Halo Substructure Boosts to the Signatures of Dark Matter Annihilation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Formulation
2.1. Subhalo Boost Factor
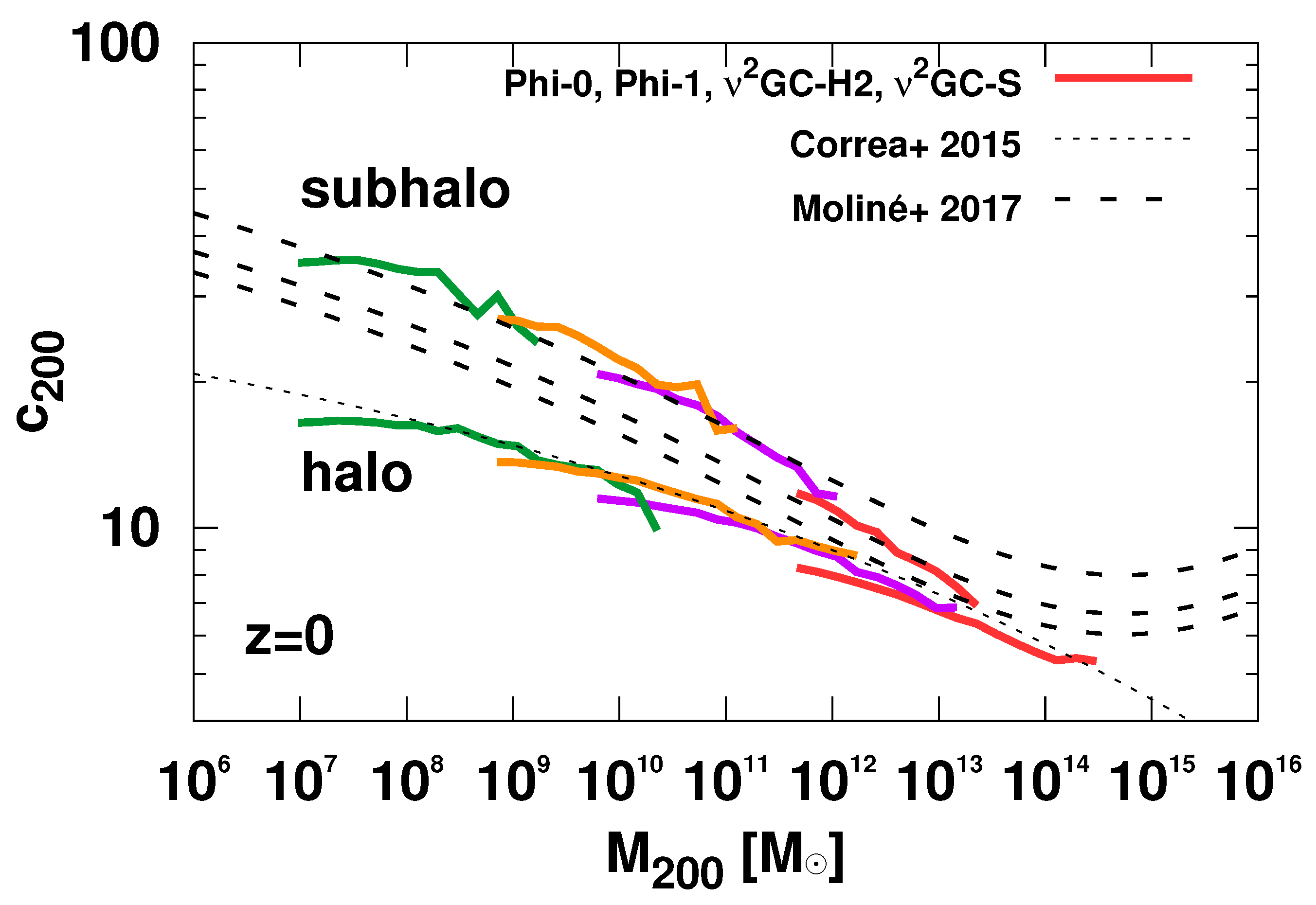
2.2. Characterization of Dark Matter Halos
3. Estimates of Annihilation Boost with Numerical Simulations
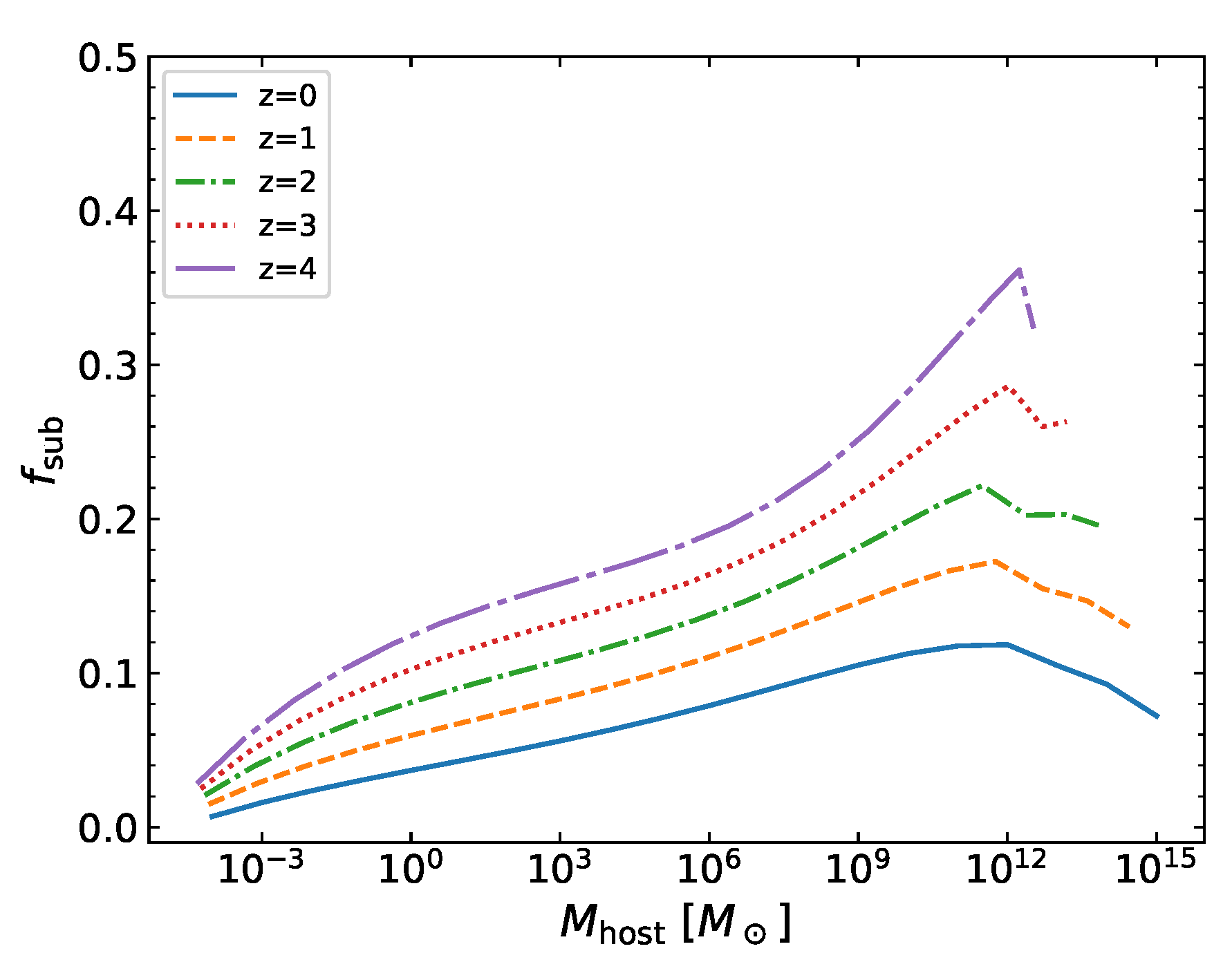
3.1. Subhalo Abundance
3.2. Density Profile of Dark Matter Halos
3.3. Density Profile of Dark Matter Subhalos
3.4. Density Profile of Dark Matter Halos Near Cutoff Scales
4. Semi-Analytic Approaches
4.1. Models Based on Structure Formation and Tidal Evolution
4.2. Models for Self-Similar Subhalos
4.3. Universal Clustering of Dark Matter in Phase Space
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Fitting Formulae
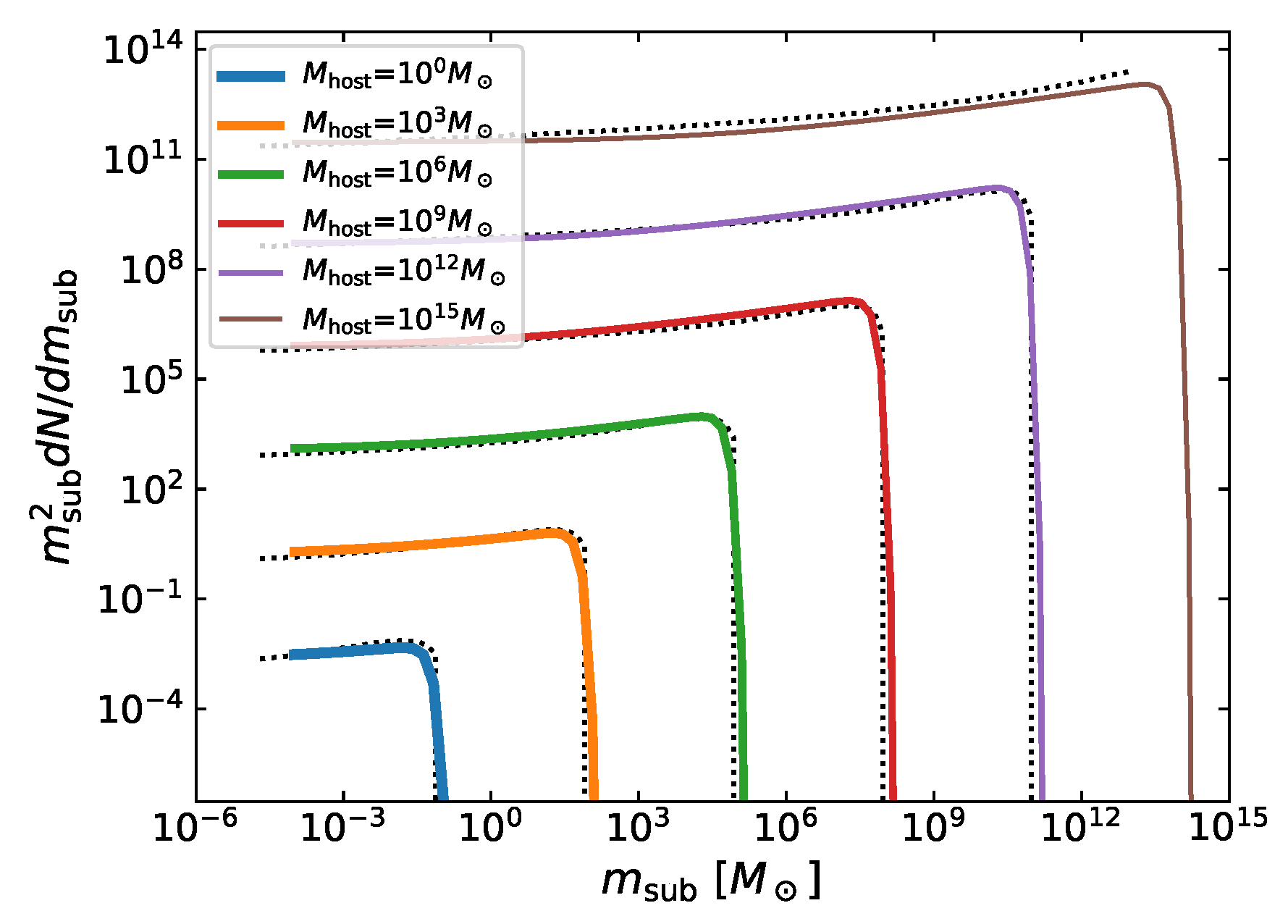
Appendix A.1. Subhalo Mass Function
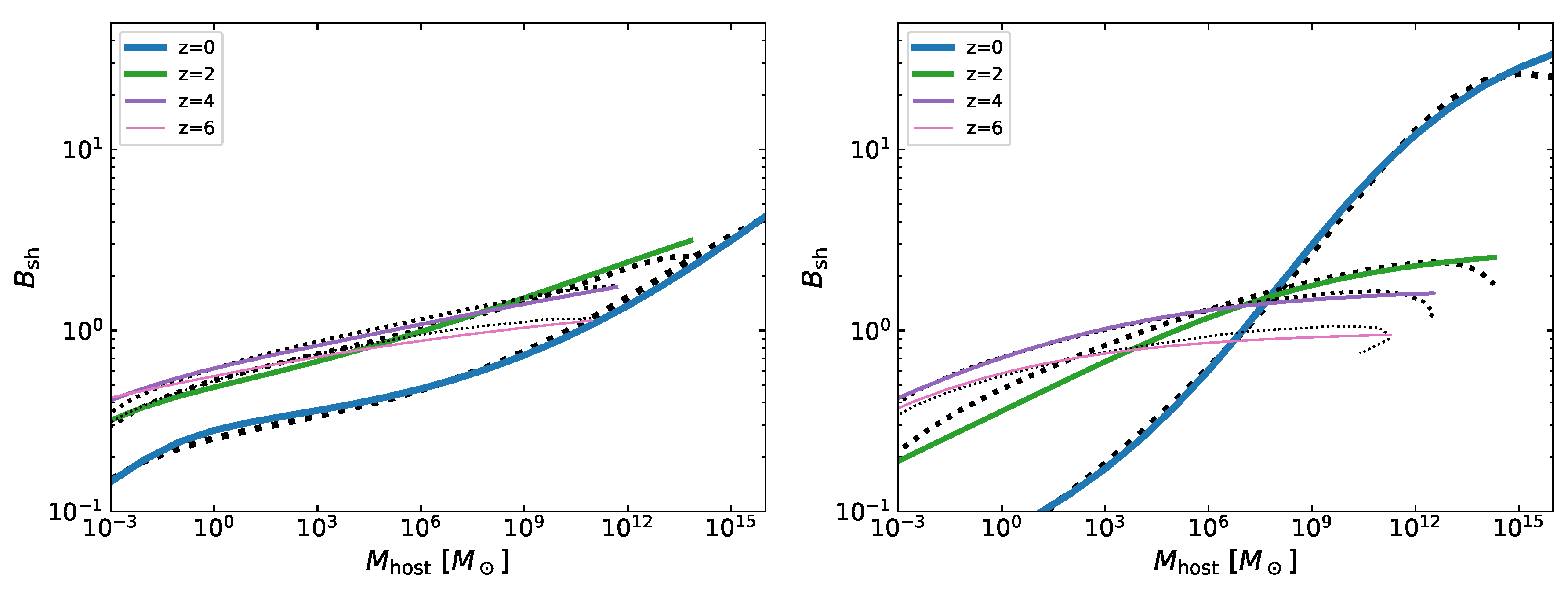
Appendix A.2. Subhalo Luminosity
Appendix A.3. Annihilation Boost Factor
Appendix A.4. Fitting Functions for the Boost Factor in the Literature
References
- Bertone, G.; Hooper, D.; Silk, J. Particle dark matter: Evidence, candidates and constraints. Phys. Rep. 2005, 405, 279–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringmann, T.; Weniger, C. Gamma Ray Signals from Dark Matter: Concepts, Status and Prospects. Phys. Dark Univ. 2012, 1, 194–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungman, G.; Kamionkowski, M.; Griest, K. Supersymmetric dark matter. Phys. Rep. 1996, 267, 195–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.; Profumo, S. Dark matter and collider phenomenology of universal extra dimensions. Phys. Rep. 2007, 453, 29–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boveia, A.; Doglioni, C. Dark Matter Searches at Colliders. Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 2018, 68, 429–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigman, G.; Dasgupta, B.; Beacom, J.F. Precise Relic WIMP Abundance and its Impact on Searches for Dark Matter Annihilation. Phys. Rev. 2012, D86, 023506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, S.; Schwarz, D.J.; Stoecker, H. Damping scales of neutralino cold dark matter. Phys. Rev. 2001, D64, 083507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.M.; Hofmann, S.; Schwarz, D.J. The power spectrum of SUSY—CDM on sub-galactic scales. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 353, L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, A.; Zaldarriaga, M. The Small-scale power spectrum of cold dark matter. Phys. Rev. 2005, D71, 103520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertschinger, E. The Effects of Cold Dark Matter Decoupling and Pair Annihilation on Cosmological Perturbations. Phys. Rev. 2006, D74, 063509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profumo, S.; Sigurdson, K.; Kamionkowski, M. What mass are the smallest protohalos? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 031301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bringmann, T. Particle Models and the Small-Scale Structure of Dark Matter. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 105027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, J.M.; Profumo, S. Earthly probes of the smallest dark matter halos. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 1206, 011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Diamanti, R.; Catalan, M.E.C.; Ando, S. Dark matter protohalos in a nine parameter MSSM and implications for direct and indirect detection. Phys. Rev. 2015, D92, 065029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silk, J.; Stebbins, A. Clumpy cold dark matter. Astrophys. J. 1993, 411, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, L.; Edsjo, J.; Gondolo, P.; Ullio, P. Clumpy neutralino dark matter. Phys. Rev. 1999, D59, 043506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, L.; Edsjo, J.; Ullio, P. Possible indications of a clumpy dark matter halo. Phys. Rev. 1998, D58, 083507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcaneo-Roldan, C.; Moore, B. The Surface brightness of dark matter: Unique signatures of neutralino annihilation in the galactic halo. Phys. Rev. 2000, D62, 123005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasitsiomi, A.; Olinto, A.V. The Detectability of neutralino clumps via atmospheric Cherenkov telescopes. Phys. Rev. 2002, D66, 083006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoehr, F.; White, S.D.M.; Springel, V.; Tormen, G.; Yoshida, N. Dark matter annihilation in the halo of the Milky Way. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 345, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Koushiappas, S.M.; Zentner, A.R.; Walker, T.P. The observability of gamma-rays from neutralino annihilations in Milky Way substructure. Phys. Rev. 2004, D69, 043501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltz, E.A.; Taylor, J.E.; Wai, L.L. Can Astrophysical Gamma Ray Sources Mimic Dark Matter Annihilation in Galactic Satellites? Astrophys. J. 2007, 659, L125–L128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, S. Can dark matter annihilation dominate the extragalactic gamma-ray background? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 171303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, T.; Totani, T.; Nagashima, M. Gamma-ray background from neutralino annihilation in the first cosmological objects. Astrophys. J. 2005, 633, L65–L68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, L.; Branchini, E.; Hofmann, S. Difficulty of detecting minihalos via gamm rays from dark matter annihilation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 211301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koushiappas, S.M. Proper motion of gamma-rays from microhalo sources. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 191301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, S.; Komatsu, E.; Narumoto, T.; Totani, T. Dark matter annihilation or unresolved astrophysical sources? Anisotropy probe of the origin of cosmic gamma-ray background. Phys. Rev. 2007, D75, 063519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, L.; Bertone, G.; Branchini, E. Dark Matter Annihilation in Substructures Revised. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 384, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemand, J.; Kuhlen, M.; Madau, P. Dark matter substructure and gamma-ray annihilation in the Milky Way halo. Astrophys. J. 2007, 657, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezinsky, V.; Dokuchaev, V.; Eroshenko, Y. Anisotropy of dark matter annihilation with respect to the Galactic plane. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2007, 011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavalle, J.; Yuan, Q.; Maurin, D.; Bi, X.J. Full Calculation of Clumpiness Boost factors for Antimatter Cosmic Rays in the light of Lambda-CDM N-body simulation results. Abandoning hope in clumpiness enhancement? Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 479, 427–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegal-Gaskins, J.M. Revealing dark matter substructure with anisotropies in the diffuse gamma-ray background. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2008, 040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ando, S.; Kamionkowski, M.; Lee, S.K.; Koushiappas, S.M. Can proper motions of dark-matter subhalos be detected? Phys. Rev. 2008, D78, 101301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Ando, S.; Kamionkowski, M. The Gamma-Ray-Flux Probability Distribution Function from Galactic Halo Substructure. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2009, 0907, 007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamionkowski, M.; Koushiappas, S.M. Galactic substructure and direct detection of dark matter. Phys. Rev. 2008, D77, 103509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springel, V.; White, S.D.M.; Frenk, C.S.; Navarro, J.F.; Jenkins, A.; Vogelsberger, M.; Wang, J.; Ludlow, A.; Helmi, A. Prospects for detecting supersymmetric dark matter in the Galactic halo. Nature 2008, 456, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springel, V.; Wang, J.; Vogelsberger, M.; Ludlow, A.; Jenkins, A.; Helmi, A.; Navarro, J.F.; Frenk, C.S.; White, S.D.M. The Aquarius Project: The subhalos of galactic halos. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 391, 1685–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, S. Gamma-ray background anisotropy from galactic dark matter substructure. Phys. Rev. 2009, D80, 023520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamionkowski, M.; Koushiappas, S.M.; Kuhlen, M. Galactic Substructure and Dark Matter Annihilation in the Milky Way Halo. Phys. Rev. 2010, D81, 043532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzke, A.; Pfrommer, C.; Bergstrom, L. Prospects of detecting gamma-ray emission from galaxy clusters: Cosmic rays and dark matter annihilations. Phys. Rev. 2011, D84, 123509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Frenk, C.S.; Jenkins, A.; Springel, V.; White, S.D.M. Where will supersymmetric dark matter first be seen? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 419, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornasa, M.; Zavala, J.; Sanchez-Conde, M.A.; Siegal-Gaskins, J.M.; Delahaye, T.; Prada, F.; Vogelsberger, M.; Zandanel, F.; Frenk, C.S. Characterization of Dark-Matter-induced anisotropies in the diffuse gamma-ray background. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 429, 1529–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.C.Y.; Laha, R.; Campbell, S.; Horiuchi, S.; Dasgupta, B.; Murase, K.; Beacom, J.F. Resolving small-scale dark matter structures using multisource indirect detection. Phys. Rev. 2014, D89, 083001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Conde, M.A.; Prada, F. The flattening of the concentration–mass relation towards low halo masses and its implications for the annihilation signal boost. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 442, 2271–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, T. Hierarchical Formation of Dark Matter Halos and the Free Streaming Scale. Astrophys. J. 2014, 788, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, R.; Ando, S. Boosting the annihilation boost: Tidal effects on dark matter subhalos and consistent luminosity modeling. Phys. Rev. 2015, D92, 123508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stref, M.; Lavalle, J. Modeling dark matter subhalos in a constrained galaxy: Global mass and boosted annihilation profiles. Phys. Rev. 2017, D95, 063003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moliné, Á.; Sánchez-Conde, M.A.; Palomares-Ruiz, S.; Prada, F. Characterization of subhalo structural properties and implications for dark matter annihilation signals. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 466, 4974–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavala, J.; Afshordi, N. Universal clustering of dark matter in phase space. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 457, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroshima, N.; Ando, S.; Ishiyama, T. Modeling evolution of dark matter substructure and annihilation boost. Phys. Rev. 2018, D97, 123002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemand, J.; Kuhlen, M.; Madau, P.; Zemp, M.; Moore, B.; Potter, D.; Stadel, J. Clumps and streams in the local dark matter distribution. Nature 2008, 454, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadel, J.; Potter, D.; Moore, B.; Diemand, J.; Madau, P.; Zemp, M.; Kuhlen, M.; Quilis, V. Quantifying the heart of darkness with GHALO—A multi-billion particle simulation of our galactic halo. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 398, L21–L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezinsky, V.S.; Dokuchaev, V.I.; Eroshenko, Y.N. Small-scale clumps of dark matter. Phys. Usp. 2014, 57, 1–36, reprinted in Usp. Fiz. Nauk 2014, 184, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H.; Schechter, P. Formation of galaxies and clusters of galaxies by selfsimilar gravitational condensation. Astrophys. J. 1974, 187, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, J.R.; Cole, S.; Efstathiou, G.; Kaiser, N. Excursion set mass functions for hierarchical Gaussian fluctuations. Astrophys. J. 1991, 379, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.; Zimmer, S.; Conrad, J.; Gustafsson, M.; Sánchez-Conde, M.; Caputo, R. Search for Gamma-Ray Lines towards Galaxy Clusters with the Fermi-LAT. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 1602, 026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.F.; Frenk, C.S.; White, S.D.M. The Structure of cold dark matter halos. Astrophys. J. 1996, 462, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.F.; Frenk, C.S.; White, S.D.M. A Universal density profile from hierarchical clustering. Astrophys. J. 1997, 490, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbonnier, A.; Combet, C.; Maurin, D. CLUMPY: A code for γ-ray signals from dark matter structures. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2012, 183, 656–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezri, E.; White, R.; Combet, C.; Maurin, D.; Pointecouteau, E.; Hinton, J.A. gamma-rays from annihilating dark matter in galaxy clusters: Stacking vs single source analysis. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 425, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ando, S.; Komatsu, E. Constraints on the annihilation cross section of dark matter particles from anisotropies in the diffuse gamma-ray background measured with Fermi-LAT. Phys. Rev. 2013, D87, 123539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hütten, M.; Combet, C.; Maier, G.; Maurin, D. Dark matter substructure modelling and sensitivity of the Cherenkov Telescope Array to Galactic dark halos. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 1609, 047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, G.L.; Norman, M.L. Statistical properties of x-ray clusters: Analytic and numerical comparisons. Astrophys. J. 1998, 495, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, C.A.; Wyithe, J.S.B.; Schaye, J.; Duffy, A.R. The accretion history of dark matter haloes—III. A physical model for the concentration–mass relation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 452, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, T.; Makino, J.; Portegies Zwart, S.; Groen, D.; Nitadori, K.; Rieder, S.; de Laat, C.; McMillan, S.; Hiraki, K.; Harfst, S. The Cosmogrid Simulation: Statistical Properties of small Dark Matter Halos. Astrophys. J. 2013, 767, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderhalden, D.; Diemand, J. Density Profiles of CDM Microhalos and their Implications for Annihilation Boost Factors. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2013, 1304, 009, Erratum in J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2013, 1308, E02, doi:10.1088/1475-7516/2013/08/E02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, T.; Sudo, K.; Yokoi, S.; Hasegawa, K.; Tominaga, N.; Susa, H. Where are the Low-mass Population III Stars? Astrophys. J. 2016, 826, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klypin, A.A.; Kravtsov, A.V.; Valenzuela, O.; Prada, F. Where are the missing Galactic satellites? Astrophys. J. 1999, 522, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.; Ghigna, S.; Governato, F.; Lake, G.; Quinn, T.R.; Stadel, J.; Tozzi, P. Dark matter substructure within galactic halos. Astrophys. J. 1999, 524, L19–L22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemand, J.; Moore, B.; Stadel, J. Velocity and spatial biases in CDM subhalo distributions. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 352, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, D.; Governato, F.; Quinn, T.R.; Gardner, J.; Stadel, J.; Lake, G. Dark matter subhaloes in numerical simulations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 359, 1537–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kase, H.; Makino, J.; Funato, Y. Missing dwarf problem in galaxy clusters. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 59, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamionkowski, M.; Liddle, A.R. The Dearth of halo dwarf galaxies: Is there power on short scales? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 4525–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spergel, D.N.; Steinhardt, P.J. Observational evidence for selfinteracting cold dark matter. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 3760–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susa, H.; Umemura, M. Effects of early cosmic reionization on the substructure problem in galactic halo. Astrophys. J. 2004, 610, L5–L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, A.J.; Frenk, C.S.; Lacey, C.G.; Baugh, C.M.; Cole, S. The effects of photoionization on galaxy formation. 2. Satellites in the local group. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2002, 333, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoehr, F.; White, S.D.M.; Tormen, G.; Springel, V. The Milky Way’s satellite population in a lambdaCDM universe. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2002, 335, L84–L88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kravtsov, A.V.; Gnedin, O.Y.; Klypin, A.A. The Tumultuous lives of Galactic dwarfs and the missing satellites problem. Astrophys. J. 2004, 609, 482–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.; Frenk, C.S.; Jenkins, A.; Theuns, T. The properties of satellite galaxies in simulations of galaxy formation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 406, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, T.; Fukushige, T.; Makino, J. Variation of the subhalo abundance in dark matter halos. Astrophys. J. 2009, 696, 2115–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.Y.; Williamson, M.; Wechsler, R.H. The Dependence of Subhalo Abundance on Halo Concentration. Astrophys. J. 2015, 810, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravtsov, A.V.; Berlind, A.A.; Wechsler, R.H.; Klypin, A.A.; Gottloeber, S.; Allgood, B.; Primack, J.R. The Dark side of the halo occupation distribution. Astrophys. J. 2004, 609, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; White, S.D.M.; Jenkins, A.; Stoehr, F.; Springel, V. The Subhalo populations of lambda-CDM dark halos. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 355, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zentner, A.R.; Berlind, A.A.; Bullock, J.S.; Kravtsov, A.V.; Wechsler, R.H. The Physics of galaxy clustering. 1. A Model for subhalo populations. Astrophys. J. 2005, 624, 505–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bosch, F.C.; Tormen, G.; Giocoli, C. The Mass function and average mass loss rate of dark matter subhaloes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 359, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giocoli, C.; Tormen, G.; Sheth, R.K.; van den Bosch, F.C. The Substructure Hierarchy in Dark Matter Haloes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 404, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Frenk, C.S.; Boylan-Kolchin, M.; Jenkins, A.; Springel, V.; White, S.D.M. The statistics of the subhalo abundance of dark matter haloes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 410, 2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giocoli, C.; Pieri, L.; Tormen, G. Analytical Approach to Subhaloes Population in Dark Matter Haloes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 387, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Mo, H.J.; Zhang, Y.; Bosch, F.C.V.D. An analytical model for the accretion of dark matter subhalos. Astrophys. J. 2011, 741, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; van den Bosch, F.C. Statistics of dark matter substructure—I. Model and universal fitting functions. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 458, 2848–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, J.E.; Gott, J.R., III. On the Infall of Matter into Clusters of Galaxies and Some Effects on Their Evolution. Astrophys. J. 1972, 176, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, P.J.; Salmon, J.K.; Zurek, W.H. Primordial density fluctuations and the structure of galactic haloes. Nature 1986, 322, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinski, J.; Carlberg, R.G. The Structure of cold dark matter halos. Astrophys. J. 1991, 378, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernquist, L. An Analytical Model for Spherical Galaxies and Bulges. Astrophys. J. 1990, 356, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushige, T.; Makino, J. On the Origin of Cusps in Dark Matter Halos. Astrophys. J. 1997, 477, L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.; Quinn, T.R.; Governato, F.; Stadel, J.; Lake, G. Cold collapse and the core catastrophe. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1999, 310, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghigna, S.; Moore, B.; Governato, F.; Lake, G.; Quinn, T.R.; Stadel, J. Density profiles and substructure of dark matter halos. Converging results at ultra-high numerical resolution. Astrophys. J. 2000, 544, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.P. The Density Profile of Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Dark Matter Halos. Astrophys. J. 2000, 535, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushige, T.; Makino, J. Structure of dark matter halos from hierarchical clustering. Astrophys. J. 2001, 557, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klypin, A.; Kravtsov, A.V.; Bullock, J.; Primack, J. Resolving the structure of cold dark matter halos. Astrophys. J. 2001, 554, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, C.; Navarro, J.F.; Jenkins, A.; Frenk, C.S.; White, S.D.M.; Springel, V.; Stadel, J.; Quinn, T.R. The Inner structure of Lambda CDM halos. 1. A Numerical convergence study. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 338, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushige, T.; Kawai, A.; Makino, J. Structure of dark matter halos from hierarchical clustering. 3. Shallowing of the Inner cusp. Astrophys. J. 2004, 606, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, E.; Navarro, J.F.; Power, C.; Jenkins, A.R.; Frenk, C.S.; White, S.D.M.; Springel, V.; Stadel, J.; Quinn, T.R. The Inner structure of lambda-CDM halos. 2. Halo mass profiles and LSB rotation curves. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 355, 794–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazantzidis, S.; Zentner, A.R.; Kravtsov, A.V. The robustness of dark matter density profiles in dissipationless mergers. Astrophys. J. 2006, 641, 647–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.P.; Suto, Y. Density profiles of dark matter halo are not universal. Astrophys. J. 2000, 529, L69–l72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemand, J.; Moore, B.; Stadel, J. Convergence and scatter of cluster density profiles. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 353, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Einasto, J. On the Construction of a Composite Model for the Galaxy and on the Determination of the System of Galactic Parameters. Tr. Astrofiz. Instituta Alma-Ata 1965, 5, 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Bullock, J.S.; Kolatt, T.S.; Sigad, Y.; Somerville, R.S.; Kravtsov, A.V.; Klypin, A.A.; Primack, J.R.; Dekel, A. Profiles of dark haloes. Evolution, scatter, and environment. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2001, 321, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.H.; Jing, Y.P.; Mo, H.J.; Borner, G. Mass and redshift dependence of dark halo structure. Astrophys. J. 2003, 597, L9–L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccio, A.V.; Dutton, A.A.; van den Bosch, F.C.; Moore, B.; Potter, D.; Stadel, J. Concentration, Spin and Shape of Dark Matter Haloes: Scatter and the Dependence on Mass and Environment. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 378, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, A.F.; Gao, L.; Bett, P.; Cole, S.; Navarro, J.F.; Frenk, C.S.; White, S.D.M.; Springel, V.; Jenkins, A. The statistics of lambda CDM Halo Concentrations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 381, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccio, A.V.; Dutton, A.A.; Bosch, F.C.V.D. Concentration, Spin and Shape of Dark Matter Haloes as a Function of the Cosmological Model: WMAP1, WMAP3 and WMAP5 results. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 391, 1940–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.H.; Jing, Y.P.; Mo, H.J.; Boerner, G. Accurate universal models for the mass accretion histories and concentrations of dark matter halos. Astrophys. J. 2009, 707, 354–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klypin, A.; Trujillo-Gomez, S.; Primack, J. Halos and galaxies in the standard cosmological model: Results from the Bolshoi simulation. Astrophys. J. 2011, 740, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada, F.; Klypin, A.A.; Cuesta, A.J.; Betancort-Rijo, J.E.; Primack, J. Halo concentrations in the standard LCDM cosmology. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 423, 3018–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klypin, A.; Yepes, G.; Gottlober, S.; Prada, F.; Hess, S. MultiDark simulations: The story of dark matter halo concentrations and density profiles. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 457, 4340–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludlow, A.D.; Bose, S.; Angulo, R.E.; Wang, L.; Hellwing, W.A.; Navarro, J.F.; Cole, S.; Frenk, C.S. The mass–concentration–redshift relation of cold and warm dark matter haloes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 460, 1214–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, R.H.; Bullock, J.S.; Primack, J.R.; Kravtsov, A.V.; Dekel, A. Concentrations of dark halos from their assembly histories. Astrophys. J. 2002, 568, 52–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellwing, W.A.; Frenk, C.S.; Cautun, M.; Bose, S.; Helly, J.; Jenkins, A.; Sawala, T.; Cytowski, M. The Copernicus Complexio: A high-resolution view of the small-scale Universe. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 457, 3492–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilipenko, S.V.; Sánchez-Conde, M.A.; Prada, F.; Yepes, G. Pushing down the low-mass halo concentration frontier with the Lomonosov cosmological simulations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 472, 4918–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemand, J.; Kuhlen, M.; Madau, P. Formation and evolution of galaxy dark matter halos and their substructure. Astrophys. J. 2007, 667, 859–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, D.S.; Koushiappas, S.M.; Gao, L. Non-universality of halo profiles and implications for dark matter experiments. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 415, 3177–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Springel, V.; White, S.D.M.; Jenkin, A.; Frenk, C.S.; Yoshida, N.; Navarro, J.; Thacker, R.; Croton, D.; Helly, J.; Peacock, J.A.; et al. Simulating the joint evolution of quasars, galaxies and their large-scale distribution. Nature 2005, 435, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullio, P.; Bergstrom, L.; Edsjo, J.; Lacey, C.G. Cosmological dark matter annihilations into gamma-rays—A closer look. Phys. Rev. 2002, D66, 123502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, L.; Lavalle, J.; Bertone, G.; Branchini, E. Implications of High-Resolution Simulations on Indirect Dark Matter Searches. Phys. Rev. 2011, D83, 023518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, T.; Enoki, M.; Kobayashi, M.A.R.; Makiya, R.; Nagashima, M.; Oogi, T. The ν2GC simulations: Quantifying the dark side of the universe in the Planck cosmology. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 67, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makiya, R.; Enoki, M.; Ishiyama, T.; Kobayashi, M.A.R.; Nagashima, M.; Okamoto, T.; Okoshi, K.; Oogi, T.; Shirakata, H. The New Numerical Galaxy Catalog (ν2GC): An updated semi-analytic model of galaxy and active galactic nucleus formation with large cosmological N-body simulations. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 68, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bosch, F.C.; Ogiya, G. Dark Matter Substructure in Numerical Simulations: A Tale of Discreteness Noise, Runaway Instabilities, and Artificial Disruption. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 475, 4066–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñarrubia, J.; Benson, A.J.; Walker, M.G.; Gilmore, G.; McConnachie, A.; Mayer, L. The impact of dark matter cusps and cores on the satellite galaxy population around spiral galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 406, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bosch, F.C.; Ogiya, G.; Hahn, O.; Burkert, A. Disruption of Dark Matter Substructure: Fact or Fiction? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 474, 3043–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemand, J.; Moore, B.; Stadel, J. Earth-mass dark-matter haloes as the first structures in the early Universe. Nature 2005, 433, 389–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, T.; Makino, J.; Ebisuzaki, T. Gamma-ray Signal from Earth-mass Dark Matter Microhalos. Astrophys. J. 2010, 723, L195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, R.E.; Hahn, O.; Ludlow, A.; Bonoli, S. Earth-mass haloes and the emergence of NFW density profiles. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 471, 4687–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogiya, G.; Hahn, O. What sets the central structure of dark matter haloes? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 473, 4339–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogiya, G.; Nagai, D.; Ishiyama, T. Dynamical evolution of primordial dark matter haloes through mergers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 461, 3385–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosenca, M.; Adamek, J.; Byrnes, C.T.; Hotchkiss, S. 3D simulations with boosted primordial power spectra and ultracompact minihalos. Phys. Rev. 2017, D96, 123519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delos, M.S.; Erickcek, A.L.; Bailey, A.P.; Alvarez, M.A. Are ultracompact minihalos really ultracompact? Phys. Rev. 2018, D97, 041303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delos, M.S.; Erickcek, A.L.; Bailey, A.P.; Alvarez, M.A. Density profiles of ultracompact minihalos: Implications for constraining the primordial power spectrum. Phys. Rev. 2018, D98, 063527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polisensky, E.; Ricotti, M. Fingerprints of the initial conditions on the density profiles of cold and warm dark matter haloes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 450, 2172–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gott, J.R., III. On the Formation of Elliptical Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1975, 201, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillmore, J.A.; Goldreich, P. Self-similiar gravitational collapse in an expanding universe. Astrophys. J. 1984, 281, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertschinger, E. Self-similar secondary infall and accretion in an Einstein-de Sitter universe. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 1985, 58, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.V.; Zybin, K.P. Large-scale structure of the Universe. Analytic theory. Phys. Uspekhi 1995, 38, 687–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghram, S.; Afshordi, N.; Zurek, K.M. Prospects for Detecting Dark Matter Halo Substructure with Pulsar Timing. Phys. Rev. 2011, D84, 043511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiyama, K.; Oguri, M. Detectability of Small-Scale Dark Matter Clumps with Pulsar Timing Arrays. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.07847. [Google Scholar]
- Dror, J.A.; Ramani, H.; Trickle, T.; Zurek, K.M. Pulsar Timing Probes of Primordial Black Holes and Subhalos. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.04490. [Google Scholar]
- Correa, C.A.; Wyithe, J.S.B.; Schaye, J.; Duffy, A.R. The accretion history of dark matter haloes—I. The physical origin of the universal function. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 450, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, E.; Navarro, J.F.; Taylor, J.E.; Stadel, J.; Quinn, T.R. The Structural evolution of substructure. Astrophys. J. 2003, 584, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behroozi, P.S.; Wechsler, R.H.; Wu, H.Y. The Rockstar Phase-Space Temporal Halo Finder and the Velocity Offsets of Cluster Cores. Astrophys. J. 2013, 762, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemand, J.; Kuhlen, M.; Madau, P. Early supersymmetric cold dark matter substructure. Astrophys. J. 2006, 649, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seljak, U. Analytic model for galaxy and dark matter clustering. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2000, 318, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Marinacci, F.; Maji, M.; Li, Y.; Springel, V.; Hernquist, L. Baryonic impact on the dark matter distribution in Milky Way-sized galaxies and their satellites. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 458, 1559–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errani, R.; Peñarrubia, J.; Laporte, C.F.P.; Gómez, F.A. The effect of a disc on the population of cuspy and cored dark matter substructures in Milky Way-like galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 465, L59–L63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.T.E.; Pillepich, A.; Rodriguez-Gomez, V.; Vogelsberger, M.; Bird, S.; Hernquist, L. Subhalo demographics in the Illustris simulation: Effects of baryons and halo-to-halo variation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 472, 4343–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, T.; Bullock, J.S.; Garrison-Kimmel, S.; Boylan-Kolchin, M.; Pawlowski, M.S.; Graus, A.S. Phat ELVIS: The inevitable effect of the Milky Way’s disk on its dark matter subhaloes. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.12413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoli, C.; Afshordi, N. Concentration, Ellipsoidal Collapse, and the Densest Dark Matter haloes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 456, 3068–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Navarro, J.F.; Frenk, C.S.; Jenkins, A.; Springel, V.; White, S.D.M. The Phoenix Project: The Dark Side of Rich Galaxy Clusters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 425, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
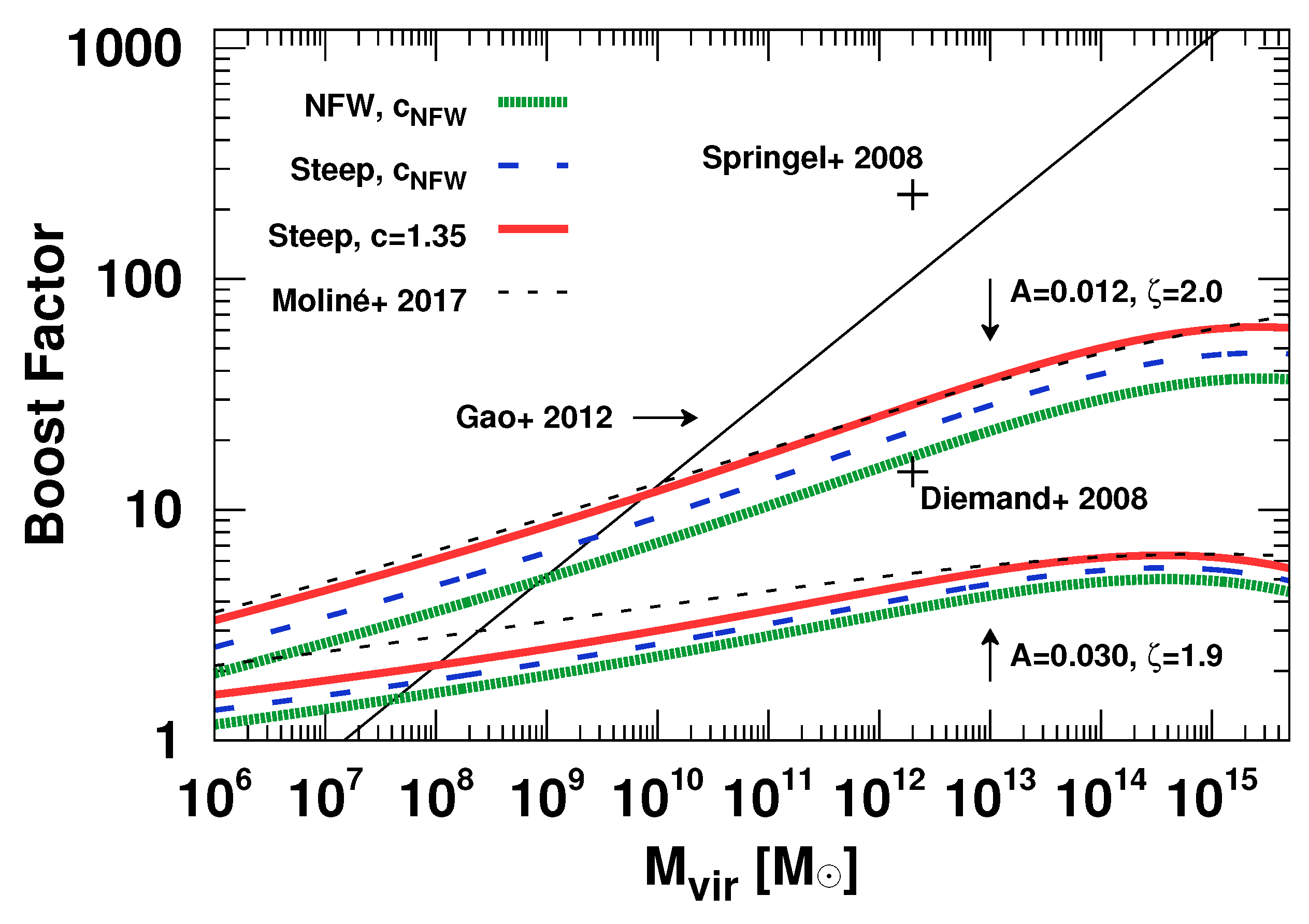
| 1 | We note, however, that the concentration has a scatter, which is often characterized by a log-normal distribution, whose mean is the function of M and z. We will include this in the latter sections. |
| 2 | For the sake of simplicity for analytic expressions, we assume that the suhbalo mass is the only parameter characterizing its density profile. One can introduce many more parameters to make the model more realistic. |
| 3 | The concentration-mass relation is defined as the average concentration parameter as a function of halo mass. |
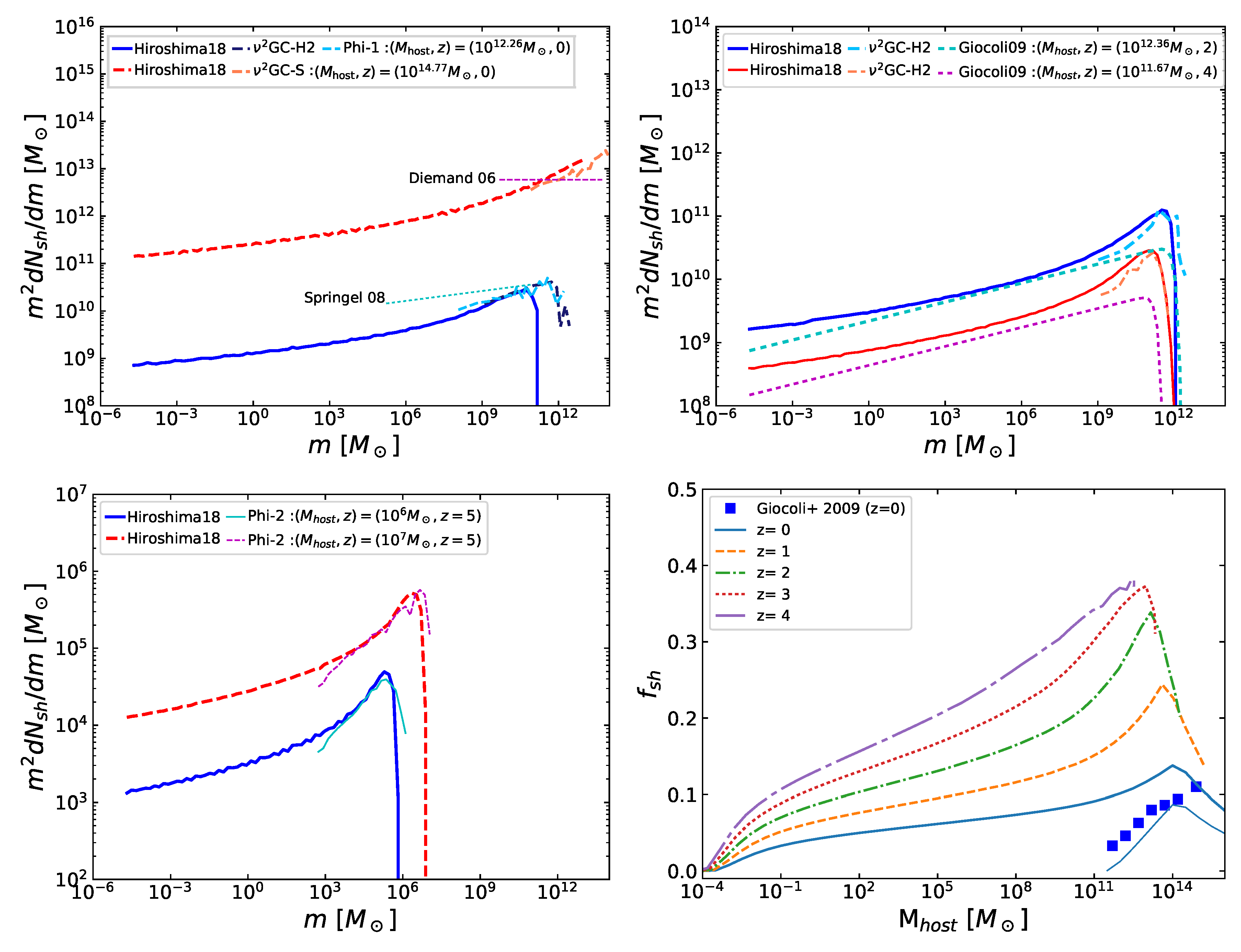
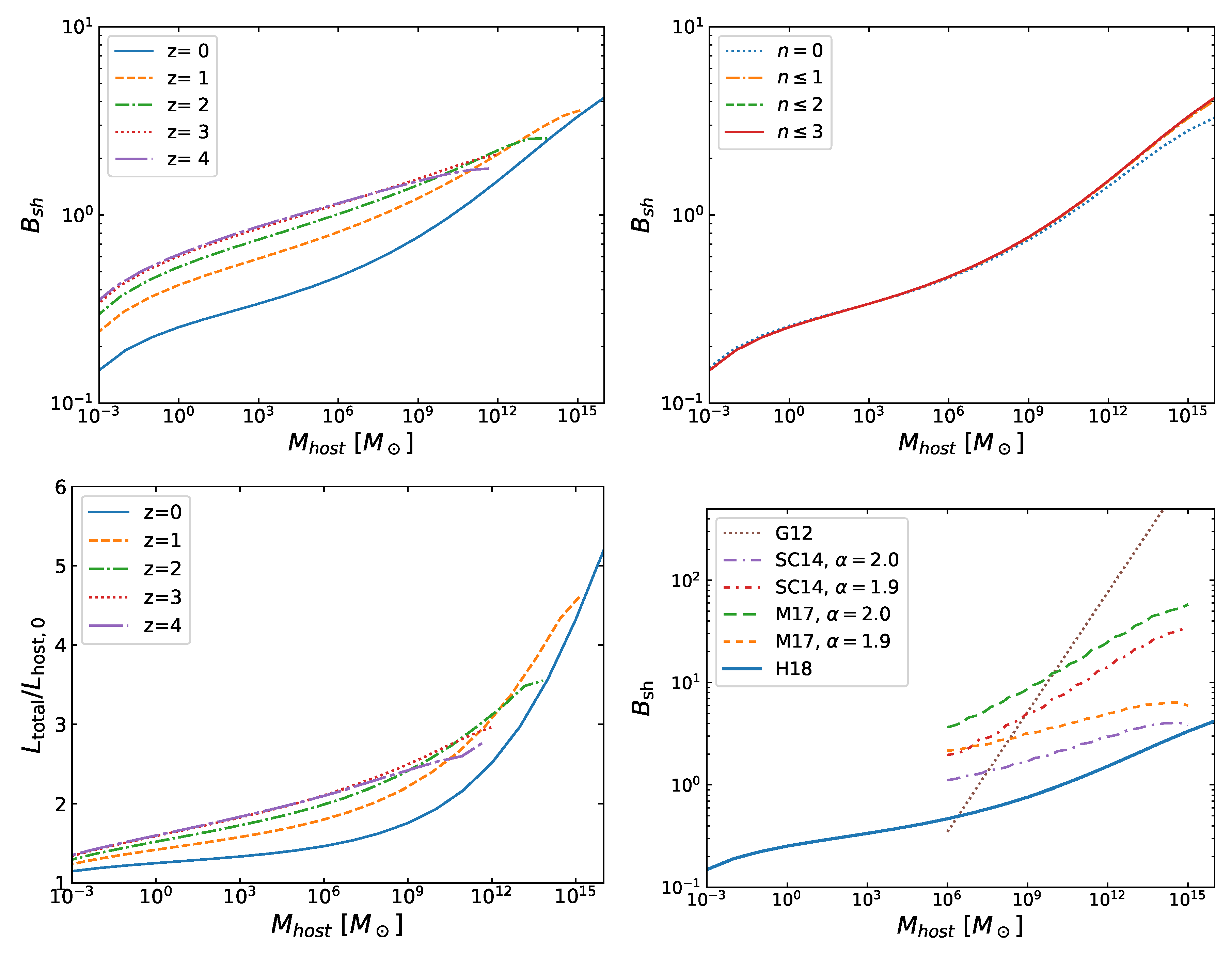
| 4 | We note that in estimating the effect of sub-subhalos in the boost factors, Reference Hiroshima et al. [50] ignored the changes of and and hence did not include the factor of in Equation (39) and in Equation (40). In addition, in Equation (43), they multiplied by a factor of instead of . We correct for all these effects in this review. |

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ando, S.; Ishiyama, T.; Hiroshima, N. Halo Substructure Boosts to the Signatures of Dark Matter Annihilation. Galaxies 2019, 7, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies7030068
Ando S, Ishiyama T, Hiroshima N. Halo Substructure Boosts to the Signatures of Dark Matter Annihilation. Galaxies. 2019; 7(3):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies7030068
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndo, Shin’ichiro, Tomoaki Ishiyama, and Nagisa Hiroshima. 2019. "Halo Substructure Boosts to the Signatures of Dark Matter Annihilation" Galaxies 7, no. 3: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies7030068
APA StyleAndo, S., Ishiyama, T., & Hiroshima, N. (2019). Halo Substructure Boosts to the Signatures of Dark Matter Annihilation. Galaxies, 7(3), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies7030068