Tribology Performance of Polyol-Ester Based TiO2, SiO2, and Their Hybrid Nanolubricants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
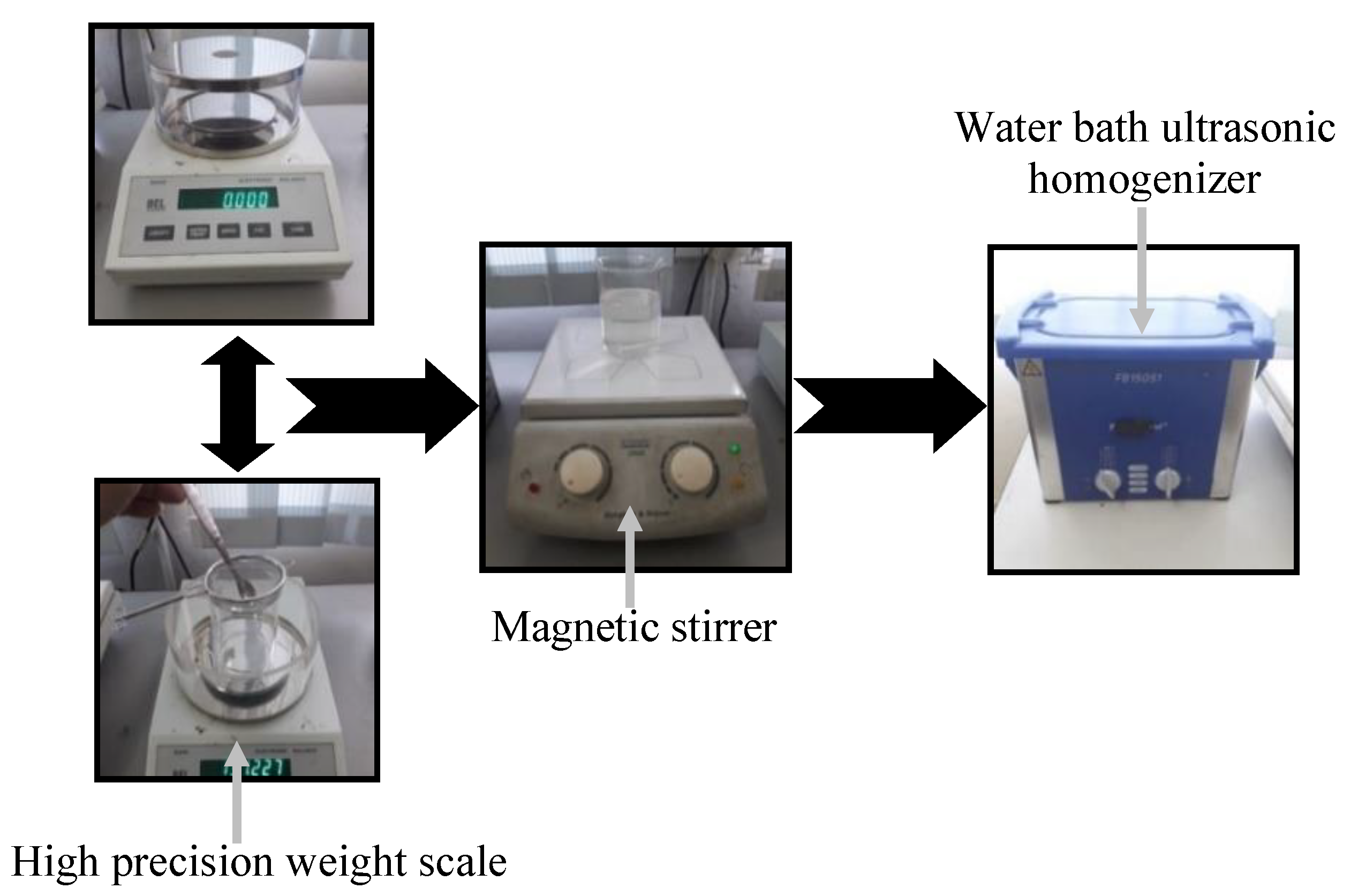
2.1. Preparation of Nanolubricants
2.2. Stability of Mono and Hybrid Nanolubricants
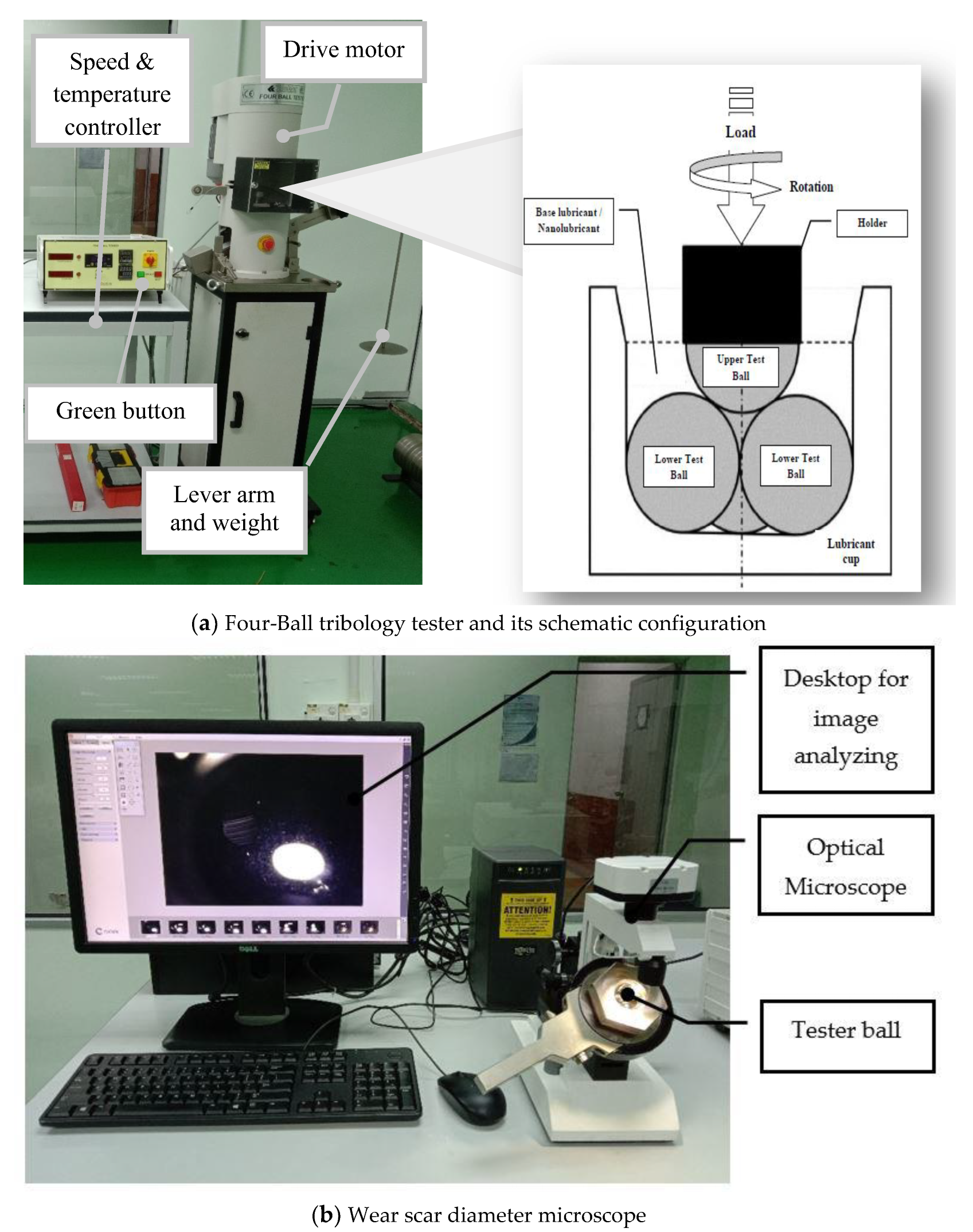
2.3. Measurement of Tribology Properties
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Stability of Nanolubricants
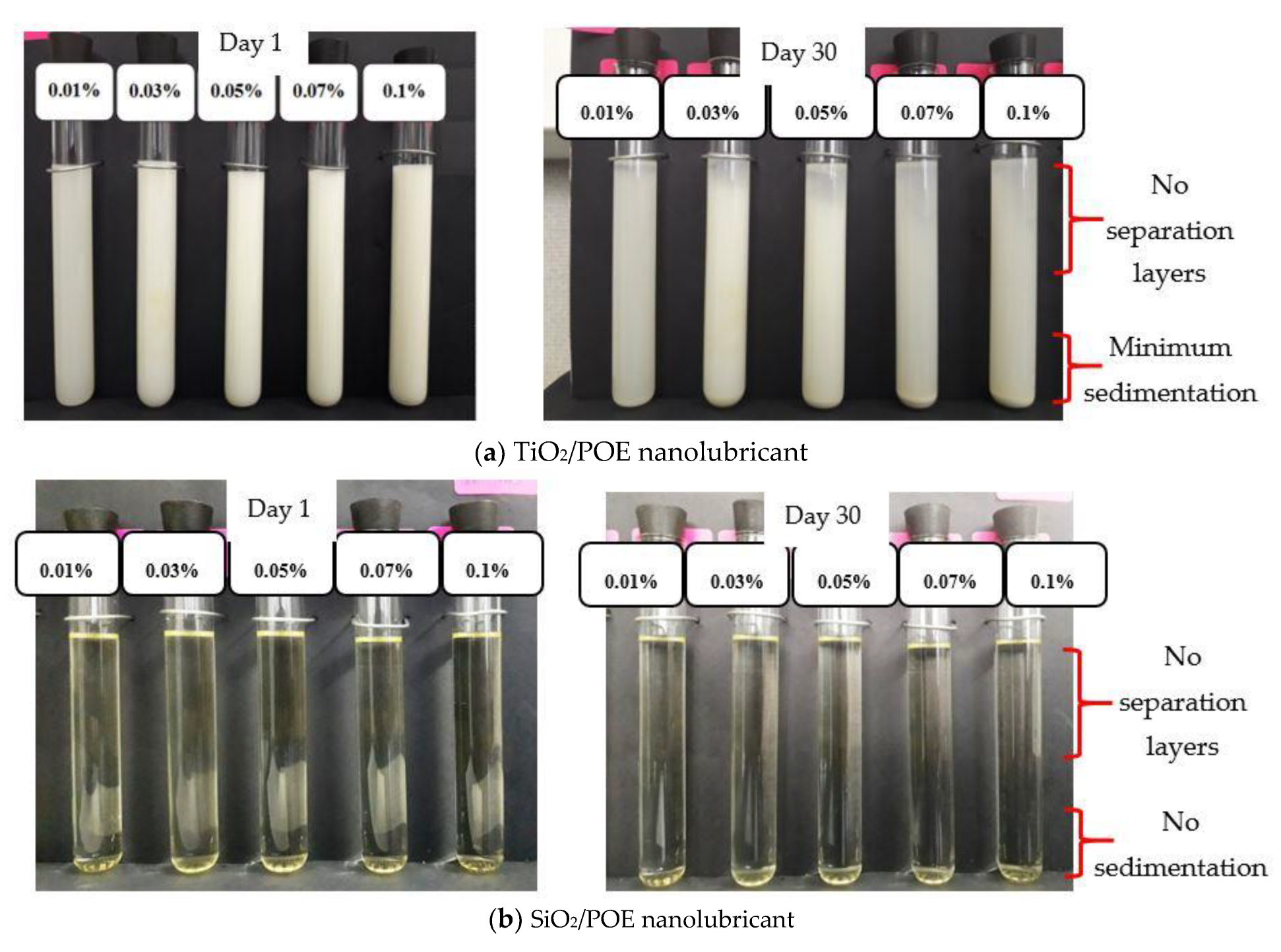
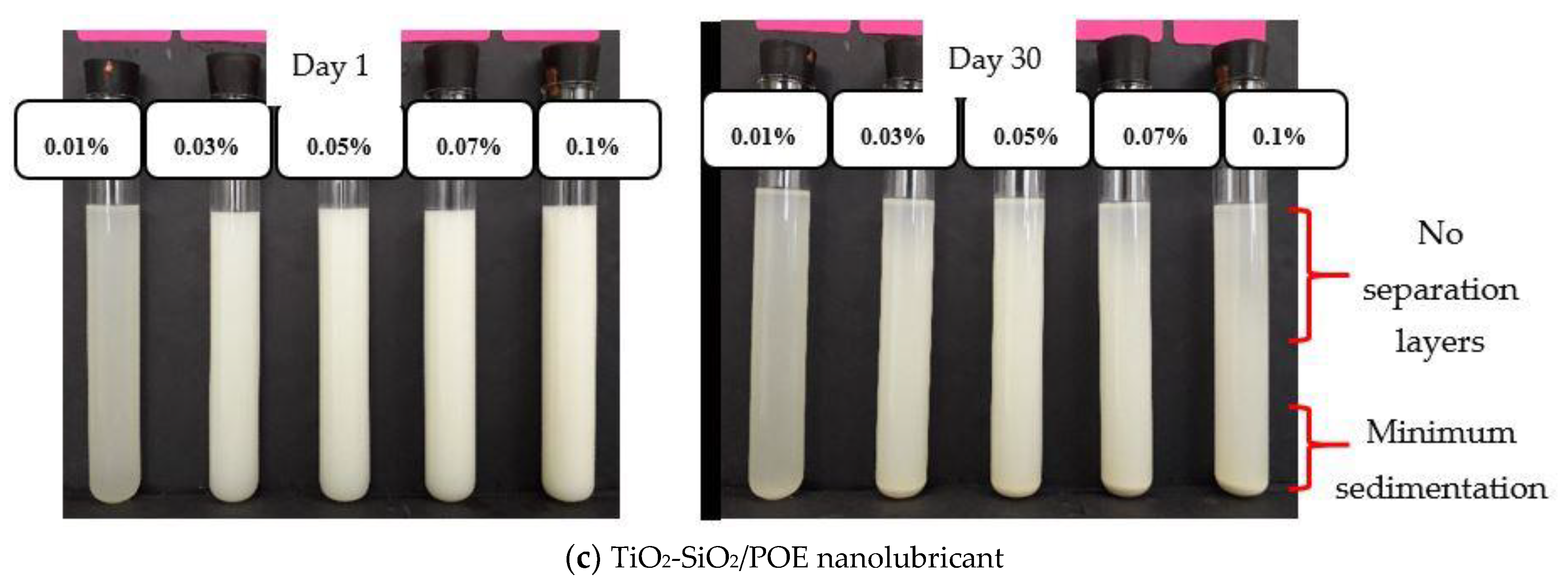
3.1.1. Sedimentation Observation
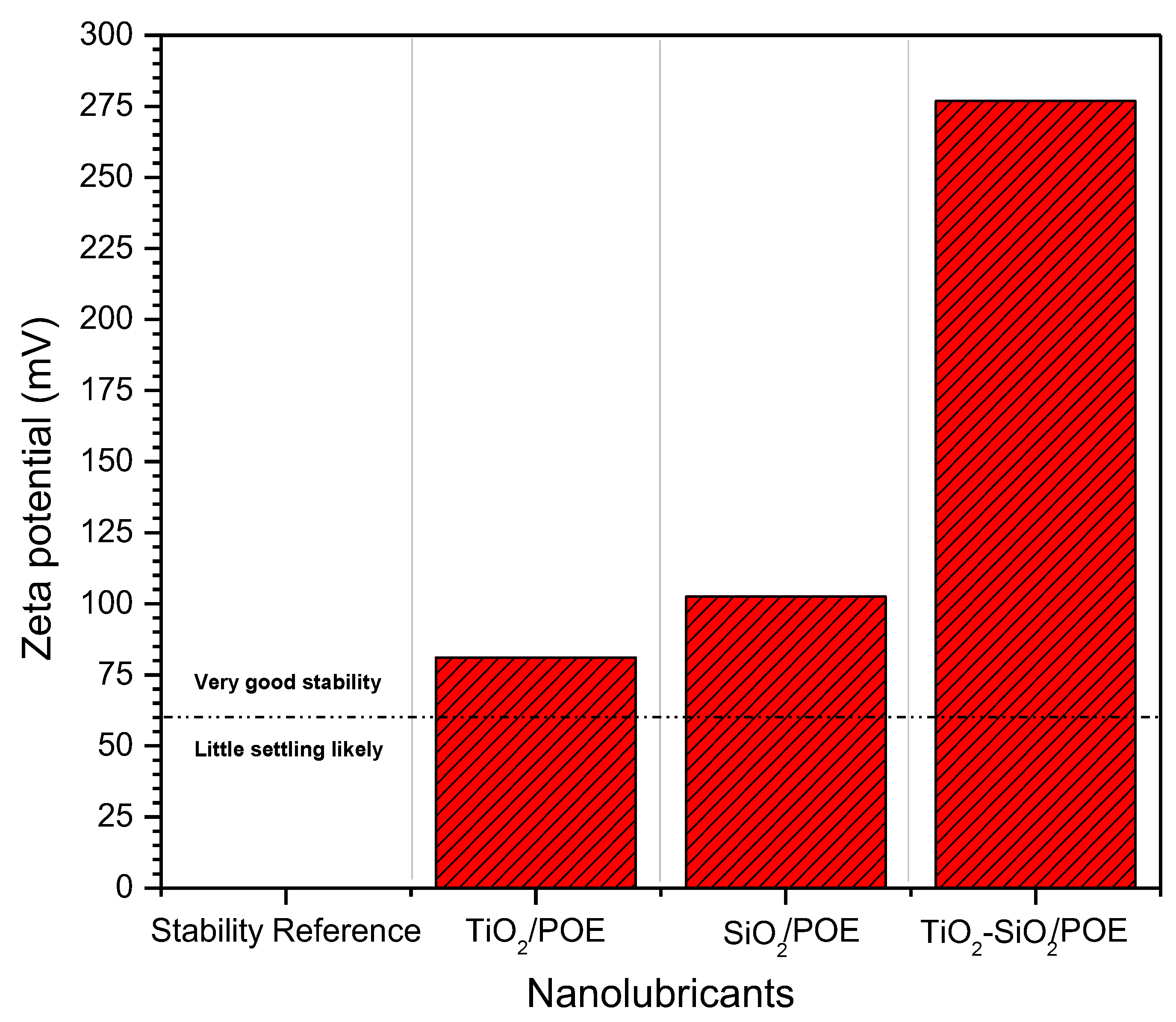
3.1.2. Zeta Potential Evaluation
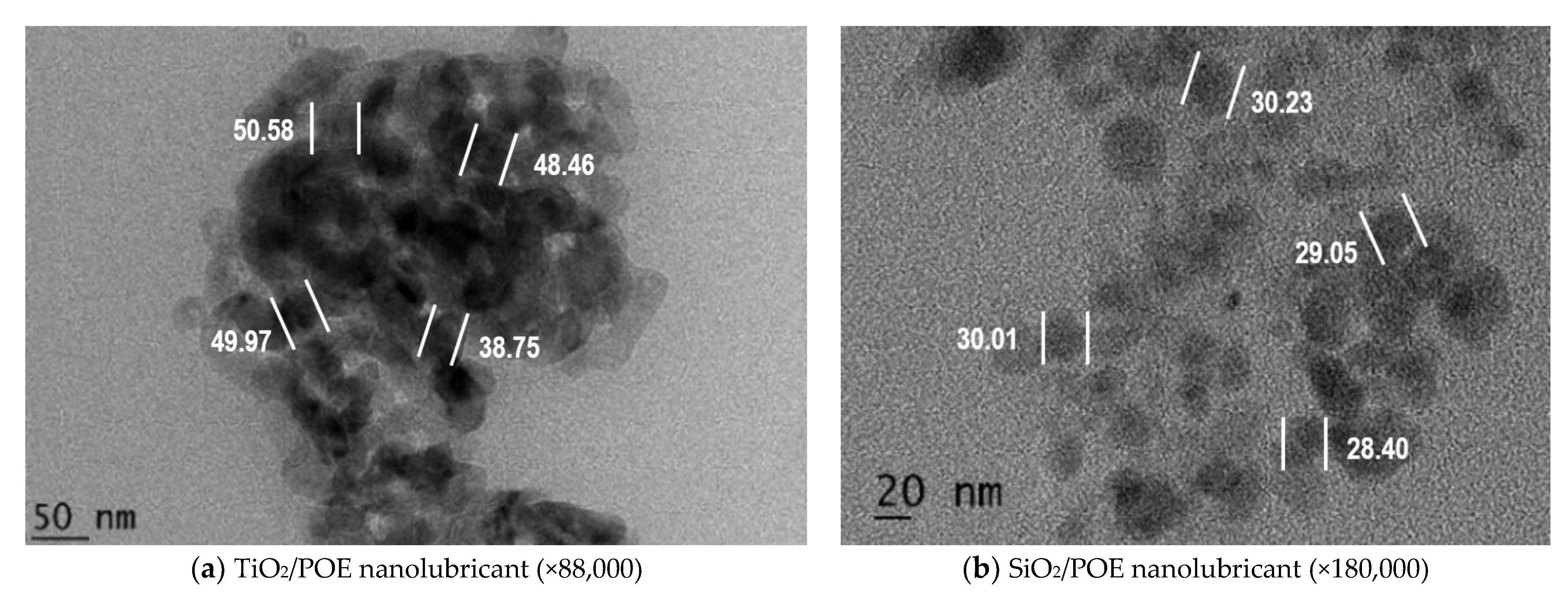
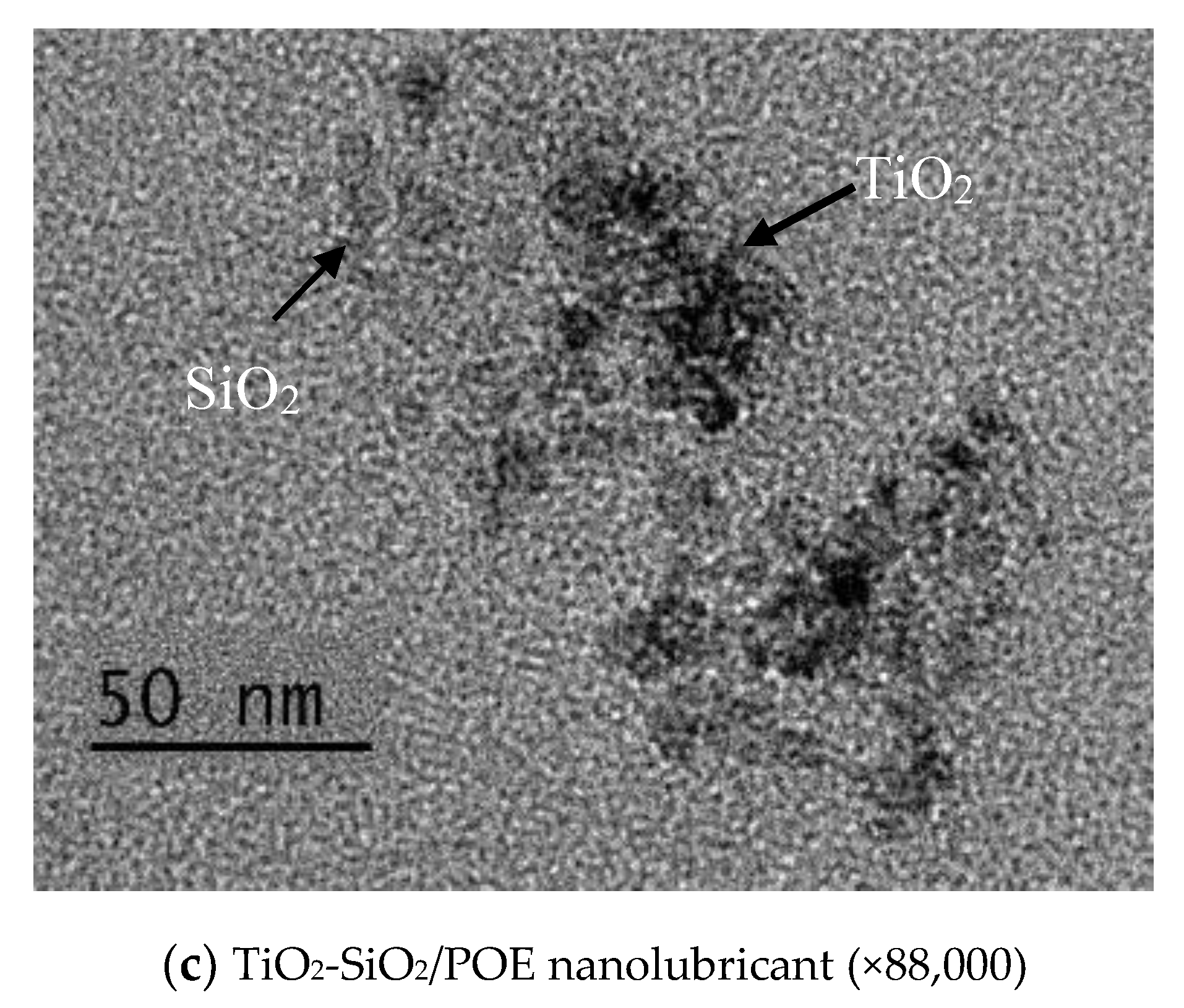
3.1.3. Micrograph Observation
3.2. Tribology Properties
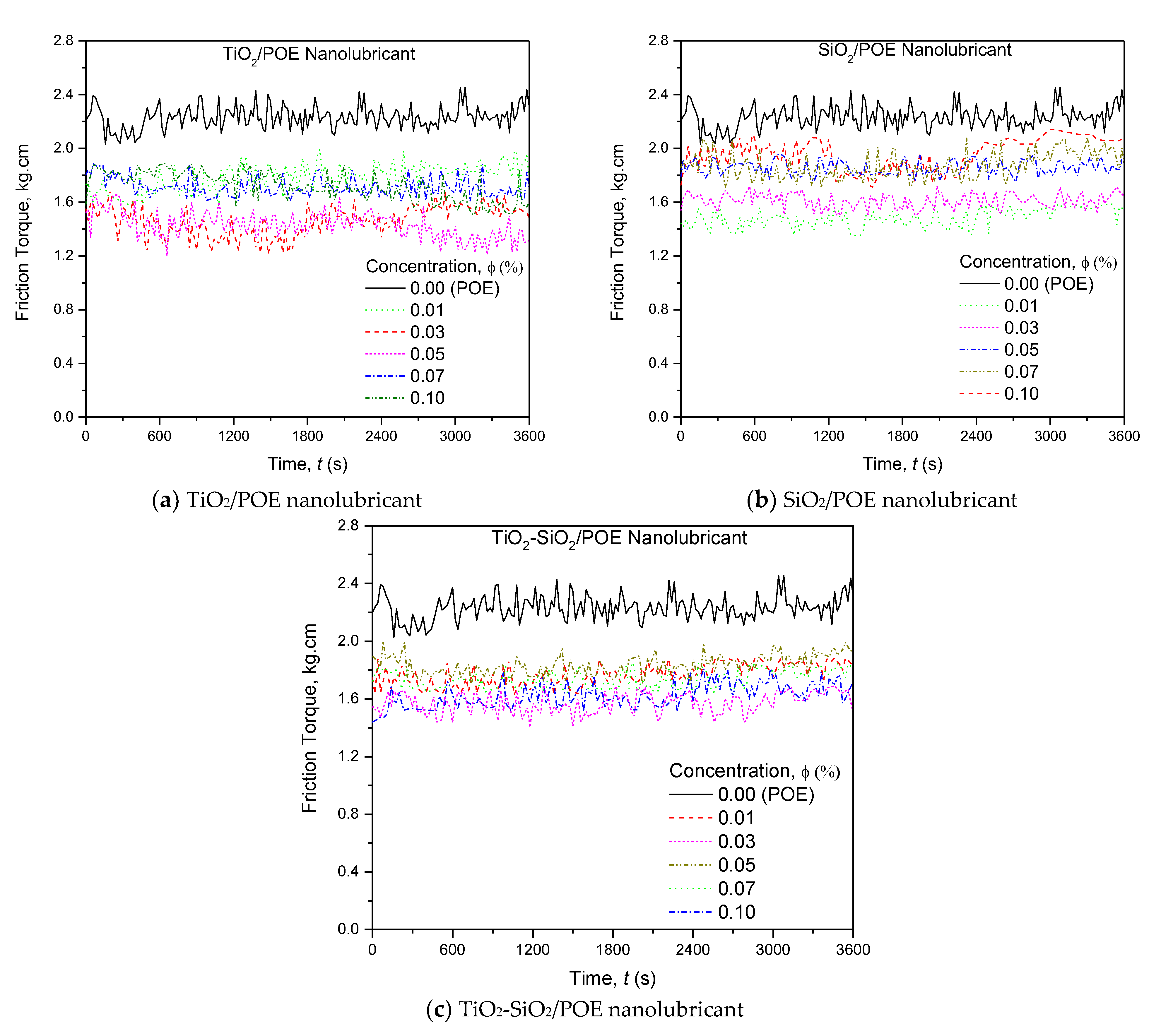
3.2.1. Friction Torque Evaluation
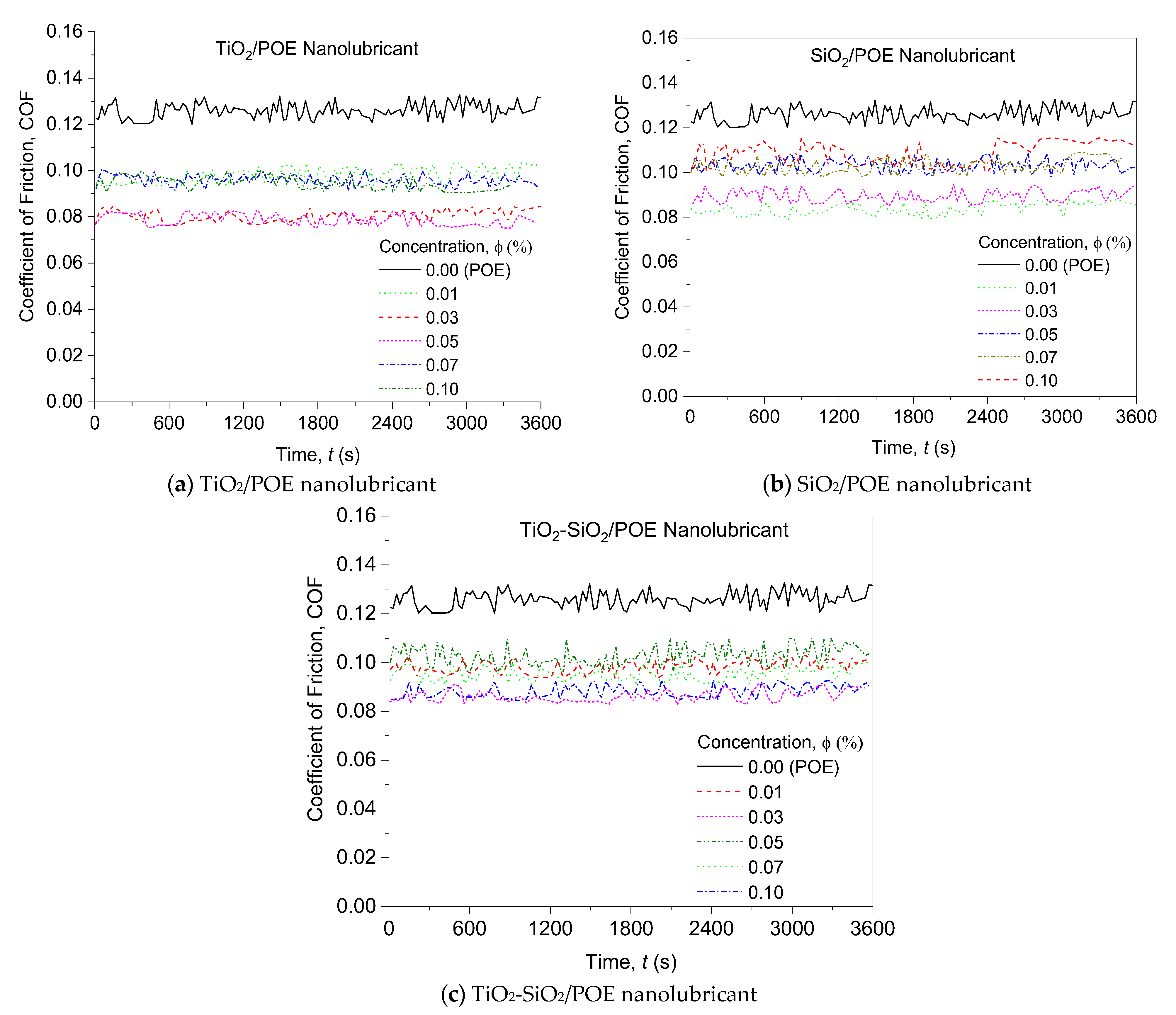
3.2.2. Coefficient of Friction Evaluation
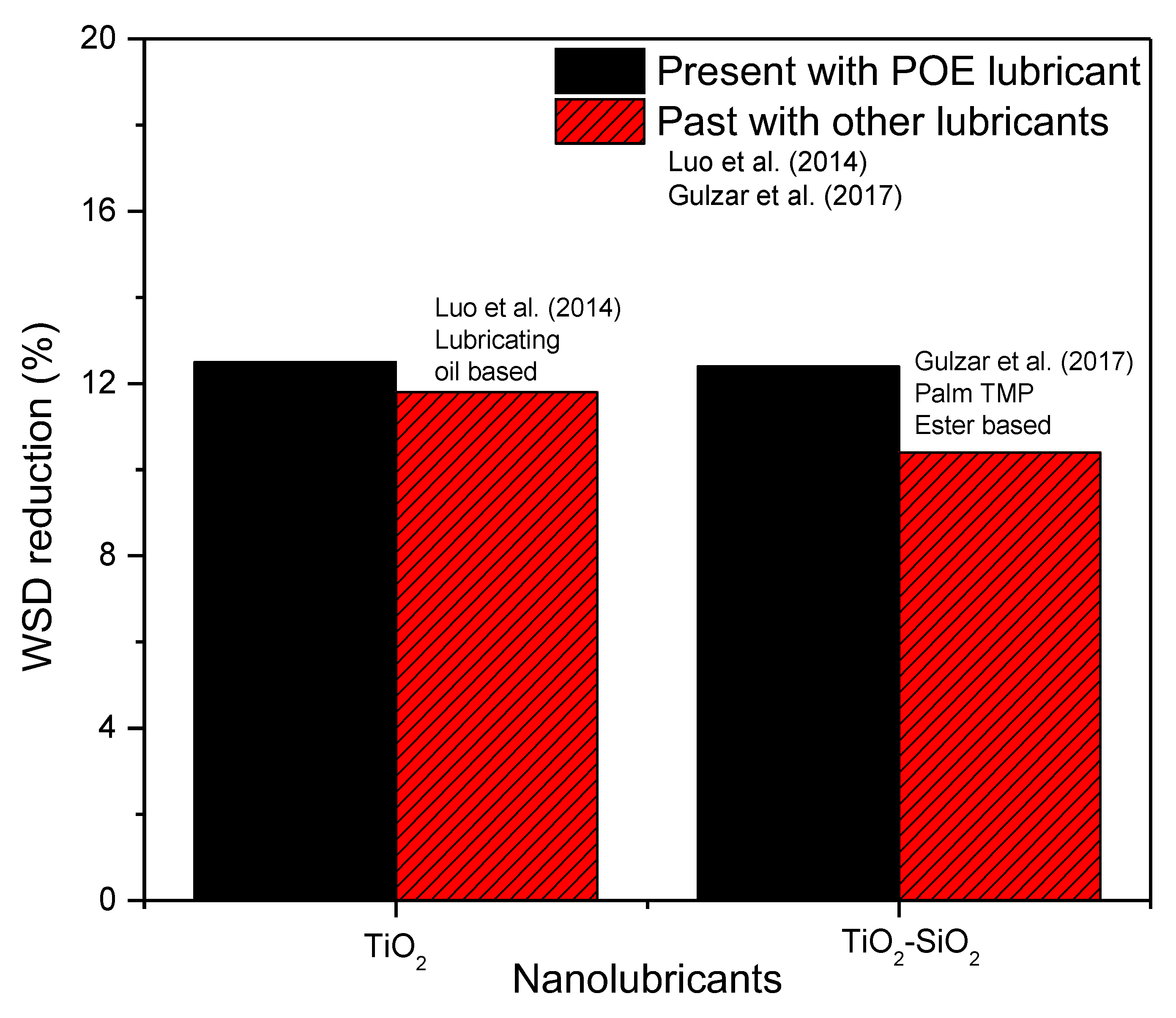
3.2.3. Wear Scar Diameter Evaluation
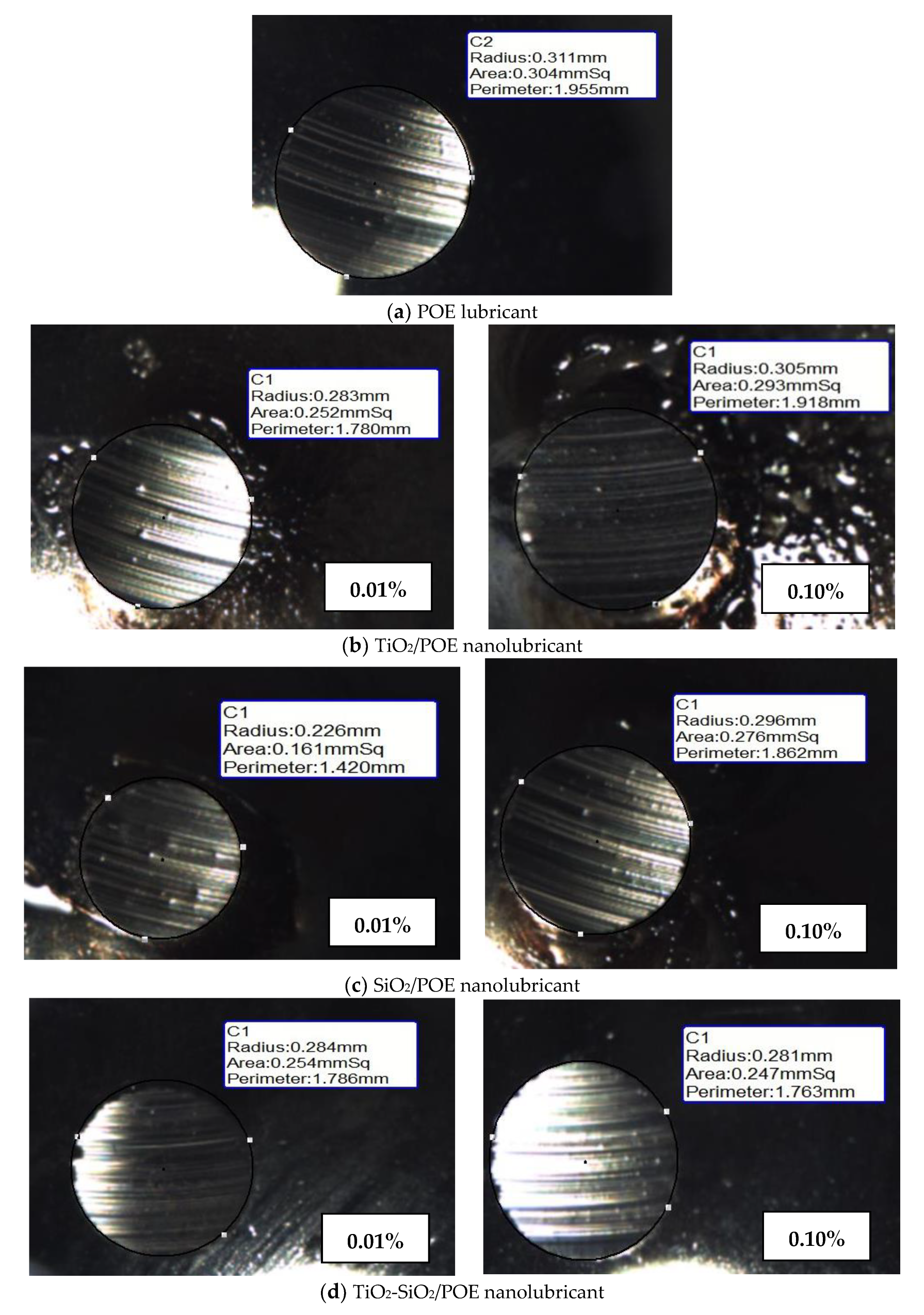
3.2.4. Microscopic Observation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mortier, R.M.; Orszulik, S.T.; Fox, M.F. Chemistry and Technology of Lubricants; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2010; Volume 107115. [Google Scholar]
- Shahnazar, S.; Bagheri, S.; Abd Hamid, S.B. Enhancing lubricant properties by nanoparticle additives. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 3153–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jwo, C.S.; Jeng, L.Y.; Teng, T.P.; Chang, H. Effects of nanolubricant on performance of hydrocarbon refrigerant system. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. Process. Meas. Phenom. 2009, 27, 1473–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidur, R.; Kazi, S.N.; Hossain, M.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Mohammed, H.A. A review on the performance of nanoparticles suspended with refrigerants and lubricating oils in refrigeration systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Xie, G.; Luo, J. Electrical bearing failures in electric vehicles. Friction 2020, 8, 4–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, K.; Erdemir, A. Influence of tribology on global energy consumption, costs and emissions. Friction 2017, 5, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, K.; Andersson, P.; Nylund, N.-O.; Mäkelä, K.; Erdemir, A. Global energy consumption due to friction in trucks and buses. Tribol. Int. 2014, 78, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhou, X. Superlubricitive engineering—Future industry nearly getting rid of wear and frictional energy consumption. Friction 2020, 8, 643–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liu, G.; Liu, S.; Ma, S.; Li, W.; Liu, W. Surface-functionalized nanoMOFs in oil for friction and wear reduction and antioxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 128306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolbaqi, M.K.; Mamat, R.; Sidik, N.A.C.; Azmi, W.H.; Selvakumar, P. Experimental investigation and development of new correlations for heat transfer enhancement and friction factor of BioGlycol/water based TiO2 nanofluids in flat tubes. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 108, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawawi, N.N.M.; Azmi, W.H.; Redhwan, A.A.M.; Sharif, M.Z.; Samykano, M. Experimental investigation on thermo-physical properties of metal oxide composite nanolubricants. Int. J. Refrig. 2018, 89, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Kheireddin, B.; Gao, H.; Liang, H. Roles of nanoparticles in oil lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2016, 102, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, M.; Dey, T.K. Effect of aggregation on the viscosity of copper oxide–gear oil nanofluids. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2011, 50, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, M.; Dey, T.K. Role of interfacial layer and clustering on the effective thermal conductivity of CuO–gear oil nanofluids. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2011, 35, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotia, A.; Ghosh, S.K. Experimental analysis for rheological properties of aluminium oxide (Al2O3)/gear oil (SAE EP-90) nanolubricant used in HEMM. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2015, 67, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Jiazheng, Z.; Kang, X. The ball-bearing effect of diamond nanoparticles as an oil additive. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1996, 29, 2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawawi, N.N.M.; Azmi, W.H.; Ghazali, M.F. Tribological performance of Al2O3–SiO2/PAG composite nanolubricants for application in air-conditioning compressor. Wear 2022, 492–493, 204238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falvo, M.R.; Superfine, R. Mechanics and friction at the nanometer scale. J. Nanopart. Res. 2000, 2, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulzar, M.; Masjuki, H.H.; Kalam, M.A.; Varman, M.; Zulkifli, N.W.M.; Mufti, R.A.; Zahid, R. Tribological performance of nanoparticles as lubricating oil additives. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tevet, O.; Von-Huth, P.; Popovitz-Biro, R.; Rosentsveig, R.; Wagner, H.D.; Tenne, R. Friction mechanism of individual multilayered nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19901–19906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Hwang, Y.; Cheong, S.; Choi, Y.; Kwon, L.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.H. Understanding the role of nanoparticles in nano-oil lubrication. Tribol. Lett. 2009, 35, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapoport, L.; Leshchinsky, V.; Lvovsky, M.; Nepomnyashchy, O.; Volovik, Y.; Tenne, R. Mechanism of friction of fullerenes. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2002, 54, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, X.; Qin, B.; Xing, D.; Guo, Y.; Fan, R. Investigation of the mending effect and mechanism of copper nano-particles on a tribologically stressed surface. Tribol. Lett. 2004, 17, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, W.; Xue, Q. Study on the structure and tribological properties of surface-modified Cu nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 1999, 34, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.K.A.; Xianjun, H.; Mai, L.; Qingping, C.; Turkson, R.F.; Bicheng, C. Improving the tribological characteristics of piston ring assembly in automotive engines using Al2O3 and TiO2 nanomaterials as nano-lubricant additives. Tribol. Int. 2016, 103, 540–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Li, S. A review of recent developments of friction modifiers for liquid lubricants (2007–present). Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2014, 18, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Lan, C.W.; Chen, C.H.; Kao, M.J.; Guo, J.B. Anti-wear and friction properties of nanoparticles as additives in the lithium grease. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2014, 15, 2059–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, R.; Battez, A.H.; Cabello, J.; Viesca, J.; Osorio, A.; Sagastume, A. Tribological behavior of polyalphaolefin with the addition of nickel nanoparticles. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 2327–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marko, M.; Kyle, J.; Branson, B.; Terrell, E. Tribological improvements of dispersed nanodiamond additives in lubricating mineral oil. J. Tribol. 2015, 137, 011802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, A.; Anand, A. Lubrication performance of synthetic oil mixed with diamond nanoparticles: Effect of concentration. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 20588–20594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elagouz, A.; Ali, M.K.A.; Xianjun, H.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Hassan, M.A. Frictional performance evaluation of sliding surfaces lubricated by zinc-oxide nano-additives. Surf. Eng. 2020, 36, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.F.; Azmi, W.H.; Mamat, R.; Ali, H.M. Thermal and Tribological Properties Enhancement of PVE Lubricant Modified with SiO2 and TiO2 Nanoparticles Additive. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawi, O.A.; Sidik, N.A.C. Applications of nanorefrigerant and nanolubricants in refrigeration, air-conditioning and heat pump systems: A review. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 68, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Guo, K.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J. Performance of a domestic refrigerator using TiO2-R600a nano-refrigerant as working fluid. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminullah, A.R.M.; Azmi, W.H.; Redhwan, A.A.M.; Sharif, M.Z.; Zawawi, N.N.M. Tribology investigation of automotive air condition (AAC) compressor by using Al2O3/PAG nanolubricant. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 15, 49–61. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, M.Z.; Azmi, W.H.; Zawawi, N.N.M.; Ghazali, M.F. Comparative air conditioning performance using SiO2 and Al2O3 nanolubricants operating with Hydrofluoroolefin-1234yf refrigerant. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 205, 118053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Lee, H.; Hwang, Y.; Radermacher, R. Recent advances in vapor compression cycle technologies. Int. J. Refrig. 2015, 60, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukri, M.F.; Musa, M.N.; Senawi, M.Y.; Nasution, H. Achieving a better energy-efficient automotive air-conditioning system: A review of potential technologies and strategies for vapor compression refrigeration cycle. Energy Effic. 2015, 8, 1201–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, K.A.; Azmi, W.H.; Nabil, M.F.; Mamat, R. Experimental investigation of nanoparticle mixture ratios on TiO2–SiO2 nanofluids heat transfer performance under turbulent flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 118, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kleinstreuer, C. Thermal performance of nanofluid flow in microchannels. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2008, 29, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawawi, N.N.M.; Azmi, W.H.; Sharif, M.Z.; Najafi, G. Experimental investigation on stability and thermo-physical properties of Al2O3–SiO2/PAG nanolubricants with different nanoparticle ratios. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 135, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redhwan, A.A.M.; Azmi, W.H.; Sharif, M.Z.; Mamat, R.; Samykano, M.; Najafi, G. Performance improvement in mobile air conditioning system using Al2O3/PAG nanolubricant. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 135, 1299–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.Z.; Azmi, W.H.; Redhwan, A.A.M.; Mamat, R.; Yusof, T.M. Performance analysis of SiO2/PAG nanolubricant in automotive air conditioning system. Int. J. Refrig. 2017, 75, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamisa, A.H.; Yusof, T.M.; Azmi, W.H.; Mamat, R.; Sharif, M.Z. The stability of TiO2/POE nanolubricant for automotive air-conditioning system of hybrid electric vehicles. Proc. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 863, 012050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimi, A.; Saidur, R.; Metselaar, H.S.C. A review of nanofluid stability properties and characterization in stationary conditions. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 54, 4051–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, I. Synthesis, characterization and application of nanofluid—An overview. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 2012, 89, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Xie, H. A review on nanofluids: Preparation, stability mechanisms, and applications. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 435873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Li, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Li, H. Dispersion behavior and thermal conductivity characteristics of Al2O3–H2O nanofluids. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2009, 9, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Jiang, B.; He, J.; Xia, X.; Pan, F. Lubrication performance of MoS2 and SiO2 nanoparticles as lubricant additives in magnesium alloy-steel contacts. Tribol. Int. 2016, 93, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Yao, Y.; He, J.; Ma, X.; Feng, J.; Liu, S.; Hou, L.; Liu, X. Tribological study of polytetrafluoroethylene lubricant additives filled with Cu microparticles or SiO2 nanoparticles. Tribol. Int. 2017, 110, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Wei, X.; Zhao, H.; Cai, G.; Zheng, X. Tribology properties of Al2O3/TiO2 nanocomposites as lubricant additives. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 10103–10109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Guan, R.; Cao, B. The tribology properties of alumina/silica composite nanoparticles as lubricant additives. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 5720–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulzar, M.; Masjuki, H.H.; Kalam, M.A.; Varman, M.; Zulkifli, N.W.M.; Mufti, R.A.; Zahid, R.; Yunus, R. Dispersion stability and tribological characteristics of TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposite-enriched biobased lubricant. Tribol. Trans. 2017, 60, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalin, M.; Kogovšek, J.; Remškar, M. Mechanisms and improvements in the friction and wear behavior using MoS2 nanotubes as potential oil additives. Wear 2012, 280, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Property | TiO2 | SiO2 |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 8.4 | 1.4 |
| Specific heat (J/kg·K) | 692 | 745 |
| Density (kg/m3) @ 20 °C | 4230 | 2220 |
| Molecular mass (g/mol) | 79.86 | 60.08 |
| Average particle diameter (nm) | 50 | 30 |
| Properties | POE RL68H |
|---|---|
| Viscosity @ 40 °C (cSt) | 66.6 |
| Viscosity @ 100 °C (cSt) | 9.4 |
| Pour Point (°C) | −39 |
| Density @ 20 °C (g/mL) | 0.977 |
| Flash Point (°C) | 270 |
| ASTM Standard | Test Method | Test Conditions | Remarks | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speed (rpm) | Load (kg) | Duration (Minutes) | Temperature (°C) | |||
| D4172-18 | Wear Preventive Characteristics of Lubricating Fluid | 1200 ± 60 | 40.0 ± 0.2 | 60 ± 1 | 75 ± 2 | Ball pot to be torqued down between 25 and 50 ft·lb |
| Nanolubricants | Volume Concentration (%) | Reduction of Friction Torque (%) | Reduction of COF (%) | Reduction of WSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2/POE | 0.01 | 20.2 | 22.1 | 12.5 |
| 0.03 | 34.9 | 36.1 | 11.6 | |
| 0.05 | 36.0 | 37.5 | 2.0 | |
| 0.07 | 23.4 | 24.1 | 1.2 | |
| 0.1 | 23.4 | 24.9 | 0.7 | |
| SiO2/POE | 0.01 | 33.7 | 33.5 | 26.4 |
| 0.03 | 28.0 | 28.9 | 8.6 | |
| 0.05 | 17.0 | 18.1 | 8.2 | |
| 0.07 | 16.1 | 18.5 | 8.6 | |
| 0.1 | 14.0 | 14.4 | 9.1 | |
| TiO2-SiO2/POE | 0.01 | 21.0 | 21.9 | 10.8 |
| 0.03 | 29.8 | 31.6 | 12.4 | |
| 0.05 | 17.9 | 18.5 | 10.6 | |
| 0.07 | 22.1 | 24.4 | 11.4 | |
| 0.1 | 26.7 | 29.9 | 8.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamisa, A.H.; Azmi, W.H.; Ismail, M.F.; Rahim, R.A.; Ali, H.M. Tribology Performance of Polyol-Ester Based TiO2, SiO2, and Their Hybrid Nanolubricants. Lubricants 2023, 11, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11010018
Hamisa AH, Azmi WH, Ismail MF, Rahim RA, Ali HM. Tribology Performance of Polyol-Ester Based TiO2, SiO2, and Their Hybrid Nanolubricants. Lubricants. 2023; 11(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamisa, Abdul Hamid, Wan Hamzah Azmi, Mohd Farid Ismail, Rosminazuin Ab Rahim, and Hafiz Muhammad Ali. 2023. "Tribology Performance of Polyol-Ester Based TiO2, SiO2, and Their Hybrid Nanolubricants" Lubricants 11, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11010018
APA StyleHamisa, A. H., Azmi, W. H., Ismail, M. F., Rahim, R. A., & Ali, H. M. (2023). Tribology Performance of Polyol-Ester Based TiO2, SiO2, and Their Hybrid Nanolubricants. Lubricants, 11(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11010018







