High Ocular Disease Burden and Increased Referral Needs in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Step Toward Personalized Care
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Retinal Photography and Eye Diseases
2.3. Assessment of Relevant Clinical Data
2.4. Outcome Definitions
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
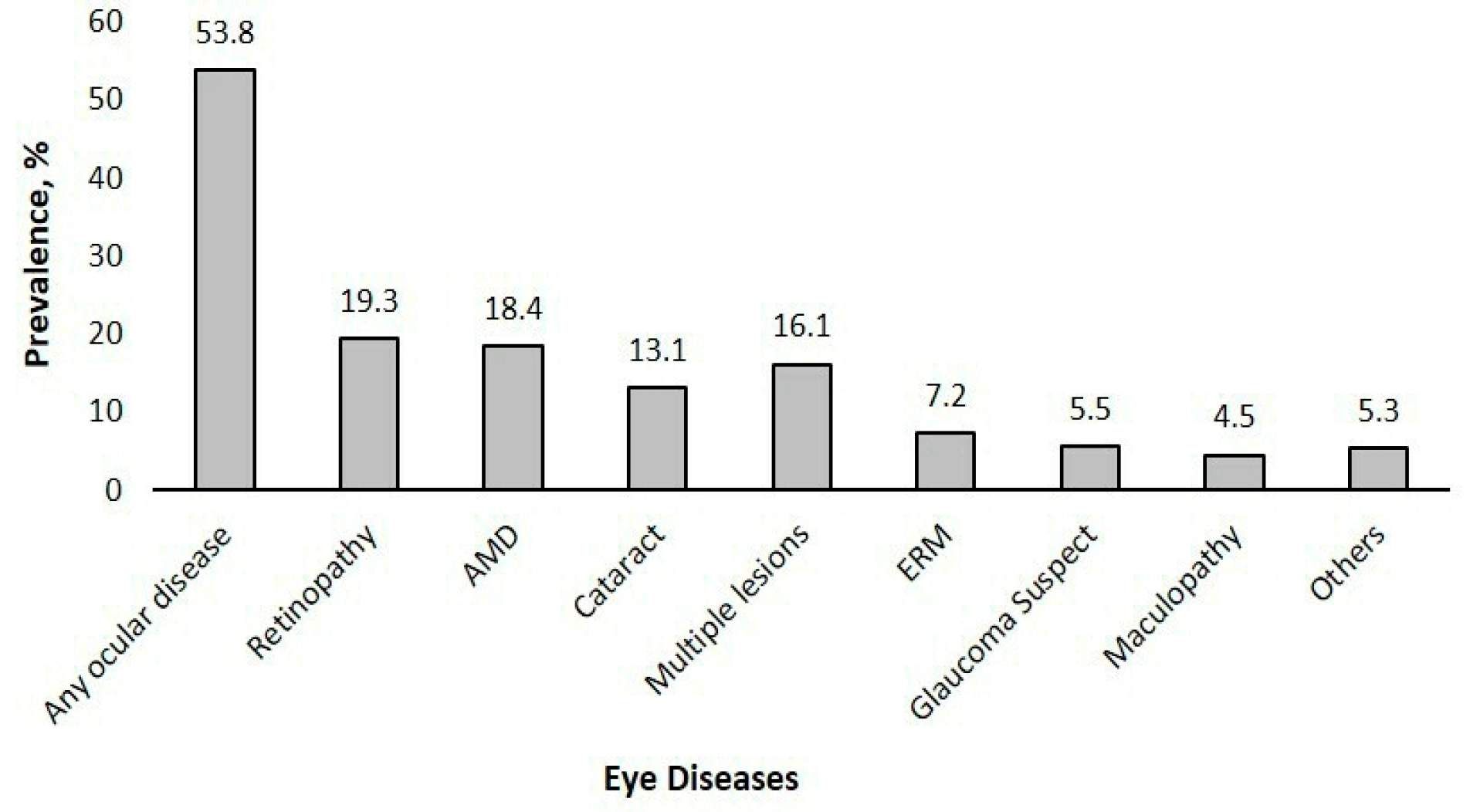
Prevalence of Eye Diseases
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMD | Age-related macular degeneration |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CRAO | Central retinal artery occlusion |
| CRVO | Central retinal vein occlusion |
| DR | Diabetic retinopathy |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| ERM | Epiretinal membrane |
| HbA1c | Glycated hemoglobin |
| IRB | Institutional review board |
| IRED | Retinal imaging in renal disease |
| NPDR | Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy |
| NUH | National University Hospital |
| PDR | Proliferative diabetic retinopathy |
| SERI | Singapore Eye Research Institute |
| UACR | Urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio |
| VI | Vision impairment |
References
- GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carney, E.F. The impact of chronic kidney disease on global health. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovesdy, C.P. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease: An update 2022. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2022, 12, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Kidney Foundation. Available online: https://nkfs.org/about-us/key-statistics/ (accessed on 23 February 2025).
- World Health Organisation. Blindness and Vision Impairment. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/blindness-and-visual-impairment (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Jiang, B.; Wu, T.; Liu, W.; Liu, G.; Lu, P. Changing Trends in the Global Burden of Cataract Over the Past 30 Years: Retrospective Data Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. JMIR Public Health Surveill 2023, 9, e47349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, J.; Guan, P.; Zhang, G.; Yu, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, L. Epidemiology, health policy and public health implications of visual impairment and age-related eye diseases in mainland China. Front. Public. Health 2022, 10, 966006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.E.; Wong, T.Y. Diabetic retinopathy: Looking forward to 2030. Front Endocrinol 2022, 13, 1077669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lamoureux, E.; Zheng, Y.; Ang, M.; Wong, T.Y.; Luo, N. Health burden associated with visual impairment in Singapore: The Singapore epidemiology of eye disease study. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 1837–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tye, S.C.; Denig, P.; Heerspink, H.J.L. Precision medicine approaches for diabetic kidney disease: Opportunities and challenges. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2021, 36, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gembillo, G.; Siligato, R.; Santoro, D. Personalized Medicine in Kidney Disease. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, J.L.; Gupta, A.; Gandhi, P. Ocular manifestations in renal diseases. Indian. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 71, 2938–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.W.; Wong, T.Y.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Sabanayagam, C. Kidney and eye diseases: Common risk factors, etiological mechanisms, and pathways. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 1290–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajracharya, L.; Shah, D.N.; Raut, K.B.; Koirala, S. Ocular evaluation in patients with chronic renal failure--a hospital based study. Nepal. Med. Coll. J. 2008, 10, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Grunwald, J.E.; Alexander, J.; Maguire, M.; Whittock, R.; Parker, C.; McWilliams, K.; Lo, J.C.; Townsend, R.; Gadegbeku, C.A.; Lash, J.P.; et al. Prevalence of ocular fundus pathology in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunwald, J.E.; Alexander, J.; Ying, G.S.; Maguire, M.; Daniel, E.; Whittock-Martin, R.; Parker, C.; McWilliams, K.; Lo, J.C.; Go, A.; et al. Retinopathy and chronic kidney disease in the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) study. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2012, 130, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.W.; Lamoureux, E.L.; Cheng, C.Y.; Cheung, G.C.; Tai, E.S.; Wong, T.Y.; Sabanayagam, C. Increased Burden of Vision Impairment and Eye Diseases in Persons with Chronic Kidney Disease—A Population-Based Study. eBioMedicine 2016, 5, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, B.W.; Koh, Y.Y.; Toh, Q.C.; Li, J.; Sinha, A.K.; Shuter, B.; Sethi, S.; Lee, E.J. Performance of the CKD-EPI creatinine-cystatin C glomerular filtration rate estimation equations in a multiethnic Asian population. Singap. Med. J. 2014, 55, 656–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singapore Ministry of Health (MOH). Diabetic Retinal Photography (DRP) Screening Technical Reference Guide Singapore; Ministry of Health: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Carollo, C.; Evola, S.; Sorce, A.; Cirafici, E.; Bennici, M.; Mulè, G.; Geraci, G. Mission and One-Year Experience of a Kidney-Heart Outpatient Service: A Patient-Centered Management Model. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.; Mohankumar, A.; Khatri, M.; Dabir, S.; Mohan, S.; Rajan, M. Prevalence and Distribution of Retinal Pathologies in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease in a Tertiary Eye Clinic in South India. TNOA J. Ophthalmic Sci. Res. 2024, 62, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronov, M.; Allon, R.; Stave, D.; Belkin, M.; Margalit, E.; Fabian, I.D.; Rosenzweig, B. Retinal Vascular Signs as Screening and Prognostic Factors for Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Current Evidence. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choe, H.R.; Park, S.H.; Do Han, K.; Kim, D.K.; Joo, K.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, E.K.; Park, U.C.; Yu, H.G.; et al. Impact of kidney transplantation on the risk of retinal vein occlusion in end-stage renal disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Nam, K.H.; Kim, D.W.; Kang, E.C.; Koh, H.J. Risk of Retinal Vein Occlusion in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease: A 12-Year, Retrospective, Nationwide Cohort Study in South Korea. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, L.; Forcier, P. Prevalence of asymptomatic ocular conditions in subjects with refractive-based symptoms. J. Optom. 2014, 7, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deva, R.; Alias, M.A.; Colville, D.; Tow, F.K.N.-F.H.; Ooi, Q.L.; Chew, S.; Mohamad, N.; Hutchinson, A.; Koukouras, I.; Power, D.A.; et al. Vision-Threatening Retinal Abnormalities in Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 3 to 5. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 1866–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.D.; Rosner, M. Ocular abnormalities associated with advanced kidney disease and hemodialysis. Semin. Dial. 2005, 18, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, G.; Mitchell, P.; Wong, T.Y.; Iyengar, S.K.; Wang, J.J. CKD increases the risk of age-related macular degeneration. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressler, S.B.; Beaulieu, W.T.; Glassman, A.R.; Gross, J.G.; Jampol, L.M.; Melia, M.; Peters, M.A.; Rauser, M.E. Factors Associated with Worsening Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy in Eyes Treated with Panretinal Photocoagulation or Ranibizumab. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, P.H. The English National Screening Programme for diabetic retinopathy 2003–2016. Acta Diabetol 2017, 54, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.; Park, J.; Jang, H.R.; Jeon, J.; Han, K.; Kim, B.; Yoon, J.M.; Lim, D.H.; Shin, D.W. Increased end-stage renal disease risk in age-related macular degeneration: A nationwide cohort study with 10-year follow-up. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ro, J.-S.; Moon, J.Y.; Park, T.K.; Lee, S.H. Association between chronic kidney disease and open-angle glaucoma in South Korea: A 12-year nationwide retrospective cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.K.; Han, J.C.; Choi, J.A.; Chae, J.E.; Kim, R.B. Association Between Chronic Renal Disease and the Risk of Glaucoma Development: A 12-year Nationwide Cohort Study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Singh, P.; Khurana, S.; Ganguly, N.K.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Rana, D.S.; Taneja, V.; Bhargava, V. Implications of oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease: A review on current concepts and therapies. Kidney Res. Clin. Pr. 2021, 40, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonfiglio, F.; Pfeiffer, N.; Gericke, A. Glaucoma and the ocular renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: Update on molecular signalling and treatment perspectives. Cell. Signal. 2024, 122, 111343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, J.; Bains, Y.; Guha, S.; Kahn, A.; Hall, D.; Bose, N.; Gugliucci, A.; Kapahi, P. The Role of Advanced Glycation End Products in Aging and Metabolic Diseases: Bridging Association and Causality. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Q.; Dai, H.; Jiang, S.; Yu, L. Advanced glycation end products in diabetic retinopathy and phytochemical therapy. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1037186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busch, M.; Franke, S.; Rüster, C.; Wolf, G. Advanced glycation end-products and the kidney. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 40, 742–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.K.; Gallo, L.A.; Borg, D.J.; Forbes, J.M. Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs) and Chronic Kidney Disease: Does the Modern Diet AGE the Kidney? Nutrients 2022, 14, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, J.B.; Wang, Y.X.; Wei, W.B.; Xu, J.; You, Q.S.; Xu, L. Chronic Kidney Disease and Eye Diseases: The Beijing Eye Study. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 1566–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.; Knudtson, M.D.; Lee, K.E.; Klein, B.E. Serum cystatin C level, kidney disease markers, and incidence of age-related macular degeneration: The Beaver Dam Eye Study. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2009, 127, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Liao, H.; Wang, W.; Scheetz, J.; Zhang, J.; He, M. Visual Impairment and Major Eye Diseases in Chronic Kidney Disease: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2005–2008. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 213, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusinovici, S.; Sabanayagam, C.; Teo, B.W.; Tan, G.S.W.; Wong, T.Y. Vision Impairment in CKD Patients: Epidemiology, Mechanisms, Differential Diagnoses, and Prevention. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 73, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Referral | Number of Cases | Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Urgent (immediate) | 6 | CRAO, macular hole, PDR, retinal detachment, retinal emboli |
| Semi-urgent (1–2 weeks) | 30 | Central Serous Retinopathy, collaterals with impending occlusion/disc collaterals, CRVO, late AMD, PDR with maculopathy, pseudo-hole due to ERM |
| Fast-track (1–3 months) | 151 | Cataracts, glaucoma suspect, late AMD, maculopathy, mild NPDR with maculopathy, moderate NPDR, ungradable, treated stable DR |
| Routine (Annual) | 341 | Early AMD, mild NPDR, myopic degeneration, presence of asteroid hyalosis |
| Characteristics | Overall (n = 528) | No Ocular Disease (n = 244) | Ocular Disease (n = 284) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 63.74 ± 10.43 | 61.2 ± 9.80 | 65.9 ± 10.5 | <0.001 * |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 338 (64.0%) | 150 (61.5%) | 188 (66.2%) | 0.3 |
| Female | 190 (36.0%) | 94 (38.5%) | 96 (33.8%) | |
| Ethnicity | ||||
| Chinese | 336 (63.6%) | 153 (62.7%) | 183 (64.4%) | 0.9 |
| Malay | 117 (22.2%) | 54 (22.1%) | 63 (22.2%) | |
| Indian | 31 (5.9%) | 14 (5.7%) | 17 (6.0%) | |
| Others | 44 (8.3%) | 23 (9.4%) | 21 (7.4%) | |
| Diabetes status | ||||
| No | 220 (41.7%) | 127 (52.0%) | 93 (32.7%) | <0.001 * |
| Yes | 308 (58.3%) | 117 (48.0%) | 191 (67.3%) | |
| Hypertension status | ||||
| No | 48 (9.1%) | 27 (11.1%) | 21 (7.4%) | 0.2 |
| Yes | 480 (90.9%) | 217 (88.9%) | 263 (92.6%) | |
| HbA1c, % | 26.99 ± 5.14 | 6.6 ± 1.3 | 7.1 ± 1.7 | <0.001 * |
| BMI, Kg/m2 | 6.88 ± 1.56 | 27.3 ± 5.3 | 26.7 ± 5.0 | 0.2 |
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg | 143.31 ± 23.71 | 140.5 ± 22.9 | 146.0 ± 24.3 | 0.02 * |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mmHg | 74.14 ± 11.21 | 75.2 ± 11.3 | 73.1 ± 11.0 | 0.07 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 26.34 ± 15.79 | 28.1 ± 16.6 | 24.8 ± 15.0 | 0.02 * |
| Any Ocular Disease | AMD | DR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Factors | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p |
| Age, per year increase | 1.05 (1.02–1.07) | <0.001 * | 1.05 (1.02–1.07) | <0.001 * | 0.95 (0.92–0.98) | <0.001 * |
| Sex, female | 0.83 (0.53–1.28) | 0.4 | 0.82 (0.54–1.26) | 0.4 | 1.28 (0.67–2.46) | 0.5 |
| Diabetes, yes | 2.52 (1.61–3.95) | <0.001 * | 2.53 (1.62–3.94) | <0.001 * | - | - |
| Hypertension, yes | 1.03 (0.5–2.15) | 0.9 | 1.02 (0.49–2.11) | 1 | 0.32 (0.08–1.31) | 0.1 |
| BMI, per unit increase | 0.96 (0.92–1.01) | 0.1 | 0.96 (0.92–1) | 0.1 | 0.94 (0.88–1) | 0.1 |
| HbA1c % | - | - | - | - | 1.24 (1.02–1.51) | <0.001 * |
| Author, Year | Study Design | Population | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deva, 2011 [26] | Cross-sectional | Patients with CKD stages 3 to 5 | Advanced CKD patients had a higher prevalence of vision-threatening retinal abnormalities, including moderate to severe microvascular retinopathy (39%), DR (28%), and macular degeneration (7%). Renal failure was identified as an independent risk factor for these retinal conditions, with 7.3% of advanced CKD patients having undiagnosed sight-threatening abnormalities requiring urgent ophthalmologic care. |
| Evans and Rosner, 2005 [27] | Narrative review | Patients on chronic hemodialysis, United States | Chronic hemodialysis patients face a range of ocular complications, including glaucoma, band keratopathy, cataracts, retinal detachment, macular leakage, retinal hemorrhage, optic neuropathy, and drug toxicity. Dialysis-induced changes may worsen ocular diseases. |
| Grunwald et al., 2012 [16] | Cross-sectional | Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort, United States | Greater severity of retinopathy and presence of hypertensive retinal vascular signs were significantly associated with lower eGFR. |
| Liew et al., 2008 [28] | Longitudinal | Blue Mountains cohort, Australia | Five-year incidence of early AMD was significantly higher in moderate CKD (17.5%) vs. no/mild CKD (3.9%). Moderate CKD was associated with increased risk of early AMD (OR: 3.2; 95% CI: 1.8–5.7, p < 0.0001); each SD decrease in eGFR doubled the AMD risk. |
| Mohan et al., 2024 [21] | Retrospective | CKD patients in a tertiary care centre, India | Retinal pathologies are highly prevalent among patients with CKD, with DR being the most frequently observed condition, followed by hypertensive retinopathy |
| Wong et al., 2016 [17] | Population-based cohort | Singapore Epidemiology of Eye Diseases | CKD patients had a higher prevalence of VI and ocular disease; CKD is associated with increased odds of VI, cataracts, retinopathy, and DR. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liem, Y.; Thyagarajan, P.; Chee, M.L.; Lim, C.C.; Teo, B.W.; Sabanayagam, C. High Ocular Disease Burden and Increased Referral Needs in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Step Toward Personalized Care. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050204
Liem Y, Thyagarajan P, Chee ML, Lim CC, Teo BW, Sabanayagam C. High Ocular Disease Burden and Increased Referral Needs in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Step Toward Personalized Care. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(5):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050204
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiem, Yulia, Pavitra Thyagarajan, Miao Li Chee, Cynthia Ciwei Lim, Boon Wee Teo, and Charumathi Sabanayagam. 2025. "High Ocular Disease Burden and Increased Referral Needs in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Step Toward Personalized Care" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 5: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050204
APA StyleLiem, Y., Thyagarajan, P., Chee, M. L., Lim, C. C., Teo, B. W., & Sabanayagam, C. (2025). High Ocular Disease Burden and Increased Referral Needs in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Step Toward Personalized Care. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(5), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050204





