Association Between Maternal Pre-Pregnancy Body Mass Index and Growth Delay in Korean Children Aged 18–36 Months: A Population-Based Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
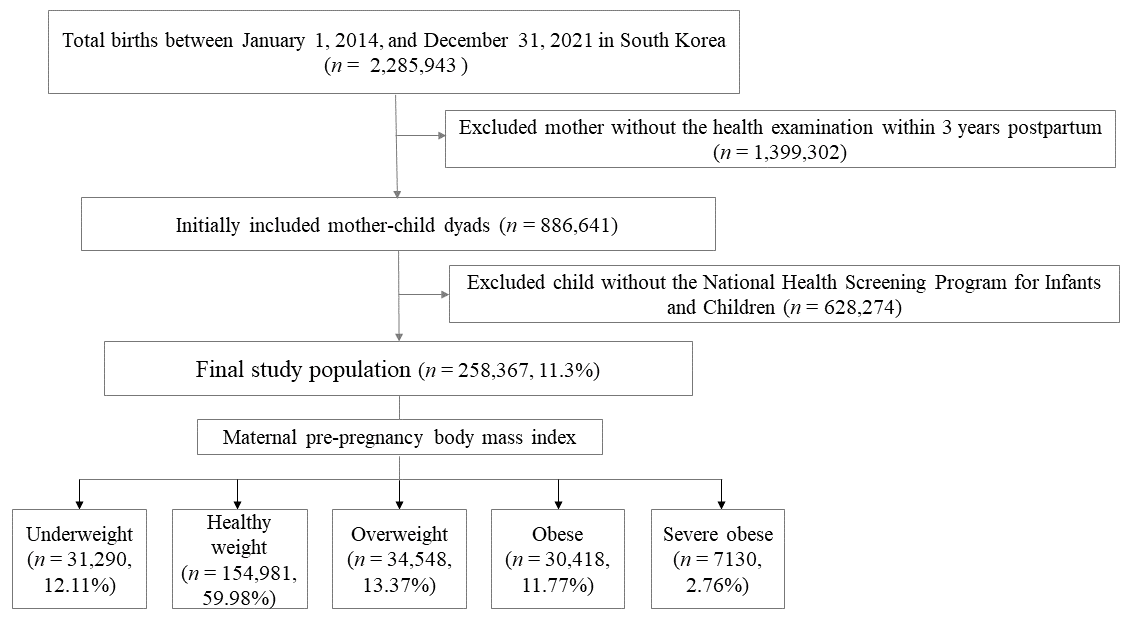
2.1. Study Data Sources and Participants
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Other Variables
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population According to Maternal Pre-Pregnancy BMI
3.2. The Risk of Growth Delay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body mass index |
| NHSPIC | National Health Screening Program for Infants and Children |
| NHIS | National Health Insurance Service |
| ICD-10 | International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| SGA | Small for gestational age |
| NICU | Neonatal intensive care unit |
| CIs | Confidence intervals |
| IRs | Incidence rates |
References
- Black, M.H.; Sacks, D.A.; Xiang, A.H.; Lawrence, J.M. The relative contribution of prepregnancy overweight and obesity, gestational weight gain, and IADPSG-defined gestational diabetes mellitus to fetal overgrowth. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Y.; Cui, M.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, G.; Zuo, H.; Xiu, Q.; Shah, P.S. Pre-pregnancy body mass index, gestational diabetes mellitus, and gestational weight gain: Individual and combined effects on fetal growth. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1354355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obesity Fact Sheet Task Force Team. Obesity Fact Sheet. 2024. Available online: https://general.kosso.or.kr/html/user/core/view/reaction/main/kosso/inc/data/2024_Obesity_Fact_sheet_web_eng.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Leonard, S.A.; Rasmussen, K.M.; King, J.C.; Abrams, B. Trajectories of maternal weight from before pregnancy through postpartum and associations with childhood obesity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrego Del Castillo, K.Y.; Dennis, C.-L.; Wamithi, S.; Briollais, L.; McGowan, P.O.; Dol, J.; Lye, S.J. Maternal BMI, breastfeeding and perinatal factors that influence early childhood growth trajectories: A scoping review. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2022, 13, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfrey, K.M.; Costello, P.M.; Lillycrop, K.A. Development, Epigenetics and Metabolic Programming. In Preventive Aspects of Early Nutrition: 85th Nestlé Nutrition Institute Workshop, London, November 2014; Fewtrell, M.S., Haschke, F., Prescott, S.L., Eds.; S.Karger AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 85, p. 71. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, J.S. Review of National Health Screening Program for Infant and Children in Korea. JKMA 2010, 53, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannino, A.; Sarapis, K.; Mourouti, N.; Karaglani, E.; Anastasiou, C.A.; Manios, Y.; Moschonis, G. The Association of Maternal Weight Status throughout the Life-Course with the Development of Childhood Obesity: A Secondary Analysis of the Healthy Growth Study Data. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.; Mao, A.; Yang, L.; Ren, Y.; Yang, X.; Song, W.; Luo, Y. Association of maternal metabolic risk factors with offspring body mass index (BMI) trajectories in early childhood: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2025, 15, e088641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-S.; Choi, Y.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, M.-H.; Lee, N. Association between the COVID-19 pandemic and childhood development aged 30 to 36 months in South Korea, based on the National health screening program for infants and children database. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Regional Office for the Western Pacific. The Asia-Pacific Perspective: Redefining Obesity and Its Treatment. 2020. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/206936 (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Physician Counseling Manual for the Infant and Child Health Screening Program. Available online: https://www.kdca.go.kr/board/board.es?mid=a20507020000&bid=0019&list_no=726955&act=view (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Lee, S.R.; Choi, E.K.; Park, S.H.; Jung, J.H.; Han, K.D.; Oh, S.; Lip, G.Y.H. Comparing Warfarin and 4 Direct Oral Anticoagulants for the Risk of Dementia in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. Stroke 2021, 52, 3459–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, M.; Magnussen, C.G.; Xi, B. Maternal Pre-pregnancy Body Mass Index Categories and Infant Birth Outcomes: A Population-Based Study of 9 Million Mother-Infant Pairs. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 789833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, T.R.; Merlino Barr, S.; Elmrayed, S.; Alshaikh, B. Expected and Desirable Preterm and Small Infant Growth Patterns. Adv. Nutr. 2024, 15, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, A.; Yorifuji, T.; Hattori, M.; Tamai, K.; Nakamura, K.; Nakamura, M.; Kageyama, M.; Kubo, T.; Ogino, T.; Kobayashi, K.; et al. Catch-up growth and behavioral development among preterm, small-for-gestational-age children: A nationwide Japanese population-based study. Brain Dev. 2019, 41, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyakotey, D.A.; Clarke, A.M.; Cormack, B.E.; Bloomfield, F.H.; Harding, J.E. Postnatal growth and neurodevelopment at 2 years’ corrected age in extremely low birthweight infants. Pediatr. Res. 2024, 96, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strobel, K.M.; Wood, T.R.; Valentine, G.C.; German, K.R.; Gogcu, S.; Hendrixson, D.T.; Kolnik, S.E.; Law, J.B.; Mayock, D.E.; Comstock, B.A.; et al. Contemporary definitions of infant growth failure and neurodevelopmental and behavioral outcomes in extremely premature infants at two years of age. J. Perinatol. 2024, 44, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Mulla, S.; Beyene, J.; Liao, G.; McDonald, S.D. Maternal underweight and the risk of preterm birth and low birth weight: A systematic review and meta-analyses. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 65–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, K.; Saijo, Y.; Yoshioka, E.; Sato, Y.; Kato, Y.; Nagaya, K.; Takahashi, S.; Ito, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Miyashita, C.; et al. Severity of low pre-pregnancy body mass index and perinatal outcomes: The Japan Environment and Children’s Study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2022, 22, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Womack, S.R.; Beam, C.R.; Giangrande, E.J.; Scharf, R.J.; Tong, X.; Ponnapalli, M.; Davis, D.W.; Turkheimer, E. Nonlinear Catch-Up Growth in Height, Weight, and Head Circumference from Birth to Adolescence: A Longitudinal Twin Study. Behav. Genet. 2023, 53, 385–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, G.; Hayes, L.; Ngongalah, L.; Bigirumurame, T.; Gaudet, L.; Odeniyi, A.; Flynn, A.; Crowe, L.; Skidmore, B.; Simon, A.; et al. Association between maternal adiposity measures and infant health outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2022, 23, e13491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunde, A.; Melve, K.K.; Gjessing, H.K.; Skjaerven, R.; Irgens, L.M. Genetic and environmental influences on birth weight, birth length, head circumference, and gestational age by use of population-based parent-offspring data. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 165, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.E.; Barry, C.; Sabhlok, A.; Russell, K.; Majors, A.; Kollins, S.H.; Fuemmeler, B.F. Maternal pre-pregnancy obesity and child neurodevelopmental outcomes: A meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 464–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.F.; Abell, S.K.; Ranasinha, S.; Misso, M.L.; Boyle, J.A.; Harrison, C.L.; Black, M.H.; Li, N.; Hu, G.; Corrado, F.; et al. Gestational weight gain across continents and ethnicity: Systematic review and meta-analysis of maternal and infant outcomes in more than one million women. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terada, S.; Isumi, A.; Doi, S.; Fujiwara, T. Association of maternal pre-pregnancy body mass index with resilience and prosociality of the offspring aged 6-7 years old: A population-based cohort study in Japan. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2024, 33, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, S.J. Association between maternal weight gain during pregnancy and child’s body mass index at preschool age. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2023, 66, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Maternal BMI | Underweight | Healthy Weight | Overweight | Obese | Severe Obese | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 31,290 | 154,981 | 34,548 | 30,418 | 7130 | |
| % | 12.11 | 59.98 | 13.37 | 11.77 | 2.76 | |
| Maternal characteristics | ||||||
| Age, mean, year | 31.59 ± 3.69 | 32.23 ± 3.84 | 32.75 ± 4.06 | 32.96 ± 4.12 | 33.1 ± 4.26 | <0.001 |
| Age (≥35 years) | 6219(19.88) | 39,910(25.75) | 10,953(31.7) | 10,300(33.86) | 2588(36.3) | <0.001 |
| Chronic hypertension | 445(1.42) | 2523(1.63) | 761(2.2) | 1163(3.82) | 682(9.57) | <0.001 |
| PIH | 2673(8.54) | 15,462(9.98) | 4235(12.26) | 4458(14.66) | 1669(23.41) | <0.001 |
| Depression | 581(1.86) | 2638(1.7) | 580(1.68) | 606(1.99) | 173(2.43) | <0.001 |
| Pregestational DM | 66(0.21) | 553(0.36) | 311(0.9) | 622(2.04) | 446(6.26) | <0.001 |
| Gestational DM | 4109(13.13) | 22,093(14.26) | 5921(17.14) | 6436(21.16) | 2059(28.88) | <0.001 |
| Preterm birth | 1365(4.36) | 6554(4.23) | 1464(4.24) | 1382(4.55) | 412(5.78) | <0.001 |
| Normal delivery | 20,162(64.44) | 89,601(57.81) | 17,480(50.6) | 13,333(43.83) | 2304(32.31) | <0.001 |
| Children’s characteristics | ||||||
| Gestational age, mean, week | 35.6 ± 2.3 | 35.5 ± 2.3 | 35.3 ± 2.5 | 35.2 ± 2.5 | 34.8 ± 2.6 | <0.001 |
| Sex, male | 15,957(51.0) | 79,252(51.1) | 17,664(51.1) | 15,415(50.7) | 3555(49.9) | 0.180 |
| Birth weight, mean, kg | 3.09 ± 0.41 | 3.17 ± 0.43 | 3.23 ± 0.45 | 3.27 ± 0.47 | 3.31 ± 0.53 | <0.001 |
| Birth weight, kg | <0.001 | |||||
| <2.00 | 345(1.1) | 1552(1) | 371(1.07) | 313(1.03) | 110(1.54) | |
| 2.00~2.99 | 10,633(33.98) | 41,003(26.46) | 7733(22.38) | 6268(20.61) | 1350(18.93) | |
| 3.00~3.99 | 19,879(63.53) | 108,432(69.96) | 25,045(72.49) | 22,060(72.52) | 4983(69.89) | |
| ≥4.00 | 433(1.38) | 3994(2.58) | 1399(4.05) | 1777(5.84) | 687(9.64) | |
| Multiple birth | 998(3.19) | 5715(3.69) | 1239(3.59) | 1086(3.57) | 303(4.25) | <0.001 |
| Preterm birth | 1365(4.36) | 6554(4.23) | 1464(4.24) | 1382(4.55) | 412(5.78) | <0.001 |
| Major anomaly | 2613(8.35) | 12,330(7.96) | 2841(8.22) | 2620(8.61) | 698(9.79) | <0.001 |
| SGA | 351(1.12) | 1306(0.84) | 253(0.73) | 183(0.60) | 59(0.83) | <0.001 |
| ICU admission | 1800(5.75) | 9065(5.85) | 2202(6.37) | 2191(7.20) | 703(9.86) | <0.001 |
| 18–24 Months | 30–36 Months | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI | N | Event | IR | RR(95% CI) | p-Value | Event | IR | RR(95% CI) | p-Value |
| Height < 10 percentile | |||||||||
| Underweight | 31,290 | 1181 | 3.77 | 0.965(0.929–1.002) | 0.065 | 1397 | 4.46 | 1.014(0.979–1.050) | 0.438 |
| Healthy weight | 154,981 | 5242 | 3.38 | 1(ref.) | 6074 | 3.92 | 1(ref.) | ||
| Overweight | 34,548 | 1214 | 3.51 | 1.133(1.092–1.175) | <0.001 | 1450 | 4.20 | 1.165(1.126–1.205) | <0.001 |
| Obese I | 30,418 | 1174 | 3.86 | 1.332(1.285–1.380) | <0.001 | 1328 | 4.37 | 1.274(1.233–1.317) | <0.001 |
| Obese II&III | 7130 | 335 | 4.70 | 1.610(1.556–1.667) | <0.001 | 332 | 4.66 | 1.310(1.267–1.355) | <0.001 |
| Weight < 10 percentile | |||||||||
| Underweight | 31,290 | 1748 | 5.59 | 1.223(1.183–1.265) | <0.001 | 1864 | 5.96 | 1.338(1.294–1.383) | <0.001 |
| Healthy weight | 154,981 | 5988 | 3.86 | 1(ref.) | 5944 | 3.84 | 1(ref.) | ||
| Overweight | 34,548 | 1070 | 3.10 | 0.916(0.883–0.950) | <0.001 | 1093 | 3.16 | 0.923(0.890–0.957) | <0.001 |
| Obese I | 30,418 | 926 | 3.04 | 1.001(0.966–1.038) | 0.948 | 912 | 3.00 | 0.989(0.954–1.026) | 0.558 |
| Obese II&III | 7130 | 187 | 2.62 | 0.861(0.828–0.894) | <0.001 | 178 | 2.50 | 0.791(0.760–0.822) | <0.001 |
| Head circumference < 10 percentile | |||||||||
| Underweight | 31,290 | 1625 | 5.19 | 1.068(1.034–1.104) | <0.001 | 1855 | 5.93 | 1.111(1.077–1.146) | <0.001 |
| Healthy weight | 154,981 | 6528 | 4.21 | 1(ref.) | 7298 | 4.71 | 1(ref.) | ||
| Overweight | 34,548 | 1367 | 3.96 | 1.031(0.997–1.067) | 0.073 | 1536 | 4.45 | 1.036(1.004–1.069) | 0.029 |
| Obese I | 30,418 | 1216 | 4.00 | 1.132(1.096–1.170) | <0.001 | 1296 | 4.26 | 1.072(1.038–1.106) | <0.001 |
| Obese II&III | 7130 | 339 | 4.75 | 1.375(1.332–1.419) | <0.001 | 332 | 4.66 | 1.191(1.154–1.228) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, E.-J.; Kim, T.-E.; Park, S.-H.; Park, H.W.; Kweon, H.J.; Choi, J.; Shin, J. Association Between Maternal Pre-Pregnancy Body Mass Index and Growth Delay in Korean Children Aged 18–36 Months: A Population-Based Study. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15060261
Oh E-J, Kim T-E, Park S-H, Park HW, Kweon HJ, Choi J, Shin J. Association Between Maternal Pre-Pregnancy Body Mass Index and Growth Delay in Korean Children Aged 18–36 Months: A Population-Based Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(6):261. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15060261
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Eun-Jung, Tae-Eun Kim, Sang-Hyun Park, Hye Won Park, Hyuk Jung Kweon, Jaekyung Choi, and Jinyoung Shin. 2025. "Association Between Maternal Pre-Pregnancy Body Mass Index and Growth Delay in Korean Children Aged 18–36 Months: A Population-Based Study" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 6: 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15060261
APA StyleOh, E.-J., Kim, T.-E., Park, S.-H., Park, H. W., Kweon, H. J., Choi, J., & Shin, J. (2025). Association Between Maternal Pre-Pregnancy Body Mass Index and Growth Delay in Korean Children Aged 18–36 Months: A Population-Based Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(6), 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15060261






