Radio Galaxies at TeV Energies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Radio Galaxies in Context
2.1. Blazar Studies
2.2. Radio Galaxies at GeV Energies
2.3. Motivations for Studying Radio Galaxies at TeV Energies
- Do all TeV-detected radio galaxies exist in dense clumpy environments, for example? What role does the environment play in decelerating radio galaxy jets, for example, and does this interaction lead to -ray emission and/or -ray orphan flares? (See [49] and the references therein.)
- Do TeV-detected radio galaxies exhibit any common kinematic characteristics? How do radio galaxies accelerate particles in their jets, and can regions with different apparent velocity profiles (over all jet scales) be correlated with -ray emission? What mechanisms give rise to features in radio galaxy jets, e.g., internal shocks, and are these responsible for gamma-ray emission?
- Is it right to classify the TeV-detected radio galaxies as misaligned blazars, or are these objects simply blazar-like, with much smaller jet inclination angles to the line-of-sight than currently derived or assumed?
- In TeV-detected radio galaxies, where does gamma-ray emission occur? Is it close to the black hole in the inner-jet region or at kpc scales further down the jet? Are there multiple -ray emission sites and components, for example, both jet and large-scale emission from the up-scatter of external photons?
- Are TeV-detected radio galaxies best described by a singular leptonic, hadronic, or mixed emission model? Which process dominates?
- Are TeV-detected radio galaxies cosmic ray sources? If -ray emission from radio galaxies can be correlated with neutrino observations, can the population of as-yet-undetected radio galaxies in our universe make a substantial contribution towards the cosmic ray background?
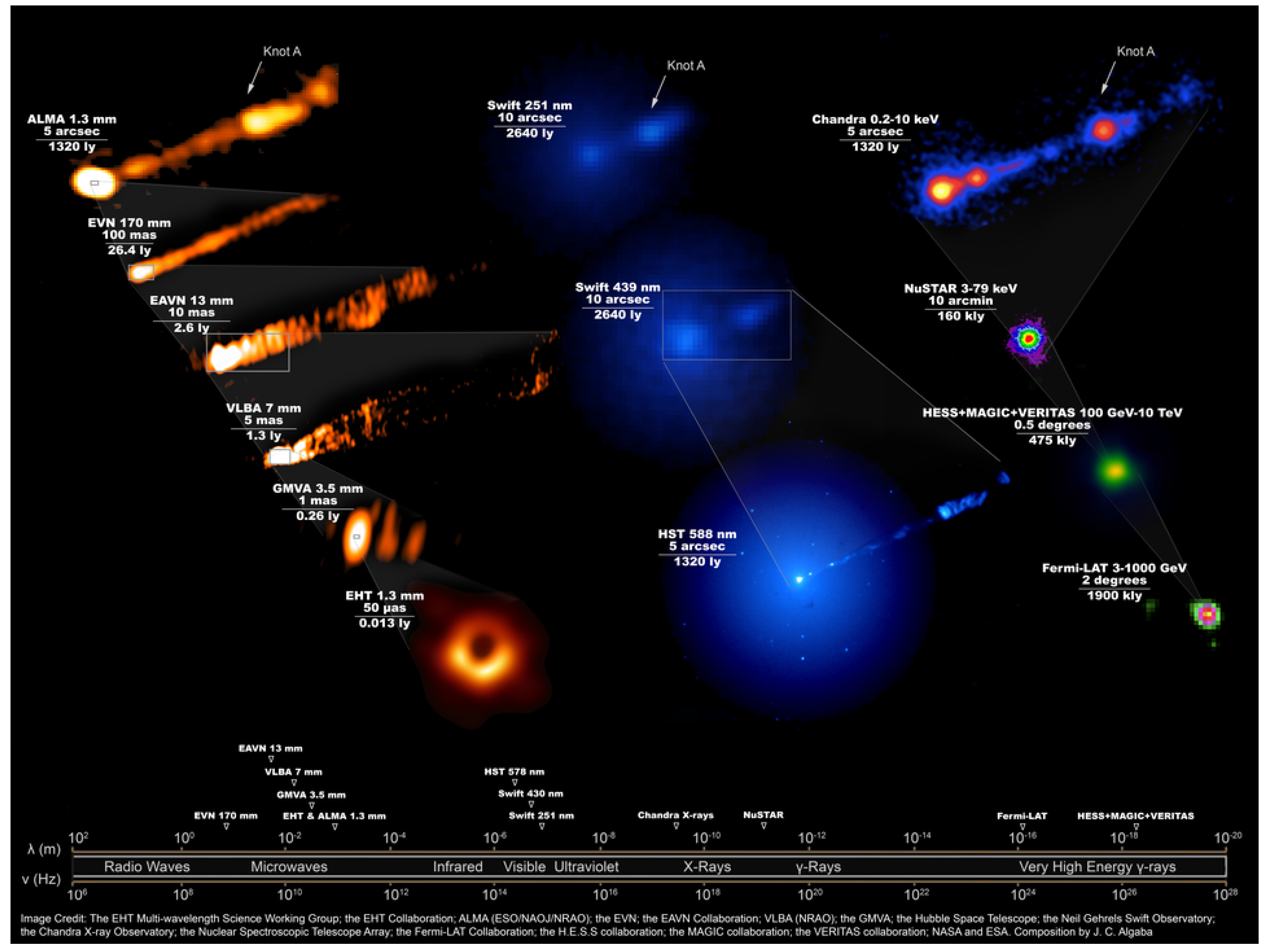
3. Results
3.1. NGC 1275
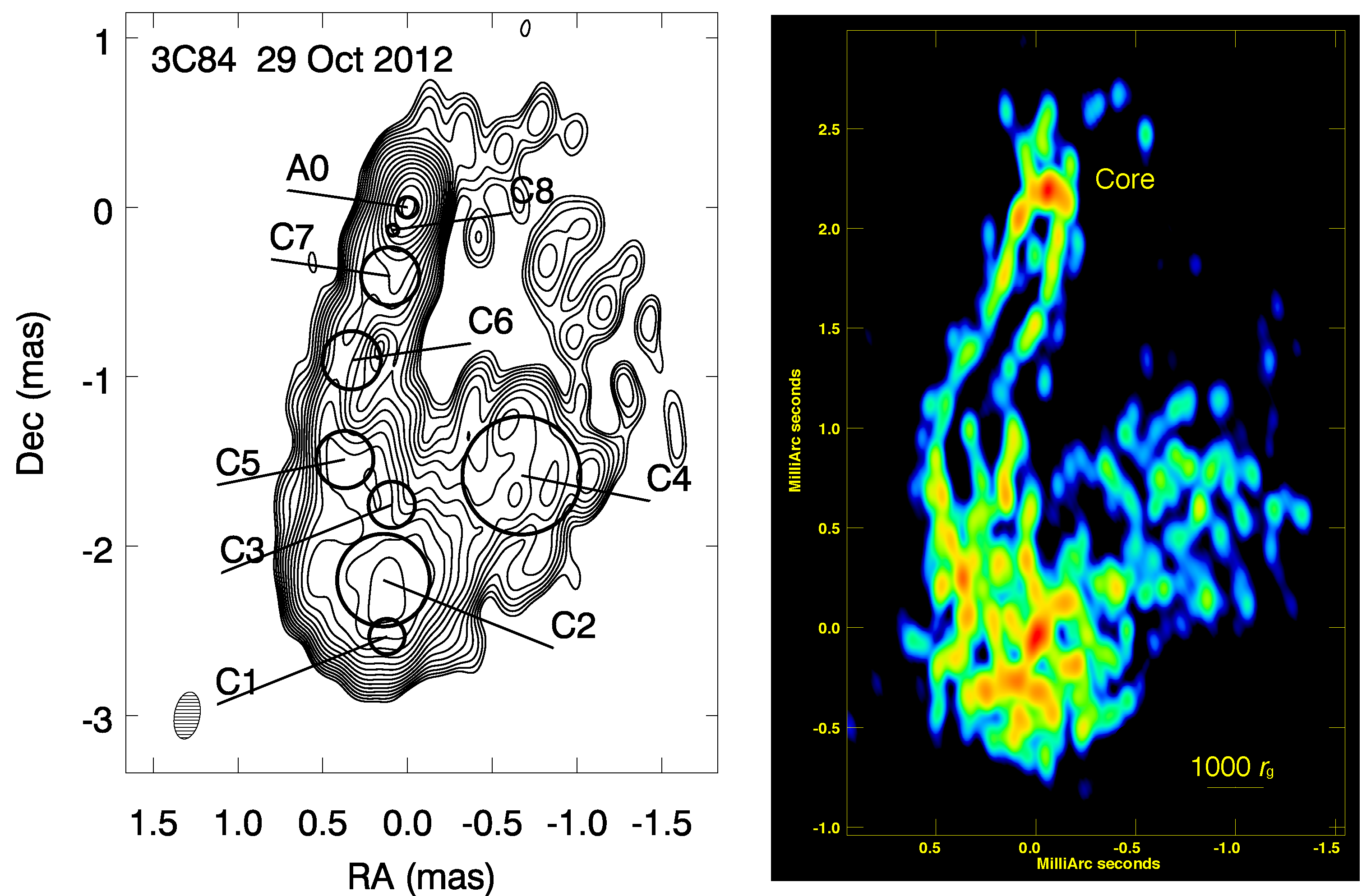
3.2. Cen A
- Inner-jet models involving a number of leptonic SSC-emitting components that propagate at different angles relative to the line-of-sight [39], inverse-Compton emission from structured jets as discussed elsewhere in this article [42], photo-meson decay processes [81,82,83,84], lepto-hadronic emission models [85,86], and -ray-induced pair cascades from different regions [87,88,89];
- Extended emission scenarios such as the interaction of energetic protons with ambient matter (proton–proton interactions) at kiloparsec scales [46], millisecond pulsar contributions as already highlighted above [47], the inverse-Compton upscattering of photons on kiloparsec scales [90], or host galaxy starlight [91];
- The self-annihilation of dark matter, as already highlighted above [47].
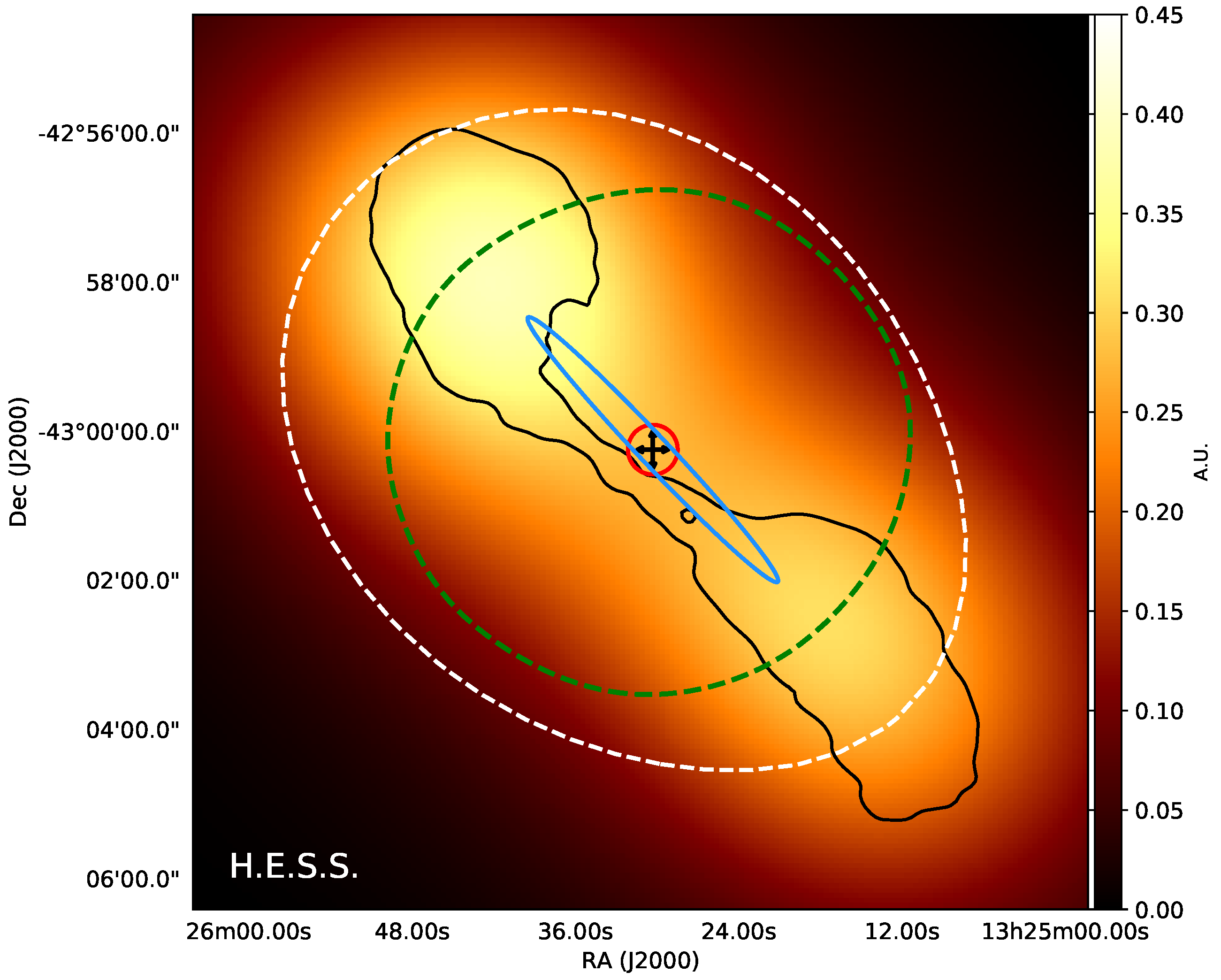
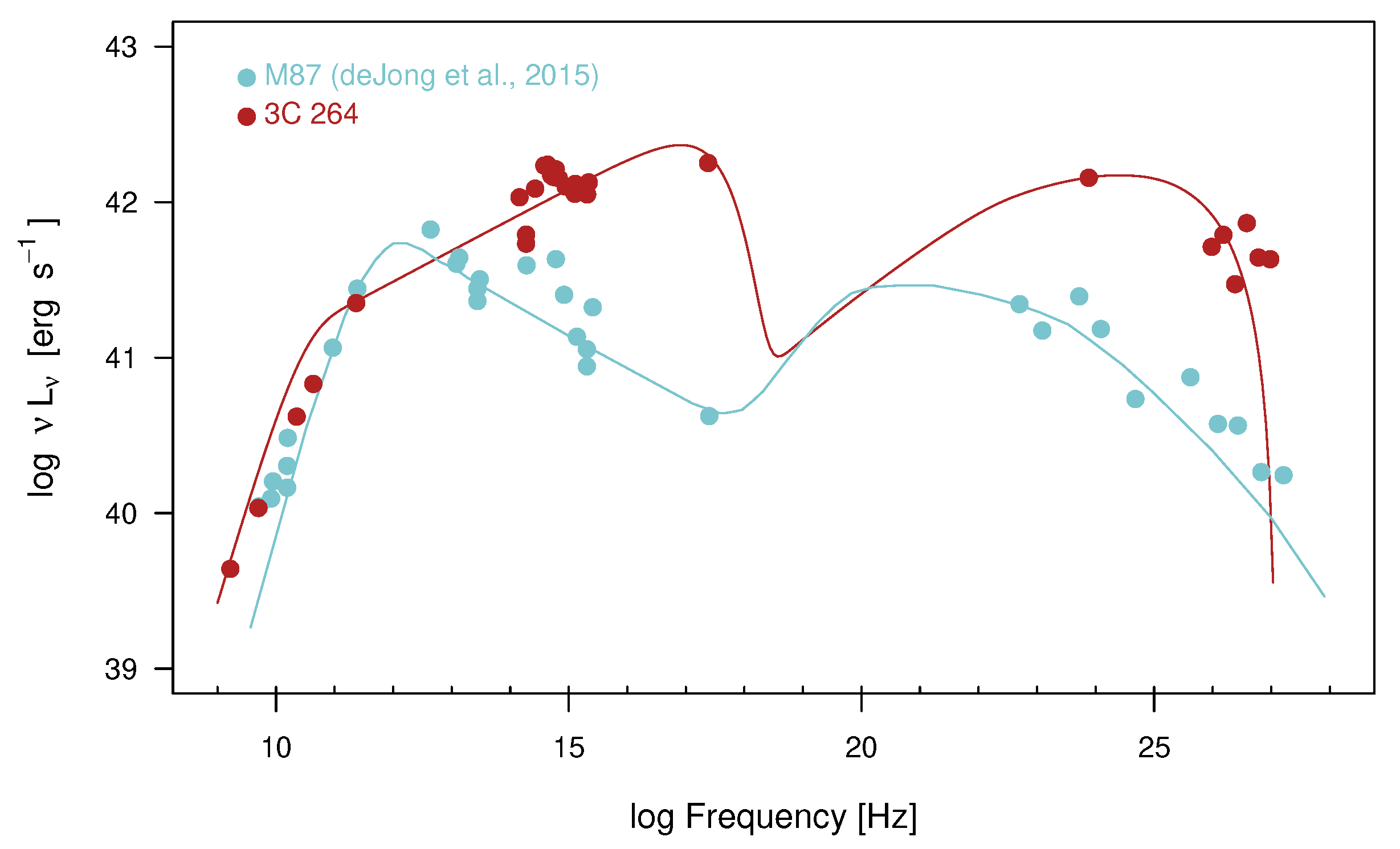
3.3. M 87
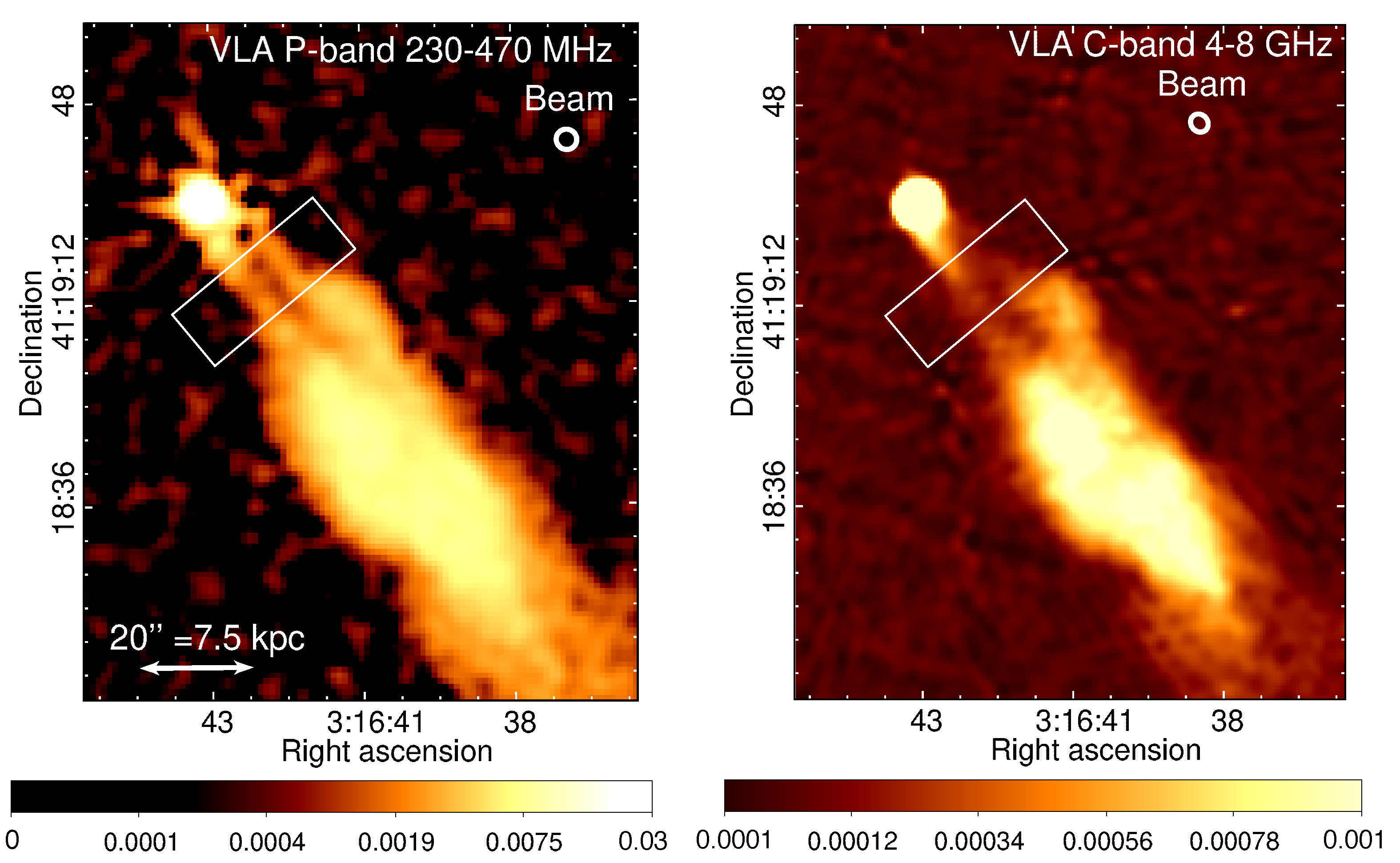
3.4. 3C 264
3.5. PKS 0625-35 and IC 310
3.6. Radio Galaxies with Water Cherenkov Detectors
4. Discussion
4.1. Radio Galaxy Environment
4.2. Kinematic Studies and Classification Considerations
4.3. Emission Sites and Variability
4.4. Emission Mechanisms and Modelling
4.5. Radio Galaxies as Cosmic Ray Sources
4.6. Radio Galaxies with Future Instruments
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGNs | Active galactic nuclei |
| CTA | Cherenkov Telescope Array |
| EBL | Extragalactic background light |
| EHT | Event Horizon Telescope |
| FR-I | Fanaroff and Riley classification Type 1 |
| FR-II | Fanaroff and Riley classification Type 2 |
| FSRQ | Flat-spectrum radio quasar |
| GeV | Giga electron Volt |
| HAWC | High Altitude Water Cherenkov |
| H.E.S.S. | High Energy Stereoscopic System |
| HSP | High synchrotron peak |
| HST | Hubble Space Telescope |
| IACT | Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescope |
| IC | Inverse-Compton |
| JWST | James Webb Space Telescope |
| LSP | Low Synchrotron Peak |
| MAGIC | Major Atmospheric Gamma Imaging Cherenkov telescopes |
| ngVLA | Next-generation Very Large Array |
| PSF | Point spread function |
| SED | Spectral energy distribution |
| SKA | Square Kilometer Array |
| SMBH | Super massive black hole |
| SSC | Synchrotron self-Compton |
| TeV | Terra electron Volt |
| UHECR | Ultra-high-energy cosmic ray |
| VERITAS | Very Energetic Radiation Imaging Telescope Array System |
| VHE | Very high energy |
| VLA | Very Large Array |
| VLBI | Very-long-baseline interferometry |
| WCD | Water Cherenkov Detector |
| 1 | In external Compton processes, the seed photons originate in regions external to the jet such as the accretion disk, the broad-line region, the AGN’s dust torus, or molecular clouds, for example. |
| 2 | In the literature, these two features are also referred to as C1 and C3, respectively, and under this alternative naming scheme, C4 (shown in Figure 1) is referred to as C2. |
References
- Wilson, A.S.; Colbert, E.J.M. The Difference between Radio-loud and Radio-quiet Active Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1995, 438, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchekhovskoy, A.; Narayan, R.; McKinney, J.C. Black Hole Spin and The Radio Loud/Quiet Dichotomy of Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2010, 711, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaberge, M.; Marconi, A. On the origin of radio loudness in active galactic nuclei and its relationship with the properties of the central supermassive black hole. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 416, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaberge, M.; Gilli, R.; Lotz, J.M.; Norman, C. Radio Loud AGNs are Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2015, 806, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.; McClintock, J.E. Observational evidence for a correlation between jet power and black hole spin. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2012, 419, L69–L73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, D.; Webster, B.; Bishop, K. Merger Signatures in Radio Loud and Radio Quiet Quasars. Acta Astron. 2020, 70, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, D.; North, M.; Belga, L.; Waddell, K. Why Radio Quiet Quasars are Preferred over Radio Loud Quasars Regardless of Environment and Redshift. Astrophys. J. 2020, 890, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waggett, P.C.; Warner, P.J.; Baldwin, J.E. NGC 6251, a very large radio galaxy with an exceptional jet. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1977, 181, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.; Meier, D.; Readhead, A. Relativistic Jets from Active Galactic Nuclei. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 57, 467–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanaroff, B.L.; Riley, J.M. The morphology of extragalactic radio sources of high and low luminosity. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1974, 167, 31P–36P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urry, C.M.; Padovani, P. Unified Schemes for Radio-Loud Active Galactic Nuclei. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1995, 107, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledlow, M.J.; Owen, F.N. 20 CM VLA Survey of Abell Clusters of Galaxies. VI. Radio/Optical Luminosity Functions. Astron. J. 1996, 112, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, Z.R.; Jorstad, S.G.; Marscher, A.P.; Morozova, D.A.; Troitsky, I.S.; Agudo, I.; Gómez, J.L.; Lähteenmäki, A.; Tammi, J.; Tornikoski, M. Kinematics of Parsec-Scale Jets of Gamma-Ray Bright Blazars at 43 GHz during Ten Years of the VLBA-BU-BLAZAR Program. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.12290. [Google Scholar]
- Prandini, E.; Ghisellini, G. The Blazar Sequence and Physical Understanding. Galaxies 2022, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q. Blazars: Time Domain. Galaxies: Special Issue “Extragalactic TeV Astronomy”. 2022; unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Sol, H.; Zech, A. Blazar Modelling. Galaxies: Special Issue “Extragalactic TeV Astronomy”. 2022; unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- De Naurois, M. The H.E.S.S. experiment: Current status and future prospects. In Proceedings of the 36th International Cosmic Ray Conference—PoS(ICRC2019), Madison, WI, USA, 24 July–1 August 2019; Volume 358, p. 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksić, J.; Ansoldi, S.; Antonelli, L.A.; Antoranz, P.; Babic, A.; Bangale, P.; Barceló, M.; Barrio, J.A.; Becerra González, J.; Bednarek, W.; et al. The major upgrade of the MAGIC telescopes, Part I: The hardware improvements and the commissioning of the system. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 72, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksić, J.; Ansoldi, S.; Antonelli, L.A.; Antoranz, P.; Babic, A.; Bangale, P.; Barceló, M.; Barrio, J.A.; Becerra González, J.; Bednarek, W.; et al. The major upgrade of the MAGIC telescopes, Part II: A performance study using observations of the Crab Nebula. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 72, 76–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holder, J. VERITAS: Status and Highlights. Int. Cosm. Ray Conf. 2011, 12, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J. VERITAS: Status and Recent Results. EPJ Web Conf. 2019, 209, 01028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wakely, S.P.; Horan, D. TeVCat: An online catalogue for Very High Energy Gamma-Ray Astronomy. Int. Cosm. Ray Conf. 2008, 3, 1341–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Acciari, V.A.; Aliu, E.; Arlen, T.; Aune, T.; Bautista, M.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Boltuch, D.; Bradbury, S.M.; Buckley, J.H.; et al. VERITAS Upper Limit on the Very High Energy Emission from the Radio Galaxy NGC 1275. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2009, 706, L275–L280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acero, F.; Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Anton, G.; Barres de Almeida, U.; Bazer-Bachi, A.R.; Becherini, Y.; Behera, B.; Bernlöhr, K.; Bochow, A.; et al. Detection of Gamma Rays from a Starburst Galaxy. Science 2009, 326, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atwood, W.B.; Abdo, A.A.; Ackermann, M.; Althouse, W.; Anderson, B.; Axelsson, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Band, D.L.; Barbiellini, G.; et al. The Large Area Telescope on the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission. Astrophys. J. 2009, 697, 1071–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CTA Consortium; Ong, R.A. The Cherenkov Telescope Array Science Goals and Current Status. Eur. Phys. J. Web Conf. 2019, 209, 01038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Meyer, E.; Georganopoulos, M.; Lister, M.; Sparks, W.; Chiaberge, M.; Perlman, E.; Van Der Marel, R.; Anderson, J. Proper Motions of Jets on kpc Scales with HST and the VLA. Bull. Am. Astron. Soc. 2020, 235, 436.03. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, D.N.B. The Space Telescope Observatory: Special Session of Commission 44, IAU 18th General Assembly, Patras, Greece, August, 1982; NASA Conference Publication: Washington, DC, USA, 1982; Volume 2244. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkner, H. The Hubble Space Telescope Before Launch: A Personal Perspective. Rev. Mod. Astron. 1990, 3, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, C.J.; Holtzman, J.A.; Faber, S.M.; Bely, P.Y.; Hasan, H.; Lynds, C.R.; Schroeder, D. The Imaging Performance of the Hubble Space Telescope. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1991, 369, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.R.; Clark, B.G.; Wade, C.M.; Napier, P.J. The Very Large Array. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1980, 44, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeschen, D.S. The Very Large Array. Sky Telesc. 1975, 49, 344. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, A.R.; Moran, J.M.; Swenson, G.W. Interferometry and Synthesis in Radio Astronomy; Springer Nature: Berlin, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Whitney, A.R.; Shapiro, I.I.; Rogers, A.E.E.; Robertson, D.S.; Knight, C.A.; Clark, T.A.; Goldstein, R.M.; Marandino, G.E.; Vandenberg, N.R. Quasars Revisited: Rapid Time Variations Observed via Very-Long-Baseline Interferometry. Science 1971, 173, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, B. Radio Galaxies—The TeV Challenge. Galaxies 2019, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraschi, L.; Ghisellini, G.; Celotti, A. On the broad band energy distribution of blazars. In Proceedings of the Multi-Wavelength Continuum Emission of AGN; Courvoisier, T., Blecha, A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; Volume 159, pp. 221–232. [Google Scholar]
- Gould, R.J. Compton and synchrotron processes in spherically-symmetric non-thermal sources. Astron. Astrophys. 1979, 76, 306–311. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, S.; Takahara, F. Electron Acceleration and Gamma-Ray Emission from Blazars. Astrophys. J. 1996, 463, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenain, J.P.; Boisson, C.; Sol, H.; Katarzyński, K. A synchrotron self-Compton scenario for the very high energy γ-ray emission of the radiogalaxy M 87. Unifying the TeV emission of blazars and other AGNs? Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 478, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, E.T.; Fossati, G.; Georganopoulos, M.; Lister, M.L. From the Blazar Sequence to the Blazar Envelope: Revisiting the Relativistic Jet Dichotomy in Radio-loud Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2011, 740, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G. The Blazar Sequence 2.0. Galaxies 2016, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G.; Tavecchio, F.; Chiaberge, M. Structured jets in TeV BL Lac objects and radiogalaxies. Implications for the observed properties. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 432, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, M.; Meyer, E.T.; Georganopoulos, M.; Reddy, K.; French, O.J. The relativistic jet dichotomy and the end of the blazar sequence. Mon. Not. R. Astron Soc. 2021, 505, 4726–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angioni, R.; Grandi, P.; Torresi, E.; Vignali, C.; Knödlseder, J. Radio galaxies with the Cherenkov Telescope Array. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 92, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermi-LAT Collaboration; Abdollahi, S.; Acero, F.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Bastieri, D.; Bellazzini, R.; Berenji, B.; Berretta, A.; Bissaldi, E.; et al. Incremental Fermi Large Area Telescope Fourth Source Catalog. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.11184. [Google Scholar]
- Sahakyan, N.; Yang, R.; Aharonian, F.A.; Rieger, F.M. Evidence for a Second Component in the High-energy Core Emission from Centaurus A? Astrophys. J. Lett. 2013, 770, L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.M.; Bœhm, C.; Graham, J.; Lacroix, T.; Chadwick, P.; Silk, J. Discovery of a new extragalactic population of energetic particles. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 063018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Fermi-LAT Collaboration. Fermi Large Area Telescope Fourth Source Catalog. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.10045. [Google Scholar]
- Kino, M.; Wajima, K.; Kawakatu, N.; Nagai, H.; Orienti, M.; Giovannini, G.; Hada, K.; Niinuma, K.; Giroletti, M. Evidence of Jet-Clump Interaction: A Flip of the Radio Jet Head of 3C 84. Astrophys. J. 2018, 864, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaberge, M.; Celotti, A.; Capetti, A.; Ghisellini, G. Does the unification of BL Lac and FR I radio galaxies require jet velocity structures? Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 358, 104–112. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, C.; Kadler, M.; Ojha, R.; Perucho, M.; Großberger, C.; Ros, E.; Wilms, J.; Blanchard, J.; Böck, M.; Carpenter, B.; et al. TANAMI monitoring of Centaurus A: The complex dynamics in the inner parsec of an extragalactic jet. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 569, A115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, M.; Harris, D.E.; Krawczynski, H. Relativistic Jets from Active Galactic Nuclei; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mertens, F.; Lobanov, A.P.; Walker, R.C.; Hardee, P.E. Kinematics of the jet in M 87 on scales of 100–1000 Schwarzschild radii. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 595, A54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.C.; Romney, J.D.; Benson, J.M. Detection of a VLBI Counterjet in NGC 1275: A Possible Probe of the Parsec-Scale Accretion Region. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1994, 430, L45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendron-Marsolais, M.; Hlavacek-Larrondo, J.; van Weeren, R.J.; Rudnick, L.; Clarke, T.E.; Sebastian, B.; Mroczkowski, T.; Fabian, A.C.; Blundell, K.M.; Sheldahl, E.; et al. High-resolution VLA low radio frequency observations of the Perseus cluster: Radio lobes, mini-halo, and bent-jet radio galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 499, 5791–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahnen, M.L.; Ansoldi, S.; Antonelli, L.A.; Arcaro, C.; Babić, A.; Banerjee, B.; Bangale, P.; Barres de Almeida, U.; Barrio, J.A.; Becerra González, J.; et al. First multi-wavelength campaign on the gamma-ray-loud active galaxy IC 310. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 603, A25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, S.A.; O’Dea, C.P.; Giovannini, G.; Cotton, W.B.; de Koff, S.; Feretti, L.; Golombek, D.; Lara, L.; Macchetto, F.D.; Miley, G.K.; et al. HST and Merlin Observations of 3C 264–A Laboratory for Jet Physics and Unified Schemes. Astrophys. J. 1997, 483, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, G.; Cotton, W.D.; Feretti, L.; Lara, L.; Venturi, T. VLBI Observations of a Complete Sample of Radio Galaxies: 10 Years Later. Astrophys. J. 2001, 552, 508–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angioni, R.; Ros, E.; Kadler, M.; Ojha, R.; Müller, C.; Edwards, P.G.; Burd, P.R.; Carpenter, B.; Dutka, M.S.; Gulyaev, S.; et al. Gamma-ray emission in radio galaxies under the VLBI scope. I. Parsec-scale jet kinematics and high-energy properties of γ-ray-detected TANAMI radio galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 627, A148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukazawa, Y.; Finke, J.; Stawarz, Ł.; Tanaka, Y.; Itoh, R.; Tokuda, S. Suzaku Observations of γ-Ray Bright Radio Galaxies: Origin of the X-ray Emission and Broadband Modeling. Astrophys. J. 2015, 798, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksić, J.; Alvarez, E.A.; Antonelli, L.A.; Antoranz, P.; Asensio, M.; Backes, M.; Barres de Almeida, U.; Barrio, J.A.; Bastieri, D.; Becerra González, J.; et al. Detection of very-high energy γ-ray emission from NGC 1275 by the MAGIC telescopes. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 539, L2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbow, W.; VERITAS Collaboration. Highlights from the VERITAS AGN Observation Program. In Proceedings of the 34th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2015), The Hague, The Netherlands, 30 July–6 August 2015; Volume 34, p. 821. [Google Scholar]
- Jorstad, S.G.; Marscher, A.P.; Morozova, D.A.; Troitsky, I.S.; Agudo, I.; Casadio, C.; Foord, A.; Gómez, J.L.; MacDonald, N.R.; Molina, S.N.; et al. Kinematics of Parsec-scale Jets of Gamma-Ray Blazars at 43 GHz within the VLBA-BU-BLAZAR Program. Astrophys. J. 2017, 846, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kino, M.; Niinuma, K.; Kawakatu, N.; Nagai, H.; Giovannini, G.; Orienti, M.; Wajima, K.; D’Ammando, F.; Hada, K.; Giroletti, M.; et al. Morphological Transition of the Compact Radio Lobe in 3C 84 via the Strong Jet-Cloud Collision. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 920, L24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, H.; Suzuki, K.; Asada, K.; Kino, M.; Kameno, S.; Doi, A.; Inoue, M.; Kataoka, J.; Bach, U.; Hirota, T.; et al. VLBI Monitoring of 3C 84 (NGC 1275) in Early Phase of the 2005 Outburst. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2010, 62, L11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, H.; Haga, T.; Giovannini, G.; Doi, A.; Orienti, M.; D’Ammando, F.; Kino, M.; Nakamura, M.; Asada, K.; Hada, K.; et al. Limb-brightened Jet of 3C 84 Revealed by the 43 GHz Very-Long-Baseline-Array Observation. Astrophys. J. 2014, 785, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, G.; Savolainen, T.; Orienti, M.; Nakamura, M.; Nagai, H.; Kino, M.; Giroletti, M.; Hada, K.; Bruni, G.; Kovalev, Y.Y.; et al. A wide and collimated radio jet in 3C84 on the scale of a few hundred gravitational radii. Nat. Astron. 2018, 2, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, H.; Fujita, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Orienti, M.; Kino, M.; Asada, K.; Giovannini, G. Enhanced Polarized Emission from the One-parsec-scale Hotspot of 3C 84 as a Result of the Interaction with the Clumpy Ambient Medium. Astrophys. J. 2017, 849, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georganopoulos, M.; Kazanas, D. Decelerating Flows in TeV Blazars: A Resolution to the BL Lacertae-FR I Unification Problem. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2003, 594, L27–L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conselice, C.J.; Gallagher, J.S., III; Wyse, R.F.G. On the Nature of the NGC 1275 System. Astron. J. 2001, 122, 2281–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiyama, K.; Mészáros, P. Galaxy Mergers as a Source of Cosmic Rays, Neutrinos, and Gamma Rays. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2014, 790, L14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzoyan, R.; on behalf of the MAGIC Collaboration. ATel# 9929: MAGIC Detection of a Giant Flaring Activity from NGC 1275 at Very-High-Energy Gamma Rays. Available online: http://www.astronomerstelegram.org/?read=9929 (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Mukherjee, R.; for the VERITAS Collaboration. ATel# 9931: VERITAS Detection of the Radio Galaxy NGC 1275 with Elevated Very-High-Energy Gamma-Ray Emission. Available online: https://www.astronomerstelegram.org/?read=9931 (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- MAGIC Collaboration; Ansoldi, S.; Antonelli, L.A.; Arcaro, C.; Baack, D.; Babić, A.; Banerjee, B.; Bangale, P.; Barres de Almeida, U.; Barrio, J.A.; et al. Gamma-ray flaring activity of NGC1275 in 2016–2017 measured by MAGIC. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 617, A91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, G.L.H.; Rejkuba, M.; Harris, W.E. The Distance to NGC 5128 (Centaurus A). Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2010, 27, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, M.; Falcke, H.; Kadler, M.; Ros, E.; Wielgus, M.; Akiyama, K.; Baloković, M.; Blackburn, L.; Bouman, K.L.; Chael, A.; et al. Event Horizon Telescope observations of the jet launching and collimation in Centaurus A. Nat. Astron. 2021, 5, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Anton, G.; de Almeida, U.B.; Bazer-Bachi, A.R.; Becherini, Y.; Behera, B.; Benbow, W.; Bernlöhr, K.; Boisson, C.; et al. Discovery of Very High Energy γ-Ray Emission from Centaurus a with H.E.S.S. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2009, 695, L40–L44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H.E.S.S. Collaboration; Abdalla, H.; Abramowski, A.; Aharonian, F.; Ait Benkhali, F.; Angüner, E.O.; Arakawa, M.; Armand, C.; Arrieta, M.; Backes, M.; et al. The γ-ray spectrum of the core of Centaurus A as observed with H.E.S.S. and Fermi-LAT. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 619, A71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, F.M.; Aharonian, F.A. Centaurus A as TeV γ-ray and possible UHE cosmic ray source. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 506, L41–L44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, F.M. Nonthermal Processes in Black Hole-Jet Magnetospheres. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2011, 20, 1547–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachelrieß, M.; Ostapchenko, S.; Tomàs, R. TeV Gamma Rays from Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Ray Interactions in the Cores of Active Galactic Nuclei: Lessons from Centaurus A. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2010, 27, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.; Zhang, B.; Fraija, N. Hadronic-origin TeV γ rays and ultrahigh energy cosmic rays from Centaurus A. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 043012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulou, M.; Lefa, E.; Dimitrakoudis, S.; Mastichiadis, A. One-zone synchrotron self-Compton model for the core emission of Centaurus A revisited. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 562, A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraija, N. Gamma-ray fluxes from the core emission of Centaurus A: A puzzle solved. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 441, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reynoso, M.M.; Medina, M.C.; Romero, G.E. A lepto-hadronic model for high-energy emission from FR I radiogalaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 531, A30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerruti, M.; Zech, A.; Emery, G.; Guarin, D. Hadronic modeling of TeV AGN: Gammas and neutrinos. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1792, 050027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitarek, J.; Bednarek, W. Time-dependent gamma-ray production in the anisotropic inverse Compton e+/− pair cascade initiated by electrons in active galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 409, 662–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roustazadeh, P.; Böttcher, M. Very High Energy Gamma-ray-induced Pair Cascades in the Radiation Fields of Dust Tori of Active Galactic Nuclei: Application to Cen A. Astrophys. J. 2011, 728, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawarz, Ł.; Aharonian, F.; Wagner, S.; Ostrowski, M. Absorption of nuclear γ-rays on the starlight radiation in FR I sources: The case of Centaurus A. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 371, 1705–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardcastle, M.J.; Croston, J.H. Modelling TeV γ-ray emission from the kiloparsec-scale jets of Centaurus A and M87. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 415, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawarz, Ł.; Sikora, M.; Ostrowski, M. High-Energy Gamma Rays from FR I Jets. Astrophys. J. 2003, 597, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H.E.S.S. Collaboration; Abdalla, H.; Adam, R.; Aharonian, F.; Ait Benkhali, F.; Angüner, E.O.; Arakawa, M.; Arcaro, C.; Armand, C.; Ashkar, H.; et al. Resolving acceleration to very high energies along the jet of Centaurus A. Nature 2020, 582, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, S.; Harris, W.E.; Blakeslee, J.P.; Flynn, C. The inner halo of M 87: A first direct view of the red-giant population. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 524, A71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biretta, J.A.; Sparks, W.B.; Macchetto, F. Hubble Space Telescope Observations of Superluminal Motion in the M87 Jet. Astrophys. J. 1999, 520, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biretta, J.A.; Zhou, F.; Owen, F.N. Detection of Proper Motions in the M87 Jet. Astrophys. J. 1995, 447, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.C.; Harris, D.E.; Stawarz, Ł. Superluminal Radio Features in the M87 Jet and the Site of Flaring TeV Gamma-ray Emission. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2007, 663, L65–L68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giroletti, M.; Hada, K.; Giovannini, G.; Casadio, C.; Beilicke, M.; Cesarini, A.; Cheung, C.C.; Doi, A.; Krawczynski, H.; Kino, M.; et al. The kinematic of HST-1 in the jet of M 87. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 538, L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalev, Y.Y.; Lister, M.L.; Homan, D.C.; Kellermann, K.I. The Inner Jet of the Radio Galaxy M87. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2007, 668, L27–L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, K.; Nakamura, M.; Doi, A.; Nagai, H.; Inoue, M. Discovery of Sub- to Superluminal Motions in the M87 Jet: An Implication of Acceleration from Sub-relativistic to Relativistic Speeds. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2014, 781, L2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebohec, S.; VERITAS Collaboration. Observations of M87 and Mkn40 at energies E > 300 GeV. In Proceedings of the International Cosmic Ray Conference, Hamburg, Germany, 7–15 August 2001; Volume 7, p. 2643. [Google Scholar]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.; Beilicke, M.; Bernlöhr, K.; Börst, H.G.; Bojahr, H.; Bolz, O.; Coarasa, T.; Contreras, J.L.; Cortina, J.; et al. Is the giant radio galaxy M 87 a TeV gamma-ray emitter? Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 403, L1–L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daum, A.; Hermann, G.; Heß, M.; Hofmann, W.; Lampeitl, H.; Pühlhofer, G.; Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Barrio, J.A.; Beglarian, A.S.; et al. First results on the performance of the HEGRA IACT array. Astropart. Phys. 1997, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Bazer-Bachi, A.R.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Berge, D.; Bernlöhr, K.; Boisson, C.; Bolz, O.; Borrel, V.; et al. Fast Variability of Tera-Electron Volt γ Rays from the Radio Galaxy M87. Science 2006, 314, 1424–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acciari, V.A.; Beilicke, M.; Blaylock, G.; Bradbury, S.M.; Buckley, J.H.; Bugaev, V.; Butt, Y.; Celik, O.; Cesarini, A.; Ciupik, L.; et al. Observation of Gamma-Ray Emission from the Galaxy M87 above 250 GeV with VERITAS. Astrophys. J. 2008, 679, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, J.; Aliu, E.; Anderhub, H.; Antonelli, L.A.; Antoranz, P.; Backes, M.; Baixeras, C.; Barrio, J.A.; Bartko, H.; Bastieri, D.; et al. Very High Energy Gamma-ray Observations of Strong Flaring Activity in M87 in 2008 February. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2008, 685, L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowski, A.; Acero, F.; Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Anton, G.; Balzer, A.; Barnacka, A.; Barres de Almeida, U.; Becherini, Y.; Becker, J.; et al. The 2010 Very High Energy γ-ray Flare and 10 Years of Multi-wavelength Observations of M 87. Astrophys. J. 2012, 746, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Radio Astronomy Observatory. Multi-Wavelength Observations Reveal Impact of Black Hole on M87 Galaxy. Available online: https://public.nrao.edu/news/m87-black-hole-multi-wavelength-eht/ (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Perlman, E.S.; Padgett, C.A.; Georganopoulos, M.; Worrall, D.M.; Kastner, J.H.; Franz, G.; Birkinshaw, M.; Dulwich, F.; O’Dea, C.P.; Baum, S.A.; et al. A Multi-Wavelength Spectral and Polarimetric Study of the Jet of 3C 264. Astrophys. J. 2010, 708, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, A.; Benbow, W.; Bird, R.; Brill, A.; Buchovecky, M.; Buckley, J.H.; Carini, M.T.; Christiansen, J.L.; Chromey, A.J.; Daniel, M.K.; et al. VERITAS Discovery of VHE Emission from the Radio Galaxy 3C 264: A Multiwavelength Study. Astrophys. J. 2020, 896, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, L.; Feretti, L.; Giovannini, G.; Baum, S.; Cotton, W.D.; O’Dea, C.P.; Venturi, T. The Radio-Optical Jet in NGC 3862 from Parsec to Subkiloparsec Scales. Astrophys. J. 1999, 513, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boccardi, B.; Migliori, G.; Grandi, P.; Torresi, E.; Mertens, F.; Karamanavis, V.; Angioni, R.; Vignali, C. The TeV-emitting radio galaxy 3C 264. VLBI kinematics and SED modeling. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 627, A89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, E.T.; Georganopoulos, M.; Sparks, W.B.; Perlman, E.; van der Marel, R.P.; Anderson, J.; Sohn, S.T.; Biretta, J.; Norman, C.; Chiaberge, M. A kiloparsec-scale internal shock collision in the jet of a nearby radio galaxy. Nature 2015, 521, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rulten, C.B.; Brown, A.M.; Chadwick, P.M. A search for Centaurus A-like features in the spectra of Fermi-LAT detected radio galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 492, 4666–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrda, M.; Wierzcholska, A.; Moderski, R.; Ostrowski, M.; Stawarz, L. Discovery of VHE gamma-rays from the radio galaxy PKS 0625-354 with H.E.S.S. In Proceedings of the 34th International Cosmic ray Conference (ICRC2015), The Hague, The Netherlands, 30 July–6 August 2015; Volume 34, p. 801. [Google Scholar]
- Ekers, R.D.; Wall, J.V.; Shaver, P.A.; Goss, W.M.; Fosbury, R.A.E.; Danziger, I.J.; Moorwood, A.F.M.; Malin, D.F.; Monk, A.S.; Ekers, J.A. A complete sample of radio galaxies—I. The radio data. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1989, 236, 737–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, T.; Morganti, R.; Tzioumis, T.; Reynolds, J. Parsec-scale structures of radio galaxies in the 2-Jy sample. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 363, 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Ojha, R.; Kadler, M.; Böck, M.; Booth, R.; Dutka, M.S.; Edwards, P.G.; Fey, A.L.; Fuhrmann, L.; Gaume, R.A.; Hase, H.; et al. TANAMI: Tracking active galactic nuclei with austral milliarcsecond interferometry. I. First-epoch 8.4 GHz images. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 519, A45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, K.A.; Morganti, R.; Tadhunter, C.N.; Robinson, T.G.; Villar-Martin, M. Emission lines and optical continuum in low-luminosity radio galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 347, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H. E. S. S. Collaboration; Abdalla, H.; Abramowski, A.; Aharonian, F.; Ait Benkhali, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Andersson, T.; Angüner, E.O.; Arrieta, M.; Aubert, P.; et al. H.E.S.S. discovery of very high energy γ-ray emission from PKS 0625-354. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 476, 4187–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, M.; MAGIC Collaboration. Discovery of Very High Energy Gamma-ray Emission from NGC1275 by MAGIC. Astron. Telegr. 2010, 2916. [Google Scholar]
- Aleksić, J.; Antonelli, L.A.; Antoranz, P.; Backes, M.; Barrio, J.A.; Bastieri, D.; Becerra González, J.; Bednarek, W.; Berdyugin, A.; Berger, K.; et al. Detection of Very High Energy γ-ray Emission from the Perseus Cluster Head-Tail Galaxy IC 310 by the MAGIC Telescopes. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 723, L207–L212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.A.; Brown, A.M.; Chadwick, P.M. Fermi-LAT observations of extreme spectral variability in IC 310. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 485, 3277–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadler, M.; Eisenacher, D.; Ros, E.; Mannheim, K.; Elsässer, D.; Bach, U. The blazar-like radio structure of the TeV source IC 310. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 538, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, R.; Benbow, W.; Berley, D.; Blaufuss, E.; Bussons, J.; Coyne, D.G.; Delay, R.S.; De Young, T.; Dingus, B.L.; Dorfan, D.E.; et al. Observation of TeV Gamma Rays from the Crab Nebula with Milagro Using a New Background Rejection Technique. Astrophys. J. 2003, 595, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, R.; Benbow, W.; Berley, D.; Blaufuss, E.; Bussons, J.; Coyne, D.G.; De Young, T.; Dingus, B.L.; Dorfan, D.E.; Ellsworth, R.W.; et al. TeV Gamma-Ray Survey of the Northern Hemisphere Sky Using the Milagro Observatory. Astrophys. J. 2004, 608, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- ARGO-YBJ Collaboration; Bacci, C.; Bao, K.Z.; Barone, F.; Bartoli, B.; Bernardini, P.; Bussino, S.; Calloni, E.; Cao, B.Y.; Cardarelli, R.; et al. Results from the ARGO-YBJ test experiment. Astropart. Phys. 2002, 17, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeysekara, A.U.; Albert, A.; Alfaro, R.; Alvarez, C.; Álvarez, J.D.; Arceo, R.; Arteaga-Velázquez, J.C.; Ayala Solares, H.A.; Barber, A.S.; Baughman, B.; et al. The 2HWC HAWC Observatory Gamma-Ray Catalog. Astrophys. J. 2017, 843, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sciascio, G. The LHAASO experiment: From Gamma-Ray Astronomy to Cosmic Rays. Nuclear Part. Phys. Proc. 2016, 279–281, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, A.; Alfaro, R.; Ashkar, H.; Alvarez, C.; Álvarez, J.; Arteaga-Velázquez, J.C.; Ayala Solares, H.A.; Arceo, R.; Bellido, J.A.; BenZvi, S.; et al. Science Case for a Wide Field-of-View Very-High-Energy Gamma-ray Observatory in the Southern Hemisphere. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.08429. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, A.; Alvarez, C.; Angeles Camacho, J.R.; Arteaga-Velázquez, J.C.; Arunbabu, K.P.; Avila Rojas, D.; Ayala Solares, H.A.; Baghmanyan, V.; Belmont-Moreno, E.; BenZvi, S.Y.; et al. A Survey of Active Galaxies at TeV Photon Energies with the HAWC Gamma-Ray Observatory. Astrophys. J. 2021, 907, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernetto, S.; LHAASO Collaboration. Gamma Ray Astronomy with LHAASO. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 718, 052043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, D.; Singh, C.B.; Zack, A. The distribution and lifetime of powerful radio galaxies as a function of environment and redshift. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, W.L.; Calistro Rivera, G.; Best, P.N.; Hardcastle, M.J.; Röttgering, H.J.A.; Duncan, K.J.; de Gasperin, F.; Jarvis, M.J.; Miley, G.K.; Mahony, E.K.; et al. LOFAR-Boötes: Properties of high- and low-excitation radio galaxies at 0.5 < z < 2.0. Mon. Not. R. Astron Soc. 2018, 475, 3429–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani, P.; Urry, C.M. Fanaroff–Riley I Galaxies as the Parent Population of BL Lacertae Objects. I. X-ray Constraints. Astrophys. J. 1990, 356, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, M.L.; Aller, M.F.; Aller, H.D.; Hodge, M.A.; Homan, D.C.; Kovalev, Y.Y.; Pushkarev, A.B.; Savolainen, T. MOJAVE. XV. VLBA 15 GHz Total Intensity and Polarization Maps of 437 Parsec-scale AGN Jets from 1996 to 2017. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2018, 234, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorstad, S.; Marscher, A. The VLBA-BU-BLAZAR Multi-Wavelength Monitoring Program. Galaxies 2016, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.P.; Mather, J.C.; Clampin, M.; Doyon, R.; Greenhouse, M.A.; Hammel, H.B.; Hutchings, J.B.; Jakobsen, P.; Lilly, S.J.; Long, K.S.; et al. The James Webb Space Telescope. Space Sci. Rev. 2006, 123, 485–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, R.; Bourke, T.; Green, J.A.; Keane, E.; Wagg, J. Advancing Astrophysics with the Square Kilometre Array. In Proceedings of the Advancing Astrophysics with the Square Kilometre Array (AASKA14), Giardini Naxos, Italy, 9–13 June 2014; p. 174. [Google Scholar]
- Lister, M.L.; Kellermann, K.I.; Kharb, P. High-resolution Imaging of Radio Jets Launched by Active Galactic Nuclei: New Insights on Formation, Structure, and Evolution Enabled by the ngVLA. Sci. Next Gener. Very Large Array 2018, 517, 619. [Google Scholar]
- Weisskopf, M.C.; Brinkman, B.; Canizares, C.; Garmire, G.; Murray, S.; Van Speybroeck, L.P. An Overview of the Performance and Scientific Results from the Chandra X-ray Observatory. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2002, 114, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.A.; Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Atwood, W.B.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Baughman, B.M.; Bechtol, K.; et al. Fermi Gamma-Ray Imaging of a Radio Galaxy. Science 2010, 328, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Benkhali, F.; Chakraborty, N.; Rieger, F.M. Complex gamma-ray behavior of the radio galaxy M 87. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 623, A2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghmanyan, V.; Gasparyan, S.; Sahakyan, N. Rapid Gamma-ray Variability of NGC 1275. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaberge, M.; Capetti, A.; Celotti, A. The BL Lac heart of Centaurus A. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2001, 324, L33–L37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.A.; Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Atwood, W.B.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Baughman, B.M.; Bechtol, K.; et al. Fermi Large Area Telescope View of the Core of the Radio Galaxy Centaurus A. Astrophys. J. 2010, 719, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannios, D.; Uzdensky, D.A.; Begelman, M.C. Fast TeV variability in blazars: Jets in a jet. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2009, 395, L29–L33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksić, J.; Ansoldi, S.; Antonelli, L.A.; Antoranz, P.; Babic, A.; Bangale, P.; Barrio, J.A.; González, J.B.; Bednarek, W.; Bernardini, E.; et al. Black hole lightning due to particle acceleration at subhorizon scales. Science 2014, 346, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieger, F.; Levinson, A. Radio Galaxies at VHE Energies. Galaxies 2018, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillas, A.M. Cosmic Rays: Recent Progress and some Current Questions. arXiv 2006, arXiv:astro-ph/0607109. [Google Scholar]
- Castellina, A. Highlights from the Pierre Auger Observatory and prospects for AugerPrime. In Proceedings of the 36th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2019), Madison, WI, USA, 24 July–1 August 2019; Volume 36, p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Pierre Auger Collaboration; Abraham, J.; Abreu, P.; Aglietta, M.; Aguirre, C.; Allard, D.; Allekotte, I.; Allen, J.; Allison, P.; Alvarez, C.; et al. Correlation of the Highest-Energy Cosmic Rays with Nearby Extragalactic Objects. Science 2007, 318, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre Auger Collaboration; Abraham, J.; Abreu, P.; Aglietta, M.; Aguirre, C.; Allard, D.; Allekotte, I.; Allen, J.; Allison, P.; Alvarez-Muñiz, J.; et al. Correlation of the highest-energy cosmic rays with the positions of nearby active galactic nuclei. Astropart. Phys. 2008, 29, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuoco, A.; Hannestad, S. Ultrahigh energy neutrinos from Centaurus A and the Auger hot spot. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 023007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachelrieß, M.; Ostapchenko, S.; Tomàs, R. High energy radiation from Centaurus A. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 065017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koers, H.B.J.; Tinyakov, P. Relation between the neutrino flux from Centaurus A and the associated diffuse neutrino flux. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 083009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker Tjus, J.; Eichmann, B.; Halzen, F.; Kheirandish, A.; Saba, S.M. High-energy neutrinos from radio galaxies. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 123005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D. A case for radio galaxies as the sources of IceCube’s astrophysical neutrino flux. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraija, N.; Marinelli, A. Neutrino, γ-Ray, and Cosmic-Ray Fluxes from the Core of the Closest Radio Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2016, 830, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, C.; Hooper, D. High-energy gamma rays and neutrinos from nearby radio galaxies. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavecchio, F.; Righi, C.; Capetti, A.; Grandi, P.; Ghisellini, G. High-energy neutrinos from FR0 radio galaxies? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 475, 5529–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, R.D.; Capetti, A.; Giovannini, G. Pilot study of the radio-emitting AGN population: The emerging new class of FR 0 radio-galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 576, A38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, R.D.; Capetti, A.; Giovannini, G. High-resolution VLA observations of FR0 radio galaxies: The properties and nature of compact radio sources. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 482, 2294–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, R.D.; Torresi, E.; Migliori, G.; Balmaverde, B. The High Energy View of FR0 Radio Galaxies. Galaxies 2019, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plavin, A.; Kovalev, Y.Y.; Kovalev, Y.A.; Troitsky, S. Observational Evidence for the Origin of High-energy Neutrinos in Parsec-scale Nuclei of Radio-bright Active Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2020, 894, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraija, N.; Marinelli, A.; Galván-Gámez, A.; Aguilar-Ruiz, E. Modeling the spectral energy distribution of the radio galaxy IC310. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 89, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EHT MWL Science Working Group; Algaba, J.C.; Anczarski, J.; Asada, K.; Baloković, M.; Chandra, S.; Cui, Y.Z.; Falcone, A.D.; Giroletti, M.; Goddi, C.; et al. Broadband Multi-wavelength Properties of M87 during the 2017 Event Horizon Telescope Campaign. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 911, L11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignall, H.E.; Croft, S.; Hovatta, T.; Koay, J.Y.; Lazio, J.; Macquart, J.P.; Reynolds, C. Time domain studies of Active Galactic Nuclei with the Square Kilometre Array. In Proceedings of the Advancing Astrophysics with the Square Kilometre Array (AASKA14), Giardini Naxos, Italy, 9–13 June 2014; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Giroletti, M.; Orienti, M.; D’Ammando, F.; Massaro, F.; Tosti, G.; LICO, R.; Giovannini, G.; Agudo, I.; Alberdi, A.; Bignall, H.E.; et al. The connection between radio and high energy emission in black hole powered systems in the SKA era. In Proceedings of the Advancing Astrophysics with the Square Kilometre Array (AASKA14), Giardini Naxos, Italy, 9–13 June 2014; p. 153. [Google Scholar]
- Garrington, S.T.; Anderson, B.; Baines, C.; Battilana, J.A.; Bentley, M.N.; Brown, D.; Burgess, P.; Diamond, P.J.; Kitching, G.J.; McCool, R.; et al. e-MERLIN. In Proceedings of the Ground-Based Telescopes; International Society for Optics and Photonics; SPIE: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; Volume 5489, pp. 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paragi, Z.; Godfrey, L.; Reynolds, C.; Rioja, M.J.; Deller, A.; Zhang, B.; Gurvits, L.; Bietenholz, M.; Szomoru, A.; Bignall, H.E.; et al. Very Long Baseline Interferometry with the SKA. In Proceedings of the Advancing Astrophysics with the Square Kilometre Array (AASKA14), Giardini Naxos, Italy, 29 May 2015; p. 143. [Google Scholar]
| 4FGL Name | Object | Model | Variability | TeVCat | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4FGL J0009.7-3217 | IC 1531 | PL | 2.24 | 27.9362 | N | |
| 4FGL J0038.7-0204 | 3C 17 | PL | 2.84 | 17.5947 | N | |
| 4FGL J0057.7+3023 | NGC 315 | PL | 2.38 | 8.81993 | N | |
| 4FGL J0153.4+7114 | TXS 0149+710 | PL | 1.93 | 13.9387 | N | |
| 4FGL J0237.7+0206 | PKS 0235+017 | PL | 2.10 | 6.75128 | N | |
| 4FGL J0308.4+0407 | NGC 1218 | PL | 2.00 | 37.8178 | N | |
| 4FGL J0312.9+4119 | B3 0309+411B | PL | 2.49 | 21.8156 | N | |
| 4FGL J0316.8+4120 | IC 310 | PL | 1.85 | 31.8913 | Y | |
| 4FGL J0322.6-3712e | Fornax A | PL | 2.05 | 14.2643 | N | |
| 4FGL J0334.3+3920 | 4C +39.12 | PL | 1.85 | 14.2155 | N | |
| 4FGL J0519.6-4544 | Pictor A | PL | 2.54 | 11.9384 | N | |
| 4FGL J0627.0-3529 | PKS 0625-35 | PL | 1.91 | 25.0043 | Y | |
| 4FGL J0708.9+4839 | NGC 2329 | PL | 1.72 | 13.1158 | N | |
| 4FGL J0758.7+3746 | NGC 2484 | PL | 2.23 | 7.38446 | N | |
| 4FGL J0931.9+6737 | NGC 2892 | PL | 2.28 | 49.7003 | N | |
| 4FGL J0958.3-2656 | NGC 3078 | PL | 2.16 | 7.16341 | N | |
| 4FGL J1116.6+2915 | B2 1113+29 | PL | 1.61 | 11.7614 | N | |
| 4FGL J1144.9+1937 | 3C 264 | PL | 2.02 | 5.42454 | Y | |
| 4FGL J1149.0+5924 | NGC 3894 | PL | 2.19 | 10.8819 | N | |
| 4FGL J1219.6+0550 | NGC 4261 | PL | 2.09 | 13.2929 | N | |
| 4FGL J1236.9-7232 | PKS 1234-723 | PL | 2.40 | 6.54389 | N | |
| 4FGL J1306.3+1113 | TXS 1303+114 | PL | 1.86 | 14.3789 | N | |
| 4FGL J1325.5-4300 | Cen A | PL | 2.59 | 33.403 | Y | |
| 4FGL J1443.1+5201 | 3C 303 | PL | 2.15 | 9.88656 | N | |
| 4FGL J1449.5+2746 | B2 1447+27 | PL | 1.46 | 12.7277 | N | |
| 4FGL J1516.5+0015 | PKS 1514+00 | PL | 2.51 | 16.249 | N | |
| 4FGL J1518.6+0614 | TXS 1516+064 | PL | 1.79 | 6.96701 | N | |
| 4FGL J1521.1+0421 | PKS B1518+045 | PL | 2.04 | 21.5818 | N | |
| 4FGL J1530.3+2709 | LEDA 55267 | PL | 2.01 | 12.2306 | N | |
| 4FGL J1724.2-6501 | NGC 6328 | PL | 2.56 | 6.27477 | N | |
| 4FGL J1843.4-4835 | PKS 1839-48 | PL | 2.03 | 4.58083 | N | |
| 4FGL J2227.9-3031 | PKS 2225-308 | PL | 1.80 | 17.3154 | N | |
| 4FGL J2302.8-1841 | PKS 2300-18 | PL | 2.26 | 14.3889 | N | |
| 4FGL J2326.9-0201 | PKS 2324-02 | PL | 2.59 | 17.579 | N | |
| 4FGL J2329.7-2118 | PKS 2327-215 | PL | 2.45 | 18.1362 | N | |
| 4FGL J2341.8-2917 | PKS 2338-295 | PL | 2.24 | 13.6434 | N |
| 4FGL Name | Object | Model | Variability | TeVCat | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4FGL J0319.8+4130 | NGC 1275 | LP | 2.05 | 0.07 | 5460.94 | Y | |
| 4FGL J0418.2+3807 | 3C 111 | LP | 2.62 | 0.23 | 40.5743 | N | |
| 4FGL J0433.0+0522 | 3C 120 | LP | 2.63 | 0.21 | 308.796 | N | |
| 4FGL J1230.8+1223 | M 87 | LP | 2.01 | 0.04 | 23.8056 | Y | |
| 4FGL J1306.7-2148 | PKS 1304-215 | LP | 1.86 | 0.24 | 16.9549 | N | |
| 4FGL J1630.6+8234 | NGC 6251 | LP | 2.25 | 0.12 | 7.34 | N | |
| 4FGL J2156.0-6942 | PKS 2153-69 | LP | 2.47 | 0.48 | 5.73628 | N |
| Name | Alt. Name | z | Refs. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cen A | NGC 5128 | 0.0018 | 12–45 | 21.97 | 12.81 | 2009-03 | [22,43,51,52] | |
| M 87 | 3C 274 | 0.0042 | 13–27 | 23.27 | 9.5 | 2003-05 | [22,43,52,53] | |
| NGC 1275 | 3C 84 | 0.0175 | 30–55 | - | 13.39 | 2010-10 | [22,54] | |
| IC 310 | B3 0313+411 | 0.0188 | - | 2010-03 | [22,55,56] | |||
| 3C 264 | NGC 3862 | 0.0216 | 23.67 | 16.30 | 2018-03 | [22,43,52,57,58] | ||
| PKS 0625-35 | TXS 0625-354 | 0.0562 | <53 | - | 2015-07 | [22,59,60] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rulten, C. Radio Galaxies at TeV Energies. Galaxies 2022, 10, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies10030061
Rulten C. Radio Galaxies at TeV Energies. Galaxies. 2022; 10(3):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies10030061
Chicago/Turabian StyleRulten, Cameron. 2022. "Radio Galaxies at TeV Energies" Galaxies 10, no. 3: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies10030061
APA StyleRulten, C. (2022). Radio Galaxies at TeV Energies. Galaxies, 10(3), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies10030061






