Correlating Patient Symptoms and CT Morphology in AI-Detected Incidental Pulmonary Embolisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Dataset
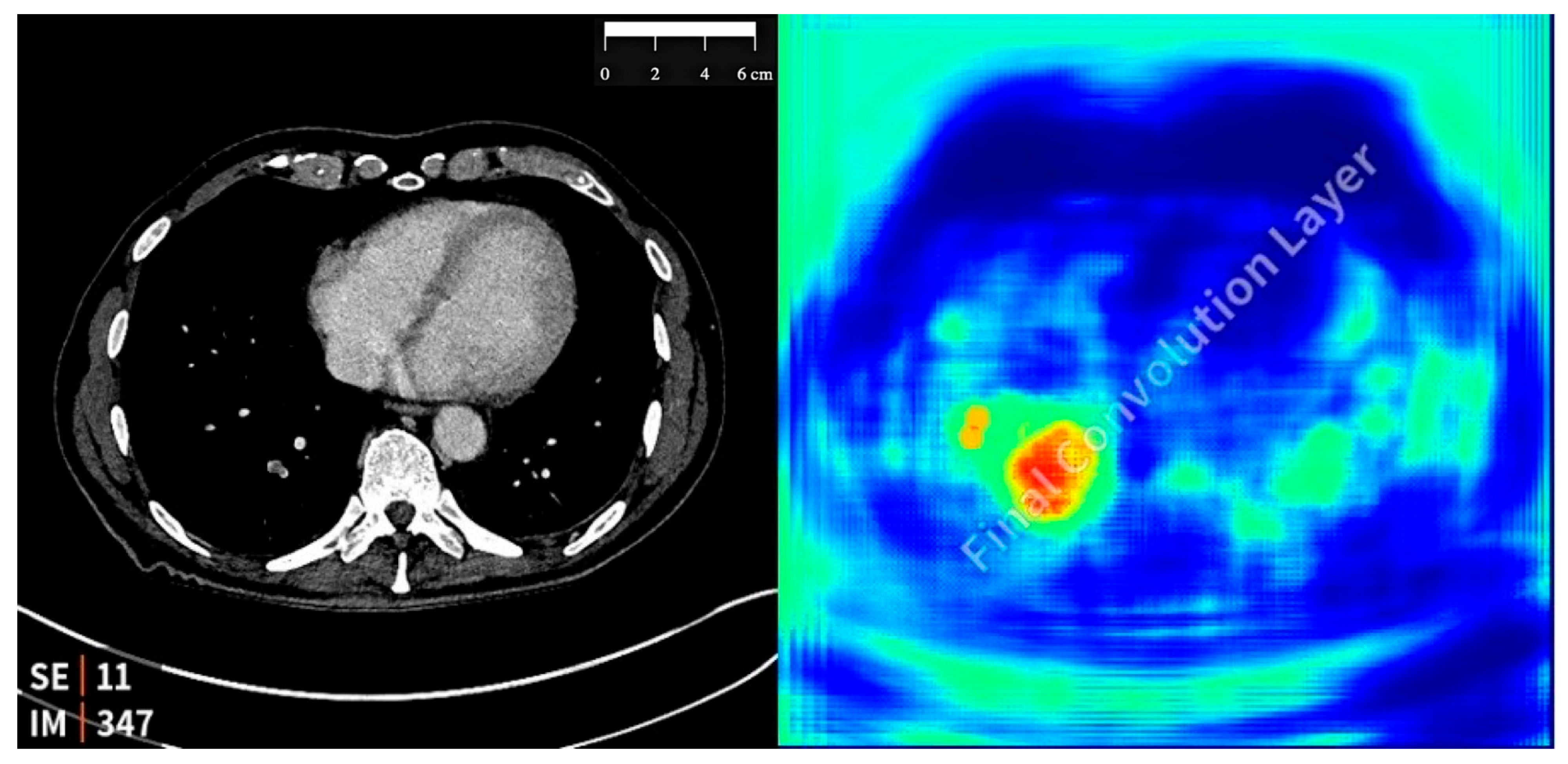
2.3. Study Design and AI Tool Implementation
2.4. Integration with Clinical Workflow
2.5. Clinical Correlation with Patient Symptoms
3. Results
3.1. Detection of Incidental Pulmonary Embolism
- A total of 25 cases (61%) involved oncological patients (15 females and 10 males);
- A total of 16 cases (39%) involved non-oncological patients (10 females and 6 males).
3.2. Symptom and CT Morphological Analysis of Oncologic Patients
3.3. Symptomatic and CT Morphological Analysis of Non-Oncologic Patients
3.4. Comparison Between Oncological and Non-Oncological Groups
4. Discussion
4.1. Principal Findings
4.2. Thrombotic Burden
4.3. Clinical Implications
4.4. Implications for Treatment
4.5. Strengths
4.6. Limitations
4.7. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute; |
| DOAJ | Directory of Open Access Journals; |
| TLA | Three-letter acronym; |
| LD | Linear dichroism; |
| IPE | Incidental pulmonary embolism; |
| PE | Pulmonary embolism; |
| AI | Artificial intelligence; |
| NLP | Natural language processing. |
References
- O’cOnnell, C. How I treat incidental pulmonary embolism. Blood 2015, 125, 1877–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, A.; Sankari, A.; Goyal, A. Acute Pulmonary Embolism; StatPearls Publishing: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Chen, C.; Chen, M.; Xin, T.; Gao, P. Pulmonary embolism presenting with itinerant chest pain and migratory pleural effusion. Medicine 2018, 97, e10944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentali, F.; Ageno, W.; Becattini, C.; Galli, L.; Gianni, M.; Riva, N.; Imberti, D.; Squizzato, A.; Venco, A.; Agnelli, G. Prevalence and Clinical History of Incidental, Asymptomatic Pulmonary Embolism: A Meta-Analysis. Thromb. Res. 2010, 125, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, H.-J.; Wienke, A.; Surov, A. Incidental pulmonary embolism in oncologic patients—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Support. Care Cancer 2021, 29, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, F.A.; Huisman, M.V. Management of incidental pulmonary embolism. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1700275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, A.G.; Meyer, H.J.; Taute, B.-M.; Surov, A. The frequency of incidental pulmonary embolism in different CT examinations. Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20150737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, H.T.; Pedersen, L.; van Es, N.; Büller, H.R.; Horváth-Puhó, E. Impact of venous thromboembolism on the mortality in patients with cancer: A population-based cohort study. Lancet Reg. Health-Eur. 2023, 34, 100739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allena, N.; Khanal, S. The Algorithmic Lung Detective: Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Embolism. Cureus 2023, 15, e51006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, K.; Xi, Y.; Al-Hreish, K.M.; Kay, F.U.; Browning, T.; Baker, C.; Peshock, R.M. Detection of Incidental Pulmonary Embolism on Conventional Contrast-Enhanced Chest CT: Comparison of an Artificial Intelligence Algorithm and Clinical Reports. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2022, 219, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammari, S.; Camez, A.O.; Ayobi, A.; Quenet, S.; Zemmouri, A.; Mniai, E.M.; Chaibi, Y.; Franciosini, A.; Clavel, L.; Bidault, F.; et al. Contribution of an Artificial Intelligence Tool in the Detection of Incidental Pulmonary Embolism on Oncology Assessment Scans. Life 2024, 14, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, M.A.; Deniz, Z.T.; Adin, M.E.; Akıl, F.; Turmak, M.; Urakcı, Z.; Cetincakmak, M.G.; Goya, C. Detection of incidental pulmonary embolism with multi-slice computed tomography in cancer patients. Clin. Imaging 2017, 41, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doo, F.; Moore, J.; Kagen, A.; Zink, S.; Somwaru, A.S. Society of Thoracic Radiology Abstracts from the 2020 Annual Meeting and Postgraduate Course March 8–11, 2020 Hyatt Regency Indian Wells Resort & Spa in Indian Wells, California. J. Thorac. Imaging 2020, 35, W130–W180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheikh, A.B.; Gorincour, G.; Nivet, H.; May, J.; Seux, M.; Calame, P.; Thomson, V.; Delabrousse, E.; Crombé, A. How artificial intelligence improves radiological interpretation in suspected pulmonary embolism. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 5831–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimian, S.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Homayounieh, F.; Bizzo, B.C.; Dreyer, K.J.; Kalra, M.K. Predictive values of AI-based triage model in suboptimal CT pulmonary angiography. Clin. Imaging 2022, 86, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhtanen, H.; Nyman, M.; Mohsen, T.; Virkki, A.; Karlsson, A.; Hirvonen, J. Automated detection of pulmonary embolism from CT-angiograms using deep learning. BMC Med. Imaging 2022, 22, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weikert, T.; Winkel, D.J.; Bremerich, J.; Stieltjes, B.; Parmar, V.; Sauter, A.W.; Sommer, G. Automated detection of pulmonary embolism in CT pulmonary angiograms using an AI-powered algorithm. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6545–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinel, F.G.; Nance, J.W.; Schoepf, U.J.; Hoffmann, V.S.; Thierfelder, K.M.; Costello, P.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; Bamberg, F. Predictive Value of Computed Tomography in Acute Pulmonary Embolism: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am. J. Med. 2015, 128, 747–759.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, L.; Tan, J.; Fang, W.; Ma, X.; Guo, T.; Gao, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Asymptomatic recurrence in patients with pulmonary embolism. Chin. Med. J. 2024, 137, 1118–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, M.V.; Barco, S.; Cannegieter, S.C.; Le Gal, G.; Konstantinides, S.V.; Reitsma, P.H.; Rodger, M.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Klok, F.A. Pulmonary embolism. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 18028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaker, D.; Douglas, E.; Blazak, J.; Xu, W.; Hughes, B.; Burge, M.; Steinke, K.; Wyld, D. An analysis of incidental and symptomatic pulmonary embolism (PE) in medical oncology patients: Is incidental pulmonary embolism common? Asia-Pacific J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 13, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westafer, L.M.; Vinson, D.R. Risk for Recurrent Venous Thromboembolism in Patients With Subsegmental Pulmonary Embolism Managed Without Anticoagulation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2022, 175, W43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’connell, C.; Razavi, P.; Ghalichi, M.; Boyle, S.; Vasan, S.; Mark, L.; Caton, A.; Duddalwar, V.; Boswell, W.; Grabow, K.; et al. Unsuspected pulmonary emboli adversely impact survival in patients with cancer undergoing routine staging multi-row detector computed tomography scanning. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupinski, E.A. Current perspectives in medical image perception. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2010, 72, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundel, H.L.; Nodine, C.F.; Carmody, D. Visual Scanning, Pattern Recognition and Decision-making in Pulmonary Nodule Detection. Investig. Radiol. 1978, 13, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langius-Wiffen, E.; de Jong, P.A.; Hoesein, F.A.M.; Dekker, L.; Hoven, A.F.v.D.; Nijholt, I.M.; Boomsma, M.F.; Veldhuis, W.B. Added value of an artificial intelligence algorithm in reducing the number of missed incidental acute pulmonary embolism in routine portal venous phase chest CT. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 34, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklund, P.; Medson, K. Incidental pulmonary embolism in abdominal CT: Detection rate and characteristics with artificial intelligence. Radiol. Adv. 2024, 1, umae009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Bindman, R.; Miglioretti, D.L.; Larson, E.B. Rising Use of Diagnostic Medical Imaging in a Large Integrated Health System. Health Aff. 2008, 27, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crobach, M.J.T.; Anijs, R.J.S.; Brækkan, S.K.; Severinsen, M.T.; Hammerstrøm, J.; Skille, H.; Kristensen, S.R.; Paulsen, B.; Tjønneland, A.; Versteeg, H.H.; et al. Survival after cancer-related venous thrombosis: The Scandinavian Thrombosis and Cancer Study. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 4072–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysokinska, E.M.; Houghton, D.E.; Vlazny, D.T.; Ashrani, A.A.; Froehling, D.A.; Meverden, R.; Hodge, D.O.; Peterson, L.G.; McBane, R.D.; Wysokinski, W.E.; et al. Incidental pulmonary embolism in cancer and noncancer patients: Prospective cohort study. Eur. J. Haematol. 2023, 110, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklund, P.; Medson, K.; Elf, J. Incidental pulmonary embolism in patients with cancer: Prevalence, underdiagnosis and evaluation of an AI algorithm for automatic detection of pulmonary embolism. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 33, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, S.M.; Woller, S.C.; Kreuziger, L.B.; Doerschug, K.; Geersing, G.-J.; Klok, F.A.; King, C.S.; Murin, S.; Vintch, J.R.; Wells, P.S.; et al. Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease. Chest 2024, 166, 388–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, M.; Yamashita, Y. Incidental Pulmonary Embolism―How Should We Treat It?―. Circ. J. 2024, 88, 205–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouleau, S.G.; Balasubramanian, M.J.; Huang, J.; Antognini, T.; Reed, M.E.; Vinson, D.R. Prevalence of and Eligibility for Surveillance Without Anticoagulation Among Adults With Lower-Risk Acute Subsegmental Pulmonary Embolism. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2326898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Razeq, H.N.; Mansour, A.H.; Ismael, Y.M. Incidental pulmonary embolism in cancer patients: Clinical characteristics and outcome—A comprehensive cancer center experience. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2011, 7, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storto, M.L.; Di Credico, A.; Guido, F.; Larici, A.R.; Bonomo, L. Incidental Detection of Pulmonary Emboli on Routine MDCT of the Chest. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2005, 184, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Order and Number of Arteries Involved | Location | Mastora | Qanadli | Ghanima | Kirchner | RV/LV | PA/AO | SVC | Azygos Vein | Anti Coagulation | Symptom Listed | Recurrent PE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 segmental | RL | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.77 | 0.88 | 12 mm | 8 mm | Yes | No | No |
| 1 segmental | RUL | 151 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0.68 | 0.77 | 14 mm | 7 mm | Yes | No | No |
| 1 segmental | Lingula | 151 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.91 | 0.63 | 11 mm | 6 mm | Yes | No | No |
| 1 segmental | ML | 152 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.86 | 0.55 | 11 mm | 6 mm | Yes | No | No |
| 1 lobar and 1 segmental | RL | 150 | 8 | 5 | 1 | 0.53 | 0.89 | 15 mm | 6 mm | No | No | Yes (progress) |
| 1 lobar and 1 segmental | LLL | 145 | 9 | 10 | 2 | 0.69 | 0.82 | 14 mm | 4 mm | No | No | No |
| 1 segmental | RLL | 152 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.78 | 0.69 | 12 mm | 6 mm | Yes | No | Yes |
| 1 segmental | RLL | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.57 | 0.87 | 11 mm | 7 mm | Yes | Yes (Dyspnea) | No |
| 1 segmental | RLL | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.72 | 0.64 | 9 mm | 6 mm | No | No | Yes |
| 3 segmental | ML | 151 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 0.66 | 0.81 | 18 mm | 7 mm | Yes | No | No |
| 2 segmental | LLL | 149 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 0.75 | 0.70 | 9 mm | 7 mm | No | No | No |
| 2 segmental | LLL | 149 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 0.52 | 0.90 | 12 mm | 6 mm | Yes | No | No |
| 1 segmental | ML | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.80 | 0.72 | 13 mm | 6 mm | Yes | No | No |
| 1 segmental | RL | 152 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.74 | 0.83 | 13 mm | 6 mm | Yes | No | No |
| 1 segmental | RL | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.93 | 0.75 | 13 mm | 5 mm | No | No | No |
| 1 segmental | RL | 152 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.59 | 0.70 | 17 mm | 8 mm | Yes | No | No |
| 1 segmental | RL | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.73 | 0.88 | 13 mm | 7 mm | No | No | No |
| 1 segmental | RL | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.88 | 0.76 | 12 mm | 8 mm | No | No | No |
| 1 segmental | ML | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.80 | 0.72 | 13 mm | 6 mm | No | No | No |
| 1 segmental | RL | 153 | 7 | 3 | 0 | 0.52 | 0.89 | 15 mm | 7 mm | No | Yes (Dyspnea) | No |
| 1 segmental | RL | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.78 | 0.88 | 11 mm | 7 mm | Yes | No | No |
| 1 segmental | RUL | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.56 | 0.75 | 9 mm | 7 mm | Yes | No | No |
| 1 segmental | RL | 152 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.85 | 0.75 | 10 mm | 6 mm | No | No | No |
| 1 segmental | RL | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.56 | 0.87 | 9 mm | 6 mm | No | No | No |
| 1 segmental | RUL | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.82 | 0.62 | 12 mm | 8 mm | Yes | No | No |
| Order and Number of Arteries Involved | Location | Mastora | Qanadli | Ghanima | Kirchner | RV/LV | PA/AO | SVC | Azygos Vein | Anticoagulation | Symptom Listed | Recurrent PE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 segmental | ML | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.78 | 0.88 | 13 mm | 9 mm | No | No | No |
| 1 segmental | RLL | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.63 | 0.79 | 8 mm | 7 mm | Yes | No | No |
| 2 segmental | RLL | 150 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0.90 | 0.97 | 17 mm | 7 mm | Yes | No | No |
| 1 lobar and 2 segmental | RLL | 151 | 2 | 7 | 2 | 0.78 | 0.65 | 20 mm | 6 mm | No | No | No |
| 1 segmental | Lingula | 152 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.83 | 0.67 | 12 mm | 4 mm | Yes | Yes (Hypoxia/tachycardia) | No |
| 1 segmental | RLL | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.81 | 0.72 | 15 mm | 5 mm | No | No | No |
| 1 segmental | RLL | 151 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0.41 | 0.89 | 14 mm | 6 mm | Yes | No | No |
| 1 segmental | RLL | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.91 | 0.71 | 12 mm | 5 mm | No | No | No |
| 1 segmental | RLL | 154 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 0.82 | 0.71 | 10 mm | 8 mm | No | Yes (tightness in chest) | No |
| 1 segmental | RLL | 151 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 25 mm | 6 mm | No | No | No |
| 1 segmental | ML | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.72 | 0.62 | 12 mm | 7 mm | No | No | No |
| 1 segmental | LUL | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.55 | 0.87 | 10 mm | 6 mm | Yes | No | No |
| 1 segmental | RUL | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.78 | 0.87 | 11 mm | 5 mm | No | No | No |
| 1 lobar and 1 segmental | RLL | 151 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 0.82 | 0.78 | 12 mm | 7 mm | Yes | No | No |
| 2 segmental | ML and RLL | 151 | 7 | 3 | 0 | 0.87 | 0.84 | 13 mm | 9 mm | Yes | No | No |
| 1 Segmental | RUL | 153 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 11 mm | 7 mm | No | No | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abed, S.; Brandstetter, L.; Hergan, K. Correlating Patient Symptoms and CT Morphology in AI-Detected Incidental Pulmonary Embolisms. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131639
Abed S, Brandstetter L, Hergan K. Correlating Patient Symptoms and CT Morphology in AI-Detected Incidental Pulmonary Embolisms. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(13):1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131639
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbed, Selim, Lucas Brandstetter, and Klaus Hergan. 2025. "Correlating Patient Symptoms and CT Morphology in AI-Detected Incidental Pulmonary Embolisms" Diagnostics 15, no. 13: 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131639
APA StyleAbed, S., Brandstetter, L., & Hergan, K. (2025). Correlating Patient Symptoms and CT Morphology in AI-Detected Incidental Pulmonary Embolisms. Diagnostics, 15(13), 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131639





