Advancing Prostate Cancer Assessment: A Biparametric MRI (T2WI and DWI/ADC)-Based Radiomic Approach to Predict Tumor–Stroma Ratio
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Cohort and Recruitment
2.2. Pathological Evaluation
2.3. MRI Protocols
2.4. Radiomic Feature Extraction
2.5. Radiomics Feature Selection and Model Building
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Feature Extraction and Selection
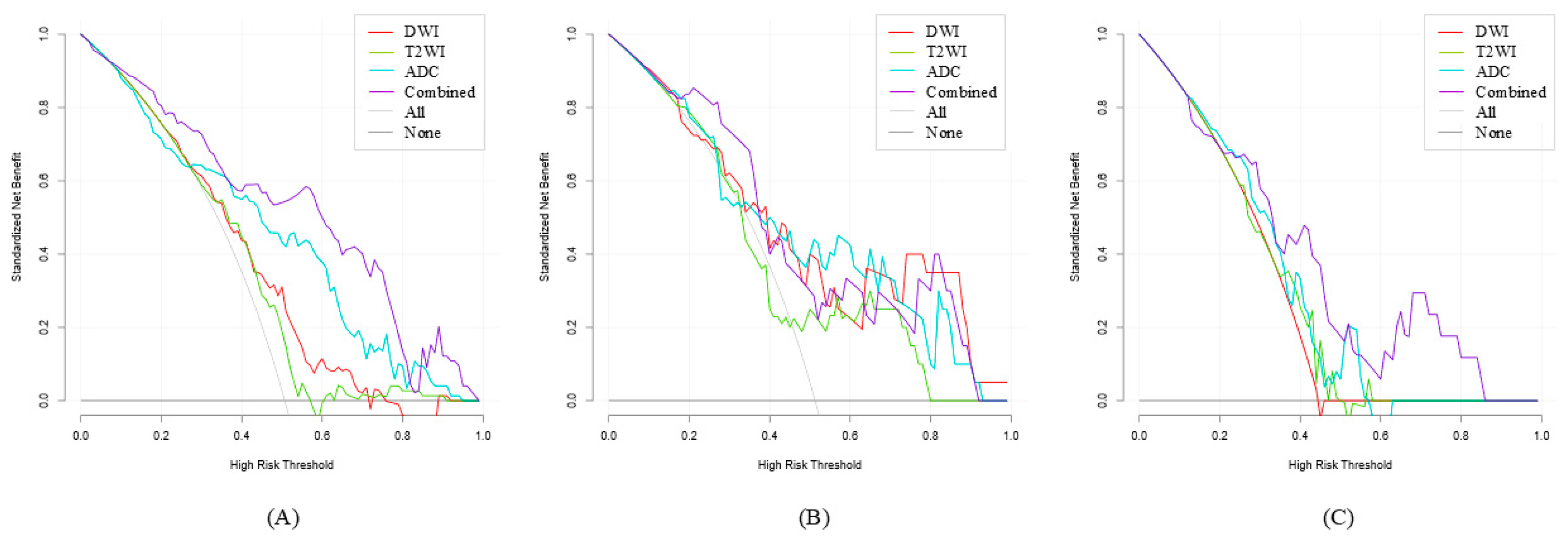
3.3. Diagnostic Performance of the ML Models
3.4. Lesion Distribution in TSR Groups
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arneth, B. Tumor Microenvironment. Medicina 2019, 56, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, T.; Xia, R.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. Targeting the tumor stroma for cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesker, W.E.; Junggeburt, J.M.; Szuhai, K.; de Heer, P.; Morreau, H.; Tanke, H.J.; Tollenaar, R.A. The carcinoma-stromal ratio of colon carcinoma is an independent factor for survival compared to lymph node status and tumor stage. Cell. Oncol. 2007, 29, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, Z.X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, F.; Cheng, Y.F. The tumor-stroma ratio is an independent predictor for survival in nasopharyngeal cancer. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2014, 37, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagenaars, S.C.; Vangangelt, K.M.H.; Van Pelt, G.W.; Karancsi, Z.; Tollenaar, R.; Green, A.R.; Rakha, E.A.; Kulka, J.; Mesker, W.E. Standardization of the tumor-stroma ratio scoring method for breast cancer research. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 193, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastały, P.; Smentoch, J.; Popęda, M.; Martini, E.; Maiuri, P.; Żaczek, A.J.; Sowa, M.; Matuszewski, M.; Szade, J.; Kalinowski, L.; et al. Low Tumor-to-Stroma Ratio Reflects Protective Role of Stroma against Prostate Cancer Progression. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vivar, A.D.; Sayeeduddin, M.; Rowley, D.; Cubilla, A.; Miles, B.; Kadmon, D.; Ayala, G. Histologic features of stromogenic carcinoma of the prostate (carcinomas with reactive stroma grade 3). Hum. Pathol. 2017, 63, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, G.; Tuxhorn, J.A.; Wheeler, T.M.; Frolov, A.; Scardino, P.T.; Ohori, M.; Wheeler, M.; Spitler, J.; Rowley, D.R. Reactive stroma as a predictor of biochemical-free recurrence in prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 4792–4801. [Google Scholar]
- Rani, P.; Gupta, A.J.; Mehrol, C.; Singh, M.; Khurana, N.; Passey, J.C. Clinicopathological correlation of tumor-stroma ratio and inflammatory cell infiltrate with tumor grade and lymph node metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of buccal mucosa and tongue in 41 cases with review of literature. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2020, 16, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangush, A.; Heikkinen, I.; Bakhti, N.; Mäkinen, L.K.; Kauppila, J.H.; Pukkila, M.; Hagström, J.; Laranne, J.; Soini, Y.; Kowalski, L.P.; et al. Prognostic impact of tumour-stroma ratio in early-stage oral tongue cancers. Histopathology 2018, 72, 1128–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeb, S.; Vellekoop, A.; Ahmed, H.U.; Catto, J.; Emberton, M.; Nam, R.; Rosario, D.J.; Scattoni, V.; Lotan, Y. Systematic review of complications of prostate biopsy. Eur. Urol. 2013, 64, 876–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liss, M.A.; Ehdaie, B.; Loeb, S.; Meng, M.V.; Raman, J.D.; Spears, V.; Stroup, S.P. An Update of the American Urological Association White Paper on the Prevention and Treatment of the More Common Complications Related to Prostate Biopsy. J. Urol. 2017, 198, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, P.; Li, D.; Zhu, H.; Meng, L.; Song, Y.; Xie, L.; Zhu, J.; Yu, T. Intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging of early cervical carcinoma: Correlation between imaging parameters and tumor-stroma ratio. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Hu, T.; Gong, J.; Huang, D.; Liu, F.; Fu, C.; Tong, T. Multiparametric MRI-based radiomics signature for preoperative estimation of tumor-stroma ratio in rectal cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 3326–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Fang, S.; Hu, J.; Tao, J.; Zhang, K.; Deng, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y. Correlation of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion and Diffusion Kurtosis MR Imaging Models with Reactive Stromal Grade in Prostate Cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 58, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, F.; Qin, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, C.; Wu, Y.; Hao, P.; Xu, Y. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI in patients with breast cancer: Correlation with tumor stroma characteristics. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 120, 108686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, R.; Panagiotaki, E. Limitations and Prospects for Diffusion-Weighted MRI of the Prostate. Diagnostics 2016, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bihan, D. What can we see with IVIM MRI? Neuroimage 2019, 187, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, G.; Bonilha, L.; Li, L.M.; Cendes, F. Texture analysis of medical images. Clin. Radiol. 2004, 59, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, X. Leveraging multimodal MRI-based radiomics analysis with diverse machine learning models to evaluate lymphovascular invasion in clinically node-negative breast cancer. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Bussink, J.; Lambin, P.; Aerts, H. Machine Learning methods for Quantitative Radiomic Biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Liu, F.; Fang, X.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Feng, X.; Lu, J.; Bian, Y.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Radiomics and Machine-learning Models: An Approach for Evaluating Tumor-stroma Ratio in Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Acad. Radiol. 2022, 29, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstens, J.L.; Shahi, P.; Van Tsang, S.; Smith, B.; Creighton, C.J.; Zhang, Y.; Seamans, A.; Seethammagari, M.; Vedula, I.; Levitt, J.M.; et al. FGFR1-WNT-TGF-β signaling in prostate cancer mouse models recapitulates human reactive stroma. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Garzón, V.; Kypta, R. WNT signalling in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2017, 14, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, S.; Lim, C.S.; McInnes, M.D.F.; Flood, T.A.; Shabana, W.M.; Lim, R.S.; Schieda, N. Evaluation of MRI for diagnosis of extraprostatic extension in prostate cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 47, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, T.R.; White, N.S.; Kuperman, J.; Chao, Y.; Yamin, G.; Bartch, H.; Schenker-Ahmed, N.M.; Rakow-Penner, R.; Bussell, R.; Nomura, N.; et al. Demonstration of Non-Gaussian Restricted Diffusion in Tumor Cells Using Diffusion Time-Dependent Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Liu, F.; Fang, X.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Feng, X.; Zhu, M.; Li, N.; et al. CT Radiomics and Machine-Learning Models for Predicting Tumor-Stroma Ratio in Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 707288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Yuan, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Liang, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, S.; Li, Y. One novel transfer learning-based CLIP model combined with self-attention mechanism for differentiating the tumor-stroma ratio in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Radiol. Med. 2024, 129, 1559–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Prasanna, P.; Bera, K.; Statsevych, V.; Hill, V.; Singh, G.; Partovi, S.; Beig, N.; McGarry, S.; Laviolette, P.; et al. Radiomic Deformation and Textural Heterogeneity (R-DepTH) Descriptor to Characterize Tumor Field Effect: Application to Survival Prediction in Glioblastoma. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 41, 1764–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hectors, S.J.; Cherny, M.; Yadav, K.K.; Beksaç, A.T.; Thulasidass, H.; Lewis, S.; Davicioni, E.; Wang, P.; Tewari, A.K.; Taouli, B. Radiomics Features Measured with Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Predict Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness. J. Urol. 2019, 202, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, D.S.; Jones, R.E.; Ransom, R.C.; Longaker, M.T.; Norton, J.A. The evolving relationship of wound healing and tumor stroma. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e99911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krušlin, B.; Ulamec, M.; Tomas, D. Prostate cancer stroma: An important factor in cancer growth and progression. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2015, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, E.; Astsaturov, I.; Cukierman, E.; DeNardo, D.G.; Egeblad, M.; Evans, R.M.; Fearon, D.; Greten, F.R.; Hingorani, S.R.; Hunter, T.; et al. A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pederzoli, F.; Raffo, M.; Pakula, H.; Ravera, F.; Nuzzo, P.V.; Loda, M. Stromal cells in prostate cancer pathobiology: Friends or foes? Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardakani, A.A.; Bureau, N.J.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Acharya, U.R. Interpretation of radiomics features-A pictorial review. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 215, 106609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomer, N.B.; Ashoobi, M.A.; Ahmadzadeh, A.M.; Sotoudeh, H.; Tabari, A.; Torigian, D.A. MRI-based Radiomics for Predicting Prostate Cancer Grade Groups: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies. Acad. Radiol. 2024, 32, 3429–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, T.; Zuo, Z.; Huang, M.; Wu, L.; Ma, J.; Huang, X.; Tang, W. Prediction of mucinous adenocarcinoma in colorectal cancer with mucinous components detected in preoperative biopsy diagnosis. Abdom. Radiol. 2024, 50, 2794–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arashi, M.; Roozbeh, M.; Hamzah, N.A.; Gasparini, M. Ridge regression and its applications in genetic studies. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, D. Data science and machine learning in anesthesiology. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2020, 73, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Frood, R.; McWilliam, A.; Davey, A.; Shortall, J.; Swinton, M.; Hulson, O.; West, C.M.; Buckley, D.; Brown, S.; et al. Prediction of prostate tumour hypoxia using pre-treatment MRI-derived radiomics: Preliminary findings. Radiol. Med. 2023, 128, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, M.; Chen, H.; Lu, Q.; Li, H.; Yan, H.; Wang, L. Machine Learning-Based Predictive Model for Mortality in Female Breast Cancer Patients Considering Lifestyle Factors. Cancer Manag. Res. 2024, 16, 1253–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borstelmann, S.M. Machine Learning Principles for Radiology Investigators. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, E.; Srinivas, S.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Armstrong, A.J.; Bekelman, J.E.; Cheng, H.; D’aMico, A.V.; Davis, B.J.; Desai, N.; Dorff, T.; et al. NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Prostate Cancer, Version 3.2024. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2024, 22, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, M.R.; Liu, K.N.; Yu, Y.; Lajkosz, K.; Kroon, L.J.; Hollemans, E.; Fleshner, N.; Finelli, A.; van Leenders, G.; Iczkowski, K.A.; et al. Addition of Cribriform and Intraductal Carcinoma Presence to Prostate Biopsy Reporting Strengthens Pretreatment Risk Stratification Using CAPRA and NCCN Tools. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2024, 22, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Kimura, T.; Onuma, H.; Egawa, S.; Takahashi, H. Transition zone prostate cancer is associated with better clinical outcomes than peripheral zone cancer. BJUI Compass 2021, 2, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garraway, L.A.; Lander, E.S. Lessons from the cancer genome. Cell 2013, 153, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.; Zhang, M.C.; Manyam, G.C.; Vykoukal, J.V.; Fahrmann, J.F.; Peng, S.; Wu, C.; Park, S.; Kondraganti, S.; Wang, D.; et al. SPOP Mutations Target STING1 Signaling in Prostate Cancer and Create Therapeutic Vulnerabilities to PARP Inhibitor-Induced Growth Suppression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 4464–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorning, B.Y.; Dass, M.S.; Smalley, M.J.; Pearson, H.B. The PI3K-AKT-mTOR Pathway and Prostate Cancer: At the Crossroads of AR, MAPK, and WNT Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.J.; Xia, Y.; Gao, Q.L. DNA Damage-driven Inflammatory Cytokines: Reprogramming of Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Application of Oncotherapy. Curr. Med. Sci. 2024, 44, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greer, M.D.; Lay, N.; Shih, J.H.; Barrett, T.; Bittencourt, L.K.; Borofsky, S.; Kabakus, I.; Law, Y.M.; Marko, J.; Shebel, H.; et al. Computer-aided diagnosis prior to conventional interpretation of prostate mpMRI: An international multi-reader study. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 4407–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
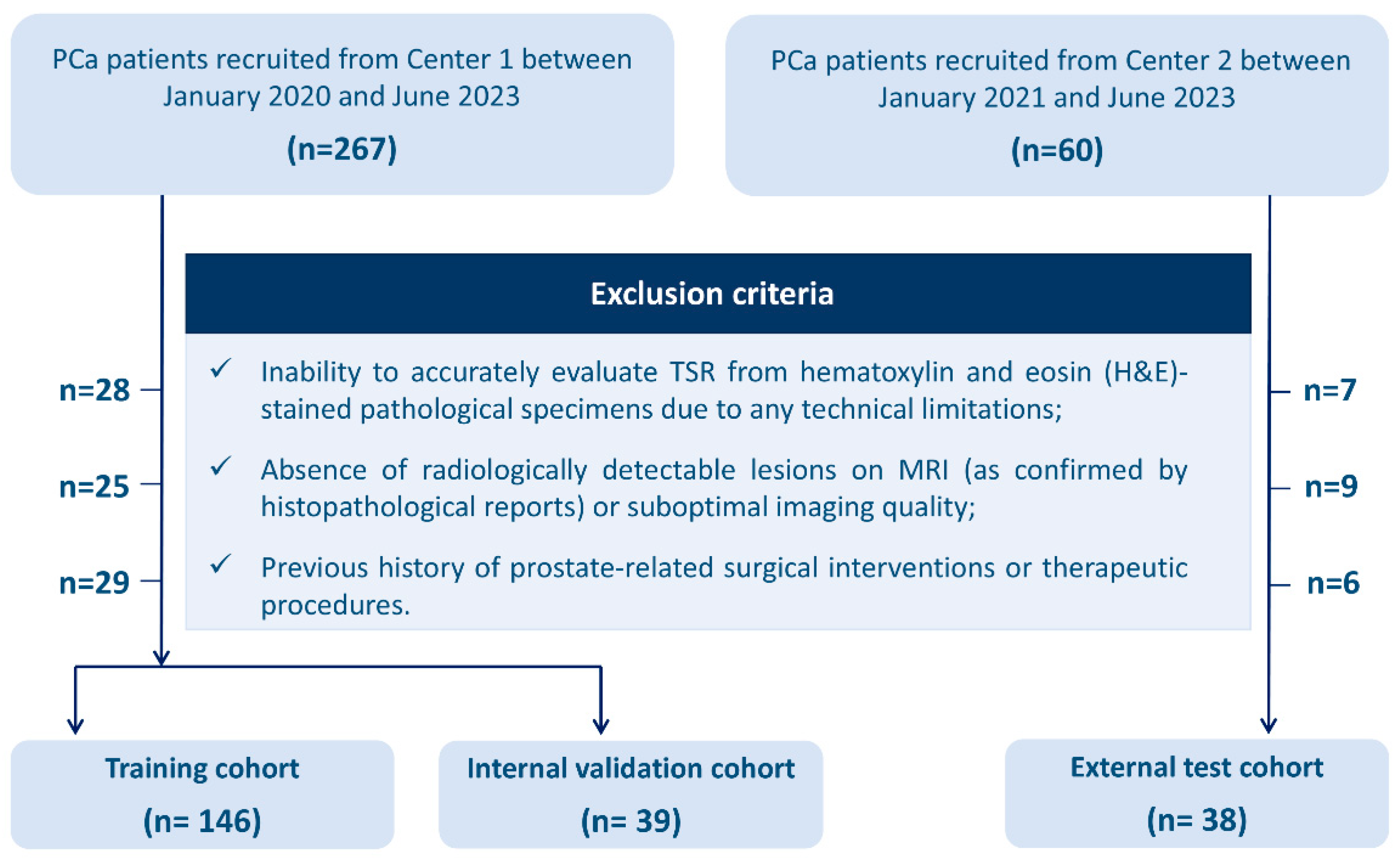


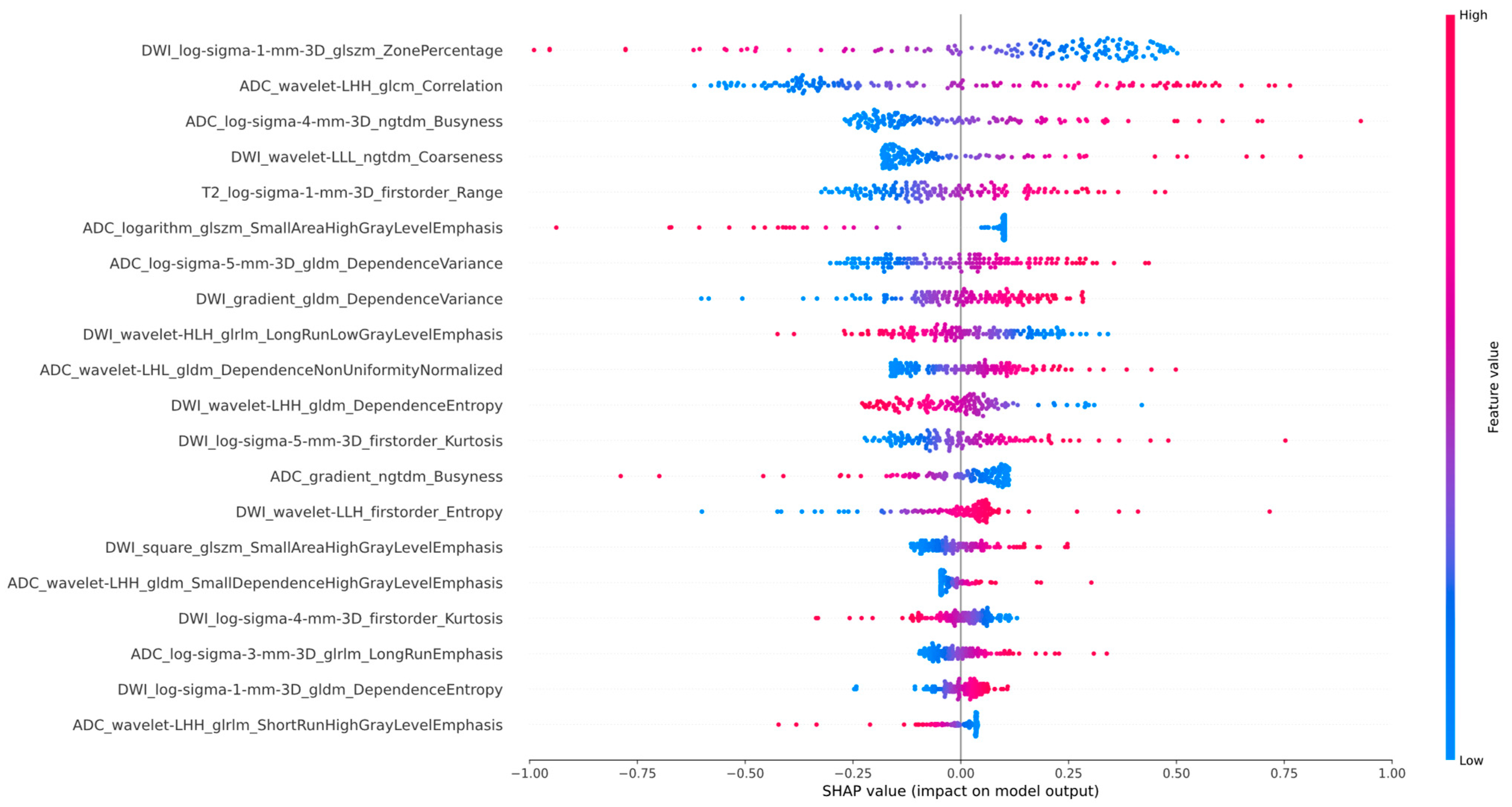
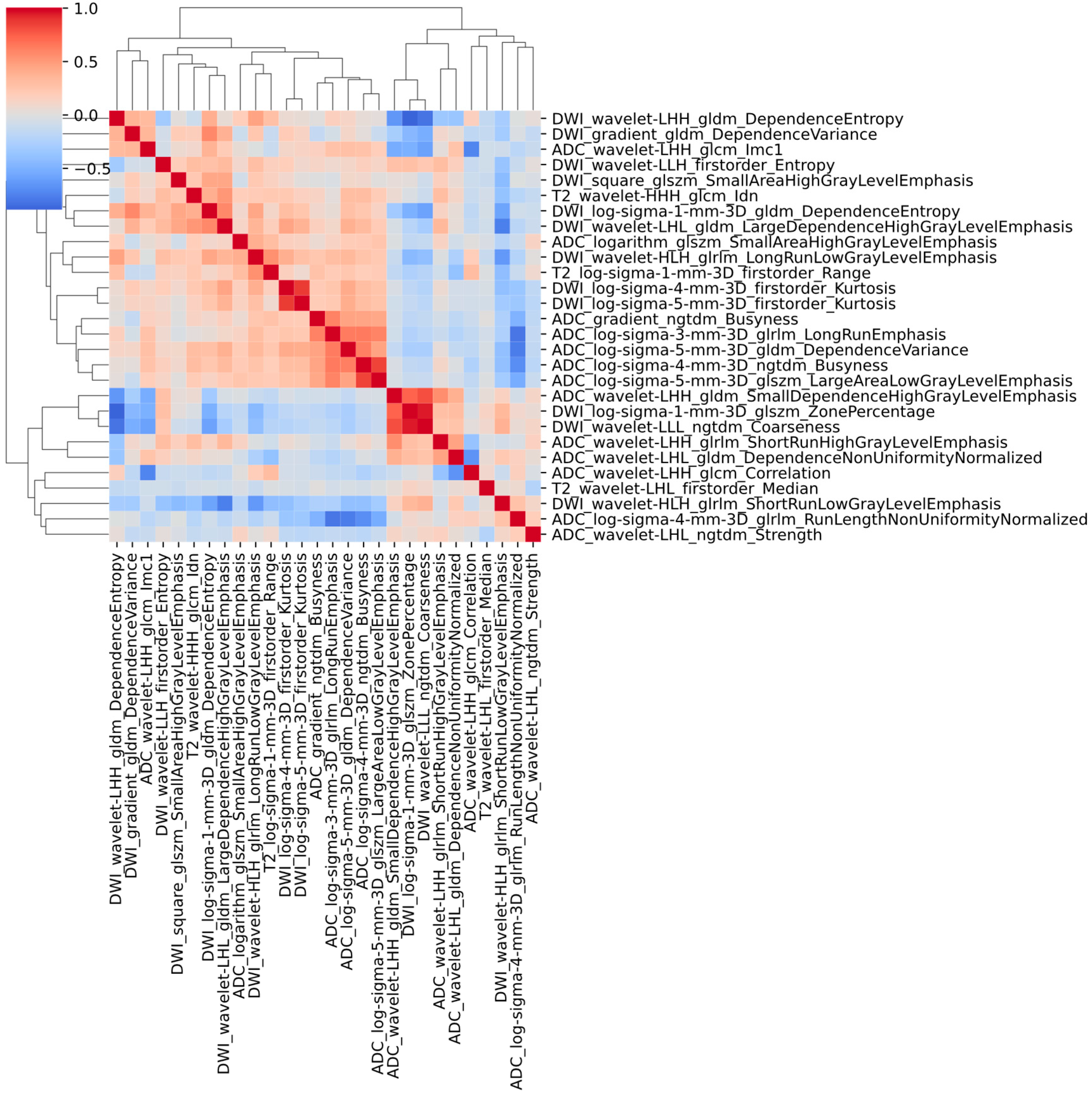

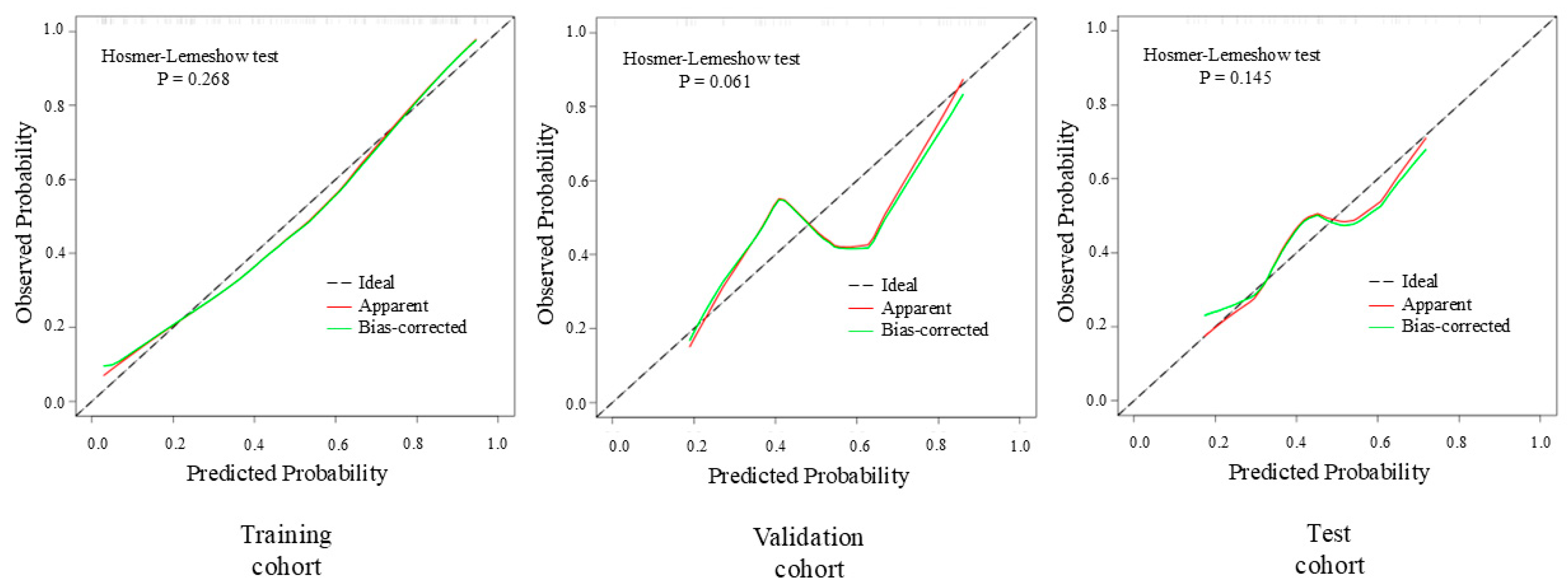
| Characteristics | Training Cohort | p-Value | Testing Cohort | p-Value | Validation Cohort | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-TSR | L-TSR | H-TSR | L-TSR | H-TSR | L-TSR | ||||
| 146 | 39 | 38 | <0.001 * | ||||||
| Case, n (%) | 74 (50.68) | 72 (49.32) | 0.907 | 20 (51.28) | 19 (48.72) | 1.000 | 21 (55.26) | 17 (33.74) | 0.491 |
| Age, mean ± SD, year | 72.43 ± 8.24 | 74.38 ± 6.69 | 72.86 ± 9.21 | 0.063 | |||||
| 72.31 ± 7.76 | 73.56 ± 8.14 | 0.858 | 71.55 ± 6.61 | 77.37 ± 5.48 | 0.005 * | 73.12 ± 8.57 | 69.67 ± 10.25 | 0.540 | |
| PSA, M(Q), ng/mL | 35.30 (11.98, 100.00) | 53.80 (13.3, 96.9) | 5.00 (3.00, 75.40) | <0.001 * | |||||
| 24.60 (11, 100.00) | 41.15 (13.30, 100.00) | 0.129 | 19.05 (10.10, 64.35) | 85.50 (36.50, 100.00) | 0.003 * | 11.20 (3.00, 100) | 5.00 (4.25, 12.24) | 0.946 | |
| fPAS, M(Q), ng/mL | 3.12 (1.21, 12.73) | 4.70 (1.74, 12.1) | 8.85 (3.08, 30.00) | 0.006 * | |||||
| 2.70 (0.89, 8.40) | 3.44 (1.32, 23.45) | 0.042 * | 1.95 (1.46, 5.20) | 6.86 (4.42, 22.90) | 0.003 * | 8.85 (1.87, 30.00) | 18.00 (4.79, 30.00) | 0.318 | |
| fPSA/PSA, M(Q) | 0.12 (0.08, 0.24) | 0.12 (0.07, 0.23) | 1.06 (0.16, 5.69) | <0.001 * | |||||
| 0.12 (0.07, 0.18) | 0.13 (0.09, 0.25) | 0.099 | 0.12 (0.07, 0.20) | 0.13 (0.07, 0.25) | 0.588 | 0.3 (0.15, 2.55) | 1.16 (0.18, 6.00) | 0.373 | |
| Prostate volume, M(Q), cm3 | 57.64 (41.13, 81.41) | 56.39 (46.74, 74.86) | 38.95 (26.63, 55.29) | <0.001 * | |||||
| 58.03 (41.02, 78.33) | 56.79 (41.71, 87.69) | 0.899 | 54.63 (43.57, 69.75) | 56.39 (48.86, 78.02) | 0.235 | 51.2 (29.52, 64.37) | 34.03 (22.57, 39.81) | 0.028 * | |
| PSAD, M(Q), ng/mL2 | 0.59 (0.23, 1.31) | 0.78 (0.24, 1.53) | 0.14 (0.05, 0.99) | 0.011 * | |||||
| 0.46 (0.18, 1.20) | 0.77 (0.27, 1.35) | 0.095 | 0.38 (0.15, 1.19) | 1.04 (0.69, 1.60) | 0.021 * | 0.31 (0.47, 1.53) | 0.14 (0.13, 0.54) | 0.876 | |
| PI-RADS score, n (%) | 0.171 | ||||||||
| 0.052 | 0.438 | 0.517 | |||||||
| 1 or 2 | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 1 (5.26) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | |||
| 3 | 12 (16.22) | 4 (5.56) | 1 (5.00) | 3 (15.79) | 2 (9.52) | 3 (17.65) | |||
| 4 | 4 (5.41) | 9 (12.50) | 3 (15.00) | 4 (21.05) | 3 (14.29) | 4 (23.53) | |||
| 5 | 58 (78.38) | 59 (81.94) | 16 (80.00) | 12 (63.16) | 16 (74.19) | 10 (58.82) | |||
| Cohorts | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | Recall (95% CI) | F1-Score | PPV | NPV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | 0.846 (0.782–0.909) | 0.80 (0.796–0.807) | 0.86 (0.852–0.871) | 0.74 (0.732–0.755) | 0.79 | 0.8 | 0.77 |
| Validation | 0.789 (0.648–0.931) | 0.72 (0.695–0.741) | 0.47 (0.422–0.525) | 0.95 (0.929–0.971) | 0.78 | 0.66 | 0.90 |
| Test | 0.745 (0.583–0.907) | 0.68 (0.660–0.708) | 0.67 (0.623–0.711) | 0.71 (0.653–0.758) | 0.67 | 0.63 | 0.74 |
| TSR | Peripheral Zone (n, %) | Transition Zone (n, %) | Cross-Zone (n, %) | Total | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-TSR | 32 (27.8%) | 35 (30.4%) | 48 (41.8%) | 115 | 0.088 |
| L-TSR | 23 (21.3%) | 24 (22.2%) | 61 (56.5%) | 108 | |
| Total | 55 (24.5%) | 59 (26.5%) | 109 (49.0%) | 223 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, J.; Gu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Ai, G.; Jia, X.; Li, Z.; Xiang, B.; et al. Advancing Prostate Cancer Assessment: A Biparametric MRI (T2WI and DWI/ADC)-Based Radiomic Approach to Predict Tumor–Stroma Ratio. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2722. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212722
Ma J, Gu X, Zhang Z, Chen J, Liu Y, Qiu Y, Ai G, Jia X, Li Z, Xiang B, et al. Advancing Prostate Cancer Assessment: A Biparametric MRI (T2WI and DWI/ADC)-Based Radiomic Approach to Predict Tumor–Stroma Ratio. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(21):2722. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212722
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Jiangqin, Xiling Gu, Zhonglin Zhang, Jun Chen, Yunfan Liu, Yang Qiu, Guangyong Ai, Xuxiang Jia, Zhenghao Li, Bo Xiang, and et al. 2025. "Advancing Prostate Cancer Assessment: A Biparametric MRI (T2WI and DWI/ADC)-Based Radiomic Approach to Predict Tumor–Stroma Ratio" Diagnostics 15, no. 21: 2722. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212722
APA StyleMa, J., Gu, X., Zhang, Z., Chen, J., Liu, Y., Qiu, Y., Ai, G., Jia, X., Li, Z., Xiang, B., & He, X. (2025). Advancing Prostate Cancer Assessment: A Biparametric MRI (T2WI and DWI/ADC)-Based Radiomic Approach to Predict Tumor–Stroma Ratio. Diagnostics, 15(21), 2722. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212722






