Identification and Validation of Hub Genes in the Stenosis of Arteriovenous Fistula
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.1. Microarray Data
2.2. Identification of the DEGs
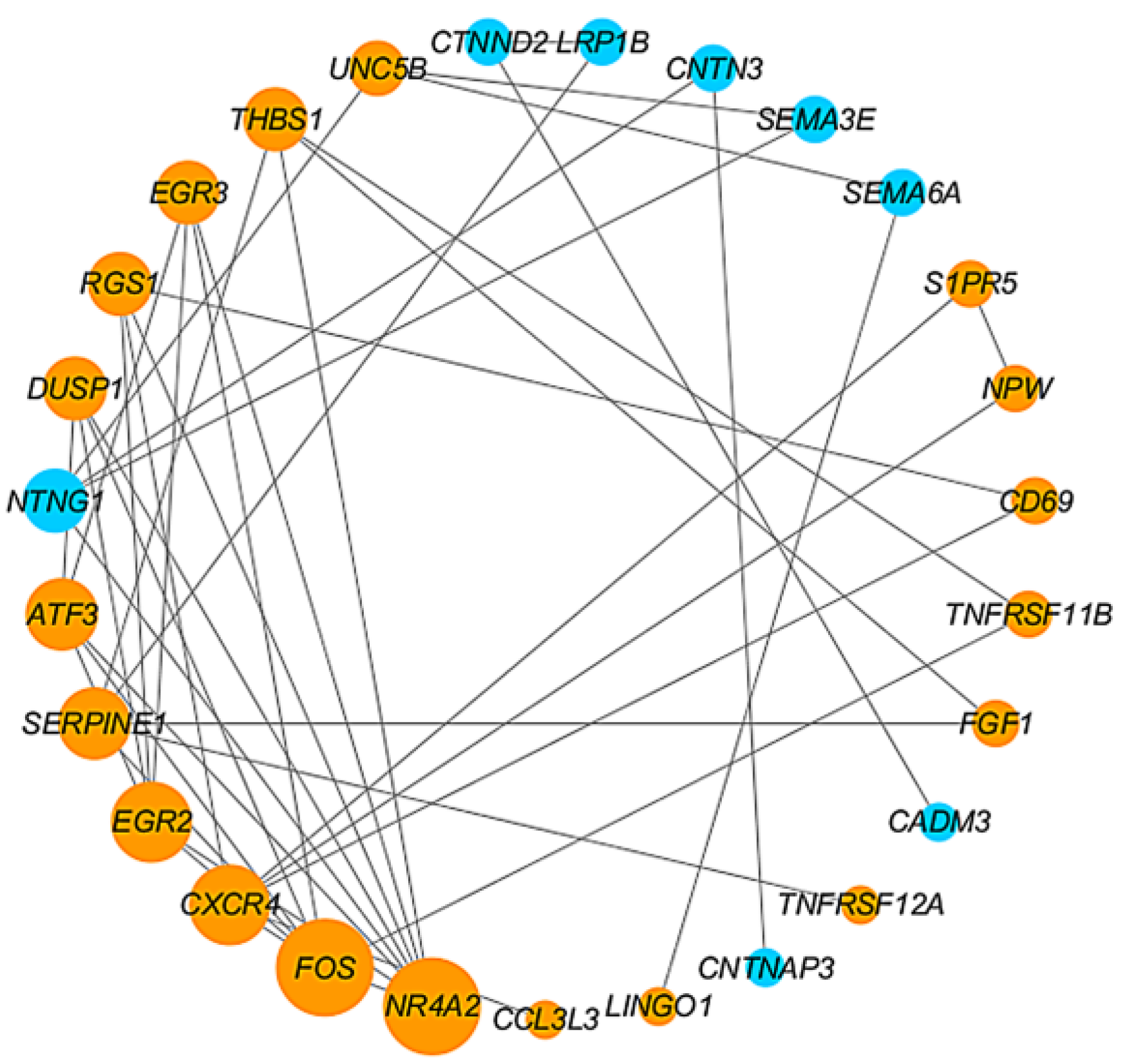
2.3. Construction of the PPI Network and Identification of Hub Genes
3. Validation of Bioinformatic Results
3.1. Patients and Sample Collection
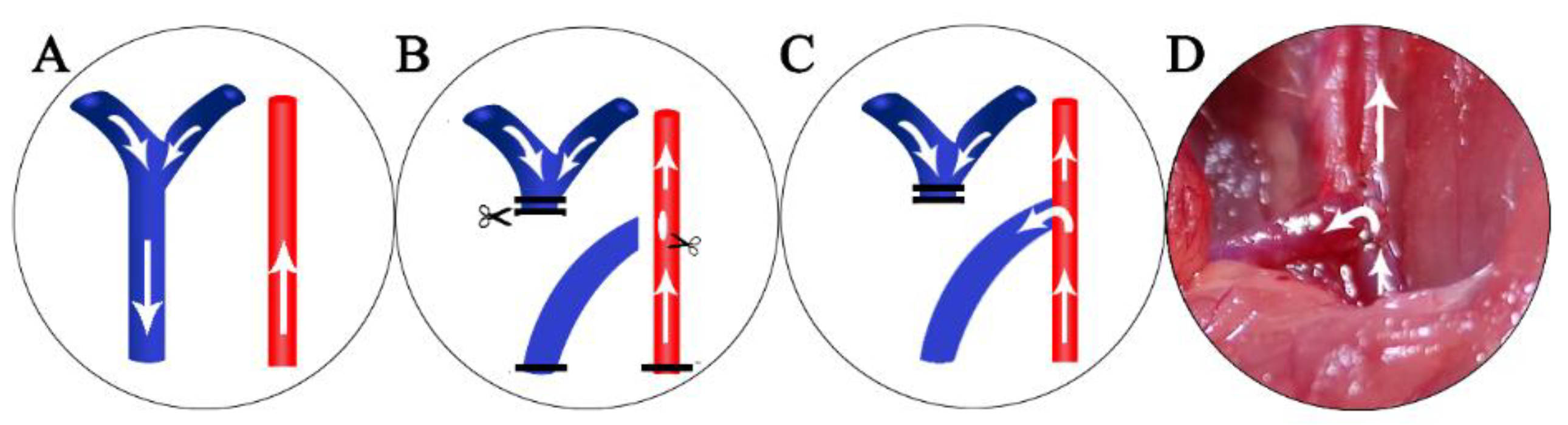
3.2. Animal Model Creation and Sample collection
3.3. RT-PCR
3.4. Western Blot
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Confirmation of the GEO Datasets
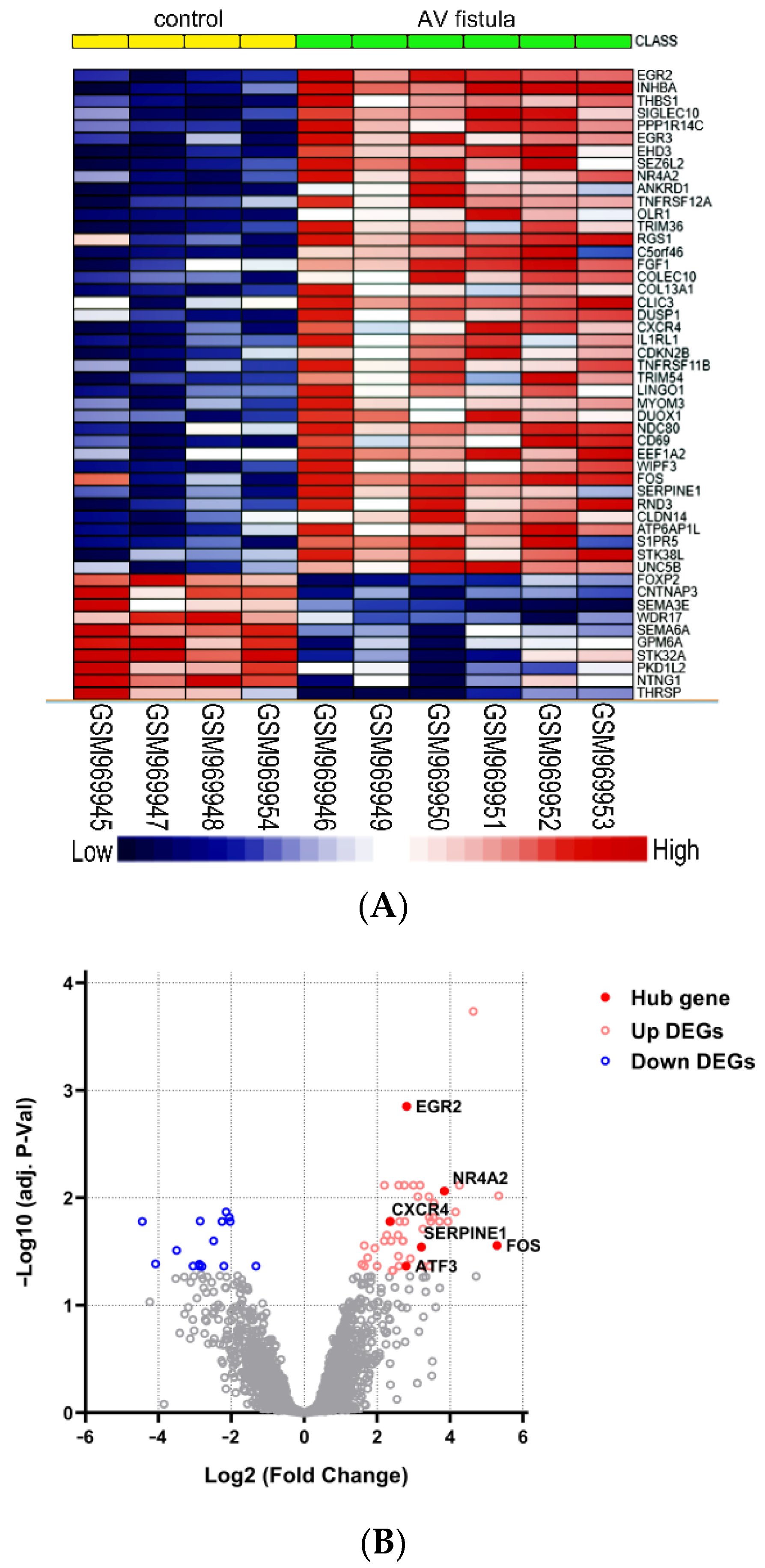
4.2. Identification of DEGs
4.3. Construction of PPI Network and Identification of Hub Genes
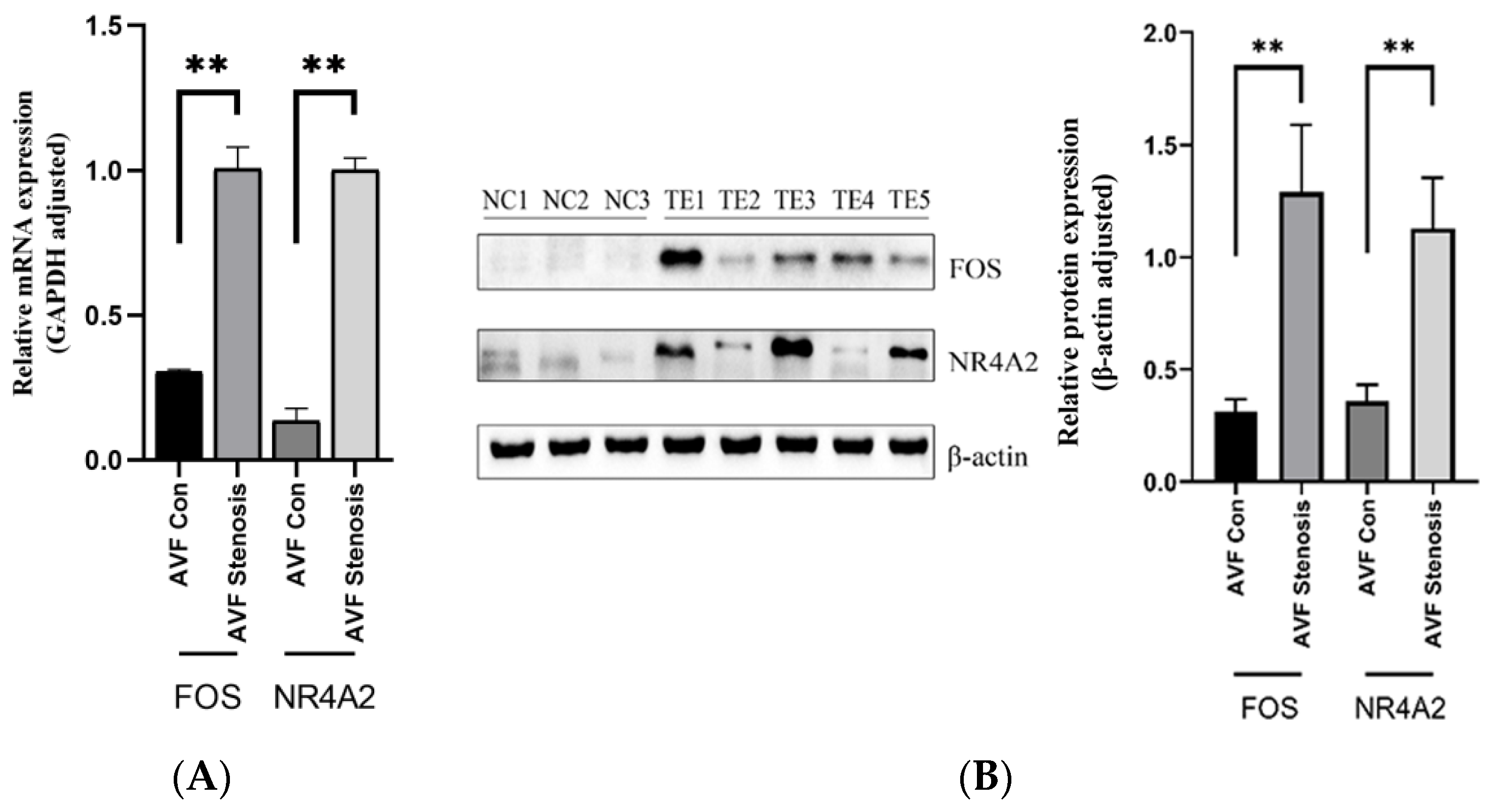
4.4. Characteristics of the Patients and the Expression Levels of FOS and NR4A2
4.5. Expression Level of the Target Genes Increased with the Increase of Stenosis Rate
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
7. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Cui, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Luo, T. Factors associated with dysfunction of autogenous arteriovenous fistula in patients with maintenance hemodialysis: A retrospective study. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 4047–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zeng, H.; Huang, F.; Fu, Q.; Luo, M.; Wu, Q.; Yang, T. Effect of radial artery calcification on survival of arteriovenous fistula and the patients in end stage renal disease patients. China Med. Abstr. (Intern. Med.) 2019, 36, 52. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- National Kidney Foundation. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Hemodialysis Adequacy: 2015 update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2015, 66, 884–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zhang, X. Renal Replacement Therapy; Shanghai Science and Technology Education Press: Shanghai, China, 2005; pp. 152–154. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Han, K.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Luo, T. Identification and validation of ADME genes as prognosis and therapy markers for hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20210583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Guan, T.; Lai, Y.; Zhan, J.; Shen, Y. Genetic predisposition and bioinformatics analysis of ATP-sensitive potassium channels polymorphisms with the risks of elevated apolipoprotein B serum levels and its related arteriosclerosis cardiovascular disease. Aging 2021, 13, 8177–8203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, J.A.; Spacek, D.V.; Snyder, M.P. High-throughput sequencing technologies. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, K.; Feng, W.; Boxiang, Z.; Maofeng, G.; Jianbin, Z.; Zhaoxuan, L.; Yangyi, Z.; Liang, C.; Haobo, S.; WenSheng, L.; et al. Identification of Pathways and Key Genes in Venous Remodeling after Arteriovenous Fistula by Bioinformatics Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 565240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.; Domrachev, M.; Lash, A.E. Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoot, M.E.; Ono, K.; Ruscheinski, J.; Wang, P.-L.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and network visualization. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. NKF-DOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Vascular Access. National Kidney Foundation-Dialysis Outcomes Quality Initiative. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1997, 30 (Suppl. 3), S150–S191. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. NKF-K/DOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Vascular Access: Update 2000. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2001, 37 (Suppl. 1), S137–S181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vascular Access Work Group. Clinical practice guidelines for vascular access. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2006, 48 (Suppl. 1), S248–S273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, G.J.; Rhee, C.M.; Obi, Y.; Chang, T.I.; Soohoo, M.; Kim, T.W.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Streja, E.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Vascular access placement and mortality in elderly incident hemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, M.; Cassel, K.; Boghosian, M.; Watson, S.; Funaki, B.; Coe, F. A cohort study showing correspondence of low wall shear stress and cephalic arch stenosis in brachiocephalic arteriovenous fistula access. J. Vasc. Access 2020, 22, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, M.; Boghosian, M.; Cassel, K.; Watson, S.; Funaki, B.; Doshi, T.; Akherat, S.M.J.M.; Hines, J.; Coe, F. Increased Inlet Blood Flow Velocity Predicts Low Wall Shear Stress in the Cephalic Arch of Patients with Brachiocephalic Fistula Access. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, P.; Karin, M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1072, 129–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Shi, J.; Cai, X.; Huang, S.; Li, G.; Xu, Y. Fuxinfang improves hypoxia-induced injury of human aortic endothelial cells by regulating c-Fos-NR4A1-p38 pathway. J. South Med. Univ. 2021, 41, 200–209. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Li, J.; Pi, J.; Chu, Q.; Wei, W.; Du, Z.; Qing, L.; Zhao, X.; Wu, W. Geniposide alleviates atherosclerosis by regulating macrophage polarization via the FOS/MAPK signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 110015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muslin, A.J. MAPK signalling in cardiovascular health and disease: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Clin. Sci. 2008, 115, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Zhao, W.; Xiong, C.; Guo, L.; Guo, J.; Qiu, Y.; Hu, C.A.A.; Ye, C.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; et al. Baicalin modulates apoptosis via RAGE, MAPK, and AP-1 in vascular endothelial cells during Haemophilus parasuis invasion. Innate Immun. 2019, 25, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M. Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades as regulators of stress responses. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 851, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widmann, C.; Gibson, S.; Jarpe, M.B.; Johnson, G.L. Mitogen-activated protein kinase: Conservation of a three-kinase module from yeast to human. Physiol. Rev. 1999, 79, 143–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Du, J.R.; Yu, Y.; Bai, B.; Zheng, X.Y. Tanshinone IIA inhibits smooth muscle proliferation and intimal hyperplasia in the rat carotid balloon-injured model through inhibition of MAPK signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 129, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| NC (n = 3) | Test (n = 5) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Y), Mean ± SD | 56.9 (11.7) | 58.1 (12.8) | 0.865 |
| Gender (Female, %) | 0 (0%) | 1 (20%) | 0.408 |
| Hypertension (Yes, %) | 1 (33.3%) | 3 (60%) | 0.465 |
| Diabetes mellitus (Yes, %) | 2 (66.7%) | 4 (80%) | 0.673 |
| Smoking (Yes, %) | 3 (100%) | 3 (60%) | 0.206 |
| Primer Name | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| Hsa-FOS-forward | GCGAGCTGTTCCCGTCAA |
| Hsa-FOS-reverse | CGTGGAAACCTGACGCAGAT |
| Hsa-NR4A2-forward | AGTCTGATCAGTGCCCTCGT |
| Hsa-NR4A2-reverse | TCGCCTGGAACCTGGAAT |
| Hsa-GAPDH-forward | GGTGAAGGTCGGAGTCAACG |
| Hsa-GAPDH-reverse | CAAAGTTGTCATGGATGHACC |
| Rno-FOS-forward | CCGGGGATAGCCTCTCTTACT |
| Rno-FOS-reverse | CCAGGTCCGTGCAGAAGTC |
| Rno-NR4A2-forward | GTTCAGGCGCAGTATGGGTC |
| Rno-NR4A2-reverse | CTCCCGAAGAGTGGTAACTGT |
| Rno-GAPDH-forward | GATGCTGGTGCTGAGTATGRCG |
| Rno-GAPDH-reverse | GTGGTGCAGGATGCATTGCTCTGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cui, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, L.; Bian, C.; Luo, T. Identification and Validation of Hub Genes in the Stenosis of Arteriovenous Fistula. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020207
Li Y, Chen Y, Cui W, Wang J, Chen X, Zhang C, Zhu L, Bian C, Luo T. Identification and Validation of Hub Genes in the Stenosis of Arteriovenous Fistula. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(2):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020207
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yu, Yue Chen, Wenhao Cui, Jukun Wang, Xin Chen, Chao Zhang, Linzhong Zhu, Chunjing Bian, and Tao Luo. 2023. "Identification and Validation of Hub Genes in the Stenosis of Arteriovenous Fistula" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 2: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020207
APA StyleLi, Y., Chen, Y., Cui, W., Wang, J., Chen, X., Zhang, C., Zhu, L., Bian, C., & Luo, T. (2023). Identification and Validation of Hub Genes in the Stenosis of Arteriovenous Fistula. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(2), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020207






