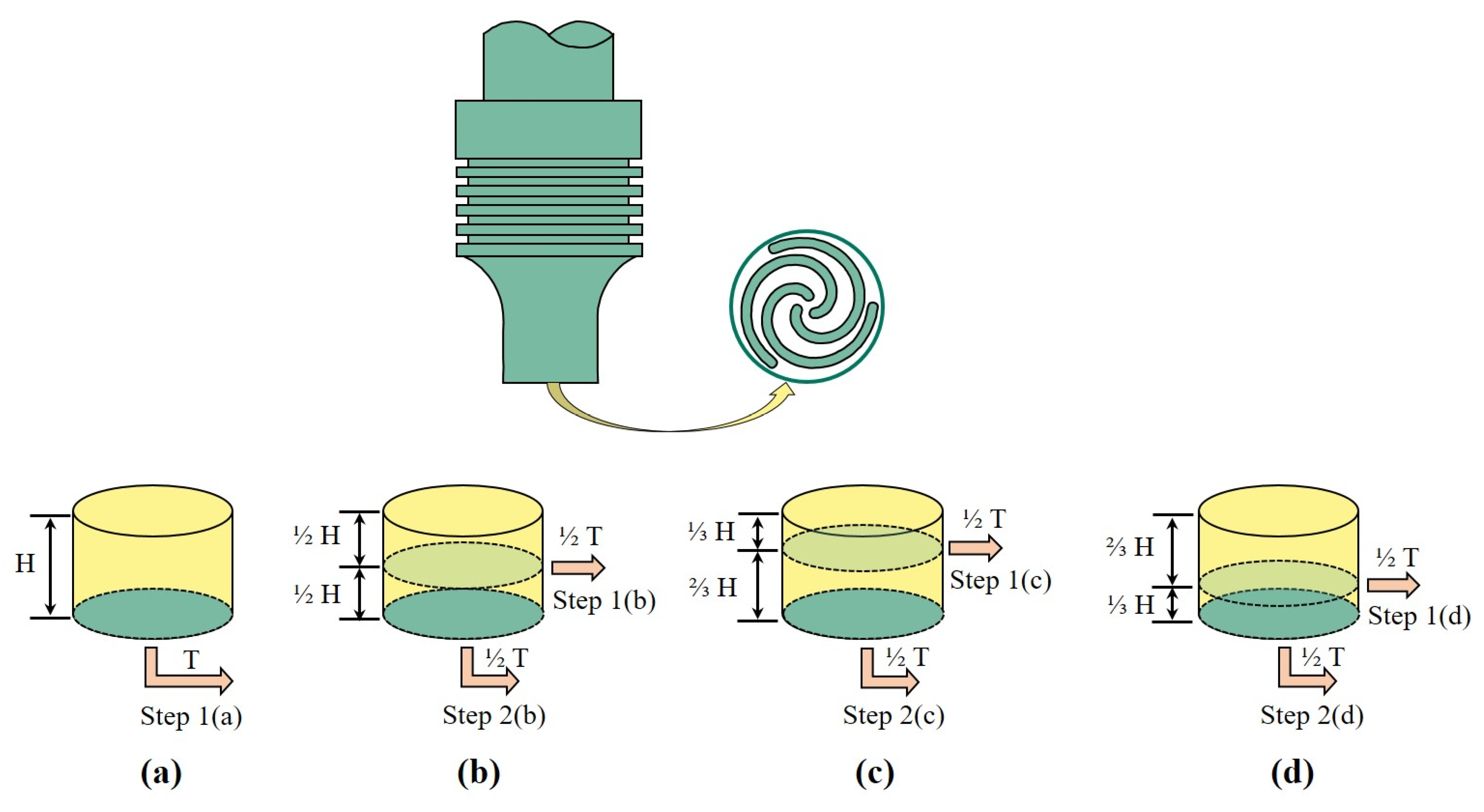



| Plunging Process | Process Parameters | Path 1 | Path 2 | Path 3 | Path 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Plunging depth (mm) | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Dwell time (s) | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | |
| Step 2 | Plunging depth (mm) | - | 0.15 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Dwell time (s) | - | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, X.; Jiang, D.; Song, W.; Wang, H. Effects of Tool Plunging Path on the Welded Joint Properties of Pinless Friction Stir Spot Welding. Lubricants 2023, 11, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11030150
Ge X, Jiang D, Song W, Wang H. Effects of Tool Plunging Path on the Welded Joint Properties of Pinless Friction Stir Spot Welding. Lubricants. 2023; 11(3):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11030150
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Xiaole, Di Jiang, Weiwei Song, and Hongfeng Wang. 2023. "Effects of Tool Plunging Path on the Welded Joint Properties of Pinless Friction Stir Spot Welding" Lubricants 11, no. 3: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11030150
APA StyleGe, X., Jiang, D., Song, W., & Wang, H. (2023). Effects of Tool Plunging Path on the Welded Joint Properties of Pinless Friction Stir Spot Welding. Lubricants, 11(3), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11030150