Development and Validation of an Ultrasound-Based Radiomics Nomogram for Identifying HER2 Status in Patients with Breast Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Cohorts
2.2. Pathological Assessment
2.3. Clinical Characteristics
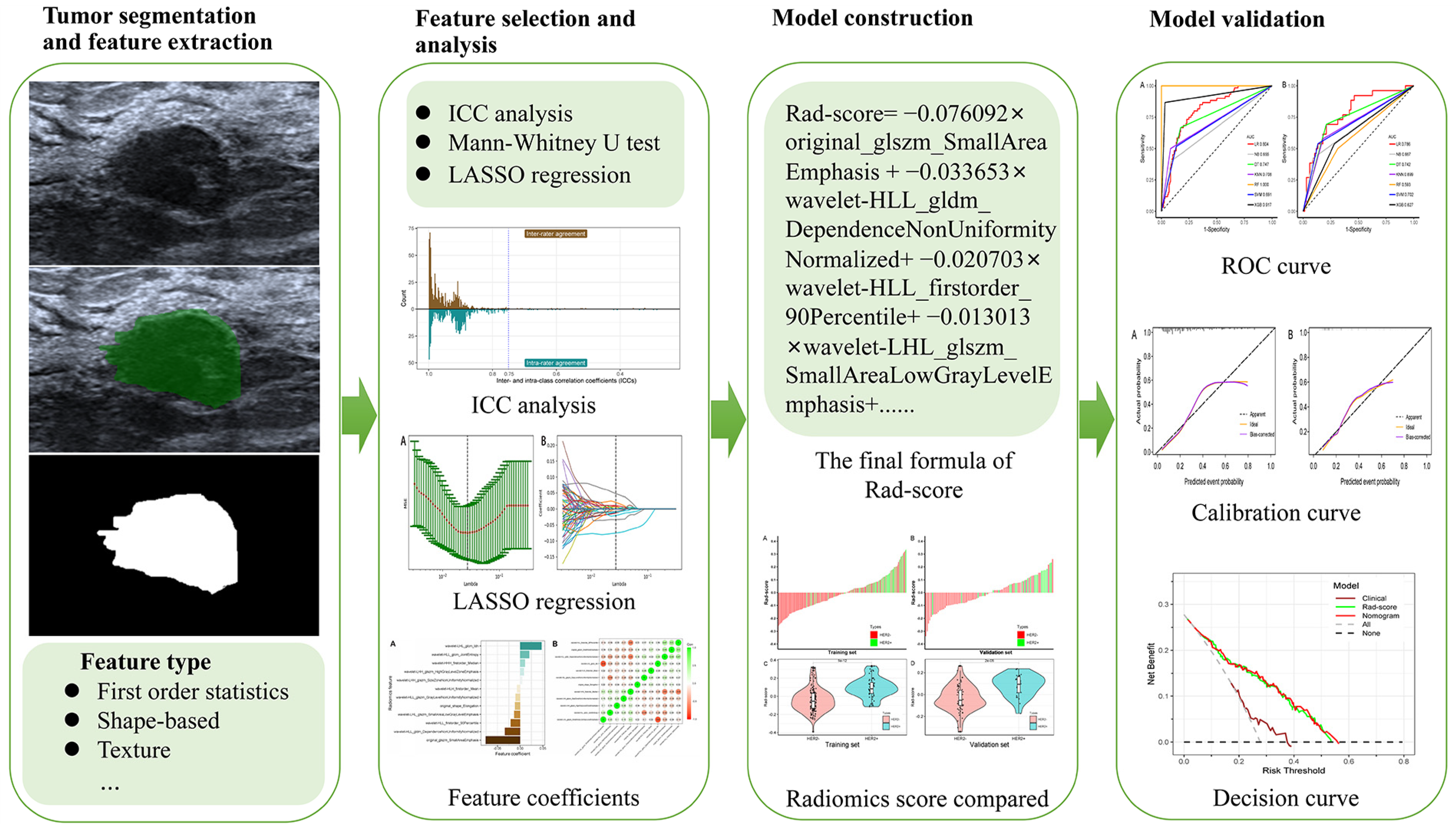
2.4. Image Acqusition and Segmentation
2.5. Radiomic Feature Extraction
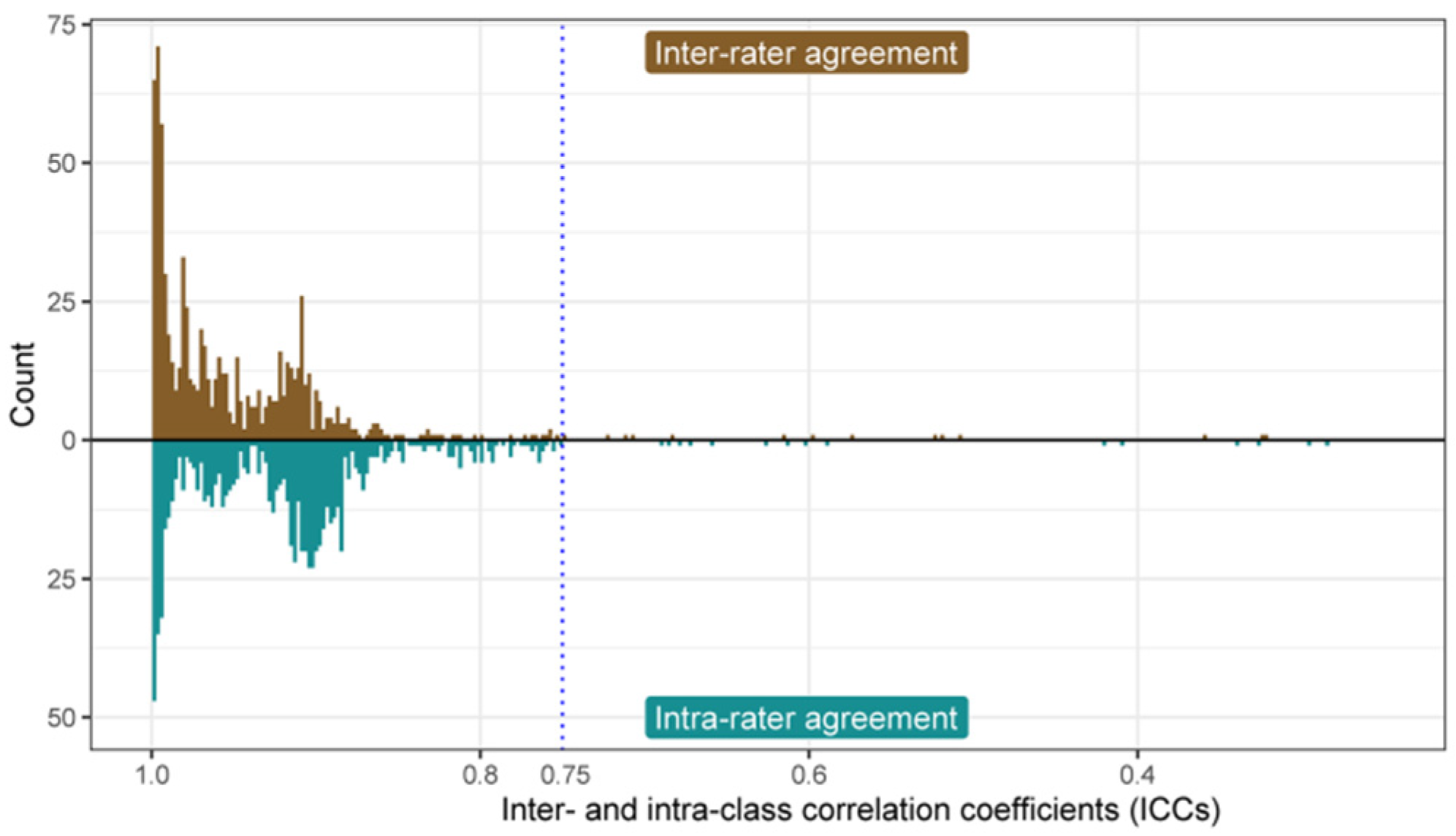
2.6. Evaluation of Inter- and Intra-Class Correlation Coefficient
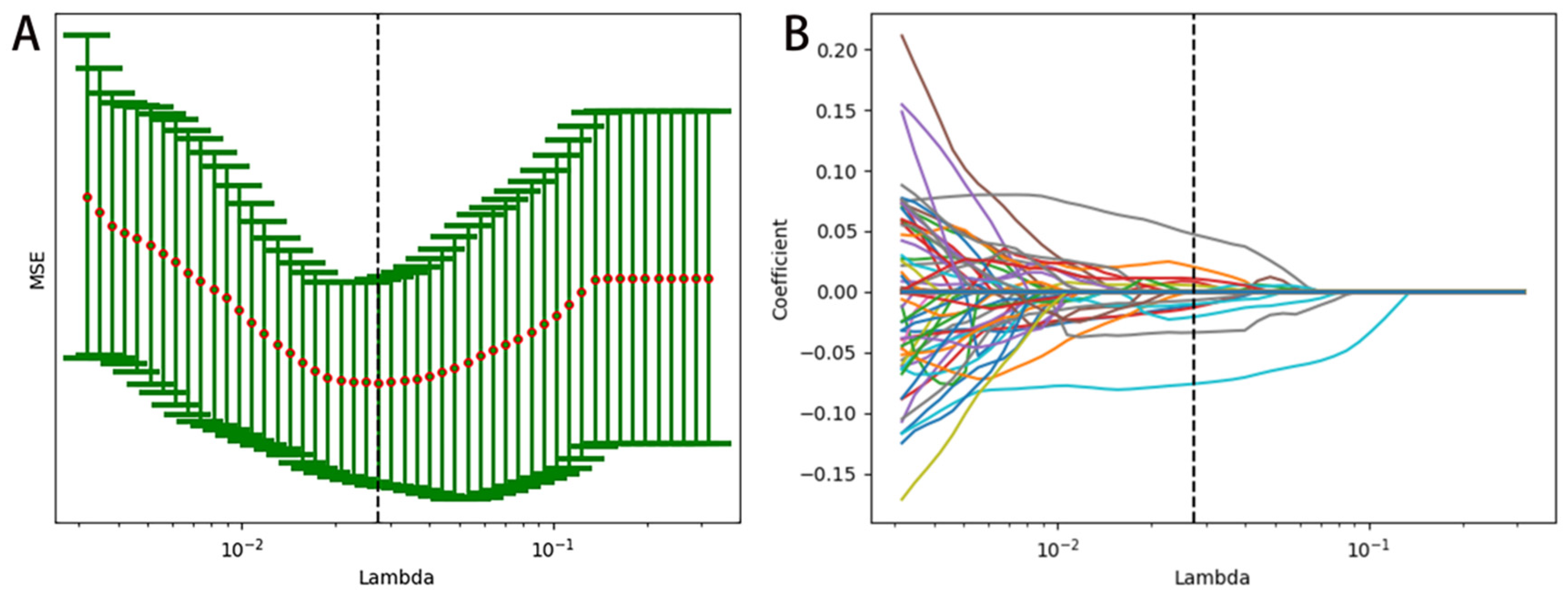
2.7. Radiomics Feature Selection
2.8. Development and Validation of the Prediction Model
2.9. Clinical Model and Nomogram Model
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Pathological Characteristics
3.2. Radiomics Feature Extraction and Selection
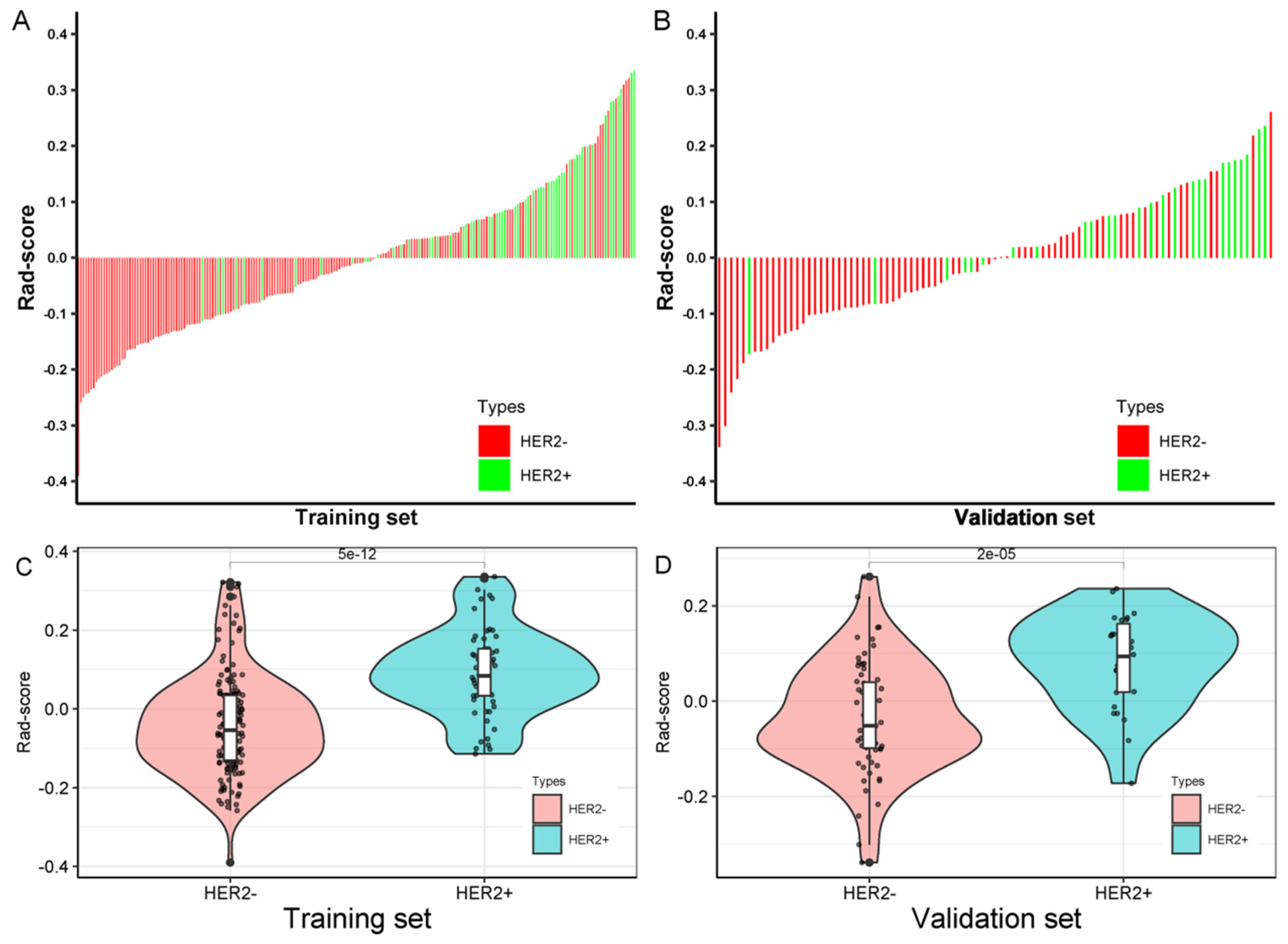
3.3. Radiomics Score Calculation
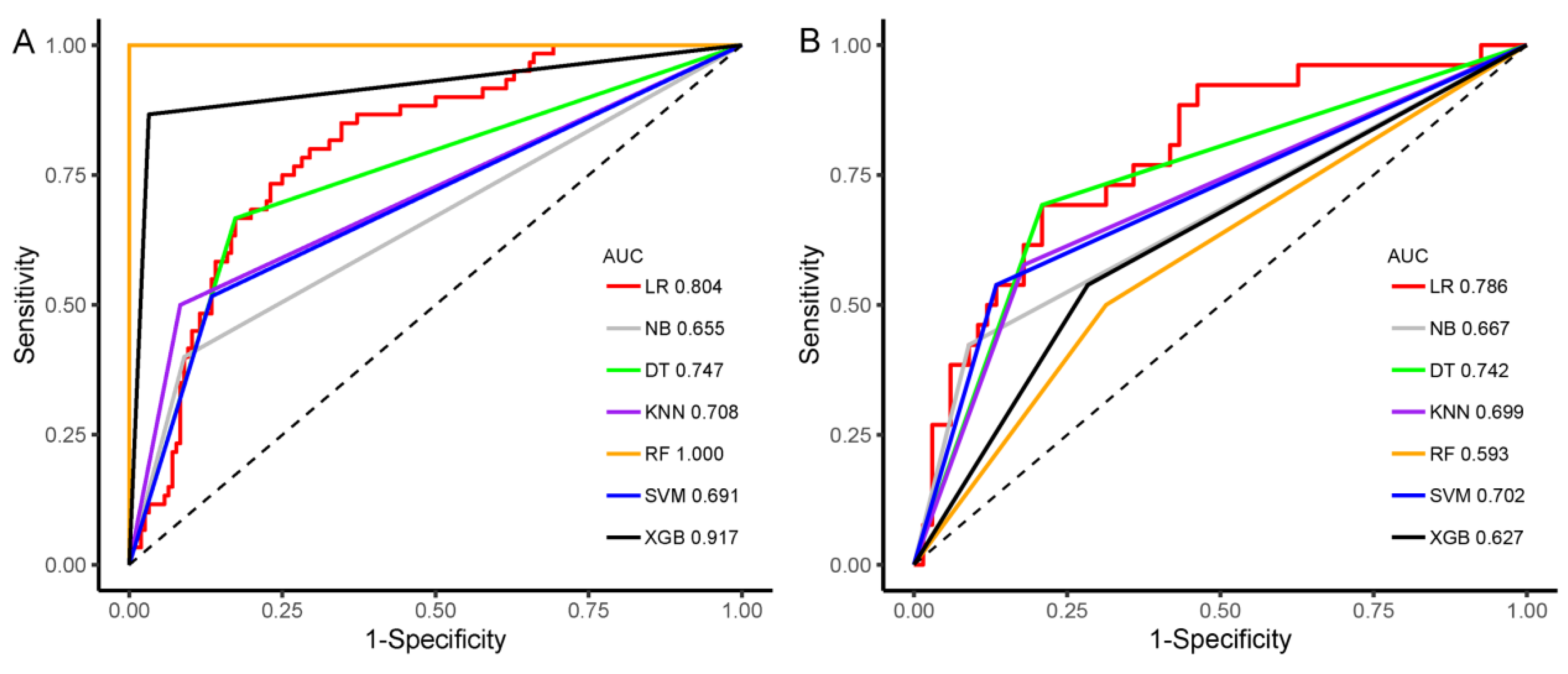
3.4. Construction and Evaluation of Machine Learning Classifier
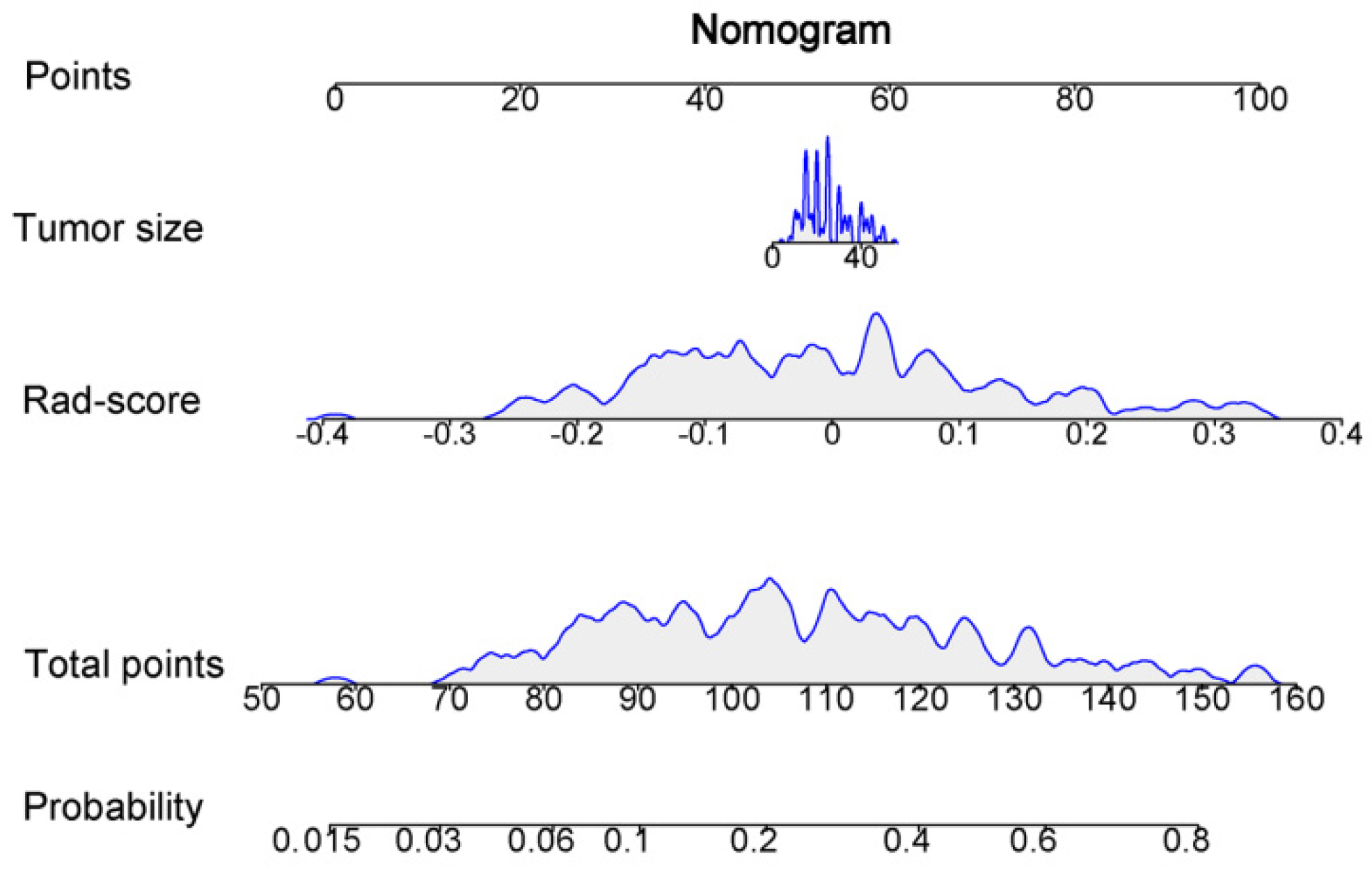
3.5. Clinical Model and Nomogram Model
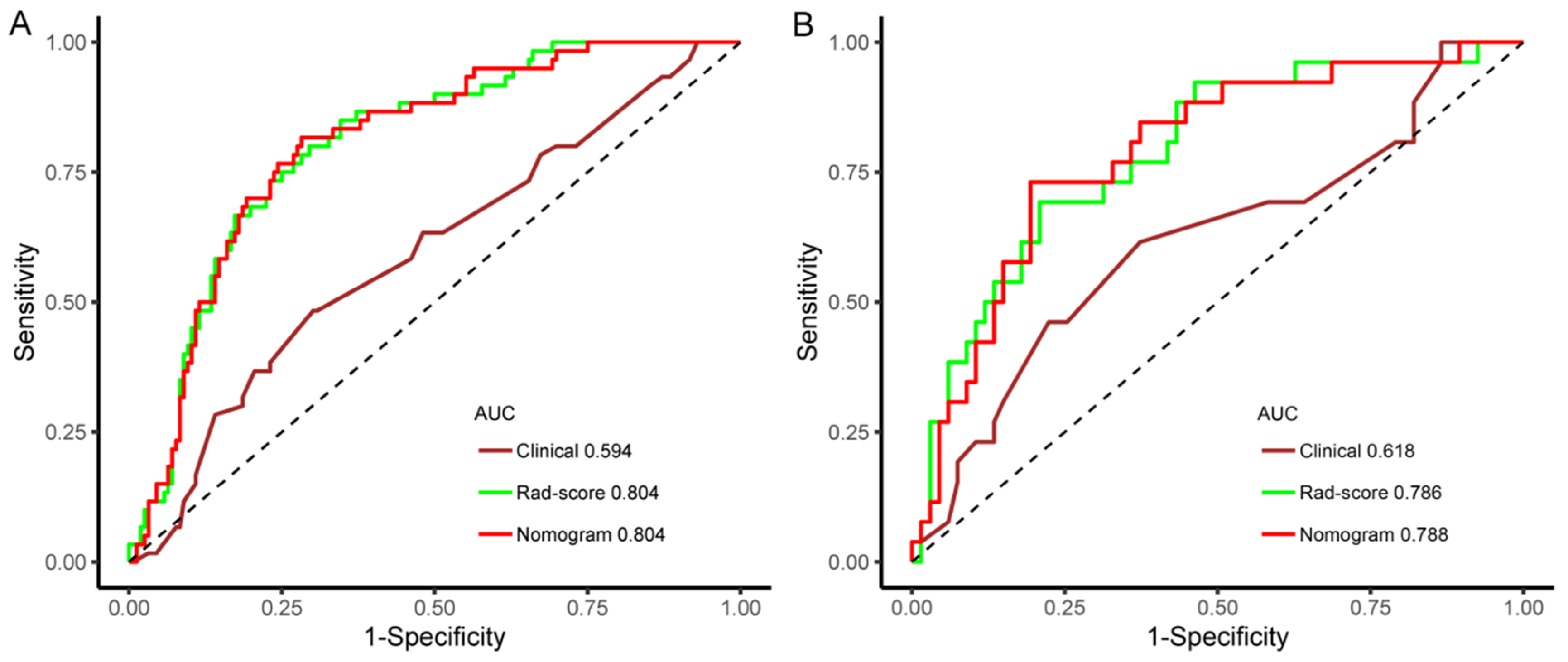
3.6. Model Performance Evaluation
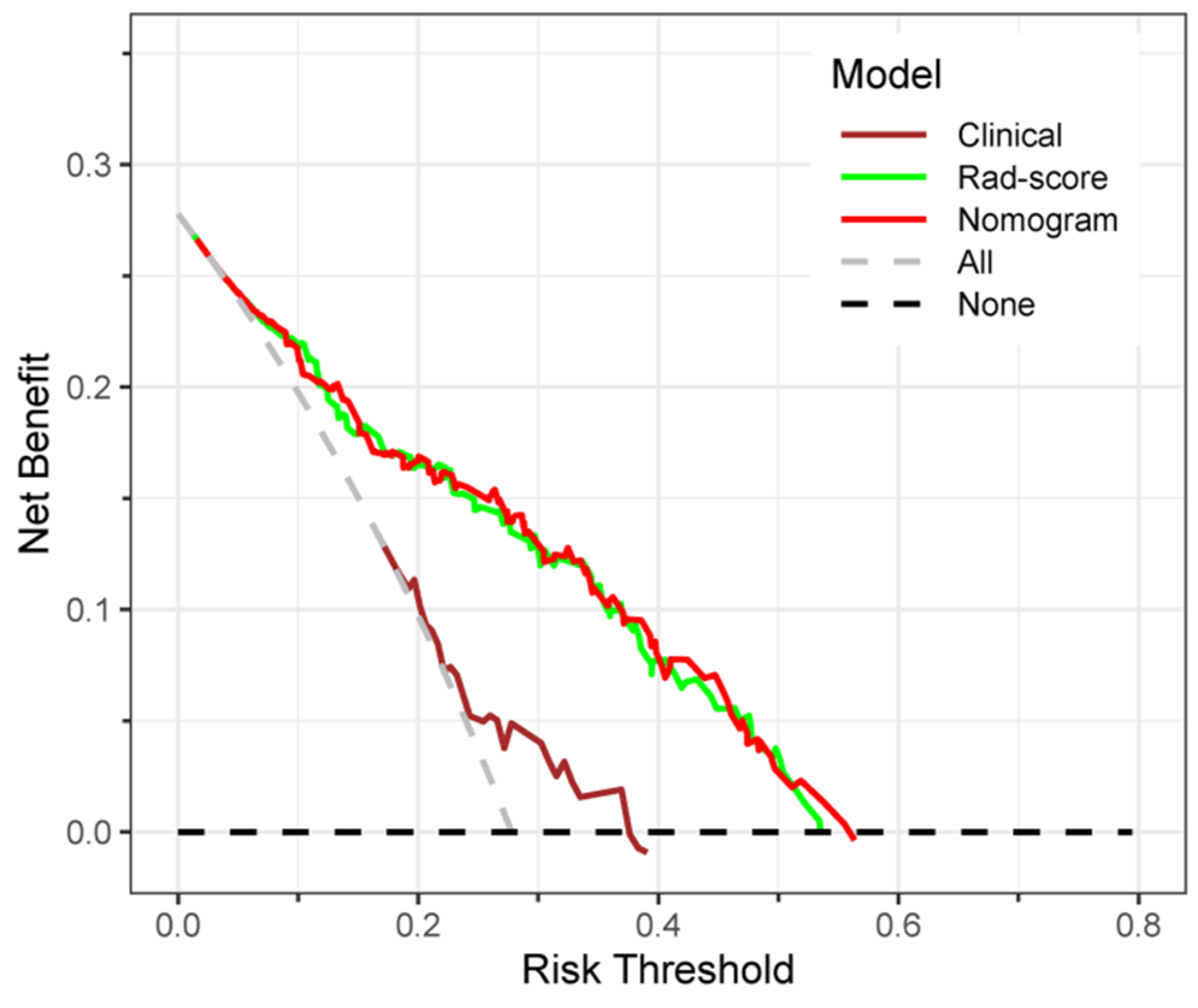
3.7. Clinical Application of the Prediction Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbeck, N.; Gnant, M. Breast cancer. Lancet 2017, 389, 1134–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Song, X.; Yang, Q. Metastatic heterogeneity of breast cancer: Molecular mechanism and potential therapeutic targets. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 60, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerl, D.; Smid, M.; Timmermans, A.M.; Sleijfer, S.; Martens, J.W.M.; Debets, R. Breast cancer genomics and immuno-oncological markers to guide immune therapies. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 52 Pt 2, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, L.A.; Perou, C.M.; Livasy, C.A.; Dressler, L.G.; Cowan, D.; Conway, K.; Karaca, G.; Troester, M.A.; Tse, C.K.; Edmiston, S.; et al. Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. JAMA 2006, 295, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldhirsch, A.; Wood, W.C.; Coates, A.S.; Gelber, R.D.; Thürlimann, B.; Senn, H.-J. Strategies for subtypes—Dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: Highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1736–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustacchi, G.; Biganzoli, L.; Pronzato, P.; Montemurro, F.; Dambrosio, M.; Minelli, M.; Molteni, L.; Scaltriti, L. HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: A changing scenario. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2015, 95, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, H.; Ludhiadch, A.; Kaur, R.P.; Chander, H.; Kumar, V.; Munshi, A. Recent advances in HER2 positive breast cancer epigenetics: Susceptibility and therapeutic strategies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 142, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarneri, V.; Dieci, M.; Barbieri, E.; Piacentini, F.; Omarini, C.; Ficarra, G.; Bettelli, S.; Conte, P. Loss of HER2 positivity and prognosis after neoadjuvant therapy in HER2-positive breast cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2990–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Minckwitz, G.; Procter, M.; de Azambuja, E.; Zardavas, D.; Benyunes, M.; Viale, G.; Suter, T.; Arahmani, A.; Rouchet, N.; Clark, E.; et al. Adjuvant Pertuzumab and Trastuzumab in Early HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneeweiss, A.; Chia, S.; Hickish, T.; Harvey, V.; Eniu, A.; Hegg, R.; Tausch, C.; Seo, J.; Tsai, Y.-F.; Ratnayake, J.; et al. Pertuzumab plus trastuzumab in combination with standard neoadjuvant anthracycline-containing and anthracycline-free chemotherapy regimens in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer: A randomized phase II cardiac safety study (TRYPHAENA). Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2278–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianni, L.; Pienkowski, T.; Im, Y.-H.; Tseng, L.-M.; Liu, M.-C.; Lluch, A.; Starosławska, E.; De La Haba-Rodríguez, J.R.; Im, S.-A.; Pedrini, J.L.; et al. 5-year analysis of neoadjuvant pertuzumab and trastuzumab in patients with locally advanced, inflammatory, or early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer (NeoSphere): A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonacho, T.; Rodrigues, F.; Liberal, J. Immunohistochemistry for diagnosis and prognosis of breast cancer: A review. Biotech. Histochem. 2020, 95, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruening, W.; Fontanarosa, J.; Tipton, K.; Treadwell, J.R.; Launders, J.; Schoelles, K. Systematic review: Comparative effectiveness of core-needle and open surgical biopsy to diagnose breast lesions. Ann. Intern. Med. 2010, 152, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebner, F.; Friedl, T.W.P.; de Gregorio, A.; Lato, K.; Bekes, I.; Janni, W.; de Gregorio, N. Seroma in breast surgery: All the surgeons fault? Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2018, 298, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, M.; Yu, J.; Peng, G.; Jun, L.; Feng, S.; Fang, L. Correlation between DCE-MRI radiomics features and Ki-67 expression in invasive breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 5084–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Rios-Velazquez, E.; Leijenaar, R.; Carvalho, S.; van Stiphout, R.G.P.M.; Granton, P.; Zegers, C.M.L.; Gillies, R.; Boellard, R.; Dekker, A.; et al. Radiomics: Extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leithner, D.; Mayerhoefer, M.E.; Martinez, D.F.; Jochelson, M.S.; Morris, E.A.; Thakur, S.B.; Pinker, K. Non-Invasive Assessment of Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes with Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Radiomics. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Seo, N.; Baek, S.-E.; Son, N.-H.; Lim, J.S.; Kim, N.K.; Koom, W.S.; Kim, S. MRI Radiomics Model Predicts Pathologic Complete Response of Rectal Cancer Following Chemoradiotherapy. Radiology 2022, 303, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; He, Z.; Ouyang, J.; Tan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, Y.; Mao, L.; Ren, W.; Wang, J.; Lin, L.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging radiomics predicts preoperative axillary lymph node metastasis to support surgical decisions and is associated with tumor microenvironment in invasive breast cancer: A machine learning, multicenter study. EBioMedicine 2021, 69, 103460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Song, Y.; Yang, S.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, J.; Hou, F.; Zhang, J. Value of contrast-enhanced CT based radiomic machine learning algorithm in differentiating gastrointestinal stromal tumors with KIT exon 11 mutation: A two-center study. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2022, 28, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, W.A.; Bandos, A.I.; Mendelson, E.B.; Lehrer, D.; Jong, R.A.; Pisano, E.D. Ultrasound as the Primary Screening Test for Breast Cancer: Analysis From ACRIN 6666. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 108, djv367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.-C.; Liu, T.-T.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Y.-X.; Guo, Y.; Yu, J.-H.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Chang, C. An Ultrasound Radiomics Nomogram for Preoperative Prediction of Central Neck Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Song, L.; Yin, J. Intratumoral and Peritumoral Radiomics Based on Functional Parametric Maps from Breast DCE-MRI for Prediction of HER-2 and Ki-67 Status. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 54, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.J.; Zhang, Y.D.; Kong, W.T.; Zhang, C.X.; Zhang, B. Preoperative prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis in patients with breast cancer based on radiomics of gray-scale ultrasonography. Gland. Surg. 2021, 10, 1989–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.E.; Han, K.; Kwak, J.Y.; Lee, E.; Kim, E.-K. Radiomics of US texture features in differential diagnosis between triple-negative breast cancer and fibroadenoma. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, M.E.H.; Hayes, D.F.; Dowsett, M.; Allred, D.C.; Hagerty, K.L.; Badve, S.; Fitzgibbons, P.L.; Francis, G.; Goldstein, N.S.; Hayes, M.; et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College Of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2784–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, P.; Qin, H.; Liu, Y.; Wan, D.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Yang, H. Preoperative ultrasound radiomics analysis for expression of multiple molecular biomarkers in mass type of breast ductal carcinoma in situ. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 21, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.Q.; Huang, Q.X.; Huang, X.W.; Hu, H.T.; Zeng, F.Q.; Wang, W. Predicting Breast Cancer in Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) Ultrasound Category 4 or 5 Lesions: A Nomogram Combining Radiomics and BI-RADS. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, V.; Cuocolo, R.; Apolito, R.; Stanzione, A.; Ventimiglia, A.; Vitale, A.; Verde, F.; Accurso, A.; Amitrano, M.; Insabato, L.; et al. Clinical value of radiomics and machine learning in breast ultrasound: A multicenter study for differential diagnosis of benign and malignant lesions. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 9511–9519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Yan, C.; Huang, M.; Jiang, T. Could Ultrasound-Based Radiomics Noninvasively Predict Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer? J. Ultrasound Med. 2020, 39, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, C.; Xiao, M.; Ma, L.; Li, W.; Qin, J.; Zhu, Q.; Jiang, Y. Nomogram based on radiomics analysis of primary breast cancer ultrasound images: Prediction of axillary lymph node tumor burden in patients. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Hu, Y.; Qiao, M.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Chang, C. Radiomics Analysis on Ultrasound for Prediction of Biologic Behavior in Breast Invasive Ductal Carcinoma. Clin. Breast Cancer 2018, 18, e335–e344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, G.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, H.; Jing, J.; Ma, X. Survival Prediction in Gallbladder Cancer Using CT Based Machine Learning. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 604288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velichko, Y.S.; Mozafarykhamseh, A.; Trabzonlu, T.A.; Zhang, Z.; Rademaker, A.W.; Yaghmai, V. Association Between the Size and 3D CT-Based Radiomic Features of Breast Cancer Hepatic Metastasis. Acad. Radiol. 2021, 28, e93–e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yang, Q.; Li, M.; Gu, J.; Du, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, B. Predicting HER2 Status in Breast Cancer on Ultrasound Images Using Deep Learning Method. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 829041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Lin, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Yan, K.; Liang, D.; Sun, D.; Li, Z.-C. Deep Learning vs. Radiomics for Predicting Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis of Breast Cancer Using Ultrasound Images: Don’t Forget the Peritumoral Region. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P. Radiomics, deep learning and early diagnosis in oncology. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2021, 5, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Characteristic | Total Set (n = 309) | Training Set (n = 216) | Validation Set (n = 93) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year, mean ± SD) | 52.88 ± 10.96 | 53.61 ± 10.98 | 51.18 ± 10.76 | 0.073 |
| Size (mm, mean ± SD) | 24.58 ± 11.06 | 25.25 ± 11.03 | 23.02 ± 11.03 | 0.106 |
| Tumor location | 0.480 | |||
| Right lobe | 165 | 112 | 53 | |
| Left lobe | 144 | 104 | 40 | |
| BI-RADS | 0.297 | |||
| 4A | 46 | 29 | 17 | |
| 4B | 116 | 79 | 37 | |
| 4C | 81 | 63 | 18 | |
| 5 | 66 | 45 | 21 | |
| ER | 0.973 | |||
| Positive | 228 | 160 | 68 | |
| Negative | 91 | 56 | 25 | |
| PR | 0.597 | |||
| Positive | 188 | 134 | 54 | |
| Negative | 121 | 82 | 39 | |
| HER2 | 1.000 | |||
| Positive | 86 | 60 | 26 | |
| Negative | 223 | 156 | 67 | |
| Histologic type | 0.581 | |||
| Invasive ductal | 259 | 184 | 75 | |
| Invasive lobular | 14 | 9 | 5 | |
| Other | 36 | 23 | 13 | |
| Ultrasound equipment | 0.636 | |||
| Siemens Acuson S2000 | 246 | 174 | 72 | |
| LOGIQ E9 | 63 | 42 | 21 | |
| US-reported LN | 0.875 | |||
| Metastasis positive | 130 | 92 | 38 | |
| Metastasis negative | 179 | 124 | 55 | |
| Pathology-reported LN | 0.868 | |||
| Metastasis positive | 170 | 120 | 50 | |
| Metastasis negative | 139 | 96 | 43 | |
| Ki-67 (%, mean ± SD) | 28.52 ± 22.16 | 28.16 ± 21.96 | 29.38 ± 22.72 | 0.663 |
| Radiomics score (median, IQR) | −0.0097 (−0.0975, 0.0794) | −0.0099 (−0.1030, 0.0787) | −0.0029 (−0.0883, 0.0808) | 0.678 |
| Image Type | Feature Class | Feature Name | Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|
| original | shape | Elongation | −0.011322 |
| original | glszm | SmallAreaEmphasis | −0.076092 |
| wavelet-LHL | glcm | Idn | 0.047259 |
| wavelet-LHL | glszm | SmallAreaLowGrayLevelEmphasis | −0.013013 |
| wavelet-LHH | glszm | HighGrayLevelZoneEmphasis | 0.008385 |
| wavelet-LHH | glszm | SizeZoneNonUniformityNormalized | 0.005098 |
| wavelet-HLL | firstorder | 90Percentile | −0.020703 |
| wavelet-HLL | glcm | JointEntropy | 0.020412 |
| wavelet-HLL | glszm | GrayLevelNonUniformityNormalized | −0.010225 |
| wavelet-HLL | gldm | DependenceNonUniformityNormalized | −0.033653 |
| wavelet-HLH | firstorder | Mean | −0.00703 |
| wavelet-HHH | firstorder | Median | 0.010776 |
| Rad-Score | HER2− (Median, IQR) | HER2+ (Median, IQR) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Training set | −0.0546 (−0.1303, 0.0338) | 0.0838 (0.0336, 0.1523) | <0.001 |
| Validation set | −0.0518 (−0.0985, 0.0394) | 0.0936 (0.0185, 0.1623) | <0.001 |
| Training Set | Time-Independent Validation Set | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | AUC (95%CI) | SEN | SPE | ACC | AUC (95%CI) | SEN | SPE | ACC |
| LR | 0.804 (0.742–0.865) | 80.0% | 70.5% | 73.1% | 0.786 (0.683–0.890) | 69.2% | 79.1% | 76.3% |
| SVM | 0.691 (0.622–0.760) | 51.7% | 86.5% | 76.9% | 0.702 (0.596–0.808) | 53.8% | 86.6% | 77.4% |
| KNN | 0.708 (0.641–0.776) | 50.0% | 91.7% | 80.1% | 0.699 (0.592–0.806) | 57.7% | 82.1% | 75.3% |
| RF | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 0.593 (0.480–0.706) | 50.0% | 68.7% | 63.4% |
| DT | 0.747 (0.680–0.814) | 66.7% | 82.7% | 78.2% | 0.742 (0.639–0.845) | 69.2% | 79.1% | 76.3% |
| XGB | 0.917 (0.872–0.963) | 86.7% | 96.8% | 94.0% | 0.627 (0.516–0.739) | 53.8% | 71.6% | 66.7% |
| NB | 0.655 (0.589–0.722) | 40.0% | 91.0% | 76.9% | 0.667 (0.564–0.770) | 42.3% | 91.0% | 77.4% |
| Model (AUC Value) | LR (0.786) | SVM (0.702) | KNN (0.699) | RF (0.593) | DT (0.742) | XGB (0.627) | NB (0.667) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR (0.786) | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SVM (0.702) | 0.023 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| KNN (0.699) | 0.054 | 0.955 | 1 | - | - | - | - |
| RF (0.593) | 0.004 | 0.164 | 0.101 | 1 | - | - | - |
| DT (0.742) | 0.124 | 0.317 | 0.225 | 0.021 | 1 | - | - |
| XGB (0.627) | 0.042 | 0.344 | 0.367 | 0.674 | 0.142 | 1 | - |
| NB (0.667) | 0.006 | 0.305 | 0.574 | 0.329 | 0.124 | 0.612 | 1 |
| Training Set (n = 216) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Feature | HER2− (n = 156) | HER2+ (n = 60) | p-Value |
| Age (year, mean ± SD) | 54.04 ± 11.78 | 52.47 ± 8.55 | 0.279 |
| Tumor location | 0.673 | ||
| Right | 79 | 33 | |
| Left | 77 | 27 | |
| Tumor size (mm, mean ± SD) | 24.21 ± 10.90 | 27.93 ± 11.02 | 0.028 |
| US equipment | 0.064 | ||
| Siemens Acuson S2000 | 131 | 43 | |
| LOGIQ E9 | 25 | 17 | |
| US-reported LN | 0.550 | ||
| Metastasis positive | 64 | 28 | |
| Metastasis negative | 92 | 31 | |
| Rad-score (median, IQR) | −0.0546 (−0.1303, 0.0338) | 0.0838 (0.0336, 0.1523) | p < 0.001 |
| Training Set | Time-Independent Validation Set | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | AUC (95%CI) | SEN | SPE | ACC | AUC (95%CI) | SEN | SPE | ACC |
| Clinical | 0.594 (0.509–0.679) | 48.3% | 69.9% | 63.9% | 0.618 (0.485–0.751) | 61.5% | 62.7% | 62.4% |
| Rad-score | 0.804 (0.742–0.865) | 80.0% | 70.5% | 73.1% | 0.786 (0.683–0.890) | 69.2% | 79.1% | 76.3% |
| Nomogram | 0.804 (0.742–0.866) | 81.7% | 71.8% | 74.5% | 0.788 (0.685–0.891) | 73.1% | 80.6% | 78.5% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Y. Development and Validation of an Ultrasound-Based Radiomics Nomogram for Identifying HER2 Status in Patients with Breast Carcinoma. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123130
Guo Y, Wu J, Wang Y, Jin Y. Development and Validation of an Ultrasound-Based Radiomics Nomogram for Identifying HER2 Status in Patients with Breast Carcinoma. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123130
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yinghong, Jiangfeng Wu, Yunlai Wang, and Yun Jin. 2022. "Development and Validation of an Ultrasound-Based Radiomics Nomogram for Identifying HER2 Status in Patients with Breast Carcinoma" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123130
APA StyleGuo, Y., Wu, J., Wang, Y., & Jin, Y. (2022). Development and Validation of an Ultrasound-Based Radiomics Nomogram for Identifying HER2 Status in Patients with Breast Carcinoma. Diagnostics, 12(12), 3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123130






