Association of Insulin Resistance with Dysglycemia in Elder Koreans: Age- and Sex-Specific Cutoff Values
Abstract
1. Introduction
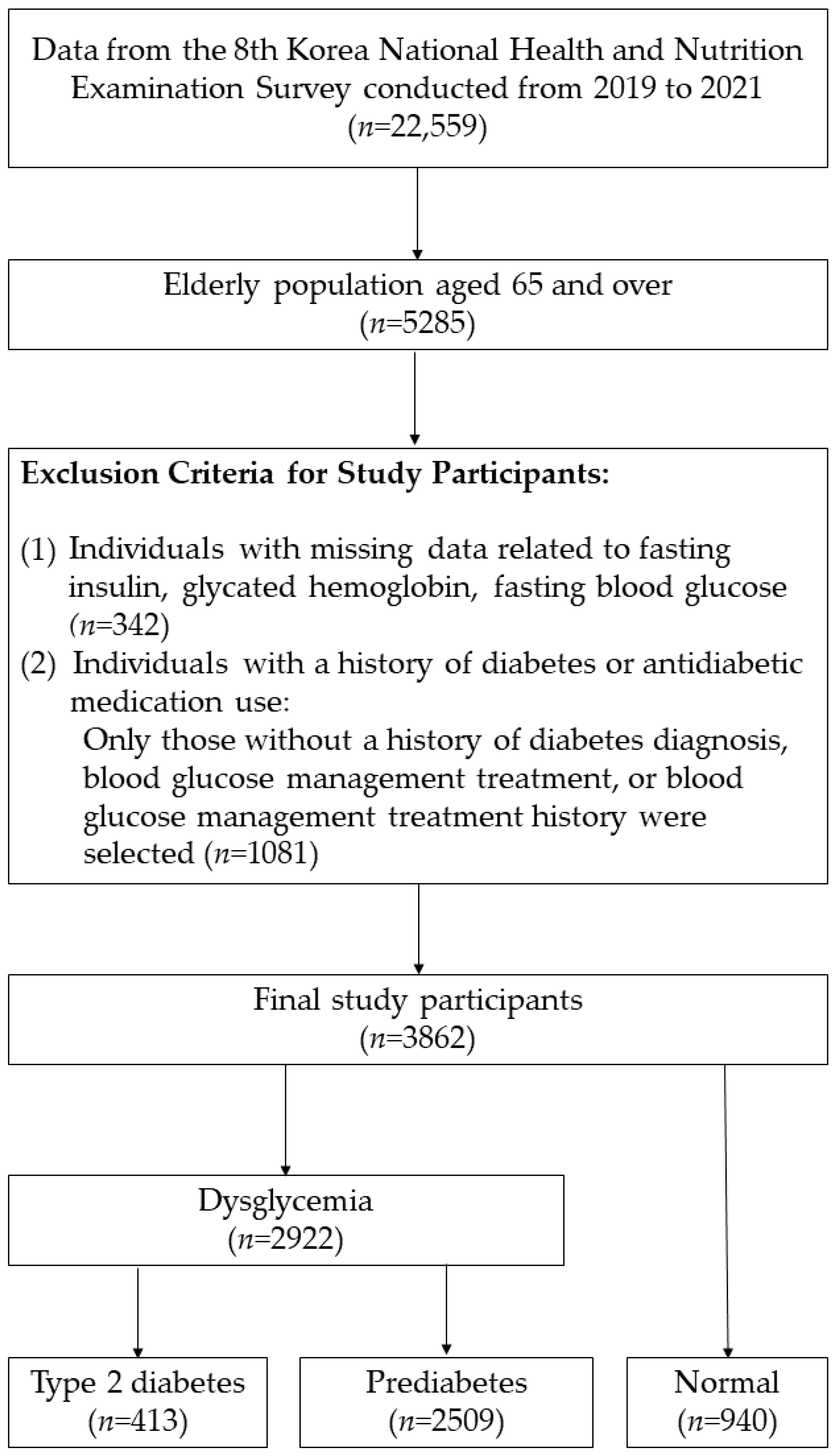
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. General Characteristics and Anthropometric Factors
2.3. HOMA-IR, HOMA-β Definition
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics
3.2. AUC and Optimal Cut-Off Point of Insulin Resistance Index
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Pre-DM | Pre-diabetes mellitus |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance |
| FPG | Fasting plasma glucose |
| HEC | Hyperinsulinemic–euglycemic clamp test |
| HOMA-β | Homeostasis Model Assessment of Beta-Cell Function |
| KNHANES | Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| ANOVA | One-way analysis of variance |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| YI | Youden index |
| PPV | Positive predictive value |
| NPV | Negative predictive value |
References
- Duan, D.; Kengne, A.P.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B. Screening for Diabetes and Prediabetes. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 50, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association, A.D. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care 2017, 41 (Suppl. S1), S13–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, K.Y.; Moon, M.K.; Park, J.S.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, S.H.; Yun, J.S.; Baek, J.H.; Noh, J.; Lee, B.W.; Oh, T.J.; et al. 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 461–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Park, S.-Y.; Choi, C.S. Insulin Resistance: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies. Diabetes Metab. J. 2022, 46, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, K. Mini-review on insulin resistance assessment: Advances in surrogate indices and clinical applications. World J. Clin. Cases 2025, 13, 108380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciarambino, T.; Crispino, P.; Guarisco, G.; Giordano, M. Gender Differences in Insulin Resistance: New Knowledge and Perspectives. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 7845–7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.H.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.Y.; Jung, J. Insulin Resistance and the Risk of Diabetes and Dysglycemia in Korean General Adult Population. Diabetes Metab. J. 2018, 42, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.K.; Moon, M.K. Are We in the Same Risk of Diabetes Mellitus? Gender- and Age-Specific Epidemiology of Diabetes in 2001 to 2014 in the Korean Population. Diabetes Metab. J. 2016, 40, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. The Eighth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VIII); Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency: Cheongju-si, Republic of Korea, 2021.
- Earnest, C.P.; Johannsen, N.M.; Swift, D.L.; Gillison, F.B.; Mikus, C.R.; Lucia, A.; Kramer, K.; Lavie, C.J.; Church, T.S. Aerobic and strength training in concomitant metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2014, 46, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Rossouw, J.; Tong, E.; Giovino, G.A.; Lee, C.C.; Chen, C.; Ockene, J.K.; Qi, L.; Margolis, K.L. Smoking and diabetes: Does the increased risk ever go away? Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 178, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.S. Current Status of Korean Alcohol Drinking in Accordance with the Korean Alcohol Guidelines for Moderate Drinking Based on Facial Flushing. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2023, 44, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.Y.; Kang, S.M.; Kang, J.H.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, K.K.; Kim, K.B.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.H.; et al. 2020 Korean Society for the Study of Obesity Guidelines for the Management of Obesity in Korea. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 30, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Quality Control of the Clinical Laboratory for the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) (2019–2021, 8th). 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, H.; Jeon, D.J.; Park, C.E.; You, H.S.; Moon, A.E. Relationship between homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance and beta cell function and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D in non-diabetic Korean adults. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2016, 59, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.; Ahn, S.; Ohn, J.H.; Shin, C.M.; Ji, E.; Kim, D.; Jung, S.J.; Lee, J. Insulin Resistance and Impaired Insulin Secretion Predict Incident Diabetes: A Statistical Matching Application to the Two Korean Nationwide, Population-Representative Cohorts. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 39, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Shih, A.Z.; Woo, Y.C.; Fong, C.H.; Leung, O.Y.; Janus, E.; Cheung, B.M.; Lam, K.S. Optimal Cut-Offs of Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) to Identify Dysglycemia and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 15-Year Prospective Study in Chinese. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.M.; Acevedo, L.A.; Pennings, N. Insulin Resistance. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi, A.; Tohidi, M.; Derakhshan, A.; Hasheminia, M.; Azizi, F.; Hadaegh, F. Cut-off points of homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance, beta-cell function, and fasting serum insulin to identify future type 2 diabetes: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Acta Diabetol. 2015, 52, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, C.M.; Batsis, J.A.; Donini, L.M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Siervo, M. Sarcopenic obesity in older adults: A clinical overview. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2024, 20, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tack, W.; De Cock, A.M.; Dirinck, E.L.; Bastijns, S.; Ariën, F.; Perkisas, S. Pathophysiological interactions between sarcopenia and type 2 diabetes: A two-way street influencing diagnosis and therapeutic options. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, A.; Tatsumi, Y.; Soyano, F.; Miyamatsu, N.; Sonoda, N.; Godai, K.; Ohno, Y.; Noda, M.; Deura, K. Increase in Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) Had a Strong Impact on the Development of Type 2 Diabetes in Japanese Individuals with Impaired Insulin Secretion: The Saku Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, C.; Mitsuhashi, T.; Hiratsuka, N.; Inabe, F.; Araida, N.; Takahashi, E. Optimal reference interval for homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance in a Japanese population. J. Diabetes Investig. 2011, 2, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmas, C.E.; Bousvarou, M.D.; Kostara, C.E.; Papakonstantinou, E.J.; Salamou, E.; Guzman, E. Insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease. J. Int. Med. Res. 2023, 51, 3000605231164548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, P.S.; Kao, T.W.; Chang, P.K.; Chen, W.L.; Peng, P.J.; Wu, L.W. Association Between HOMA-IR and Frailty among U.S. Middle-aged and Elderly Population. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yoon, K.-H. Evolving Characteristics of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in East Asia. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 40, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Ghani, M.A.; Tripathy, D.; DeFronzo, R.A. Contributions of β-Cell Dysfunction and Insulin Resistance to the Pathogenesis of Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Impaired Fasting Glucose. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, B.; Livingstone, C.; Kaddam, I.; Ferns, G. Selection of the appropriate method for the assessment of insulin resistance. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2011, 11, 158. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitriadis, G.D.; Maratou, E.; Kountouri, A.; Board, M.; Lambadiari, V. Regulation of Postabsorptive and Postprandial Glucose Metabolism by Insulin-Dependent and Insulin-Independent Mechanisms: An Integrative Approach. Nutrients 2021, 13, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Dyglycemia (n = 2922) | Normal (n = 940) | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2DM (n = 413) | Pre-DM (n = 2509) | ||||||
| N | (W%) | N | (W%) | N | (W%) | ||
| Sex | |||||||
| Male | 195 | (49.45) | 1051 | (42.80) | 404 | (42.56) | 0.086 |
| Female | 218 | (50.55) | 1458 | (57.20) | 536 | (57.44) | |
| Age | |||||||
| Mean ± SE | 73.03 | (±0.32) | 72.87 | (±0.15) | 72.74 | (±0.22) | 0.738 |
| 65–69 | 124 | (35.05) | 786 | (34.08) | 313 | (36.30) | 0.650 |
| 70–74 | 103 | (22.36) | 699 | (25.05) | 244 | (22.96) | |
| ≥75 | 186 | (42.59) | 1024 | (40.87) | 383 | (40.74) | |
| Regular aerobic exercise (per week) 1 | |||||||
| Yes | 114 | (27.57) | 701 | (28.53) | 258 | (27.71) | 0.213 |
| No | 230 | (56.46) | 1523 | (59.80) | 567 | (60.67) | |
| Missing | 69 | (15.96) | 285 | (11.67) | 115 | (11.62) | |
| Regular strength exercise (per week) 2 | |||||||
| None at all | 272 | (65.69) | 1742 | (68.23) | 664 | (70.29) | 0.087 |
| 1–3 days | 19 | (4.45) | 173 | (7.05) | 69 | (7.71) | |
| ≥4 days | 54 | (14.26) | 314 | (13.37) | 98 | (11.26) | |
| Missing | 68 | (15.60) | 280 | (11.34) | 109 | (10.75) | |
| Smoking | |||||||
| Non-smoker | 234 | (53.60) | 1585 | (61.97) | 579 | (60.86) | 0.001 |
| Former smoker | 120 | (30.92) | 655 | (26.50) | 264 | (28.96) | |
| Current Smoker | 44 | (12.09) | 236 | (10.29) | 71 | (7.27) | |
| Missing | 15 | (3.39) | 33 | (1.25) | 26 | (2.91) | |
| Education | |||||||
| ≤Elementary | 159 | (35.30) | 1020 | (38.59) | 375 | (36.79) | 0.129 |
| Middle–High | 144 | (39.43) | 913 | (37.28) | 357 | (41.46) | |
| 2–4 years college | 35 | (7.69) | 248 | (10.59) | 78 | (8.84) | |
| ≥Postgraduate | 7 | (1.97) | 48 | (2.21) | 19 | (1.97) | |
| Missing | 68 | (15.60) | 280 | (11.33) | 111 | (10.94) | |
| Heavy alcoholics 3 | |||||||
| None at all | 301 | (71.65) | 1974 | (78.15) | 728 | (76.73) | <0.0001 |
| ≤1 per week | 82 | (19.96) | 429 | (17.53) | 175 | (19.42) | |
| Almost every day | 17 | (5.35) | 74 | (3.10) | 13 | (1.18) | |
| Missing | 13 | (3.03) | 32 | (1.22) | 24 | (2.67) | |
| Household income | |||||||
| Lower | 205 | (46.71) | 1098 | (40.49) | 424 | (43.96) | 0.428 |
| Middle–lower | 109 | (25.77) | 745 | (30.13) | 266 | (27.00) | |
| Upper middle | 60 | (15.78) | 407 | (17.64) | 147 | (17.16) | |
| Upper | 35 | (10.57) | 237 | (10.69) | 96 | (11.27) | |
| Missing | 4 | (1.16) | 22 | (1.05) | 7 | (0.61) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | |||||||
| Mean ± SE | 24.75 | (±0.21) | 24.02 | (±0.07) | 23.19 | (±0.11) | <0.0001 |
| < 23 | 119 | (30.07) | 978 | (39.49) | 480 | (50.24) | <0.0001 |
| 23.0–24.9 | 103 | (23.86) | 652 | (25.72) | 232 | (25.01) | |
| ≥25 | 191 | (46.07) | 879 | (34.79) | 228 | (24.75) | |
| FPG, (mg/dL) | |||||||
| Mean ± SE | 128.23 *† | (±1.35) | 100.94 *† | (±0.20) | 91.31 *† | (±0.21) | <0.0001 |
| HbA1c (%) | |||||||
| Mean ± SE | 6.76 *† | (±0.05) | 5.87 *† | (±0.01) | 5.43 *† | (±0.01) | <0.0001 |
| Fasting insulin, (µIU/mL) | |||||||
| Mean ± SE | 15.79 *† | (±0.90) | 9.39 *† | (±0.18) | 7.02 *† | (±0.21) | <0.0001 |
| HOMA-IR | |||||||
| Mean ± SE | 5.28 *† | (±0.35) | 2.37 *† | (±0.05) | 1.59 *† | (±0.05) | <0.0001 |
| HOMA-β | |||||||
| Mean ± SE | 88.30 | (±4.46) | 90.65 | (±1.96) | 89.66 | (±2.53) | 0.869 |
| Variable | HOMA-IR | HOMA-β | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | AUC | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | AUC | |
| Pre-DM | ||||||
| Men | ||||||
| Overall | 1.34 (1.07–1.68) | 0.013 | 0.671 | 0.999 (0.996–1.001) | 0.321 | 0.639 |
| 65–69 | 1.34 (0.95–1.88) | 0.094 | 0.704 | 0.997 (0.992–1.002) | 0.195 | 0.691 |
| 70–74 | 1.40 (0.75–2.62) | 0.289 | 0.742 | 0.995 (0.991–0.999) | 0.017 | 0.712 |
| ≥75 | 1.38 (0.93–2.06) | 0.107 | 0.719 | 0.999 (0.998–1.001) | 0.375 | 0.684 |
| Women | ||||||
| Overall | 1.78 (1.50–2.12) | <0.0001 | 0.709 | 1.001 (0.999–1.002) | 0.310 | 0.606 |
| 65–69 | 2.14 (1.58–2.91) | <0.0001 | 0.722 | 0.999 (0.995–1.003) | 0.640 | 0.625 |
| 70–74 | 2.38 (1.58–3.59) | <0.0001 | 0.794 | 1.004 (0.999–1.009) | 0.090 | 0.698 |
| ≥75 | 1.60 (1.16–2.20) | 0.004 | 0.719 | 1.001 (0.999–1.004) | 0.265 | 0.641 |
| T2DM | ||||||
| Men | ||||||
| Overall | 1.87 (1.34–2.62) | 0.001 | 0.844 | 0.995 (0.991–0.999) | 0.016 | 0.717 |
| 65–69 | 1.86 (1.14–3.04) | 0.013 | 0.864 | 0.985 (0.972–0.998) | 0.027 | 0.852 |
| 70–74 | 3.87 (1.13–13.22) | 0.031 | 0.939 | 0.976 (0.945–1.009) | 0.145 | 0.828 |
| ≥75 | 2.32 (1.07–5.05) | 0.034 | 0.900 | 0.999 (0.996–1.002) | 0.648 | 0.754 |
| Women | ||||||
| Overall | 2.31 (1.79–2.98) | <0.0001 | 0.865 | 0.999 (0.996–1.002) | 0.433 | 0.674 |
| 65–69 | 5.23 (2.89–9.46) | <0.0001 | 0.939 | 1.002 (0.996–1.008) | 0.552 | 0.784 |
| 70–74 | 2.81 (1.50–5.25) | 0.002 | 0.915 | 0.983 (0.966–0.999) | 0.041 | 0.871 |
| ≥75 | 1.58 (1.11–2.26) | 0.013 | 0.853 | 0.999 (0.996–1.003) | 0.724 | 0.721 |
| Variable | Cut-Off | AUC | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | PPV (95% CI) | NPV (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-DM | ||||||
| Men | ||||||
| Overall | 1.73 | 0.682 | 54.34 (50.96–57.72) | 70.23 (64.88–75.58) | 83.32 (79.98–86.67) | 35.97 (32.01–39.93) |
| 65–69 | 1.49 | 0.702 | 61.65 (55.26–68.04) | 60.55 (50.68–70.43) | 80.34 (74.52–86.16) | 37.65 (29.65–45.66) |
| 70–74 | 1.69 | 0.747 | 62.16 (56.10–68.23) | 72.23 (62.67–81.79) | 86.67 (81.75–91.60) | 39.66 (32.24–47.08) |
| ≥75 | 1.94 | 0.700 | 46.42 (40.72–52.11) | 78.19 (71.01–85.38) | 85.41 (80.13–90.69) | 34.66 (29.49–39.82) |
| Women | ||||||
| Overall | 1.85 | 0.665 | 55.77 (52.55–58.99) | 73.98 (70.00–77.96) | 85.32 (82.97–87.67) | 38.15 (34.60–41.71) |
| 65–69 | 1.82 | 0.662 | 53.55 (48.02–59.09) | 69.36 (62.09–76.63) | 81.43 (76.86–85.99) | 37.32 (31.35–43.29) |
| 70–74 | 1.78 | 0.700 | 61.38 (55.85–66.90) | 76.27 (68.94–83.60) | 88.68 (84.93–92.43) | 39.47 (32.44–46.50) |
| ≥75 | 1.41 | 0.683 | 73.09 (69.05–77.12) | 60.32 (52.68–67.97) | 83.36 (79.75–86.96) | 45.19 (38.63–51.75) |
| T2DM | ||||||
| Men | ||||||
| Overall | 2.25 | 0.828 | 72.40 (65.24–79.56) | 81.82 (77.25–86.39) | 66.86 (59.41–74.32) | 85.40 (81.26–89.54) |
| 65–69 | 1.62 | 0.837 | 85.86 (76.61–95.10) | 63.91 (53.94–73.87) | 57.54 (46.45–68.63) | 88.80 (81.38–96.23) |
| 70–74 | 2.28 | 0.889 | 65.38 (48.00–82.76) | 85.08 (77.60–92.56) | 60.83 (43.95–77.72) | 87.40 (80.06–94.73) |
| ≥75 | 2.59 | 0.865 | 75.45 (65.97–84.93) | 87.43 (81.82–93.04) | 76.61 (66.48–86.75) | 86.70 (81.04–92.37) |
| Women | ||||||
| Overall | 2.03 | 0.823 | 79.36 (73.63–85.09) | 79.44 (75.78–83.09) | 59.69 (53.46–65.92) | 90.93 (88.30–93.57) |
| 65–69 | 1.79 | 0.819 | 79.68 (68.15–91.21) | 68.46 (61.18–75.74) | 43.11 (31.87–54.34) | 91.83 (87.12–96.53) |
| 70–74 | 2.08 | 0.842 | 72.65 (59.84–85.45) | 84.58 (78.28–90.89) | 69.63 (58.38–80.89) | 86.41 (79.51–93.30) |
| ≥75 | 1.97 | 0.848 | 85.72 (78.91–92.52) | 79.12 (72.67–85.56) | 62.18 (52.09–72.27) | 93.26 (89.86–96.66) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, S.M.; Park, B. Association of Insulin Resistance with Dysglycemia in Elder Koreans: Age- and Sex-Specific Cutoff Values. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15090438
Yoon SM, Park B. Association of Insulin Resistance with Dysglycemia in Elder Koreans: Age- and Sex-Specific Cutoff Values. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(9):438. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15090438
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Sang Min, and Boyoung Park. 2025. "Association of Insulin Resistance with Dysglycemia in Elder Koreans: Age- and Sex-Specific Cutoff Values" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 9: 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15090438
APA StyleYoon, S. M., & Park, B. (2025). Association of Insulin Resistance with Dysglycemia in Elder Koreans: Age- and Sex-Specific Cutoff Values. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(9), 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15090438






