Interstitial Lung Diseases and Lung Cancer: A Review on Similarities, Common Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Incidence and Risk Factors for Lung Cancer in Interstitial Lung Diseases
- Smoking history: the relationship between cigarette smoking and ILDs is well known. In fact, cigarette smoking is the basis of the pathogenesis of desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP), respiratory bronchiolitis–interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD) and Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Smoking is also a common risk factor for LC and ILD, especially for IPF, causing a nine-fold increase in LC in former smokers and a twenty-fold increase in active smokers. However, even if typically strongly related to ILDs and LC, smoking is not always the main risk factor for the relationship between these two entities. For example, in systemic-sclerosis-associated ILD, LC does not have a higher prevalence in smokers than non-smokers and is probably more related to the inflammatory and immune processes of connective tissue disease [24,25];
- Diffuse inflammatory process, present both in ILDs and in LC, includes epithelial abnormalities ranging from metaplasia to carcinomatous transformation, myofibroblast proliferation and soluble mediator release in the context of an abnormal healing process [16];
- Gene alteration and aging with telomere attrition: mutations or variants in genes, for example, the gene for surfactant protein A (SFTPA) inducing tumor growth factor beta (TGFβ) secretion, squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA), a serine protease inhibitor typically expressed by dysplastic/neoplastic cells of epithelial origin, abnormal telomere shortening (such as h-TERT or h-TERC mutation) and cellular senescence were found both in lung cancer and ILDs [26,27,28,29].
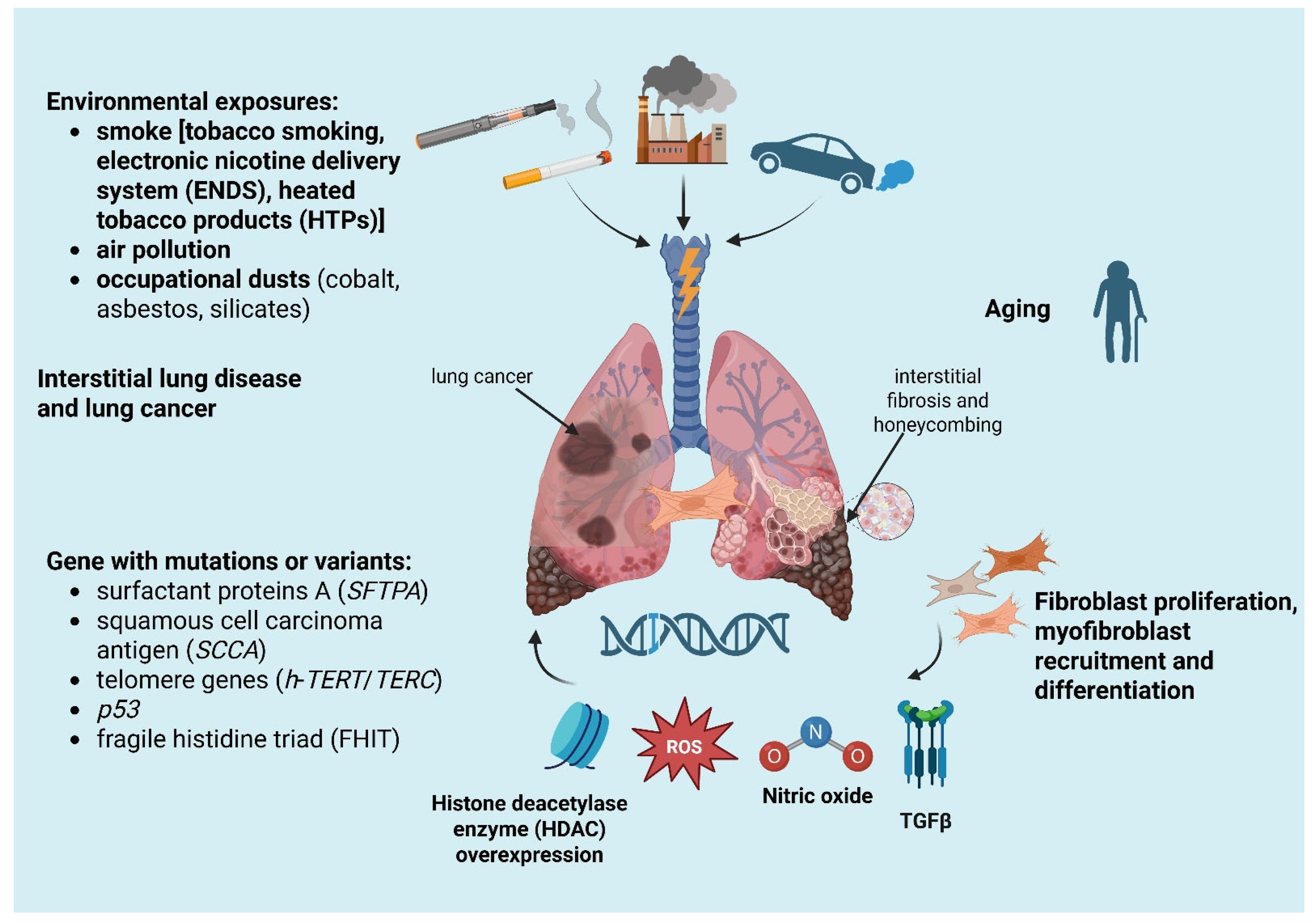
3. Pathogenesis of Lung Cancer in Interstitial Lung Diseases
- Uncontrolled proliferation: the hyperplasia of pulmonary cells, both cuboidal and mucous cells, the evasion of apoptosis and an altered cell-to-cell communications appear linked to epithelial metaplasia and cancerogenesis. In lung tissue, transition zones from metaplasia to invasive cancer are located close to fibrotic areas [41];
- Tissue invasion: myofibroblast recruitment and differentiation, with their ability to infiltrate tissues, together with invasive molecule expression are specifically linked to carcinogenesis. In pulmonary fibrosis, during myofibroblast differentiation Xie et al. observed the activation of the Warburg effect, a metabolic perturbation typical of cancer cells in which glycolysis is preferred over oxidative phosphorylation, even in the presence of oxygen [42,43];
- Signal transduction pathways: the production of cytokines and nitro derivatives in the microenvironment facilitates carcinomatous transformation during fibrogenesis [32]. In particular, TGFβ, involved in fibrogenesis and myofibroblast transformation, normally exerts an antiproliferative action on epithelial cells [44]. Takenaka et al. proved that in IPF-LC patients Smad4 expression levels were significantly lower than in LC alone, promoting a diminished growth inhibitory response to TGFβ [45]. Nitric oxide (NO) production by stressed epithelial cells, like the ones in ILDs, causes guanine nitrification in cellular DNA. Terasaki et al. observed a NO overexpression and guanine nitration, especially in IPF and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), compared to a control population regardless of smoking history [46];
- Histone deacetylase enzyme (HDAC) overexpression: HDAC overexpression has been observed in myofibroblasts and abnormal bronchiolar epithelium of IPF [47]. Of interest, HDAC catalyzes deacetylation of many non-histone proteins, such as tumor suppressor p53, resulting in inhibition of its proapoptotic activity [48].
4. Distribution and Histopathology of Lung Cancer in Interstitial Lung Diseases
5. Genetic Mutations: Similarities and Common Pathways
6. Molecular Characterization of Lung Cancer in Interstitial Lung Diseases
7. Management and Diagnostic Approach of Suspected Nodules in Interstitial Lung Disease Patients
8. Surgical Treatment
9. Chemotherapy, Immunotherapy and Radiotherapy
10. Palliative Care and End of Life Communication
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Troy, L.; Corte, T. Interstitial Lung Disease in 2015: Where Are We Now? Aust. Fam. Physician 2015, 44, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; King, T.E.; Bateman, E.D.; Lynch, D.A.; Capron, F.; Center, D.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.F.; DuBois, R.M.; Galvin, J.; et al. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 277–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, W.D.; Costabel, U.; Hansell, D.M.; King, T.E.; Lynch, D.A.; Nicholson, A.G.; Ryerson, C.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Selman, M.; Wells, A.U.; et al. An Official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society Statement: Update of the International Multidisciplinary Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, A.U.; Hirani, N. Interstitial Lung Disease Guideline: The British Thoracic Society in Collaboration with the Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand and the Irish Thoracic Society. Thorax 2008, 63, v1–v58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Statement: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Evidence-Based Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah Gupta, R.; Koteci, A.; Morgan, A.; George, P.M.; Quint, J.K. Incidence and Prevalence of Interstitial Lung Diseases Worldwide: A Systematic Literature Review. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2023, 10, e001291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, K.R.; King, T.E.; Raghu, G.; Lynch, J.P.; Colby, T.V.; Travis, W.D.; Gross, B.H.; Kazerooni, E.A.; Toews, G.B.; Long, Q.; et al. Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia: What Is the Effect of a Multidisciplinary Approach to Diagnosis? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, T.; Tajiri, M.; Baba, T.; Ogura, T.; Iwasawa, T.; Okudela, K.; Takemura, T.; Oba, M.S.; Maehara, T.; Nakayama, H.; et al. Pulmonary Resection for Lung Cancer in Patients with Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 100, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassetti, S.; Gurioli, C.; Ryu, J.H.; Decker, P.A.; Ravaglia, C.; Tantalocco, P.; Buccioli, M.; Piciucchi, S.; Sverzellati, N.; Dubini, A.; et al. The Impact of Lung Cancer on Survival of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Chest 2015, 147, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, Y.; Suda, T.; Naito, T.; Enomoto, N.; Hashimoto, D.; Fujisawa, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Inui, N.; Nakamura, H.; Chida, K. Cumulative Incidence of and Predictive Factors for Lung Cancer in IPF. Respirology 2009, 14, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczi, E.; Nagy, T.; Starobinski, L.; Kolonics-Farkas, A.; Eszes, N.; Bohacs, A.; Tarnoki, A.D.; Tarnoki, D.L.; Müller, V. Impact of Interstitial Lung Disease and Simultaneous Lung Cancer on Therapeutic Possibilities and Survival. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spain, D.M. The Association of Terminal Bronchiolar Carcinoma with Chronic Interstitial Inflammation and Fibrosis of the Lungs. Am. Rev. Tuberc. 1957, 76, 559–566. [Google Scholar]
- Haddad, R.; Massaro, D. Idiopathic Diffuse Interstitial Pulmonary Fibrosis (Fibrosing Alveolitis), Atypical Epithelial Proliferation and Lung Cancer. Am. J. Med. 1968, 45, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Héluain, V.; Prévot, G.; Cabarrou, B.; Calvayrac, O.; Taranchon- Clermont, E.; Didier, A.; Tabourier-Gouin, S.; Milia, J.; Mazières, J. Clinical and Molecular Analysis of Lung Cancers Associated with Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Disease. Respir. Med. Res. 2023, 83, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibiot, Q.; Monnet, I.; Levy, P.; Brun, A.L.; Antoine, M.; Chouaïd, C.; Cadranel, J.; Naccache, J.M. Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Lung Cancer: A Case–Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naccache, J.M.; Gibiot, Q.; Monnet, I.; Antoine, M.; Wislez, M.; Chouaid, C.; Cadranel, J. Lung Cancer and Interstitial Lung Disease: A Literature Review. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 3829–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaji, N.; Tadokoro, A.; Kita, N.; Murota, M. Impact of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis on Advanced Non—Small Cell Lung Cancer Survival. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 1855–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.A.W.; Dobelle, M.; Padilla, M.; Agovino, M.; Wisnivesky, J.P.; Hashim, D.; Boffetta, P. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2019, 16, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, T.N.; Butt, Y.M.; Batra, K.; Glazer, C.S. Cobalt Related Interstitial Lung Disease. Respir. Med. 2017, 129, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, M.; Thompson, C.M.; Brorby, G.P.; Mittal, L.; Proctor, D.M. Inhalation Cancer Risk Assessment of Cobalt Metal. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 79, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, K.M.A.; Mclaughlin, A.M.; Beckett, W.S.; Sime, P.J. Asbestos-Related Lung Disease. Am. Fam. Physician 2007, 75, 683–688. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, C.C.; Yu, I.T.S.; Chen, W. Silicosis. Lancet 2012, 379, 2008–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straif, K.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Baan, R.; Grosse, Y.; Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Guha, N.; Freeman, C.; Galichet, L.; et al. A Review of Human Carcinogens—Part C: Metals, Arsenic, Dusts, and Fibres. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, L.; Lovly, C.M. Neoplasms of the Lung. In Harrison’s Principles of iIternal Medicine; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-259-64403-0. [Google Scholar]
- Behr, J.; Kreuter, M.; Hoeper, M.M.; Wirtz, H.; Klotsche, J.; Kosche, D.; Andreas, S.; Claussen, M.; Grohé, C.; Wilkens, H.; et al. Management of Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in Clinical Practice: The INSIGHTS-IPF Registry. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kuan, P.J.; Xing, C.; Cronkhite, J.T.; Torres, F.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; DiMaio, J.M.; Kinch, L.N.; Grishin, N.V.; Garcia, C.K. Genetic Defects in Surfactant Protein A2 Are Associated with Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, F.; Lunardi, F.; Giacometti, C.; Marulli, G.; Gnoato, M.; Pontisso, P.; Saetta, M.; Valente, M.; Rea, F.; Perissinotto, E.; et al. Overexpression of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Antigen in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Clinicopathological Correlations. Thorax 2008, 63, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, S.; Driscoll, B. Regeneration of the Aging Lung: A Mini-Review. Gerontology 2017, 63, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuyts, W.A.; Agostini, C.; Antoniou, K.M.; Bouros, D.; Chambers, R.C.; Cottin, V.; Egan, J.J.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Lories, R.; Parfrey, H.; et al. The Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Moving Target. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.J.; Collard, H.R.; Pardo, A.; Raghu, G.; Richeldi, L.; Selman, M.; Swigris, J.J.; Taniguchi, H.; Wells, A.U. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kewalramani, N.; Machahua, C.; Poletti, V.; Cadranel, J.; Wells, A.U.; Funke-Chambour, M. Lung Cancer in Patients with Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases: An Overview of Current Knowledge and Challenges. ERJ Open Res. 2022, 8, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancheri, C.; Failla, M.; Crimi, N.; Raghu, G. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Disease with Similarities and Links to Cancer Biology. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, A.; Chiyotani, A.; Nakadate, T.; Konno, K. Lung Cancer in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1992, 167, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, H.; Nagai, K.; Yokose, T.; Yoshida, J.; Nishimura, M.; Takahashi, K.; Suzuki, K.; Kakinuma, R.; Nishiwaki, Y. Clinicopathological Characteristics of Surgically Resected Lung Cancer Associated with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Surg. Oncol. 2001, 76, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Cho, Y.J.; Yoon, H.I.; Lee, J.H.; Jheon, S.; Lee, C.T.; Park, J.S. Lung Cancer in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Clinical Characteristics and Impact on Survival. Respir. Med. 2014, 108, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, E.C.; Liebow, A.A. Relationship of Interstitial Pneumonia Honeycombing and Atypical Epithelial Proliferation to Cancer of the Lung. Cancer 1965, 18, 322–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraire, A.E.; Greenberg, S.D. Carcinoma and Diffuse Interstitial Fibrosis of Lung. Cancer 1973, 31, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, J.C.; Osterholzer, J.J.; Marazioti, A.; Stathopoulos, G.T. “Scar-Cinoma”: Viewing the Fibrotic Lung Mesenchymal Cell in the Context of Cancer Biology. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 1842–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Kawabata, Y.; Koyama, N.; Ikeya, T.; Hoshi, E.; Takayanagi, N.; Koyama, S. A Clinicopathological Study of Surgically Resected Lung Cancer in Patients with Usual Interstitial Pneumonia. Respir. Med. 2017, 129, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouvelekis, A.; Gomatou, G.; Bouros, E.; Trigidou, R.; Tzilas, V.; Bouros, D. Common Pathogenic Mechanisms Between Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer. Chest 2019, 156, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hironaka, M.; Fukayama, M. Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Carcinoma: A Comparative Study of Metaplastic Epithelia in Honeycombed Areas of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia with or without Lung Carcinoma. Pathol. Int. 1999, 49, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, M.; Li, L.; Chen, L. Involvement of the Warburg Effect in Non-Tumor Diseases Processes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 233, 2839–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, N.; Tan, Z.; Banerjee, S.; Cui, H.; Ge, J.; Liu, R.M.; Bernard, K.; Thannickal, V.J.; Liu, G. Glycolytic Reprogramming in Myofibroblast Differentiation and Lung Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 1462–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, R.T.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A. Fibroblasts in Fibrosis: Novel Roles and Mediators. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenaka, K.; Gemma, A.; Yoshimura, A.; Hosoya, Y.; Nara, M.; Hosomi, Y.; Okano, T.; Kunugi, S.; Koizumi, K.; Fukuda, Y.; et al. Reduced Transcription of the Smad4 Gene during Pulmonary Carcinogenesis in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2008, 2, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaki, Y.; Akuta, T.; Terasaki, M.; Sawa, T.; Mori, T.; Okamoto, T.; Ozaki, M.; Takeya, M.; Akaike, T. Guanine Nitration in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Its Implication for Carcinogenesis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korfei, M.; Skwarna, S.; Henneke, I.; MacKenzie, B.A.; Klymenko, O.; Saito, S.; Ruppert, C.; Von Der Beck, D.; Mahavadi, P.; Klepetko, W.; et al. Aberrant Expression and Activity of Histone Deacetylases in Sporadic Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Thorax 2015, 70, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlig, K.M.; Wagner, T.; Knauer, S.K.; Brandl, A.; Schneider, G.; Krämer, O.H.; Heinzel, T.; Stauber, R.H.; Melchior, F. Dynamically Regulated Sumoylation of HDAC2 Controls P53 Deacetylation and Restricts Apoptosis Following Genotoxic Stress. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 4, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, N.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Naccache, J.M.; Borie, R.; Urban, T.; Jouneau, S.; Marchand, E.; Ravel, A.C.; Kiakouama, L.; Etienne-Mastroianni, B.; et al. Lung Cancer in Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: A Series of 47 Western Patients. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, M.M.; Liu, Y.; Peng, B.; Hsu, H.Y.; Saqi, A.; Tsai, W.Y.; Leu, C.S.; Jambawalikar, S. Comparison of Lung Cancer Occurring in Fibrotic versus Non-Fibrotic Lung on Chest CT. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, A.G.; Tsao, M.S.; Beasley, M.B.; Borczuk, A.C.; Brambilla, E.; Cooper, W.A.; Dacic, S.; Jain, D.; Kerr, K.M.; Lantuejoul, S.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Advances Since 2015. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 362–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Yoh, K.; Goto, K.; Niho, S.; Umemura, S.; Ohmatsu, H.; Ohe, Y. Safety and Efficacy of Platinum Agents plus Etoposide for Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer with Interstitial Lung Disease. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, S.; Saeki, K.; Waseda, Y.; Murata, A.; Takato, H.; Ichikawa, Y.; Yasui, M.; Kimura, H.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Matsushita, T.; et al. Lung Cancer in Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: Clinical Features and Impact on Outcomes. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.; Jeong, B.H.; Chung, M.J.; Lee, K.S.; Kwon, O.J.; Chung, M.P. Risk Factors and Clinical Characteristics of Lung Cancer in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezka, H.; Igor, P.; Izidor, K. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in Patients with Early-Stage Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer after Surgical Resection. Radiol. Oncol. 2019, 53, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Nie, D.; Huang, X. Association between Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Risk of Different Pathological Types of Lung Cancer: A Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 7751–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, T.; Sakashita, H.; Suzuki, T.; Tateishi, T.; Miyazaki, Y. Real World Data of Combined Lung Cancer and Interstitial Lung Disease. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 4144–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Liu, M.; Yang, X.; Ren, Y.; Xie, B.; Geng, J.; Deng, M.; Dai, H.; Wang, C. Malignancies in Patients with Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Single Center Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.J.; Kim, H.H.; Hyun, D.G.; Ji, W.; Choi, C.M.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, H.C. Clinical Characteristics and Outcome of Lung Cancer in Patients with Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Disease. BMC Pulm. Med. 2024, 24, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, K.; Uruga, H.; Fujii, T.; Fujimori, S.; Kohno, T.; Kurosaki, A.; Kishi, K.; Abe, S. Characteristics of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Interstitial Pneumonia: Variation in Cancer Location, Histopathology, and Frequency of Postoperative Acute Exacerbations in Interstitial Pneumonia. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Vaccarella, S.; Morgan, E.; Li, M.; Etxeberria, J.; Chokunonga, E.; Manraj, S.S.; Kamate, B.; Omonisi, A.; Bray, F. Global Variations in Lung Cancer Incidence by Histological Subtype in 2020: A Population-Based Study. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 1206–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, S.H.L.; Huang, T.; Ho, J.M.W.; Lam, A.S.M.; Yau, S.T.Y.; Yuen, T.W.H.; Dong, G.H.; Tsoi, K.K.F.; Sung, J.J.Y. Rise and Fall of Lung Cancers in Relation to Tobacco Smoking and Air Pollution: A Global Trend Analysis from 1990 to 2012. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 269, 118835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaji, N.; Shimizu, J.; Sakai, K.; Ueda, Y.; Miyawaki, H.; Watanabe, N.; Uemura, T.; Hida, T.; Inoue, T.; Watanabe, N.; et al. Clinical Features of Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treated with Chemotherapy or Chemoradiotherapy. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2020, 14, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.J.; Lim, S.Y.; Park, J.S.; Yoon, H.I.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Jung, J.Y.; Kang, Y.A.; Park, M.S.; Kim, Y.S.; et al. Prognosis of Small Cell Lung Cancer with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Assessment According to GAP Stage. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 5437390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legendre, M.; Butt, A.; Borie, R.; Debray, M.P.; Bouvry, D.; Filhol-Blin, E.; Desroziers, T.; Nau, V.; Copin, B.; Dastot-Le Moal, F.; et al. Functional Assessment and Phenotypic Heterogeneity of SFTPA1 and SFTPA2 Mutations in Interstitial Lung Diseases and Lung Cancer. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2002806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.M.; Bittar, H.T.; Sullivan, D.I.; Silva, A.G.; Bahudhanapati, H.; Parikh, A.H.; Zhang, Y.; Gibson, K.; McDyer, J.F.; Kass, D.J.; et al. Rare Surfactant-Related Variants in Familial and Sporadic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Hum. Mutat. 2022, 43, 2091–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Chen, C.; Gandhi, C.K.; Wu, R.; Pardo, A.; Selman, M.; Floros, J. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNP) and SNP-SNP Interactions of the Surfactant Protein Genes Are Associated With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in a Mexican Study Group; Comparison With Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 842745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, N.; Giraud, V.; Picard, C.; Nunes, H.; Moal, F.D.L.; Copin, B.; Galeron, L.; De Ligniville, A.; Kuziner, N.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; et al. Germline SFTPA1 Mutation in Familial Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia and Lung Cancer. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudon, A.; Legendre, M.; Mageau, A.; Bermudez, J.; Bonniaud, P.; Bouvry, D.; Cadranel, J.; Cazes, A.; Crestani, B.; Dégot, T.; et al. High Risk of Lung Cancer in Surfactant-Related Gene Variant Carriers. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 63, 2301809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Pan, H.; Wu, Y.; Huang, J.; Liang, W.; et al. SFTPA1 Is a Potential Prognostic Biomarker Correlated with Immune Cell Infiltration and Response to Immunotherapy in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 71, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressen, A.; Abbas, A.R.; Cabanski, C.; Reeder, J.; Ramalingam, T.R.; Neighbors, M.; Bhangale, T.R.; Brauer, M.J.; Hunkapiller, J.; Reeder, J.; et al. Analysis of Protein-Altering Variants in Telomerase Genes and Their Association with MUC5B Common Variant Status in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Candidate Gene Sequencing Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borie, R.; Berteloot, L.; Kannengiesser, C.; Griese, M.; Cazes, A.; Crestani, B.; Hadchouel, A.; Debray, M.P. Rare Genetic Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Pictorial Essay. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2024, 33, 240101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippot, Q.; Kannengiesser, C.; Debray, M.P.; Gauvain, C.; Ba, I.; Vieri, M.; Gondouin, A.; Naccache, J.M.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Uzunhan, Y.; et al. Interstitial Lung Diseases Associated with Mutations of Poly(A)-Specific Ribonuclease: A Multicentre Retrospective Study. Respirology 2022, 27, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhou, Z.; Wei, S.; Liu, Z.; Pooley, K.A.; Dunning, A.M.; Svenson, U.; Roos, G.; Hosgood, H.D.; Shen, M.; et al. Shortened Telomere Length Is Associated with Increased Risk of Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S.; Nounu, A.; Zheng, J.; Okoli, G.N.; Bowden, J.; Wade, K.H.; Timpson, N.J.; Evans, D.M.; Willeit, P.; et al. Association between Telomere Length and Risk of Cancer and Non-Neoplastic Diseases a Mendelian Randomization Study. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 636–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomatou, G.; Masaoutis, C.; Vamvakaris, I.; Kotteas, E.; Bouros, E.; Tzilas, V.; Bouros, D. Differential Immunohistochemical Expression of HTERT in Lung Cancer Patients with and without Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Pulmonology 2024, 30, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Munakata, M.; Ohtsuka, Y.; Nisihara, H.; Nasuhara, Y.; Kamachi-Satoh, A.; Dosaka-Akita, H.; Homma, Y.; Kawakami, Y. Expression and Alteration of Ras and P53 Proteins in Patients with Lung Carcinoma Accompanied by Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cancer 2002, 95, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, H.; Ogura, T.; Yokose, T.; Nagai, K.; Nishiwaki, Y.; Esumi, H. P53 Gene Alteration in Atypical Epithelial Lesions and Carcinoma in Patients With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Hum. Pathol. 2001, 32, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyard, A.; Danel, C.; Théou-Anton, N.; Debray, M.P.; Gibault, L.; Mordant, P.; Castier, Y.; Crestani, B.; Zalcman, G.; Blons, H.; et al. Morphologic and Molecular Study of Lung Cancers Associated with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Other Pulmonary Fibroses. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsubo, K.; Iwama, E.; Ijichi, K.; Kubo, N.; Yoneshima, Y.; Inoue, H.; Tanaka, K.; Osoegawa, A.; Tagawa, T.; Nakanishi, Y.; et al. Paired Genetic Analysis by Next-Generation Sequencing of Lung Cancer and Associated Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 2482–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, C.E.; Saldivar, J.C.; Hosseini, S.A.; Huebner, K. The FHIT Gene Product: Tumor Suppressor and Genome “Caretaker”. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 4577–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uematsu, K.; Yoshimura, A.; Gemma, A.; Hosoya, Y.; Matsuda, K.; Seike, M.; Kurimoto, F.; Takenaka, K.; Kudoh, S.; Koizumi, K.; et al. Aberrations in the Fragile Histidine Triad (FHIT) Gene in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 8527–8533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.A.; Kim, D.; Chun, S.; Bae, S.; Song, J.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Koo, H.J.; Song, J.W.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, J.C.; et al. Genomic Profiles of Lung Cancer Associated with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2018, 244, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demopoulos, K.; Arvanitis, D.A.; Vassilakis, D.A.; Siafakas, N.M.; Spandidos, D.A. MYCL1, FHIT, SPARC, P16INK4 and TP53 Genes Associated to Lung Cancer in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2002, 6, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masai, K.; Tsuta, K.; Motoi, N.; Shiraishi, K.; Furuta, K.; Suzuki, S.; Asakura, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Sakurai, H.; Watanabe, S.I.; et al. Clinicopathological, Immunohistochemical, and Genetic Features of Primary Lung Adenocarcinoma Occurring in the Setting of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia Pattern. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 2141–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usui, K.; Ushijima, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Tanai, C.; Noda, H.; Abe, N.; Horiuchi, H.; Ishihara, T. The Frequency of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation of Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer According to the Underlying Pulmonary Diseases. Pulm. Med. 2011, 2011, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, D.; Tomii, K.; Otoshi, T.; Kawamura, T.; Tamai, K.; Takeshita, J.; Tanaka, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Monden, K.; Nagata, K.; et al. Preexisting Interstitial Lung Disease Is Inversely Correlated to Tumor Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation in Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2013, 80, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, A.; Tamura, K.; Satoh, H.; Tanaka, T.; Tsunoda, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Takoi, H.; Lin, S.-Y.; Yatagai, Y.; Hashizume, T.; et al. Prevalence of Underlying Lung Disease in Smokers with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutant Lung Cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 2005–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, Y.; Okudela, K.; Matsumura, M.; Omori, T.; Baba, T.; Sekine, A.; Woo, T.; Umeda, S.; Takemura, T.; Mitsui, H.; et al. The Pathological Features of Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia-Associated Pulmonary Adenocarcinomas. Histopathology 2017, 70, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronborg-white, S.; Madsen, L.B.; Bendstrup, E.; Poletti, V. Pd-l1 Expression in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karampitsakos, T.; Galaris, A.; Chrysikos, S.; Papaioannou, O.; Vamvakaris, I.; Barbayianni, I.; Kanellopoulou, P.; Grammenoudi, S.; Anagnostopoulos, N.; Stratakos, G.; et al. Expression of PD-1/PD-L1 Axis in Mediastinal Lymph Nodes and Lung Tissue of Human and Experimental Lung Fibrosis Indicates a Potential Therapeutic Target for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, D.; Sato, Y.; Morimoto, T.; Uehara, K.; Ito, M.; Otsuka, K.; Nagata, K.; Sakanoue, I.; Hamakawa, H.; Nakagawa, A.; et al. Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 Expression in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients With Interstitial Lung Disease: A Matched Case-Control Study. Clin. Lung Cancer 2018, 19, e667–e673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celada, L.J.; Kropski, J.A.; Herazo-Maya, J.D.; Luo, W.; Creecy, A.; Abad, A.T.; Chioma, O.S.; Lee, G.; Hassell, N.E.; Shaginurova, G.I.; et al. PD-1 up-Regulation on CD4 + T Cells Promotes Pulmonary Fibrosis through STAT3-Mediated IL-17A and TGF-Β1 Production. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaar8356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Jeune, I.; Gribbin, J.; West, J.; Smith, C.; Cullinan, P.; Hubbard, R. The Incidence of Cancer in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Sarcoidosis in the UK. Respir. Med. 2007, 101, 2534–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; Cottin, V.; du Bois, R.M.; Selman, M.; Kimura, T.; Bailes, Z.; Schlenker-Herceg, R.; Stowasser, S.; Brown, K.K. Nintedanib in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Combined Evidence from the TOMORROW and INPULSIS® Trials. Respir. Med. 2016, 113, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuter, M.; Ehlers-Tenenbaum, S.; Schaaf, M.; Oltmanns, U.; Palmowski, K.; Hoffmann, H.; Schnabel, P.A.; Heußel, C.-P.; Puderbach, M.; Herth, F.J.F.; et al. Treatment and Outcome of Lung Cancer in Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. Off. J. WASOG 2015, 31, 266–274. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, H.J.; Do, K.H.; Lee, J.B.; Alblushi, S.; Lee, S.M. Lung Cancer in Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakopanagiotakis, F.; Krauss, E.; Michailidou, I.; Drosos, V.; Anevlavis, S.; Günther, A.; Steiropoulos, P. Lung Cancer and Interstitial Lung Diseases. Cancers 2024, 16, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMahon, H.; Naidich, D.P.; Goo, J.M.; Lee, K.S.; Leung, A.N.C.; Mayo, J.R.; Mehta, A.C.; Ohno, Y.; Powell, C.A.; Prokop, M.; et al. Guidelines for Management of Incidental Pulmonary Nodules Detected on CT Images: From the Fleischner Society 2017. Radiology 2017, 284, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelli, A.; Kim, A.W.; Berger, K.I.; Addrizzo-Harris, D.J. Physiologic Evaluation of the Patient with Lung Cancer Being Considered for Resectional Surgery: Diagnosis and Management of Lung Cancer, 3rd Ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2013, 143, e166S–e190S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenmotsu, H.; Naito, T.; Kimura, M.; Ono, A.; Shukuya, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Tsuya, A.; Kaira, K.; Murakami, H.; Takahashi, T.; et al. Therisk of Cytotoxic Chemotherapy-Related Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease with Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, Y.; Inui, N.; Kato, T.; Baba, T.; Karayama, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Ogura, T.; Suda, T. Low Forced Vital Capacity Predicts Cytotoxic Chemotherapy-Associated Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2016, 96, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiyo, M.; Sekine, Y.; Iwata, T.; Tatsumi, K.; Yasufuku, K.; Iyoda, A.; Otsuji, M.; Yoshida, S.; Shibuya, K.; Iizasa, T.; et al. Impact of Interstitial Lung Disease on Surgical Morbidity and Mortality for Lung Cancer: Analyses of Short-Term and Long-Term Outcomes. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2003, 126, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, A.; Higami, T.; Ohori, S.; Koyanagi, T.; Nakashima, S.; Mawatari, T. Is Lung Cancer Resection Indicated in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis? J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2008, 136, 1357–1363.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Kawai, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Ikeya, T.; Murai, K.; Kawabata, Y.; Hoshi, E. Survival after Surgery for Pathologic Stage IA Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Associated with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 92, 1812–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minegishi, Y.; Takenaka, K.; Mizutani, H.; Sudoh, J.; Noro, R.; Okano, T.; Azuma, A.; Yoshimura, A.; Ando, M.; Tsuboi, E.; et al. Exacerbation of Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias Associated with Lung Cancer Therapy. Intern. Med. 2009, 48, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Goldstraw, P.; Yamada, K.; Nicholson, A.G.; Wells, A.U.; Hansell, D.M.; DuBois, R.M.; Ladas, G. Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: Risk and Benefit Analysis of Pulmonary Resection. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2003, 125, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Teramukai, S.; Kondo, H.; Watanabe, A.; Ebina, M.; Kishi, K.; Fujii, Y.; Mitsudomi, T.; Yoshimura, M.; Maniwa, T.; et al. Impact and Predictors of Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Diseases after Pulmonary Resection for Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 1604–1611.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, K.; Hirata, T.; Hirai, K.; Mikami, I.; Okada, D.; Yamagishi, S.; Kawashima, T.; Nakajima, Y.; Shimizu, K. Surgical Treatment of Lung Cancer Combined with Interstitial Pneumonia: The Effect of Surgical Approach on Postoperative Acute Exacerbation. Ann. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2004, 10, 340–346. [Google Scholar]
- Hiraki, T.; Gobara, H.; Mimura, H.; Matsui, Y.; Toyooka, S.; Kanazawa, S. Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation of Clinical Stage i Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 142, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Watanabe, A.; Kondo, H.; Kanzaki, M.; Okubo, K.; Yokoi, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Marutsuka, T.; Shinohara, H.; Teramukai, S.; et al. Long-Term Results and Predictors of Survival after Surgical Resection of Patients with Lung Cancer and Interstitial Lung Diseases. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 149, 64–70.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, T.; Okazaki, T.; Matsukura, T.; Hanawa, T.; Yamashita, N.; Nishimura, K.; Kuwabara, M.; Matsubara, Y. Operation for Lung Cancer in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Surgical Contraindication? Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2003, 76, 1674–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Kondo, H.; Watanabe, A.; Nakajima, J.; Niwa, H.; Horio, H.; Okami, J.; Okumura, N.; Sugio, K.; Teramukai, S.; et al. A Simple Risk Scoring System for Predicting Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Pneumonia after Pulmonary Resection in Lung Cancer Patients. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 63, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintani, Y.; Ohta, M.; Iwasaki, T.; Ikeda, N.; Tomita, E.; Kawahara, K.; Ohno, Y. Predictive Factors for Postoperative Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Pneumonia Combined with Lung Cancer. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010, 58, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, K.; Tanai, C.; Tanaka, Y.; Noda, H.; Ishihara, T. The Prevalence of Pulmonary Fibrosis Combined with Emphysema in Patients with Lung Cancer. Respirology 2011, 16, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, H.; Sugino, K.; Hata, Y.; Makino, T.; Koezuka, S.; Isobe, K.; Tochigi, N.; Shibuya, K.; Homma, S.; Iyoda, A. Clinical Features and Outcomes of Patients with Lung Cancer as Well as Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 5, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimae, T.; Suzuki, K.; Tsuboi, M.; Nagai, K.; Ikeda, N.; Mitsudomi, T.; Saji, H.; Okumura, S.; Okumura, M.; Yoshimura, K.; et al. Surgical Outcomes of Lung Cancer in Patients with Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, N.; Taniguchi, H.; Kondoh, Y.; Kimura, T.; Kataoka, K.; Nishiyama, O.; Kondo, M.; Hasegawa, Y. Efficacy of Chemotherapy for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respiration 2013, 85, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazaki, K.; Miura, Y.; Taguchi, M.; Nishima, S.; Hida, N.; Yoshida, K.; Hyodo, K.; Kanazawa, J.; Nemoto, K.; Takaku, T.; et al. The Efficacy of Pirfenidone in the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Single-Institution Retrospective Study in Japan. Chest 2016, 150, 483A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, T.; Yoshida, S.; Nagato, K.; Nakajima, T.; Suzuki, H.; Tagawa, T.; Mizobuchi, T.; Ota, S.; Nakatani, Y.; Yoshino, I. Experience with Perioperative Pirfenidone for Lung Cancer Surgery in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Surg. Today 2015, 45, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, T.; Yoshino, I.; Yoshida, S.; Ikeda, N.; Tsuboi, M.; Asato, Y.; Katakami, N.; Sakamoto, K.; Yamashita, Y.; Okami, J.; et al. A Phase II Trial Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Perioperative Pirfenidone for Prevention of Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in Lung Cancer Patients Undergoing Pulmonary Resection: West Japan Oncology Group 6711 L (PEOPLE Study). Respir. Res. 2016, 17, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.-Y.; Kim, H.; Bae, Y.; Song, J.W. Pirfenidone and Risk of Lung Cancer Development in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Eur. Respir. J. 2025, 65, 2401484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; du Bois, R.M.; Raghu, G.; Azuma, A.; Brown, K.K.; Costabel, U.; Cottin, V.; Flaherty, K.R.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Nintedanib in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Kaiser, R.; Mellemgaard, A.; Douillard, J.Y.; Orlov, S.; Krzakowski, M.; von Pawel, J.; Gottfried, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Liao, M.; et al. Docetaxel plus Nintedanib versus Docetaxel plus Placebo in Patients with Previously Treated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (LUME-Lung 1): A Phase 3, Double-Blind, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronte, G.; Passiglia, F.; Galvano, A.; Barraco, N.; Listì, A.; Castiglia, M.; Rizzo, S.; Fiorentino, E.; Bazan, V.; Russo, A. Nintedanib in NSCLC: Evidence to Date and Place in Therapy. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2016, 8, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novello, S.; Kaiser, R.; Mellemgaard, A.; Douillard, J.Y.; Orlov, S.; Krzakowski, M.; Von Pawel, J.; Gottfried, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Liao, M.; et al. Analysis of Patient-Reported Outcomes from the LUME-Lung 1 Trial: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase III Study of Second-Line Nintedanib in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S. Nintedanib: A Review of Its Use as Second-Line Treatment in Adults with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer of Adenocarcinoma Histology. Target. Oncol. 2015, 10, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabholkar, S.; Gao, B.; Chuong, B. Nintedanib—A Case of Treating Concurrent Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Respirol. Case Rep. 2022, 10, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kai, Y.; Matsuda, M.; Fukuoka, A.; Hontsu, S.; Yamauchi, M.; Yoshikawa, M.; Muro, S. Remarkable Response of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to Nintedanib Treatment in a Patient with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 1457–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratori, T.; Tanaka, H.; Tabe, C.; Tsuchiya, J.; Ishioka, Y.; Itoga, M.; Taima, K.; Takanashi, S.; Tasaka, S. Effect of Nintedanib on Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in a Patient with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Case Report and Literature Review. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 1720–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, L.; Shah, S.; Pai-Scherf, L.; Larkins, E.; Vallejo, J.; Li, X.; Rodriguez, L.; Mishra-Kalyani, P.; Goldberg, K.B.; Kluetz, P.G.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Atezolizumab and Durvalumab in Combination with Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncologist 2021, 26, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, S.; Kato, T.; Kenmotsu, H.; Ogura, T.; Sato, Y.; Hino, A.; Harada, T.; Kubota, K.; Tokito, T.; Okamoto, I.; et al. Atezolizumab for Pretreated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia: Final Analysis of Phase II AMBITIOUS Study. Oncologist 2022, 27, 720-e702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Fan, Y.; Nie, L.; Wang, G.; Sun, K.; Cheng, Y. Clinical Outcomes of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Preexisting Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Chest 2022, 161, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakawa, H.; Oba, T.; Ohta, H.; Tsukahara, Y.; Kida, G.; Tsumiyama, E.; Nishizawa, T.; Kawabe, R.; Sato, S.; Akasaka, K.; et al. Nintedanib Allows Retreatment with Atezolizumab of Combined Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer/Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis after Atezolizumab-Induced Pneumonitis: A Case Report. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Shimizu, J.; Shigematsu, F.; Watanabe, N.; Hasegawa, T.; Horio, Y.; Inaba, Y.; Fujiwara, Y. Atezolizumab and Nintedanib in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Interstitial Lung Disease. J. Thorac. Dis. 2024, 16, 3371–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, S.; Ichiyasu, H.; Ikeda, T.; Inaba, M.; Kashiwabara, K.; Sadamatsu, T.; Sato, N.; Akaike, K.; Okabayashi, H.; Saruwatari, K.; et al. Protective Effect of Bevacizumab on Chemotherapy-Related Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Advanced Non-Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gong, X.; Hu, Y.; Yi, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Miao, L.; Zhou, Y. Anti-Angiogenic Drugs Inhibit Interstitial Lung Disease Progression in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 873709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaaban, S.; McCormick, J.; Gleason, D.; McFarlin, J.M. Palliative Care for the Interstitial Lung Disease Patient a Must and Not Just a Need. Am. J. Hosp. Palliat. Med. 2022, 39, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramhill, C.; Langan, D.; Mulryan, H.; Eustace-Cook, J.; Russell, A.M.; Brady, A.M. A Scoping Review of the Unmet Needs of Patients Diagnosed with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF). PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0297832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, V.A.; Emanuel, L. Navigating and Communicating about Serious Illness and End of Life. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korfage, I.J.; Carreras, G.; Arnfeldt Christensen, C.M.; Billekens, P.; Bramley, L.; Briggs, L.; Bulli, F.; Caswell, G.; Červ, B.; van Delden, J.J.M.; et al. Advance Care Planning in Patients with Advanced Cancer: A 6-Country, Cluster-Randomised Clinical Trial. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernacki, R.; Paladino, J.; Neville, B.A.; Hutchings, M.; Kavanagh, J.; Geerse, O.P.; Lakin, J.; Sanders, J.J.; Miller, K.; Lipsitz, S.; et al. Effect of the Serious Illness Care Program in Outpatient Oncology: A Cluster Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2019, 179, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakitas, M.; Lyons, K.D.; Hegel, M.T.; Bakitas, M. Effects of a Palliative Care Intervention. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2009, 302, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temel, J.S.; Greer, J.A.; Admane, S.; Gallagher, E.R.; Jackson, V.A.; Lynch, T.J.; Lennes, I.T.; Dahlin, C.M.; Pirl, W.F. Longitudinal Perceptions of Prognosis and Goals of Therapy in Patients With Metastatic Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results of a Randomized Study of Early Palliative Care. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2319–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temel, J.S.; Greer, J.A.; Muzikansky, A.; Gallagher, E.R.; Admane, S.; Jackson, V.A.; Dahlin, C.M.; Blinderman, C.D.; Jacobsen, J.; Pirl, W.F.; et al. Early Palliative Care for Patients with Metastatic Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, C.; Swami, N.; Krzyzanowska, M.; Hannon, B.; Leighl, N.; Oza, A.; Moore, M.; Rydall, A.; Rodin, G.; Tannock, I.; et al. Early Palliative Care for Patients with Advanced Cancer: A Cluster-Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2014, 383, 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuter, M.; Bendstrup, E.; Russell, A.M.; Bajwah, S.; Lindell, K.; Adir, Y.; Brown, C.E.; Calligaro, G.; Cassidy, N.; Corte, T.J.; et al. Palliative Care in Interstitial Lung Disease: Living Well. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajwah, S.; Koffman, J.; Higginson, I.J.; Ross, J.R.; Wells, A.U.; Birring, S.S.; Riley, J. ‘I Wish I Knew More …’ the End-of-Life Planning and Information Needs for End-Stage Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Disease: Views of Patients, Carers and Health Professionals. BMJ Support. Palliat. Care 2013, 3, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, E.; Kavanagh, E.; Visram, S.; Bourke, A.M.; Forrest, I.; Exley, C. Which Factors Influence the Quality of End-of-Life Care in Interstitial Lung Disease? A Systematic Review with Narrative Synthesis. Palliat. Med. 2022, 36, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Mann, J.; Goh, N.; Smallwood, N. Investigation Burden for Patients with Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Disease at the End of Life. Intern. Med. J. 2020, 50, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, M.; Lu-Song, J.; Younus, S.; Nabipoor, M.; Richman-Eisenstat, J.; Ohinmaa, A.; Bakal, J.A. Health Care Costs at the End of Life for Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Evaluation of a Pilot Multidisciplinary Collaborative Interstitial Lung Disease Clinic. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2020, 17, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu-Song, J.; Bakal, J.A.; Younus, S.; Moran-Mendoza, O.; Harle, I.; Morales, M.; Rippon, N.; Barratt, S.L.; Adamali, H.; Kalluri, M. The Impact of Integrated Palliative Care on Survival in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Retrospective Multicenter Comparison. Am. J. Hosp. Palliat. Med. 2024, 41, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, G.T.; Neo, H.Y.; Abisheganaden, J.; Hum, A.Y.M. Impact of Palliative Care in End-of-Life of Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Disease Patients. Am. J. Hosp. Palliat. Med. 2022, 39, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crombeen, A.M.; Lilly, E.J. Management of Dyspnea in Palliative Care. Curr. Oncol. 2020, 27, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Spencer, L.G.; Banya, W.; Westoby, J.; Tudor, V.A.; Rivera-Ortega, P.; Chaudhuri, N.; Jakupovic, I.; Patel, B.; Thillai, M.; et al. Morphine for Treatment of Cough in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (PACIFY COUGH): A Prospective, Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Two-Way Crossover Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2024, 12, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, E.J.; Edwards, Z.; Boland, J.W.; Maddocks, M.; Fettes, L.; Malia, C.; Mulvey, M.R.; Bennett, M.I. Practice Review: Evidence-Based and Effective Management of Pain in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Palliat. Med. 2020, 34, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyauchi, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Sato, K.; Hozumi, H.; Karayama, M.; Furuhashi, K.; Fujisawa, T.; Enomoto, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Inui, N.; et al. Impact of End-of-Life Respiratory Modalities on Quality of Dying and Death and Symptom Relief in Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease: A Multicenter Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Mutational Prevalence in ILD-LC | Mutation Prevalence in ILD-LC (%) | Mutation Prevalence in LC (%) | Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR | Low prevalence | 0.5–8% | 24.3–47% | [17,85,86,87,88,89,93] |
| ALK | Low prevalence | 0–1% | 4% | [79,89] |
| ROS1 | Low prevalence | 0% | 1–2% | [79] |
| KRAS | Low prevalence | 8% | 25% | [89] |
| MET | High prevalence | 8–20% | 2–7% | [79] |
| BRAF | High prevalence, especially non-V600E mutations | 17% | 2–4% | [83] |
| PD-L1 | Rarely described, the expression of PD-L1 in ILD-LC seems to be low (median expression PD-L1 expression 1%, 37.5–85% not expressing PD-L1) | [14,69,79,92] | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castelli, G.; Cocconcelli, E.; Grimaudo, G.; Di Leo, I.; Bellani, S.; Fiorentù, G.; Giulianelli, G.; Bernardinello, N.; Balestro, E.; Spagnolo, P. Interstitial Lung Diseases and Lung Cancer: A Review on Similarities, Common Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Approach. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050213
Castelli G, Cocconcelli E, Grimaudo G, Di Leo I, Bellani S, Fiorentù G, Giulianelli G, Bernardinello N, Balestro E, Spagnolo P. Interstitial Lung Diseases and Lung Cancer: A Review on Similarities, Common Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Approach. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(5):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050213
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastelli, Gioele, Elisabetta Cocconcelli, Giuliana Grimaudo, Irene Di Leo, Serena Bellani, Giordano Fiorentù, Giacomo Giulianelli, Nicol Bernardinello, Elisabetta Balestro, and Paolo Spagnolo. 2025. "Interstitial Lung Diseases and Lung Cancer: A Review on Similarities, Common Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Approach" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 5: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050213
APA StyleCastelli, G., Cocconcelli, E., Grimaudo, G., Di Leo, I., Bellani, S., Fiorentù, G., Giulianelli, G., Bernardinello, N., Balestro, E., & Spagnolo, P. (2025). Interstitial Lung Diseases and Lung Cancer: A Review on Similarities, Common Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Approach. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(5), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050213






