Enhancing Predictive Tools for Skeletal Growth and Craniofacial Morphology in Syndromic Craniosynostosis: A Focus on Cranial Base Variables
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Characteristics of Craniofacial Region Between SC and Controls
3.1.1. Demographic Data
3.1.2. Craniofacial Morphology
3.2. The Predictive Tool of Skeletal Growth
3.2.1. Variables Selection
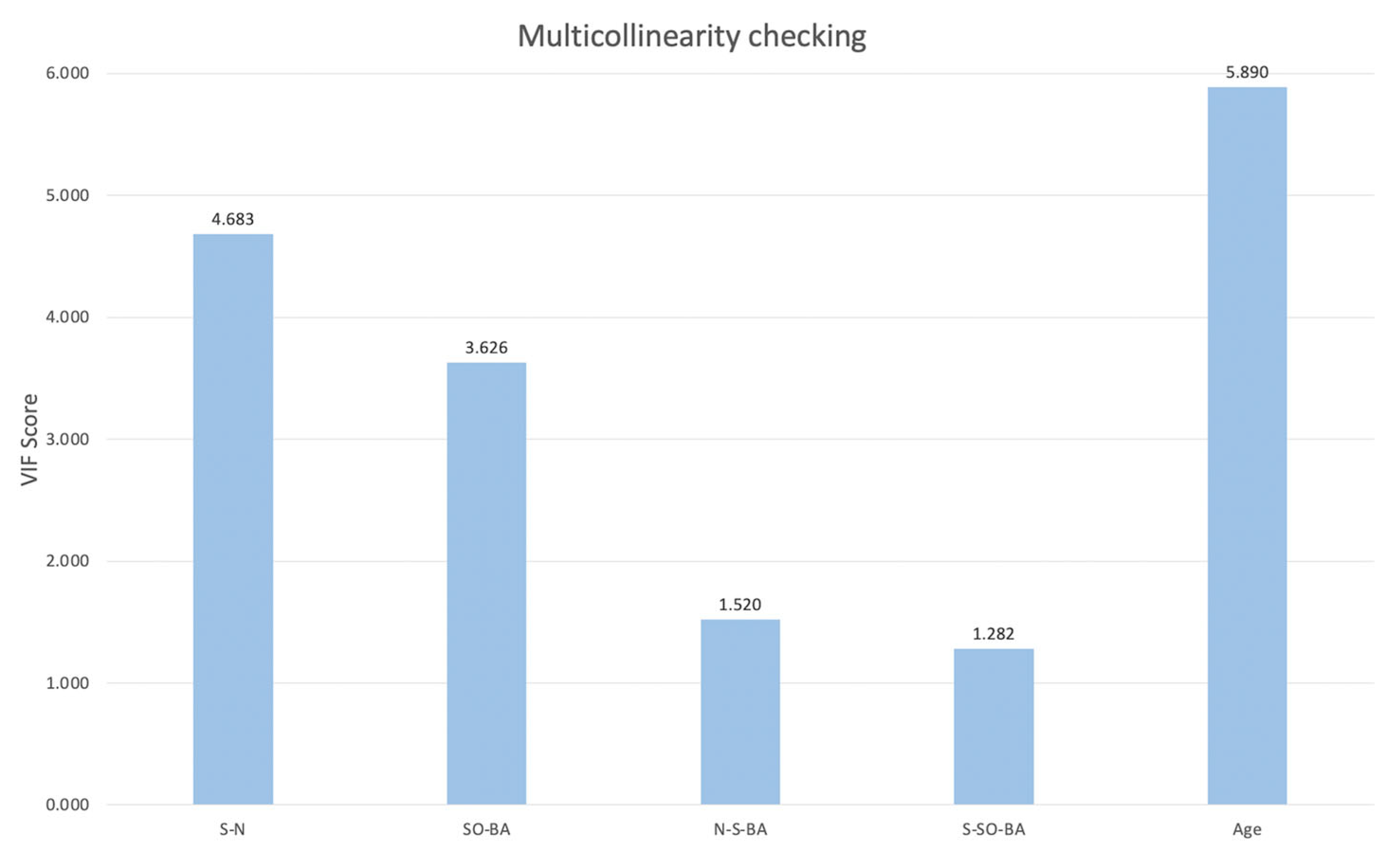
3.2.2. Correlation Analysis and Multicollinearity Checking
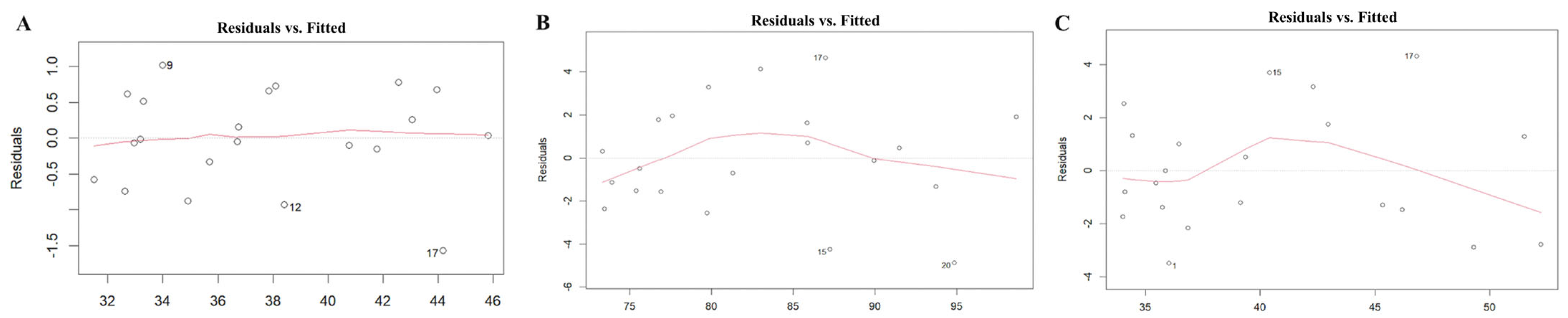
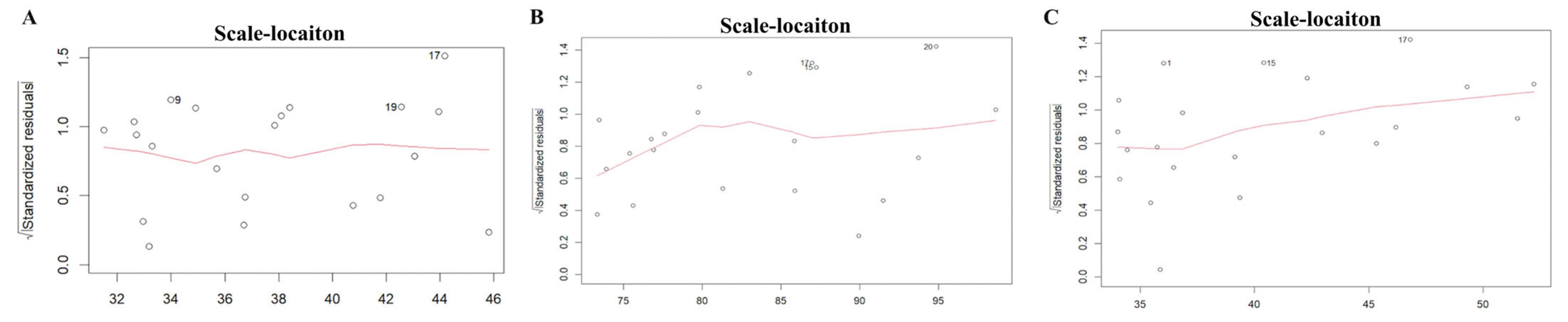
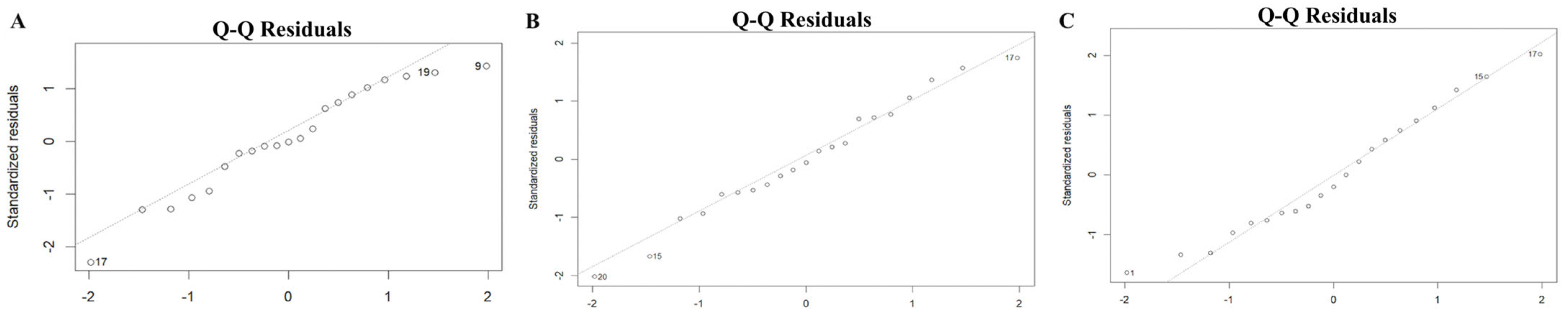
3.2.3. Model Fitting and Adequacy
3.2.4. Multiple Regression Models and Cross-Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANS | anterior nasal spine |
| ANS-PNS | the distance between anterior and posterior nasal spine points |
| BA | basion |
| CT | computed tomographic |
| IQR | interquartile range (25–75%) |
| MAE | mean absolute error |
| N | nasion |
| N-ANS | the distance between the nasion and anterior nasal spine points |
| N-BA | the distance between the nasion and basion points |
| N-S-BA | the angle formed by the nasion, sella, and basion points |
| N-S-SO | the angle formed by the nasion, the sella, and spheno-occipital synchondrosis |
| N-SO | the distance between the nasion and pheno-occipital synchondrosis |
| N-SO-BA | the angle formed by the nasion, spheno-occipital synchondrosis, and the basion |
| PNS | posterior nasal spine |
| RMSE | root mean square error |
| S | sella |
| S-BA | the distance between the sella and basion |
| SC | syndromic craniosynostosis |
| S-N | the distance between the sella and nasion |
| S-SO | the distance between the sella and spheno-occipital synchondrosis |
| S-SO-BA | the angle formed by the sella, spheno-occipital synchondrosis, and the basion |
| SO | spheno-occipital synchondrosis |
| SO-BA | the distance between spheno-occipital synchondrosis and the basion |
| VIF | Variance Inflation Factor |
| ZF(L/R) | zygomaticofrontal suture |
| ZFL-ZFR | the length between the bilateral zygomaticofrontal suture |
| ZMs-ZTi | the length between the zygomaticomaxillary suture and zygomaticotemporal suture |
| ZMs(L/R) | zygomaticomaxillary suture |
| ZMsL-ZMsR | the length between the bilateral zygomaticomaxillary suture |
| ZTi(L/R) | zygomaticotemporal suture |
| ZX-ZF | the height between the zygomatic point and zygomaticofrontal suture |
| ZX(L/R) | zygomatic point |
References
- Tonne, E.; Due-Tonnessen, B.J.; Wiig, U.; Stadheim, B.F.; Meling, T.R.; Helseth, E.; Heimdal, K.R. Epidemiology of craniosynostosis in Norway. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2020, 26, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yapijakis, C.; Pachis, N.; Sotiriadou, T.; Vaila, C.; Michopoulou, V.; Vassiliou, S. Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Craniosynostosis. Vivo 2023, 37, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, J.W.; Samra, F.; Bauder, A.; Mitchell, B.T.; Taylor, J.A.; Bartlett, S.P. An Algorithm for Managing Syndromic Craniosynostosis Using Posterior Vault Distraction Osteogenesis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 137, 829E–841E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitsma, J.H.; Ongkosuwito, E.M.; Buschang, P.H.; Prahl-Andersen, B. Facial growth in patients with apert and crouzon syndromes compared to normal children. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2012, 49, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Forte, A.J.; Sawh-Martinez, R.; Wu, R.; Cabrejo, R.; Wilson, A.; Steinbacher, D.M.; Alperovich, M.; Alonso, N.; Persing, J.A. Spatial and temporal changes of midface in Apert’s syndrome. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2019, 53, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri, F.; Malek, R.A.; Abdullah, N.A.; Hassan, S.F. Midface hypoplasia in syndromic craniosynostosis: Predicting craniofacial growth via a novel regression model from anatomical morphometric analysis. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 53, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, A.J.; Alonso, N.; Persing, J.A.; Pfaff, M.J.; Brooks, E.D.; Steinbacher, D.M. Analysis of Midface Retrusion in Crouzon and Apert Syndromes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 134, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Forte, A.J.; Sawh-Martinez, R.; Wu, R.; Cabrejo, R.; Gabrick, K.; Steinbacher, D.M.; Alperovich, M.; Alonso, N.; Persing, J.A. Temporal Evaluation of Craniofacial Relationships in Apert Syndrome. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2019, 30, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Ogura, K.; Hikita, R.; Tsuji, M.; Moriyama, K. Craniofacial, oral, and cervical morphological characteristics in Japanese patients with Apert syndrome or Crouzon syndrome. Eur. J. Orthod. 2021, 43, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.K.; Alfawzan, A.A.; Srivastava, K.C.; Shrivastava, D.; Ganji, K.K.; Manay, S.M. Craniofacial morphology in Apert syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.J.; McLaughlin, C.; Thompson, J.T. Analysis of Cranial Base Suture Fusion Patterns. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2021, 32, 1679–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calandrelli, R.; Pilato, F.; Massimi, L.; Panfili, M.; D’Apolito, G.; Gaudino, S.; Colosimo, C. Quantitative evaluation of facial hypoplasia and airway obstruction in infants with syndromic craniosynostosis: Relationship with skull base and splanchnocranium sutural pattern. Neuroradiology 2018, 60, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, B.K.; Choi, D.S.; Jang, I.S.; Yook, H.T.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, S.K. Aberrant growth of the anterior cranial base relevant to severe midface hypoplasia of Apert syndrome. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 40, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Forte, A.J.; Wilson, A.T.; Park, K.E.; Allam, O.; Mozaffari, M.A.; Alperovich, M.; Steinbacher, D.M.; Alonso, N.; Persing, J.A. What Is the Difference in Cranial Base Morphology in Isolated and Syndromic Bicoronal Synostosis? Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 146, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Forte, A.J.; Sawh-Martinez, R.; Wu, R.; Cabrejo, R.; Steinbacher, D.M.; Alperovich, M.; Alonso, N.; Persing, J.A. Orbit, zygoma, and maxilla growth patterns in Crouzon syndrome. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, K.; Singh, N.; Richtsmeier, J.T. Understanding craniosynostosis as a growth disorder. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2016, 5, 429–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramrud, L. External and internal cranial base: A cross sectional study of growth and of association in form. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2009, 17, 239–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayatian, M.; Azarbayejani, S.; Omrani, A.; Etemadi Borujeni, S. Correlation of Clivus Length and Angle with Chronological Age, Gender, Sagittal Growth Pattern of the Jaws, and Skeletal Maturation Using Lateral Cephalometry. J. Dent. 2023, 25, 251–261. [Google Scholar]
- al-Qattan, M.M.; Phillips, J.H. The cranial base angle and maxillary hypoplasia in unoperated Crouzon patients. J. Craniofac. Surg. 1996, 7, 69–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enlow, D.H.; Kuroda, T.; Lewis, A.B. The morphological and morphogenetic basis for craniofacial form and pattern. Angle Orthod. 1971, 41, 161–188. [Google Scholar]
- Kakutani, H.; Sato, Y.; Tsukamoto-Takakusagi, Y.; Saito, F.; Oyama, A.; Iida, J. Evaluation of the maxillofacial morphological characteristics of Apert syndrome infants. Congenit. Anom. 2017, 57, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreiborg, S.; Marsh, J.L.; Cohen, M.M., Jr.; Liversage, M.; Pedersen, H.; Skovby, F.; Borgesen, S.E.; Vannier, M.W. Comparative three-dimensional analysis of CT-scans of the calvaria and cranial base in Apert and Crouzon syndromes. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 1993, 21, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushida, C.A.; Efron, B.; Guilleminault, C. A predictive morphometric model for the obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Ann. Intern. Med. 1997, 127 Pt 1, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.; Aleem, F.; Ormiston, I.W. Does the Kushida morphometric model predict outcomes following maxillomandibular advancement surgery for obstructive sleep apnoea? J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 1675–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posnick, J.C.; Ruiz, R.L. The craniofacial dysostosis syndromes: Current surgical thinking and future directions. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2000, 37, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
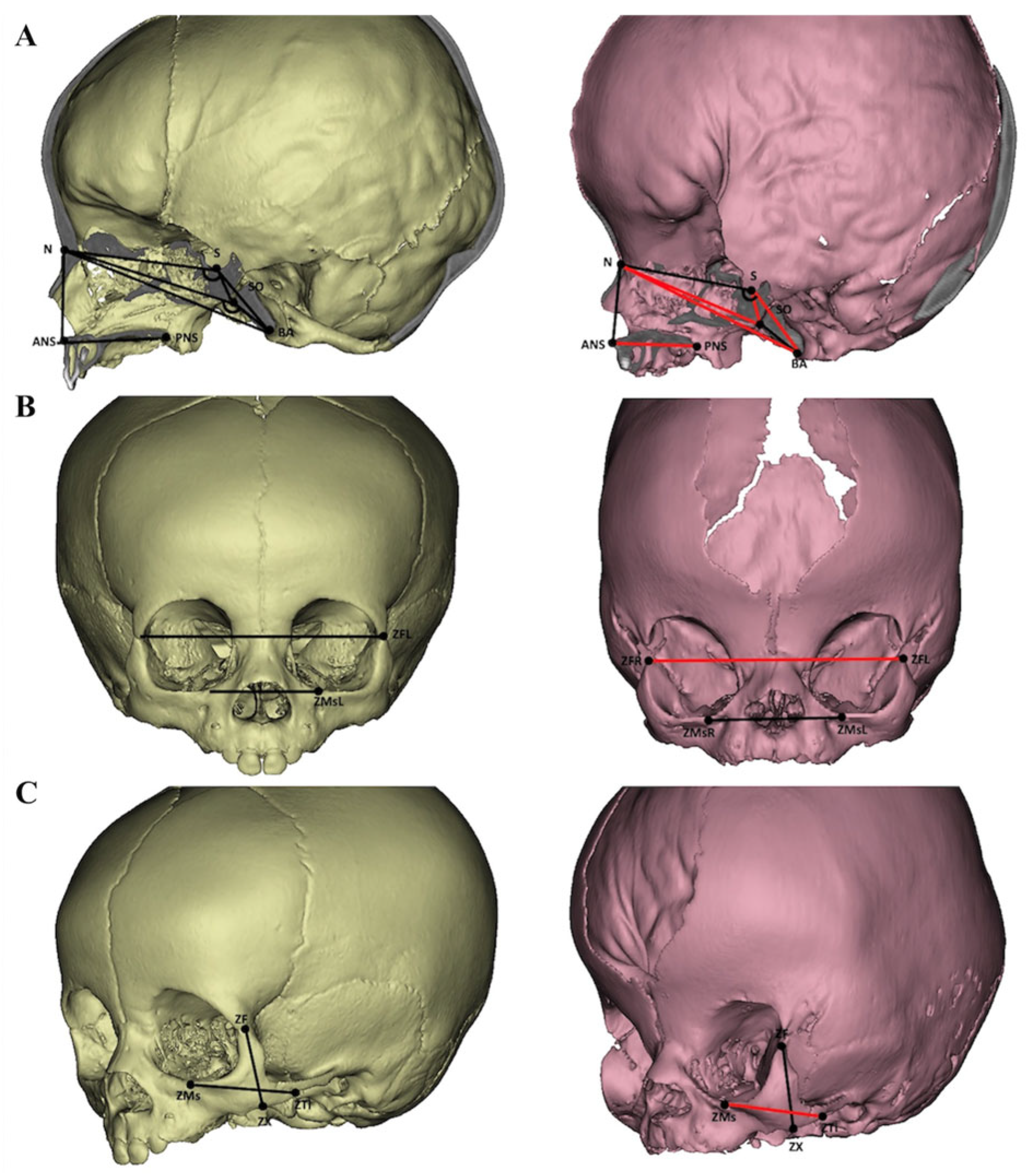
| Abbreviations | Name | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| ANS | Anterior nasal spine | It is the anterior tip of the sharp bony process of the maxilla |
| BA | Basion | The most inferior and posterior point on the most anterior margin of the foramen magnum |
| N | Nasion | The most anterior and canter point where the frontal and two nasal bones meet |
| PNS | Posterior nasal spine | The most posterior midpoint of the posterior nasal spine of the palatine bone |
| S | Sella | The lowest and center point of the hypophyseal fossa |
| SO | Spheno-occipital synchondrosis | The most anterior point on the midline of the occipital bone at the spheno-occipital synchondrosis |
| ZF(L/R) | Zygomaticofrontal suture | The intersection points of the zygomatic frontal suture on both sides |
| ZMs(L/R) | Zygomaticomaxillary suture | The point at the zygomaticomaxillary suture on the inferior orbital rim on each side |
| ZTi(L/R) | Zygomaticotemporal suture | The inferior point of the zygomaticotemporal suture |
| ZX(L/R) | Zygomatic point | The most middle point of the inferior border of the zygomatic bone |
| SC | Control | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Median | IQR | Median | IQR | D | D (%) | p-Value |
| Cranial base | |||||||
| N-BA | 67.22 | (63.41, 73.25) | 73.65 | (69.71, 82.89) | −6.43 | 91% | 0.014 * |
| N-S-BA | 138.21 | (128.00, 141.11) | 140.80 | (137.66, 144.73) | −2.58 | 98% | 0.054 |
| N-S-SO | 117.48 | (108.09, 127.74) | 127.09 | (120.63, 130.54) | −9.60 | 92% | 0.031 * |
| N-SO | 52.90 | (50.48, 61.64) | 59.87 | (56.29, 64.27) | −6.97 | 88% | 0.013 * |
| N-SO-BA | 157.75 | (151.64, 162.45) | 166.16 | (162.17, 169.76) | −8.41 | 95% | 0.002 ** |
| S-BA | 23.83 | (21.77, 26.12) | 27.82 | (25.73, 31.39) | −3.99 | 86% | 0.001 ** |
| S-N | 47.10 | (44.72, 54.60) | 49.86 | (47.06, 55.64) | −2.76 | 94% | 0.264 |
| S-SO | 10.53 | (9.65, 11.20) | 14.34 | (12.85, 15.33) | −3.81 | 73% | 0.000 ** |
| S-SO-BA | 146.52 | (143.66, 156.12) | 151.57 | (147.45, 153.66) | −5.05 | 97% | 0.195 |
| SO-BA | 14.56 | (12.59, 16.51) | 14.28 | (13.09, 17.35) | 0.29 | 102% | 0.601 |
| Midface | |||||||
| ANS-PNS | 29.74 | (27.79, 34.39) | 35.19 | (33.20, 38.50) | −5.45 | 85% | 0.003 ** |
| N-ANS | 32.29 | (27.34, 38.50) | 32.08 | (29.04, 38.86) | 0.21 | 101% | 0.471 |
| ZMsL-ZMsR | 42.61 | (38.94, 48.54) | 42.43 | (38.65, 47.28) | 0.18 | 100% | 0.986 |
| ZFL-ZFR | 87.11 | (80.76, 94.12) | 79.05 | (74.19, 87.00) | 8.06 | 110% | 0.034 * |
| ZMs-ZTi | 32.11 | (30.01, 40.08) | 36.23 | (34.44, 43.01) | −4.12 | 89% | 0.044 * |
| ZX-ZF | 31.11 | (28.84, 33.70) | 30.80 | (27.47, 34.51) | 0.31 | 101% | 0.857 |
| Variables | S-N | SO-BA | N-S-BA | S-SO-BA | Age |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANS-PNS | 0.891 | 0.916 | −0.605 | −0.315 | 0.951 |
| ZFL-ZFR | 0.884 | 0.816 | −0.384 | −0.244 | 0.912 |
| ZMs-ZTi | 0.854 | 0.856 | −0.329 | −0.233 | 0.902 |
| Measurement | Model | R2 | Adjusted R2 | LOOCV | 3-Fold | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | R2 | MAE | RMSE | R2 | MAE | ||||
| Midface Length | ANS-PNS = 23.976 + 0.139 S-N + 0.545 SO-BA − 0.120 N-S-BA + 0.078 S-SO-BA + 0.051 Age | 0.978 | 0.971 | 0.904 | 0.959 | 0.736 | 1.058 | 0.945 | 0.843 |
| Midface Width | ZFL-ZFR = −15.618 + 0.666 S-N + 0.241 N-S-BA + 0.155 S-SO-BA + 0.121 Age | 0.903 | 0.879 | 3.191 | 0.874 | 2.679 | 3.158 | 0.840 | 2.584 |
| Zygoma Length | ZMs-ZTi = −14.403 + 0.765 SO-BA + 0.266 N-S-BA + 0.111 Age | 0.878 | 0.857 | 2.824 | 0.798 | 2.409 | 3.720 | 0.947 | 3.076 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, L.; Abdullah, N.A.; Ramli, N.M.; Mohamed, N.A.; Hisam, M.N.F.; Hariri, F. Enhancing Predictive Tools for Skeletal Growth and Craniofacial Morphology in Syndromic Craniosynostosis: A Focus on Cranial Base Variables. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131640
Zheng L, Abdullah NA, Ramli NM, Mohamed NA, Hisam MNF, Hariri F. Enhancing Predictive Tools for Skeletal Growth and Craniofacial Morphology in Syndromic Craniosynostosis: A Focus on Cranial Base Variables. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(13):1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131640
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Lantian, Norli Anida Abdullah, Norlisah Mohd Ramli, Nur Anisah Mohamed, Mohamad Norikmal Fazli Hisam, and Firdaus Hariri. 2025. "Enhancing Predictive Tools for Skeletal Growth and Craniofacial Morphology in Syndromic Craniosynostosis: A Focus on Cranial Base Variables" Diagnostics 15, no. 13: 1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131640
APA StyleZheng, L., Abdullah, N. A., Ramli, N. M., Mohamed, N. A., Hisam, M. N. F., & Hariri, F. (2025). Enhancing Predictive Tools for Skeletal Growth and Craniofacial Morphology in Syndromic Craniosynostosis: A Focus on Cranial Base Variables. Diagnostics, 15(13), 1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131640






