New Insights into the Role of miR-29a in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Implications in Mechanisms and Theragnostics
Abstract
1. Introduction
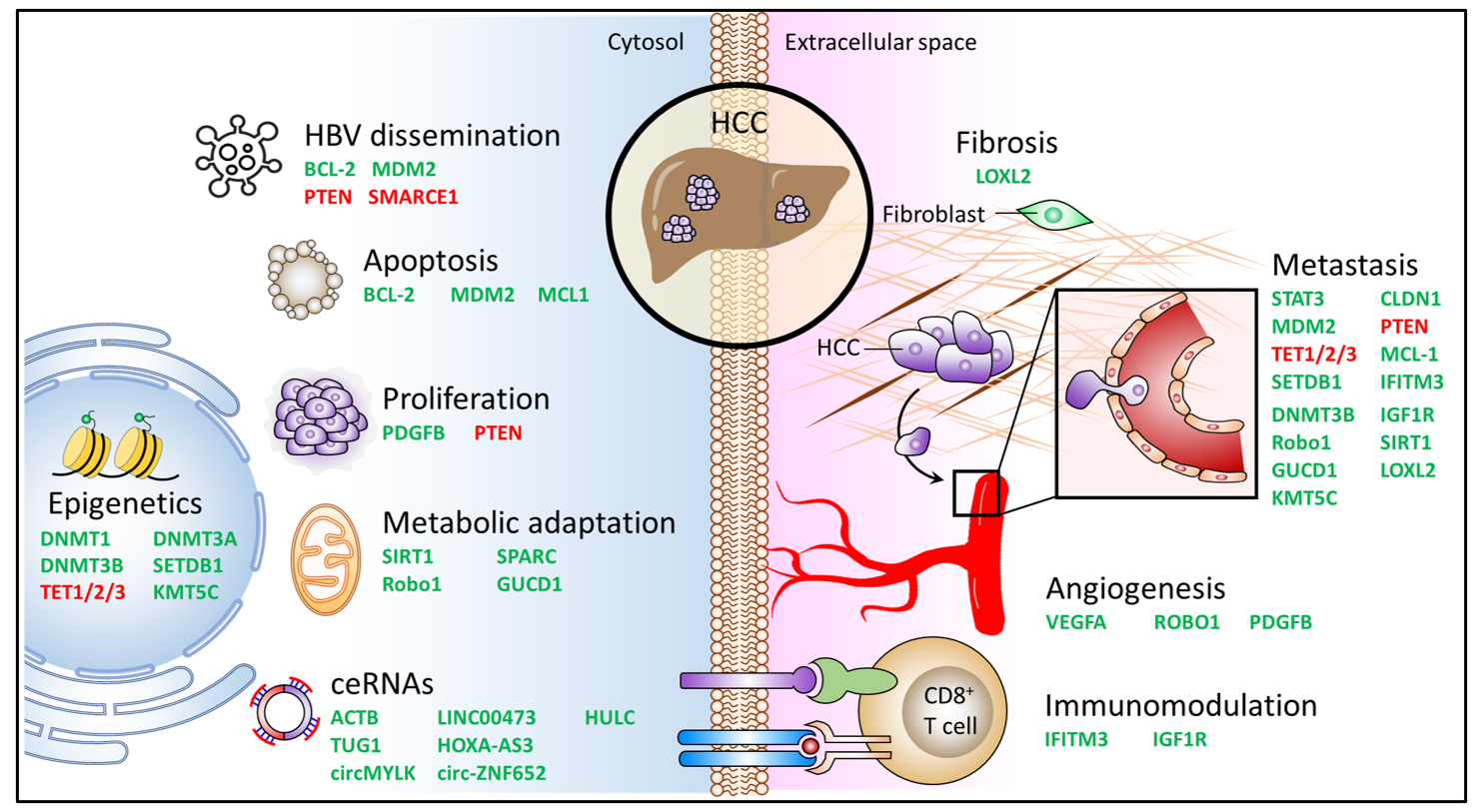
2. miR-29a in Carcinogenesis
3. miR-29a as an Epigenetic Regulator
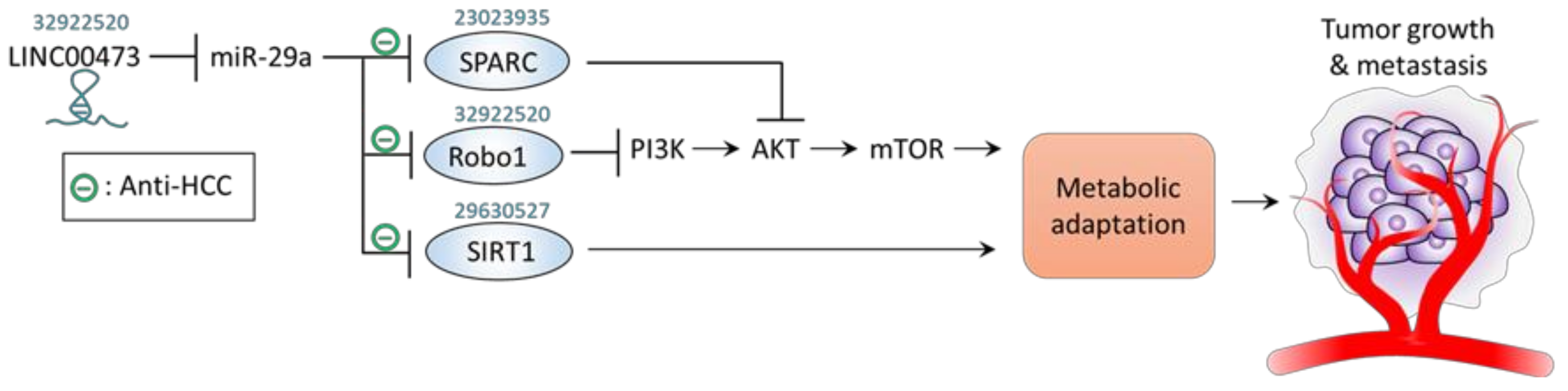
4. miR-29a Acts to Counteract Metabolic Adaptation
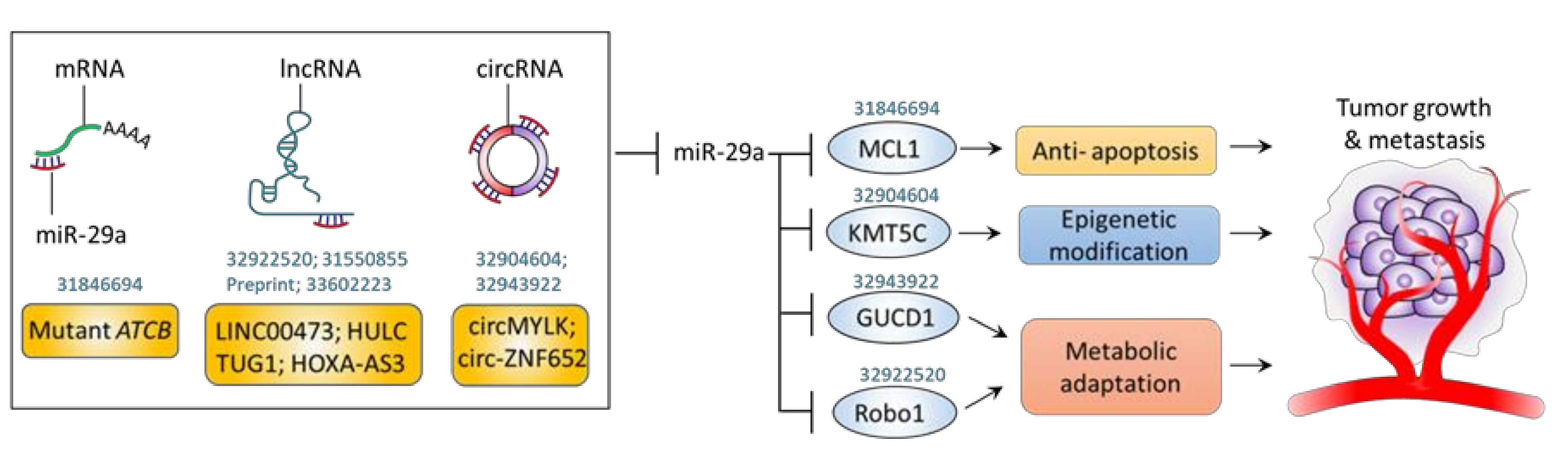
5. Molecular Sponges Targeting miR-29a: ceRNAs
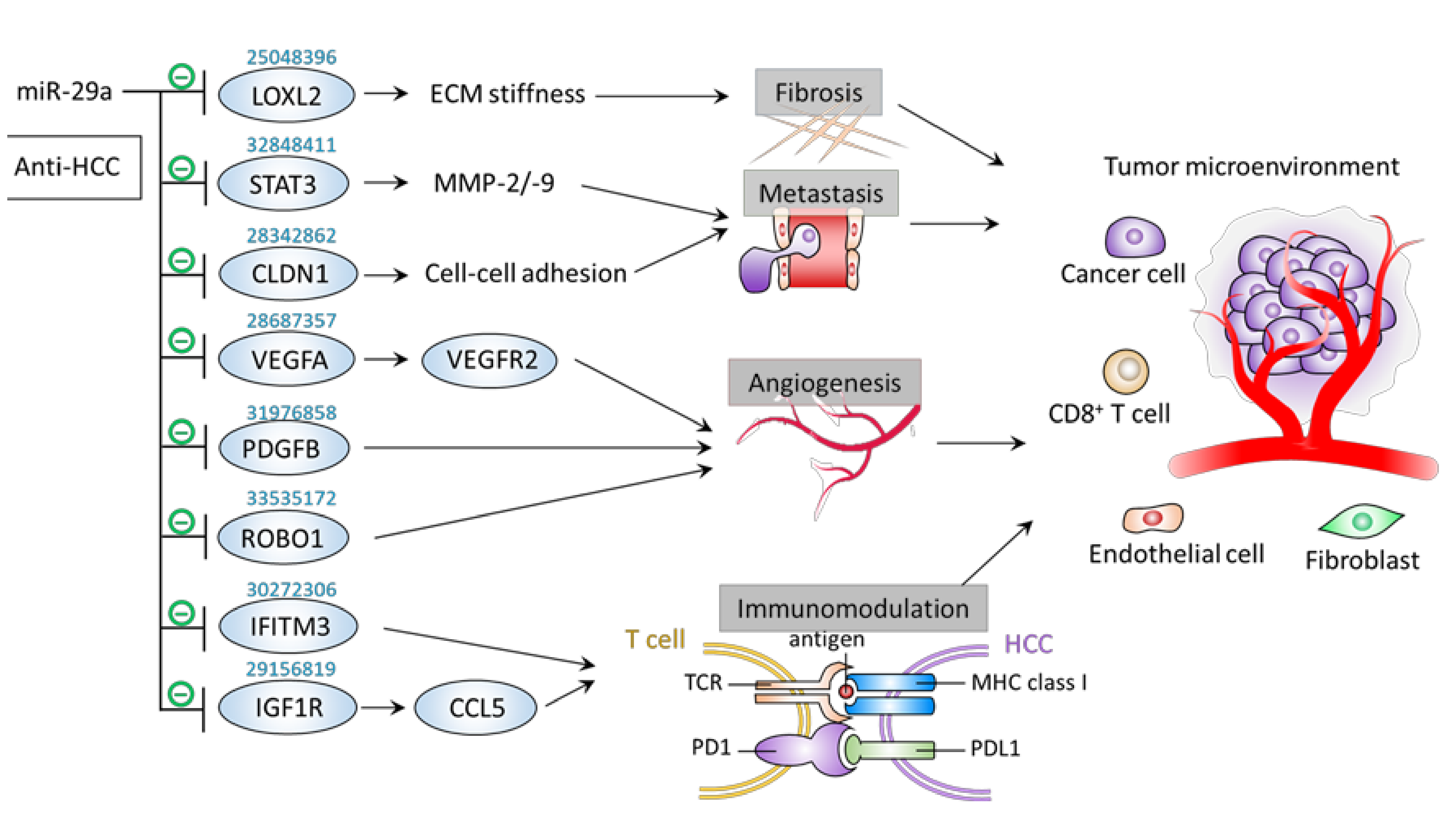
6. Inhibitory Effect of miR-29a on Tumor Microenvironment Components
6.1. Metastasis
6.2. Fibrosis
6.3. Angiogenesis
6.4. Immunomodulation
7. miR-29a as a Diagnostic/Prognostic Indicator
8. Therapeutic Approaches Targeting miR-29a for the Treatment of HCC
9. Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aly, A.; Ronnebaum, S.; Patel, D.; Doleh, Y.; Benavente, F. Epidemiologic, humanistic and economic burden of hepatocellular carcinoma in the USA: A systematic literature review. Hepatic Oncol. 2020, 7, HEP27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maluccio, M.; Covey, A. Recent progress in understanding, diagnosing, and treating hepatocellular carcinoma. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2012, 62, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimbach, J.K.; Kulik, L.M.; Finn, R.S.; Sirlin, C.B.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Zhu, A.X.; Murad, M.H.; Marrero, J.A. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 358–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Kim, Y.; Spolverato, G.; Gani, F.; Pawlik, T.M. Racial disparities in treatment and survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. HepatoBiliary Surg. Nutr. 2016, 5, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Li, R.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, L. Conditional survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Results from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results registry. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 12, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracken, C.P.; Scott, H.S.; Goodall, G.J. A network-biology perspective of microRNA function and dysfunction in cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carthew, R.W.; Sontheimer, E.J. Origins and Mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Ishizuka, A.; Siomi, H.; Siomi, M.C. Processing of Pre-microRNAs by the Dicer-1–Loquacious Complex in Drosophila Cells. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lian, S.L.; Moser, J.J.; Fritzler, M.J.; Fritzler, M.J.; Satoh, M.; Chan, E.K.L. Identification of GW182 and its novel isoform TNGW1 as translational repressors in Ago2-mediated silencing. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 4134–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodall, G.J.; Wickramasinghe, V.O. RNA in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.-W.; Wentzel, E.A.; Mendell, J.T. A Hexanucleotide Element Directs MicroRNA Nuclear Import. Science 2007, 315, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zou, J.; Wang, G.-K.; Zhang, J.-T.; Huang, S.; Qin, Y.-W.; Jing, Q. Uracils at nucleotide position 9–11 are required for the rapid turnover of miR-29 family. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 4387–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.-H.; Yang, J.-H. starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein–RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D92–D97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, S.Y.; Chao, Y.X.; Dheen, S.T.; Tan, E.-K.; Tay, S.S.-W. Role of MicroRNAs in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Song, G.; Yin, Z.; Fu, Z.; Ye, Z. MiR-29a and Messenger RNA Expression of Bone Turnover Markers in Canonical Wnt Pathway in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis. Clin. Lab. 2017, 63, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Jäkel, L.; Bruinsma, I.B.; Claassen, J.A.; Kuiperij, H.B.; Verbeek, M.M. MicroRNA-29a Is a Candidate Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease in Cell-Free Cerebrospinal Fluid. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 2894–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-Q.; Cai, A.-P.; Chen, J.-Y.; Huang, C.; Li, J.; Feng, Y.-Q. The Relationship of Plasma miR-29a and Oxidized Low Density Lipoprotein with Atherosclerosis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 40, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Qiu, C. Underexpression of CACNA1C Caused by Overexpression of microRNA-29a Underlies the Pathogenesis of Atrial Fibrillation. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 2175–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Suzuki, K.; Fujii, R.; Kawado, M.; Hashimoto, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Iso, H.; Fujino, Y.; Wakai, K.; Tamakoshi, A. Circulating miR-21, miR-29a, and miR-126 are associated with premature death risk due to cancer and cardiovascular disease: The JACC Study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afum-Adjei, A.; Ueberberg, B.; Owusu-Dabo, E.; Frempong, M.; Jacobsen, M. Dynamics of T-cell IFN-gamma and miR-29a expression during active pulmonary tuberculosis. Int. Immunol. 2014, 26, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.A.; Stroud, R.E.; O’Quinn, E.C.; Black, L.E.; Barth, J.L.; Elefteriades, J.A.; Bavaria, J.E.; Gorman, J.H., 3rd; Gorman, R.C.; Spinale, F.G.; et al. Selective MicroRNA Suppression in Human Thoracic Aneurysms: Relationship of miR-29a to Aortic Size and Proteolytic Induction. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2011, 4, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, N.L.; Gilchrist, D.S.; Akbar, M.; Reilly, J.H.; Kerr, S.C.; Campbell, A.L.; Murrell, G.A.C.; Liew, F.Y.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; McInnes, I.B. MicroRNA29a regulates IL-33-mediated tissue remodelling in tendon disease. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-C.; Chang, P.-J.; Ho, C.; Huang, Y.-T.; Shih, Y.-H.; Wang, C.-J.; Lin, C.-L. Protective effects of miR-29a on diabetic glomerular dysfunction by modulation of DKK1/Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashita, Y.; Jinnin, M.; Makino, T.; Kajihara, I.; Makino, K.; Honda, N.; Masuguchi, S.; Fukushima, S.; Inoue, Y.; Ihn, H. Circulating miR-29a levels in patients with scleroderma spectrum disorder. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2011, 61, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldschmidt, I.; Thum, T.; Baumann, U. Circulating miR-21 and miR-29a as Markers of Disease Severity and Etiology in Cholestatic Pediatric Liver Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wu, B.; Zhong, S.; Deng, W.; Lin, F. miR-29a-3p suppresses hepatic fibrosis pathogenesis by modulating hepatic stellate cell proliferation via targeting PIK3R3 gene expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 529, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Kuo, H.-C.; Yang, Y.-L.; Wang, F.-S. MicroRNA-29a is a key regulon that regulates BRD4 and mitigates liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation. Int. J. Med Sci. 2019, 16, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Tiao, M.-M.; Huang, L.-T.; Chuang, J.-H.; Kuo, K.-C.; Yang, Y.-L.; Wang, F.-S. Activation of Mir-29a in Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells Modulates Its Profibrogenic Phenotype through Inhibition of Histone Deacetylases 4. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.-L.; Huang, F.-C.; Tiao, M.-M.; Lin, Y.-C.; Tsai, M.-H.; Wang, F.-S. MicroRNA-29a mitigation of endoplasmic reticulum and autophagy aberrance counteracts in obstructive jaundice-induced fibrosis in mice. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.-L.; Wang, F.-S. The Role of miR-29a in the Regulation, Function, and Signaling of Liver Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.-C.; Wang, F.-S.; Yang, Y.-L.; Tiao, M.-M.; Chuang, J.-H.; Huang, Y.-H. Microarray Study of Pathway Analysis Expression Profile Associated with MicroRNA-29a with Regard to Murine Cholestatic Liver Injuries. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Wang, F.-S.; Yang, Y.-L.; Huang, Y.-H. MicroRNA-29a Suppresses CD36 to Ameliorate High Fat Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis and Liver Fibrosis in Mice. Cells 2019, 8, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Wang, F.-S.; Yang, Y.-L.; Chuang, Y.-T.; Huang, Y.-H. MicroRNA-29a mitigation of toll-like receptor 2 and 4 signaling and alleviation of obstructive jaundice-induced fibrosis in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiao, M.-M.; Wang, F.-S.; Huang, L.-T.; Chuang, J.-H.; Kuo, H.-C.; Yang, Y.-L.; Huang, Y.-H. MicroRNA-29a protects against acute liver injury in a mouse model of obstructive jaundice via inhibition of the extrinsic apoptosis pathway. Apoptosis 2014, 19, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-L.; Kuo, H.-C.; Wang, F.-S.; Huang, Y.-H. MicroRNA-29a Disrupts DNMT3b to Ameliorate Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-L.; Wang, F.-S.; Li, S.-C.; Tiao, M.-M.; Huang, Y.-H. MicroRNA-29a Alleviates Bile Duct Ligation Exacerbation of Hepatic Fibrosis in Mice through Epigenetic Control of Methyltransferases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-L.; Wang, F.-S.; Lin, H.-Y.; Huang, Y.-H. Exogenous Therapeutics of Microrna-29a Attenuates Development of Hepatic Fibrosis in Cholestatic Animal Model through Regulation of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase p85 Alpha. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-L.; Wang, P.-W.; Wang, F.-S.; Lin, H.-Y.; Huang, Y.-H. miR-29a Modulates GSK3beta/SIRT1-Linked Mitochondrial Proteostatic Stress to Ameliorate Mouse Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayob, A.Z.; Ramasamy, T.S. Cancer stem cells as key drivers of tumour progression. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levrero, M.; Zucman-Rossi, J. Mechanisms of HBV-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S84–S101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Shan, C.; Ye, L.; Zhang, X. Upregulated MicroRNA-29a by Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Enhances Hepatoma Cell Migration by Targeting PTEN in Cell Culture Model. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-J.; Zhuo, Y.; Zhou, Y.-C.; Wang, X.-W.; Wang, Y.-P.; Si, C.-Y.; Wang, X.-H. miR-29a promotes hepatitis B virus replication and expression by targeting SMARCE1 in hepatoma carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 4569–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ding, H. XPD suppresses cell proliferation and migration via miR-29a-3p-Mdm2/PDGF-B axis in HCC. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Sun, K.; Dong, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, H.; Sha, Z.; Mao, J.; Ding, G.; Guo, W.; et al. microRNA-29a regulates liver tumor-initiating cells expansion via Bcl-2 pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 387, 111781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Shi, C.; Feng, F.; Yang, L. Mutant ACTB mRNA 3′-UTR promotes hepatocellular carcinoma development by regulating miR-1 and miR-29a. Cell. Signal. 2020, 67, 109479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braconi, C.; Kogure, T.; Valeri, N.; Huang, N.; Nuovo, G.J.; Costinean, S.; Negrini, M.; Miotto, E.; Croce, C.M.; Patel, T.B. microRNA-29 can regulate expression of the long non-coding RNA gene MEG3 in hepatocellular cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 4750–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parpart, S.; Roessler, S.; Dong, F.; Rao, V.; Takai, A.; Ji, J.; Qin, L.-X.; Ye, Q.-H.; Jia, H.-L.; Tang, Z.-Y.; et al. Modulation of miR-29 expression by alpha-fetoprotein is linked to the hepatocellular carcinoma epigenome. Hepatology 2014, 60, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogure, T.; Kondo, Y.; Kakazu, E.; Ninomiya, M.; Kimura, O.; Shimosegawa, T. Involvement of miRNA-29a in epigenetic regulation of transforming growth factor-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2014, 44, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.-M.; Wei, L.; Law, C.-T.; Ho, D.W.-H.; Tsang, F.H.-C.; Au, S.L.-K.; Sze, K.M.-F.; Lee, J.M.-F.; Wong, C.C.-L.; Ng, I.O.-L. Up-regulation of histone methyltransferase SETDB1 by multiple mechanisms in hepatocellular carcinoma promotes cancer metastasis. Hepatology 2016, 63, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, E.; Liu, W.; Yang, Q.; Xie, C.; Ai, J.; Zhou, F.; Liao, W.; Wu, L. Circular RNA MYLK Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression Through the miR29a/KMT5C Signaling Pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 8615–8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ying-Hong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; Li, X.-D.; Zhou, Z.-J.; Zhou, S.-L.; Gao, D.-M.; Hu, J.; Jin, C.; et al. MicroRNA-29a induces loss of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and promotes metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through a TET–SOCS1–MMP9 signaling axis. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossenta, M.; Busato, D.; Dal Bo, M.; Toffoli, G. Glucose Metabolism and Oxidative Stress in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Role and Possible Implications in Novel Therapeutic Strategies. Cancers 2020, 12, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.-C.; Dong, Q.-Z.; Zhang, X.-F.; Deng, B.; Jia, H.-L.; Ye, Q.-H.; Qin, L.-X.; Wu, X.-Z. microRNA-29a suppresses cell proliferation by targeting SPARC in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Xiu, M. MiR-29a suppresses cell proliferation by targeting SIRT1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 22, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zang, H.; Zhang, X.; Huang, G. Exosomal Circ-ZNF652 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion and Glycolysis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via miR-29a-3p/GUCD1 Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 7739–7751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Zhang, H.; He, J.; Kong, H.; Tao, R.; Huang, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Wei, L.; et al. Long non-coding RNA LINC00473 acts as a microRNA-29a-3p sponge to promote hepatocellular carcinoma development by activating Robo1-dependent PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, D.W.; Dinger, D.W.T.M.E. Endogenous microRNA sponges: Evidence and controversy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.R.; Feng, J.L.; Liu, X.J.; Wang, J.M. LncRNA HULC promots HCC growth by downregulating miR-29. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 2019, 41, 659–666. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Feng, Q.; Liao, W.; Gao, J.; Ai, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, E.; Wu, L. TUG1 as ceRNA combined with miR-29a to promotes the expression of IFITM3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Res. Square 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Zhu, B.; Hu, Y.-L.; Mao, Q.-S.; Feng, Y. LncRNA HOXA-AS3 promotes gastric cancer progression by regulating miR-29a-3p/LTβR and activating NF-κB signaling. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascut, D.; Pratama, M.Y.; Vo, N.V.; Masadah, R.; Tiribelli, C. The Crosstalk between Tumor Cells and the Microenvironment in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Role of Exosomal microRNAs and Their Clinical Implications. Cancers 2020, 12, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.C.-L.; Tse, A.P.-W.; Huang, Y.-P.; Zhu, Y.-T.; Chiu, D.K.-C.; Lai, R.K.-H.; Au, S.L.-K.; Kai, A.K.-L.; Lee, J.M.-F.; Wei, L.L.; et al. Lysyl oxidase-like 2 is critical to tumor microenvironment and metastatic niche formation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Kong, W.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, Y. Traditional Chinese Medicine Xiaoai Jiedu Recipe Suppresses the Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Regulating the microRNA-29a/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Axis. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 7329–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahati, S.; Xiao, L.; Yang, Y.; Mao, R.; Bao, Y. miR-29a suppresses growth and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating CLDN1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 486, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, X.; Guo, X.; Yu, R.; Qian, M.; Wang, S.; Gao, X.; Qiu, W.; Guo, Q.; Xu, J.; et al. MicroRNA-29a-3p delivery via exosomes derived from engineered human mesenchymal stem cells exerts tumour suppressive effects by inhibiting migration and vasculogenic mimicry in glioma. Aging 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosano, S.; Corà, D.; Parab, S.; Zaffuto, S.; Isella, C.; Porporato, R.; Hoza, R.M.; Calogero, R.A.; Riganti, C.; Bussolino, F.; et al. A regulatory microRNA network controls endothelial cell phenotypic switch during sprouting angiogenesis. eLife 2020, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Huang, M.; Lv, M.; He, Y.; Duan, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J. Circular RNA MYLK as a competing endogenous RNA promotes bladder cancer progression through modulating VEGFA/VEGFR2 signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2017, 403, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Li, E.; Min, J.; Gong, C.; Gao, J.; Ai, J.; Liao, W.; Wu, L. miR-29a suppresses the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through IFITM3. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 3261–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Cao, L.; Zhang, T.; Yue, D.; Wang, L.; Ping, Y.; He, Q.; Zhang, C.; Wang, M.; et al. miR-29a-3p suppresses cell proliferation and migration by downregulating IGF1R in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 86592–86603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, Y.H.; Yoon, C.-H.; Kim, R.-K.; Lim, E.-J.; Oh, Y.S.; Hwang, S.-G.; An, S.; Yoon, G.; Gye, M.C.; Yi, J.-M.; et al. Claudin-1 induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition through activation of the c-Abl-ERK signaling pathway in human liver cells. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4873–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Cheung, S.T. STAT3: An Emerging Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Njah, K.; Hong, W. Agrin Mediates Angiogenesis in the Tumor Microenvironment. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Li, C.-J.; Yang, Y.-L.; Huang, Y.-H.; Hsiau, Y.-T.; Chu, P.-Y. Roles of Lysyl Oxidase Family Members in the Tumor Microenvironment and Progression of Liver Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.; Semela, D.; Bruix, J.; Colle, I.; Pinzani, M.; Bosch, J. Angiogenesis in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 604–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Duda, D.G.; Sahani, D.V.; Jain, R.K. HCC and angiogenesis: Possible targets and future directions. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, M.A.; Sun, W.; Kim, R.; He, A.R.; Abada, P.B.; Mynderse, M.; Finn, R.S. The Role of Angiogenesis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.F.; De Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Park, J.O.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Yen, C.-J.; Poon, R.; Pastorelli, D.; Blanc, J.-F.; Chung, H.C.; Baron, A.D.; Pfiffer, T.E.F.; et al. Ramucirumab versus placebo as second-line treatment in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma following first-line therapy with sorafenib (REACH): A randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Pavlasova, G.M.; Seda, V.; Cerna, K.A.; Vojackova, E.; Filip, D.; Ondrisova, L.; Sandova, V.; Kostalova, L.; Zeni, P.F.; et al. miR-29 Modulates CD40 Signaling in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia by Targeting TRAF4: An Axis Affected by BCR inhibitors. Blood 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.-Q.; Xia, T.; Hu, Y.-H.; Sun, M.-S.; Yan, S.; Lei, C.-Q.; Shu, H.-B.; Guo, J.-H.; Liu, Y. IFITM3 inhibits virus-triggered induction of type I interferon by mediating autophagosome-dependent degradation of IRF3. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Cheung, I.Y.; Guo, H.-F.; Cheung, N.-K.V. MicroRNA miR-29 Modulates Expression of Immunoinhibitory Molecule B7-H3: Potential Implications for Immune Based Therapy of Human Solid Tumors. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6275–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Tian, L.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, K.; Li, S.; Li, T. Antitumor activity of sevoflurane in HCC cell line is mediated by miR-29a-induced suppression of Dnmt3a. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 18152–18161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Shen, S. Combined low miRNA-29s is an independent risk factor in predicting prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy: A Chinese population-based study. Medicine 2017, 96, e8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.-T.; Dong, Q.-Z.; Sheng, Y.-Y.; Wei, J.-W.; Wang, G.; Zhou, H.-J.; Ren, N.; Jia, H.-L.; Ye, Q.-H.; Qin, L.-X. MicroRNA-29a-5p Is a Novel Predictor for Early Recurrence of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Surgical Resection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Kim, S.S.; Nam, J.S.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, B.; Wang, H.J.; Kim, B.W.; Lee, J.-D.; Kang, D.Y.; et al. Low levels of circulating microRNA-26a/29a as poor prognostic markers in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who underwent curative treatment. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2017, 41, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.-T.; Hasan, A.M.E.; Liu, R.-B.; Zhang, Z.-C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.-Y.; Wang, F.; Shao, J.-Y. Serum microRNA profiles as prognostic biomarkers for HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 45637–45648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.-J.; Chong, Y.; Guo, Z.-W.; Xie, C.; Yang, X.-J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.-P.; Xiong, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Min, J.; et al. A serum microRNA classifier for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: A multicentre, retrospective, longitudinal biomarker identification study with a nested case-control study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 804–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Qin, L.; Hu, R. Development and validation of serum exosomal microRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.; Sadeghizadeh, M.; Behmanesh, M.; Najafi, F. Dendrosomal curcumin increases expression of the long non-coding RNA gene MEG3 via up-regulation of epi-miRs in hepatocellular cancer. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-Z.; Zheng, T.-S.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.-B.; Zhang, W.-H.; Pan, S.-H.; Jiang, H.-C.; Liu, L.-X. microRNA expression alteration after arsenic trioxide treatment in HepG-2 cells. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 26, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Xu, Q.; Chen, L.; Chen, R. A Meta-Analysis of Arsenic Trioxide Combined with Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Treatment of Primary Hepatic Carcinoma. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
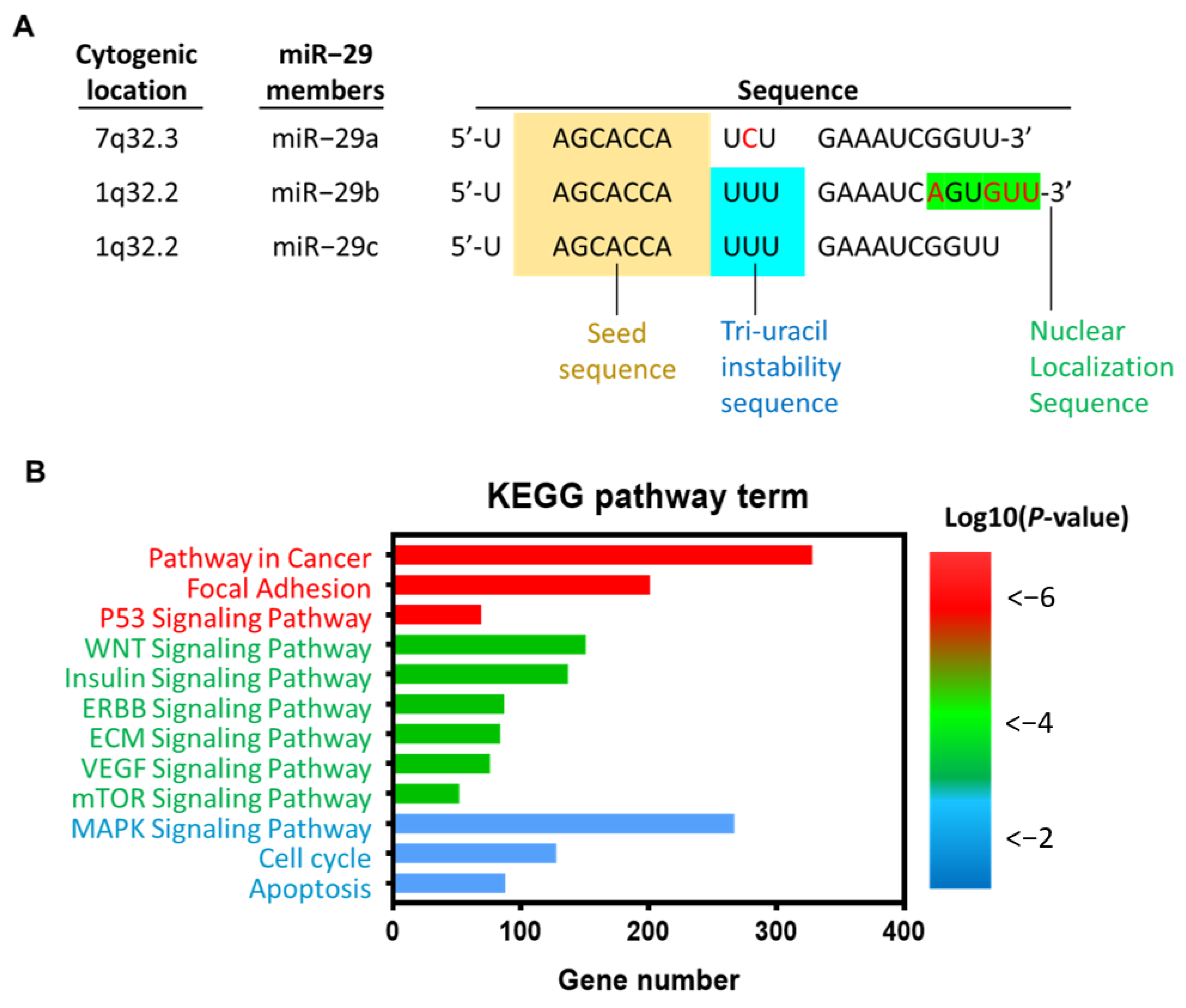
| Role of miR-29a | Involved Mechanism | Used Model | Target Gene | Pathway | Outcome | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
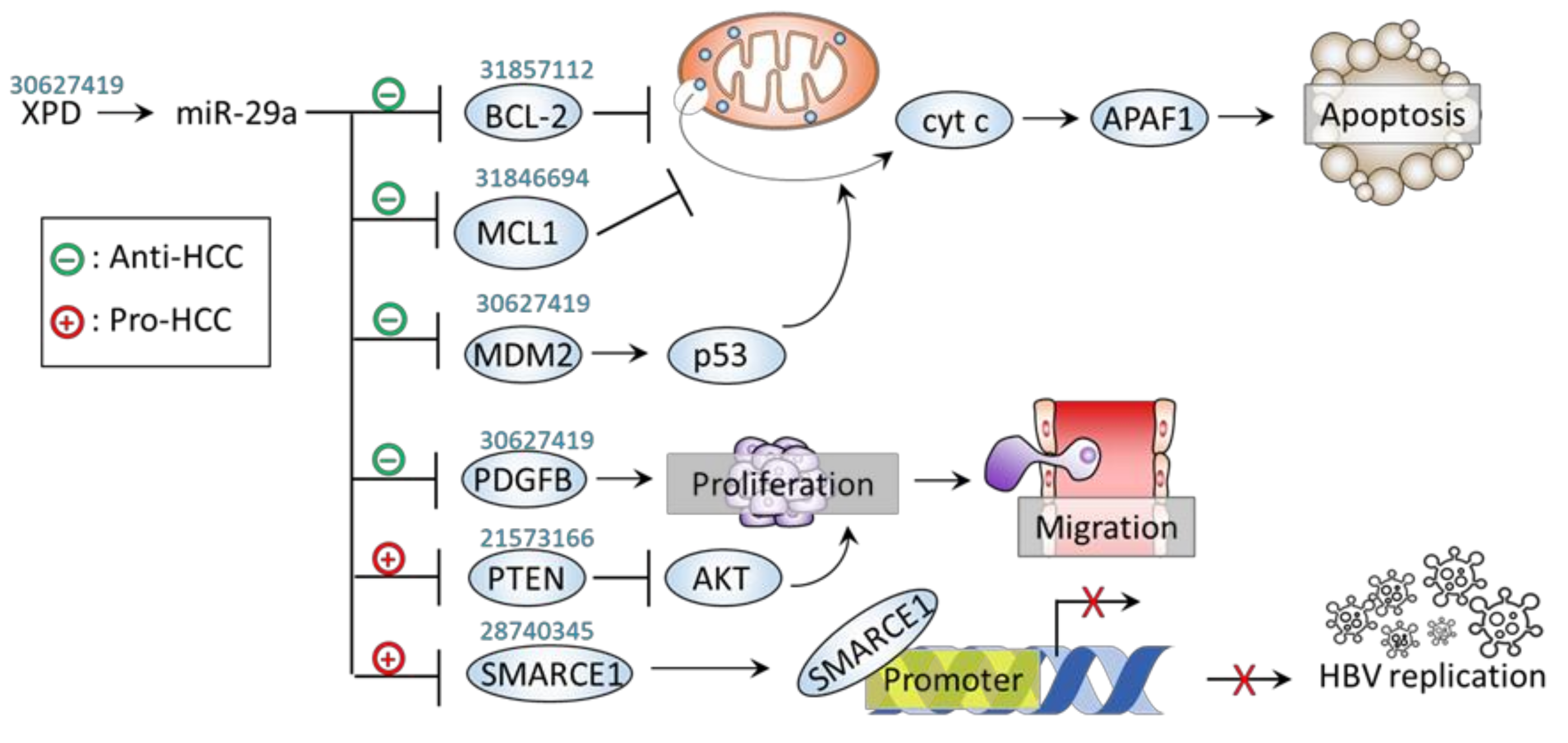
| − | Stemness, apoptosis | CSC | BCL-2 | ↑miR-29a →↓BCL-2 | ↓CSC self renewal ↑Sorafenib response ↓PDX growth | [46] |
| − | Apoptosis | SMMC7721 and Hep3B cells | MDM2 | ↑XPD→↑miR-29a →↓MDM2→↑p53 | ↓Proliferation ↓Migration | [45] |
| − | Apoptosis | Hep3B, HepG2 cells; Xenograft mice; Human HCC tissue | MCL1 | Mutant ATCB →↓miR-29a →↑MCL1 | ↑Proliferation ↑Migration ↑Invasion ↑Tumor growth | [47] |
| − | Proliferation | SMMC7721 and Hep3B cells | PDGFB | ↑XPD→↑miR-29a →↓PDGFB | ↓Proliferation ↓Migration | [45] |
| + | HBsAg dissemination | HepG2 cell | SMARCE1 | ↑miR-29a →↓SMARCE1 →↑HBsAg | ↑HBV replication | [44] |
| + | Proliferation | HepG2 and HepG2-X cell | PTEN | ↑HBx →↑miR-29a →↓PTEN →↑p-AKT | ↑Migration | [43] |
| Role of miR-29a | Involved Mechanism | Used Model | Target Gene | Pathway | Outcome | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
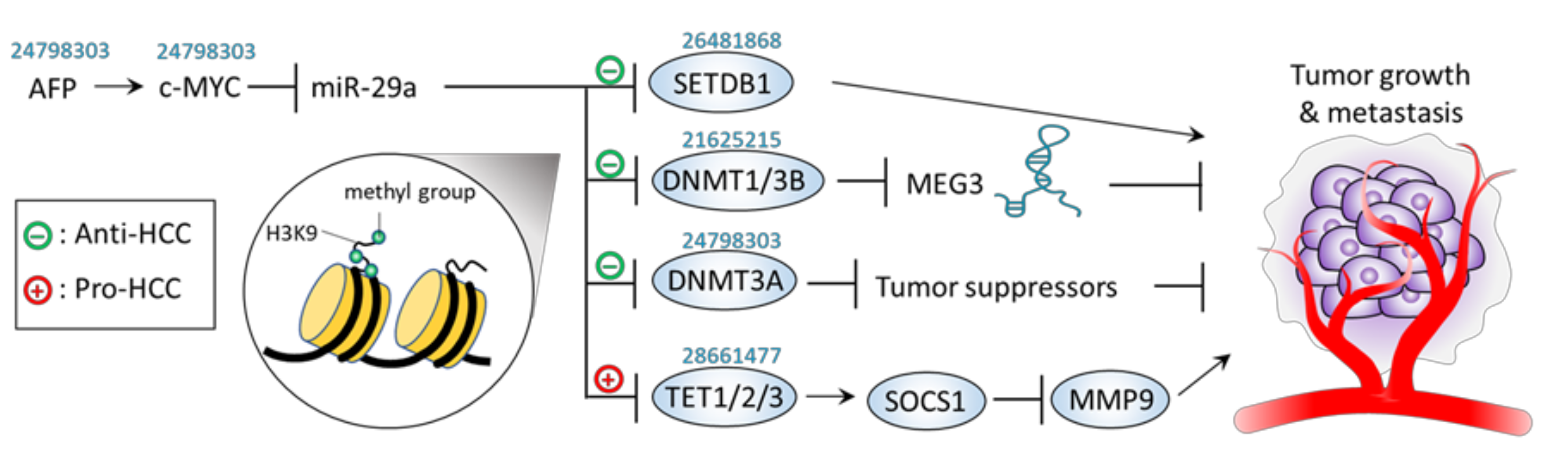
| − | Epigenetic control | Hep3B and MHCC97L cells; Xenograft mice | SETDB1 | ↑miR-29a →↓SETDB1 | ↓Proliferation ↓Migration ↓Tumor growth ↓Tumor metastasis | [51] |
| − | Epigenetic control | HLE and SNU-475 cells; Xenograft mice; Human HCC tissue | DNMT3A | ↑AFP→↑c-MYC →↓miR-29a →↑DNMT3A →↓tumor suppressor genes | AFP overexpression promotes a c-MYC-mediated miR-29a inhibition, leading to tumor growth and cellular proliferation, migration, and invasion. | [49] |
| − | Epigenetic control | HepG2, Huh-7, PLC/PRF-5, Hep-3B cell | DNMT1, DNMT3B | ↑miR-29a →↓DNMT1, ↓DNMT3B →↑MEG3 | ↓Proliferation | [48] |
| + | Epigenetic control | HepG2, SMMC-7721, MHCC97H, and HCCLM3 cell; Xenograft mice | TET1/2/3 | ↑miR-29a →↓TET1/2/3 →↓SOCS1 →↑MM9 | ↓Apoptosis ↑Proliferation ↑Migration ↑Invasion ↑tumor growth ↑lung metastasis | [53] |
| Role of miR-29a | Involved Mechanism | Used Model | Target Gene | Pathway | Outcome | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| − | Metabolic adaptation | HepG2, Huh7, HCCLM3 and SK-Hep-1 cells; Xenograft mice; Human HCC tissue | Robo1 | ↓LINC00473 →↑miR-29a →↓Robo1 →↓p-PI3K/p-AKT/p-mTOR | ↓Proliferation ↓Migration ↓Invasion ↓Tumor growth ↓Tumor metastasis | [58] |
| − | Metabolic adaptation | MHCC97H cells | SIRT1 | ↑miR-29a→↓SIRT1 | ↓Proliferation ↓Cell cycle | [56] |
| − | Metabolic adaptation | 97L and PLC cell | SPARC | ↑miR-29a →↓SPARC →↓p-AKT →↓p-mTOR, ↓p-ERK | ↓Proliferation | [55] |
| ceRNA | Effect of ceRNA | Involved Mechanism | Used Model | Upregulated Gene | Pathway | Outcome | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mutant ATCB 3’UTR | + | Apoptosis | Hep3B, HepG2 cells; Xenograft mice; Human HCC tissue | MCL1 | Mutant ATCB →↓miR-29a →↑MCL1 | ↑Proliferation ↑Migration ↑Invasion ↑Tumor growth | [47] |
| LINC00473 | + | Metabolic regulation | HepG2, Huh7, HCCLM3 and SK-Hep-1 cells; Xenograft mice; Human HCC tissue | ROBO1 | ↑LINC00473 →↓miR-29a →↑Robo1 →↑p-PI3K/p-AKT/p-mTOR | ↑Proliferation ↑Migration ↑Invasion ↑Tumor growth ↑Tumor metastasis | [58] |
| HULC | + | Epigenetic control | Hep3B, Huh7 cells | SETDB1 | ↑HULC →↓miR-29 →↑SETDB1 | ↑Proliferation | [60] |
| TUG1 | + | Immunomodulation | MHCC-97H, HCC-LM3 cells | IFITM3 | ↑TUG →↓miR-29a →↑IFITM3 | ↑Proliferation↑Migration ↑Invasion↑Tumor growth | [61] |
| HOXA-AS3 | + | Immunomodulation | Gastric cancer cells | LTBR | ↑HOXA-AS3 →↓miR-29a →↑LTBR →↑NF-κB | ↑Proliferation↑Migration ↑Invasion↑Tumor metastasis | [62] |
| circMYLK | + | Epigenetic control | MHCC-97H and HCC-LM3 cells; Xenograft mice; Human HCC tissue | KMT5C | ↑circMYLK →↓miR-29a →↑KMT5C | ↑Proliferation ↑Migration ↑Invasion ↑Tumor growth ↑Tumor metastasis | [52] |
| circ-ZNF652 | + | Metabolic regulation | SNU-387 and Huh-7 cells; Xenograft mice; Human HCC tissue | GUCD1 | ↑circ-ZNF652 →↓miR-29a →↑GUCD1 →↑HK2 | ↑Glycolysis ↑Proliferation ↑Migration ↑Invasion ↑Tumor growth | [57] |
| Role of miR-29a | Involved Mechanism | Used Model | Target Gene | Pathway | Outcome | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| − | Fibrosis | MHCC97L cells | LOXL2 | ↑miR-29a →↓LOXL2 | ↓Tissue stiffness ↓Tumor metastasis | [64] |
| − | Metastasis | SK-Hep-1 and Hep3B cells | STAT3 | ↑miR-29a →↓STAT3 →↓MMP-2/9 | ↓Proliferation ↓Migration ↓Invasion | [65] |
| − | Metastasis | HepG2 and HLE cells; Xenograft mice | CLDN1 | ↑miR-29a →↓CLDN1 | ↓Proliferation ↓Migration ↓Tumor growth | [66] |
| − | Angiogenesis | Glioma cells | ROBO1 | ↑miR-29a →↓ROBO1 | ↓Angiogenesis ↓Migration | [67] |
| − | Angiogenesis | EC | PDGFB | ↑miR-29a →↓PDGFB | ↓EC sprouting activity | [68] |
| − | Angiogenesis | Bladder cancer cells | VEGFA | circMYLK knockdown →↑miR-29a →↓VEGFA | ↓Angiogenesis ↑Apoptosis ↓Proliferation ↓Migration | [69] |
| − | Immunomodulation | HCCLM3 cells | IFITM3 | ↑miR-29a→↓IFITM3 | ↑Apoptosis ↓Proliferation ↓Migration ↓Invasion | [70] |
| − | Immunomodulation | HepG2 cells | IGF1R | ↑miR-29a →↓IGF1R (HepG2 cells) →↓CCL5 (CD8+ T cells) | ↓Proliferation ↓Migration ↓Invasion ↑T cell recruitment | [71] |
| Source | miR-29a Levels | Clinical Relevance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor | ↓ | Biomarker for HCC; Predictor for lymph node metastasis, late TNM stage (III-IV) | [65] |
| Tumor | ↓ | Biomarker for HCC | [84] |
| Tumor | ↓ | Biomarker for HCC | [45] |
| Tumor | ↓ | Biomarker for HCC; Predictor for tumor size > 5 cm, vascular invasion, and poor DFS and OS | [56] |
| Tumor | ↓ | Biomarker for HCC; Predictor for tumor size > 5 cm, multifocal tumors, venous invasion, and poor OS | [70] |
| Tumor | ↓ | Biomarker for HCC | [85] |
| Tumor | ↓ | Biomarker for HCC; Predictor for poor OS | [66] |
| Tumor | ↑ | Biomarker for HCC; Predictor for poor OS | [53] |
| Tumor | ↓ | Inversely correlated with serum AFP of patients Predictor for poor prognosis | [49] |
| Tumor | ↓ | Biomarker for HCC | [55] |
| Tumor | ↑ | Predictor for early recurrence, and poor OS in HBV-related HCC after surgical resection | [86] |
| plasma | ↓ | Predictor for poor DFS and poor liver transplantation-free survival | [87] |
| Serum | ↑ | Differential biomarker for HBV-positive HCC; Predictor for poor OS and PFS | [88] |
| Serum | ↑ | Superior diagnostic factor to AFP; Predictor for small size, early-stage, AFP-negative HCC | [89] |
| Serum exosomes | ↑ | Diagnostic factor for HCC | [90] |
| Therapeutics | Biological Property | Model | Pathway | Outcome | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silencing of circ-ZNF652 | shRNA-targeting circRNA | SNU-387 and Huh-7 cells; Xenograft mice | ↓circ-ZNF652 →↑miR-29a →↓GUCD1 →↓HK2 | ↓Glycolysis ↓Proliferation ↓Migration ↓Invasion ↓Tumor growth | [57] |
| Silencing of circMYLK | siRNA-targeted circRNA | MHCC-97H and HCC-LM3 cells; Xenograft mice | ↑miR-29a →↓KMT5C | ↓Proliferation ↓Migration ↓Invasion ↓Tumor growth ↓Tumor metastasis | [52] |
| Silencing of LINC00473 | shRNA-targeting lncRNA | HepG2, Huh7, HCCLM3 and SK-Hep-1 cells; Xenograft mice | ↑miR-29a →↓Robo1 →↑p-PI3K/p-AKT/p-mTOR | ↓Proliferation ↓Migration ↓Invasion ↓Tumor growth ↓Tumor metastasis | [58] |
| Xiaoai Jiedu Recipe (XJP) | Traditional Chinese medicine | SK-Hep-1 and Hep3B cells; Xenograft mice | ↑miR-29a →↓STAT3 →↓MMP-2/9 | ↓Proliferation ↓Migration ↓Invasion ↓Tumor growth | [65] |
| Sevoflurane | Anesthetics | Huh-7 and HepG2 cells | ↑miR-29a →↓DNMT3A | ↑PTEN, ↓p-PI3K, ↓p-AKT ↑Apoptosis ↓Migration | [84] |
| Dendrosomal curcumin (DNC) | Natural phenol, delivered by dendrosome nanoparticle | Huh-7 and HepG2 cells | ↑miR-29a/↑miR-185 →↓DNMT3A/↓DNMT3B/↓DNMT1 →↑MEG3 | ↓Cell viability | [91] |
| Arsenic trioxide | arsenic compound | HepG2 cell | ↑miR-29a→↓PPM1D | ↑Apoptosis | [92] |
| Meta-analysis | NA | Potentiate therapeutic effect of TACE on: ↓AFP ↑one-year survival rate ↑life quality of PHC patients ↓chemotherapeutic side effects | [93] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.-L.; Chang, Y.-H.; Li, C.-J.; Huang, Y.-H.; Tsai, M.-C.; Chu, P.-Y.; Lin, H.-Y. New Insights into the Role of miR-29a in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Implications in Mechanisms and Theragnostics. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11030219
Yang Y-L, Chang Y-H, Li C-J, Huang Y-H, Tsai M-C, Chu P-Y, Lin H-Y. New Insights into the Role of miR-29a in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Implications in Mechanisms and Theragnostics. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(3):219. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11030219
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Ya-Ling, Yen-Hsiang Chang, Chia-Jung Li, Ying-Hsien Huang, Ming-Chao Tsai, Pei-Yi Chu, and Hung-Yu Lin. 2021. "New Insights into the Role of miR-29a in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Implications in Mechanisms and Theragnostics" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 3: 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11030219
APA StyleYang, Y.-L., Chang, Y.-H., Li, C.-J., Huang, Y.-H., Tsai, M.-C., Chu, P.-Y., & Lin, H.-Y. (2021). New Insights into the Role of miR-29a in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Implications in Mechanisms and Theragnostics. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(3), 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11030219